Tegsedi (Inotersen): An Antisense Oligonucleotide Approved for the Treatment of Adult Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis
Abstract
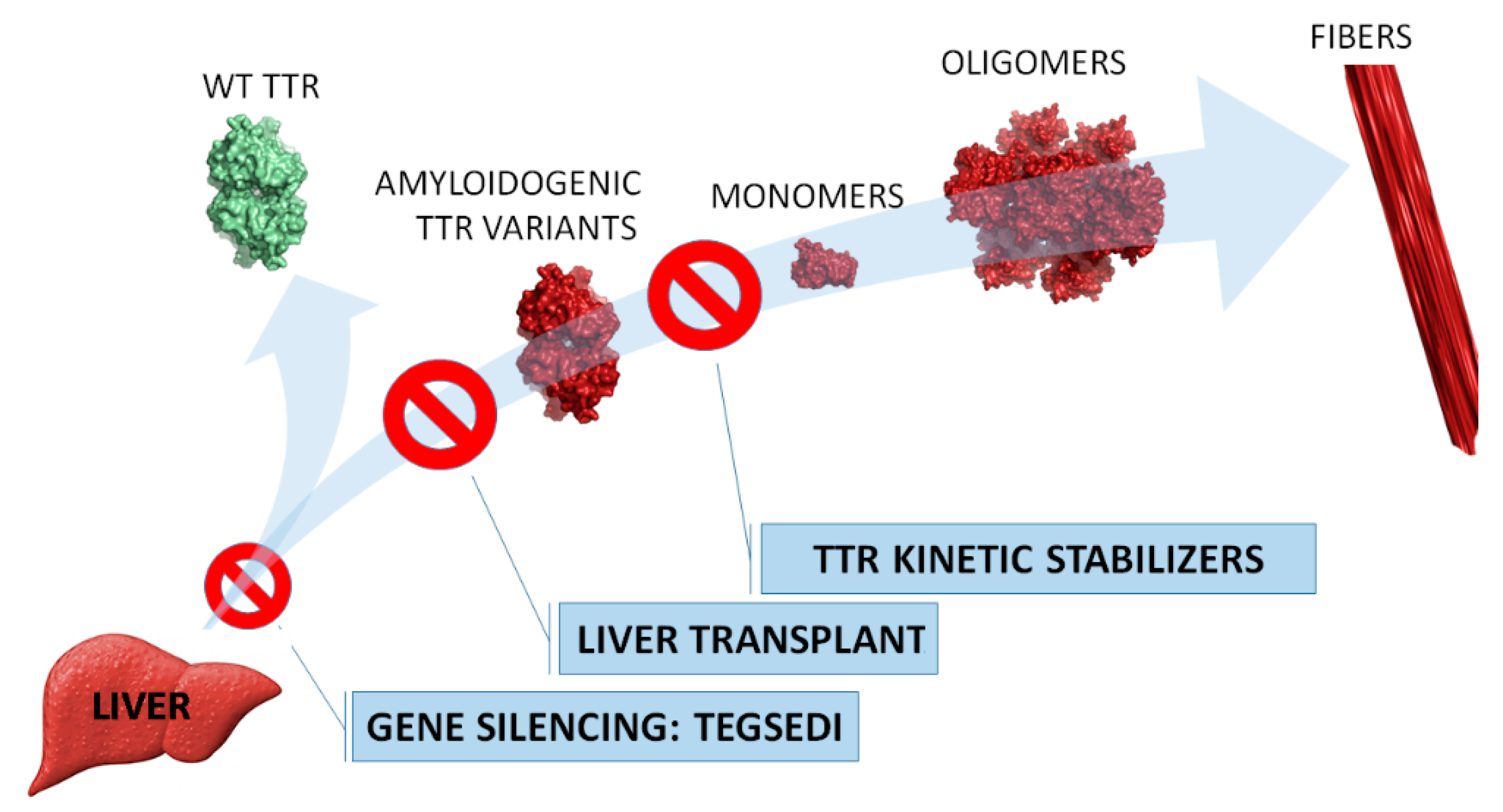
1. Introduction
2. Tegsedi (Inotersen)
2.1. Name
2.2. Uses
2.3. Mechanism of Action
2.4. Clinical Studies
3. Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blake, C.C.F.; Geisow, M.J.; Oatley, S.J.; Rérat, B.; Rérat, C. Structure of prealbumin: Secondary, tertiary and quaternary interactions determined by Fourier refinement at 1.8 Å. J. Mol. Biol. 1978, 121, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas Saraiva, M.J.; Birken, S.; Costa, P.P.; Goodman, D.S. Amyloid fibril protein in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy, Portuguese type. Definition of molecular abnormality in transthyretin (prealbumin). J. Clin. Invest. 1984, 74, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.; Suhr, O.B.; Hund, E.; Obici, L.; Tournev, I.; Campistol, J.M.; Slama, M.S.; Hazenberg, B.P.; Coelho, T.; European Network for, T.-F. First European consensus for diagnosis, management, and treatment of transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2016, 29, S14–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, T.; Adams, D.; Silva, A.; Lozeron, P.; Hawkins, P.N.; Mant, T.; Perez, J.; Chiesa, J.; Warrington, S.; Tranter, E.; et al. Safety and efficacy of RNAi therapy for transthyretin amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, M.D.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Berk, J.L.; Polydefkis, M.; Dyck, P.J.; Wang, A.K.; Planté-Bordeneuve, V.; Barroso, F.A.; Merlini, G.; Obici, L.; et al. Inotersen treatment for patients with Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.; Gonzalez-Duarte, A.; O’Riordan, W.D.; Yang, C.C.; Ueda, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Tournev, I.; Schmidt, H.H.; Coelho, T.; Berk, J.L.; et al. Patisiran, an RNAi therapeutic, for hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, H. FDA approves patisiran to treat hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.F. Therapeutic antisense oligonucleotides are coming of age. Ann. Rev. Med. 2019, 70, 307–321. [Google Scholar]
- Crooke, S.T.; Witztum, J.L.; Bennett, C.F.; Baker, B.F. RNA-Targeted Therapeutics. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 714–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, E.J.; Guo, S.; Benson, M.D.; Booten, S.; Freier, S.; Hughes, S.G.; Kim, T.W.; Jesse Kwoh, T.; Matson, J.; Norris, D.; et al. Suppressing transthyretin production in mice, monkeys and humans using 2nd-Generation antisense oligonucleotides. Amyloid 2016, 23, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.R.; Gales, L.; Damas, A.M.; Cardoso, I.; Saraiva, M.J. Small transthyretin (TTR) ligands as possible therapeutic agents in TTR amyloidoses. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 2005, 4, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gales, L.; Aronson, J.K. Thyroid hormones, iodine and iodides, and antithyroid drugs. In Side Effects of Drugs Annual; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2014; Volume 35, pp. 747–761. [Google Scholar]
- Bulawa, C.E.; Connelly, S.; DeVit, M.; Wang, L.; Weigel, C.; Fleming, J.A.; Packman, J.; Powers, E.T.; Wiseman, R.L.; Foss, T.R.; et al. Tafamidis, a potent and selective transthyretin kinetic stabilizer that inhibits the amyloid cascade. PNAS 2012, 109, 9629–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.S.; Schwartz, J.H.; Gundapaneni, B.; Elliott, P.M.; Merlini, G.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Grogan, M.; Witteles, R.; Damy, T.; et al. Tafamidis treatment for patients with transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, N.; Gonçalves, N.P.; Saraiva, M.J.; Almeida, M.R. Curcumin: A multi-Target disease-modifying agent for late-stage transthyretin amyloidosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia, F.; Almeida, M.D.R.; Gales, L.; Kijjoa, A.; Pinto, M.M.M.; Saraiva, M.J.; Damas, A.M. The binding of xanthone derivatives to transthyretin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk, J.L.; Suhr, O.B.; Obici, L.; Sekijima, Y.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Yamashita, T.; Heneghan, M.A.; Gorevic, P.D.; Litchy, W.J.; Wiesman, J.F.; et al. Repurposing diflunisal for familial amyloid polyneuropathy: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA—J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2013, 310, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sant’Anna, R.; Gallego, P.; Robinson, L.Z.; Pereira-Henriques, A.; Ferreira, N.; Pinheiro, F.; Esperante, S.; Pallares, I.; Huertas, O.; Almeida, M.R.; et al. Repositioning tolcapone as a potent inhibitor of transthyretin amyloidogenesis and associated cellular toxicity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gales, L.; Almeida, M.R.; Arsequell, G.; Valencia, G.; Saraiva, M.J.; Damas, A.M. Iodination of salicylic acid improves its binding to transthyretin. BBA-Proteins Proteom. 2008, 1784, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gales, L.; Macedo-Ribeiro, S.; Arsequell, G.; Valencia, G.; Saraiva, M.J.; Damas, A.M. Human transthyretin in complex with iododiflunisal: Structural features associated with a potent amyloid inhibitor. Biochem. J. 2005, 388, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairal, T.; Nieto, J.; Pinto, M.; Almeida, M.R.; Gales, L.; Ballesteros, A.; Barluenga, J.; Pérez, J.J.; Vázquez, J.T.; Centeno, N.B.; et al. Iodine atoms: A new molecular feature for the design of potent transthyretin fibrillogenesis inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.; Pereira-Henriques, A.; Attar, A.; Klärner, F.G.; Schrader, T.; Bitan, G.; Gales, L.; Saraiva, M.J.; Almeida, M.R. Molecular Tweezers Targeting Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Neurotherapeutics 2014, 11, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gales, L.; Saraiva, M.J.; Damas, A.M. Structural basis for the protective role of sulfite against transthyretin amyloid formation. BBA-Proteins Proteom. 2007, 1774, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Mizuguchi, M. Crown Ethers as Transthyretin Amyloidogenesis Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 2076–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooke, S.T.; Baker, B.F.; Witztum, J.L.; Kwoh, T.J.; Pham, N.C.; Salgado, N.; McEvoy, B.W.; Cheng, W.; Hughes, S.G.; Bhanot, S.; et al. The Effects of 2′-O-Methoxyethyl Containing Antisense Oligonucleotides on Platelets in Human Clinical Trials. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2017, 27, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyck, P.J.; Kincaid, J.C.; Dyck, P.J.B.; Chaudhry, V.; Goyal, N.A.; Alves, C.; Salhi, H.; Wiesman, J.F.; Labeyrie, C.; Robinson-Papp, J.; et al. Assessing mNIS+7 Ionis and international neurologists’ proficiency in a familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy trial. Muscle Nerve 2017, 56, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peripheral Nerve, S. Diabetic polyneuropathy in controlled clinical trials: Consensus report of the peripheral nerve society. Ann. Neurol. 1995, 38, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinik, E.J.; Vinik, A.I.; Paulson, J.F.; Merkies, I.S.J.; Packman, J.; Grogan, D.R.; Coelho, T. Norfolk QOL-DN: Validation of a patient reported outcome measure in transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2014, 19, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gales, L. Tegsedi (Inotersen): An Antisense Oligonucleotide Approved for the Treatment of Adult Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12020078
Gales L. Tegsedi (Inotersen): An Antisense Oligonucleotide Approved for the Treatment of Adult Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Pharmaceuticals. 2019; 12(2):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12020078
Chicago/Turabian StyleGales, Luís. 2019. "Tegsedi (Inotersen): An Antisense Oligonucleotide Approved for the Treatment of Adult Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis" Pharmaceuticals 12, no. 2: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12020078
APA StyleGales, L. (2019). Tegsedi (Inotersen): An Antisense Oligonucleotide Approved for the Treatment of Adult Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Pharmaceuticals, 12(2), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12020078




