A Portable Low-Power Acquisition System with a Urease Bioelectrochemical Sensor for Potentiometric Detection of Urea Concentrations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of the MEMS-Based Bioelectrochemical Sensor
2.2. Electrochemical Detection of Urea Concentration
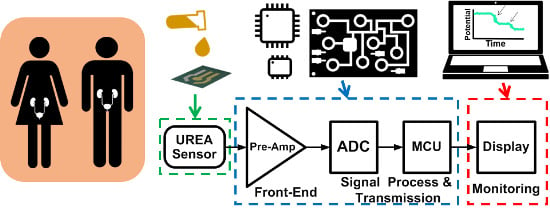
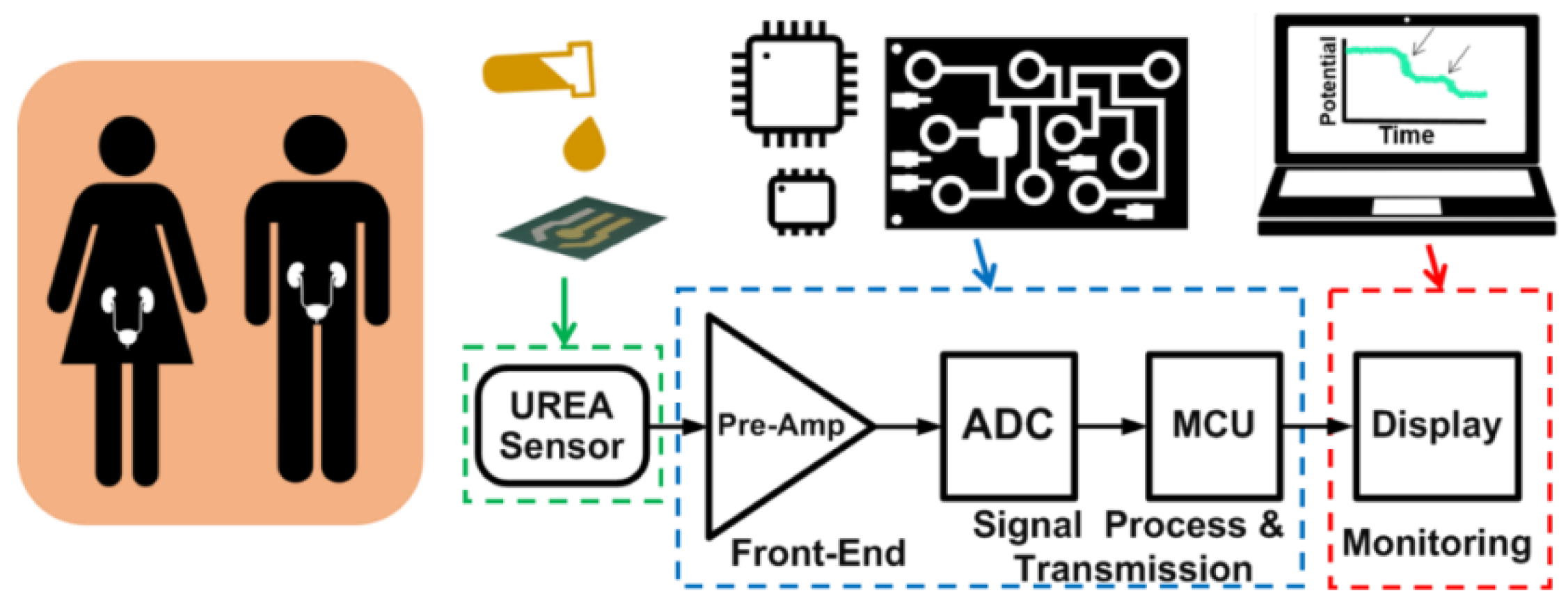
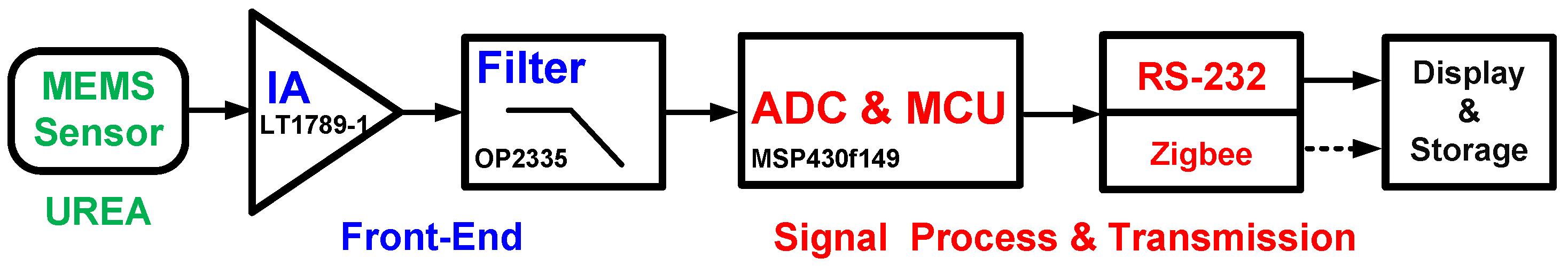
2.3. Low-Power Battery-Driven Bioelectrochemical Acquisition System
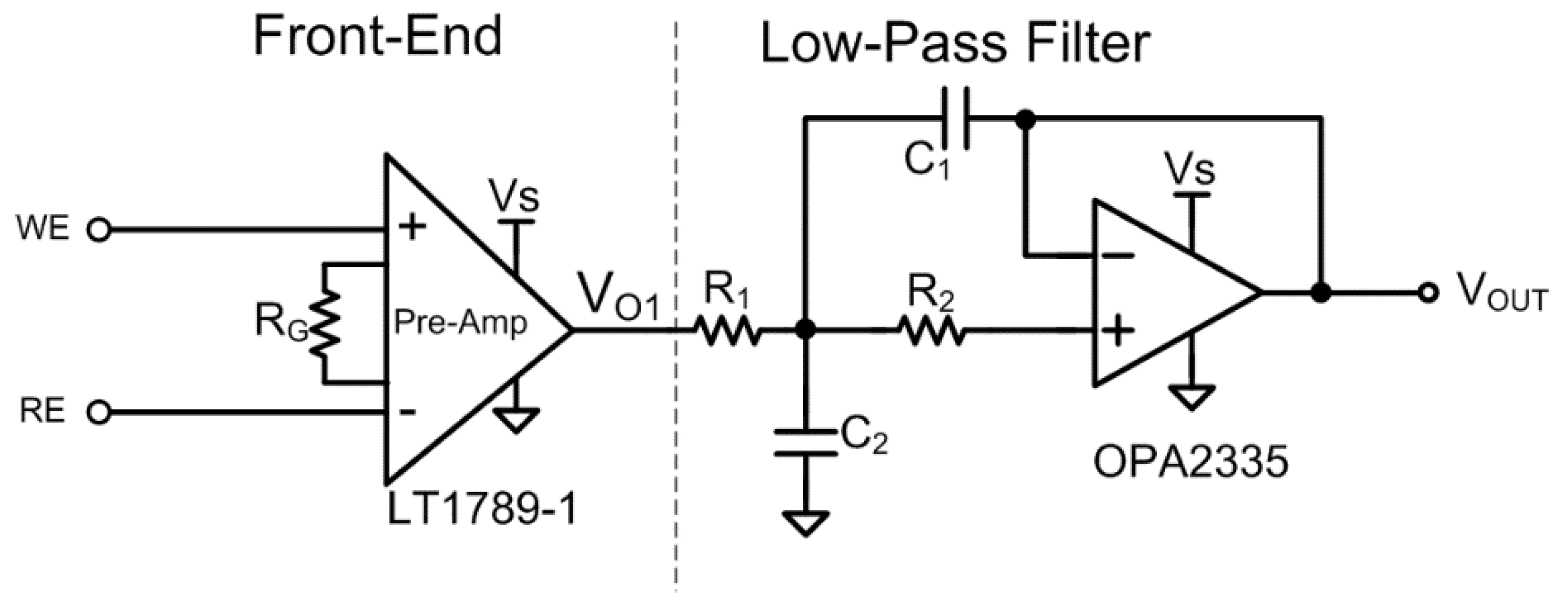
2.4. Bioelectrochemical Readout Circuit
2.5. Microcontrol Unit Usage
2.6. Peripheral Device for Signal Monitoring and Storage
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Urea Disposable Sensing Microchip
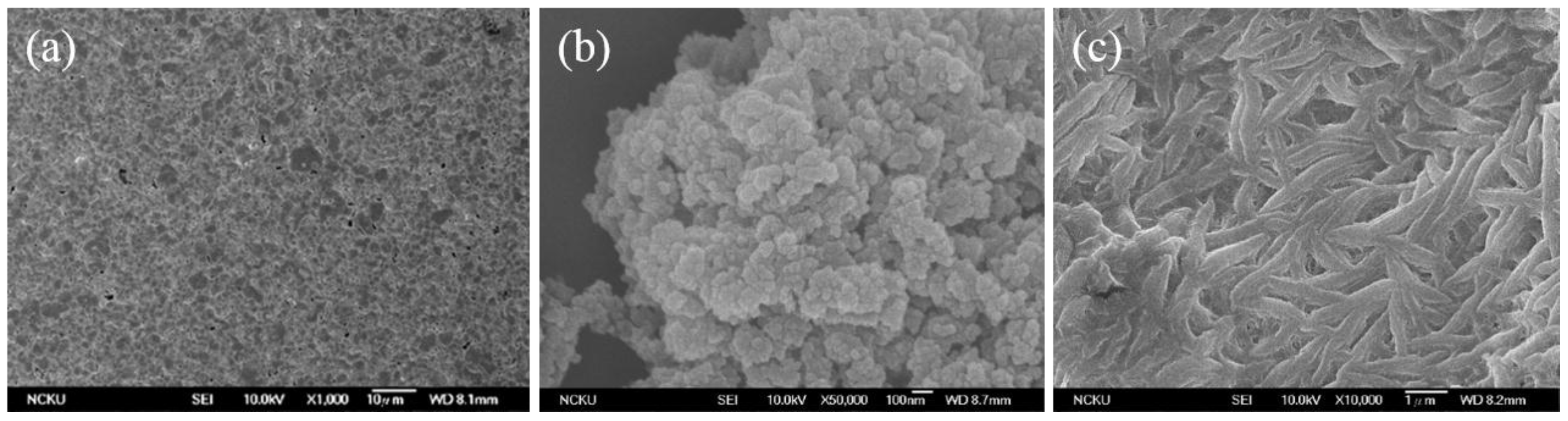
3.2. SEM Images of the Poly Film Fabricated on the Au Electrode
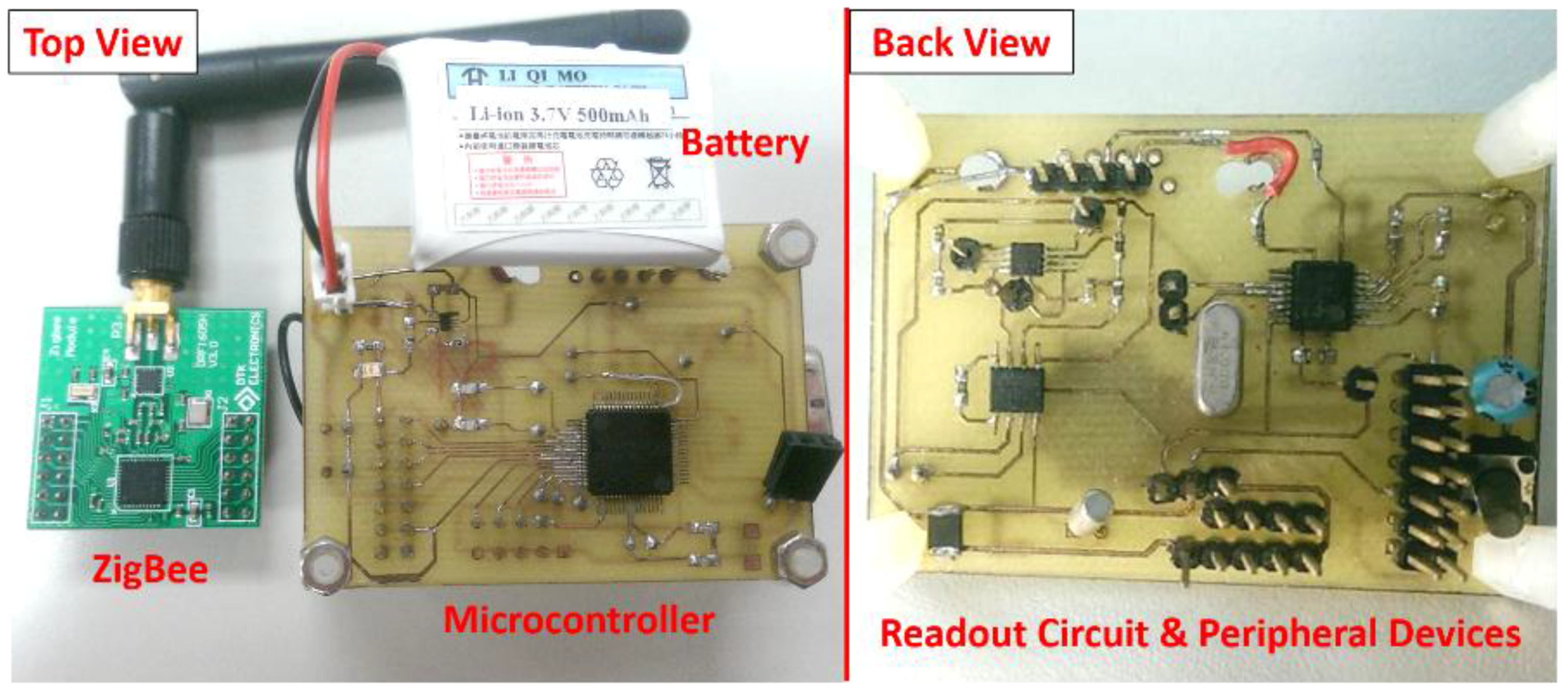
3.3. The Proposed Bioelectrochemical Signal Acquisition System
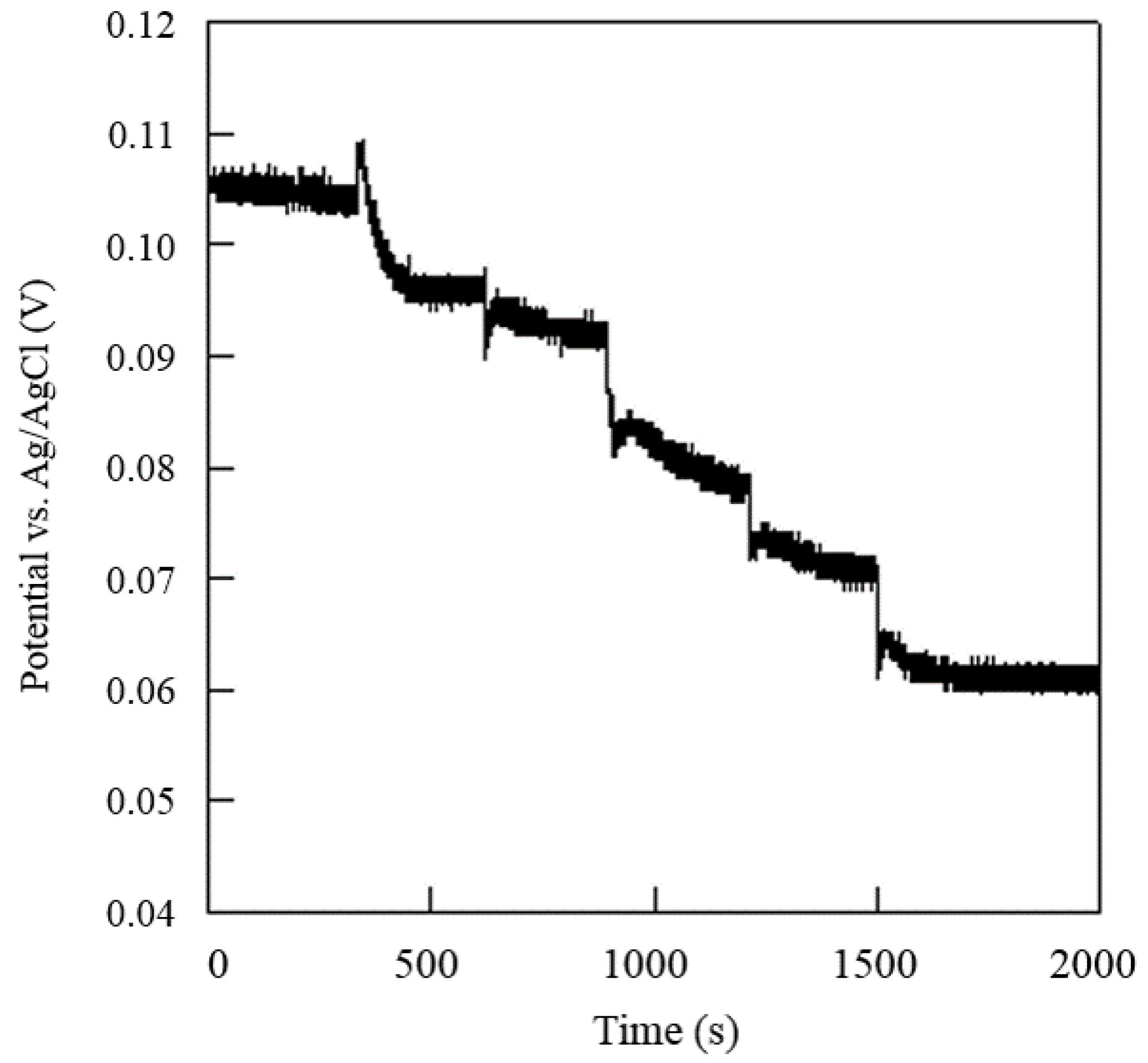
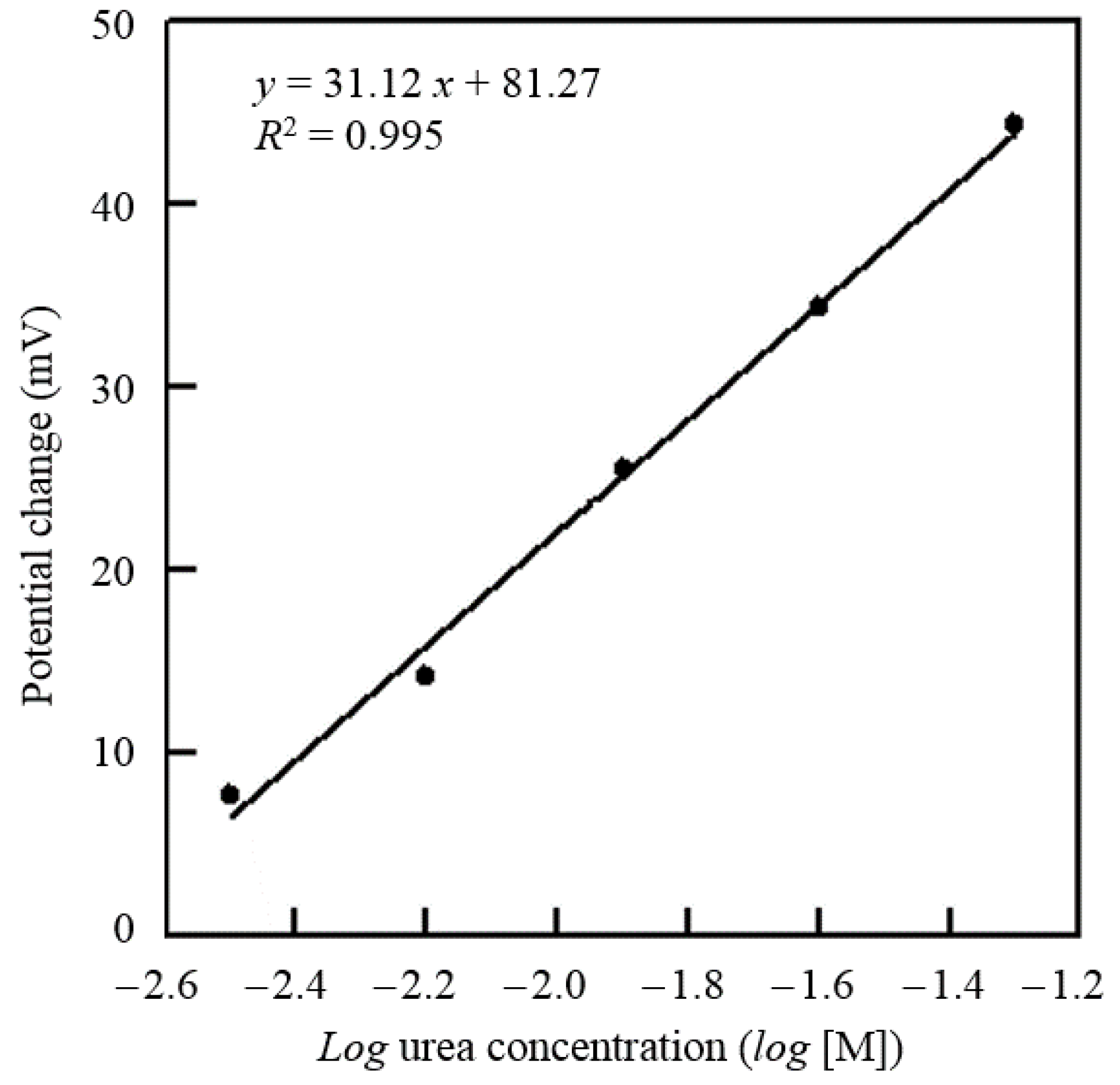
3.4. Detection of Urea Concentration by the Proposed System Device and Sensor
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aronson, D.; Mittleman, M.A.; Burger, A.J. Elevated blood urea nitrogen level as a predictor of mortality in patients admitted for decompensated heart failure. Am. J. Med. 2004, 116, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Bellomo, R.; Homel, P.; Brendolan, A.; Dan, M.; Piccinni, P.; Greca, G.L. Effect of different doses in continuous veno-venous hemofiltration on outcomes of acute renal failure: A prospective randomized trial. Lancet 2000, 356, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A. A novel nanocomposite matrix based on silylated chitosan and multiwall carbon nanotubes for the immobilization of urease. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2009, 19, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozgeyik, I.; Senel, M.; Cevik, E.; Abasıyanık, M.F. A novel thin film amperometric urea biosensor based on urease-immobilized on poly (N-glycidylpyrrole-co-pyrrole). Curr. Appl. Phys. 2011, 11, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.O.; Krause, S.; McNeil, C.J.; Pritchard, J.A.; Armstrong, R.D.; Athey, D.; Rawson, K. Electrochemical Sensor for Measurement of Urea and Creatinine in Serum Based on ac Impedance Measurement of Enzyme-Catalyzed Polymer Transformation. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 1940–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gau, J.J.; Lan, E.H.; Dunn, B.; Ho, C.M.; Woo, J.C.S. A MEMS based amperometric detector for E. coli bacteria using self-assembled monolayers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.W.; Maduraiveeran, G.; Xu, J.C.; Hunter, G.W.; Dutta, P.K. Design, fabrication, and testing of MEMS-based miniaturized potentiometric nitric oxide sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, H.; Sawada, T.; Kazawa, E.; Yoshida, H.; Iwasaki, Y.; Mitsubayashi, K. A Flexible and wearable glucose sensor based on functional polymers with Soft-MEMS techniques. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, J.; Han, J.I.; Choi, Y.; Yoon, D.S.; Oh, K.W. DNA hybridization electrochemical sensor using conducting polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggenstein, C.; Borchardt, M.; Diekmann, C.; Gründig, B.; Dumschat, C.; Cammann, K.; Knoll, M.; Spener, F. A disposable biosensor for urea determination in blood based on an ammonium-sensitive transducer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1999, 14, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.T.; Lin, Y.T.; Leu, Y.C.; Hu, C.Y. Enzyme immobilization on nitrocellulose film for pH-EGFET type biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 148, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senillou, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Martelet, C.; Cosnier, S. A miniaturized urea sensor based on the integration of both ammonium based urea enzyme field effect transistor and a reference field effect transistor in a single chip. Talanta 1999, 50, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koncki, R.; Radomska, A.; Gląb, S. Potentiometric determination of dialysate urea nitrogen. Talanta 2000, 52, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.H.; Pake, S.H.; Lee, C.W.; Min, N.K.; Hong, S.I. Fabrication of amperometric urea sensor based on nano-porous silicon technology. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2003, 42, S735–S738. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Verma, N.; Garg, A.K.; Redhu, N. Urea biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 134, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syu, M.J.; Chang, Y.S. Ionic effect investigation of a potentiometric sensor for urea and surface morphology observation of entrapped urease/polypyrrole matrix. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2671–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herlem, B.G.; Lakard, S.; Antoniou, A.; Fahys, B. Urea potentiometric biosensor based on modified electrodes with urease immobilized on polyethylenimine films. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar]
- Lakard, B.; Magnin, D.; Deschaume, O.; Vanlancker, G.; Glinel, K.; Demoustier-Champagne, S.; Nysten, B.; Jonas, A.M.; Bertrand, P.; Yunus, S. Urea potentiometric enzymatic biosensor based on charged biopolymers and electrodeposited polyaniline. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4139–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, G.; Yoon, H.H. Amperometric urea biosensors based on sulfonated graphene/polyaniline nanocomposite. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.Z.; Su, L.; Lei, Yu. Pt nanoflower/polyaniline composite nanofibers based urea biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 30, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.W.; Chou, J.C.; Sun, T.P.; Hsiung, S.K. Solid-state urea biosensor based on the differential method. IEEE Sens. J. 2006, 6, 269–275. [Google Scholar]
- Slaugther, G. A gold interdigitated microelectrodes fabricated on polyhydroxybutyrate substrate for the determination of urea using impedimetric measurements. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurinavicius, V.; Razumiene, J.; Gureviciene, V. Bioelectrochemical conversion of urea on carbon black electrode and application. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 2208–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, N.H.; Chou, J.C.; Sun, T.P.; Hsiung, S.K. Measurement and comparison of potentiometric selectivity coefficients of urea biosensors based on ammonium ion-selective electrodes. IEEE Sens. J. 2005, 5, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Kim, J. Porous tin-oxide-coated regenerated cellulose as disposable and low-cost alternative transducer for urea detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 2223–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Pan, L.J.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, W.; Shi, Y.; Yu, G.H. A nanostructured conductive hydrogels-based biosensor platform for human metabolite detection. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Shi, Y.; Pan, L.J.; Shi, Y.; Yu, G.H. Rational design and applications of conducting polymer hydrogels as electrochemical biosensors. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2015, 3, 2920–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, B.; Pan, L.J.; Yu, G.H. 3D nanostructured conductive polymer hydrogels for high-performance electrochemical devices. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2856–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vering, T.; Adam, S.; Drewer, H.; Dumschat, C.; Steinkuhl, R.; Schulze, A.; Siegel, E.G.; Knoll, M. Wearable microdialysis system for continuous in vivo monitoring of glucose. Analyst 1998, 123, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.P.; Du, X.G.; Louie, R.; Kost, G.J. Effect of drugs on glucose measurements with handheld glucose meters and a portable glucose analyzer. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2000, 113, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, M.M.; Jullien, G.A. A wireless-implantable microsystem for continuous blood glucose monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2009, 3, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucani, D.; Cataldo, G.; Cruz, J.; Villegas, G.; Wong, S. A portable ECG monitoring device with bluetooth and holter capabilities for telemedicine applications. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual International Conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, New York, NY, USA, 29–30 August 2006; pp. 5244–5247.
- Wen, C.; Yeh, M.F.; Chang, K.C.; Lee, R.G. Real-time ECG tele-monitoring system design with mobile phone platform. Measurement 2008, 41, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaw, F.S.; Tseng, Y.L.; Jang, J.K. Modular design of a long-term portable recorder for physiological signals. Measurement 2010, 43, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, N.H.; Chou, J.C.; Sun, T.P.; Hsiung, S.K. Study on the disposable urea biosensors based on PVC-COOH membrane ammonium ion-selective electrodes. IEEE Sens. J. 2006, 6, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, P.K.; Brosha, E.L. Trace detection of 2, 4, 6-trinitrotoluene using electrochemical gas sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 1624–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Mu, X.; Yang, Y.; Mason, A.J. Low power multimode electrochemical gas sensor array system for wearable health and safety monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 3391–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, V.; Bishop, D.; Alonas, E.; LaBelle, J.; Joshi, L.; Alford, T.L. A Low-Cost Electrochemical Biosensor for Rapid Bacterial Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Lee, C.H.; Fiering, J.O.; Ufer, S.; Scarantino, C.W.; Nagle, H.T. Manipulation of microenvironment with a built-in electrochemical actuator in proximity of a dissolved oxygen microsensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2004, 4, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.S.; Huang, H.Y.; Chen, S.C.; Ho, K.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Chou, T.C.; Wu, C.H.; Wang, W.F.; Wu, C.F.; Luo, C.H. Real-time telemetry system for amperometric and potentiometric electrochemical sensor. Sensors 2011, 11, 8593–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, W.Y.; Yeh, M.H.; Chen, J.C.; Hsiung, S.K. Design of a low-voltage instrumentation amplifier for enzyme-extended-gate field effect transistor based urea sensor application. In Proceedings of the First IEEE International Workshop on Electronic Design, Test and Applications, Christchurch, New Zealand, 29–31 January 2002; pp. 177–180.
- Wang, J.Q.; Chou, J.C.; Sun, T.P.; Hsiung, S.K.; Hsiung, G.B. pH-based potentio-metrical flow injection biosensor for urea. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 91, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.J.; Huang, H.Y.; Luo, C.H. A low power analog front-end (AFE) circuit dedicated for driving bio-electrochemical sensors and peripheral device. In Proceedings of the IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems (BioCAS) Conference, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 28–30 November 2012; pp. 120–123.
- Lambrechts, M.; Sansen, W. Biosensors: Microelectrochemical. Devices, 1st ed.; Institute of Physics Publishing: Bristol, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Texas Instrument. MASP430F149 Texas Instrument Mixed Signal Microcontroller, 2011. Available online: http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/msp430f149 (accessed on 18 November 2015).
- Huang, C.J.; Lin, J.L.; Chen, P.H.; Syu, M.J.; Lee, G.B. A multi-functional electrochemical sensing system using micro-fluid technology for detection of urea and creatinine. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Ti | Au | Ag | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Deposition rate | 0.01 nm/s | 0.01 nm/s | 0.01 nm/s |
| 1st Thickness | 5 nm | 5 nm | 5 nm |
| 2nd Deposition rate | 0.1 nm/s | 0.1 nm/s | 0.1 nm/s |
| 2nd Thickness | 10 nm | 115 nm | 115 nm |
| Vacuum | 3 × 10−6 torr | ||
| Cable Mode | Front-End | MCU | MAX3232 | Regulator |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P.C. (mW) | 0.32 | 7.88 | 3.31 | 0.92 |
| % of Total P.C. | 2.57% | 63.40% | 26.63% | 7.40% |
| Total Power | 12.43 mW | |||
| Device lifetime | 4–5 days (A 3.7V Li-ion 500 mA·h battery) | |||
| Wireless mode | Front-end | MCU | ZigBee | Regulator |
| P.C. (mW) | 0.32 | 7.88 | 23.5 | 0.92 |
| % of Total P.C. | 0.98 | 24.15% | 72.04% | 2.82% |
| Total Power | 32.62 mW | |||
| Device lifetime | 1–2 days (A 3.7V Li-ion 500 mA·h battery) | |||
| Specification | [47] | This Work | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Background Solvent | water | serum | water | serum |
| Sensitivity (mV/log [M]) | 28.68 ± 0.01 | 2.71 ± 0.56 | 31.12 | 1.59 ± 0.47 |
| Sampling Time (s) | 400 | 400 | 100 | 100 |
| Response Time (s) | ~800 | ~1200 | ~100 | ~500 |
| Sample Volume (mL) | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Working Volume (mL) | 5 | 5 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Key Item | Specification | |
|---|---|---|
| System Power Supply | 3.3 V | |
| Power Consumption | Cable | ZigBee |
| (Cable mode & Wireless mode) | 12.42 mW | 32.62 mW |
| Linearity (R2) | 0.995 | |
| Sensitivity (mV/log [M]) | 31.12 | |
| UART Baud rate | 9600 | |
| Device Size | 6.0 × 4.3 cm2 | |
| Sensor Size | 0.7 × 1.0 cm2 | |
| Specification | [40] | This Work |
|---|---|---|
| Circuit Composition | CMOS/FPGA | Commercial Chip |
| Power Supply | 1.8V/3.3 V | 3.3 V |
| Linearity | 0.998 | 0.995 |
| Power consumption | 157.25 mW | 32.62 mW |
| Data transmission | 433 MHz/ISM | 2.4 GHz/ZigBee |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, W.-J.; Luo, C.-H.; Lin, J.-L.; Chou, S.-H.; Chen, P.-H.; Syu, M.-J.; Kuo, S.-H.; Lai, S.-C. A Portable Low-Power Acquisition System with a Urease Bioelectrochemical Sensor for Potentiometric Detection of Urea Concentrations. Sensors 2016, 16, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040474
Ma W-J, Luo C-H, Lin J-L, Chou S-H, Chen P-H, Syu M-J, Kuo S-H, Lai S-C. A Portable Low-Power Acquisition System with a Urease Bioelectrochemical Sensor for Potentiometric Detection of Urea Concentrations. Sensors. 2016; 16(4):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040474
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Wei-Jhe, Ching-Hsing Luo, Jiun-Ling Lin, Sin-Houng Chou, Ping-Hung Chen, Mei-Jywan Syu, Shin-Hung Kuo, and Shin-Chi Lai. 2016. "A Portable Low-Power Acquisition System with a Urease Bioelectrochemical Sensor for Potentiometric Detection of Urea Concentrations" Sensors 16, no. 4: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040474
APA StyleMa, W.-J., Luo, C.-H., Lin, J.-L., Chou, S.-H., Chen, P.-H., Syu, M.-J., Kuo, S.-H., & Lai, S.-C. (2016). A Portable Low-Power Acquisition System with a Urease Bioelectrochemical Sensor for Potentiometric Detection of Urea Concentrations. Sensors, 16(4), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040474