An SOI CMOS-Based Multi-Sensor MEMS Chip for Fluidic Applications †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Multi-Sensor Chip Design
2.1. Temperature Sensor
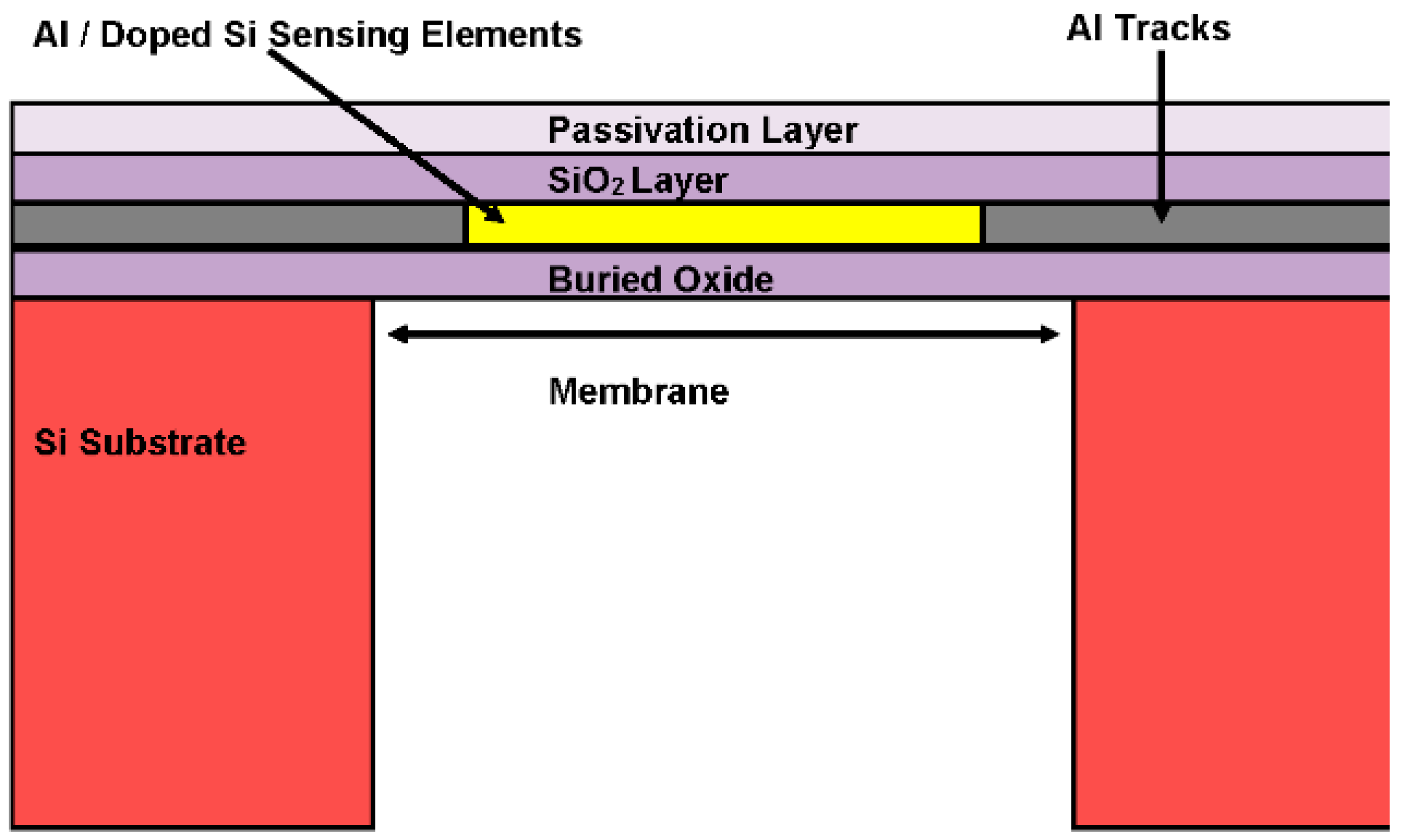
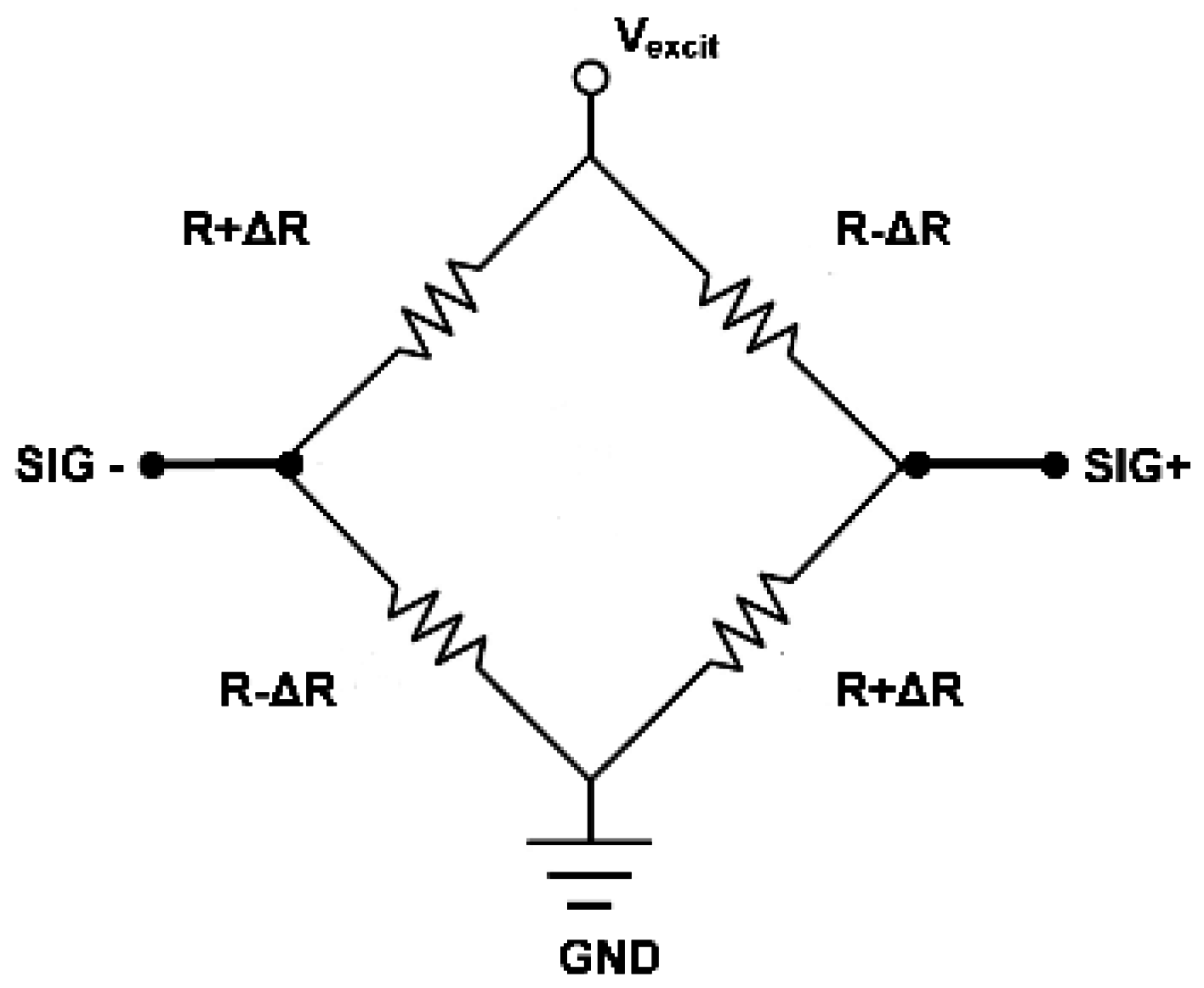
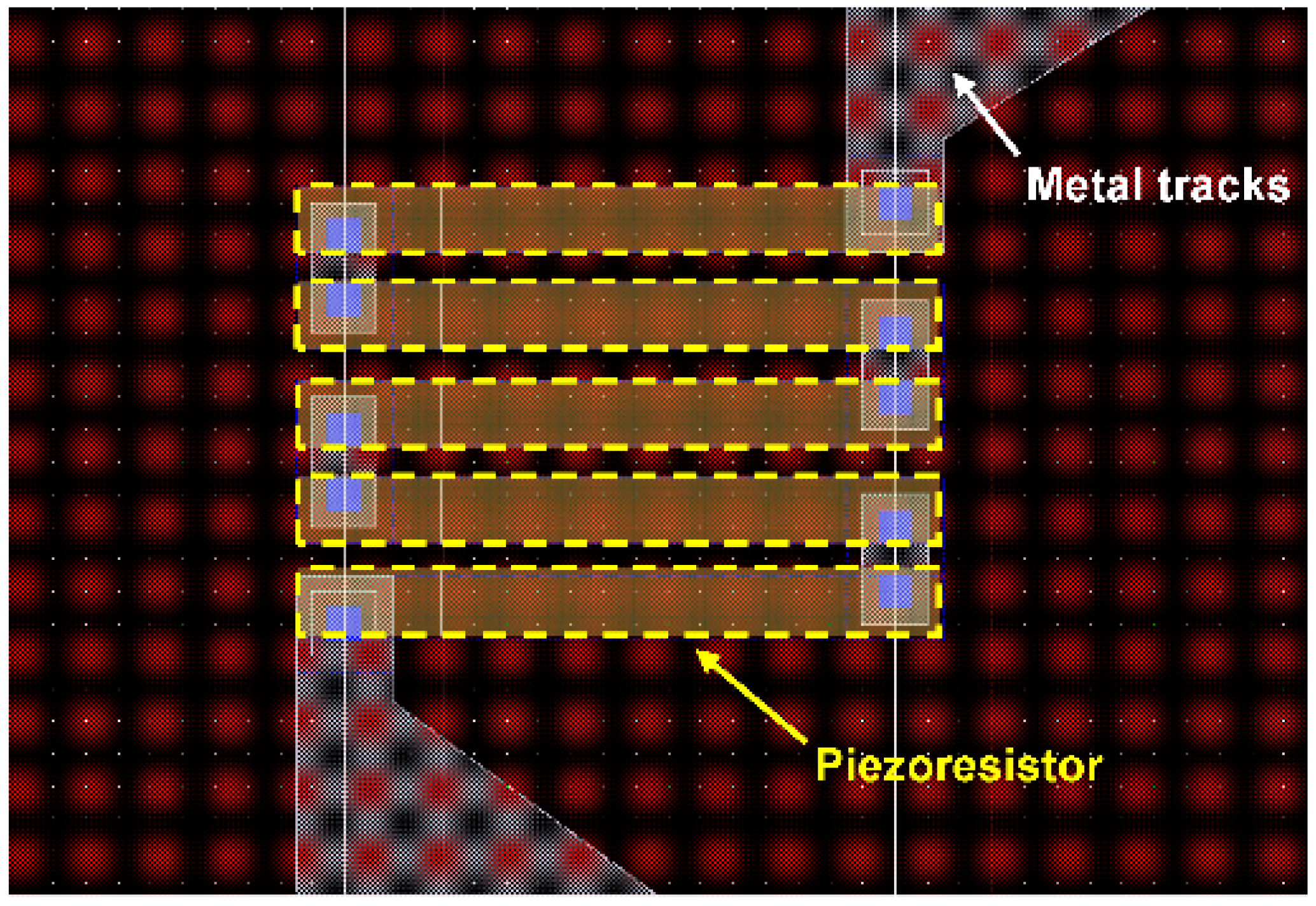
2.2. Pressure Sensor
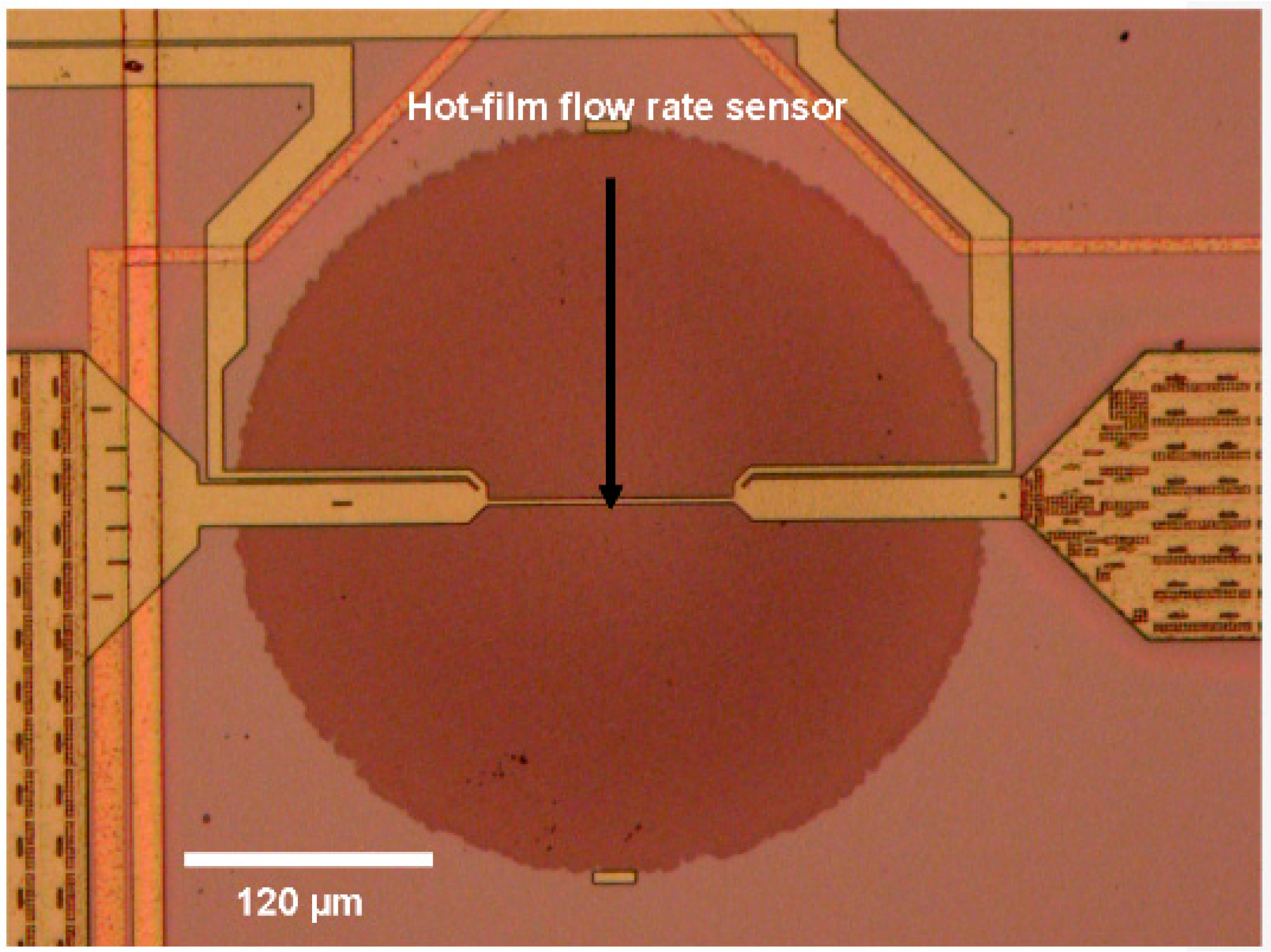
2.3. Flow Sensor
3. Calibration Setups
3.1. Temperature Sensors
3.2. Pressure Sensor
3.3. Flow Rate Sensor
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Temperature Sensors
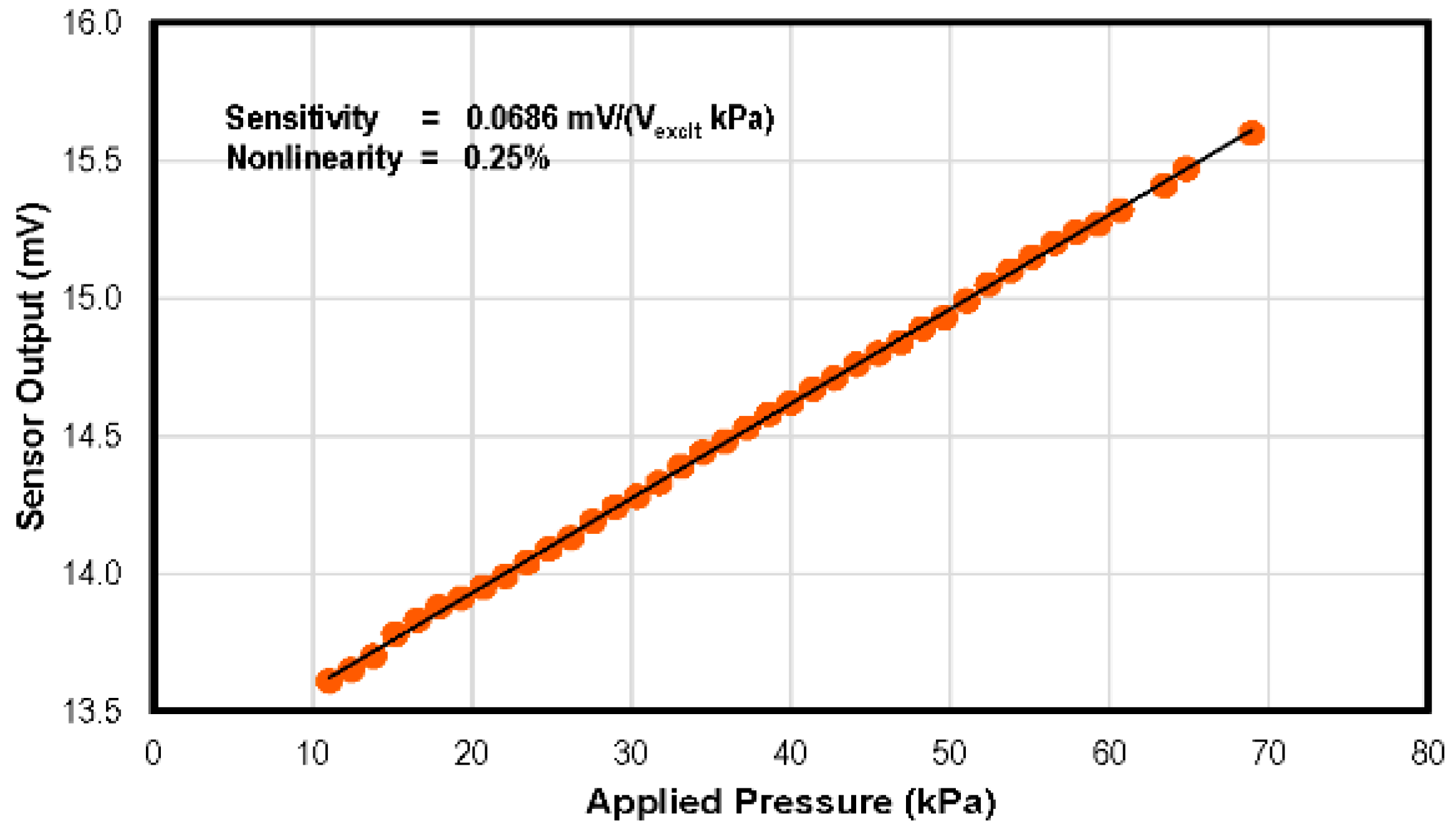
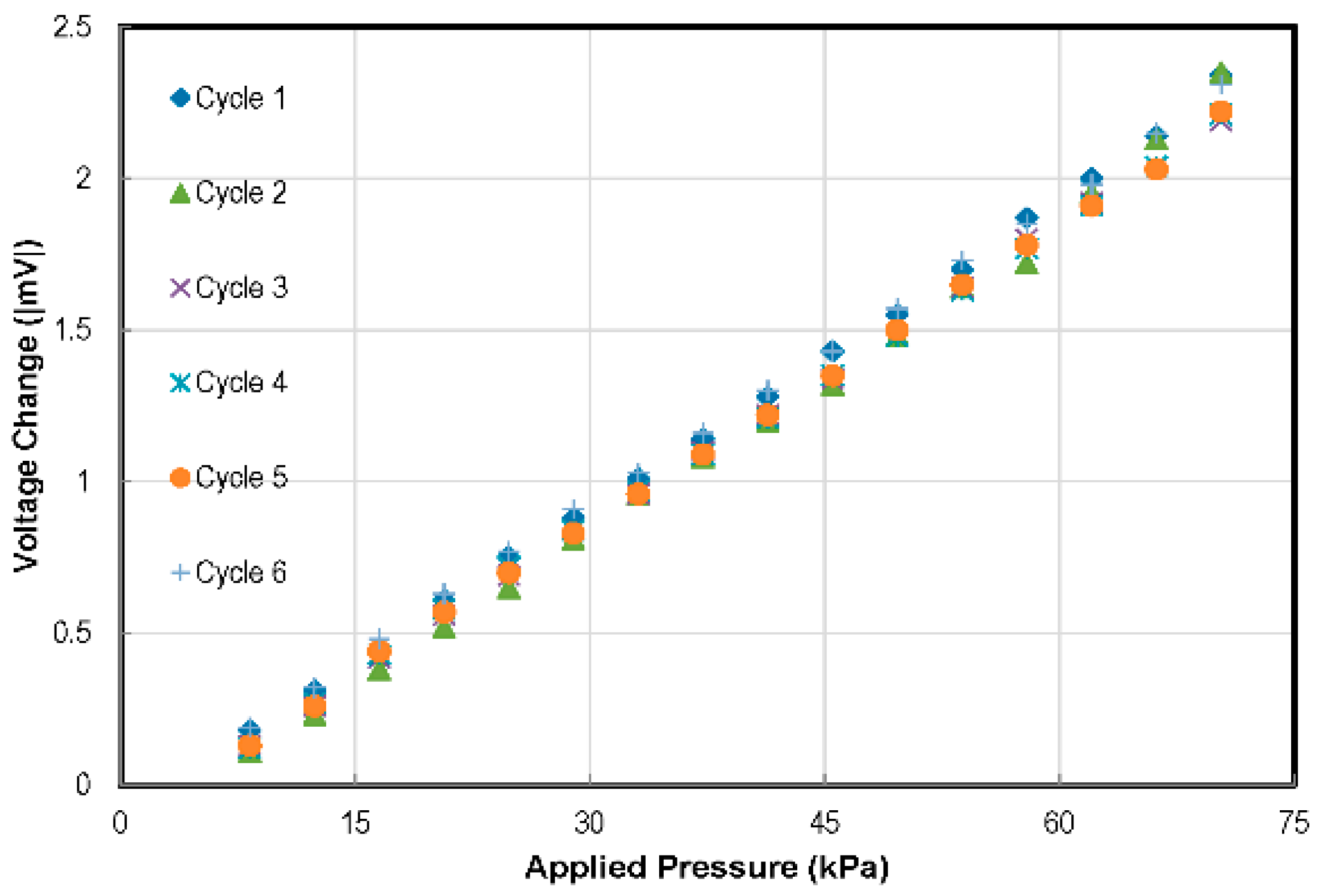
4.2. Pressure Sensor
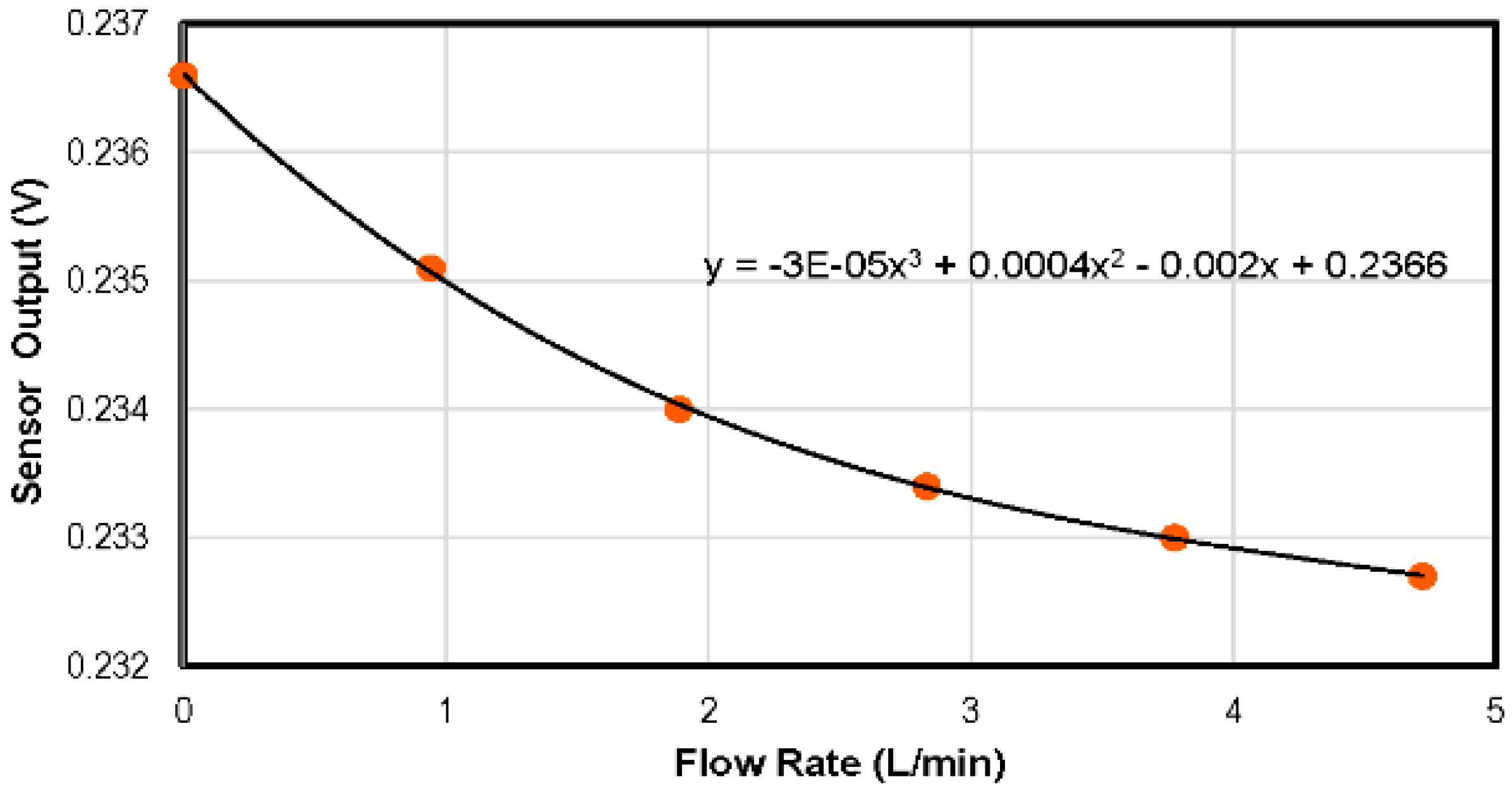
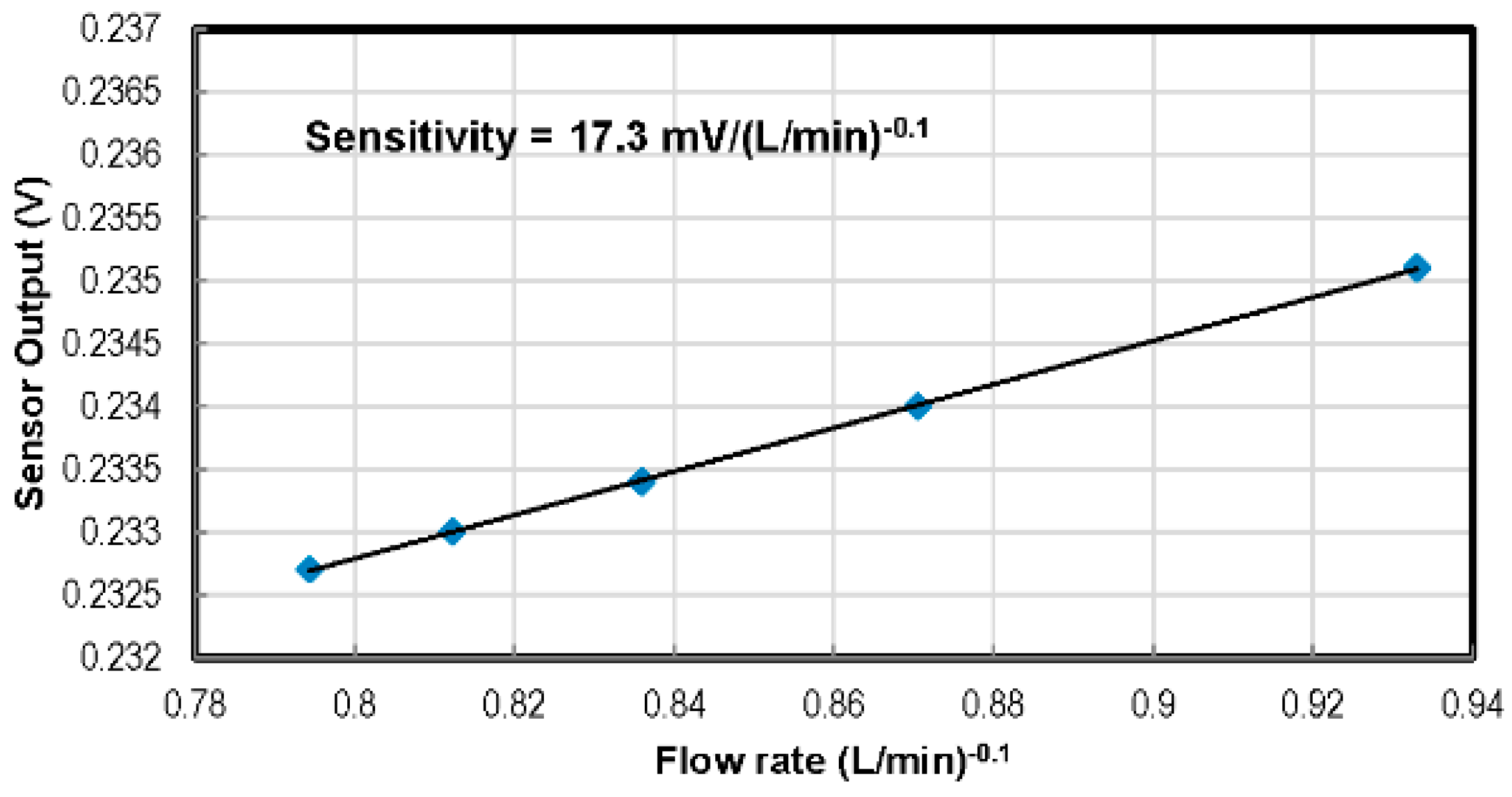
4.3. Flow Rate Sensor
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dixon, R. MEMS: What to Look for in 2013; MEMS Market Brief—Issue 1; iSuppli: El Segundo, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Chiu, C.-W.; Jiang, F.; Lin, Q.; Tai, Y.-C. Mass flowmeter using a multi-sensor chip. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE Annual International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Miyazaki, Japan, 23–27 January 2000; pp. 541–546.
- Hagleitner, C.; Lange, D.; Hierlemann, A.; Brand, O.; Baltes, H. CMOS single-chip gas detection system comprising capacitive, calorimetric and mass-sensitive microsensors. IEEE J. Solid-State Circ. 2002, 37, 1867–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.; Smith, R.; Massoud-Ansari, S.; Najafi, N. Coriolis mass flow, density and temperature sensing with a single vacuum sealed mems chip. In Proceedings of the Solid-State Sensor, Actuator and Microsystems Workshop, Hilton Head Island, SC, USA, 4–8 June 2004; pp. 75–78.
- Xu, Y.; Chiu, C.-W.; Jiang, F.; Lin, Q.; Tai, Y.-C. A MEMS multi-sensor chip for gas flow sensing. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2005, 121, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.H.; Wang, D.A.; Hsueh, T.H.; Lee, C.Y. A MEMS-based flow rate and flow direction sensing platform with integrated temperature compensation scheme. Sensors 2009, 9, 5460–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roozeboom, C.L.; Hopcroft, M.A.; Smith, W.S.; Sim, Y.S.; Wickeraad, D.A.; Hartwell, P.G.; Pruitt, B.L. Integrated multifunctional environmental sensors. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2013, 22, 779–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, T.; Zhang, D. A monolithic piezoresistive pressure-flow sensor with integrated signal-conditioning circuit. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 2122–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, O.; Inagaki, H.; Igarashi, I. Monolithic pressure-flow sensor. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 1987, 34, 2456–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kälvesten, E.; Vieider, C.; Löfdahl, L.; Stemme, G. An integrated pressure—Flow sensor for correlation measurements in turbulent gas flows. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1996, 52, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyldgard, A.; Olafsdottir, I.; Olesen, M.; Hedegaard, T.; Hansen, O.; Thomsen, E.V. Fish & chips: Four electrode conductivity/salinity sensor on a silicon multi-sensor chip for fisheries research. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors Conference, Irvine, CA, USA, 30 October–3 November 2005; pp. 1124–1127.
- Mansoor, M.; Haneef, I.; Akhtar, S.; Rafiq, M.; Ali, S.; Udrea, F. SOI CMOS Multi-Sensors MEMS Chip for Aerospace Applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Sensors Conference, Valencia, Spain, 2–5 November 2014; pp. 1204–1207.
- Kimura, M.; Takei, M.; Ho, C.-M.; Saito, Y.; Horii, K. Visualization of shear stress with micro imaging chip and discrete wavelet transform. J. Fluids Eng. 2002, 124, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berns, A.; Obermeier, E. Aeromems sensor arrays for time resolved wall pressure and wall shear stress measurements. In Imaging Measurement Methods for Flow Analysis; Nitsche, W., Dobriloff, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 106, pp. 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, E.; Wise, K.D. An integrated mass flow sensor with on-chip CMOS interface circuitry. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 1992, 39, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Fukumoto, Y.; Suzuki, F.; Maenaka, K. SOI-MEMS sensor for multi-environmental sensing-system. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Networked Sensing Systems (INSS ‘07), Brainschweig, Germany, 6–8 June 2007; pp. 146–149.
- DeHennis, A.D.; Wise, K.D. A wireless microsystem for the remote sensing of pressure, temperature, and relative humidity. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2005, 14, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagleitner, C.; Hierlemann, A.; Lange, D.; Kummer, A.; Kerness, N.; Brand, O.; Baltes, H. Smart single-chip gas sensor microsystem. Nature 2001, 414, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.S.; Han, I.Y.; Yu, J.; Kim, S.J.; Byun, K.Y. Thermal characterization of thermally conductive underfill for a flip-chip package using novel temperature sensing technique. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 455, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, P.R.N.; Greenwood, J.R.; Long, C.A. Review of temperature measurement. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2000, 71, 2959–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A.; Pathirana, V.; Ali, S.Z.; Udrea, F. Silicon on insulator thermodiode with extremely wide working temperature range. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (TRANSDUCERS & EUROSENSORS XXVII), Transducers & Eurosensors XXVII, Barcelona, Spain, 16–20 June 2013; pp. 1911–1914.
- Santra, S.; Guha, P.K.; Ali, S.Z.; Haneef, I.; Udrea, F. Silicon on insulator diode temperature sensor—A detailed analysis for ultra-high temperature operation. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 10, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A.; Pathirana, V.; Ali, S.Z.; Dragomirescu, D.; Udrea, F. Experimental, analytical and numerical investigation of non-linearity of SOI diode temperature sensors at extreme temperatures. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 222, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, H. Concerning a thermometer with solid-state diodes. Sci. Am. 1961, 204, 192. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, M.; Kikuchi, K. Thermistor-like pn diode temperature sensor and a new method to measure the absolute humidity using these temperature sensors combined with a microheater. In Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE Sensors Conference, Toronto, ON, Canada, 22–24 October 2003; pp. 636–641.
- Udrea, F.; Santra, S.; Gardner, J.W. CMOS temperature sensors—Concepts, state-of-the-art and prospects. In Proceedings of the 31st International Semiconductor Conference (CAS ‘08), Sinaia, Romania, 13–15 October 2008; pp. 31–40.
- Mansoor, M.; Haneef, I.; Akhtar, S.; De Luca, A.; Udrea, F. Silicon diode temperature sensors—A review of applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 232, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, W.P.; Smith, J.H. Micromachined pressure sensors: Review and recent developments. Smart Mater. Struct. 1997, 6, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeby, S. MEMS Mechanical Sensors; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Van Putten, A.F.P.; Middelhoek, S. Integrated silicon anemometer. Electron. Lett. 1974, 10, 425–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N. Micromachined flow sensors—A review. Flow Meas. Instrum. 1997, 8, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailly, F.; Giani, A.; Bonnot, R.; Temple-Boyer, P.; Pascal-Delannoy, F.; Foucaran, A.; Boyer, A. Anemometer with hot platinum thin film. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2001, 94, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, A.; Mailly, F.; Bonnot, R.; Pascal-Delannoy, F.; Foucaran, A.; Boyer, A. Thermal model of thin film anemometer. Microelectron. J. 2002, 33, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.W.; Varadan, V.K. Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices; John Wiley & Sons: Malden, MA, USA, 2001; p. 522. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.C.; Wise, K.D. Temperature sensitivity in silicon piezoresistive pressure transducers. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1983, 30, 802–810. [Google Scholar]
- White, F.M. Fluid Mechanics, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill Higher Education: Columbus, OH, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Holman, J. Heat Transfer, 10th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: Columbus, OH, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Fan, Z.; Zou, J.; Engel, J.; Liu, C. Two-dimensional micromachined flow sensor array for fluid mechanics studies. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2003, 16, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrich, F.; Kliche, K.; Storz, M.; Billat, S.; Ashauer, M.; Zengerle, R. Thermal flow sensors for MEMS spirometric devices. Sens. Actuators A. Phys. 2010, 162, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



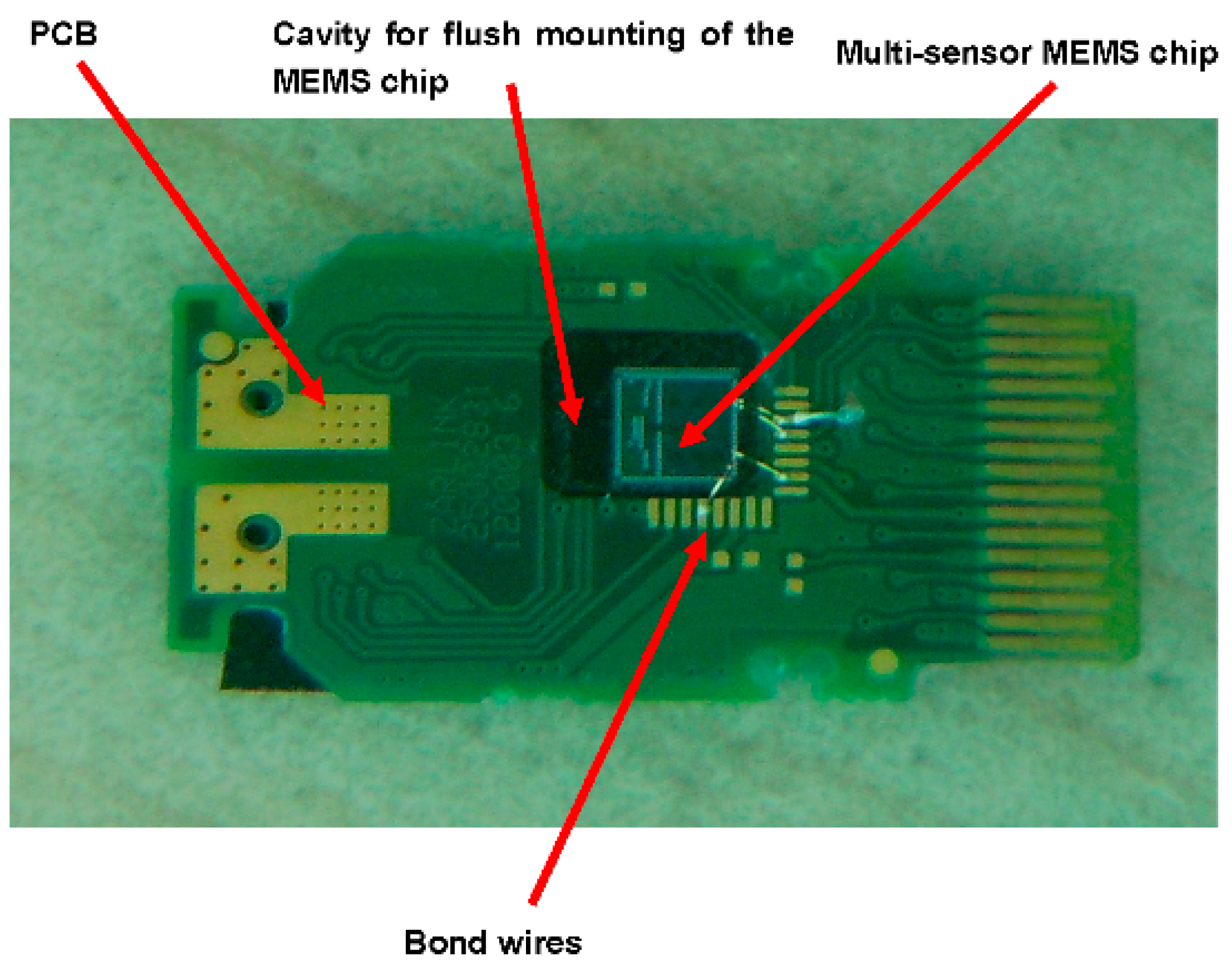
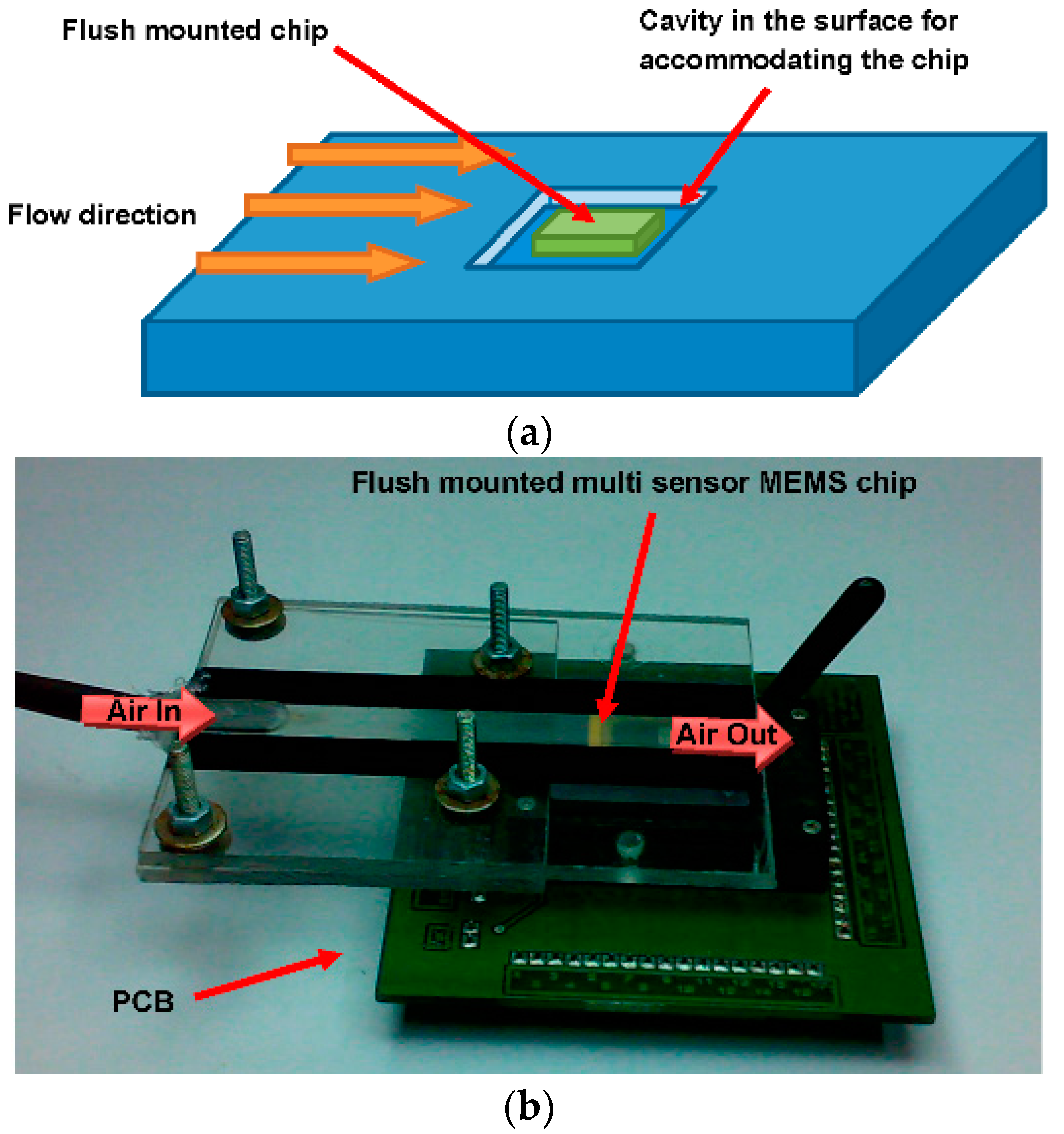
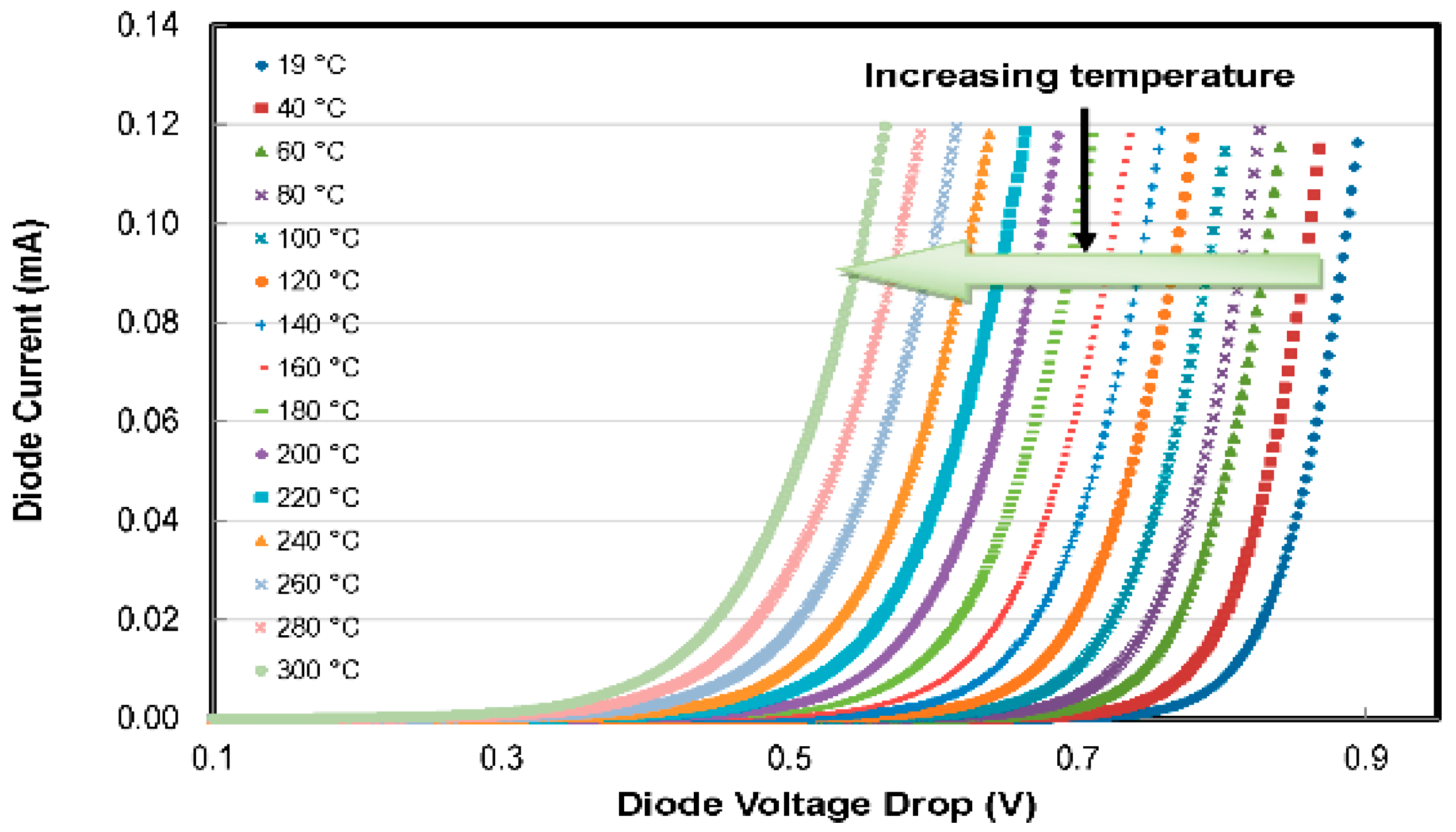
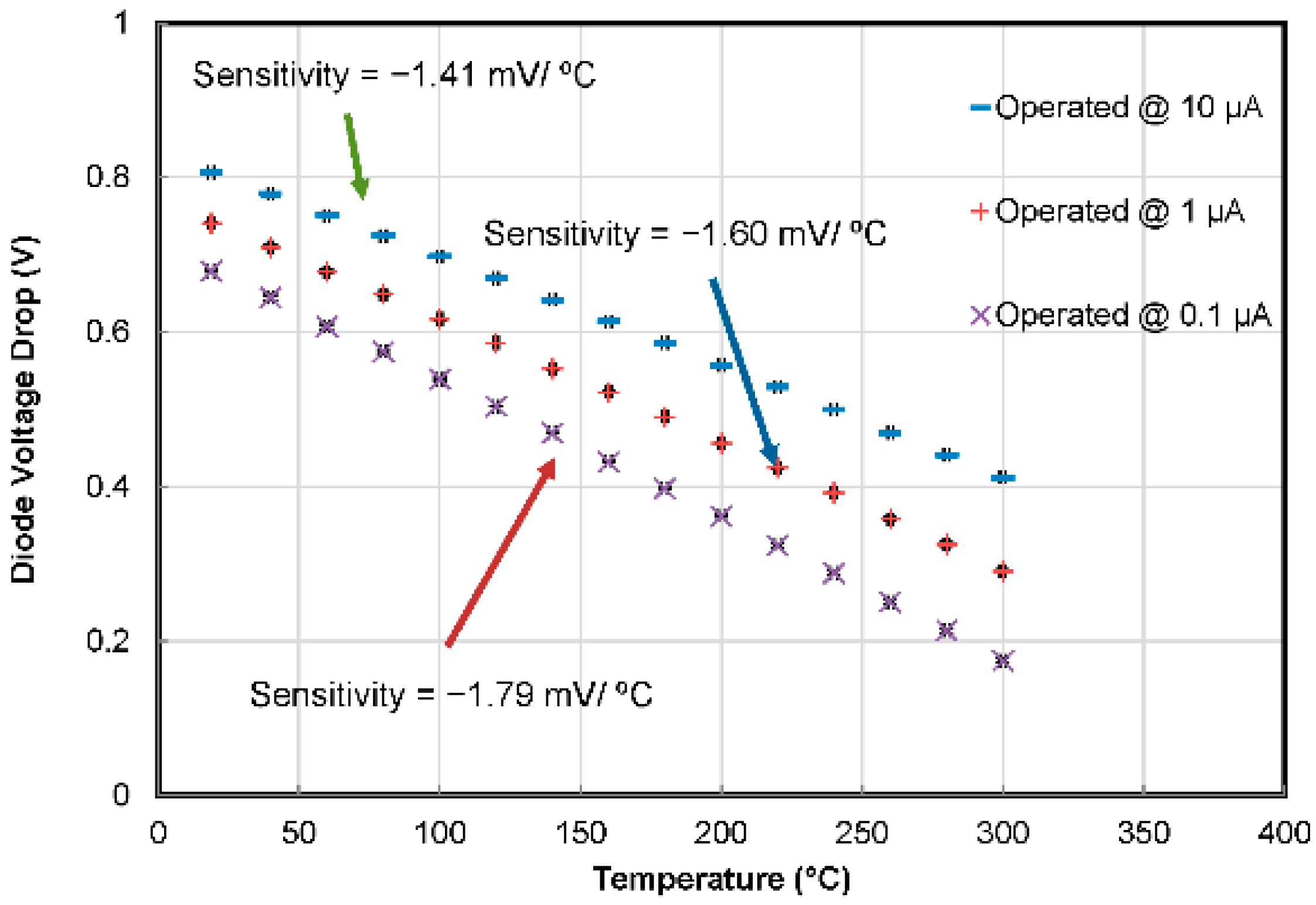
| S No | Year | Ref. | No of Sensors | Parameters Sensed | Substrate | CMOS Process | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Rate/Mass Flow | Wall Shear Stress | Pressure | Temperature | Gas | Density | Light Intensity | Electric Conductivity | Flow Direction | Humidity | Air Speed | Magnetic Field | Acceleration | Silicon | SOI | Yes | No | ||||
| 1 | 1987 | [9] | 3 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||
| 2 | 1992 | [15] | 5 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||
| 3 | 1996 | [10] | 3 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||
| 4 | 2000 | [2] | 4 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 5 | 2001 | [18] | 4 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||||
| 6 | 2002 | [3] | 4 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||||
| 7 | 2004 | [4] | 3 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||
| 8 | 2005 | [11] | 4 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 9 | 2005 | [5] | 3 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||
| 10 | 2005 | [17] | 3 | √ | √ | √ | √ 1 | √ 2 | ||||||||||||
| 11 | 2007 | [16] | 4 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ 2 | |||||||||||
| 12 | 2009 | [6] | 3 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||
| 13 | 2011 | [8] | 2 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||||
| 14 | 2013 | [7] | 8 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| Reference | Year | Parameter | Chip Dimensions (mm × mm) | No. of Sensors on the Chip | Sensor Density (Number of Sensors Per mm2 of Chip Area) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure | Temperature | Flow Rate | ||||||||
| Range (kPa) | Sensitivity |µV/(V·kPa)| | Range (°C) | Sensitivity | Range (L/min) | Sensitivity (V/(L/min)) | |||||
| [9] | 1987 | 0–40 | 9.9 at 1 mA | 25–45 | N/R 1 | 0–7 | N/R | 4 × 8 | 3 | 0.1875 |
| [15] | 1992 | 0–107 | 92.3 | −55 to 125 | 4 mV/°C | N/R | N/R | 3.5 × 5 | 6 | 0.3429 |
| [5] | 2005 | 0–140 | 82.9 | 30–90 | TCR 2 0.104% °C−1 | 0–5 | 0.17 to 0.62 | 20 × 10 | 15 | 0.0750 |
| [17] | 2005 | 67–160 | 113 fF/kPa | 20–100 | 15 fF/°C | N/R | N/R | ~3 × 4 | 5 | 0.4167 |
| [8] | 2011 | 0–50 | 3900 @ 21 gain | N/R | N/R | 0–5 | 0.01 to 0.09 | 4.5 × 9 | 2 | 0.0494 |
| [7] | 2013 | 67–100 | 16,000 @ 500 gain | 30–50 | 0.72–2.9 mV/°C | N/R | N/R | 10 × 10 | 12 | 0.1200 |
| This work | 2016 | 0–75 | 69 | 20–300 | −1.41 to −1.79 mV/°C | 0–4.7 | −0.32 to −1.59 | 3.8 × 3.8 | 20 | 1.3800 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mansoor, M.; Haneef, I.; Akhtar, S.; Rafiq, M.A.; De Luca, A.; Ali, S.Z.; Udrea, F. An SOI CMOS-Based Multi-Sensor MEMS Chip for Fluidic Applications. Sensors 2016, 16, 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111608
Mansoor M, Haneef I, Akhtar S, Rafiq MA, De Luca A, Ali SZ, Udrea F. An SOI CMOS-Based Multi-Sensor MEMS Chip for Fluidic Applications. Sensors. 2016; 16(11):1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111608
Chicago/Turabian StyleMansoor, Mohtashim, Ibraheem Haneef, Suhail Akhtar, Muhammad Aftab Rafiq, Andrea De Luca, Syed Zeeshan Ali, and Florin Udrea. 2016. "An SOI CMOS-Based Multi-Sensor MEMS Chip for Fluidic Applications" Sensors 16, no. 11: 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111608
APA StyleMansoor, M., Haneef, I., Akhtar, S., Rafiq, M. A., De Luca, A., Ali, S. Z., & Udrea, F. (2016). An SOI CMOS-Based Multi-Sensor MEMS Chip for Fluidic Applications. Sensors, 16(11), 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111608






