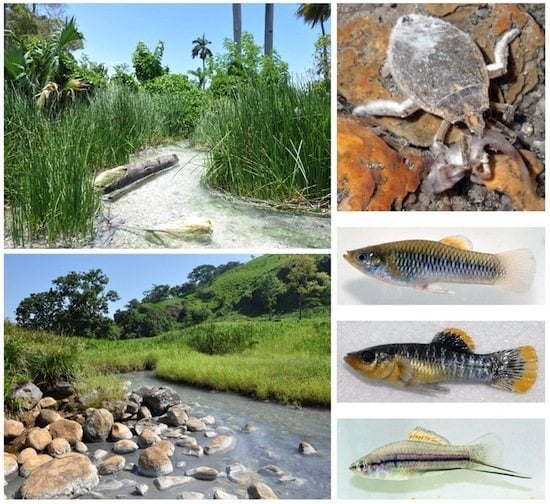
Patterns of Macroinvertebrate and Fish Diversity in Freshwater Sulphide Springs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Freshwater Sulphide Springs: Occurrence and Environmental Variation
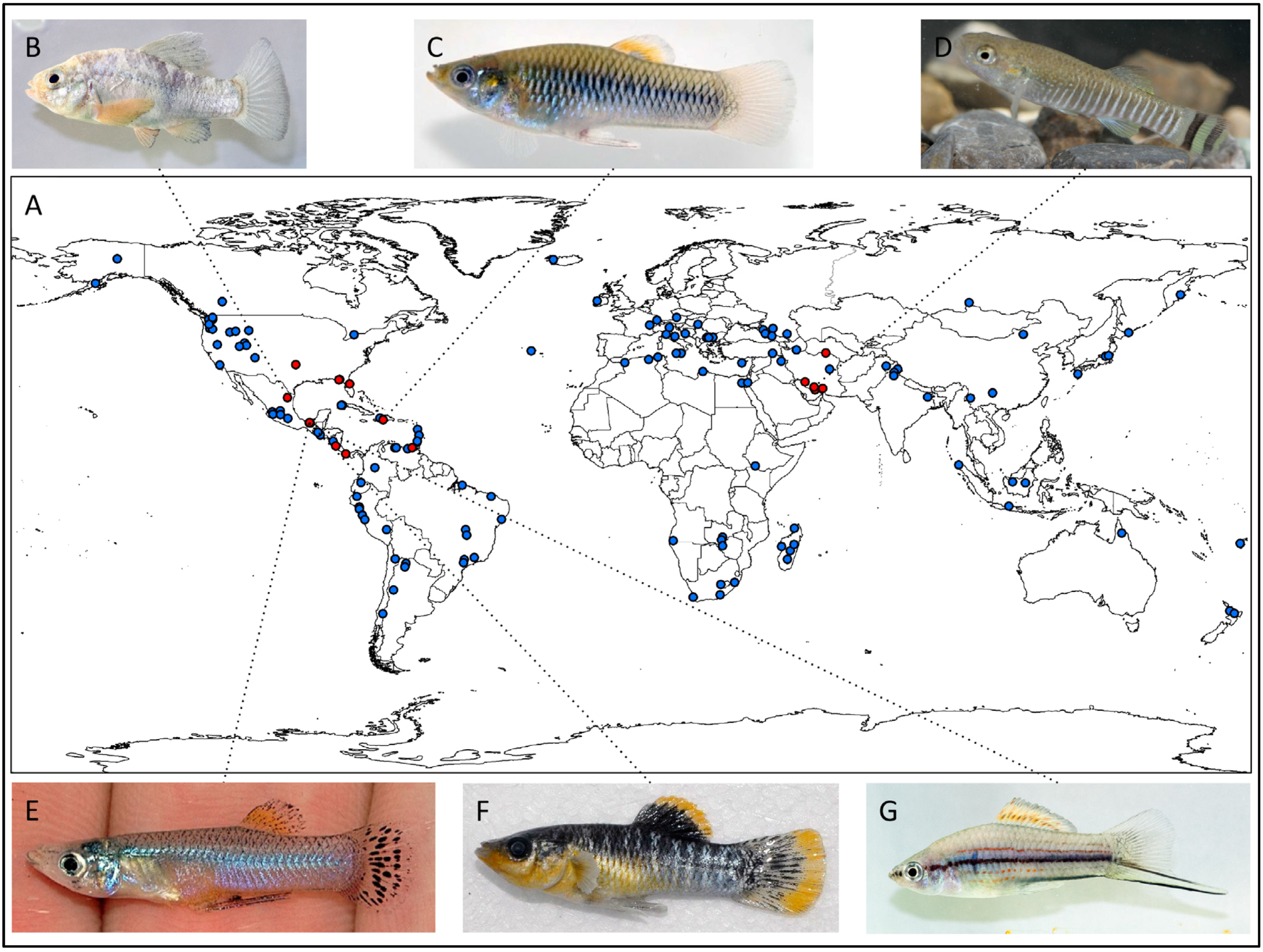
| Species | Locations | References |
|---|---|---|
| Synbranchidae | ||
| Ophisternon aenigmaticum | El Azufre II (Rio Tacotalpa drainage) and La Gloria (Rio Pichucalco drainage) springs, Mexico | This study |
| Cyprinodontidae | ||
| Cyprinodon bobmilleri † | Baños de San Ignacio (Rio San Fernando drainage), Mexico | [60]; Schlupp (personal communication) |
| Aphanius ginaonis † | Ginao spring (Hormuzgan drainage), Iran | [61,62] |
| Aphanius dispar * | Khurgu, Faryab, and Howba springs (Hormuzgan drainage), Dalaki and Mirahmad springs (Helleh drainage), Iran | [62,63] |
| Aphanius furcatus * | Khurgu and Faryab springs (Hormuzgan drainage), Iran | [62,63] |
| Poeciliidae | ||
| Acanthophacelus reticulata | Poza Azufre (Rio San Juan drainage), Venezuela | [64,65] |
| Brachyrhaphis roseni | Spring near David (Rio David drainage), Panama | S. Ingley (personal communication) |
| Gambusia affinis | Vendome Well/Black Sulphur Springs (Red River drainage), Oklahoma | [66,67] |
| Gambusia eurystoma † | Baños del Azufre (Rio Pichucalco drainage), Mexico | [68,69] |
| Gambusia holbrooki * | Green (St. John’s River drainage), Newport (Wakulla River drainage), and Panacea Mineral Springs (Dickerson Bay area), Florida | [70] |
| Gambusia sexradiata | Mogote del Puyacatengo (Puyacatengo drainage), Mexico | [71] |
| Limia sulphurophila * ,† | Balnearios La Zurza and La Zufrada (Lake Enriquillo basin), Dominican Republic | [72,73] |
| Poecilia formosa | Baños de San Ignacio (Río San Fernando drainage), México | Schlupp (personal communication) |
| Poecilia latipinna | Panacea Mineral Springs (Dickerson Bay area), Florida | [74] |
| Poecilia mexicana limantouri | Baños de San Ignacio (Río San Fernando drainage), México | Schlupp (personal communication) |
| Poecilia mexicana mexicana | El Azufre springs and Cueva del Azufre (Tacotalpa drainage), Mexico | [75,76] |
| Poecilia mexicana mexicana | La Lluvia and Puyacatengo springs (Puyacatengo drainage), Mexico | [76,77] |
| Poecilia sulphuraria †,* | Baños del Azufre and La Gloria springs (Pichucalco drainage), Mexico | [76,77] |
| Poecilia thermalis † | La Esperanza springs (Ixtapangajoya drainage), Mexico | [77] |
| Poeciliopsis elongata | Spring near David (Rio David drainage), Panama | S. Ingley (personal communication) |
| Priapichthys annectens | Spring in Rincón de la Vieja National Park (Rio Colorado drainage), Costa Rica | J. Johnson (personal communication) |
| Priapichthys panamensis | Spring near David (Rio David drainage), Panama | S. Ingley (personal communication) |
| Pseudoxiphophorus bimaculatus | La Gloria springs (Pichucalco drainage), Mexico | This study |
| Xiphophorus hellerii * | La Lluvia (Puyacatengo drainage) and La Gloria springs (Pichucalco drainage), Mexico | This study |
3. An Overview of Biodiversity in Sulphide Springs

3.1. Macroinvertebrates in Sulphide Spring Environments
3.2. Fish in Sulphide Spring Environments
3.2.1. Overview
3.2.2. Adaptation to Sulphide Spring Environments in the Family Poeciliidae
3.2.3. Ecological Speciation in Sulphide Spring Environments?
4. A Case Study: Comparative Analyses of Sulphide Springs and Adjacent Non-Sulphidic Habitats in Mexico
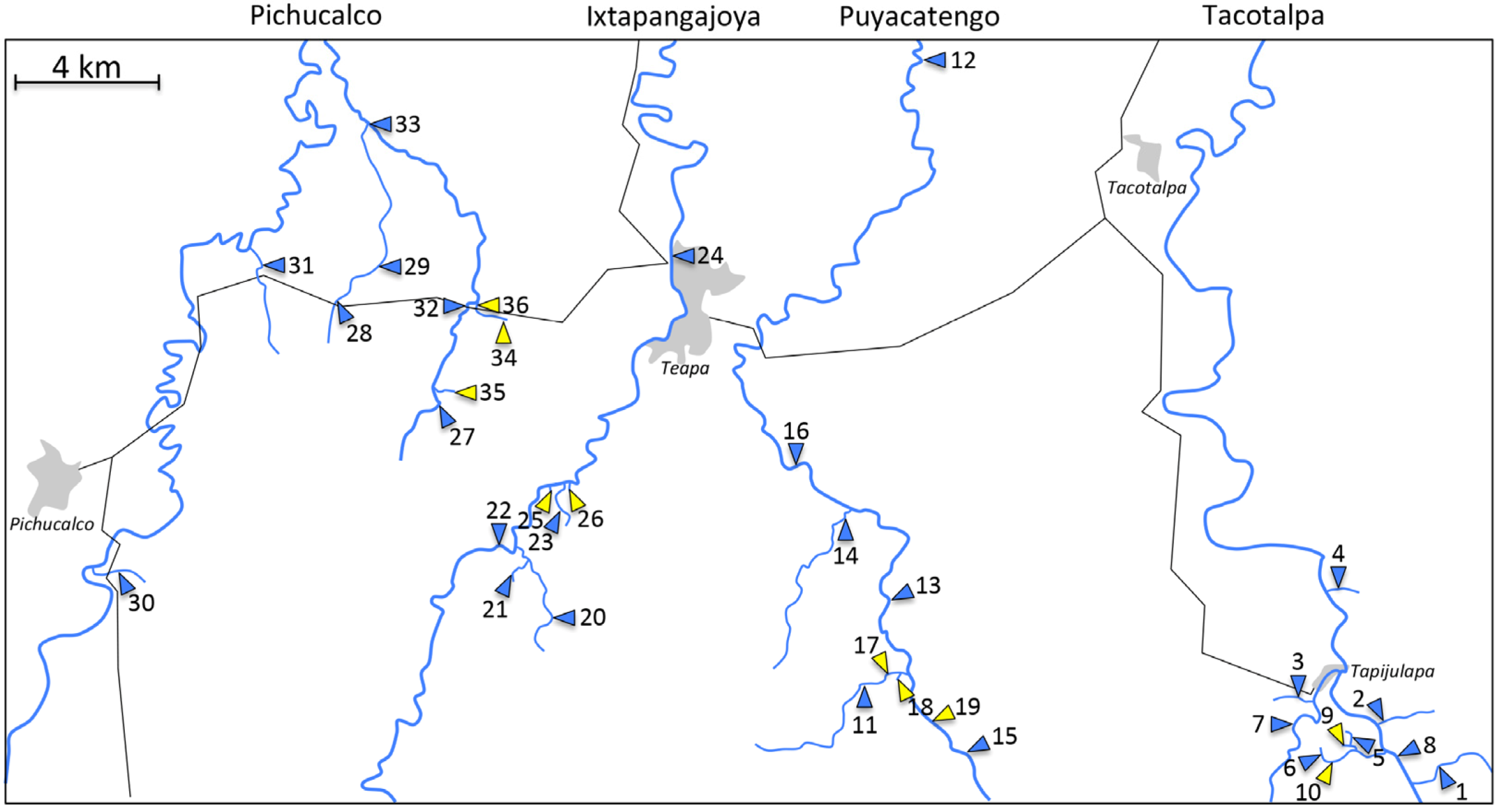
| ID | Location | H2S | Latitude | Longitude | Times Sampled (fish) | Number of Species (fish) | Times Sampled (Invertebrates) | Number of Genera (Invertebrates) | Density (Invertebrates) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tacotalpa drainage | |||||||||
| 1 | Arroyo Bonita * | - | 17.427 | −92.752 | 11 | 16 | 1 | 8.6 | 3.54 × 105 |
| 2 | Arroyo Cristal | - | 17.451 | −92.764 | 9 | 15 | 1 | 8.3 | 4.11 × 104 |
| 3 | Arroyo Tacubaya | - | 17.454 | −92.785 | 10 | 15 | 2 | 8.9 | 1.06 × 105 |
| 4 | Arroyo Tres | - | 17.484 | −92.776 | 9 | 11 | 1 | 9.0 | 1.59 × 105 |
| 5 | El Azufre, tributary | - | 17.442 | −92.775 | 4 | 4 | |||
| 6 | El Azufre, upstream | - | 17.436 | −92.77431 | 5 | 6 | 2 | 4.1 | 3.77 × 105 |
| 7 | Rio Amatán | - | 17.449 | −92.787 | 1 | 12 | |||
| 8 | Rio Oxolotán | - | 17.444 | −92.763 | 3 | 19 | |||
| 9 | El Azufre I* | + | 17.442 | −92.775 | 13 | 1 | 2 | 0.4 | 9.01 × 105 |
| 10 | El Azufre II | + | 17.438 | −92.775 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 1.0 | 1.01 × 106 |
| Puyacatengo drainage | |||||||||
| 11 | Arroyo La Lluvia, upstream * | - | 17.461 | −92.897 | 5 | 8 | 1 | 5.2 | 8.56 × 104 |
| 12 | Rio Puyacatengo, Miguel Hidalgo | - | 17.668 | −92.900 | 1 | 10 | |||
| 13 | Rio Puyacatengo, road crossing | - | 17.470 | −92.896 | 8 | 12 | 1 | 5.2 | 1.77 × 105 |
| 14 | Rio Puyacatengo, tributary | - | 17.505 | −92.908 | 5 | 8 | |||
| 15 | Rio Puyacatengo, upstream | - | 17.456 | −92.888 | 3 | 10 | 1 | 7.5 | 1.60 × 105 |
| 16 | Rio Puyacatengo, Vicente Guerrero | - | 17.510 | −92.915 | 8 | 11 | |||
| 17 | La Lluvia, big spring | + | 17.462 | −92.896 | 7 | 1 | |||
| 18 | La Lluvia, small spring * | + | 17.464 | −92.895 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 0.3 | 4.49 × 105 |
| 19 | Puyacatengo springs | + | 17.458 | −92.889 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 | 3.11 × 103 |
| Ixtapangajoya drainage | |||||||||
| 20 | Arroyo Chiflon | - | 17.476 | −92.986 | 1 | 3 | |||
| 21 | Arroyo La Joya | - | 17.499 | −92.993 | 1 | 5 | |||
| Ixtapangajoya drainage | |||||||||
| 22 | Rio Ixtapangajoya | - | 17.495 | −92.998 | 9 | 7 | |||
| 23 | Rio Ixtapangajoya, tributary | - | 17.510 | −92.980 | 3 | 5 | |||
| 24 | Rio Teapao | - | 17.495 | −92.997 | 1 | 15 | |||
| 25 | La Esperanza, big spring | + | 17.511 | −92.983 | 3 | 1 | |||
| 26 | La Esperanza, small spring | + | 17.511 | −92.980 | 2 | 1 | |||
| Pichucalco drainage | |||||||||
| 27 | Arroyo Caracol | - | 17.534 | −93.016 | 3 | 7 | |||
| 28 | Arroyo Rafael I | - | 17.558 | −93.043 | 6 | 11 | 1 | 9.6 | 4.4 × 105 |
| 29 | Arroyo Rafael II | - | 17.564 | −93.039 | 1 | 11 | |||
| 30 | Arroyo Rosita | - | 17.485 | −93.104 | 11 | 15 | 1 | 6.6 | 1.45 × 105 |
| 31 | Arroyo Santa Ana | - | 17.566 | −93.064 | 4 | 7 | |||
| 32 | Rio El Azufre, west branch * | - | 17.556 | −93.008 | 11 | 13 | 2 | 8.0 | 6.96 × 104 |
| 33 | Rio Pichucalco | - | 17.605 | −93.036 | 9 | 22 | |||
| 34 | Baños del Azufre * | + | 17.552 | −92.999 | 13 | 2 | |||
| 35 | La Gloria springs | + | 17.532 | −93.015 | 10 | 4 | |||
| 36 | Rio El Azufre, east branch | + | 17.557 | −93.006 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 0.4 | 4.06 × 104 |
4.1. Aquatic Macroinvertebrate Communities
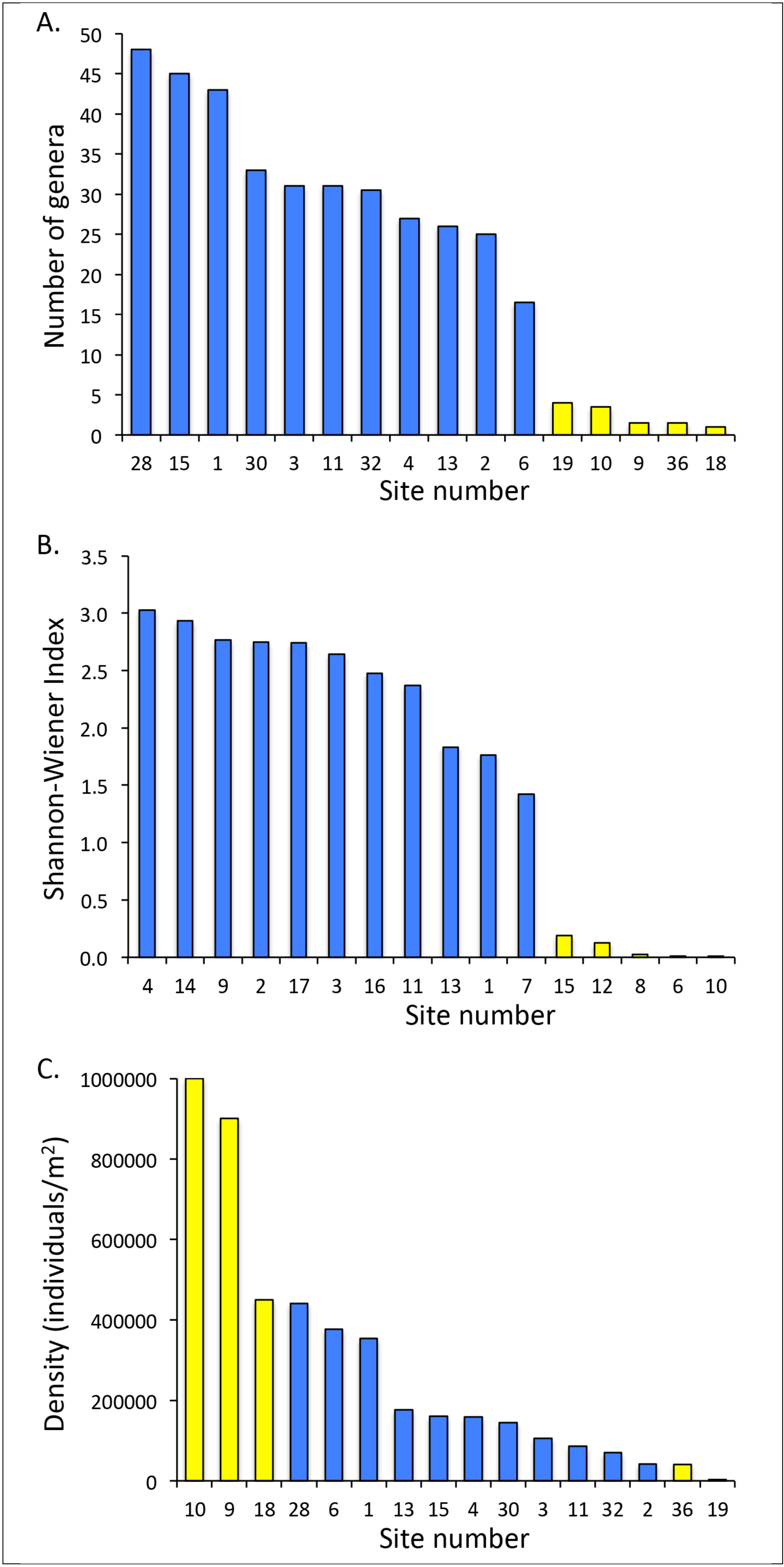
| Pichucalco Drainage | Puyacatengo Drainage | Tacotalpa Drainage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Sulphidic | Sulphidic | Non-Sulphidic | Sulphidic | Non-Sulphidic | Sulphidic | |
| Ephemeroptera: Baetidae | ||||||
| Americabaetis | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Baetodes | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Camelobaetidius | + | - | + | + | + | - |
| Cloeodes | + | + | + | - | + | - |
| Fallceon | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| Paracloeodes | + | - | + | - | - | - |
| Ephemeroptera: Caenidae | ||||||
| Caenis | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Ephemeroptera: Heptageniidae | ||||||
| Mccaffertium | + | - | - | - | + | - |
| Ephemeroptera: Leptohyphidae | ||||||
| Allenhyphes | + | - | - | - | + | - |
| Asioplax | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Leptohyes | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Tricorythodes | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Vacupernius | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Ephemeroptera: Leptophlebiidae | ||||||
| Farrodes | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Leptophlebia | - | - | + | - | + | - |
| Thraulodes | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Ulmeritus | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| Odonata: Calopterygidae | ||||||
| Hetaerina | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Odonata: Coenagrionidae | ||||||
| Argia | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Odonata: Gomphidae | ||||||
| Erpetogomphus | - | - | + | - | + | - |
| Odonata: Libellulidae | ||||||
| Brechmorhoga | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Macrothemis | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| Odonata: Platystictidae | ||||||
| Palaemnema | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Plecoptera: Perlidae | ||||||
| Anacroneuria | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Hemiptera: Belostomatidae | ||||||
| Belostoma | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Hemiptera: Gerridae | ||||||
| Trepobates | - | - | + | - | - | - |
| Hemiptera: Naucoridae | ||||||
| Ambrysus | + | - | + | - | - | - |
| Cryphocricos | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Limnocoris | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Hemiptera: Veliidae | ||||||
| Rhagovelia | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Neuroptera: Corydalidae | ||||||
| Corydalus | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Coleoptera: Curculionidae | ||||||
| Unidentified genus | - | - | + | - | - | - |
| Coleoptera: Elmidae | ||||||
| Austrolimnius | + | - | - | - | + | - |
| Heterelmis | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Hexacylloepus | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Macrelmis | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Microcylloepus | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Neocylloepus | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Neoelmis | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Phanocerus | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| Stenelmis | + | - | - | - | + | - |
| Coleoptera: Hydrophilidae | ||||||
| Tropisternus | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| Coleoptera: Lutrochidae | ||||||
| Lutrochus | - | - | + | - | - | - |
| Coleoptera: Psephenidae | ||||||
| Psephenus | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Coleoptera: Ptilodactylidae | ||||||
| Anchytarsus | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Trichoptera: Calamoceratidae | ||||||
| Phylloicus | - | - | + | - | - | - |
| Trichoptera: Glossomatidae | ||||||
| Protoptila | - | - | + | - | + | - |
| Trichoptera: Heliocopsychidae | ||||||
| Heliocopsyche | - | - | + | - | + | - |
| Trichoptera: Hydropsychidae | ||||||
| Cheumatopsyche | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Rhyacophylax | + | - | + | - | - | - |
| Smicridea | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| Trichoptera: Hydroptilidae | ||||||
| Hydroptila | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Leucotrichia | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Mayatrichia | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| Neotrichia | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Oxytheria | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Trichoptera: Leptoceridae | ||||||
| Nectopsyche | + | - | + | - | - | - |
| Oecetis | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Trichoptera: Philopotamidae | ||||||
| Chimarra | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| Wormaldia | + | - | - | - | + | - |
| Unidentified genus | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| Trichoptera: Polycentropodidae | ||||||
| Cernotina | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cyrnellus | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| Polyplectropus | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Trichoptera: Xiphocentronidae | ||||||
| Xiphocentron | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Lepidoptera: Unidentified family | ||||||
| Unidentified genus | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Diptera: Athericidae | ||||||
| Atherix | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| Unidentified genus | + | - | - | - | + | - |
| Diptera: Ceratopogonidae | ||||||
| Atrichopogon | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Ceratopogon | + | - | - | - | + | - |
| Culicoides | + | - | - | + | + | - |
| Forcipomyia | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Probezzia | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Diptera: Chironomidae | ||||||
| Unidentified genus (Chiromini) | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Unidentified genus (Orthocladinae) | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Unidentified genus (Pseudochironomini) | + | - | + | - | - | - |
| Unidentified genus (Tanypodinae) | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Unidentified genus (Tanytarsini) | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Diptera: Empididae | ||||||
| Hemerodromia | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Diptera: Ephyridae | ||||||
| Unidentified genus | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| Diptera: Psychodidae | ||||||
| Maruina | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Diptera: Simulidae | ||||||
| Simulium | + | - | - | - | + | - |
| Diptera: Stratiomyiidae | ||||||
| Nemotelus | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| Diptera: Tabanidae | ||||||
| Unidentified genus | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| Diptera: Tipulidae | ||||||
| Unidentified genus (Limoniinae) | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Unidentified genus (Tipulinae) | + | - | - | - | + | - |
| Crustacea: Ostracoda | ||||||
| Unidentified genus | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Crustacea: Palaemonidae | ||||||
| Macrobrachium | - | - | - | - | + | - |
4.2. Fish Communities
| Pichucalco Drainage | Ixtapangajoya Drainage | Puyacatengo Drainage | Tacotalpa Drainage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Sulphidic | Sulphidic | Non-Sulphidic | Sulphidic | Non-Sulphidic | Sulphidic | Non-Sulphidic | Sulphidic | |
| Characidae | ||||||||
| Astyanax aeneus | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Brycon guatemalensis | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - |
| Hyphessobrycon compressa | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ariidae | ||||||||
| Potamarius nelsoni | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| Pimelodidae | ||||||||
| Rhamdia guatemalensis | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Rhamdia laticauda | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | - |
| Loricariidae | ||||||||
| Pterygoplichthys pardalis* | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Batrachoidae | ||||||||
| Batrachoides goldmani | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | - |
| Atherinopsidae | ||||||||
| Atherinella alvarezi | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Belonidae | ||||||||
| Strongylura hubbsi | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - |
| Poeciliidae | ||||||||
| Belonesox belizanus | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Carlhubbsia kidderi | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gambusia eurystoma | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gambusia sexradiata | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | - |
| Heterandria bimaculata | + | + | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Heterophallus milleri | + | - | + | - | - | - | + | - |
| Phallichthys fairweatheri | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Poecilia mexicana | + | - | + | - | + | + | + | + |
| Poecilia petenense | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Poecilia sulphuraria | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Poecilia thermalis | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| Priapella chamulae | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| Priapella compressa | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Xiphophorus hellerii | + | + | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Synbranchidae | ||||||||
| Ophisternon aenigmaticum | - | + | + | - | - | - | + | + |
| Cichlidae | ||||||||
| Astatheros robertsoni | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| “Cichlasoma” urophthalmus | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| “Cichlasoma” salvini | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Oreochromis cf. aureus* | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Parachromis managuensis* | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Paraneetroplus gibbiceps | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | - |
| Petenia splendida | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Rocio octofasciata | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Theraps lentiginosus | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Thorichthys helleri | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Thorichthys meeki | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | - |
| Vieja bifasciata | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Vieja intermedia | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| Eleotridae | ||||||||
| Gobiomorus dormitor | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - |

5. Synthesis and Open Questions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cosgrove, W.J.; Rijsberman, F.R. World Water Vision: Making Water Everybody’S Business; World Water Council, Earthscan: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Collen, B.; Whitton, F.; Dyer, E.E.; Baillie, J.E.M.; Cumberlidge, N.; Darwall, W.R.; Pollock, C.; Richman, N.I.; Soulsby, A.-M.; Böhm, M. Global patterns of freshwater species diversity: Threat and endemism. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.-I.; Knowler, D.J.; Leveque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.-H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status, and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar]
- Abell, R.; Thieme, M.L.; Revenga, C.; Bryer, M.; Kottelat, M.; Bogutskaya, N.; Coad, B.; Mandrak, N.; Contreras-Balderas, S.; Bussing, W.; et al. Freshwater ecoregions of the world: A new map of biogeographic units for freshwater biodiversity conservation. Bioscience 2008, 58, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, C.R.; Begon, M.E.; Harper, J.L. Essentials of Ecology, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sibly, R.M.; Calow, P. A life-cycle theory of responses to stress. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1989, 37, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, J.; Culver, D.C.; Dole-Olivier, M.-J.; Malard, F.; Christman, M.C.; Deharveng, L. Assessing and conserving groundwater biodiversity: Synthesis and perspectives. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.; Paulson, K. It’s a wonderful hypogean life: A guide to the troglomorphic fishes of the world. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2001, 62, 12–41. [Google Scholar]
- Shepard, W.D. Desert springs: Both rare and endangered. Aquat. Conserv.-Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 1933, 3, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, R.A.; Lang, B.K.; Berg, D.J. Phylogeographic analysis reveals multiple cryptic species of amphipods (Crustacea: Amphipoda) in Chihuahuan desert springs. Biol. Conserv. 2009, 142, 2303–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laybourn-Parry, J.; Pearce, D. The biodiversity and ecology of Antarctic lakes: Models for evolution. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B-Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 2273–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, L.J.; Kaufman, L.; Chapman, C.A.; McKenzie, F.E. Hypoxia tolerance in twelve species of East African cichlids: Potential for low oxygen refugia in Lake Victoria. Conserv. Biol. 1995, 9, 1274–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Waterman, T.H. The evolutionary challenges of extreme environments (part 1). J. Exp. Zool. 1999, 285, 326–359. [Google Scholar]
- Waterman, T.H. Evolutionary challenges of extreme environments (part 2). J. Exp. Zool. 2001, 291, 130–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiffenstein, R.; Hulbert, W.; Roth, S. Toxicology of hydrogen sulfide. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1992, 1992, 109–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagarinao, T. Sulfide as an environmental factor and toxicant: Tolerance and adaptations in aquatic organisms. Aquat. Toxicol. 1992, 24, 21–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.L. The toxicity of hydrogen sulphide and other sulphides. Quart. J. Exp. Physiol. 1967, 52, 231–248. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, C.E.; Brown, G.C. The inhibition of mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase by the gases carbon monoxide, nitric oxide, hydrogen cyanide and hydrogen sulfide: Chemical mechanism and physiological significance. J. Bioenergy Biomembr. 2008, 40, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Nagel, R.; Blumberg, W.; Peisach, J.; Maliozzo, R. Sulfhemoglobin: Properties of partially sulfurated tetramers. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 8805–8810. [Google Scholar]
- Torrans, E.; Clemens, H. Physiological and biochemical effects of acute exposure of fish to hydrogen sulfide. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1982, 71C, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Grieshaber, M.K.; Völkel, S. Animal adaptations for tolerance and exploitation of poisonous sulfide. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 1998, 60, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyzer, G.; Stams, A.J.M. The ecology and biotechnology of sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 441–454. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen, B.B. Ecology of the bacteria of the sulphur cycle with special reference to anoxic/oxic interface environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B-Biol. Sci. 1982, 298, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luther, G.W.; Ma, S.; Trouborst, R.; Glazer, B.; Blickley, M.; Scarborough, R.W.; Mensinger, M.G. The roles of anoxia, H2S, and sorm events in fish kills of dead-end canals of Delaware inland bays. Estuaries 2004, 27, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagarinao, T.; Vetter, R.D. Sulfide tolerance and detoxification in shallow water marine fishes. Mar. Biol. 1989, 103, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunnicliffe, V. The biology of hydrothermal vents: Ecology and evolution. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 1991, 29, 319–407. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dover, C.L. The Ecology of Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vents; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2000; p. 352. [Google Scholar]
- Tsurumi, M. Diversity at hydrothermal vents. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2003, 12, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrazin, J.; Juniper, S. Biological characteristics of a hydrothermal edifice mosaic community. Mar. Ecol. Ser. 1999, 185, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, A. Simultaneous ‘hotspots’ and ‘coldspots’ of marine biodiversity and implications for global conservation. Mar. Ecol. Ser. 2002, 241, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibuet, M.; Olu, K. Biogeography, biodiversity, and fluid dependence of deep-sea cold-seep communities at active and passive margins. Deep-Sea Res. Part II-Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 1998, 45, 517–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnipseed, M.; Knick, K.E.; Lipcius, R.N.; Dreyer, J.; van Dover, C.L. Diversity in mussel beds at deep-sea hydrothermal vents and cold seeps. Ecol. Lett. 2003, 6, 518–523. [Google Scholar]
- Cordes, E.E.; Cunha, M.R.; Galeron, J.; Mora, C.; Olu-LeRoy, K.; Sibuet, M.; van Gaever, S.; Vanreusel, A.; Levin, L.A. The influence of geological, geochemical, and biogenic habitat heterogeneity on seep biodiversity. Mar. Ecol. 2009, 31, 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Rosales Lagarde, L.; Boston, P.J.; Campbell, A.; Stafford, K.W. Possible structural connection between Chichón Volcano and the sulfur-rich springs of Villa Luz Cave (a. k. a. Cueva de las Sardinas), Southern Mexico. Assoc. Mex. Cave Stud. Bull. 2006, 19, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Waring, G.A. Thermal springs of the United States and other countries of the world: A summary. U. S. Geol. Surv. Prof. Paper 1965, 492, 1–383. [Google Scholar]
- Jannasch, H.W. The chemosynthetic support if life and the microbial diversity at deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Proc. R. Soc. B 1985, 225, 277–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannasch, H.W.; Taylor, C.D. Deep-Sea microbiology. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 1984, 38, 487–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.S.; Childress, J.J.; Hessler, R.R.; Sakamoto-Arnold, C.M.; Beehler, C.L. Chemical and biological interactions in the Rose Garden hydrothermal vent field, Galapagos spreading center. Deep-Sea Res. 1988, 35, 1723–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales Lagarde, L. Investigation of karst brackish-sulfidic springs and their role in the hydrogeology, subsurface water-rock interactions, and speleogenesis at northern Sierra de Chiapas, Mexico. New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology: Socorro, NM, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Iurkiewicz, A.A.; Stevanovic, Z. Reconnaissance study of active sulfide springs and cave systems in the southern part of the Sulaimani Governorate (NE Iraq). Carbonates Evaporites 2010, 25, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernousova, E.Y.; Akimov, V.N.; Gridneva, E.V.; Dubinina, G.A.; Grabovich, M.Y. Phylogenetic in situ/ex situ analysis of a sulfur mat microbial community from a thermal sulfide spring in the north Caucasus. Microbiology 2008, 77, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.L.; Newman, D.K. Geomicrobiology, 5th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Buljan, M. New geochemical method of distinguishing the varieties of natural water. Croat. Chem. Acta 1962, 34, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Drew, D. Lisdoonvarna springs and spa wells, County Clare, Ireland. Environmen. Geol. 1996, 27, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, W.W. A new genus and species of Ephydridae (Diptera) from a California sulphur spring. Wasmann J. Biol. 1954, 12, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Lobkova, L.E.; Barinova, E.S.; Dulov, L.E.; Galchenko, V.F. Interactions between larvae of the hoverfly Eristalinus sepulchralis and microorganisms in the hydrothermal springs of the Uzon Caldera, Kamchatka. Microbiology 2007, 76, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dul’tseva, N.M.; Tourova, T.P.; Spiridonova, E.M.; Kolganova, T.V.; Osipov, G.A.; Gorlenko, V.M. Thiobacillus sajanensis sp. nov., a new obligately autotrophic sulfur-oxidizing bacterium isolated from Khoito-Gol hydrogen-sulfide springs, Buryatia. Microbiology 2006, 75, 582–592. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, S.; Douglas, D.D. Structural and geomicrobiological characteristics of a microbial community from a cold sulfide spring. Geomicrobiol. J. 2001, 18, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; Peng, X. Hot sprong deposits on a cliff face: A case study from Jifei, Yunnan Province, China. Sediment. Geol. 2014, 302, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.A.; Staley, J.T. Observations on the biology of Thiothrix. Arch. Microbiol. 1978, 117, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortecci, G.; Boschetti, T.; Mussi, M.; Lameli, C.H.; Mucchino, C.; Barbieri, M. New chemical and original isotopic data on waters from El Tatio geothermal field, northern Chile. Geochem. J. 2005, 39, 547–571. [Google Scholar]
- Hamad, S.M. Status of water resources of Al Jabal Al Akhdar region, North East Libya. Libyan Agr. Res. Cent. J. Int. 2012, 3, 247–259. [Google Scholar]
- Hippe, H.; Vainshtein, M.; Gogotova, G.I.; Stackebrandt, E. Reclassification of Desulfobacterium macestii as Desulfomicrobium macestii comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1127–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, H. Springs in Egypt. Environ. Geol. 1996, 27, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castenholz, R.W.; Jorgensen, B.B.; D’Amelio, E.; Bauld, J. Photosynthetic and behavioral versatility of the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria boryana in a sulfide-rich microbial mat. FEMS Microb. Ecol. 1991, 86, 43–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lavrinenko, K.; Chernousova, E.; Gridneva, E.; Dubinina, G.; Akimov, V.; Kuever, J.; Lysenko, A.; Grabovich, M. Azospirillum thiophilum sp. nov., a diazotrophic bacterium isolated from a sulfide spring. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2010, 60, 2832–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Schoonen, M.A.A.; Nordstrom, D.K.; Cunningham, K.M.; Ball, J.W. Sulfur geochemistry of hydrothermal waters in Yellowstone National Park: I. The origin of thiosulfate in hot spring water. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 3729–3743. [Google Scholar]
- Skirnisdottir, S.; Hreggvidsson, G.O.; Hjorleifsdottir, S.; Marteinsson, V.T.; Petursdottir, S.K.; Holst, O.; Kristjansson, J.K. Influence of sulfide and temperature on species composition and community structure of hot spring microbial mats. Appl. Environ. Micr. 2000, 66, 2835–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourova, T.P.; Kovaleva, O.L.; Gorlenko, V.M.; Ivanovsky, R.N. Use of genes of carbon metabolism enzymes as molecular markers of Chlorobi phylum representatives. Microbiology 2013, 82, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Vilano, M.; Contreras-Balderas, S. Cyprinodon bobmilleri: New species of Pubfish from Nuevo Leon, Mexico (Pisces: Cyprinodontidae). Copeia 1999, 1999, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coad, B.W. A re-description of Aphanius ginaonis (Holly, 1929) from southern Iran (Osteichthyes: Cyprinodontiformes). J. Nat. Hist. 1980, 14, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teimori, A. The Evolutionary History and Taxonomy of Aphanius (Teleostei: Cyprinodontidae) Species in Iran and the Persian Gulf Region. Ph.D. Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Munich, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Teimori, A.; Esmaeili, H.R.; Erpenbeck, D.; Reichenbacher, B. A new and unique species of the genus Aphanius Nardo, 1827 (Teleostei: Cyprinodontidae) from Southern Iran: A case of regressive evolution. Zool. Anz. 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Winemiller, K.O.; Leslie, M.; Roche, R. Phenotypic variation in male guppies from natural inland populations: an additional test of Haskins’ sexual selection/predation hypthesis. Environ. Biol. Fish. 1990, 29, 173–191. [Google Scholar]
- Willing, E.-M.; Bentzen, P.; Van Oosterhout, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Cable, J.; Breden, F.; Weigel, D.; Dreyer, C. Genome-wide nucleotide polymorphisms reveal population history and adaptive divergence in wild guppies. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 968–984. [Google Scholar]
- Covich, A. Chemical refugia from predation for thin-shelled gastropods in a sulfide-enriched stream. Verh. Int. Ver. fuer Limnol. 1981, 21, 1632–1636. [Google Scholar]
- Tobler, M.; Hastings, L. Convergent patterns of body shape differentiation in four different clades of poeciliid fishes inhabiting sulfide springs. Evol. Biol. 2011, 38, 412–421. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, R.R. Five New Species of Mexican Poeciliid Fishes of the Genera Poecilia, Gambusia, and Poeciliopsis; Occasional Papers of the Museum of Zoology: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Tobler, M.; Riesch, R.; Garcia de Leon, F.J.; Schlupp, I.; Plath, M. Two endemic and endangered fishes, Poecilia sulphuraria (Alvarez, 1948) and Gambusia eurystoma Miller, 1975 (Poeciliidae, Teleostei), as only survivors in a small sulfidic habitat. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 72, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesch, R.; Tobler, M.; Lerp, H.; Jourdan, J.; Doumas, L.T.; Nosil, P.; Langerhans, R.B.; Plath, M. University of Sheffield: Sheffield, UK, Unpublished work. 2013.
- Riesch, R.; Plath, M.; Garcia de Leon, F.J.; Schlupp, I. Convergent life-history shifts: Toxic environments result in big babies in two clades of poeciliids. Naturwissenschaften 2010, 97, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Rivas, L.R. Eight new species of poeciliid fishes of the genus Limia from Hispaniola. Northeast Gulf Sci. 1980, 2, 98–112. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, A. Phylogeny of Limia (Teleostei; Poeciliidae) based on NADH dehydrogenase subunit 2 sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2001, 19, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesch, R.; Plath, M.; Schlupp, I.; Tobler, M.; Langerhans, R.B. Colonization of toxic springs drives predictable life-history shift in livebearing fishes (Poeciliidae). Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, M.; DeWitt, T.J.; Schlupp, I.; Garcia de Leon, F.J.; Herrmann, R.; Feulner, P.; Tiedemann, R.; Plath, M. Toxic hydrogen sulfide and dark caves: Phenotypic and genetic divergence across two abiotic environmental gradients in Poecilia mexicana. Evolution 2008, 62, 2643–2649. [Google Scholar]
- Tobler, M.; Palacios, M.; Chapman, L.J.; Mitrofanov, I.; Bierbach, D.; Plath, M.; Arias-Rodriguez, L.; Garcia de Leon, F.J.; Mateos, M. Evolution in extreme environments: replicated phenotypic differentiation in livebearing fish inhabiting sulfidic springs. Evolution 2011, 65, 2213–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, M.; Arias-Rodriguez, L.; Plath, M.; Eifert, C.; Lerp, H.; Lamboj, A.; Voelker, G.; Tobler, M. The redescovery of a long described species reveals additional complexity in speciation patterns of poeciliid fishes in sulfide springs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71069. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, A.; Rochera, C.; Silvestre, J.J.; Vincente, E.; Hahn, M.W. Spatial dominance and inorganic carbon assimilation by conspicuous autotrophic biofilms in a physical and chemical gradient of a cold sulfurous spring: the role of differential ecological strategies. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 50, 172–184. [Google Scholar]
- Pimenov, N.V.; Kuranov, G.V.; Bryikhanov, A.L.; Vesopolova, E.F.; Koryukina, I.P.; Maslov, Y.N. The sulfate-reducing bacterial community of sulfide-rich water of the Ust'-Kachka Resort Spring, Perm Krai, Russia. Microbiology 2012, 81, 721–726. [Google Scholar]
- Stambuk-Giljanovic, N. Characteristics and origin of the hydrogen silphide spring water from the Split spa (Southern Croatia). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 140, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadd, B. Handbook of the Canadian Rockies; Corax Press: Canmore, Alberta, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nordstrom, D.K.; McCleskey, R.B.; Ball, J.W. Sulfur geochemistry of hydrothermal waters in Yellowstone National Park: IV Acid-sulfate waters. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, J.; Richards, F. Oxygenation of hydrogen sulfide in seawater at constant salinity, temerature, and pH. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1969, 3, 838–843. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Morris, J. Kinetics of oxidation of aqueous sulfide by O2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1972, 6, 529–537. [Google Scholar]
- Canfield, D.E.; Farquhar, J. The global sulfur cycle. In Fundamentals of Geobiology; Knoll, A.H., Canfield, D.E., Konhauser, K.O., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Overmann, J.; van Gemerden, H. Microbial interactions involving sulfur bacteria: Implications for the ecology and evolution of bacterial communities. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 24, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Baskaran, V.; Nemati, M. Bacteria of the sulphur cycle: An overview of microbiology, bioknetics and their role in petroleum and mining industries. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 44, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, L.L.; Fauque, G.D. Biochemistry, physiology and biotechnology of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 68, 41–98. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, C.G. Physiology and genetics of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 1998, 39, 235–289. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, W.; Dam, B. Biochemistry and molecular biology of lithotrophic sulfur oxidation by taxonomically and ecologically diverse bacteria and archaea. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 999–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Elshahed, M.S.; Senko, J.M.; Najar, F.Z.; Kenton, S.M.; Roe, B.A.; Dewers, T.A.; Spear, J.R.; Krumholz, L.R. Bacterial diversity and sulfur cycling in a mesophilic sulfide-rich spring. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5609–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Tekai, K. Deep-Sea vent chemoautotrophs: diversity, biochemistry and ecological significance. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 65, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, S.M.; Kane, T.C.; Kinkle, B.K. A chemoautotrophically based cave ecosystem. Science 1996, 272, 1953–1955. [Google Scholar]
- Roach, K.; Tobler, M.; Winemiller, K.O. Hydrogen sulfide, bacteria, and fish: A unique, subterranean food chain. Ecology 2011, 92, 2056–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, E.S. Biology of Acid-Sulfate-Chloride Springs in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming, United States of America; Montana State University: Bozeman, MT, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Brues, C.T. Animal life in hot springs. Quart. Rev. Biol. 1927, 2, 181–203. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, N.C. Population biology of a brine fly (Diptera: Ephydridae) in the presence of abundant algal food. Ecology 1975, 56, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar]
- Arif, I.A. Composition of blue-green algal mats and water chemistry of the Bani Malik hot spring (Gizan Province), Saudi Arabia. Kuwait J. Sci. Eng. 1997, 24, 109–122. [Google Scholar]
- Brues, C.T. Studies on the fauna of hot springs in the western United States and the biology of thermophilous animals. Proc. Am. Acad. Arts Sci. 1928, 63, 139–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, J.; Ehrlich, S. A freshwater prosobranch, Melanoides tuberculata, in a hydrogen sulphide stream. J. Conchol. 1995, 35, 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Brues, C.T. Observations on animal life in the thermal waters of Yellowstone Park, with a consideration of the thermal environment. Proc. Am. Acad. Arts Sci. 1924, 59, 371–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, M. Does a predatory insect contribute to the divergence between cave- and surface adapted fish populations? Biol. Lett. 2009, 5, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macalady, J.L.; Lyon, E.H.; Koffman, B.; Albertson, L.K.; Meyer, K.; Galdenzi, S.; Mariani, S. Dominant microbial populations in limestone-corroding stream biofilms, Frasassi cave system, Italy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5596–5609. [Google Scholar]
- Latella, L.; Di Russo, C.; De Pasquale, L.; Dell’anna, L.; Nardi, G.; Rampini, M. Preliminary investigations on a new sulphurous cave in central Italy. Mémoires de Biospéologie 1999, 53, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Hose, L.; Palmer, A.N.; Palmer, M.; Northup, D.E.; Boston, P.J.; DuChene, H.R. Microbiology and geochemistry in a hydrogen-sulphide-rich karst environment. Chem. Geol. 2000, 169, 399–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, M.; Schlupp, I.; Heubel, K.; Riesch, R.; Garcia de Leon, F.J.; Giere, O.; Plath, M. Life on the edge: Hydrogen sulfide and the fish communities of a Mexican cave and surrounding waters. Extremophiles 2006, 10, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, A.S.; Lee, N.; Porter, M.L.; Stern, L.A.; Bennett, P.C.; Wagner, M. Filamentous “Epsilonproteobacteria” dominate microbial mats from sulfidic cave springs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5503–5511. [Google Scholar]
- Rye, R.O.; Back, W.; Hanshaw, B.B.; Rightmire, C.T.; Peason, F.J. The origin and isotopic composition of dissolved sulfide in groundwater from carbonate aquifers in Florida and Texas. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1981, 45, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers Engel, A. Observations on the biodiversity of sulfidic karst habitats. J. Cave Karst Stud. 2007, 69, 187–206. [Google Scholar]
- Culver, D.C.; Sket, B. Hotspots of subterranean biodiversity in caves and wells. J. Cave Karst Stud. 2000, 62, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Menke, A. Family Belostomatidae-Giant water bugs. In the Semiaquatic and Aquatic Hemiptera of California (Heteroptera: Hemiptera); Menke, A., Ed.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1979; pp. 76–86. [Google Scholar]
- McCafferty, W. Aquatic Entomology; Jones and Bartlett Publishers: Sudbury, Canada, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Vismann, B. Sulfide tomerance: physiological mechanisms and ecological implications. Ophelia 1991, 34, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Parzefall, J. A review of morphological and behavioural changes in the cave molly, Poecilia mexicana, from Tabasco, Mexico. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2001, 62, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.S.; Rosen, D.E. A cavernicolous form of the poeciliid fish Poecilia sphenops from Tabasco, México. Copeia 1962, 1962, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, L.J.; McKenzie, D.J. Behavioral responses and ecological consequences. In Hypoxia; Richards, J.G., Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 25–77. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, D.L. Dissolved oxygen and fish behavior. Environ. Biol. Fish. 1987, 18, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauner, C.J.; Ballantyne, C.L.; Randall, D.J.; Val, A.L. Air-Breathing in the armored catfish (Hoplosternum littorale) as an adaptation to hypoxic, acidic, and hydrogen sulfide-rich waters. Can. J. Zool. Rev. Can. Zool. 1995, 73, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.B. Air-Breathing Fishes: Evolution, Diversity and Adaptation. Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, D.L.; McClure, M. Aquatic surface respiration, a widespread adaptation to hypoxia in tropical freshwater fishes. Environ. Biol. Fish. 1982, 7, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W. Morphological adaptations of cyprinodontoids for inhabiting oxygen deficient waters. Copeia 1970, 1970, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, Y.K.; Kuah, S.S.L.; Chew, S.F. Strategies adopted by the mudskipper Boleophthalmus boddaerti to survive sulfide exposure in normoxia or hypoxia. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2004, 77, 824–837. [Google Scholar]
- Greven, H. Gonads, genitals, and reproductive biology. In Ecology and Evolution of Poeciliid Fishes; Evans, J.P., Pilastro, A., Schlupp, I., Eds.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2011; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn, D.G. Viviparity and oviparity: Evolution and reproductive strategies. In Encyclopedia of Reproduction; Knobil, T.E., Neill, J.D., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 4, pp. 994–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Tobler, M.; Riesch, R.; Tobler, C.M.; Plath, M. Compensatory behaviour in response to sulfide-induced hypoxia affects time budgets, feeding efficiency, and predation risk. Evol. Ecol. Res. 2009, 11, 935–948. [Google Scholar]
- Plath, M.; Tobler, M.; Riesch, R.; Garcia de Leon, F.J.; Giere, O.; Schlupp, I. Survival in an extreme habitat: The role of behaviour and energy limitation. Naturwissenschaften 2007, 94, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfenninger, M.; Lerp, H.; Tobler, M.; Passow, C.; Kelley, J.L.; Funke, E.; Greshake, B.; Erkoc, U.K.; Berberich, T.; Plath, M. Parallel evolution of cox genes in H2S-tolerant fish as key adaptation to a toxic envrionment. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3873. [Google Scholar]
- Shahak, Y.; Hauska, G. Sulfide oxidation from cyanobacteria to humans: Sulfide-Quinone oxidoreductase (SQR). In Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Hell, R., Dahl, C., Knaff, D.B., Leustek, T., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 319–335. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, J.L.; Passow, C.; Arias-Rodriguez, L.; Yee, M.C.; Tobler, M. Washington State University: Pullman, WA, USA, Unpublished work. 2014.
- Tobler, M.; Henpita, C.; Bassett, B.; Kelley, J.L.; Shaw, J. H2S exposure elicits differential expression of candidate genes in fish adapted to sulfidic and non-sulfidic environments. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2014, 175, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Tobler, M.; Plath, M. Living in extreme habitats. In Ecology and Evolution of Poeciliid Fishes; Evans, J., Pilastro, A., Schlupp, I., Eds.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2011; pp. 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Tobler, M. Divergence in trophic ecology characterizes colonization of extreme habitats. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2008, 95, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passow, C.; Greenway, R.; Arias-Rodriguez, L.; Jeyasingh, P.D.; Tobler, M. Kansas State University: Manhattan, KS, USA, Unpublished work. 2014.
- Riesch, R.; Plath, M.; Schlupp, I. Toxic hydrogen sulfide and dark caves: Life-History adaptations in a livebearing fish (Poecilia mexicana, Poeciliidae). Ecology 2010, 91, 1494–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluter, D. Ecology and the origin of species. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundle, H.D.; Nosil, P. Ecological speciation. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 336–352. [Google Scholar]
- Chevin, L.-M.; Decorzent, G.; Lenormand, T. Niche dimensionality and the genetics of ecological speciation. Evolution 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Plath, M.; Pfenninger, M.; Lerp, H.; Riesch, R.; Eschenbrenner, C.; Slattery, P.; Bierbach, D.; Herrmann, N.; Schulte, M.; Arias-Rodriguez, L.; et al. Genetic differentiation and selection against migrants in evolutionarily replicated extreme environments. Evolution 2013, 67, 2647–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, M.; Riesch, R.; Tobler, C.M.; Schulz-Mirbach, T.; Plath, M. Natural and sexual selection against immigrants maintains differentiation among micro-allopatric populations. J. Evol. Biol. 2009, 22, 2298–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plath, M.; Riesch, R.; Oranth, A.; Dzienko, J.; Karau, N.; Schiessl, A.; Stadler, S.; Wigh, A.; Zimmer, C.; Arias-Rodriguez, L.; et al. Complementary effects of natural and sexual selection against immigrants maintains differentiation between locally adapted fish. Naturwissenschaften 2010, 97, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierbach, D.; Klein, M.; Sassmannshausen, V.; Schlupp, I.; Riesch, R.; Parzefall, J.; Plath, M. Divergent evolution of male aggressive behavior: Another reproductive isolation barrier in extremophile poeciliid fishes? Int. J. Evol. Biol. 2012, 2012. Article 148745. [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni, M.; Templeton, A.; Mishmar, D. Mitochondrial bioenergetics as a major motive force of speciation. Bioessays 2009, 31, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.R. Geographical distribution of Central American freshwater fishes. Copeia 1966, 1966, 773–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.; Cooper, W.; de Mello, W.; Saltzman, E.; Zika, R. Variability of biogenic sulfur emissions from Florida wetlands. In Biogenic Sulfur in the Environment; Saltzman, E., Cooper, W., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 31–43. [Google Scholar]
- Merritt, R.W.; Cummins, K.W. An Introduction to the Aquatic Insects of North America, 4th ed.; Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company: Dubuque, IA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins, G.B. Larvae of the North American Caddisfly Genera, 2nd ed.; University of Toronto Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Needham, J.G.; Westfall, M.J.; May, M.L. Dragonflies of North America; Scientific Publishers: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez, A.; Pringle, C.M. Structure and production of a benthic insect assemblage in a neotropical stream. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1998, 17, 443–462. [Google Scholar]
- Flowers, R.W. Diversity of stream-living insects in northwestern Panama. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1991, 10, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, D.; Cressa, C.; Mathooko, J.M.; Dudgeon, D. Macroinvertebrates: Composition, life histories and production. In Tropical Stream Ecology; Dudgeon, D., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 65–105. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez, A.; Pringle, C.M. Invertebrate drift and benthic community dynamics in a lowland neotropical stream, Costa Rica. Hydrobiologia 1998, 386, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, C.M.; Ramírez, A. Use of both benthic and drift sampling techniques to assess tropical stream invertebrate communities along an altitudinal gradient, Costa Rica. Freshw. Biol. 1998, 39, 359–373. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly, N.M.; Crossland, M.R.; Pearson, R.G. Effect of low dissolved oxygen on suvival, emergence, and drift of tropical stream macroinvertebrates. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2004, 23, 251–270. [Google Scholar]
- Walshe, B.M. The oxygen requirements and thermal resistance of chironomid larvae from flowing and still waters. J. Exp. Biol. 1948, 25, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- De Jonge, J.; den Besten, P.J.; Oosterbaan, J. Sediment pollution and predation affect structure and production of benthic macroinvertebrate communities in the Rhine-Meuse delta, the Netherlands. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2004, 23, 557–579. [Google Scholar]
- Helson, J.E.; Williams, D.D.; Turner, D. Larval chironomid community organization in four tropical rivers: Human impacts and longitudinal zonation. Hydrobiologia 2006, 559, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carew, M.E.; Pettigrove, V.; Cox, R.L.; Hoffmann, A.A. The response of Chironomidae to sediment pollution and other environmental characteristics in urban wetlands. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 2444–2462. [Google Scholar]
- Magni, P.; Rajagopal, S.; van der Velde, G.; Fenzi, G.; Kassenberg, J.; Vizzini, S.; Mazzola, A.; Guiordani, G. Sediment features, macrozoobenthic assemblages and trophic relationships (δ13 C and δ15 N analysis) following a dystrophic event with anoxia and sulphide development in the Santa Giusta Lagoon (western Sardinia, Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 57, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, S.; Kikuchi, E.; Doi, H.; Shikano, S. Swimming behavior of Chironomus acerbiphilus larvae in Lake Katanuma. Hydrobiologia 2005, 548, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, S.; Plath, M. Predation on a cave fish by the freshwater crab Avotrichodactylus bidens (Bott, 1969) (Brachyura, Trichodactylidae) in a Mexican sulfur cave. Custaceana 2011, 84, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, R.W. Guide to Aquatic Macroinvertebrates of the Upper Midwest; Water Resources Center, University of Minnesota: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, T.L.; Lawrence, T.M. Environmental Requirements and Pollution Tolerance of Trichoptera; US EPA, Environmental Monitoring and Support Laboratory: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard, M.D.; Peters, W.L. Environmental Requirements and Pollution Tolerance of Ephemeroptera; US EPA Environmental Monitoring and Support Laboratory: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Oseid, D.M.; Smith, L.L. Factors influencing acute toxicity estimates of hydrogen sulfide to freshwater invertebrates. Water Res. 1974, 8, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.L.; Oseid, D.M.; Adelman, I.R.; Broderius, S.J. Effects of Hydrogen Sulfide on Fish and Invertebrates, Part 1: Acute and Chronic Toxicity Studies; EPA-600/3-76-062a; US Environmental Protection Agency: Duluth, MN, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Hilsenhoff, W.L. Rapid field assessment of organic pollution with a family-level biotic index. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1988, 7, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, U.; Tietböhl, R.S. A mayfly from tropical Brazil capable of tolerating short-term dehydration. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1996, 15, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCafferty, W.P.; Lugo-Ortiz, C.R. Cloeodes hydation, n. sp. (Ephemeroptera: Baetidae): An extraoridinarily, drought tolerant mayfly from Brazil. Entomol. News 1995, 106, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Gooderham, J.; Tsyrlin, E. The Waterbug Book: A Guide to the Freshwater Macroinvertebrates of Temperate Australia; CSIRO Publishing: Collingwood, Victoria, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe, W.H.; Crisp, D.J. Studies on plastron respiration: I. Rge biology of Aphelocheirus [Hemiptera, Aphelocheiridae (Naucoridae)] and the mechanism of plastron retention. J. Exp. Biol. 1947, 24, 227–269. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, H.E. Plastron respiration in adult beetles of the suborder Myxophaga. J. Zool. 1969, 159, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resh, V.H.; Unzicker, J.D. Water quality monitoring and aquatic organisms: The importance of species identification. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1975, 47, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Tobler, M.; Roach, K.; Winemiller, K.O.; Morehouse, R.L.; Plath, M. Population structure, habitat use, and diet of giant waterbugs in a sulfidic cave. Southw. Nat. 2013, 58, 420–426. [Google Scholar]
- Tobler, M.; Schlupp, I.; Plath, M. Predation of a cave fish (Poecilia mexicana, Poeciliidae) by a giant water-bug (Belostoma, Belostomatidae) in a Mexican sulfur cave. Ecol. Entomol. 2007, 32, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plath, M.; Riesch, R.; Culumber, Z.W.; Streit, B.; Tobler, C.M. Giant waterbug (Belostoma sp.) predation on a cavefish (Poecilia mexicana): Effects of female body size and gestational state. Evol. Ecol. Res. 2011, 13, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, R.R.; Minckley, W.; Norris, S. Freshwater Fishes of Mexico; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Greenway, R.; Tobler, M. Kansas State University: Manhattan, KS, USA, Unpublished work. 2014.
- Bagarinao, T.; Lantin-Olaguer, I. The sulfide tolerance of milkfish and tilapia in relation to fish kills in farms and natural waters in the Philippines. Hydrobiologia 1999, 382, 137–150. [Google Scholar]
- Affonso, E.; Rantin, F. Respiratory responses of the air-breathing fish Hoplosternum littorale to hypoxia and hydrogen sulfide. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C: Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 141, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Rose, P.; Moore, P.K. Hydrogen sulfide and cell signaling. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 51, 169–187. [Google Scholar]
- Szabo, C. Hydrogen sulphide and its therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 917–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, O.A. Species conservation and systematics: The dilemma of subspecies. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1986, 1, 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tobler, M.; Plath, M. Threatened fishes of the world: Gambusia eurystoma Miller, 1975 (Poeciliidae). Environ. Biol. Fish. 2009, 85. Article 251. [Google Scholar]
- Tobler, M.; Plath, M. Threatened fishes of the world: Poecilia sulphuraria (Alvarez, 1948) (Poeciliidae). Environ. Biol. Fish. 2009, 85, 333–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN Red List of threatened species, version 2013.2. Available online: http://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 14 April 2014).
- SEDESOL. NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-059-ECOL-1994, que determina las especies y subspecies de flora y fauna silvestres terrestres y acuáticas en peligro de extinción, amenazadas, raras y las sujetas a protección especial, y que establece especificaciones para su protección. Diario Oficial 1994, 488, 2–60. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Greenway, R.; Arias-Rodriguez, L.; Diaz, P.; Tobler, M. Patterns of Macroinvertebrate and Fish Diversity in Freshwater Sulphide Springs. Diversity 2014, 6, 597-632. https://doi.org/10.3390/d6030597
Greenway R, Arias-Rodriguez L, Diaz P, Tobler M. Patterns of Macroinvertebrate and Fish Diversity in Freshwater Sulphide Springs. Diversity. 2014; 6(3):597-632. https://doi.org/10.3390/d6030597
Chicago/Turabian StyleGreenway, Ryan, Lenin Arias-Rodriguez, Pete Diaz, and Michael Tobler. 2014. "Patterns of Macroinvertebrate and Fish Diversity in Freshwater Sulphide Springs" Diversity 6, no. 3: 597-632. https://doi.org/10.3390/d6030597
APA StyleGreenway, R., Arias-Rodriguez, L., Diaz, P., & Tobler, M. (2014). Patterns of Macroinvertebrate and Fish Diversity in Freshwater Sulphide Springs. Diversity, 6(3), 597-632. https://doi.org/10.3390/d6030597





