Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases 3/6 Reduce Auxin Signaling via Stabilizing Indoleacetic Acid-Induced Proteins 8/9 in Plant Abiotic Stress Adaptation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Auxin Signaling Output Is Tightly Controlled in Plant Abiotic Stress Responses
2.2. MPK3/6 Interact with Many Auxin Signaling Components
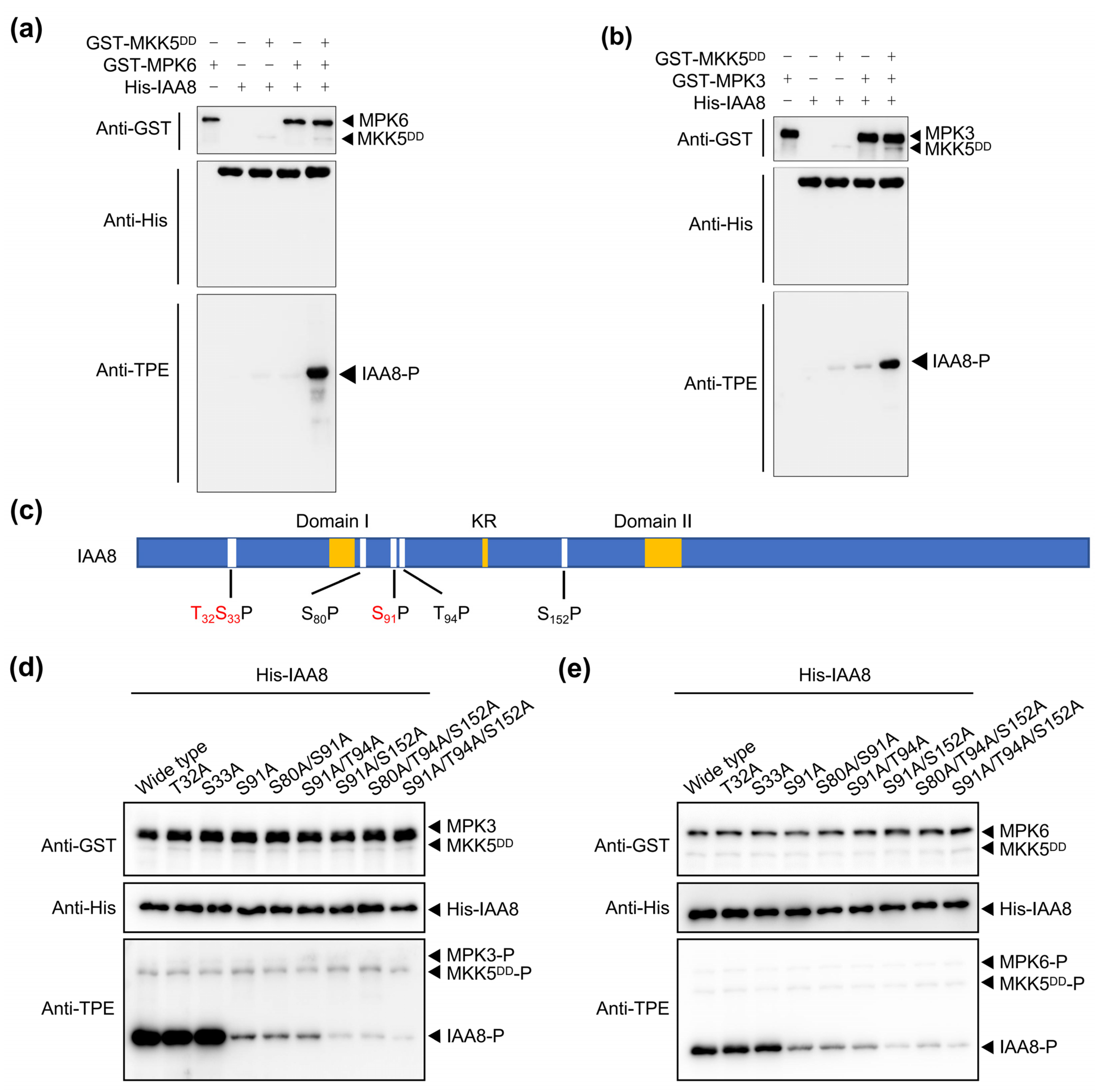
2.3. MPK3/6 Phosphorylate IAA8 at S91, T94, and S152 Residues
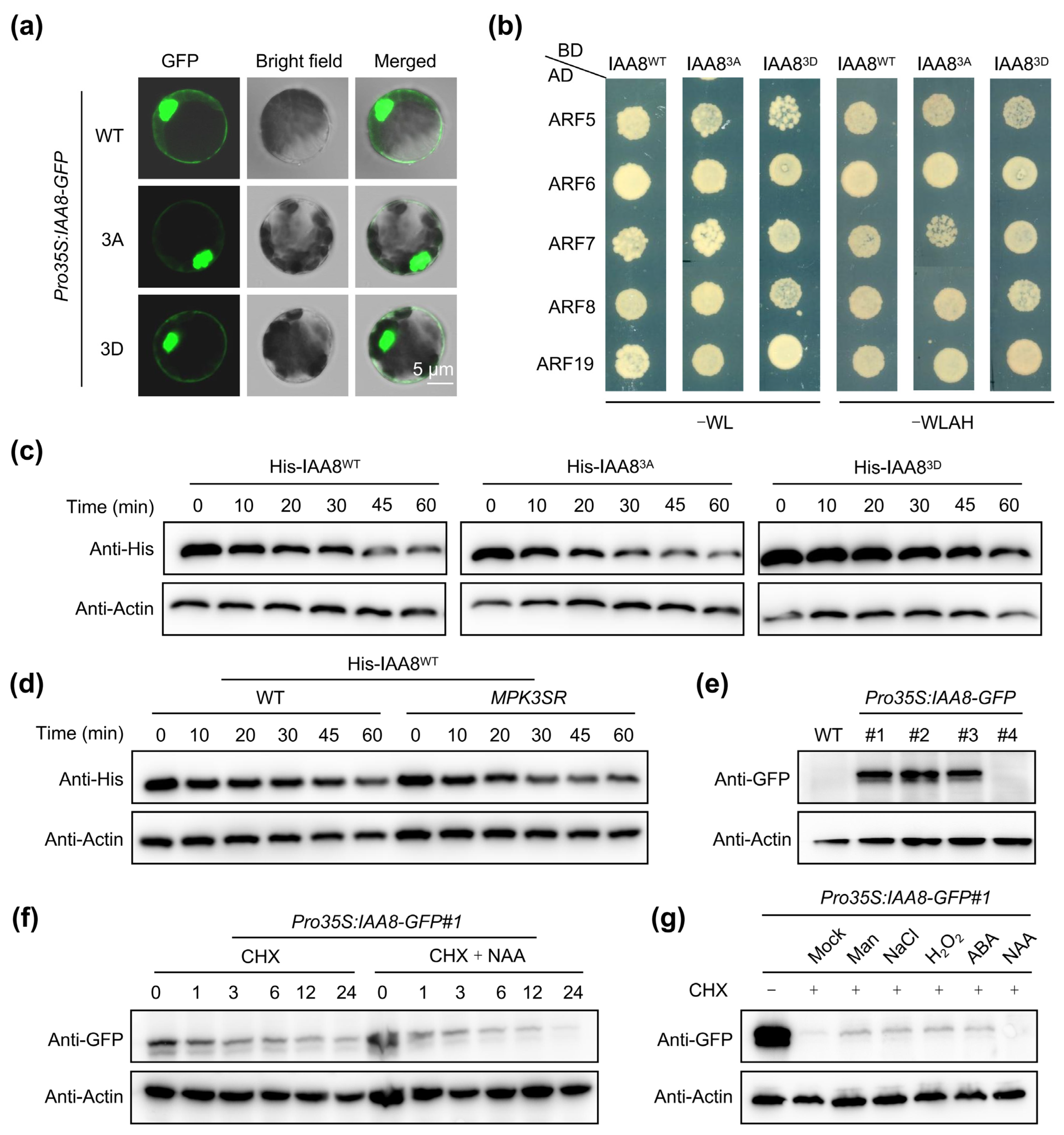
2.4. MPK3/6-Mediated Phosphorylation Stabilizes IAA8
2.5. MPK6 Phosphorylates IAA9 at S88 Residue
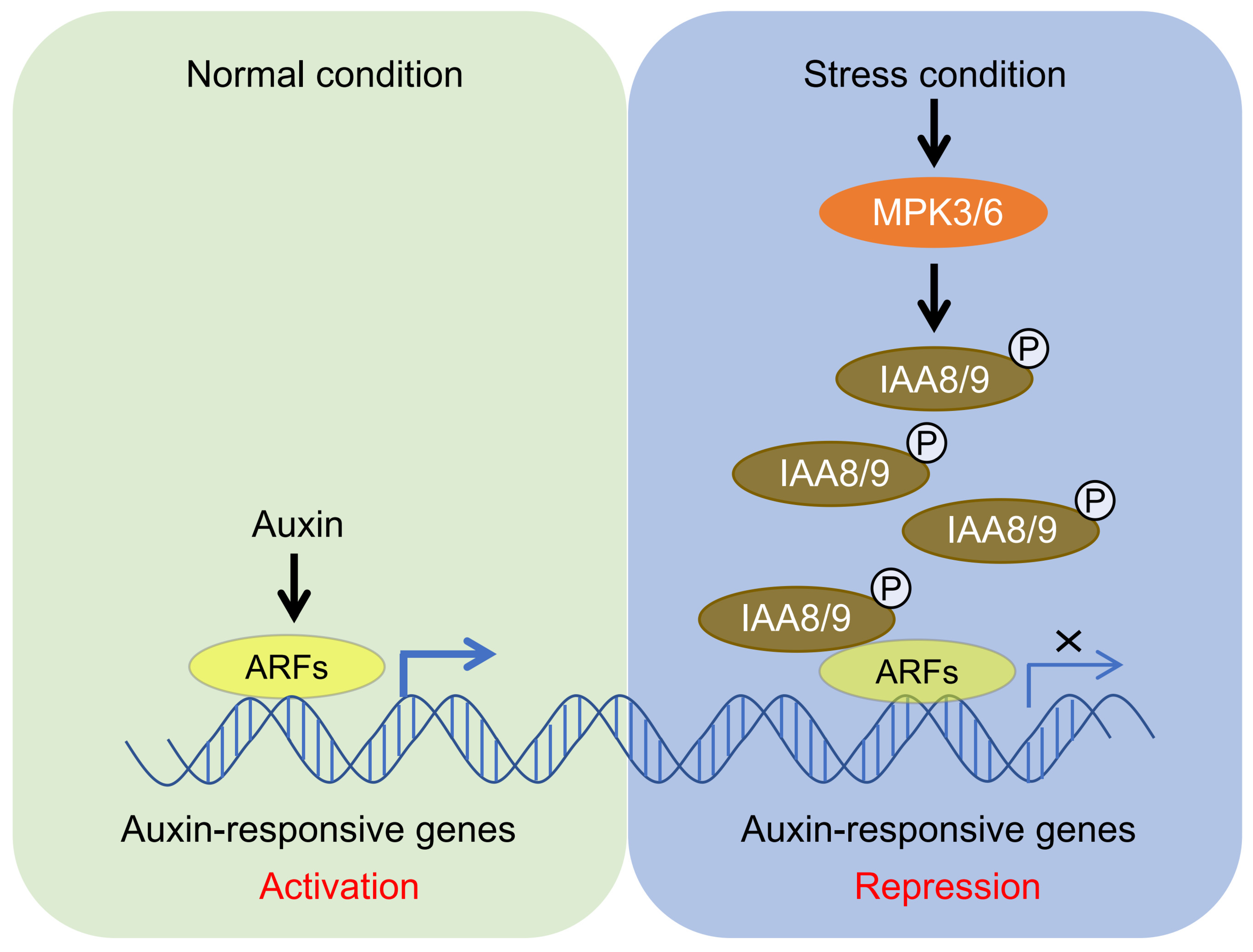
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Yeast Two-Hybrid Assay (Y2H)
4.3. Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC) Assay in Arabidopsis Mesophyll Protoplasts
4.4. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) Assay in Arabidopsis Mesophyll Protoplasts
4.5. In Vitro Kinase Assay
4.6. Cell-Free Assay
4.7. Protein Stability Detection
4.8. β-Glucuronidase (GUS) Staining
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPK3 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 |
| IAA8 | Indoleacetic acid-induced protein 8 |
| Aux/IAA | Auxin/indole-3-3 acetic acid |
| ARF | Auxin response factor |
| NAA | 1-naphthaleneacetic acid |
| ABA | Abscisic acid |
| JA | Jasmonic acid |
| RLKs | Receptor-like kinases |
| MAP3K | MAP kinase kinase kinase |
| MAP2K | MAP kinase kinase |
| TIR1 | Transport inhibitor response 1 |
| AFBs | Auxin signaling F-boxs |
| MPK3SR | mpk3 mpk6 MPK3pro:MPK3TG |
| MPK6SR | mpk3 mpk6 MPK6pro:MPK6TG |
| TPL | TOPLESS |
| Y2H | Yeast two-hybrid |
| BiFC | Bimolecular fluorescence complementation |
| Co-IP | Co-immunoprecipitation |
| GST | Glutathione S-transferase |
| NA-PP1 | 4-amino-1-tert-butyl-3-(1′-naphthyl) pyrazolo[3,4-d] pyrimidine |
| anti-TPE | Anti-thiophosphate ester-specific antibody |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| ABI3 | ABA-insensitive 3 |
| CHX | Cycloheximide |
References
- Bai, Y.; Kissoudis, C.; Yan, Z.; Visser, R.G.F.; van der Linden, G. Plant behaviour under combined stress: Tomato responses to combined salinity and pathogen stress. Plant J. 2018, 93, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Chen, X.; Xiao, F.; Lin, H.; Guo, Y. Insights into plant salt stress signaling and tolerance. J. Genet. Genom. 2024, 51, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, V.V.; Roy, A.; Vijayan, R.; Banerjee, P.; Verma, V.C.; Nalia, A.; Pramanik, M.; Mukherjee, B.; Ghosh, A.; Reja, M.H.; et al. Drought and Heat Stress in Cool-Season Food Legumes in Sub-Tropical Regions: Consequences, Adaptation, and Mitigation Strategies. Plants 2021, 10, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauw, P.; Coppens, F.; Korte, A.; Herman, D.; Slabbinck, B.; Dhondt, S.; Van Daele, T.; De Milde, L.; Vermeersch, M.; Maleux, K.; et al. Leaf Growth Response to Mild Drought: Natural Variation in Arabidopsis Sheds Light on Trait Architecture. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 2417–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claeys, H.; Inzé, D. The agony of choice: How plants balance growth and survival under water-limiting conditions. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 1768–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julkowska, M.M.; Testerink, C. Tuning plant signaling and growth to survive salt. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Wilkinson, E.G.; Sageman-Furnas, K.; Strader, L.C. Auxin and abiotic stress responses. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 7000–7014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, S. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in signaling plant growth and development. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonak, C.; Okrész, L.; Bögre, L.; Hirt, H. Complexity, cross talk and integration of plant MAP kinase signalling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagodzik, P.; Tajdel-Zielinska, M.; Ciesla, A.; Marczak, M.; Ludwikow, A. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Cascades in Plant Hormone Signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Su, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S. Conveying endogenous and exogenous signals: MAPK cascades in plant growth and defense. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zheng, R.; He, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, T. Noncanonical auxin signaling regulates cell division pattern during lateral root development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 21285–21290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ding, Z. Auxin promotes hypocotyl elongation by enhancing BZR1 nuclear accumulation in Arabidopsis. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Li, P.; Ma, Y.; Nie, X.; Grebe, M.; Men, S. Membrane Sterol Composition in Arabidopsis thaliana Affects Root Elongation via Auxin Biosynthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.J.; Tian, H.Y.; Zhang, M.X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.X.; Yu, Q.Q.; Ding, Z.J. STOP1 attenuates the auxin response to maintain root stem cell niche identity. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 113617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braybrook, S.A. Auxin and Organogenesis: Initiation of Organs and Nurturing a Scientific Spirit. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Qu, X.; Lv, B.; Li, X.; Sui, J.; Yu, Q.; Ding, Z. MAC3A and MAC3B mediate degradation of the transcription factor ERF13 and thus promote lateral root emergence. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 3162–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, P.; Liang, T.; Li, X.; Liu, H. UV-B photoreceptor UVR8 interacts with MYB73/MYB77 to regulate auxin responses and lateral root development. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e101928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Friml, J.; Ding, Z. Auxin signaling: Research advances over the past 30 years. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, B.S.; Wei, K.J.; Hu, K.Q.; Tian, T.; Zhang, F.; Yu, Z.P.; Zhang, D.J.; Su, Y.H.; Sang, Y.L.; Zhang, X.S.; et al. MPK14-mediated auxin signaling controls lateral root development via ERF13-regulated very-long-chain fatty acid biosynthesis. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.K.; Shao, Y.M.; Ge, S.T.; Zhang, M.M.; Zhang, T.S.; Hu, X.T.; Liu, Y.D.; Walker, J.; Zhang, S.Q.; Xu, J. A MAPK cascade downstream of IDA-HAE/HSL2 ligand-receptor pair in lateral root emergence. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Chen, R.; Li, P.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, R.; Ge, D.; Zheng, W.; Wang, X.; Gu, Y.; Gelová, Z.; et al. TMK1-mediated auxin signalling regulates differential growth of the apical hook. Nature 2019, 568, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.J.; Li, M.Q.; Brinkworth, C.S.; Paulson, J.L.; Wang, D.; Hubner, A.; Chou, W.H.; Davis, R.J.; Burlingame, A.L.; Messing, R.O.; et al. A semisynthetic epitope for kinase substrates. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leissing, F.; Nomoto, M.; Bocola, M.; Schwaneberg, U.; Tada, Y.; Conrath, U.; Beckers, G.J.M. Substrate thiophosphorylation by Arabidopsis mitogen-activated protein kinases. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, S. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plant signaling. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 301–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.P.; Xu, Y.; Yu, M.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, S.Z.; Yang, G.D.; Huang, J.G.; Yan, K.; Zheng, C.C.; et al. Regulation of the stability and ABA import activity of NRT1.2/NPF4.6 by CEPR2-mediated phosphorylation in. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancé, C.; Martin-Arevalillo, R.; Boubekeur, K.; Dumas, R. Auxin response factors are keys to the many auxin doors. New Phytol. 2022, 235, 402–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Sun, T.; Liu, Y.; Lukowitz, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S. Regulation of Stomatal Immunity by Interdependent Functions of a Pathogen-Responsive MPK3/MPK6 Cascade and Abscisic Acid. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 526–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lama, S.; Broda, M.; Abbas, Z.; Vaneechoutte, D.; Belt, K.; Säll, T.; Vandepoele, K.; Van Aken, O. Neofunctionalization of Mitochondrial Proteins and Incorporation into Signaling Networks in Plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovtun, Y.; Chiu, W.L.; Tena, G.; Sheen, J. Functional analysis of oxidative stress-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2940–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Wang, S.; Sritubtim, S.; Chen, J.G.; Ellis, B.E. Arabidopsis mitogen-activated protein kinase MPK12 interacts with the MAPK phosphatase IBR5 and regulates auxin signaling. Plant J. 2009, 57, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dory, M.; Hatzimasoura, E.; Kállai, B.M.; Nagy, S.K.; Jäger, K.; Darula, Z.; Nádai, T.V.; Mészáros, T.; López-Juez, E.; Barnabás, B.; et al. Coevolving MAPK and PID phosphosites indicate an ancient environmental control of PIN auxin transporters in land plants. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yan, D.W.; Yuan, T.T.; Gao, X.; Lu, Y.T. A gain-of-function mutation in IAA8 alters Arabidopsis floral organ development by change of jasmonic acid level. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 82, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Hussain, S.; Pham, H.T.T.; Kadam, U.S.; Bahk, S.; Ramadany, Z.; Lee, J.; Song, Y.H.; Lee, K.O.; Hong, J.C.; et al. Phosphorylation of auxin signaling repressor IAA8 by heat-responsive MPKs causes defective flower development. Plant Physiol. 2024, 196, 2825–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Kim, S.H.; Bahk, S.; Ali, A.; Nguyen, X.C.; Yun, D.J.; Chung, W.S. The Auxin Signaling Repressor IAA8 Promotes Seed Germination Through Down-Regulation of ABI3 Transcription in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Xie, C.; Lv, B.; Yu, Z.; Dai, S.; Liu, X.; Xia, G.; Tian, H.; et al. MPK3/6-induced degradation of ARR1/10/12 promotes salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e52457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Leary, E.; Saffaf, O.; Frank Baker, R.; Zhang, S. Overlapping functions of YDA and MAPKKK3/MAPKKK5 upstream of MPK3/MPK6 in plant immunity and growth/development. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ding, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Gong, Z.; Yang, S. MPK3- and MPK6-Mediated ICE1 Phosphorylation Negatively Regulates ICE1 Stability and Freezing Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2017, 43, 630–642.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Bahk, S.; Nguyen, N.T.; Pham, M.L.A.; Kadam, U.S.; Hong, J.C.; Chung, W.S. Phosphorylation of the auxin signaling transcriptional repressor IAA15 by MPKs is required for the suppression of root development under drought stress in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 10544–10561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Lu, Y.; Li, Q.; Luo, S.; Shen, S.; Li, N.; Chen, X. TIR1/AFB proteins: Active players in abiotic and biotic stress signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1083409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, A.; Mangano, S.; Toribio, R.; Fernández-Calvino, L.; Del Pozo, J.C.; Castellano, M.M. The co-chaperone HOP participates in TIR1 stabilisation and in auxin response in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2022, 45, 2508–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Wang, S.; Feng, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhang, M.; Xia, Y.; Peng, C.; et al. FERONIA-mediated TIR1/AFB2 oxidation stimulates auxin signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2024, 17, 772–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Cui, X.; Xu, W.; Li, K.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Yu, L.; Guo, R. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases 3/6 Reduce Auxin Signaling via Stabilizing Indoleacetic Acid-Induced Proteins 8/9 in Plant Abiotic Stress Adaptation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051964
Wang C, Li X, Zhao H, Cui X, Xu W, Li K, Xu Y, Yu Z, Yu L, Guo R. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases 3/6 Reduce Auxin Signaling via Stabilizing Indoleacetic Acid-Induced Proteins 8/9 in Plant Abiotic Stress Adaptation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051964
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chunyan, Xiaoxuan Li, Han Zhao, Xiankui Cui, Wenhong Xu, Ke Li, Yang Xu, Zipeng Yu, Luyao Yu, and Rui Guo. 2025. "Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases 3/6 Reduce Auxin Signaling via Stabilizing Indoleacetic Acid-Induced Proteins 8/9 in Plant Abiotic Stress Adaptation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051964
APA StyleWang, C., Li, X., Zhao, H., Cui, X., Xu, W., Li, K., Xu, Y., Yu, Z., Yu, L., & Guo, R. (2025). Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases 3/6 Reduce Auxin Signaling via Stabilizing Indoleacetic Acid-Induced Proteins 8/9 in Plant Abiotic Stress Adaptation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051964






