Identification and Characterization of ERK2 Dimerization Inhibitors by Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Screening
Abstract
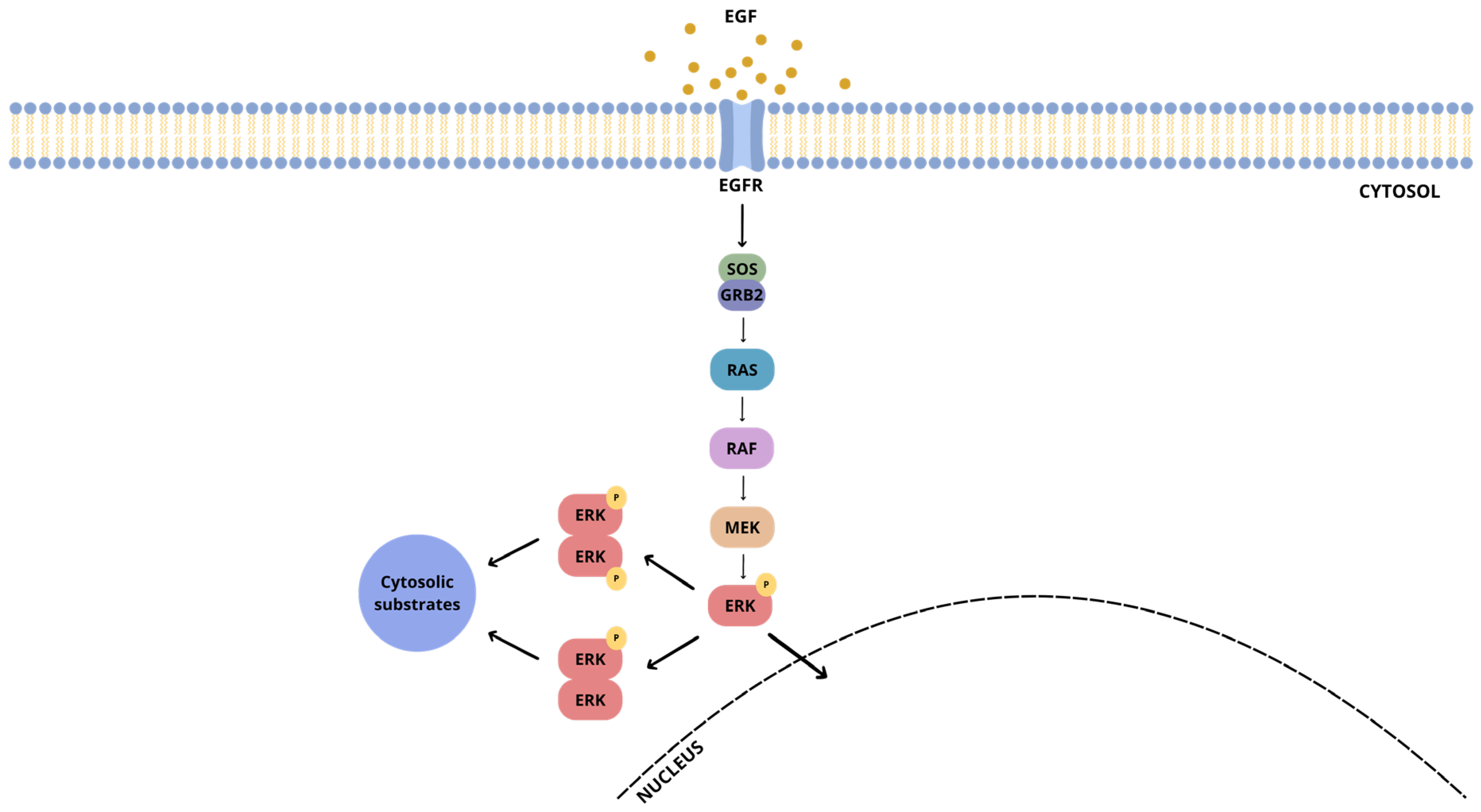
1. Introduction
2. Results
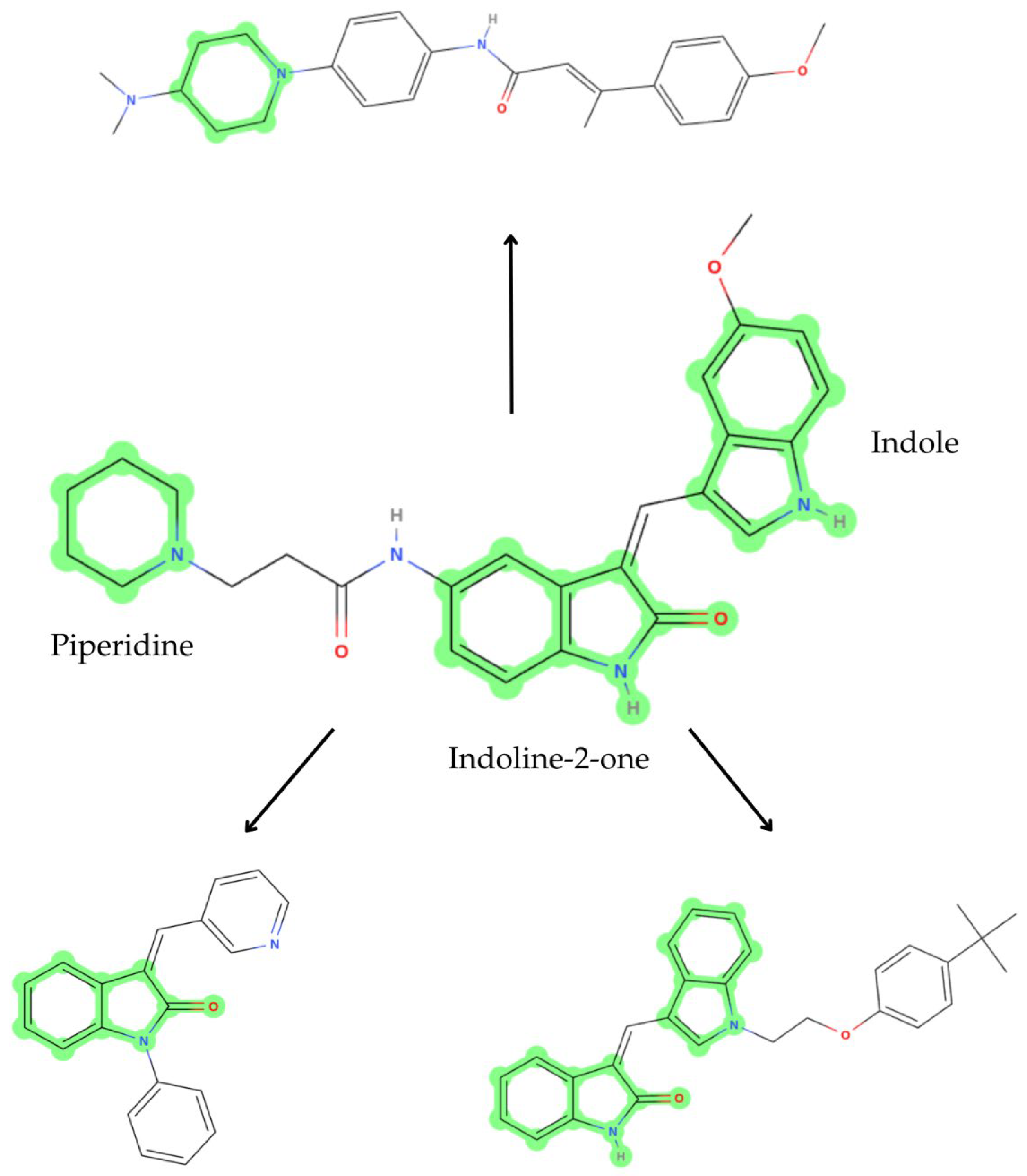
2.1. Scaffold Hopping
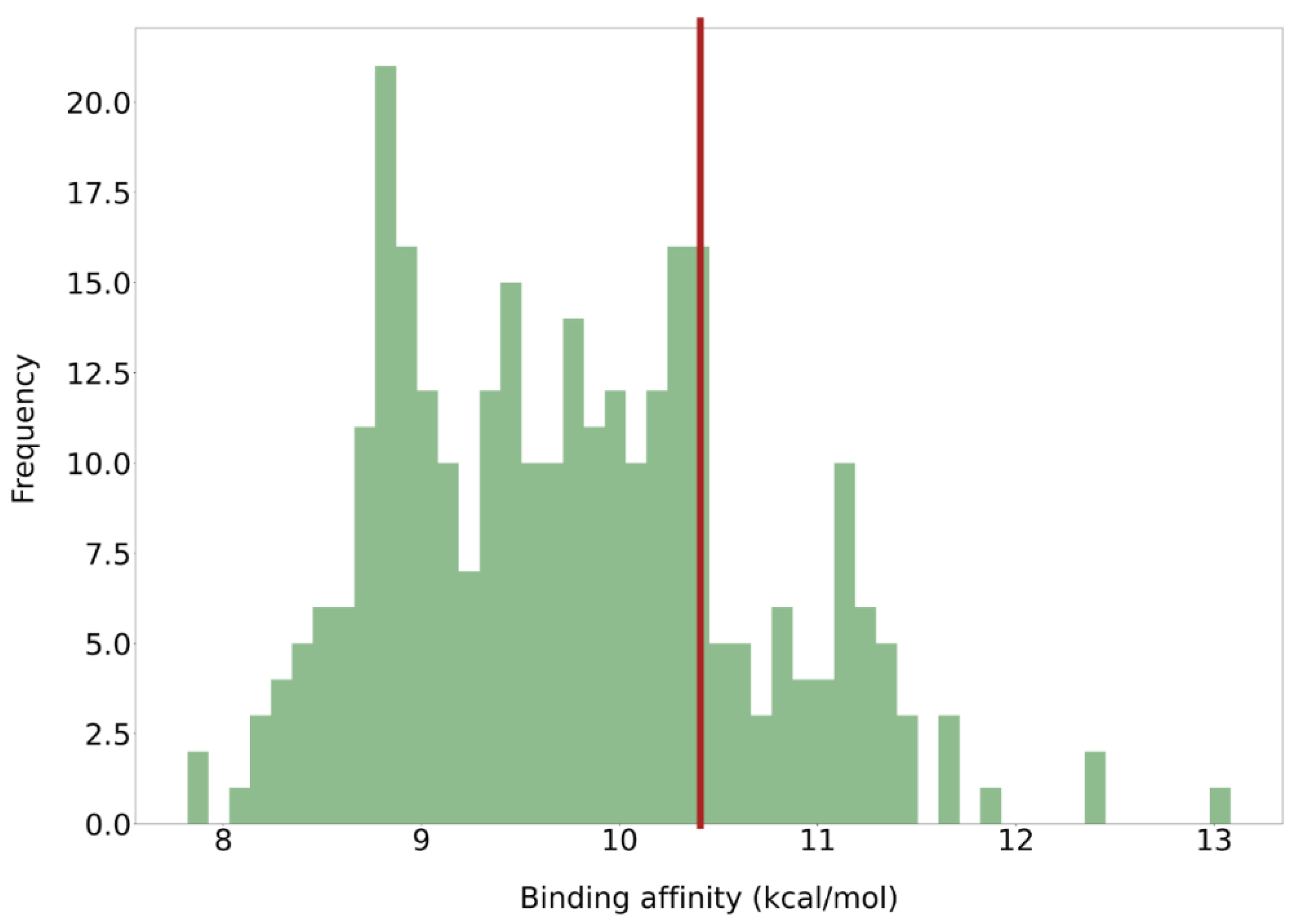
2.2. Virtual Screening
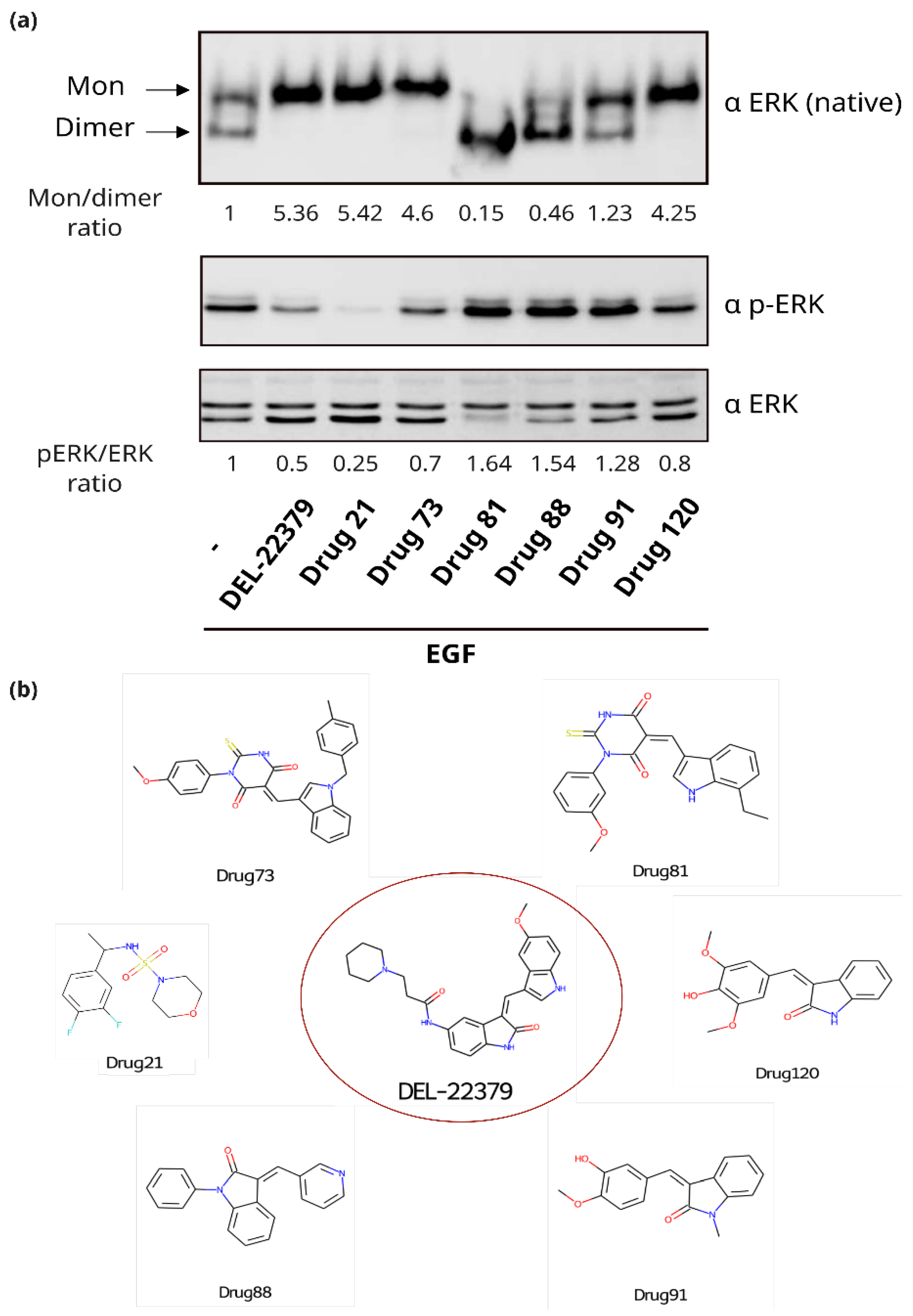
2.3. Experimental Evaluation
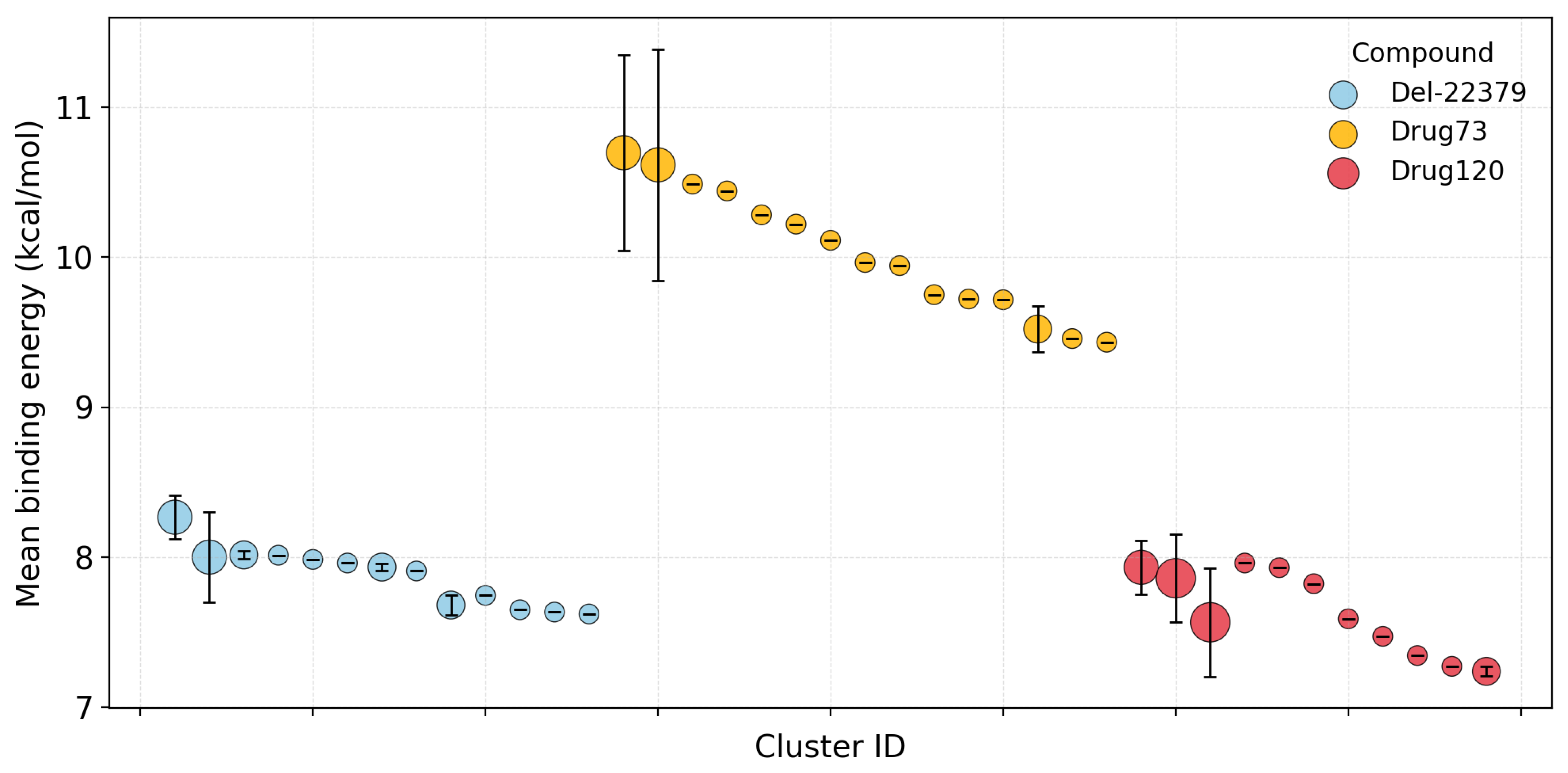
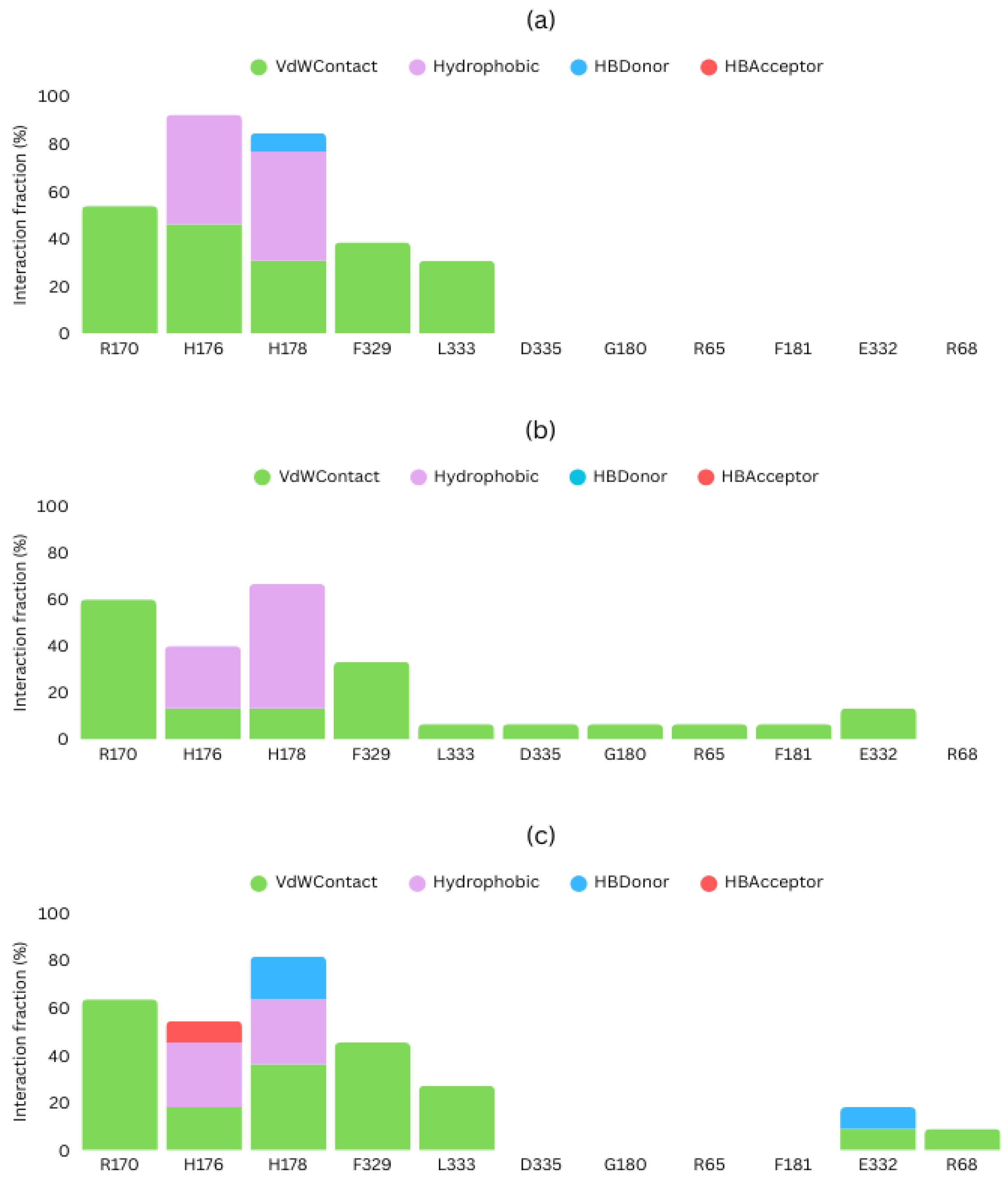
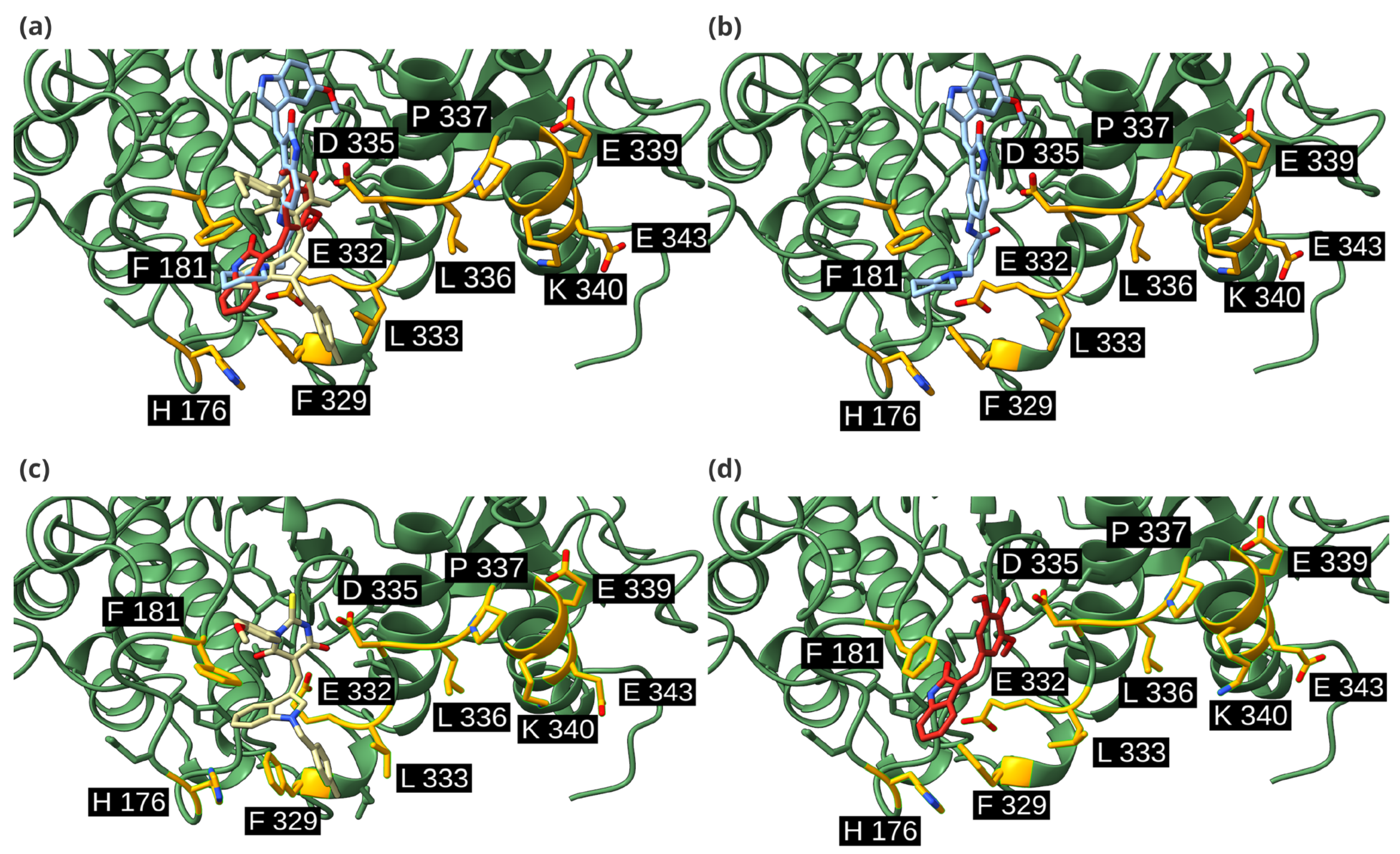
2.4. Detailed Docking of Candidates
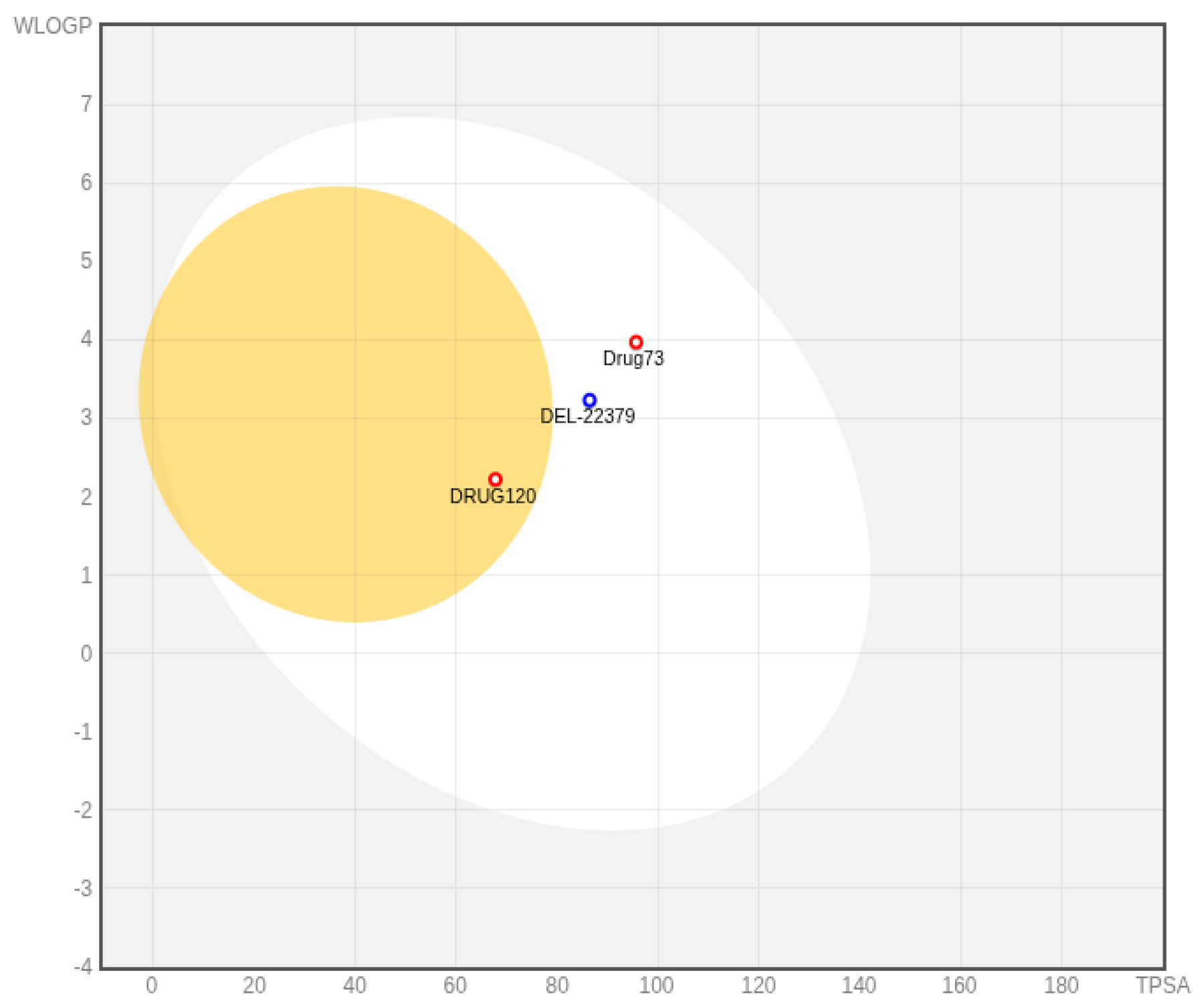
2.5. Chemical Profile Predictions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Scaffold Hopping and Virtual Screening
4.2. Experimental Evaluation Protocol
4.3. Detailed Molecular Docking
4.4. Protein-Ligand Interaction Analysis
4.5. Chemical Profile Predictions Procedure
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| ERK | Extracellular regulated-kinase |
| MEK | MAPK/ERK kinase |
| PPIs | Protein–protein interactions |
| ATP | Adenosin triphosphate |
| RSK1 | Ribosomal S6 Kinase 1 |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| EMT | epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| KSR1 | Kinase Suppressor of Ras 1 |
| PAGE | PolyAcrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| QSAR | Quantitative structure-activity relationship |
| QMRF | QSAR Model Reporting Format |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| ADMET | Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, and Toxicity |
| LD50 | Lethal dose 50 |
| LOAEL | Lowest observed adverse effect level |
| P-gp | P-glycoprotein |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| HIA | Human Intestinal Absorption |
References
- Arkin, M.R.; Tang, Y.; Wells, J.A. Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Protein-Protein Interactions: Progressing toward the Reality. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1102–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolch, W. Meaningful Relationships: The Regulation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK Pathway by Protein Interactions. Biochem. J. 2000, 351, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.A.; Khuri, F.R.; Fu, H. Targeting Protein-Protein Interactions as an Anticancer Strategy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R. ERK1/2 MAP Kinases: Structure, Function, and Regulation. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 66, 105–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, A.S.; Hagan, S.; Rath, O.; Kolch, W. MAP Kinase Signalling Pathways in Cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.J.; Der, C.J. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Cascade for the Treatment of Cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3291–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Nielsen, T.E.; Clausen, M.H. Small-Molecule Kinase Inhibitors: An Analysis of FDA-Approved Drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.E.; Bayly, A.R.; Abell, C.; Skidmore, J. Small Molecules, Big Targets: Drug Discovery Faces the Protein-Protein Interaction Challenge. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.; Wu, Z.; Xing, C.; Miao, Z. Small Molecules Inhibiting Keap1-Nrf2 Protein-Protein Interactions: A Novel Approach to Activate Nrf2 Function. Medchemcomm 2016, 8, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasovic, A.; Brand, T.; Schanbacher, C.; Kramer, S.; Hümmert, M.W.; Godoy, P.; Schmidt-Heck, W.; Nordbeck, P.; Ludwig, J.; Homann, S.; et al. Interference with ERK-Dimerization at the Nucleocytosolic Interface Targets Pathological ERK1/2 Signaling without Cardiotoxic Side-Effects. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente-Vivas, D.; Cappitelli, V.; García-Gómez, R.; Valero-Díaz, S.; Amato, C.; Rodriguéz, J.; Duro-Sánchez, S.; von Kriegsheim, A.; Grusch, M.; Lozano, J.; et al. ERK1/2 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Dimerization Is Essential for the Regulation of Cell Motility. Mol. Oncol. 2025, 19, 452–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, A.; Pinto, A.; Colón-Bolea, P.; Casar, B.; Jones, M.; Agudo-Ibáñez, L.; Vidal, R.; Tenbaum, S.P.; Nuciforo, P.; Valdizán, E.M.; et al. Small Molecule Inhibition of ERK Dimerization Prevents Tumorigenesis by RAS-ERK Pathway Oncogenes. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaballos, M.A.; Acuña-Ruiz, A.; Morante, M.; Riesco-Eizaguirre, G.; Crespo, P.; Santisteban, P. Inhibiting ERK Dimerization Ameliorates BRAF-Driven Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casar, B.; Pinto, A.; Crespo, P. ERK Dimers and Scaffold Proteins: Unexpected Partners for a Forgotten (Cytoplasmic) Task. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscà, R.; Pouysségur, J.; Lenormand, P. ERK1 and ERK2 Map Kinases: Specific Roles or Functional Redundancy? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Tao, L.; Yang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, Y. Structure-Activity Relationship Study of DEL-22379: ERK Dimerization Inhibitors with Increased Safety. Mol. Divers. 2021, 25, 1051–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzara, P.R.; Moore, T.W. Scaffold-Hopping as a Strategy to Address Metabolic Liabilities of Aromatic Compounds. RSC Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Tawa, G.; Wallqvist, A. Classification of Scaffold Hopping Approaches. Drug Discov. Today 2011, 17, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petta, I.; Lievens, S.; Libert, C.; Tavernier, J.; De Bosscher, K. Modulation of Protein-Protein Interactions for the Development of Novel Therapeutics. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Zhou, Q.; He, J.; Jiang, Z.; Peng, C.; Tong, R.; Shi, J. Recent Advances in the Development of Protein–Protein Interactions Modulators: Mechanisms and Clinical Trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McReynolds, A.C.; Karra, A.S.; Li, Y.; Lopez, E.D.; Turjanski, A.G.; Dioum, E.; Lorenz, K.; Zaganjor, E.; Stippec, S.; McGlynn, K.; et al. Phosphorylation or Mutation of the ERK2 Activation Loop Alters Oligonucleotide Binding. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiser, R.; Andrlová, H.; Meiss, F. Trametinib (GSK1120212). Recent. Results Cancer Res. 2018, 211, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, V.K.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Prajapati, V.; Kalsi, A.S.; Khalilullah, H.; Jaremko, M.; Emwas, A.H.; Verma, A.; Kumar, P. Advances in ERK1/2 Inhibition: A Medicinal Chemistry Perspective on Structure and Regulation. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2025, 40, 2555510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grogan, L.; Shapiro, P. Progress in the Development of ERK1/2 Inhibitors for Treating Cancer and Other Diseases. Adv. Pharmacol. 2024, 100, 181–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammons, R.M.; Dalby, K.N. A Toolbox of Structural Biology and Enzyme Kinetics Reveals the Case for ERK Docking Site Inhibition. In Next Generation Kinase Inhibitors: Moving Beyond the ATP Binding/Catalytic Sites; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 109–139. [Google Scholar]
- Ojea Ramos, S.; Medina, C.; Krawczyk, M.D.; Millán, J.; Acutain, M.F.; Romano, A.G.; Baez, M.V.; Urbano Suarez, F.J.; Boccia, M.M.; Feld, M. Hippocampal ERK2 Dimerization Is Critical for Memory Reconsolidation and Synaptic Plasticity. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilsbacher, J.L.; Juang, Y.C.; Khokhlatchev, A.V.; Gallagher, E.; Binns, D.; Goldsmith, E.J.; Cobb, M.H. Characterization of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Dimers. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 13175–13182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Sarkar, B.; Ghosh, R.; Roy, S.; Singh, N.K.; Rakshit, G. Scaffold Hopping and De Novo Drug Design. In Computational Methods for Rational Drug Design; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, A.; Ojeda-Montes, M.J.; Tomás-Hernández, S.; Cereto-Massagué, A.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Mulero, M.; Pujadas, G.; Garcia-Vallvé, S. The Light and Dark Sides of Virtual Screening: What Is There to Know? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paggi, J.M.; Pandit, A.; Dror, R.O. The Art and Science of Molecular Docking. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2024, 93, 389–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regev, C.; Jang, H.; Nussinov, R. ERK Allosteric Activation: The Importance of Two Ordered Phosphorylation Events. J. Mol. Biol. 2025, 437, 169130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Gao, W.; Hu, H.; Zhou, S. Why 90% of Clinical Drug Development Fails and How to Improve It? Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3049–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S. Improving Early Drug Discovery through ADME Modelling: An Overview. Drugs R D 2007, 8, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcule. Advanced Tools to Find and Order Molecules Online. Available online: https://mcule.com/ (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Ozvoldik, K.; Stockner, T.; Krieger, E. YASARA Model-Interactive Molecular Modeling from Two Dimensions to Virtual Realities. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2023, 63, 6177–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, E.; Vriend, G. YASARA View—Molecular Graphics for All Devices—From Smartphones to Workstations. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2981–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BIOVIA. Discovery Studio; Dassault Systèmes: Waltham, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Landrum, G. RDKit: Open-Source Cheminformatics. Available online: https://www.rdkit.org/ (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Pinto, A.; Crespo, P. Analysis of ERKs’ Dimerization by Electrophoresis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 661, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, S.K.; Bhatt, R.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Biester, A.; Biswas, P.; Bittrich, S.; Blaumann, S.; Brown, R.; Chao, H.; et al. Updated Resources for Exploring Experimentally-Determined PDB Structures and Computed Structure Models at the RCSB Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D564–D574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurrus, E.; Engel, D.; Star, K.; Monson, K.; Brandi, J.; Felberg, L.E.; Brookes, D.H.; Wilson, L.; Chen, J.; Liles, K.; et al. Improvements to the APBS Biomolecular Solvation Software Suite. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forli, S.; Huey, R.; Pique, M.E.; Sanner, M.F.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Computational Protein-Ligand Docking and Virtual Drug Screening with the AutoDock Suite. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Python Software Foundation. Python: A Programming Language. Available online: https://www.python.org/ (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Gowers, R.J.; Linke, M.; Barnoud, J.; Reddy, T.J.E.; Melo, M.N.; Seyler, S.L.; Domański, J.; Dotson, D.L.; Buchoux, S.; Kenney, I.M.; et al. MDAnalysis: A Python Package for the Rapid Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Simulations. In Proceedings of the 15th Python in Science Conference (SCIPY 2016), Austin, TX, USA, 11–17 July 2016; pp. 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Michaud-Agrawal, N.; Denning, E.J.; Woolf, T.B.; Beckstein, O. MDAnalysis: A Toolkit for the Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 2319–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouysset, C.; Fiorucci, S. ProLIF: A Library to Encode Molecular Interactions as Fingerprints. J. Cheminform. 2021, 13, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, E.C.; Goddard, T.D.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Pearson, Z.J.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Tools for Structure Building and Analysis. Protein Sci. 2023, 32, e4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ProtoQSAR. ProtoPRED: A Computational Platform for QSAR Predictions. Available online: https://protopred.protoqsar.com/ (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Deep-PK. Deep Learning for Small Molecule Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Prediction. Available online: https://biosig.lab.uq.edu.au/deeppk/ (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A Free Web Tool to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics, Drug-Likeness and Medicinal Chemistry Friendliness of Small Molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ADMET Properties | DEL-22379 | Drug73 | Drug120 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lipinski rule violations | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 |
| Bioavailability 20% | Negative | Positive | Positive |
| Bioavailability 30% | Negative | Positive | Positive |
| Caco-2 permeability (log cm/s) 4 | −5.34 | −4.89 | −4.78 |
| HIA | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| Half-life (h) | 6.60 | 7.1 | 4.4 |
| Acute oral toxicity (300 mg/kg) | Toxic | Non-toxic | Non-toxic |
| Neurotoxicity [LD50] (mg/kg) | 216.4 | 551.9 | 497 |
| Acute toxicity in rats [LD50] | 1.9 | 2.57 | 2.32 |
| Chronic toxicity in rats (LOAEL) | 2.69 | 1.83 | 2.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortiz-González, C.; Casar, B.; Gozalbes, R.; Serrano-Candelas, E.; Crespo, P.; Carpio, L.E. Identification and Characterization of ERK2 Dimerization Inhibitors by Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Screening. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311481
Ortiz-González C, Casar B, Gozalbes R, Serrano-Candelas E, Crespo P, Carpio LE. Identification and Characterization of ERK2 Dimerization Inhibitors by Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Screening. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311481
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtiz-González, Carmen, Berta Casar, Rafael Gozalbes, Eva Serrano-Candelas, Piero Crespo, and Laureano E. Carpio. 2025. "Identification and Characterization of ERK2 Dimerization Inhibitors by Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Screening" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311481
APA StyleOrtiz-González, C., Casar, B., Gozalbes, R., Serrano-Candelas, E., Crespo, P., & Carpio, L. E. (2025). Identification and Characterization of ERK2 Dimerization Inhibitors by Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Screening. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311481









