Salivary Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Peri-Implant Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
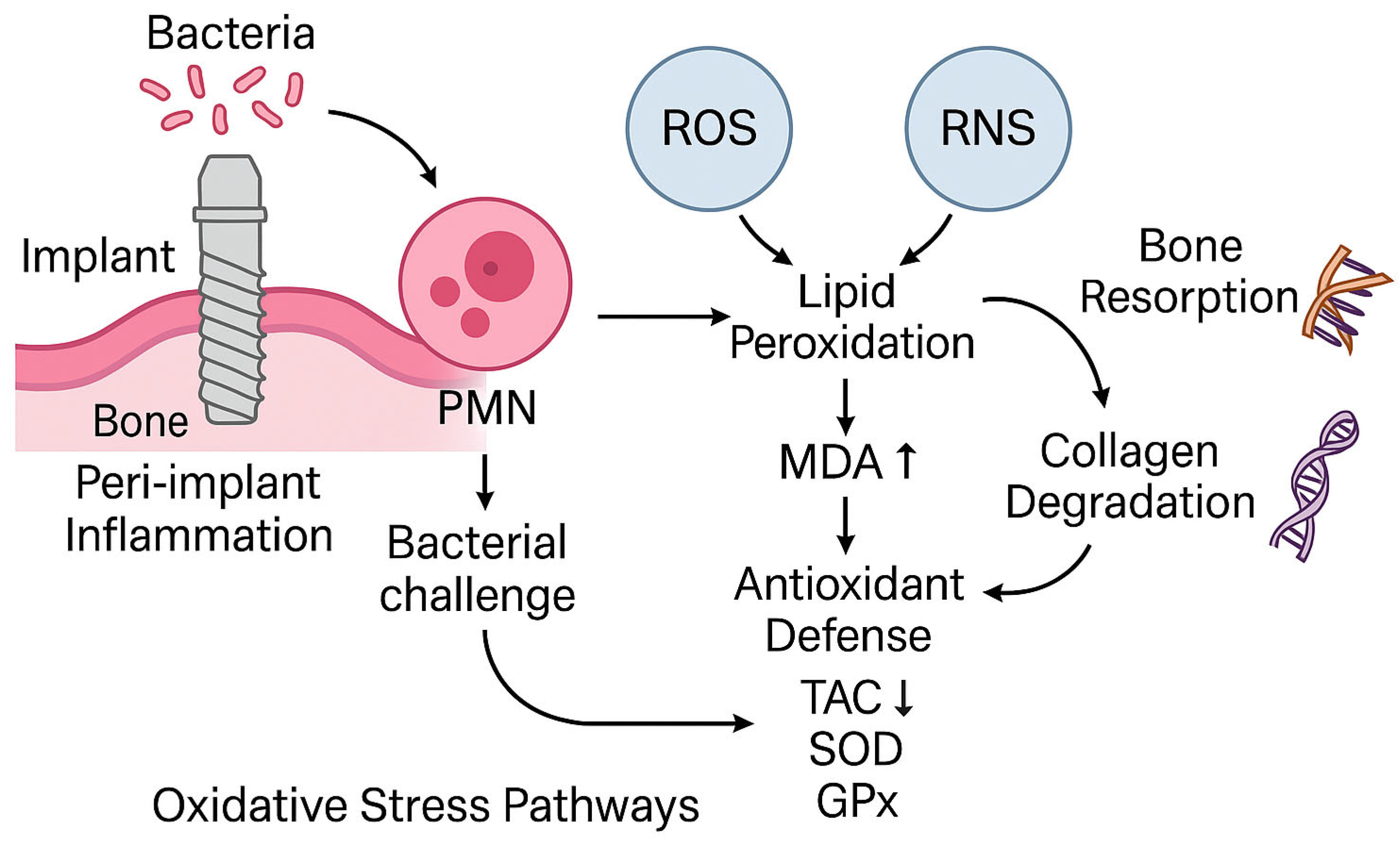
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Focused Question and Objectives
- Population (P): Adult patients with dental implants, either healthy or diagnosed with peri-implantitis or peri-implant mucositis.
- Intervention (I): Quantitative measurement of salivary oxidative stress biomarkers (e.g., malondialdehyde [MDA], total antioxidant capacity [TAC], 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine [8-OHdG]), defined as values reported as absolute concentration, normalized units (e.g., per protein or volume), or assay-specific readouts (e.g., relative fluorescence). Saliva was selected as a non-invasive matrix supported by prior diagnostic overviews [7,8]. For the purposes of this review, “peri-implant disease” was defined as either peri-implant mucositis (reversible inflammatory changes in the peri-implant mucosa without radiographic bone loss) or peri-implantitis (inflammatory changes with concomitant radiographic evidence of supporting bone loss), according to each study’s definition. Studies including either condition, or both, were eligible for inclusion. When a study reported both conditions as separate groups, we extracted data for each comparison (vs healthy controls) if reported in sufficient detail; otherwise, the study’s overall diseased group was used. For meta-analytic pooling, peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis groups were combined under the umbrella term “peri-implant disease.” Diagnostic definitions followed the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Condition [1]. The potential implications of combining these conditions are addressed in the Discussion.
- Comparison (C): Healthy controls with no signs of peri-implant disease.
- Outcome (O): Association between biomarker levels and disease presence or implant success/failure.
- Study design (S): Observational studies (cross-sectional, case–control, cohort), and experimental clinical studies.
2.3. Information Sources and Search Strategy
- Search terms: (“saliva” OR “salivary”) AND (“oxidative stress” OR “oxidative damage” OR “redox status”) AND (“biomarker” OR “marker” OR “indicator”) AND (“malondialdehyde” OR “MDA” OR “total antioxidant capacity” OR “TAC” OR “8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine” OR “8-OHdG”) AND (“peri-implantitis” OR “peri-implant mucositis” OR “dental implants”)
- Language: English only
- Publication period: January 2004 to September 2025
- Study type: Original research articles (excluding reviews, case reports, conference abstracts, in vitro and animal studies)
2.4. Eligibility Criteria
- Human studies including participants with dental implants
- Salivary biomarkers related to oxidative stress were quantified (MDA, TAC, 8-OHdG, or related)
- Comparison between healthy and diseased implant conditions
- Quantitative outcomes reported or extractable (means, SDs, or AUC)
- Original full-text research articles (excluding reviews, case reports, conference abstracts, in vitro and animal studies).
2.5. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.6. Risk-of-Bias Assessment
2.7. Data Synthesis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
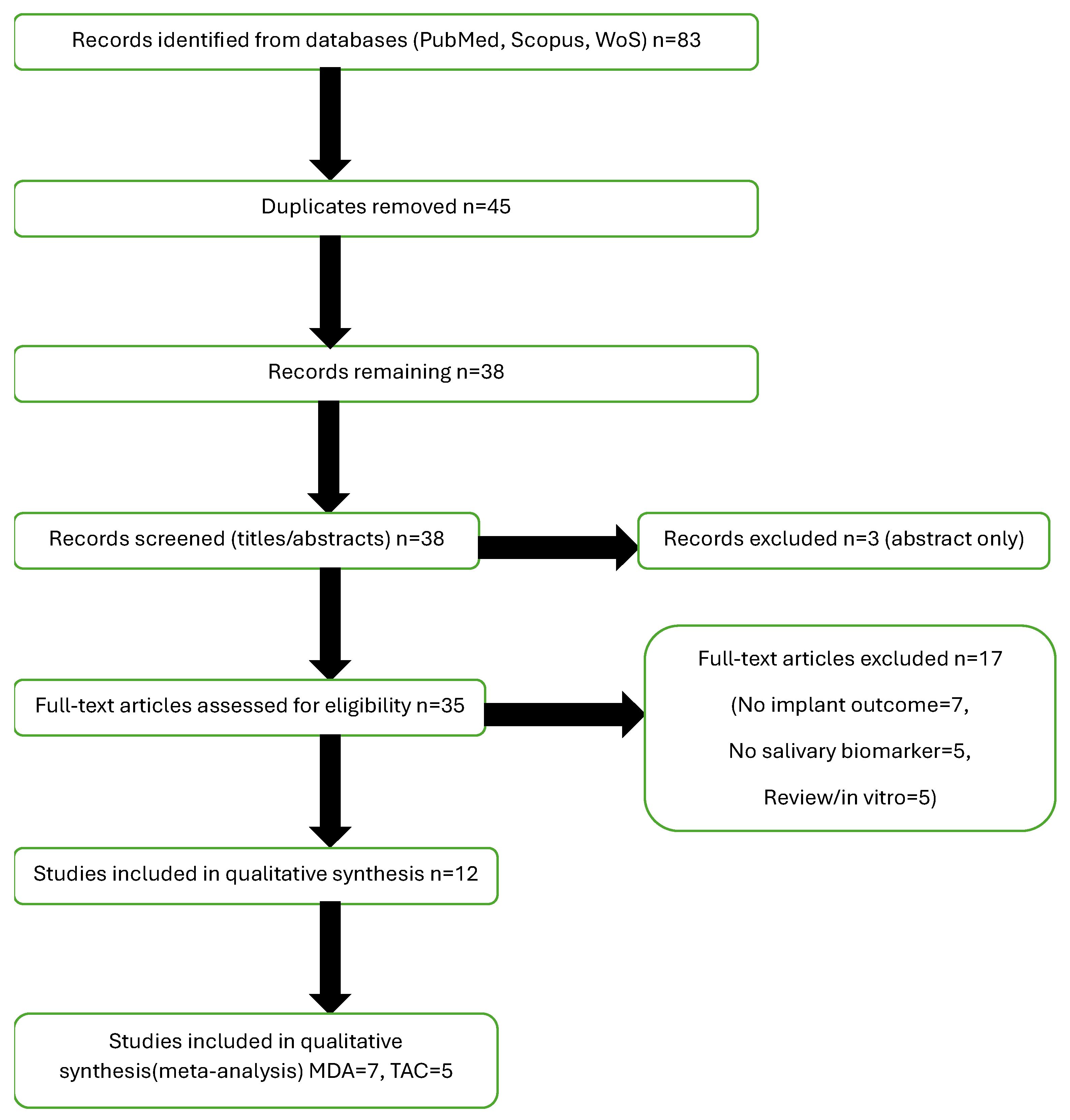
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Risk-of-Bias Assessment
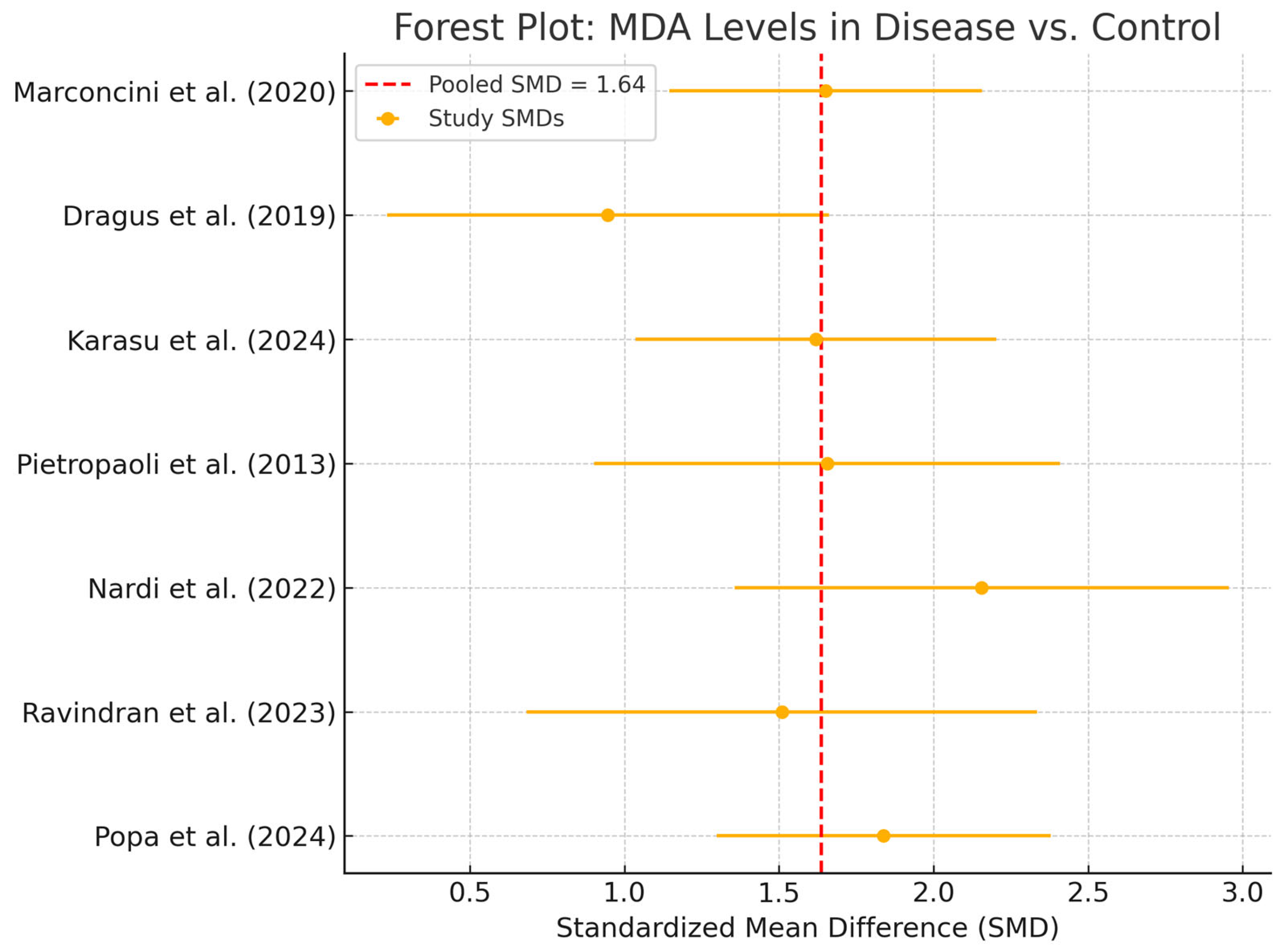
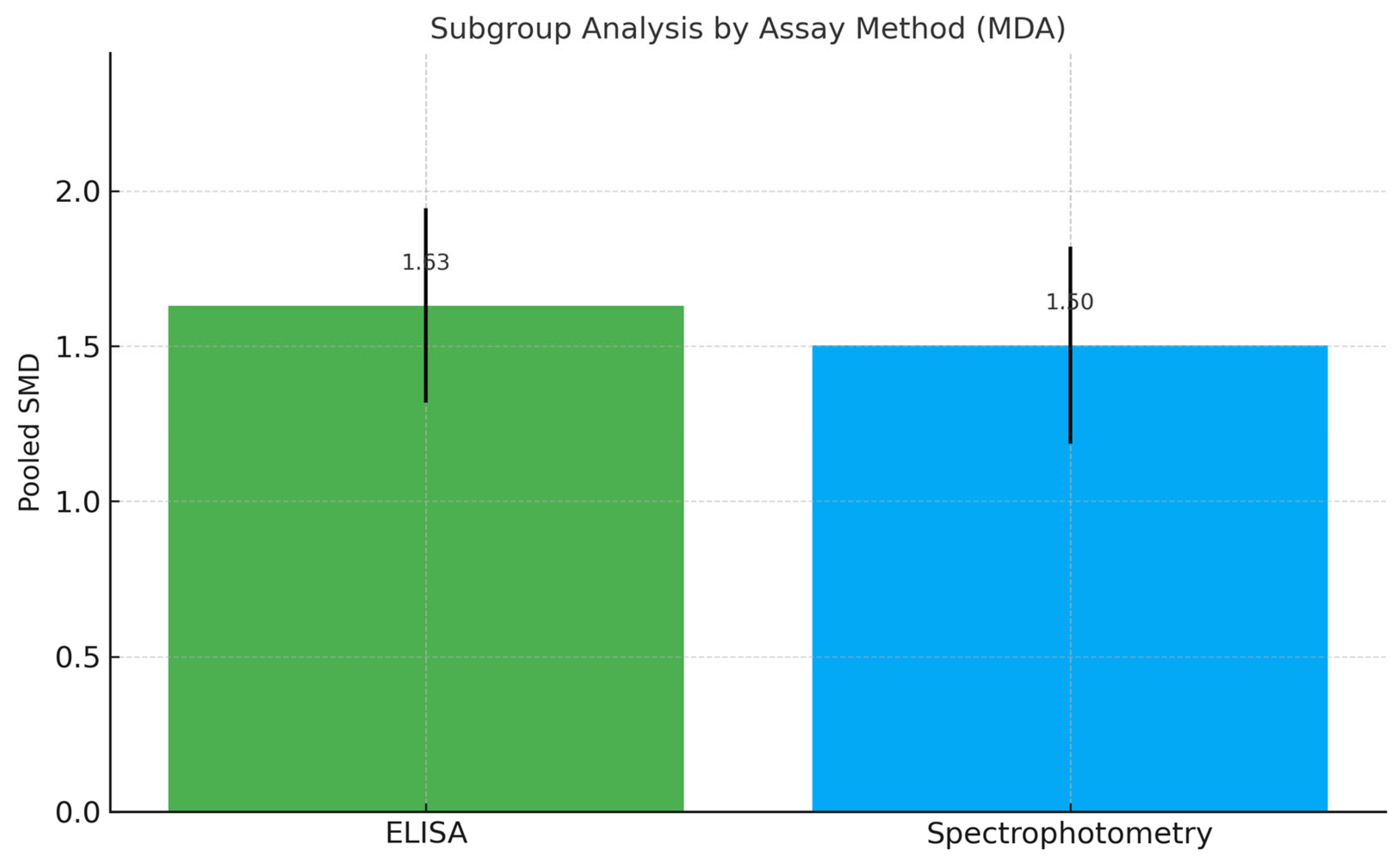
3.4. Meta-Analysis of MDA Levels
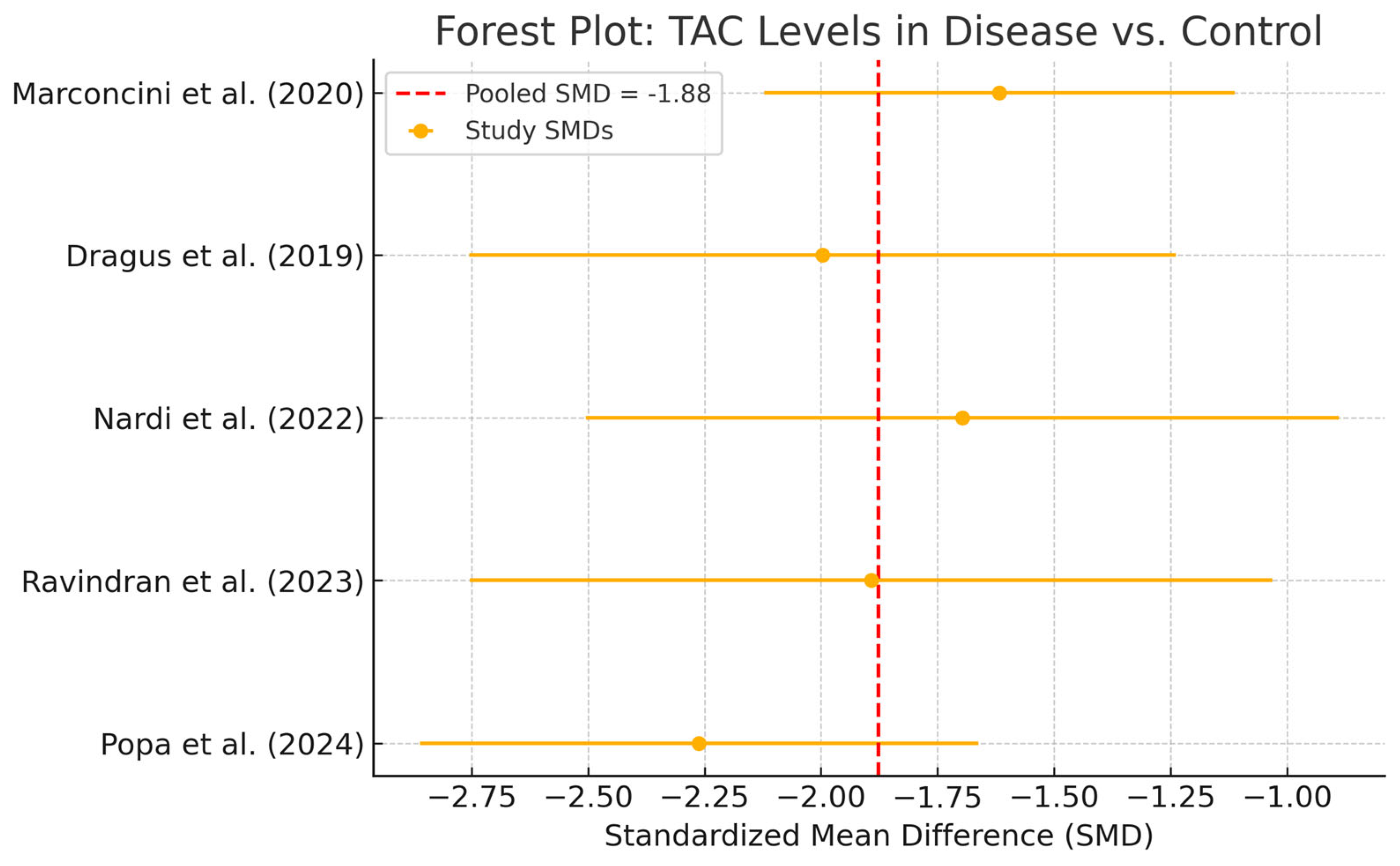
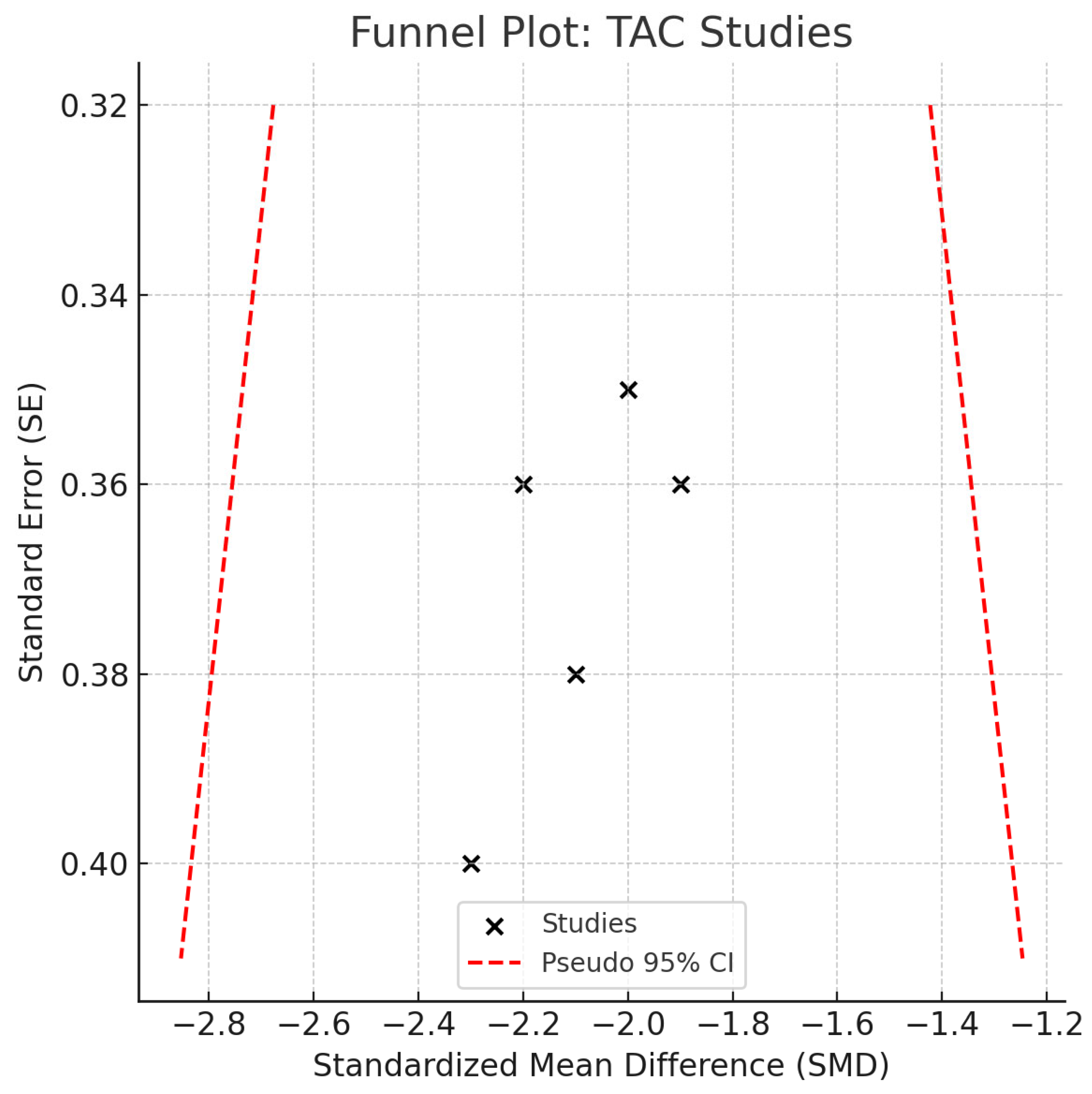
3.5. Meta-Analysis of TAC Levels
3.6. Certainty of Evidence (GRADE Assessment)
3.7. Qualitative Synthesis of 8-OHdG
3.8. Summary of Findings
4. Discussion
- Heterogeneous protocols for saliva collection and biomarker normalization
- Moderate risk of bias in several studies
- Potential language/publication bias, despite no funnel-plot asymmetry.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berglundh, T.; Armitage, G.; Araujo, M.G.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Blanco, J.; Camargo, P.M.; Chen, S.; Cochran, D.; Derks, J.; Figuero, E.; et al. Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions: Consensus Report of Workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45 (Suppl. S20), S286–S291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Quirynen, M. Risk Indicators for Peri-Implantitis. A Narrative Review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26 (Suppl. S11), 15–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viglianisi, G.; Tartaglia, G.M.; Santonocito, S.; Amato, M.; Polizzi, A.; Mascitti, M.; Isola, G. The Emerging Role of Salivary Oxidative Stress Biomarkers as Prognostic Markers of Periodontitis: New Insights for a Personalized Approach in Dentistry. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, H.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Yan, Y.; Wang, R.; Pesavento, R.P.; Mathew, M.T. Intelligent Salivary Biosensors for Periodontitis: In Vitro Simulation of Oral Oxidative Stress Conditions. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2024, 62, 2409–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindran, N.; Sudhakar, U.; Mithradas, N.; Suresh, S.; Asirvatham, S.L.; Steffy, J.; Kotaru, J.L.; Bakkiya, A.; Sundaran, K.R.; Bhavishya, B. Insight Into the Laboratory Diagnosis of Periimplantitis Using Reactive Oxygen Metabolite Levels—A Biochemical Study. Cureus 2023, 15, e41324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaman, D.; Ustaoğlu, G.; Avcı, E. Oxidative Stress and Peri-Implantitis: The Role of Oxidants and Antioxidants. J. Oral Health Oral Epidemiol. 2023, 12, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Bai, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, X.; Ying, B. Promising Applications of Human-Derived Saliva Biomarker Testing in Clinical Diagnostics. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2023, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-Z.; Cheng, X.-Q.; Li, J.-Y.; Zhang, P.; Yi, P.; Xu, X.; Zhou, X.-D. Saliva in the Diagnosis of Diseases. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2016, 8, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormas, I.; Pedercini, C.; Pedercini, A.; Raptopoulos, M.; Alassy, H.; Wolff, L.F. Peri-Implant Diseases: Diagnosis, Clinical, Histological, Microbiological Characteristics and Treatment Strategies. A Narrative Review. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, P.Ș.; Popa-Cazacu, E.C.; Zaharescu, A.; Popa, G.V.; Matei, M.N. Minimizing Oxidative Stress in Oral Surgery: A Comparative Study of Laser-Assisted and Conventional Third Molar Extractions. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrcanovic, B.R.; Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. Reasons for Failures of Oral Implants. J. Oral Rehabil. 2014, 41, 443–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel-Chirino, C.; Gómez-Landeros, J.C.; Carabantes-Campos, E.P.; Carmona-Ruiz, D.; Valero-Princet, Y.; Márquez-Correa, C.; Morales-González, J.A. The Impact of Oxidative Stress on Dental Implants. Eur. J. Dent. Oral Health 2021, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan Karasu, Y.; Maden, O.; Çanakçı, C.F. Oxidative Damage Biomarkers and Antioxidant Enzymes in Saliva of Patients with Peri-Implant Diseases. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2024, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Jornet, P.; Hynninen, J.N.; Parra-Perez, F.; Peres-Rubio, C.; Pons-Fuster, E.; Tvarijonaviciute, A. The Role of Salivary Biomarkers in Monitoring Oral Health in Patients with Implants and Periodontitis. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóthová, L.; Celec, P. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in the Diagnosis and Therapy of Periodontitis. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapple, I.L.C.; Matthews, J.B. The Role of Reactive Oxygen and Antioxidant Species in Periodontal Tissue Destruction. Periodontol. 2000 2007, 43, 160–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hong, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; et al. The Role of Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in the Development of Peri-Implant Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Dent. 2024, 146, 105026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Available online: https://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org/ (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Current Version)|Cochrane. Available online: https://www.cochrane.org/authors/handbooks-and-manuals/handbook/current (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Non-Randomised Studies of Interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Bossuyt, P.M.M.; QUADAS-2 Group. QUADAS-2: A Revised Tool for the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, G.M.; Mazur, M.; Papa, G.; Petruzzi, M.; Grassi, F.R.; Grassi, R. Treatment of Peri-Implant Mucositis with Standard of Care and Bioptron Hyperlight Therapy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in Meta-Analysis Detected by a Simple, Graphical Test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the Sample Mean and Standard Deviation from the Sample Size, Median, Range and/or Interquartile Range. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J. GRADE: An Emerging Consensus on Rating Quality of Evidence and Strength of Recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconcini, S.; Giammarinaro, E.; Corre-Ja, J.A.; Maltagliati, A.; Salvado, F.; Covani, U. Clinical Performance of Titanium-Zirconia Tissue-Level Implants in Patients with Well-Controlled and Poorly-Controlled Type 2 Diabetes: A Cohort Study with Chair-Side Assessment of Oxidative Stress. ORAL Implantol. 2022, 15, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Dragus, L.; Benea, L.; Simionescu, N.; Ravoiu, A.; Neaga, V. Effect of the Inflammatory Conditions and Albumin Presence on the Corrosion Behavior of Grade 5 Titanium Alloy in Saliva Biological Solution. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 572, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietropaoli, D.; Ortu, E.; Severino, M.; Ciarrocchi, I.; Gatto, R.; Monaco, A. Glycation and Oxidative Stress in the Failure of Dental Implants: A Case Series. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permuy, M.; Lopez-Pena, M.; Gonzalez-Cantalapiedra, A.; Munoz, F. Melatonin: A Review of Its Potential Functions and Effects on Dental Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buranasin, P.; Kominato, H.; Mizutani, K.; Mikami, R.; Saito, N.; Takeda, K.; Iwata, T. Influence of Reactive Oxygen Species on Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration in Periodontal and Peri-Implant Tissues in Diabetic Patients. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodratizadeh, S.; Shenasa, N.; Tavakol, O.; Mohamadinia, M.; Gandomkar, H.; Roudsari, M.B.; Sadighi, K. Narrative Review of Biomarkers in Patients with Peri-Implantitis: Narrative Review of Biomarkers in Patients with Peri-Implantitis. Galen Med. J. 2024, 13, e3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popa, P.Ș.; Popa, G.V.; Earar, K.; Popa-Cazacu, C.E.; Matei, M.N. Salivary Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Peri-Implant Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311269
Popa PȘ, Popa GV, Earar K, Popa-Cazacu CE, Matei MN. Salivary Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Peri-Implant Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311269
Chicago/Turabian StylePopa, Paul Șerban, Gabriel Valeriu Popa, Kamel Earar, Claudia Elisabeta Popa-Cazacu, and Mădălina Nicoleta Matei. 2025. "Salivary Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Peri-Implant Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311269
APA StylePopa, P. Ș., Popa, G. V., Earar, K., Popa-Cazacu, C. E., & Matei, M. N. (2025). Salivary Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Peri-Implant Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311269





