Characterisation of Plasmid-Associated Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Coastal Marine Enterobacterales from the Central Adriatic Sea: De Novo Assembly and Bioinformatic Profiling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterisation of Reconstructed Plasmid-like Sequences from Marine Enterobacterales
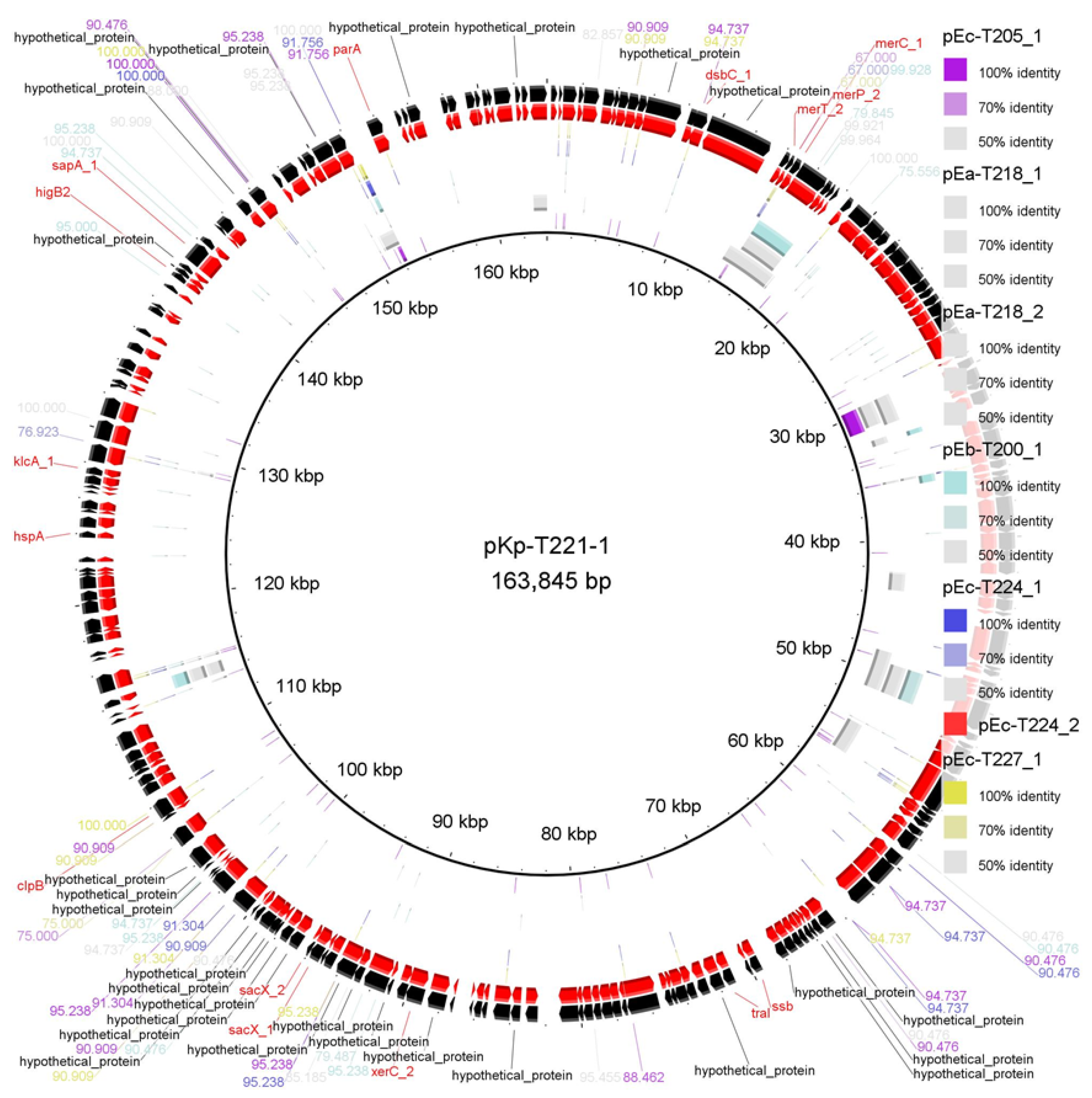
2.1.1. Reconstruction and General Characteristics of the Predicted Plasmids
2.1.2. Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARGs)
2.1.3. Mobile Elements and Structural Features
2.1.4. Virulence Determinants
2.2. Comparative Alignment and ARG Mapping
3. Discussion
3.1. Comparative Resistome Features in Adriatic Plasmid Assemblies
3.2. Methodological Strengths and Limitations
3.3. Future Directions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Area and Seawater Sampling
4.2. Extraction of Plasmid DNA
4.3. Preparation of Plasmid Libraries and Illumina Sequencing
4.4. Assembly and Annotation of Putative Plasmid-Derived Contigs
4.5. Putative Plasmid Sequence Clustering and Visualisation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARGs | antibiotic resistance genes |
| IS | insertion sequences |
| Inc | incompatibility |
| MGEs | mobile genetic elements |
| CRE | carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae |
| MEM | meropenem |
| LB | Luria–Bertani |
| S1-PFGE | S1-nuclease pulsed-field gel electrophoresis |
| NGS | next generation sequencing |
| BLTs | bead-linked transposomes |
| IPB | Illumina Purification Beads |
References
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655, Erratum in Lancet 2022, 400, 1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02653-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partridge, S.; Kwong, S.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S. Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A. Plasmids and the spread of resistance. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendonk, T.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Cytryn, E.; Walsh, F.; Bürgmann, H.; Sorum, H.; Norström, M.; Pons, M.; et al. Tackling antibiotic resistance: The environmental framework. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, T. Occurrence, abundance, and diversity of tetracycline resistance genes in 15 sewage treatment plants across China and other global locations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2598–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.Y.; Lau, C.P.; Cheung, K.T. Exploring urban coastal areas: Investigating the urban coastal areas as a reservoirs of antibiotic resistance Genes. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 204, 106874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, S.; Jacob, T.; Jacob, J.; AlSosowaa, A.A.; Cherian, T.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Vijayan, S. Klebsiella pneumoniae: A growing threat in the era of antimicrobial resistance. Microbe 2025, 7, 100333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Söderquist, B.; Jass, J. Prevalence and Diversity of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Swedish Aquatic Environments Impacted by Household and Hospital Wastewater. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvesic, M.; Kalinic, H.; Dzelalija, M.; Samanic, I.; Andricevic, R.; Maravic, A. Microbiome and antibiotic resistance profiling in submarine effluent-receiving coastal waters in Croatia. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzelalija, M.; Kvesic, M.; Novak, A.; Fredotovic, Ä.; Kalinic, H.; Samanic, I.; Ordulj, M.; Jozic, S.; Barisic, I.; Tonkic, M.; et al. Microbiome profiling and characterization of virulent and vancomycin- resistant Enterococcus faecium from treated and untreated wastewater, beach water and clinical sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerminiaux, N.; Cameron, A. Horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in clinical environments. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanic, I.; Kalinic, H.; Fredotovic, Z.; Dzelalija, M.; Bungur, A.; Maravic, A. Bacteria tolerant to colistin in coastal marine environment: Detection, microbiome diversity and antibiotic resistance genes’ repertoire. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzelalija, M.; Fredotovic, Z.; Udikovic-Kolic, N.; Kalinic, H.; Jozic, S.; Samanic, I.; Ordulj, M.; Maravic, A. Large-Scale Biogeographical Shifts of Abundance of Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Marine Bacterial Communities as Their Carriers along a Trophic Gradient. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.; Nash, J. MOB-suite: Software tools for clustering, reconstruction and typing of plasmids from draft assemblies. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. ABRicate: Mass Screening of Contigs for Antibiotic Resistance Genes; GitHub: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.; Larsen, M. Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Tang, H. ISEScan: Automated identification of insertion sequence elements in prokaryotic genomes. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3340–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.; Petty, N.; Beatson, S. Easyfig: A genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, B.; Raphenya, A.; Lau, T.; Tsang, K.; Bouchard, M.; Edalatmand, A.; Huynh, W.; Nguyen, A.; Cheng, A.; Liu, S.; et al. CARD 2020: Antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D517–D525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmids using PlasmidFinder and Plasmid Multilocus Sequence Typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhan, N.; Petty, N.; Ben Zakour, N.; Beatson, S. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensen, K.; Tetzschner, A.; Iguchi, A.; Aarestrup, F.; Scheutz, F. Rapid and Easy In Silico Serotyping of Escherichia coli Isolates by Use of Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2410–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozwandowicz, M.; Brouwer, M.; Fischer, J.; Wagenaar, J.; Gonzalez-Zorn, B.; Guerra, B.; Mevius, D.; Hordijk, J. Plasmids carrying antimicrobial resistance genes in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1121–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haudiquet, M.; de Sousa, J.; Touchon, M.; Rocha, E. Selfish, promiscuous and sometimes useful: How mobile genetic elements drive horizontal gene transfer in microbial populations. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2022, 377, 20210234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuda, M.; Shintani, M. Microbial evolution through horizontal gene transfer by mobile genetic elements. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e14408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debroas, D. Global analysis of the metaplasmidome: Ecological drivers and spread of antibiotic resistance genes across ecosystems. Microbiome 2025, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsberg, K.; Reyes, A.; Bin, W.; Selleck, E.; Sommer, M.; Dantas, G. The Shared Antibiotic Resistome of Soil Bacteria and Human Pathogens. Science 2012, 337, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tett, A.; Spiers, A.; Crossman, L.; Ager, D.; Ciric, L.; Dow, J.; Fry, J.; Harris, D.; Lilley, A.; Oliver, A.; et al. Sequence-based analysis of pQBR103; a representative of a unique, transferproficient mega plasmid resident in the microbial community of sugar beet. ISME J. 2007, 1, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.; Holt, K. Klebsiella pneumoniae as a key trafficker of drug resistance genes from environmental to clinically important bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, A.; Jones, K.; Cheung, M.; Thomas, C. The IncP-6 plasmid Rms149 consists of a small mobilizable backbone with multiple large insertions. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 4728–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménard, L.; Dubreuil, J. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin 1 (EAST1): A new toxin with an old twist. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 28, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Gu, D.; Huang, Y.; Chan, E.; Chen, G.; Chen, S. Comparative genetic characterization of Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli strains recovered from clinical and non-clinical settings. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muloi, D.; Hassell, J.; Wee, B.; Ward, M.; Bettridge, J.; Kivali, V.; Kiyong’a, A.; Ndinda, C.; Gitahi, N.; Ouko, T.; et al. Genomic epidemiology of Escherichia coli: Antimicrobial resistance through a One Health lens in sympatric humans, livestock and peri-domestic wildlife in Nairobi, Kenya. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redhead, S.; Nieuwland, J.; Esteves, S.; Lee, D.; Kim, D.; Mathias, J.; Cha, C.; Toleman, M.; Dinsdale, R.; Guwy, A.; et al. Fate of antibiotic resistant E. coli and antibiotic resistance genes during full scale conventional and advanced anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doijad, S.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Yao, Y.; Pati, N.; Falgenhauer, L.; Hain, T.; Foesel, B.; Abt, B.; Overmann, J.; Mirambo, M.; et al. Enterobacter bugandensis sp nov., isolated from neonatal blood. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukkar, I.; Valcek, A.; Dolejska, M. VIM-1-producing Enterobacter asburiae with mobile colistin resistance genes from wastewaters. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvesic, M.; Samanic, I.; Novak, A.; Fredotovic, Ä.; Dzelalija, M.; Kamenjarin, J.; Barisic, I.; Tonkic, M.; Maravic, A. Submarine Outfalls of Treated Wastewater Effluents are Sources of Extensively- and Multidrug-Resistant KPC- and OXA-48-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Coastal Marine Environment. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 858821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzelalija, M.; Kvesic-Ivankovic, M.; Jozic, S.; Ordulj, M.; Kalinic, H.; Pavlinovic, A.; Samanic, I.; Maravic, A. Marine resistome of a temperate zone: Distribution, diversity, and driving factors across the trophic gradient. Water Res. 2023, 246, 120688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.; Lesin, V.; Nikolenko, S.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.; Enns, E.; Marinier, E.; Mandal, A.; Herman, E.; Chen, C.; Graham, M.; Van Domselaar, G.; Stothard, P. Proksee: In-depth characterization and visualization of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W484–W492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M.; Olsen, H.; Paten, B.; Akeson, M. The Oxford Nanopore MinION: Delivery of nanopore sequencing to the genomics community. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 239, Erratum in Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 256. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-1122-x. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, A.; Au, K. PacBio Sequencing and Its Applications. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 7 June 2025).
- Bolger, A.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cock, P.; Antao, T.; Chang, J.; Chapman, B.; Cox, C.; Dalke, A.; Friedberg, I.; Hamelryck, T.; Kauff, F.; Wilczynski, B.; et al. Biopython: Freely available Python tools for computational molecular biology and bioinformatics. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1422–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

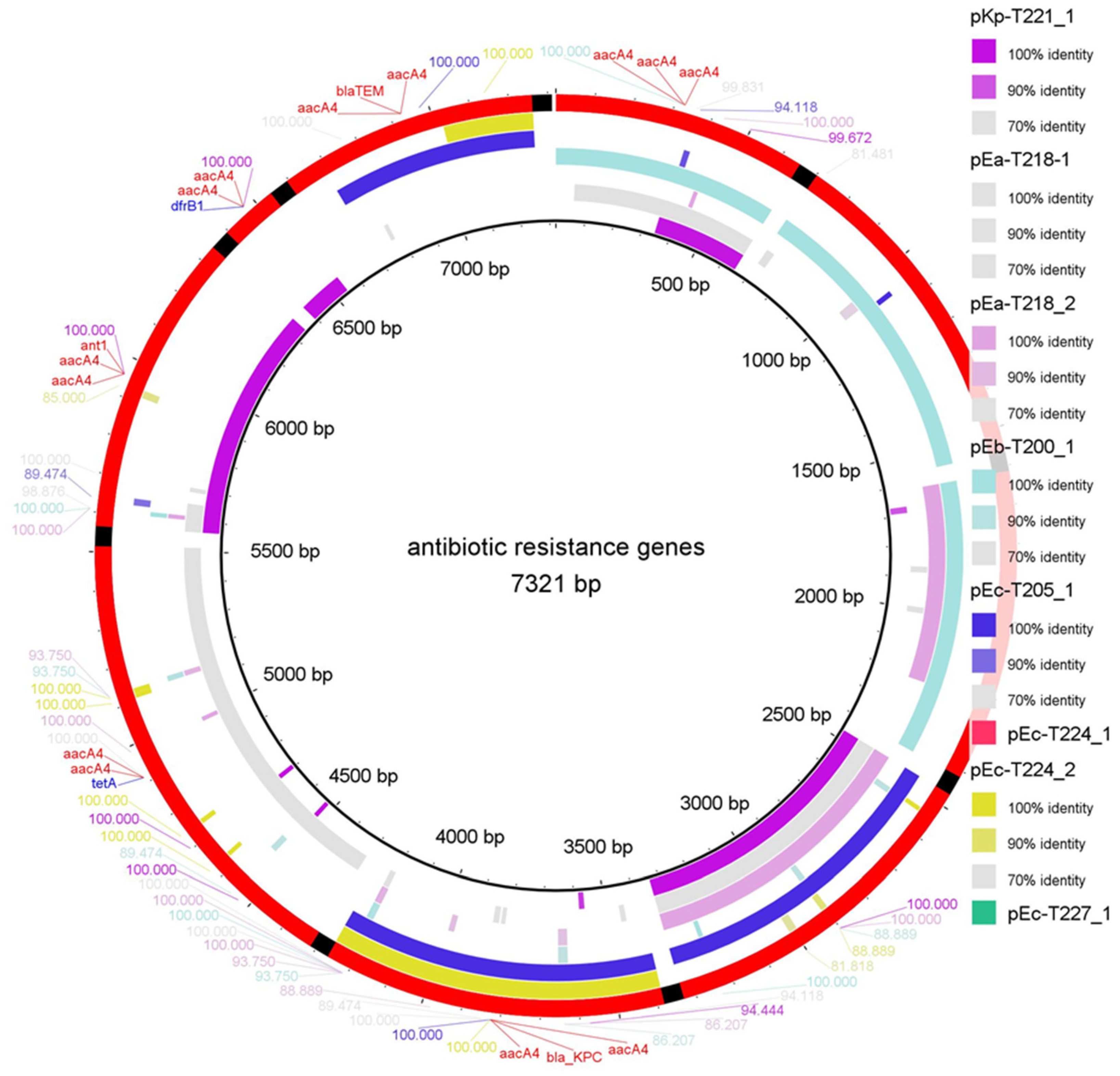

| Resistance Class | Gene | Mechanism of Action | Target Antibiotic(s) | Plasmid(s) Detected | Host Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-lactamase | blaKPC | Class A serine carbapenemase (hydrolyzes β-lactams) | Carbapenems, penicillins, cephalosporins | pEc-T224_1, pEc-T224_2, pEc-T227_1, pEc-T205_1 | E. coli |
| β-lactamase | blaTEM | Broad-spectrum β-lactamase | Penicillins, early cephalosporins | pEc-T227_1, pEc-T205_1 | E. coli |
| β-lactamase | blaGES | ESBL; some variants hydrolyze carbapenems | Cephalosporins, carbapenems (variant-dependent) | pEb-T200_1 | E. bugandensis |
| β-lactamase | blaOXA | Class D β-lactamase (oxacillinase) | Penicillins, cephalosporins | pEb-T200_1 | E. bugandensis |
| Aminoglycoside | aacA4 | Aminoglycoside acetyltransferase (modifies 6′-amine group) | Gentamicin, tobramycin, netilmicin | pEa-T218_1, pEb-T200_1 | E. asburiae, E. bugandensis |
| Aminoglycoside | ant(3″)-Ia (ant1) | Streptomycin adenylyltransferase | Streptomycin | pKp-T221_1 | K. pneumoniae |
| Sulfonamide | folP | Dihydropteroate synthase variant (target alteration) | Sulfonamides | pEa-T218_1, pEa-T218_2, pKp-T221_1, pEc-T205_1 | E. asburiae, K. pneumoniae, E. coli |
| Trimethoprim | dfrB1 | Trimethoprim-resistant dihydrofolate reductase | Trimethoprim | pKp-T221_1 | K. pneumoniae |
| Tetracycline | tetA | Efflux pump (major facilitator superfamily) | Tetracyclines | pEa-T218_1 | E. asburiae |
| Plasmid | Resistance Genes (CARD/NCBI/ResFinder) | Incompatibility Groups (PlasmidFinder) | Insertion Sequences (ISEScan) | Virulence Genes (VFDB/VirulenceFinder) | MOB Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pEa-T218_1 | tetA; folP; aacA4 | IS256; IS6; IS110; IS91 | astA | ||
| pEa-T218_2 | folP; | IS110; IS3; IS6 | |||
| pKp-T221_1 | ant1; folP; dfrB1 | IncA/C2 | IS21; IS4; IS5; ISNCY; IS110; ISL3; IS91 | clpK2 | MOBP |
| pEc-T224_1 | blaKPC | IncP6 | IS481; IS1182; IS110 | MOBP | |
| pEc-T224_2 | blaKPC | IS21 | |||
| pEc-T227_1 | blaKPC; blaTEM | IncP6 | IS1182; IS4; IS481; IS110; IS630 | MOBP | |
| pEb-T200_1 | blaOXA; blaGES; aacA4 | IS110 | MOBQ | ||
| pEc-T205_1 | blaKPC; blaTEM; folP | IncP6 | IS110; IS1182; IS4; IS481; IS630; ISNCY; IS6 | MOBP |
| Plasmid-Derived Assembly | Species | Primary Cluster ID | Size (bp) | Contigs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pEa-T218_1 | E. asburiae | AA002 | 77,664 | 33 |
| pEa-T218_2 | E. asburiae | AC303 | 20,793 | 6 |
| pKp-T221_1 | K. pneumoniae | AA860 | 163,845 | 85 |
| pEc-T224_1 | E. coli | AA364 | 28,914 | 11 |
| pEc-T224_2 | E. coli | AA364 | 7544 | 6 |
| pEc-T227_1 | E. coli | AA364 | 35,093 | 10 |
| pEb-T200_1 | E. bugandensis | AC303 | 24,221 | 8 |
| pEc-T205_1 | E. coli | AA364 | 43,424 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šamanić, I.; Dželalija, M.; Bellulovich, E.; Kalinić, H.; Jozić, S.; Ordulj, M.; Udiković-Kolić, N.; Maravić, A. Characterisation of Plasmid-Associated Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Coastal Marine Enterobacterales from the Central Adriatic Sea: De Novo Assembly and Bioinformatic Profiling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210910
Šamanić I, Dželalija M, Bellulovich E, Kalinić H, Jozić S, Ordulj M, Udiković-Kolić N, Maravić A. Characterisation of Plasmid-Associated Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Coastal Marine Enterobacterales from the Central Adriatic Sea: De Novo Assembly and Bioinformatic Profiling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):10910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210910
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠamanić, Ivica, Mia Dželalija, Ema Bellulovich, Hrvoje Kalinić, Slaven Jozić, Marin Ordulj, Nikolina Udiković-Kolić, and Ana Maravić. 2025. "Characterisation of Plasmid-Associated Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Coastal Marine Enterobacterales from the Central Adriatic Sea: De Novo Assembly and Bioinformatic Profiling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 10910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210910
APA StyleŠamanić, I., Dželalija, M., Bellulovich, E., Kalinić, H., Jozić, S., Ordulj, M., Udiković-Kolić, N., & Maravić, A. (2025). Characterisation of Plasmid-Associated Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Coastal Marine Enterobacterales from the Central Adriatic Sea: De Novo Assembly and Bioinformatic Profiling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 10910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210910






