EZH2 Inhibition in Mesothelioma Cells Increases the Release of Extracellular Vesicles That Skew Neutrophils Toward a Protumor Phenotype
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
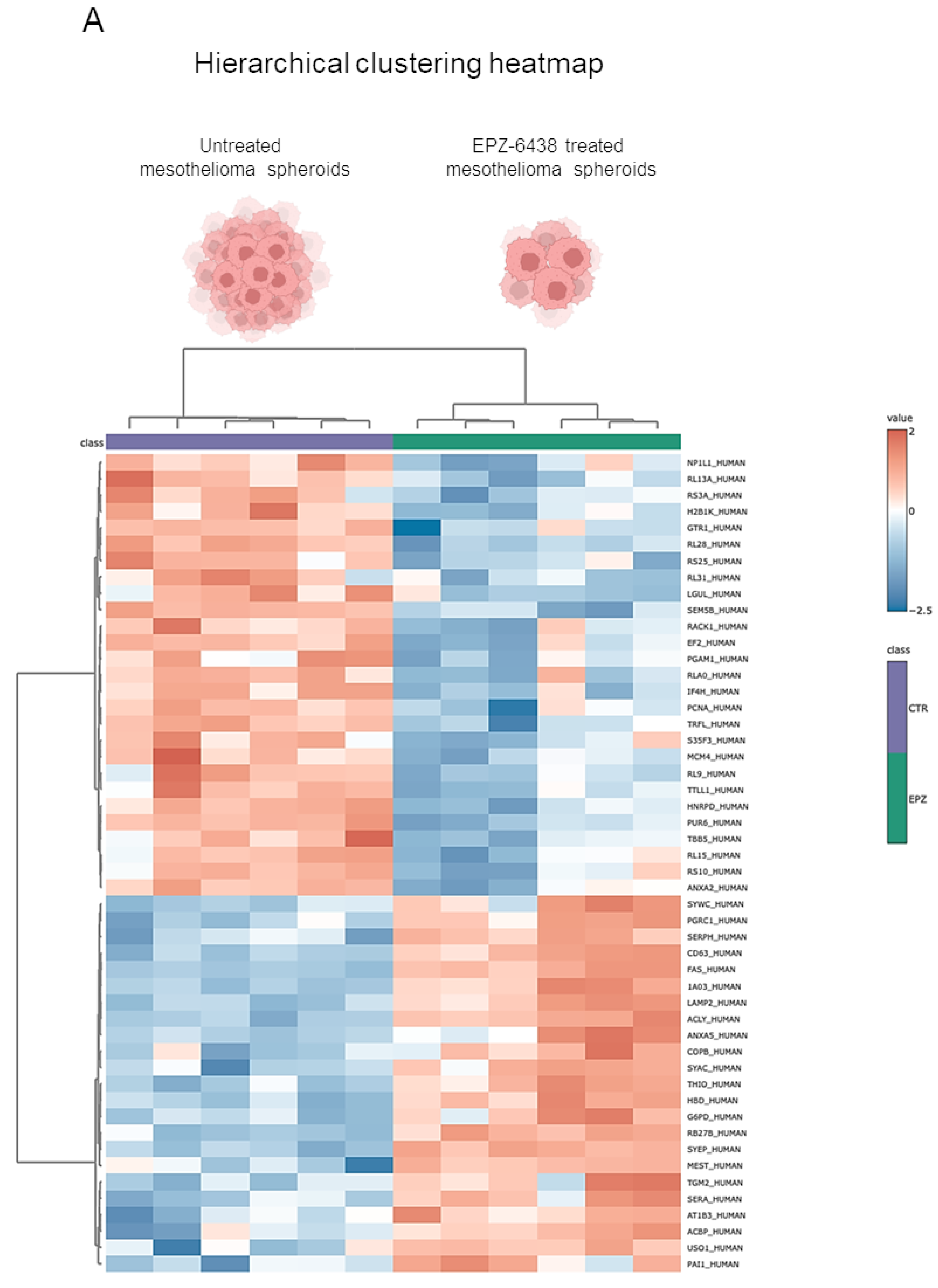
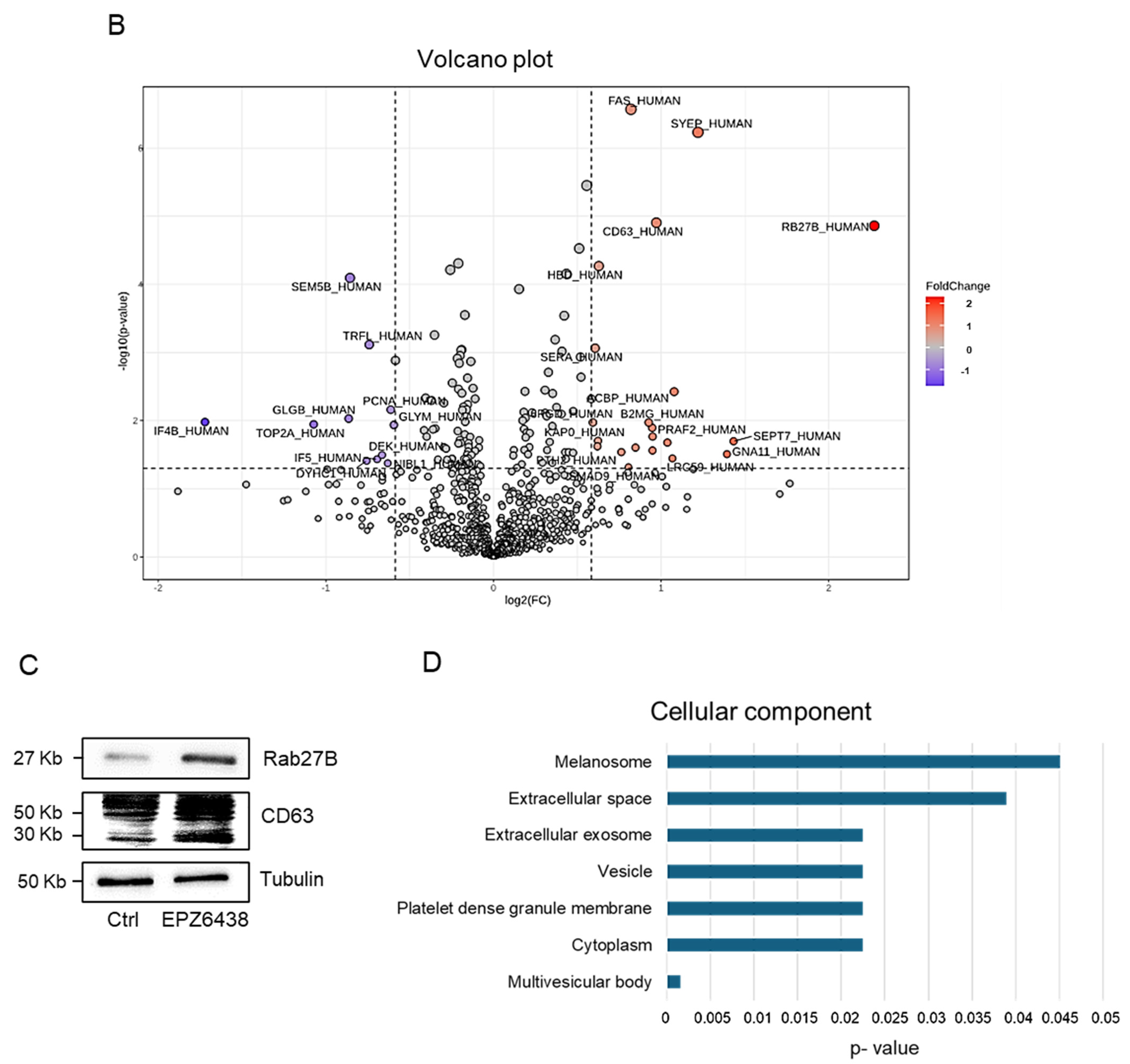
2.1. EPZ-6438 Treatment Induced RAB27b and CD63 Expression in MSTO-211H Spheroids, as Evidenced by Quantitative Proteomic Analysis
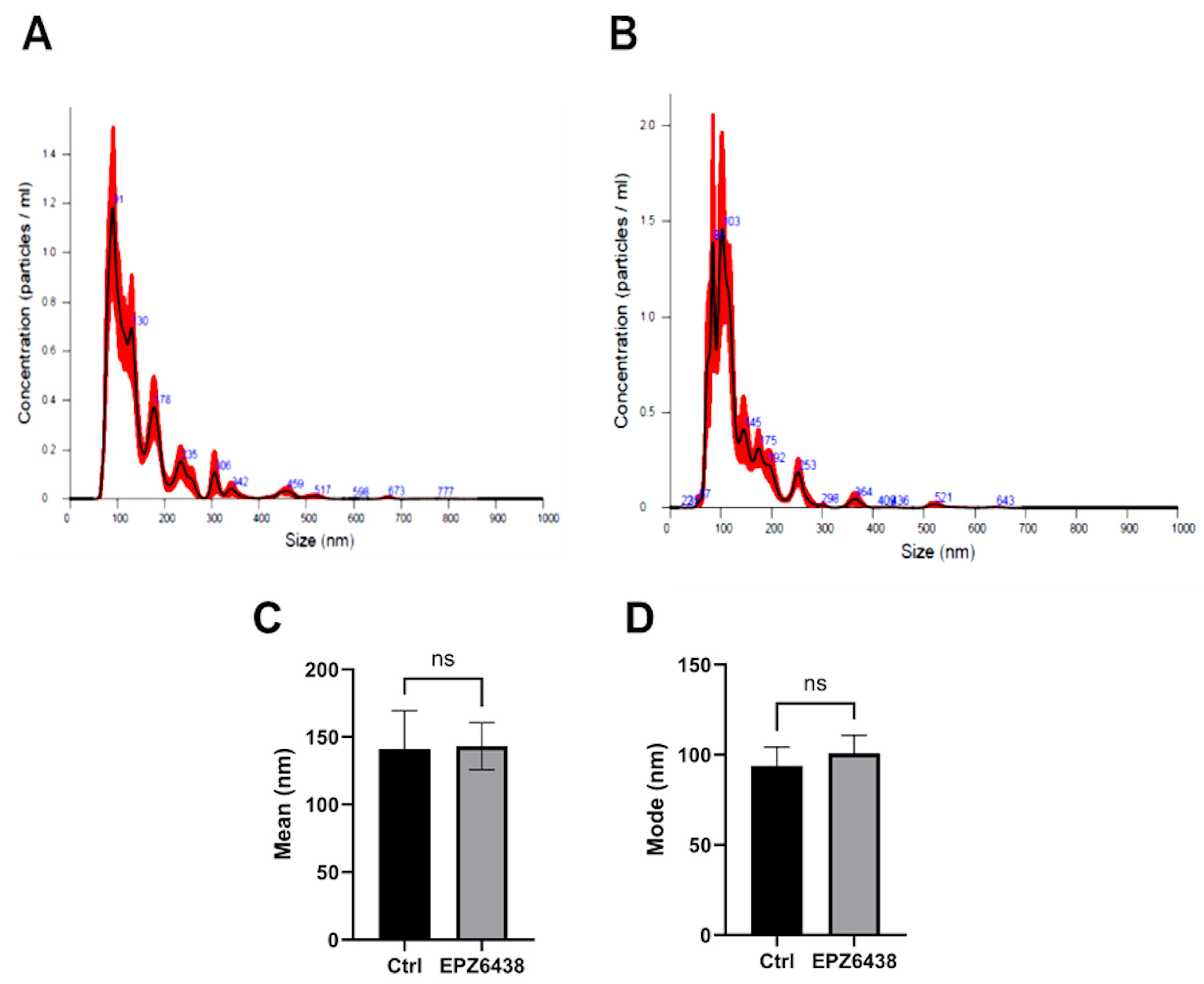
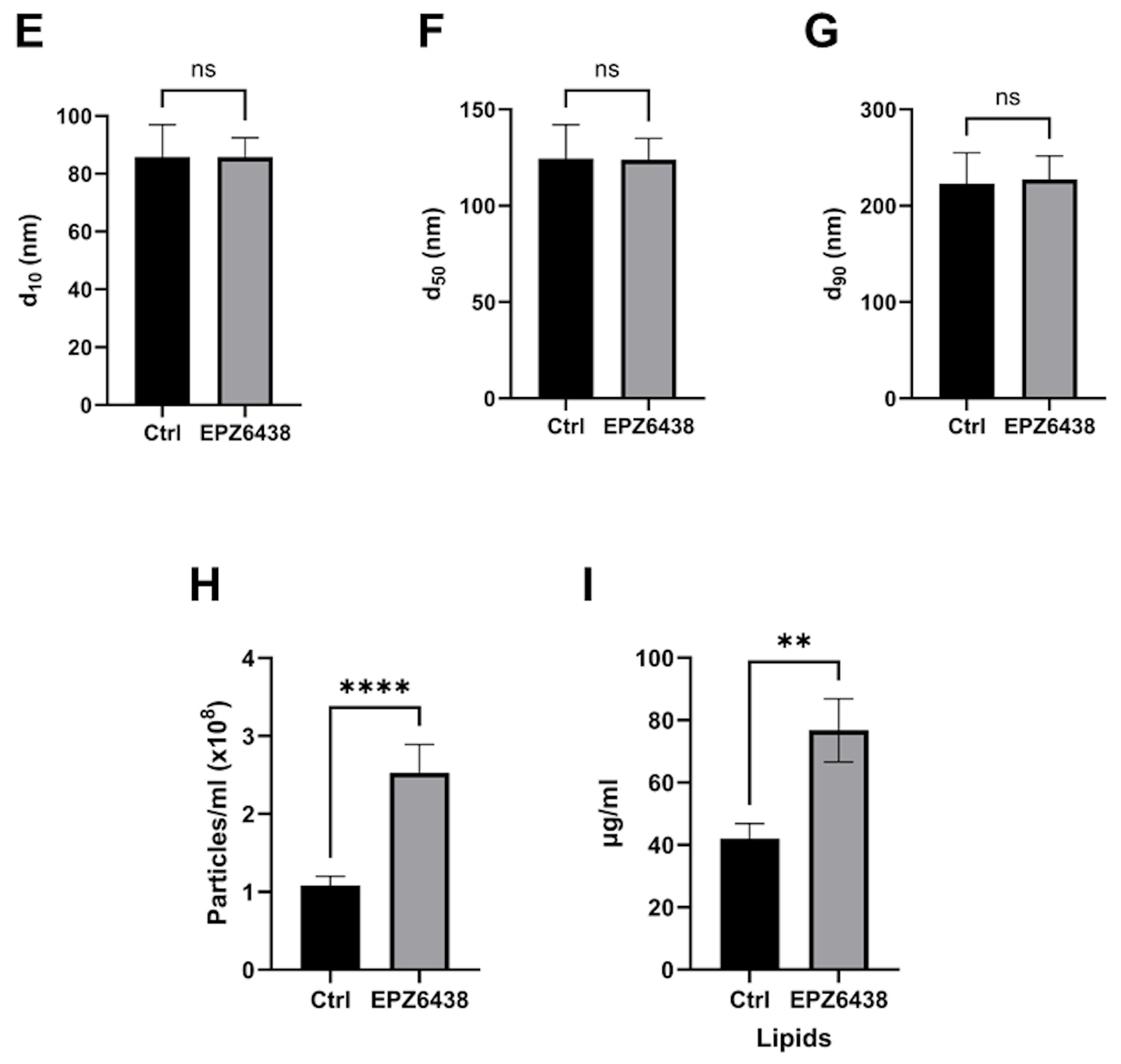
2.2. EPZ-6438 Treatment of MSTO-211H Spheroids Resulted in a Doubling of Extracellular Vesicle Release
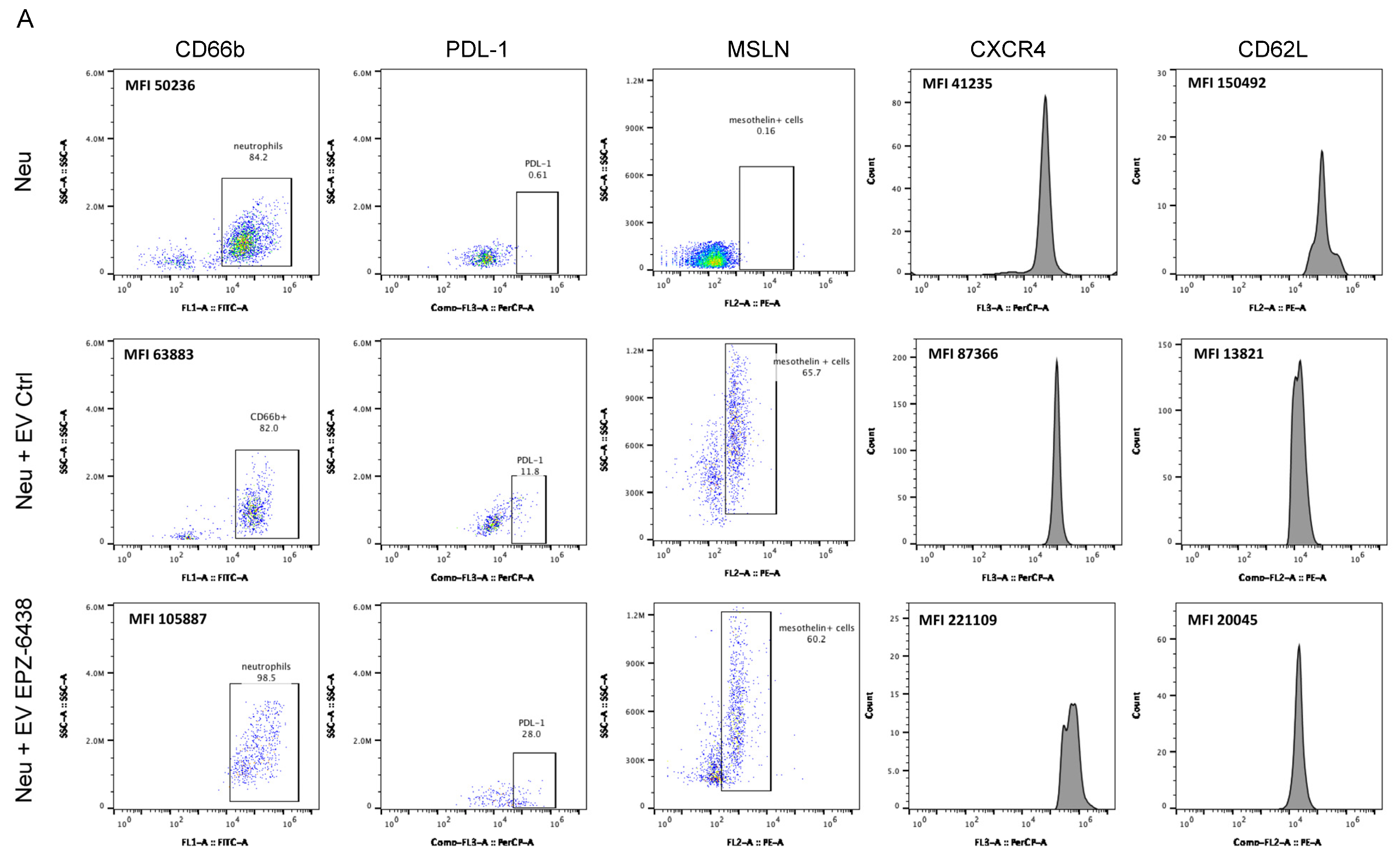
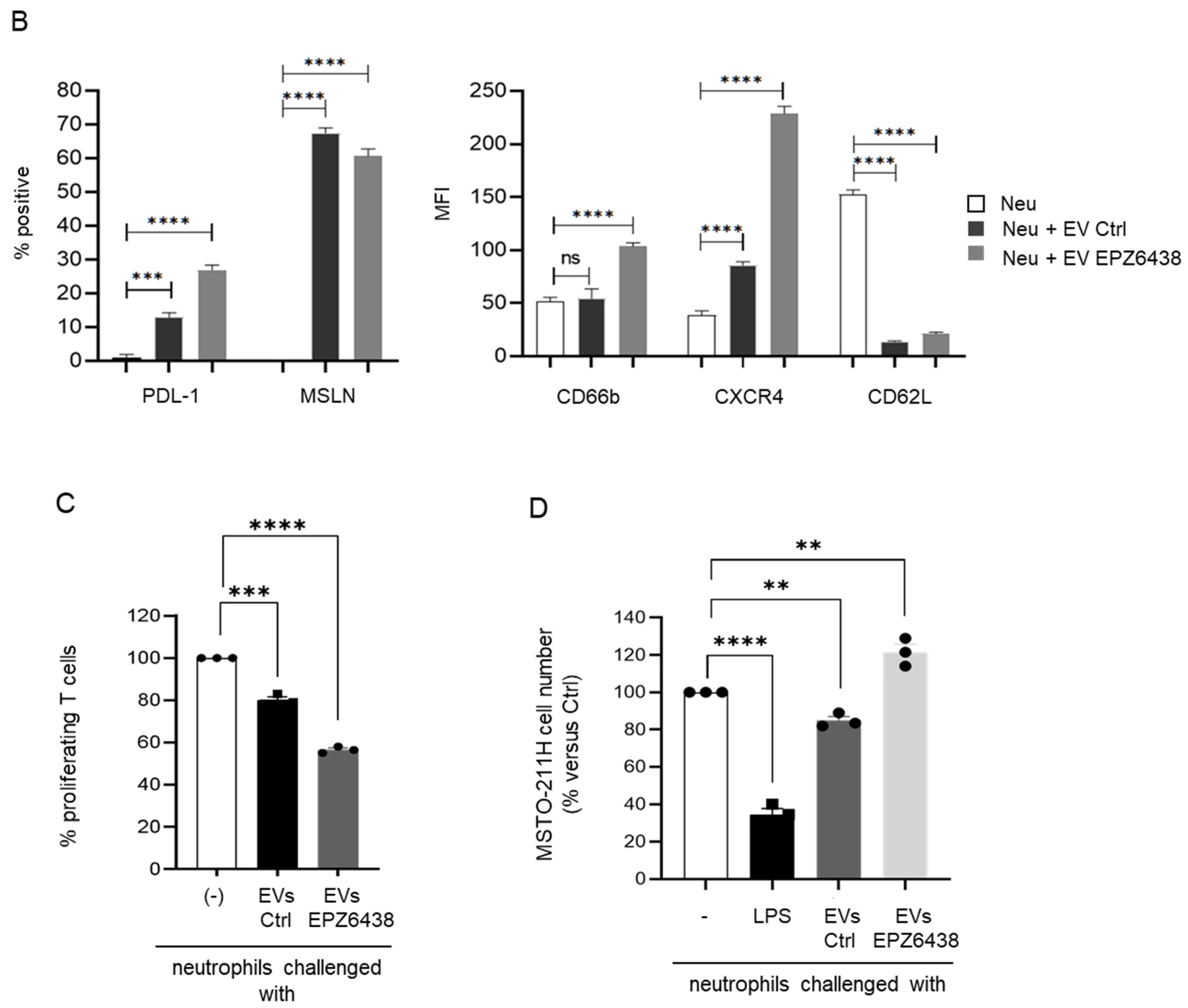
2.3. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from EPZ-6438-Treated MSTO-211H Spheroids Induced PD-L1 Expression on Neutrophils and Enhanced Their Immunosuppressive Functions
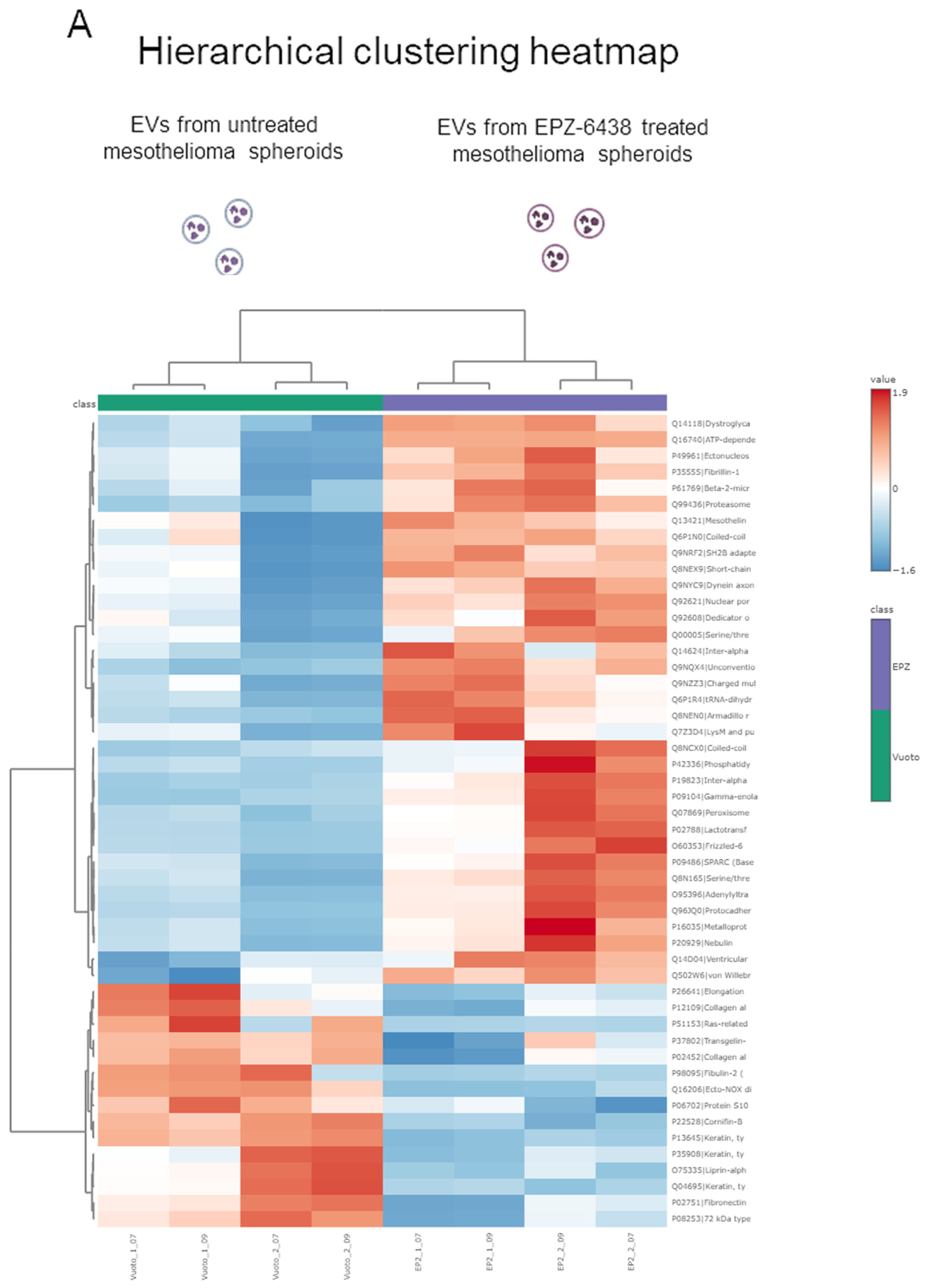
2.4. Proteomic Analysis Identified Differentially Regulated Proteins in Extracellular Vesicles Derived from EPZ-6438-Treated MSTO-211H Spheroids
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Multicellular Spheroids
4.3. Cell Lysis and Immunoblotting
4.4. Collection of EVs from MSTO-211H Spheroids
4.5. Lyophilization of EVs
4.6. Determination of the Particle Size Distribution
4.7. Nile Red Staining
4.8. Neutrophil/CD3+ Lymphocyte Isolation
4.9. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.10. Coculture of Neutrophils with T Cells and PM Multicellular Spheroids
4.11. Statistical Analysis
4.12. Proteomic Analysis and Data Processing
4.12.1. In-Solution Digestion
4.12.2. Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Cell Lysates
4.13. Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thives, L.P.; Ghisi, E.; Júnior, J.J.T.; Vieira, A.S. Is asbestos still a problem in the world? A current review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popat, S.; Baas, P.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Girard, N.; Nicholson, A.G.; Nowak, A.K.; Opitz, I.; Scherpereel, A.; Reck, M.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelzang, N.J.; Rusthoven, J.J.; Symanowski, J.; Denham, C.; Kaukel, E.; Ruffie, P.; Gatzemeier, U.; Boyer, M.; Emri, S.; Manegold, C.; et al. Phase III study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, P.; Scherpereel, A.; Nowak, A.K.; Fujimoto, N.; Peters, S.; Tsao, A.S.; Mansfield, A.S.; Popat, S.; Jahan, T.; Antonia, S.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 375–386, Erratum in Lancet 2021, 397, 670.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Q.; Perrone, F.; Greillier, L.; Tu, W.; Piccirillo, M.C.; Grosso, F.; Russo, G.L.; Florescu, M.; Mencoboni, M.; Morabito, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy in untreated advanced pleural mesothelioma in Canada, Italy, and France: A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, S.G.; Meirson, T.; Mutti, L. Based on the Real-World Results From Australia, Immunotherapy Is Not a Good Option for Patients with Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2024, 19, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Gu, W.; Li, X.; Xie, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z. PD-L1 and prognosis in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: A meta-analysis and bioinformatics study. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920962362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedres, S.; Valdivia, A.; Iranzo, P.; Callejo, A.; Pardo, N.; Navarro, A.; Martinez-Marti, A.; Assaf-Pastrana, J.D.; Felip, E.; Garrido, P. Current State-of-the-Art Therapy for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma and Future Options Centered on Immunotherapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KaKaplan, M.A.; Şendur, M.A.N.; Cangır, A.K.; Fırat, P.; Göker, E.; Kılıçkap, S.; Oyan, B.; Öz, A.B.; Özdemir, F.; Özyiğit, G. Established and new treatment roadmaps for pleural mesothelioma: Opinions of the Turkish Collaborative Group. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2023, 47, 101017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincenzi, F.; Rotondo, J.C.; Pasquini, S.; Di Virgilio, F.; Varani, K.; Tognon, M. A3 Adenosine and P2X7 Purinergic Receptors as New Targets for an Innovative Pharmacological Therapy of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 679285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, E.H.; Richards, W.G.; Gill, R.R.; Goodman, B.M.; Winfrey, O.K.; Eisen, H.M.; Mak, R.H.; Chen, A.B.; Kozono, D.E.; Bueno, R.; et al. Updated patterns of failure after multimodality therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 149, 1374–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zauderer, M.G.; Szlosarek, P.W.; Le Moulec, S.; Popat, S.; Taylor, P.; Planchard, D.; Scherpereel, A.; Koczywas, M.; Forster, M.; Cameron, R.B.; et al. EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat in patients with relapsed or refractory, BAP1-inactivated malignant pleural mesothelioma: A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, X.X.; Zhuang, Y.W.; Jiang, Y.; Melcher, K.; Xu, H.E. Structure of the PRC2 complex and application to drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinton, G.; Wang, Z.; Balzano, C.; Missaglia, S.; Tavian, D.; Boldorini, R.; Fennell, D.A.; Griffin, M.; Moro, L. CDKN2A Determines Mesothelioma Cell Fate to EZH2 Inhibition. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 678447, Correction in Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1081632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mola, S.; Pinton, G.; Erreni, M.; Corazzari, M.; De Andrea, M.; Grolla, A.A.; Martini, V.; Moro, L.; Porta, C. Inhibition of the Histone Methyltransferase EZH2 Enhances Protumor Monocyte Recruitment in Human Mesothelioma Spheroids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasugi, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Ohtani, N. Cellular senescence and the tumour microenvironment. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 3333–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faget, D.V.; Ren, Q.; Stewart, S.A. Unmasking senescence: Context-dependent effects of SASP in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; McAndrews, K.M. The role of extracellular vesicles in cancer. Cell 2023, 186, 1610–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Vayalil, J.; Lee, G.; Wang, Y.; Peng, G. Emerging role of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles in T-cell suppression and dysfunction in the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e003217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, G.M.; Marchiò, C.; Bari, E.; Ferrarotti, I.; Bertuccio, F.R.; Di Gennaro, A.; Abbott, D.M.; Putignano, P.; Campo, I.; Torre, M.L.; et al. The Genes-Stemness-Secretome Interplay in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Molecular Dynamics and Clinical Hints. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Miguel-Perez, D.; Russo, A.; Arrieta, O.; Ak, M.; Barron, F.; Gunasekaran, M.; Mamindla, P.; Lara-Mejia, L.; Peterson, C.B.; Er, M.E.; et al. Extracellular vesicle PD-L1 dynamics predict durable response to immune-checkpoint inhibitors and survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Chen, G. Small extracellular vesicle PD-L1 in cancer: The knowns and unknowns. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukaida, N.; Sasaki, S.-I.; Baba, T. Two-Faced Roles of Tumor-Associated Neutrophils in Cancer Development and Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wu, W.; Du, Y.; Yin, H.; Chen, Q.; Yu, W.; Wang, W.; Yu, J.; Liu, L.; Lou, W.; et al. The evolution and heterogeneity of neutrophils in cancers: Origins, subsets, functions, orchestrations and clinical applications. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilionis, R.; Engblom, C.; Pfirschke, C.; Savova, V.; Zemmour, D.; Saatcioglu, H.D.; Krishnan, I.; Maroni, G.; Meyerovitz, C.V.; Kerwin, C.M.; et al. Single-Cell transcriptomics of human and mouse lung cancers reveals conserved myeloid populations across individuals and species. Immunity 2019, 50, 1317–1334.e1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okita, R.; Kawamoto, N.; Okada, M.; Inokawa, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Murakami, T.; Ikeda, E. Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio correlates with PD-L1 expression in immune cells of patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma and predicts prognosis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, E.; Perteghella, S.; Di Silvestre, D.; Sorlini, M.; Catenacci, L.; Sorrenti, M.; Marrubini, G.; Rossi, R.; Tripodo, G.; Mauri, P.; et al. Pilot Production of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Freeze-Dried Secretome for Cell-Free Regenerative Nanomedicine: A Validated GMP-Compliant Process. Cells 2018, 7, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, J.W.; D’SOuza-Schorey, C. Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Multifunctional Entities in the Tumor Microenvironment. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2023, 18, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giese, M.A.; Hind, L.E.; Huttenlocher, A. Neutrophil plasticity in the tumor microenvironment. Blood 2019, 133, 2159–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabour-Takanlou, M.; Sabour-Takanlou, L.; Biray-Avci, C. EZH2-associated tumor malignancy: A prominent target for cancer treatment. Clin. Genet. 2024, 106, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Li, Y.; Cao, P.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Kang, S. Exploring the therapeutic potential of targeting polycomb repressive complex 2 in lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1216289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straining, R.; Eighmy, W. Tazemetostat: EZH2 Inhibitor. J. Adv. Pract. Oncol. 2022, 13, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Eccleston, M.; Clermont, P.L.; Latarani, M.; Male, D.K.; Wang, Y.; Crea, F. EZH2 inhibition: A promising strategy to prevent cancer immune editing. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 1457–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yu, F.; Xu, D.; Zheng, H.; Li, M. EZH2, a prominent orchestrator of genetic and epigenetic regulation of solid tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, A.; Choudhary, F.; Mudgal, P.; Khan, R.; Qureshi, K.A.; Farooqi, H.; Aspatwar, A. PD-1 and PD-L1: Architects of immune symphony and immunotherapy breakthroughs in cancer treatment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1296341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.T.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, Y.C.; Tang, M.; Lin, J.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, W.D.; Jin, J.M.; et al. Neutrophils as potential therapeutic targets for breast cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 198, 106996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.A.; Baba, S.K.; Sadida, H.Q.; Marzooqi, S.A.; Jerobin, J.; Altemani, F.H.; Algehainy, N.; Alanazi, M.A.; Abou-Samra, A.B.; Kumar, R.; et al. Extracellular vesicles as tools and targets in therapy for diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, A.; Wei, Z.; Chen, H.J. Editorial: Extracellular vesicles and cell–cell communication in normal cellular processes and cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1172797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F.R.; Capasso, M.; Hagemann, T. The tumor microenvironment at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125 Pt 23, 5591–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandini, S.; Ulivi, P.; Rossi, T. Extracellular Vesicles, Circulating Tumor Cells, and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Hints and Promises. Cells 2024, 13, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ye, X.; Spanos, M.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, G.; Xiao, J.; Zhou, L. Exosomal Non-Coding RNA Mediates Macrophage Polarization: Roles in Cardiovascular Diseases. Biology 2023, 12, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Mao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Liu, W.; Shi, H.; Ji, R.; Xu, W.; Qian, H.; Zhang, X. Extracellular Vesicles From Gastric Cancer Cells Induce PD-L1 Expression on Neutrophils to Suppress T-Cell Immunity. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Qin, T.; Chen, P.; Li, K. Immune-independent acquired resistance to PD-L1 antibody initiated by PD-L1 upregulation via PI3K/AKT signaling can be reversed by anlotinib. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 15337–15349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Kong, W.; Li, D.; Zhao, G.; Anwar, M.; Xia, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Ma, X. M2-type tumor-associated macrophages upregulated PD-L1 expression in cervical cancer via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Liu, C.; Victor, A.R.; Cao, D.Y.; Veiras, L.C.; Bernstein, E.A.; Khan, Z.; Giani, J.F.; Cui, X.; Bernstein, K.E.; et al. Tumors exploit CXCR4hiCD62Llo aged neutrophils to facilitate metastatic spread. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1870811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, X.; Wu, P.; Sun, S.; Pan, J.; Su, K.; Jia, F.; et al. Aged neutrophils form mitochondria-dependent vital NETs to promote breast cancer lung metastasis. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002875, Correction in Aged neutrophils form mitochondria-dependent vital NETs to promote breast cancer lung metastasis. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzada, T.; Vijayan, A.; Vafaee, F.; Azimi, A.; Reid, G.; Clarke, S.; Kao, S.; Grau, G.E.; Hosseini-Beheshti, E. Small and Large Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Pleural Mesothelioma Cell Lines Offer Biomarker Potential. Cancers 2023, 15, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Lou, Y.; Lu, L.; Fan, X. Mesothelin-targeted second generation CAR-T cells inhibit growth of mesothelin-expressing tumors in vivo. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, K.M.; Bazhenova, L. Emerging New Targets in Systemic Therapy for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers 2024, 16, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Chu, X.; Adams, C.; Ilina, T.V.; Guerrero, M.; Lin, G.; Chen, C.; Jelev, D.; Ishima, R.; Li, W.; et al. Preclinical assessment of a novel human antibody VH domain targeting mesothelin as an antibody-drug conjugate. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2023, 31, 100726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitti, R.M.; Marsters, S.A.; Lawrence, D.A.; Roy, M.; Kischkel, F.C.; Dowd, P.; Huang, A.; Donahue, C.J.; Sherwood, S.W.; Baldwin, D.T.; et al. Genomic amplification of a decoy receptor for Fas ligand in lung and colon cancer. Nature 1998, 396, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, A.B.; Parish, C.R. Determination of lymphocyte division by flow cytometry. J. Immunol. Methods 1994, 171, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinton, G.; Bari, E.; Fallarini, S.; Gigliotti, V.; De Giorgis, V.; Chiazza, F.; Torre, M.L.; Manfredi, M.; Moro, L. EZH2 Inhibition in Mesothelioma Cells Increases the Release of Extracellular Vesicles That Skew Neutrophils Toward a Protumor Phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110328
Pinton G, Bari E, Fallarini S, Gigliotti V, De Giorgis V, Chiazza F, Torre ML, Manfredi M, Moro L. EZH2 Inhibition in Mesothelioma Cells Increases the Release of Extracellular Vesicles That Skew Neutrophils Toward a Protumor Phenotype. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110328
Chicago/Turabian StylePinton, Giulia, Elia Bari, Silvia Fallarini, Valentina Gigliotti, Veronica De Giorgis, Fausto Chiazza, Maria Luisa Torre, Marcello Manfredi, and Laura Moro. 2025. "EZH2 Inhibition in Mesothelioma Cells Increases the Release of Extracellular Vesicles That Skew Neutrophils Toward a Protumor Phenotype" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110328
APA StylePinton, G., Bari, E., Fallarini, S., Gigliotti, V., De Giorgis, V., Chiazza, F., Torre, M. L., Manfredi, M., & Moro, L. (2025). EZH2 Inhibition in Mesothelioma Cells Increases the Release of Extracellular Vesicles That Skew Neutrophils Toward a Protumor Phenotype. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110328






