In Vitro and In Vivo Comparative Analysis of Muscle Regenerative Processes Induced by Different Microcurrent Waveforms in Skeletal Muscle Atrophy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Establishment of Muscle Cell Differentiation and Muscle Reduction Cell Model
2.2. DAPI Staining
2.3. Clinical Parameters
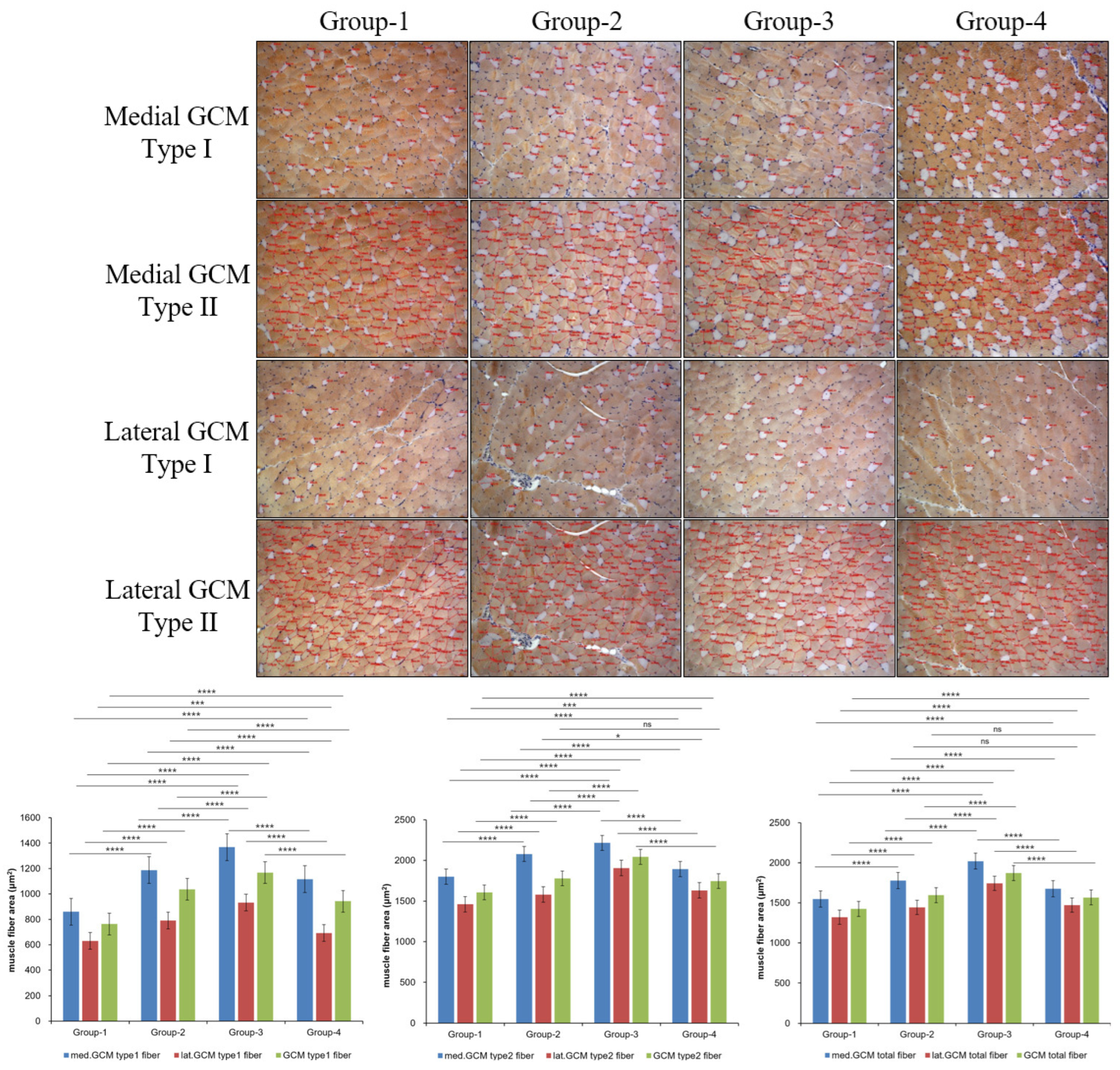
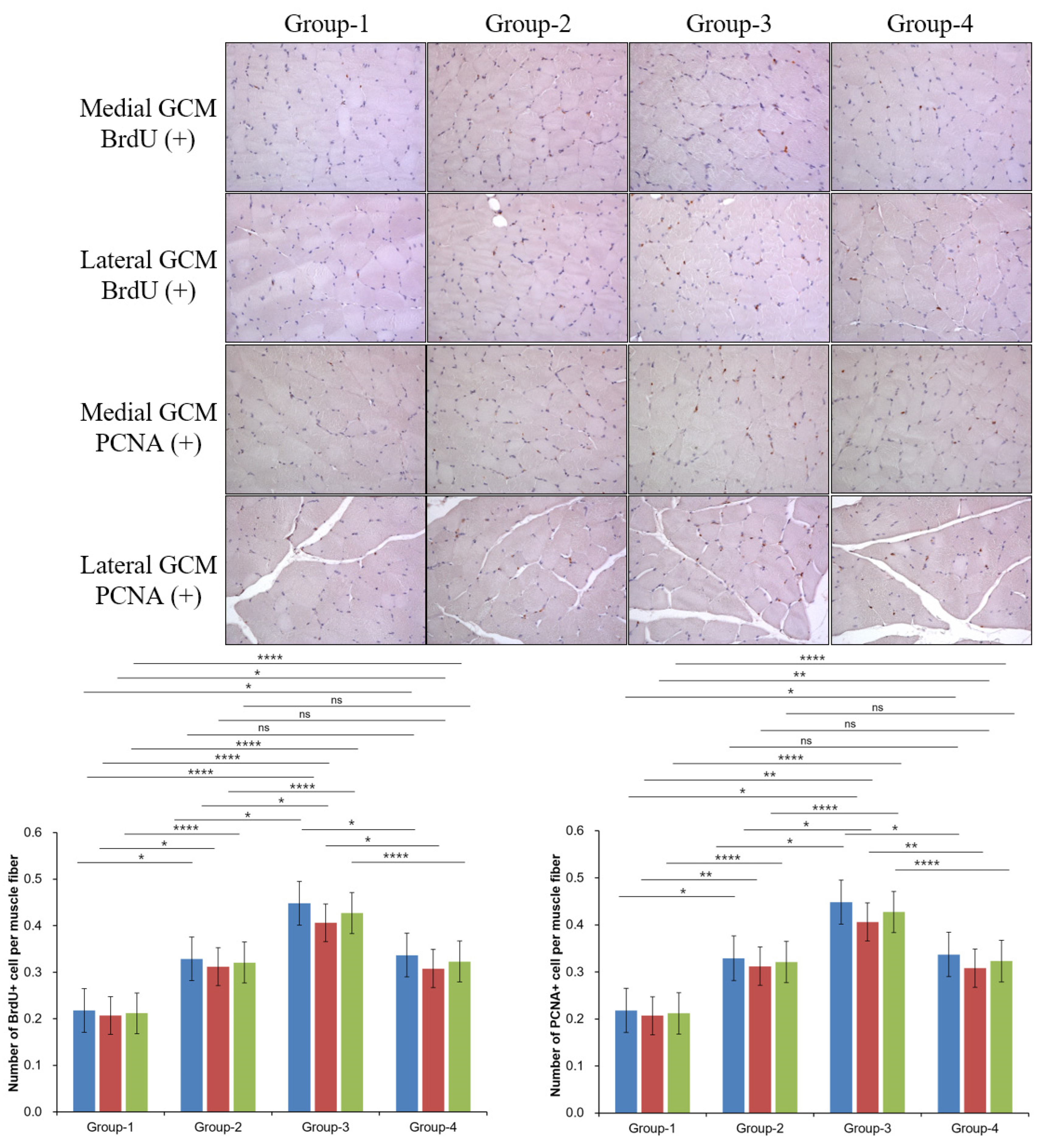
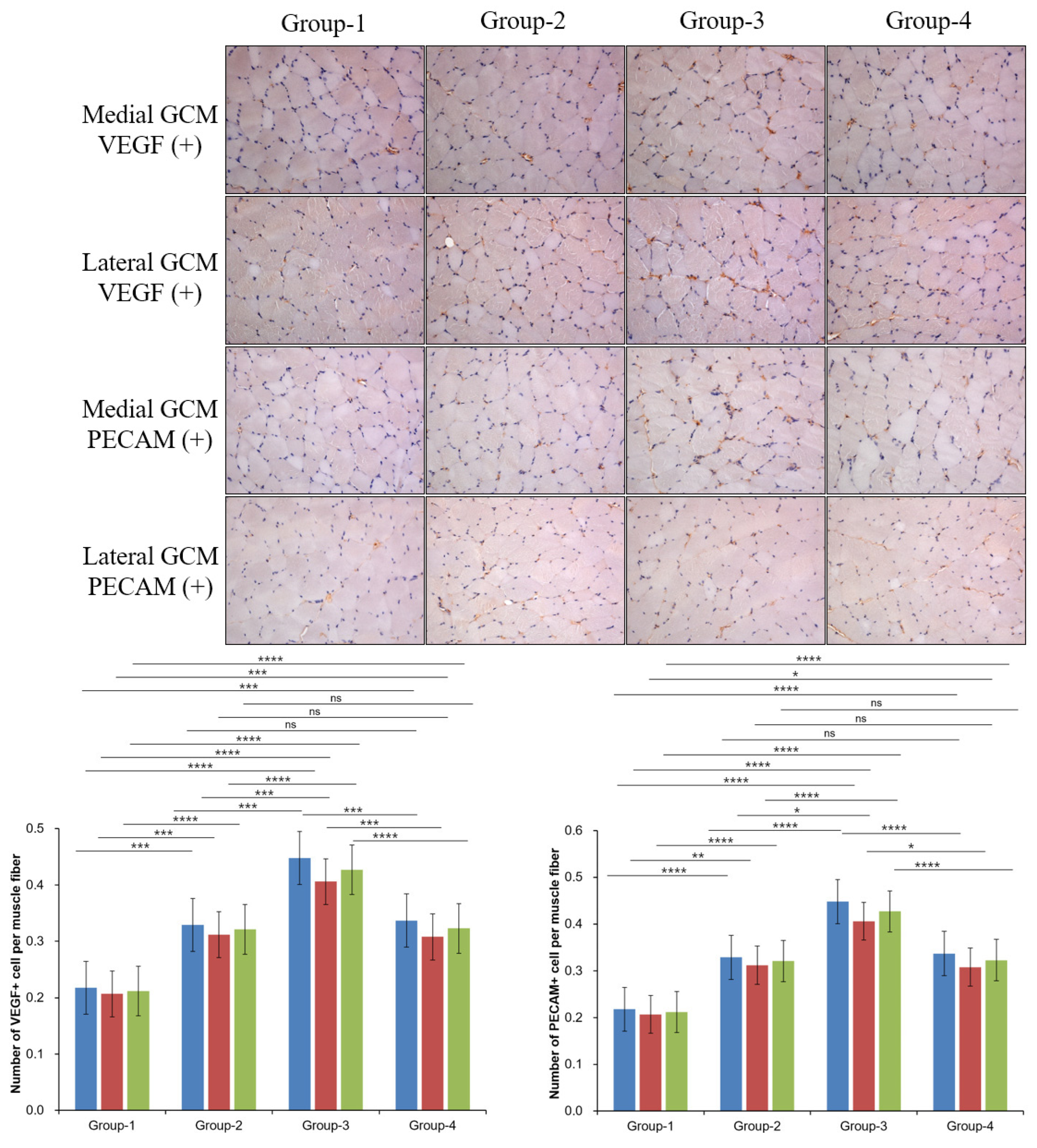
2.4. Histological Examination
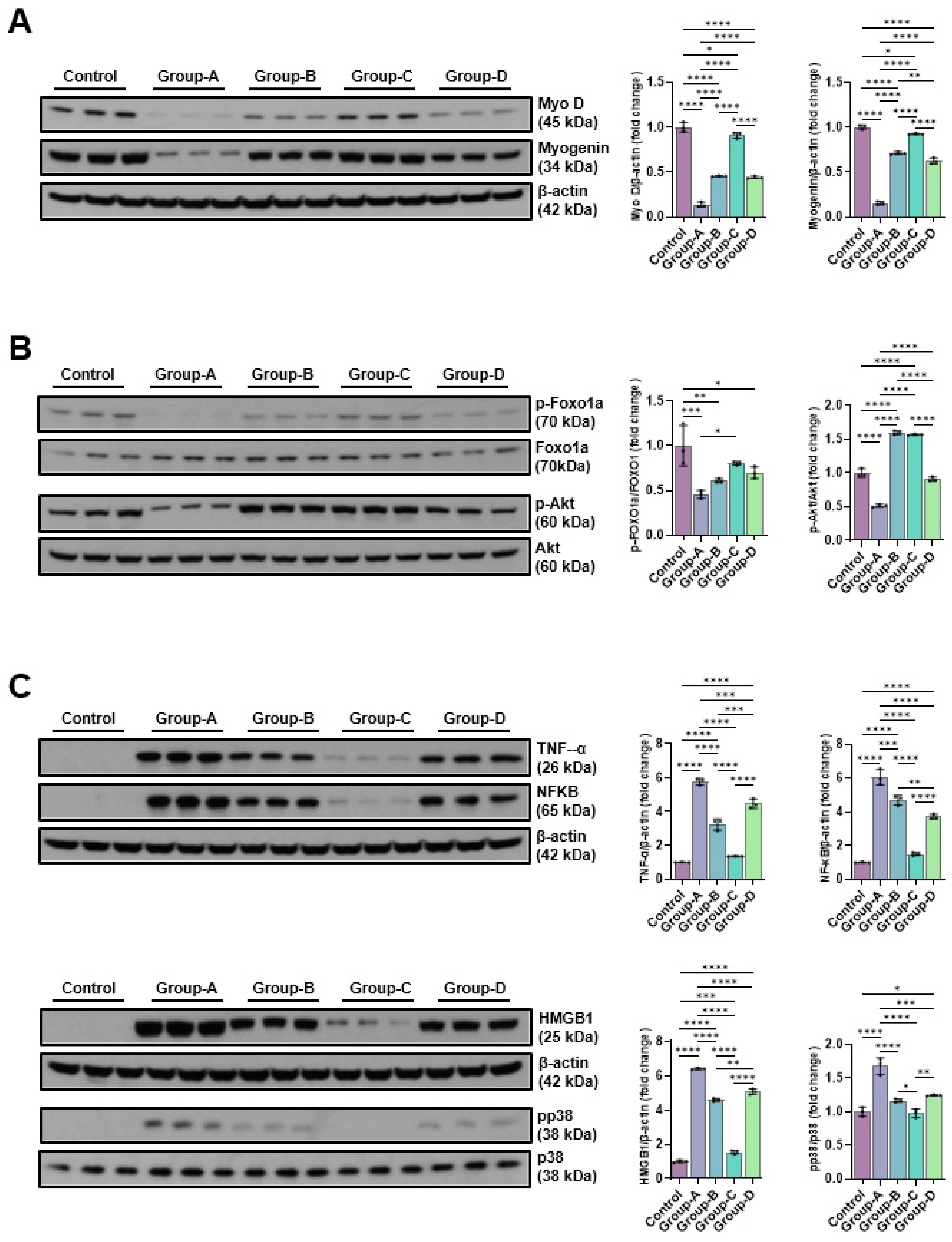
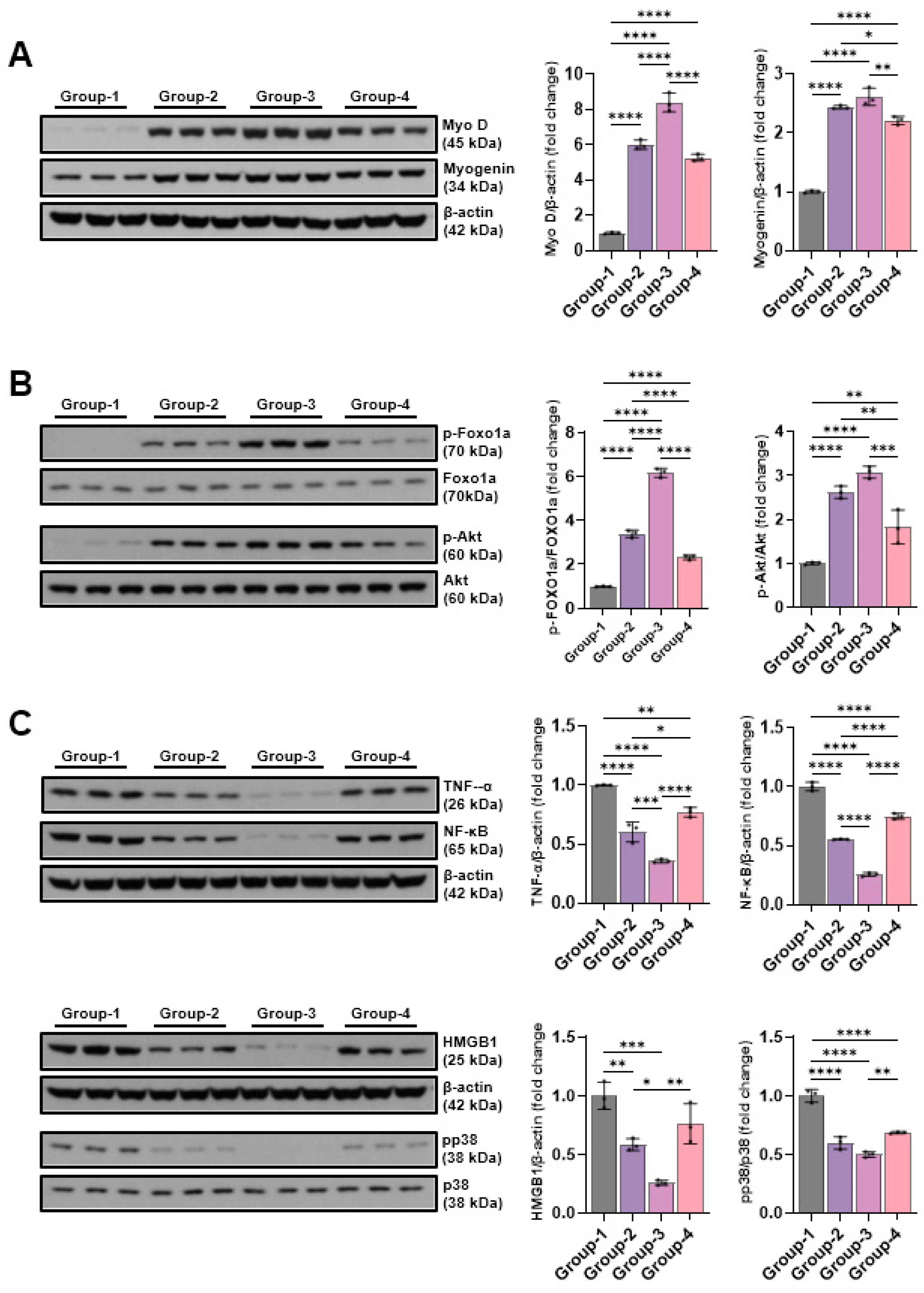
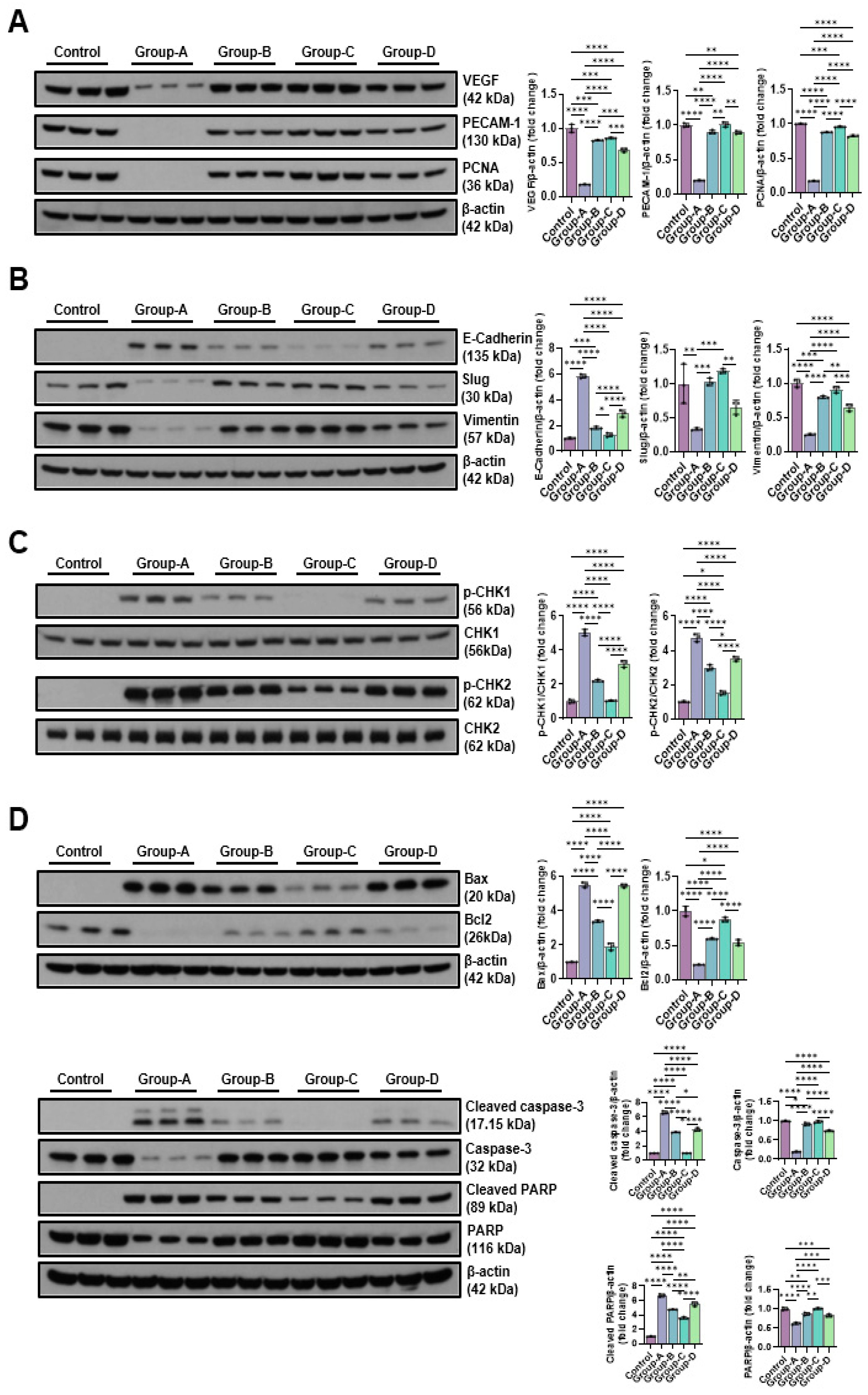
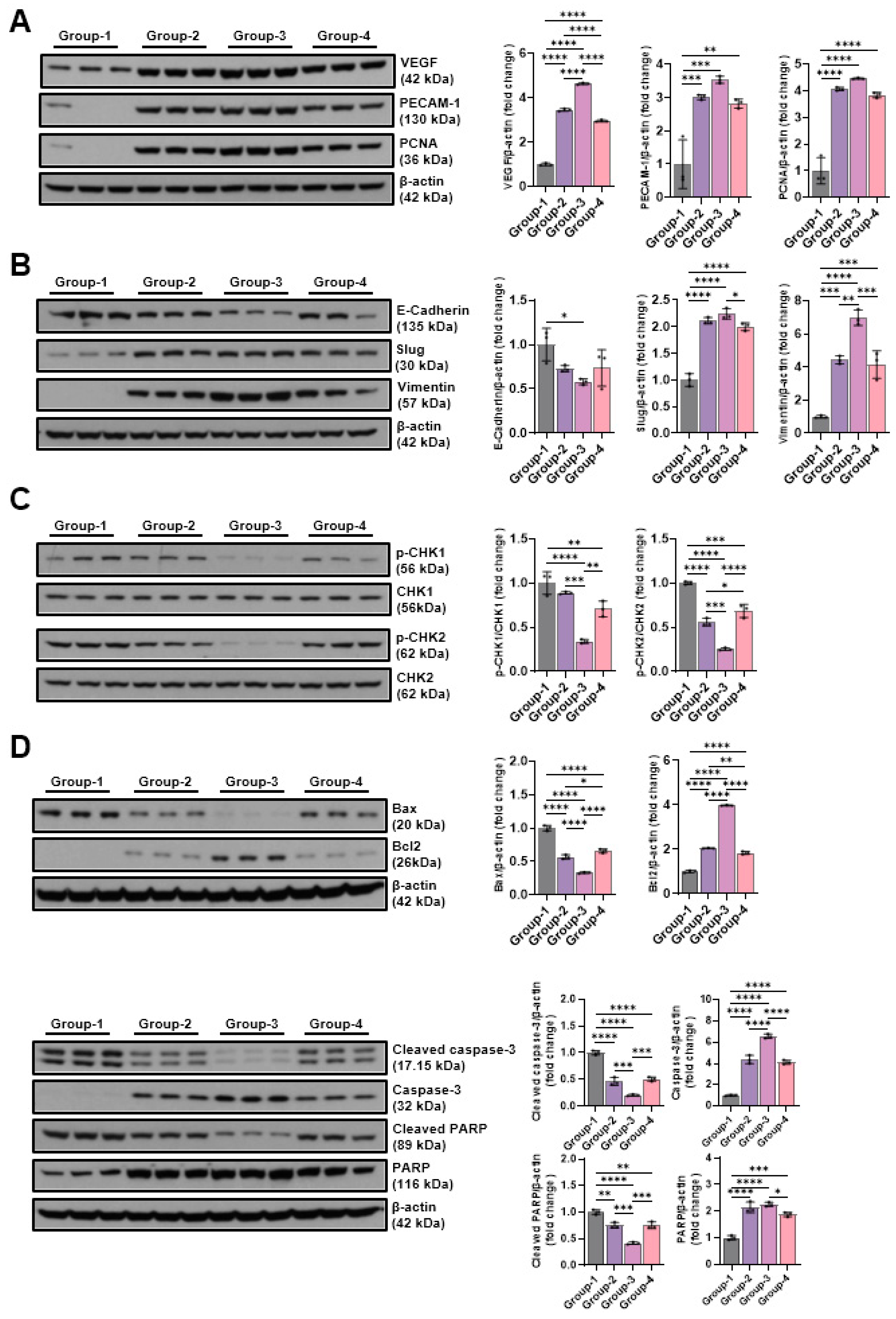
2.5. Western Blot
2.5.1. Effects of Microcurrent Waveforms on Muscle Growth, Anti-Atrophy Signaling Pathway, and Expression of Proteins Related to Inflammation In Vitro and In Vivo
2.5.2. Effects of Microcurrent Waveforms on Angiogenic Factors, Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT), DNA Damage Markers, and Apoptosis Markers In Vitro and In Vivo
3. Discussion
Study Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. In Vitro Study
4.1.1. In Vitro Study Design
4.1.2. DAPI Staining
4.1.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.2. In Vivo Study
4.2.1. Animal Grouping
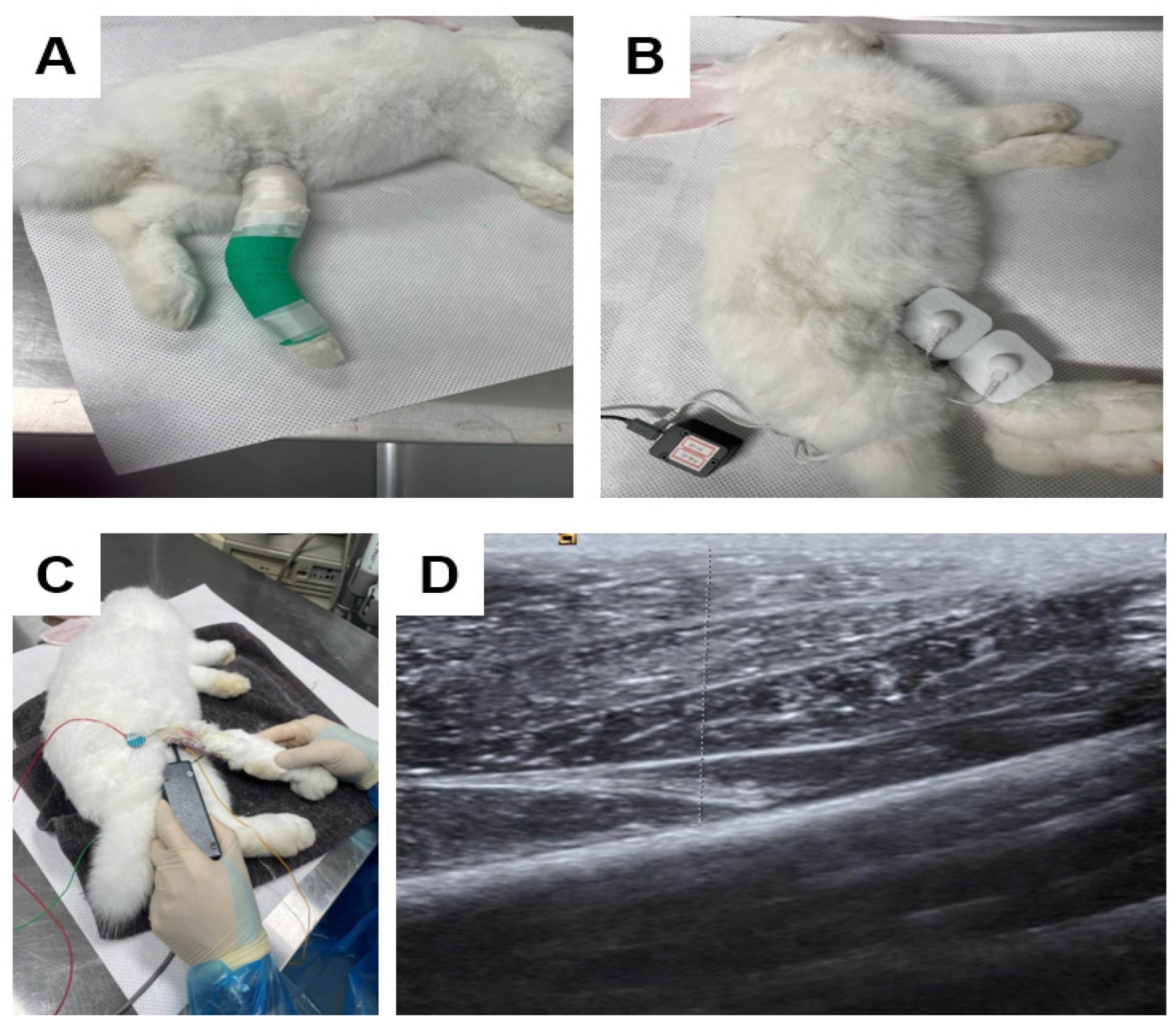
4.2.2. Immobilized-by-Cast (IC)
4.2.3. Microcurrent (MC)
4.2.4. Clinical Parameters
4.2.5. Tissue Preparation
4.2.6. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
4.2.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.2.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, P.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, F. Muscle-enriched microRNA-486-mediated regulation of muscular atrophy and exercise. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 80, 795–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Li, N.; Jia, W.; Wang, N.; Liang, M.; Yang, X.; Du, G. Skeletal muscle atrophy: From mechanisms to treatments. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 172, 105807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonik, S.; Rothka, A.J.; Cherin, N. Investigating the therapeutic efficacy of microcurrent therapy: A narrative review. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2025, 16, 20406223251361677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi, M.R.; Torkaman, G.; Hedayati, M. Effect of sensory and motor electrical stimulation in vascular endothelial growth factor expression of muscle and skin in full-thickness wound. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2011, 48, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Hirayama, Y.; Fujita, N.; Fujino, H. Electrical stimulation using sine waveform prevents unloading-induced muscle atrophy in the deep calf muscles of rat. Acta Histochem. 2014, 116, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrofsky, J.; Laymon, M.; Prowse, M.; Gunda, S.; Batt, J. The transfer of current through skin and muscle during electrical stimulation with sine, square, Russian and interferential waveforms. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2009, 33, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, Y.S.; Kwon, D.R.; Lee, Y.J. Therapeutic effect of microcurrent on calf muscle atrophy in immobilized rabbit. Muscle Nerve 2018, 58, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Bae, H. Bee Venom Phospholipase A2: Yesterday’s Enemy Becomes Today’s Friend. Toxins 2016, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebestyén, E.; Csige, D.; Antal-Szalmás, P.; Horváth, Á.; Végh, E.; Soós, B.; Pethő, Z.; Bodnár, N.; Hamar, A.; Bodoki, L.; et al. Effects of Tofacitinib Therapy on Circulating Tumour-Associated Antigens and Their Relationship with Clinical, Laboratory and Vascular Parameters in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Moon, Y.S.; Kwon, D.R.; Cho, S.C.; Kim, E.H. Polydeoxyribonucleotide and Shock Wave Therapy Sequence Efficacy in Regenerating Immobilized Rabbit Calf Muscles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Hu, Y.; Sang, Z.; Li, Y.; Mei, X.; Chen, Z. Preparation of Au-modified metal organic framework nanozyme with tunable catalytic activity used for diabetic wound healing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 687, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orea-Soufi, A.; Paik, J.; Bragança, J.; Donlon, T.A.; Willcox, B.J.; Link, W. FOXO transcription factors as therapeutic targets in human diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 1070–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.L.; Wang, D.Y.; Xie, W.G. Enhancing Mechanisms of p38MAPK/NF-κB in Regulating Postdebridement Inflammatory Response during the Shock Period in Burned Rats. J. Burn Care Res. 2025, 46, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, B.C.; Kwon, E.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Jung, J.I.; Moon, Y.S.; Kwon, D.R. Comparison of Muscle Regeneration Effects at Different Melittin Concentrations in Rabbit Atrophied Muscle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.R.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Paik, N.J.; Lim, S.J.; Ko, K.R.; Kim, H.C. Ideal Carrier Waveform for Functional Electrical Stimulation in Upper Extremity. J. Korean Acad. Rehabil. Med. 2000, 24, 492–501. [Google Scholar]
- Morey-Holton, E.R.; Globus, R.K. Hindlimb unloading rodent model: Technical aspects. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 92, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, F.W.; Thomason, D.B. Molecular and cellular adaptation of muscle in response to exercise: Perspectives of various models. Physiol. Rev. 1991, 71, 541–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appell, H.J. Muscular atrophy following immobilisation. A review. Sports Med. 1990, 10, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Atrophic Change (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | Circumference on Rt Calf (cm) | CMAP on Rt. Tibial Nerve (mV) | Rt. GCM Thickness (mm) | |
| Medial | Lateral | |||
| G1 (Control) | 11.1 ± 4.1 | 37.7 ± 4.6 | 24.2 ± 5.7 | 21.1 ± 4.9 |
| G2 (square 50 μA) | 10.6 ± 2.3 | 35.8 ± 4.4 | 26.1 ± 7.2 | 21.5 ± 7.8 |
| G3 (sine 50 μA) | 11.0 ± 3.4 | 30.2 ± 7.6 | 26.7 ± 7.4 | 23.2 ± 7.4 |
| G4 (triangle 50 μA) | 11.7 ± 1.6 | 35.0 ± 3.6 | 24.1 ± 4.7 | 21.8 ± 7.5 |
| Regenerative Change (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | Circumference on Rt Calf (cm) | CMAP on Rt. Tibial Nerve (mV) | Rt. GCM Thickness (mm) | |
| Medial | Lateral | |||
| G1 (Control) | 3.8 ± 2.5 a | 14.7 ± 5.4 a | 6.8 ± 2.3 a | 4.5 ± 2.9 a |
| G2 (square 50 μA) | 10.9 ± 2.3 b | 27.8 ± 5.3 b | 16.9 ± 2.4 b | 13.4 ± 3.3 b |
| G3 (sine 50 μA) | 16.1 ± 1.6 c | 43.2 ± 6.4 c | 21.8 ± 2.7 c | 19.0 ± 3.0 c |
| G4 (triangle 50 μA) | 10.6 ± 1.5 b | 25.8 ± 7.8 b | 14.2 ± 3.3 b | 10.6 ± 3.4 b |
| Motion Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Groups | Total Walking Distance (cm) | Mean Walking Speed (cm/sec) |
| G1 (control) | 1275.1 ± 276.2 a | 4.3 ± 1.0 a |
| G2 (square 50 μA) | 3479.8 ± 531.4 b | 11.6 ± 1.8 b |
| G3 (sine 50 μA) | 3734.1 ± 1077.0 b | 12.4 ± 3.6 b |
| G4 (triangle 50 μA) | 2922.1 ± 358.9 b | 9.2 ± 1.7 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.-J.; Kwon, E.S.; Moon, Y.S.; Kwon, D.R. In Vitro and In Vivo Comparative Analysis of Muscle Regenerative Processes Induced by Different Microcurrent Waveforms in Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9333. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199333
Lee Y-J, Kwon ES, Moon YS, Kwon DR. In Vitro and In Vivo Comparative Analysis of Muscle Regenerative Processes Induced by Different Microcurrent Waveforms in Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9333. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199333
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Yoon-Jin, Eun Sang Kwon, Yong Suk Moon, and Dong Rak Kwon. 2025. "In Vitro and In Vivo Comparative Analysis of Muscle Regenerative Processes Induced by Different Microcurrent Waveforms in Skeletal Muscle Atrophy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9333. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199333
APA StyleLee, Y.-J., Kwon, E. S., Moon, Y. S., & Kwon, D. R. (2025). In Vitro and In Vivo Comparative Analysis of Muscle Regenerative Processes Induced by Different Microcurrent Waveforms in Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9333. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199333






