UNC13D c.2588G>A Nucleotide Variant Impairs NK-Cell Cytotoxicity in Adult-Onset EBV-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Pedigree Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Detailed Case Presentation
2.1. Patient, Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
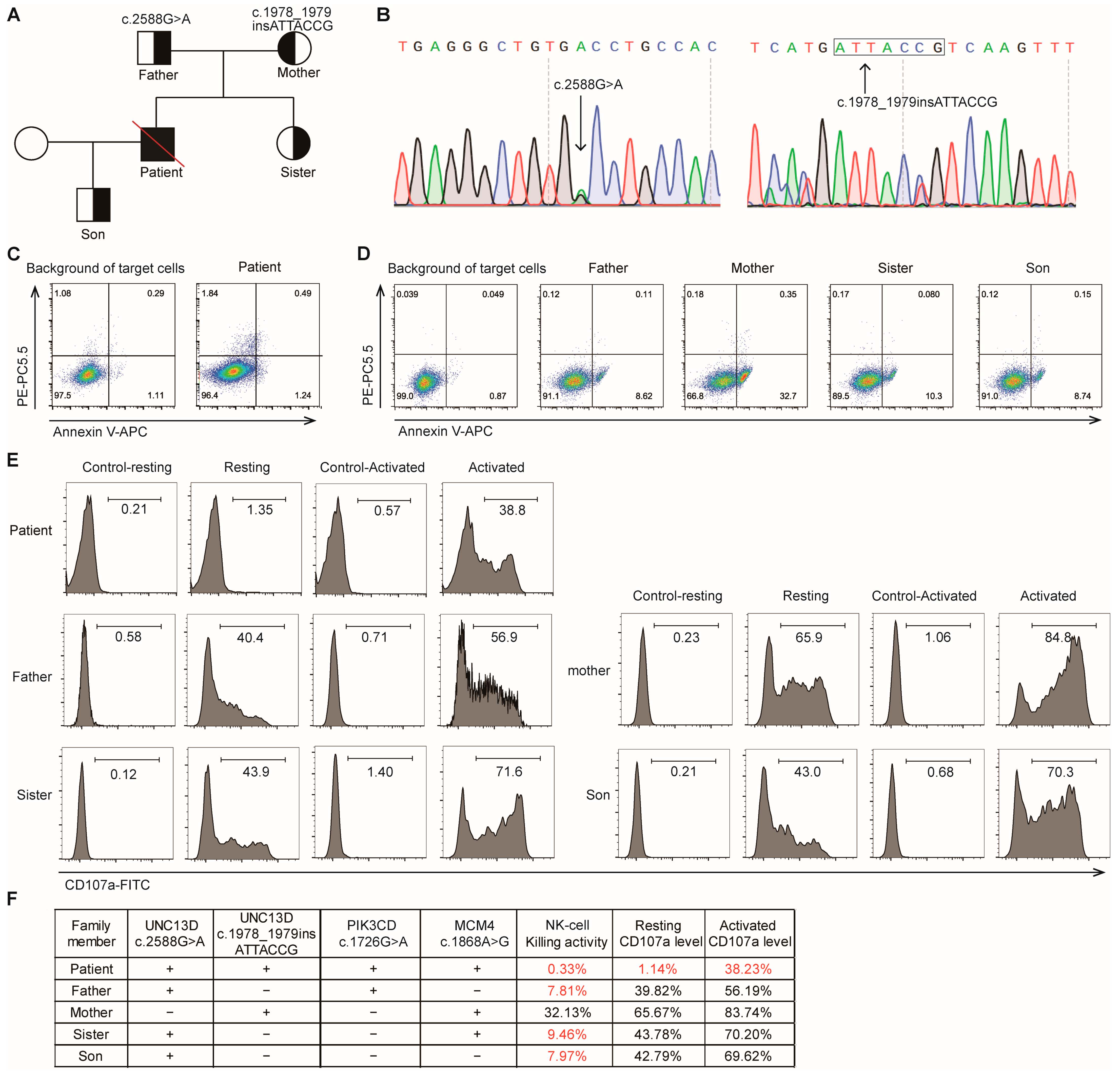
2.2. Genetic Testing
2.3. NK Cell Cytotoxicity Assays
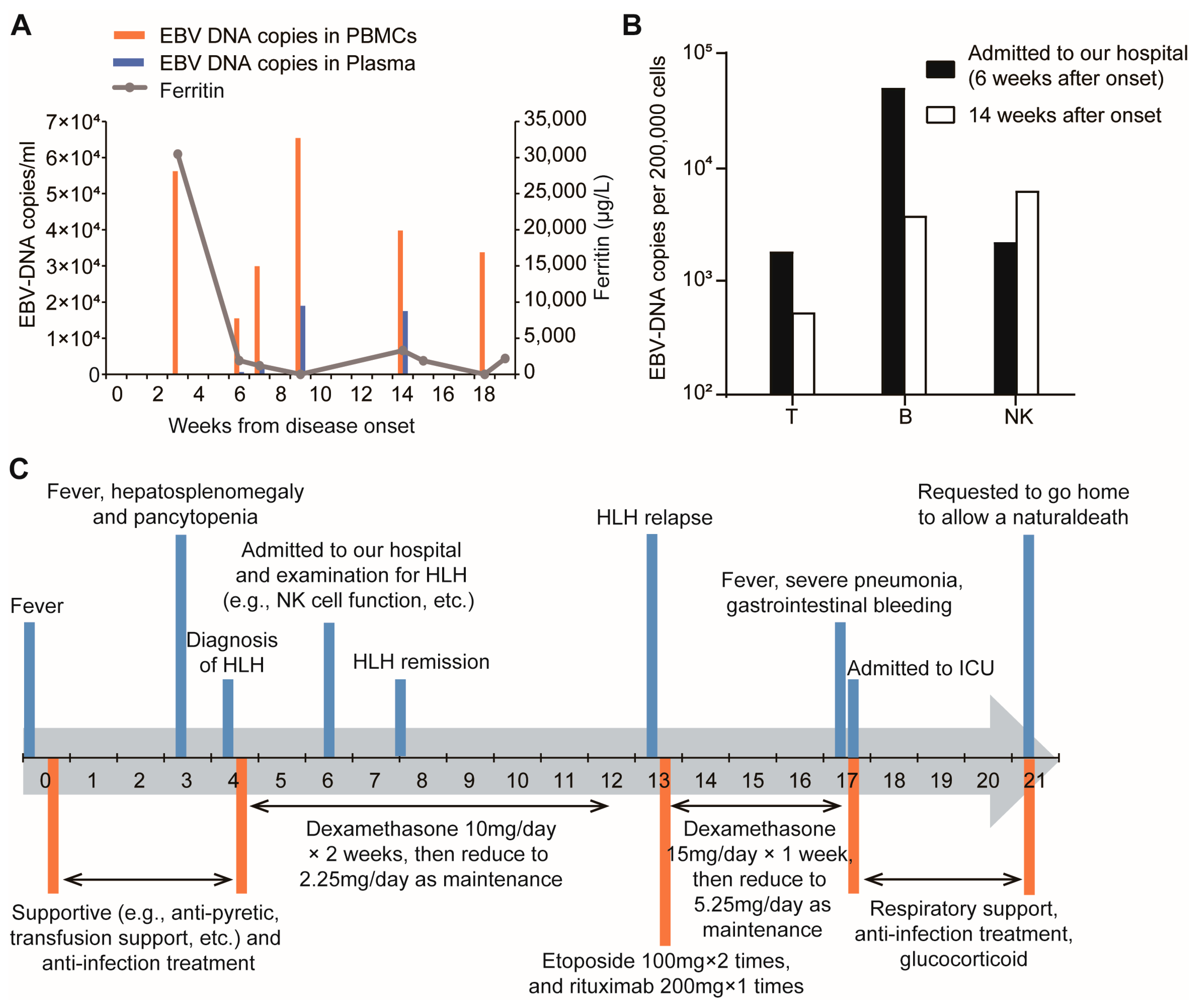
2.4. Treatment and Disease Progression
2.5. Literature Review
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. NK Cell Killing Activity Analysis
4.2. NK Cell CD107a Degranulation Assay
4.3. EBV-DNA Sorting PCR
4.4. Whole-Exome Sequencing Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NK | nature killer |
| CTLs | cytotoxic T lymphocytes |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| HLH | hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis |
| WBC | white blood cell |
| DNA | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| PBMCs | peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| IL-2 | interleukin-2 |
| sIL-2R | soluble interleukin-2 receptor |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| PET-CT | positron emission tomography/computed tomography |
| WES | whole-exome sequencing |
| ICU | intensive care unit |
| ALPS | autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome |
| MAS | macrophage activation syndrome |
| CD | cluster of differentiation |
| COVID | coronavirus disease |
| EGFP | enhanced green fluorescent protein |
| APC | allophycocyanin |
| PI | propidium iodide |
| PerCP | Peridinin-Chlorophyll-Protein |
References
- Côte, M.; Ménager, M.M.; Burgess, A.; Mahlaoui, N.; Picard, C.; Schaffner, C.; Al-Manjomi, F.; Al-Harbi, M.; Alangari, A.; Le Deist, F.; et al. Munc18-2 deficiency causes familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 5 and impairs cytotoxic granule exocytosis in patient NK cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3765–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, J.; Callebaut, I.; Raposo, G.; Certain, S.; Bacq, D.; Dumont, C.; Lambert, N.; Ouachée-Chardin, M.; Chedeville, G.; Tamary, H.; et al. Munc13-4 is essential for cytolytic granules fusion and is mutated in a form of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL3). Cell 2003, 115, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadt, U.Z.; Schmidt, S.; Kasper, B.; Beutel, K.; Diler, A.S.; Henter, J.-I.; Kabisch, H.; Schneppenheim, R.; Nürnberg, P.; Janka, G.; et al. Linkage of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL) type-4 to chromosome 6q24 and identification of mutations in syntaxin 11. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadt, U.Z.; Rohr, J.; Seifert, W.; Koch, F.; Grieve, S.; Pagel, J.; Strauß, J.; Kasper, B.; Nürnberg, G.; Becker, C.; et al. Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 5 (FHL-5) is caused by mutations in Munc18-2 and impaired binding to syntaxin 11. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryceson, Y.T.; Pende, D.; Maul-Pavicic, A.; Gilmour, K.C.; Ufheil, H.; Vraetz, T.; Chiang, S.C.; Marcenaro, S.; Meazza, R.; Bondzio, I.; et al. A prospective evaluation of degranulation assays in the rapid diagnosis of familial hemophagocytic syndromes. Blood 2012, 119, 2754–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeths, M.; Bryceson, Y.T. Genetics and pathophysiology of haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Acta Paediatr. 2021, 110, 2903–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canna, S.W.; Marsh, R.A. Pediatric hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2020, 135, 1332–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Saint Basile, G.; Menasche, G.; Latour, S. Inherited defects causing hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytic syndrome. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1246, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Saint Basile, G.; Ménasché, G.; Fischer, A. Molecular mechanisms of biogenesis and exocytosis of cytotoxic granules. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcenaro, S.; Gallo, F.; Martini, S.; Santoro, A.; Griffiths, G.M.; Aricó, M.; Moretta, L.; Pende, D. Analysis of natural killer-cell function in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL): Defective CD107a surface expression heralds Munc13-4 defect and discriminates between genetic subtypes of the disease. Blood 2006, 108, 2316–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieni, E.; Cetica, V.; Santoro, A.; Beutel, K.; Mastrodicasa, E.; Meeths, M.; Ciambotti, B.; Brugnolo, F.; Stadt, U.Z.; Pende, D.; et al. Genotype-phenotype study of familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 3. J. Med. Genet. 2011, 48, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, T.; Rudd-Schmidt, J.A.; Kane, A.; Frith, K.; Gray, P.E.; Hu, H.; Hsu, D.; Chung, C.W.; Hodel, A.W.; Trapani, J.A.; et al. A cell-based functional assay that accurately links genotype to phenotype in familial HLH. Blood 2023, 141, 2330–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.-R.; Liu, H.-X.; Xie, J.-J.; Wang, F.; Cai, P.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Teng, W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.-F.; et al. [The study of gene mutations in unknown refractory viral infection and primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis]. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 2011, 50, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, M.; Teng, W.; Lin, Y.; Han, X.; Jin, F.; Xu, Y.; Cao, P.; et al. Germline cytotoxic lymphocytes defective mutations in Chinese patients with lymphoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 5249–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Zhu, H.-Y.; Qiao, C.; Xia, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zou, Y.-X.; Miao, Y.-Q.; Chen, X.; Cao, L.; Wu, W.; et al. Pathogenic Gene Mutations or Variants Identified by Targeted Gene Sequencing in Adults with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henter, J.; Horne, A.; Aricó, M.; Egeler, R.M.; Filipovich, A.H.; Imashuku, S.; Ladisch, S.; McClain, K.; Webb, D.; Winiarski, J.; et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2007, 48, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardet, L.; Galicier, L.; Lambotte, O.; Marzac, C.; Aumont, C.; Chahwan, D.; Coppo, P.; Hejblum, G. Development and validation of the HScore, a score for the diagnosis of reactive hemophagocytic syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 2613–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Tang, R.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Gao, Z.; Pei, R.; Wang, Z. Application of an improved flow cytometry-based NK cell activity assay in adult hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Int. J. Hematol. 2017, 105, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Tang, X.; An, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tomomasa, D.; Hijikata, A.; Yang, X.; Kanegane, H.; Zhao, X. Atypical familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 3 in children: A report of cases and literature review. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2024, 35, e14136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Gao, Z.; Lai, W.; Wang, Z. Primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults: The utility of family surveys in a single-center study from China. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, W.; Wang, G.; Chen, L.; Cao, Y.; Wei, J.; Xiao, M.; Liu, X.; Huang, G.; et al. Germline variants in UNC13D and AP3B1 are enriched in COVID-19 patients experiencing severe cytokine storms. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 29, 1312–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Ma, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Wu, R. Synergistic defects of novo FAS and homozygous UNC13D leading to autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome-like disease: A 10-year-old Chinese boy case report. Gene 2018, 672, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Cao, J.; Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; et al. Genotype characteristics and immunological indicator evaluation of 311 hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis cases in China. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yan, X.; Luo, C.; An, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, X.; Zhao, X.; Yang, X. Clinical and genetic analysis of macrophage activation syndrome complicating juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Pediatr. Res. 2024, 97, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, D.; Kanda, J.; Hanyu, Y.; Amagase, H.; Kondo, T.; Miyamoto, T.; Yasumi, T.; Yoshinaga, N.; Takaori-Kondo, A. Successful Second CBT for Graft Failure After First CBT for Adult-Onset Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Type 3: A Case Report. Transplant. Proc. 2024, 56, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Lian, H.; Ma, H.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z. Genetic and clinical characteristics of primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in children. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 103, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Ma, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, R. Genetic characterization of pediatric primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in China: A single-center study. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 2303–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, P.E.; Shadur, B.; Russell, S.; Mitchell, R.; Gallagher, K.; Thia, K.; Palasanthiran, P.; Voskoboinik, I. Neonatal Cytomegalovirus Palatal Ulceration and Bocavirus Pneumonitis Associated With a Defect of Lymphocyte Cytotoxicity Caused by Mutations in UNC13D. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. Soc. 2019, 8, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, L.A.; Li, H.; Henderson, L.A.; Solomon, I.H.; Soldatos, A.; Murphy, J.; Bielekova, B.; Kennedy, A.L.; Rivkin, M.J.; Davies, K.J.; et al. Pediatric CNS-isolated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 6, e560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yao, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, P.; Zhang, X.; Kanegane, H.; Zhao, X.; et al. UNC13D mutation in a patient with juvenile polymyositis with recurrent macrophage activation syndrome. Rheumatology 2021, 60, e404–e406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Teng, W.; Wang, M.; Nie, D.; Zhou, X.; Wang, D.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, P.; et al. Genetic variant spectrum in 265 Chinese patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Molecular analyses of PRF1, UNC13D, STX11, STXBP2, SH2D1A, and XIAP. Clin. Genet. 2018, 94, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Yang, L.; Huang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Deng, J.; Zheng, M.; Luo, H.; Jiang, L.; Xiao, M.; Li, C.; et al. Clinical and genetic features of Epstein-Barr virus-triggered late-onset primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Ten pedigrees study. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfstedt, A.; Ahlm, C.; Tesi, B.; Bergdahl, I.A.; Nordenskjöld, M.; Bryceson, Y.T.; Henter, J.; Meeths, M. Haploinsufficiency of UNC13D increases the risk of lymphoma. Cancer 2019, 125, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kernan, K.F.; Ghaloul-Gonzalez, L.; Shakoory, B.; Kellum, J.A.; Angus, D.C.; Carcillo, J.A. Adults with septic shock and extreme hyperferritinemia exhibit pathogenic immune variation. Genes Immun. 2019, 20, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alfoldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.P.; et al. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gineau, L.; Cognet, C.; Kara, N.; Lach, F.P.; Dunne, J.; Veturi, U.; Picard, C.; Trouillet, C.; Eidenschenk, C.; Aoufouchi, S.; et al. Partial MCM4 deficiency in patients with growth retardation, adrenal insufficiency, and natural killer cell deficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zeng, C.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, J.; Gu, J.; Mao, X.; Zhang, W.; Cao, Y.; Luo, H.; Xu, B.; et al. Determination of Epstein-Barr Virus-Infected Lymphocyte Cell Types in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells as a Valuable Diagnostic Tool in Hematological Diseases. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, ofz171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| References | Patients | Sex | Age of Onset | Diseases | Zygosity | EBV Infection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | P1 | Female | 54 years | NK/T-NHL | Heterozygous | NA |
| [14] | P2 | Male | 46 years | NHL | Heterozygous | NA |
| [14] | P3 | Female | 12 years | NHL | Heterozygous | NA |
| [14] | P4 | Male | 40 years | B-NHL | Heterozygous | NA |
| [14] | P5 | Female | 30 years | NK/T-NHL | Heterozygous | NA |
| [14] | P6 | Male | 28 years | NHL | Heterozygous | NA |
| [14] | P7 | Male | 9 years | HL | Homozygous | + |
| [14] | P8 | Female | 54 years | NK/T-NHL | Heterozygous | NA |
| [19] | P9 | Male | 13 years | HLH | Compound heterozygous | NA |
| [19] | P10 | Male | 15 years | HLH | Homozygous | NA |
| [20] | P11 | Female | 52 years | HLH | Homozygous | + |
| [21] | P12 | Female | 64 years | Severe COVID-19 | Compound heterozygous | NA |
| [22] | P13 | Male | 10 years | ALPS | Homozygous | + |
| [23] | P14 | Male | 13 years | HL | Homozygote | NA |
| [23] | P15 | Female | 27 years | HLH | Homozygote | NA |
| [23] | P16 | Male | 35 years | HLH | Homozygote | NA |
| [23] | P17 | Male | 52 years | HLH | Homozygote | NA |
| [23] | P18 | Female | 29 years | HLH | Heterozygous | NA |
| [23] | P19 | Male | 5 years | HLH | Heterozygous | NA |
| [23] | P20 | Male | 31 years | HLH | Heterozygous | NA |
| [24] | P21 | NA | NA | MAS | homozygote | NA |
| [25] | P22 | Male | 38 years | HLH | Compound heterozygous | − |
| [26] | P23 | NA | NA | HLH | Compound heterozygous | NA |
| [26] | P24 | NA | NA | HLH | Heterozygous | NA |
| [26] | P25 | NA | NA | HLH | Compound heterozygous | NA |
| [27] | P26 | Female | 9 years | HLH | Compound heterozygous | NA |
| [28] | P27 | Male | 1 month | HLH | Compound heterozygous | − |
| [29] | P28 | Female | 7 years | CNS-HLH | Compound heterozygous | − |
| [29] | P29 | Female | NA | CNS-HLH | Compound heterozygous | − |
| [30] | P30 | Male | 15 years | MAS | Homozygous | NA |
| [20] | P31 | Male | 52 years | HLH | Homozygous | + |
| [31] | P32 | Male | 2 years | HLH | Heterozygous | NA |
| [31] | P33 | Male | 3 years | HLH | Heterozygous | NA |
| [32] | P34 | Female | 18 years | HLH | Compound heterozygous | + |
| [32] | P35 | Male | 21 years | HLH | Compound heterozygous | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, J.; An, N.; Wang, X.; Xiao, M.; Luo, H. UNC13D c.2588G>A Nucleotide Variant Impairs NK-Cell Cytotoxicity in Adult-Onset EBV-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Pedigree Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178683
Gu J, An N, Wang X, Xiao M, Luo H. UNC13D c.2588G>A Nucleotide Variant Impairs NK-Cell Cytotoxicity in Adult-Onset EBV-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Pedigree Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178683
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Jia, Ning An, Xinran Wang, Min Xiao, and Hui Luo. 2025. "UNC13D c.2588G>A Nucleotide Variant Impairs NK-Cell Cytotoxicity in Adult-Onset EBV-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Pedigree Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178683
APA StyleGu, J., An, N., Wang, X., Xiao, M., & Luo, H. (2025). UNC13D c.2588G>A Nucleotide Variant Impairs NK-Cell Cytotoxicity in Adult-Onset EBV-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Pedigree Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178683





