Molecular Mechanisms of Estrogens in the Induction of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis in Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of the Estrogen Receptors
3. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Breast Cancer
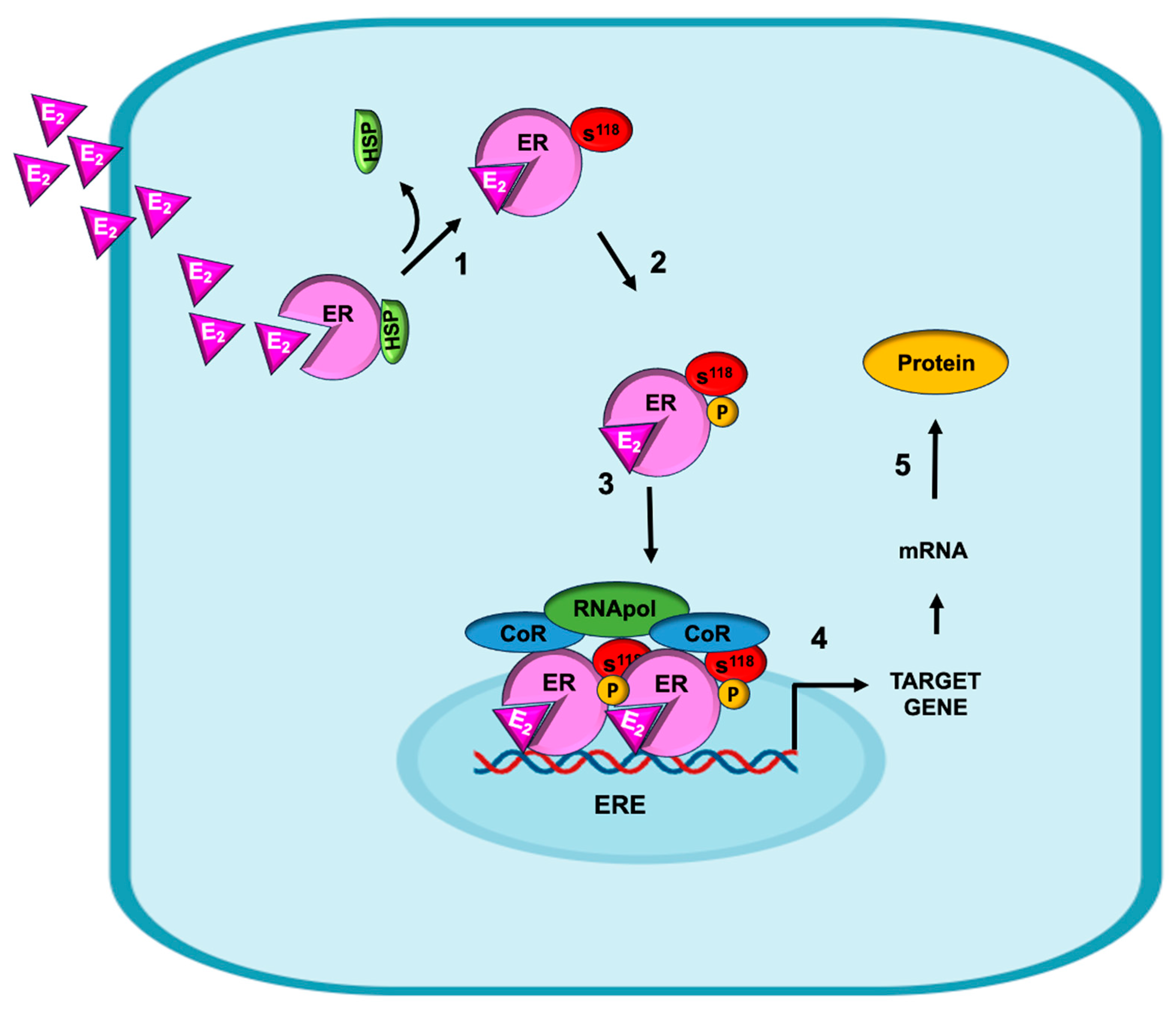
4. Genomic Mechanisms by Which E2 Induces EMT in Breast Cancer
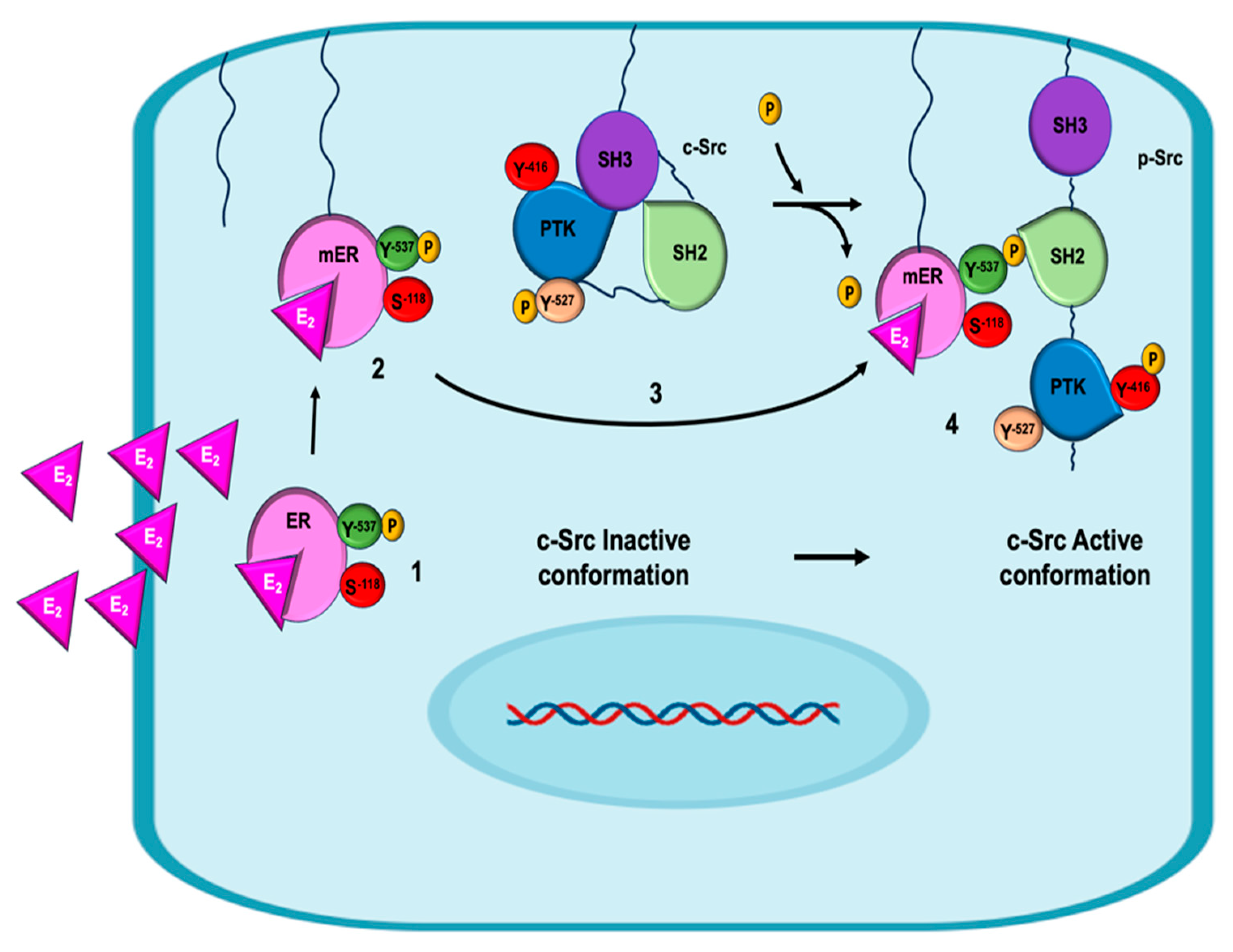
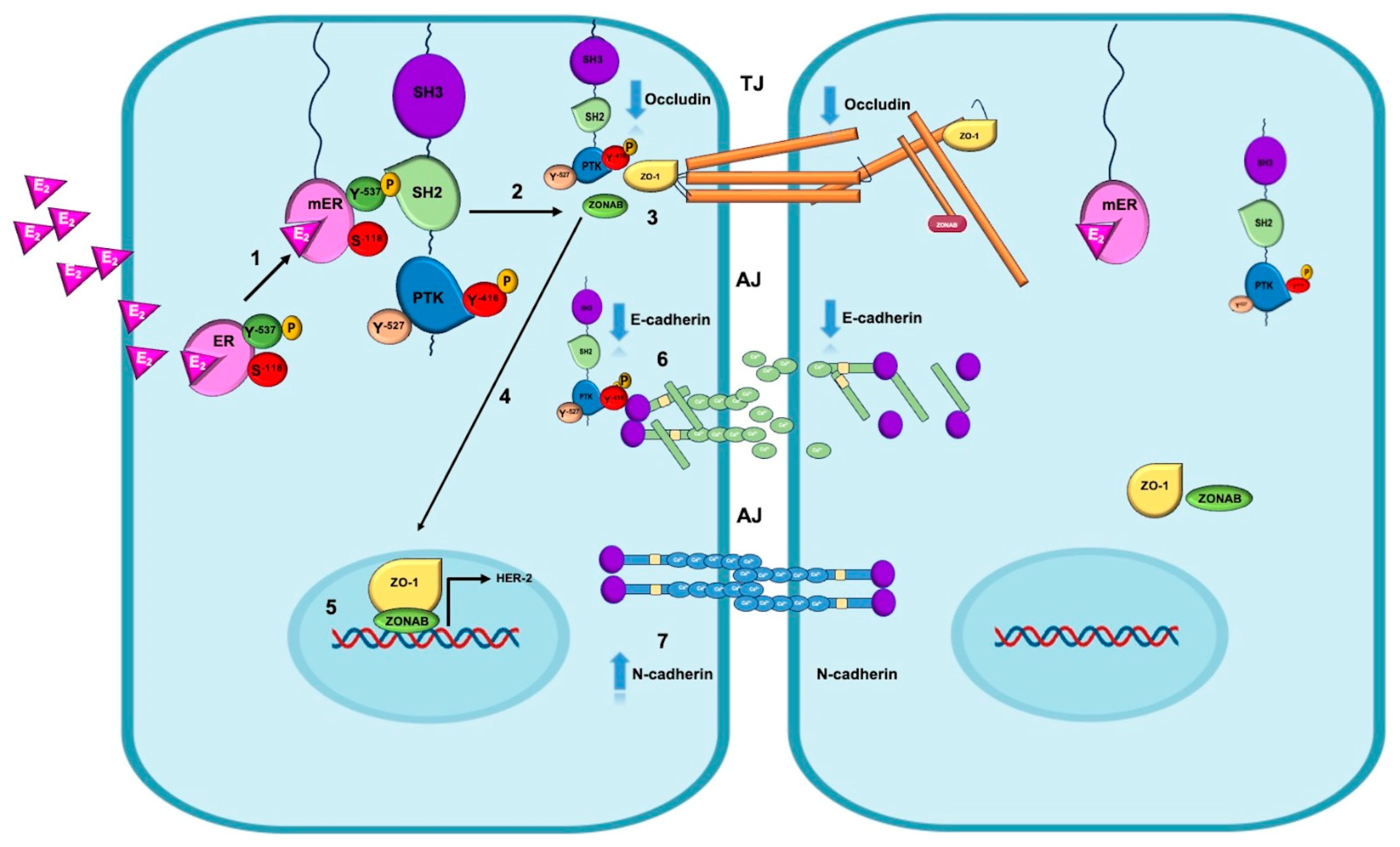
5. Non-Genomic Mechanisms of Estrogen on EMT in Breast Cancer
6. Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of Estrogens and the Regulation of EMT in Clinical Practice
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.; Harper, A.; McCormack, V.; Sung, H.; Houssami, N.; Morgan, E.; Mutebi, M.; Garvey, G.; Soerjomataram, I.; Fidler-Benaoudia, M.M. Global Patterns and Trends in Breast Cancer Incidence and Mortality across 185 Countries. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyuk, B.; Jin, S.; Ye, K. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Signaling Pathways Responsible for Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2022, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Antin, P.; Berx, G.; Blanpain, C.; Brabletz, T.; Bronner, M.; Campbell, K.; Cano, A.; Casanova, J.; Christofori, G.; et al. Guidelines and Definitions for Research on Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, R.; Mestre-Farrera, A.; Yang, J. Update on Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity in Cancer Progression. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2024, 19, 133–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, D.; Shu, X.; Gassama-Diagne, A.; Thiery, J.P. Mesenchymal–Epithelial Transition in Development and Reprogramming. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.; Tan, W.; Diadhiou, C.M.M.; McGinnis, C.S.; Abbasi, A.; Hasnain, S.; Durney, S.; Atamaniuc, E.; Superville, D.; Awni, L.; et al. Single-Cell Analysis of Breast Cancer Metastasis Reveals Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity Signatures Associated with Poor Outcomes. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e164227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, N.M.; Maddipati, R.; Norgard, R.J.; Balli, D.; Li, J.; Yuan, S.; Yamazoe, T.; Black, T.; Sahmoud, A.; Furth, E.E.; et al. EMT Subtype Influences Epithelial Plasticity and Mode of Cell Migration. Dev. Cell 2018, 45, 681–695.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas-Silva, M.D.; Waltz, P.K. Estrogen Promotes Reversible Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal-like Transition and Collective Motility in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 104, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puram, S.V.; Parikh, A.S.; Tirosh, I. Single Cell RNA-Seq Highlights a Role for a Partial EMT in Head and Neck Cancer. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2018, 5, e1448244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouad, P.; Zhang, Y.; De Martino, F.; Stibolt, C.; Ali, S.; Ambrosini, G.; Mani, S.A.; Maggs, K.; Quinn, H.M.; Sflomos, G.; et al. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity Determines Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer Dormancy and Epithelial Reconversion Drives Recurrence. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunbier, A.K.; Anderson, H.; Ghazoui, Z.; Lopez-Knowles, E.; Pancholi, S.; Ribas, R.; Drury, S.; Sidhu, K.; Leary, A.; Martin, L.-A.; et al. ESR1 Is Co-Expressed with Closely Adjacent Uncharacterised Genes Spanning a Breast Cancer Susceptibility Locus at 6q25.1. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arao, Y.; Korach, K.S. The Physiological Role of Estrogen Receptor Functional Domains. Essays Biochem. 2021, 65, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božović, A.; Mandušić, V.; Todorović, L.; Krajnović, M. Estrogen Receptor Beta: The Promising Biomarker and Potential Target in Metastases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipowicz, J.M.; Malińska, A.; Nowicki, M.; Rawłuszko-Wieczorek, A.A. Genes Co-Expressed with ESR2 Influence Clinical Outcomes in Cancer Patients: TCGA Data Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biason-Lauber, A.; Lang-Muritano, M. Estrogens: Two Nuclear Receptors, Multiple Possibilities. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2022, 554, 111710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marczell, I.; Balogh, P.; Nyiro, G.; Kiss, A.L.; Kovacs, B.; Bekesi, G.; Racz, K.; Patocs, A. Membrane-Bound Estrogen Receptor Alpha Initiated Signaling Is Dynamin Dependent in Breast Cancer Cells. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2018, 23, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micevych, P.E.; Kelly, M.J. Membrane Estrogen Receptor Regulation of Hypothalamic Function. Neuroendocrinology 2012, 96, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zárate, S.; Jaita, G.; Ferraris, J.; Eijo, G.; Magri, M.L.; Pisera, D.; Seilicovich, A. Estrogens Induce Expression of Membrane-Associated Estrogen Receptor α Isoforms in Lactotropes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathe, R.; Houston, D.R. Fatty-Acylation Target Sequence in the Ligand-Binding Domain of Vertebrate Steroid Receptors Demarcates Evolution from Estrogen-Related Receptors. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 184, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedram, A.; Razandi, M.; Deschenes, R.J.; Levin, E.R. DHHC-7 and -21 Are Palmitoylacyltransferases for Sex Steroid Receptors. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonn Eisinger, K.R.; Woolfrey, K.M.; Swanson, S.P.; Schnell, S.A.; Meitzen, J.; Dell’Acqua, M.; Mermelstein, P.G. Palmitoylation of Caveolin-1 Is Regulated by the Same DHHC Acyltransferases That Modify Steroid Hormone Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 15901–15911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.S.; Micevych, P.E.; Mermelstein, P.G. Membrane Estrogen Signaling in Female Reproduction and Motivation. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1009379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Bender, J.R. Membrane-Initiated Actions of Estrogen on the Endothelium. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 308, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagandla, H.; Thomas, C. Estrogen Signals through ERβ in Breast Cancer; What We Have Learned since the Discovery of the Receptor. Receptors 2024, 3, 182–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlanmerini, M.; Fontaine, C.; Gourdy, P.; Arnal, J.-F.; Lenfant, F. Segregation of Nuclear and Membrane-Initiated Actions of Estrogen Receptor Using Genetically Modified Animals and Pharmacological Tools. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2022, 539, 111467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatpe, A.; Adebayo, A.; Herodotou, C.; Kumar, B.; Nakshatri, H. Nexus between PI3K/AKT and Estrogen Receptor Signaling in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.K.L.; Siu, M.K.Y.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Wang, J.-J.; Wang, Y.; Leung, T.H.Y.; Liu, S.S.; Cheung, A.N.Y.; Ngan, H.Y.S. Differential Expression of Estrogen Receptor Subtypes and Variants in Ovarian Cancer: Effects on Cell Invasion, Proliferation and Prognosis. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.; Filardo, E.J.; Lolait, S.J.; Thomas, P.; Maggiolini, M.; Prossnitz, E.R. Twenty Years of the G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor GPER: Historical and Personal Perspectives. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 176, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, B.; Chiarella, A.M.; Pitarresi, J.R.; Rustgi, A.K. EMT, MET, Plasticity, and Tumor Metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, P.; Huirem, R.S.; Dutta, P.; Palchaudhuri, S. Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Its Transcription Factors. Biosci. Rep. 2022, 42, BSR20211754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Salazar, J.E.; Rivera-Escobar, R.M.; Damián-Ferrara, R.; Maldonado-Cubas, J.; Rincón-Pérez, C.; Tarragó-Castellanos, R.; Damián-Matsumura, P. Estradiol-Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition and Migration Are Inhibited by Blocking c-Src Kinase in Breast Cancer Cell Lines. J. Breast Cancer 2023, 26, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; He, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhou, W.; Duan, C.; Zhang, C. PRKAR1A Is a Functional Tumor Suppressor Inhibiting ERK/Snail/E-Cadherin Pathway in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, S.; Itoh, Y.; Omata, C.; Saitoh, M.; Miyazawa, K. ZEB1 and Oncogenic Ras Constitute a Regulatory Switch for Stimulus-dependent E-cadherin Downregulation. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Ogishima, S. Network Biology Approach to Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer Metastasis: Three Stage Theory. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 7, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casal, J.I.; Bartolomé, R.A. Beyond N-Cadherin, Relevance of Cadherins 5, 6 and 17 in Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili-Tanha, G.; Radisky, E.S.; Radisky, D.C.; Shoari, A. Matrix Metalloproteinase-Driven Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: Implications in Health and Disease. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.J. Matrix Metalloproteinases as Therapeutic Targets in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 12, 1108695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangani, S.; Piperigkou, Z.; Koletsis, N.E.; Ioannou, P.; Karamanos, N.K. Estrogen Receptors and Extracellular Matrix: The Critical Interplay in Cancer Development and Progression. FEBS J. 2025, 292, 1558–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niland, S.; Riscanevo, A.X.; Eble, J.A. Matrix Metalloproteinases Shape the Tumor Microenvironment in Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhamad, A.E.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, J.; Du, Y. Systematic Proteomic Identification of the Heat Shock Proteins (Hsp) That Interact with Estrogen Receptor Alpha (ERα) and Biochemical Characterization of the ERα-Hsp70 Interaction. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simanjuntak, M.V.; Jauhar, M.M.; Syaifie, P.H.; Arda, A.G.; Mardliyati, E.; Shalannanda, W.; Hermanto, B.R.; Anshori, I. Revealing Propolis Potential Activity on Inhibiting Estrogen Receptor and Heat Shock Protein 90 Overexpressed in Breast Cancer by Bioinformatics Approaches. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2024, 18, 11779322231224187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrod, A.; Fulton, J.; Nguyen, V.T.M.; Periyasamy, M.; Ramos-Garcia, L.; Lai, C.-F.; Metodieva, G.; De Giorgio, A.; Williams, R.L.; Santos, D.B.; et al. Genomic Modelling of the ESR1 Y537S Mutation for Evaluating Function and New Therapeutic Approaches for Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2286–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Z.; Shi, W.; Zhou, F.; Yan, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y. The Role of Estrogen Receptors in Intracellular Estrogen Signaling Pathways, an Overview. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2025, 245, 106632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Li, B.; Ou-Yang, L. Role of Estrogen Receptors in Health and Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 839005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Qi, S.; Liu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, X. Normal Endometrial Stromal Cells Regulate 17β-Estradiol-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via Slug and E-Cadherin in Endometrial Adenocarcinoma Cells In Vitro. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2017, 33, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalet, B.T.; Anglin, S.R.; Handschy, A.; O’Donoghue, L.E.; Halsey, C.; Chubb, L.; Korch, C.; Duval, D.L. Transcription Factor Ets1 Cooperates with Estrogen Receptor α to Stimulate Estradiol-Dependent Growth in Breast Cancer Cells and Tumors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Bang, H.; Seong, C.; Kim, E.-S.; Kim, S. Transcription Factors and Hormone Receptors: Sex-specific Targets for Cancer Therapy (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2024, 29, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavathi, B.; Singh, K.; Kumar, R. MTA Family of Coregulators in Nuclear Receptor Biology and Pathology. Nucl. Recept. Signal 2007, 5, nrs.05010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Huo, M.; Hu, T.; Ma, T.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; et al. The Feedback Loop between MTA1 and MTA3/TRIM21 Modulates Stemness of Breast Cancer in Response to Estrogen. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Cheung, L.W.T.; Wong, A.S.T.; Leung, P.C.K. Estrogen Regulates Snail and Slug in the Down-Regulation of E-Cadherin and Induces Metastatic Potential of Ovarian Cancer Cells through Estrogen Receptor α. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 2085–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, N.; Kajita, M.; Taysavang, P.; Wade, P.A. Hormonal Regulation of Metastasis-Associated Protein 3 Transcription in Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 2937–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Wei, J.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, B.; Feng, X.; Xiong, M.; Zhao, J.; Shi, C.; Li, Z. Metastasis-Associated Protein 1 Participates in Regulating Luminal Acidification of the Epididymis via Repressing Estrogen Receptor Alpha Transcription. Andrology 2024, 12, 1872–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sade, H.; Holloway, K.; Romero, I.A.; Male, D. Transcriptional Control of Occludin Expression in Vascular Endothelia: Regulation by Sp3 and YY1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gene Regul. Mech. 2009, 1789, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Salazar, J.E.; Posadas-Rodríguez, P.; Lazzarini-Lechuga, R.C.; Luna-López, A.; Zentella-Dehesa, A.; Gómez-Quiroz, L.E.; Königsberg, M.; Domínguez-Gómez, G.; Damián-Matsumura, P. Membrane-Initiated Estradiol Signaling of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition-Associated Mechanisms Through Regulation of Tight Junctions in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Horm. Cancer 2014, 5, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumata, M.; Uchikawa, M.; Kamachi, Y.; Kondoh, H. Multiple N-Cadherin Enhancers Identified by Systematic Functional Screening Indicate Its Group B1 SOX-Dependent Regulation in Neural and Placodal Development. Dev. Biol. 2005, 286, 601–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, W.; Yearsley, K.; Gao, J.X.; Shetuni, B.; Barsky, S.H. ERalpha Signaling through Slug Regulates E-Cadherin and EMT. Oncogene 2010, 29, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.; Kuperwasser, C. SLUG: Critical Regulator of Epithelial Cell Identity in Breast Development and Cancer. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2014, 8, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bu, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, Q.; Sha, W. Bmi-1 Promotes the Invasion and Migration of Colon Cancer Stem Cells through the Downregulation of E-Cadherin. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.-H.; Hsu, D.S.-S.; Wang, H.-W.; Wang, H.-J.; Lan, H.-Y.; Yang, W.-H.; Huang, C.-H.; Kao, S.-Y.; Tzeng, C.-H.; Tai, S.-K.; et al. Bmi1 Is Essential in Twist1-Induced Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 982–992, Correction in Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 533–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Fu, T.; Wei, N.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X. Bmi-1 Promotes the Proliferation, Migration and Invasion, and Inhibits Cell Apoptosis of Human Retinoblastoma Cells via RKIP. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ming, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J. ERβ1 Inhibits the Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells through Upregulation of E-Cadherin in a Id1-Dependent Manner. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 457, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, R.; Geranpayeh, L.; Omrani, M.D.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Expression Analysis of Inhibitor Of DNA Binding 1 (ID-1) Gene in Breast Cancer. Hum. Antibodies 2019, 27, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulin, D.; Lilienbaum, A.; Kardjian, S.; Agbulut, O.; Li, Z. Vimentin: Regulation and Pathogenesis. Biochimie 2022, 197, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Klundert, F.A.J.M.; Van Eldik, G.J.; Pieper, F.R.; Jansen, H.J.; Bloemendal, H. Identification of Two Silencers Flanking an AP-1 Enhancer in the Vimentin Promoter. Gene 1992, 122, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauvais-Jarvis, F.; Lange, C.A.; Levin, E.R. Membrane-Initiated Estrogen, Androgen, and Progesterone Receptor Signaling in Health and Disease. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 720–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbalagan, M.; Rowan, B.G. Estrogen Receptor Alpha Phosphorylation and Its Functional Impact in Human Breast Cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 418, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkoyluoglu, E.; Madak-Erdogan, Z. Nuclear and Extranuclear-Initiated Estrogen Receptor Signaling Crosstalk and Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer. Steroids 2016, 114, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Zazzo, E.; Galasso, G.; Giovannelli, P.; Di Donato, M.; Bilancio, A.; Perillo, B.; Sinisi, A.A.; Migliaccio, A.; Castoria, G. Estrogen Receptors in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erratum in MacDonald, G.; Nalvarte, I.; Smirnova, T.; Vecchi, M.; Aceto, N.; Doelemeyer, A.; Frei, A.; Lienhard, S.; Wyckoff, J.; Hess, D.; et al. Memo Is a Copper-Dependent Redox Protein with an Essential Role in Migration and Metastasis. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, 329, Erratum in: Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, A.; MacDonald, G.; Lund, I.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Hynes, N.E.; Nalvarte, I. Memo Interacts with C-Src to Control Estrogen Receptor Alpha Sub-Cellular Localization. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 56170–56182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schotanus, M.D.; Van Otterloo, E. Finding MEMO—Emerging Evidence for MEMO1′s Function in Development and Disease. Genes 2020, 11, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Salazar, J.E.; Damian-Ferrara, R.; Arteaga, M.; Batina, N.; Damián-Matsumura, P. Non-Genomic Actions of Estrogens on the DNA Repair Pathways Are Associated with Chemotherapy Resistance in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 631007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derouane, F.; Ambroise, J.; Van Marcke, C.; Van Bockstal, M.; Berlière, M.; Galant, C.; Dano, H.; Lougué, M.; Benidovskaya, E.; Jerusalem, G.; et al. Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Early Breast Cancers Is Associated with Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes. Mol. Oncol. 2025, 19, 2330–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiménez-Salazar, J.; Garcia-Melo, L.; Batina, N.; Alarcón-Aguilar, A.; Luna-López, A.; Hernández-Garcés, P.; Damián-Ferrara, R.; Damián-Matsumura, P. Molecular Mechanisms of Estrogens in the Induction of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178589
Jiménez-Salazar J, Garcia-Melo L, Batina N, Alarcón-Aguilar A, Luna-López A, Hernández-Garcés P, Damián-Ferrara R, Damián-Matsumura P. Molecular Mechanisms of Estrogens in the Induction of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis in Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178589
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiménez-Salazar, Javier, Luis Garcia-Melo, Nikola Batina, Adriana Alarcón-Aguilar, Armando Luna-López, Paulina Hernández-Garcés, Rebeca Damián-Ferrara, and Pablo Damián-Matsumura. 2025. "Molecular Mechanisms of Estrogens in the Induction of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis in Breast Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178589
APA StyleJiménez-Salazar, J., Garcia-Melo, L., Batina, N., Alarcón-Aguilar, A., Luna-López, A., Hernández-Garcés, P., Damián-Ferrara, R., & Damián-Matsumura, P. (2025). Molecular Mechanisms of Estrogens in the Induction of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis in Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178589






