Hyaluronic and Succinic Acid: New Biostimulating Combination to Counteract Dermal and Subcutaneous Aging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
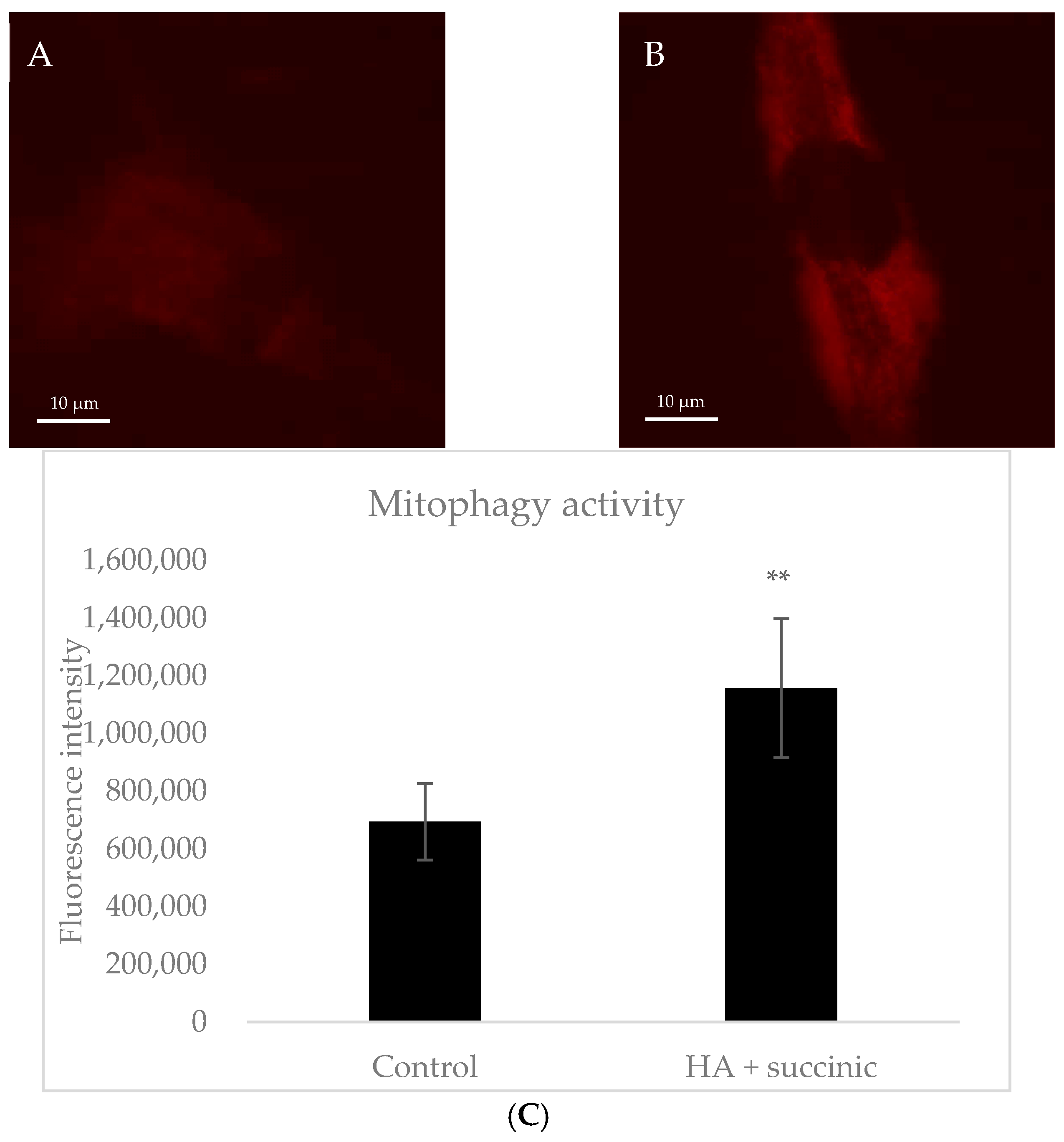
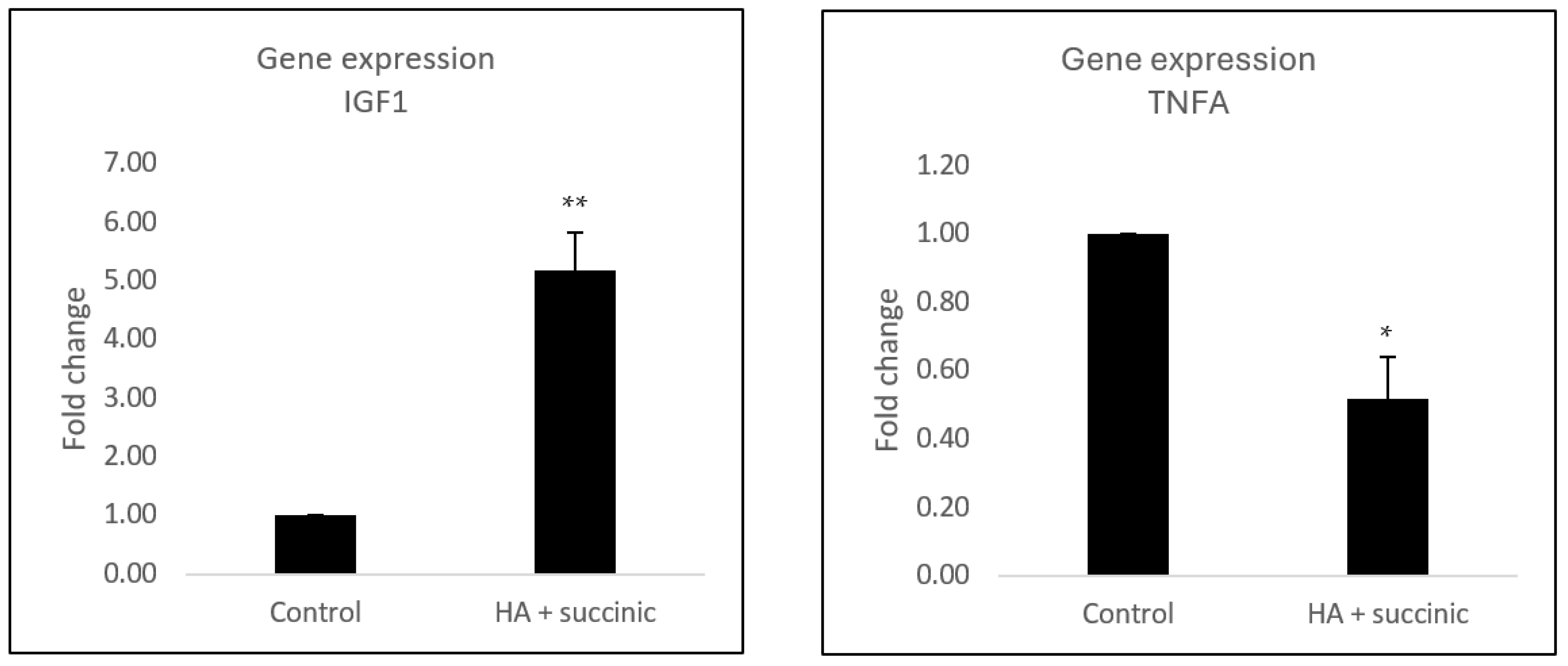
2.1. Effect of Hyaluronic Acid and Succinic Acid on Human Dermal Senescent Fibroblasts
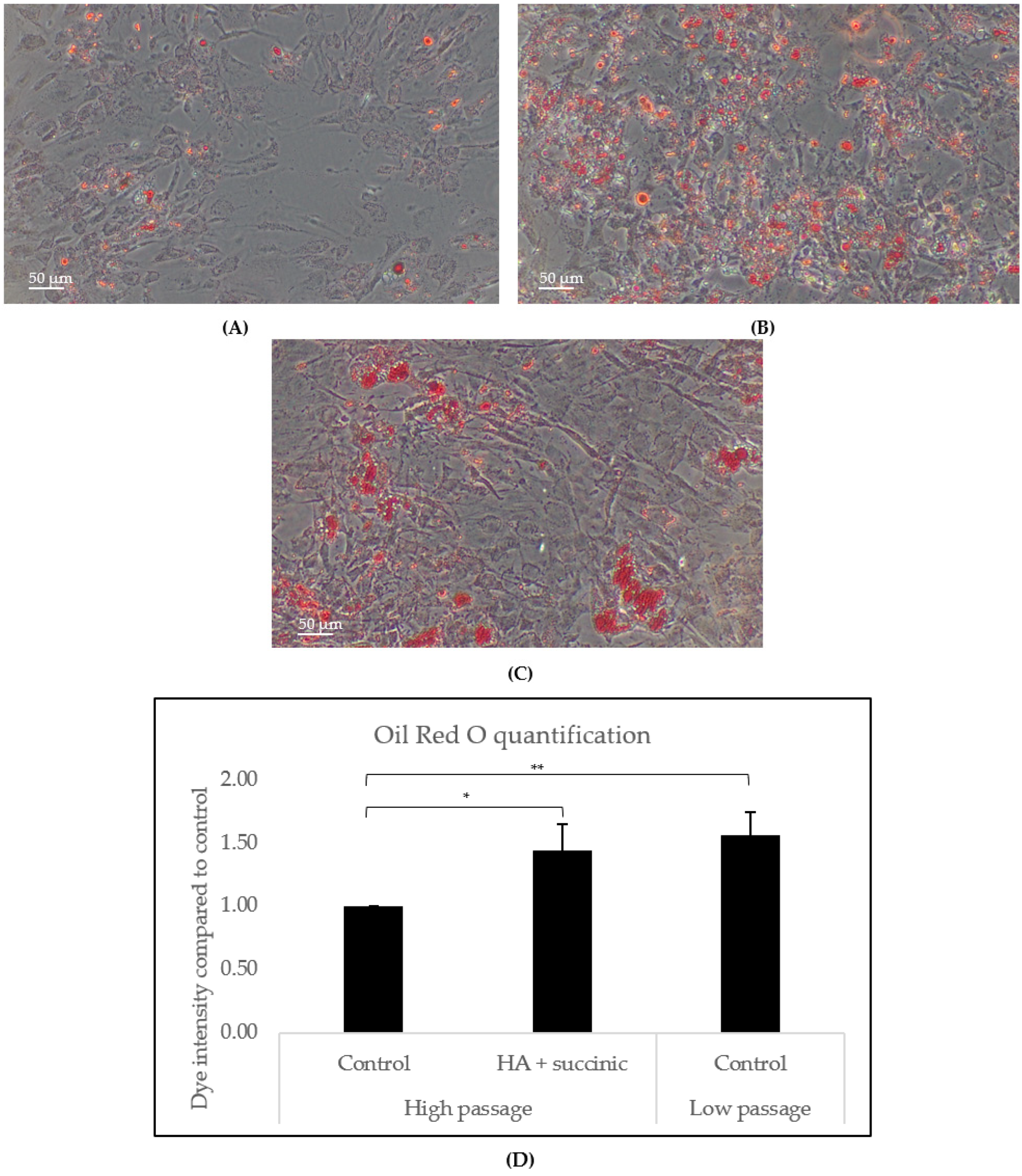
2.2. Effect of Hyaluronic Acid and Succinic Acid on Human Subcutaneous Adipocytes
2.3. Effect of Hyaluronic Acid and Succinic Acid on Human Subcutaneous Adipocytes and Dermal Fibroblast Communication
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Gene Expression Assay in Fibroblast Dermal Senescent Cells
4.3. Microscopic Analysis of Mitophagy in Fibroblast Dermal Senescent Cells
4.4. Adipogenesis Assay in Subcutaneous Adipocytes
4.5. Gene Expression Assay in Subcutaneous Adipocytes and Effect of Subcutaneous Adipocyte-Conditioned Medium Effect on Dermal Fibroblasts
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Landau, M.; Fagien, S. Science of Hyaluronic Acid Beyond Filling. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 136, 188S–195S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, S.; Galadari, H.; Patil, A.; Goldust, M.; Al Salam, S.; Guida, S. Evaluation of the biostimulatory effects and the level of neocollagenesis of dermal fillers: A review. Int. J. Dermatol. 2022, 61, 1284–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, J.D.; Carruthers, J.A.; Humphrey, S. Fillers and Neocollagenesis. Dermatol. Surg. 2014, 40 (Suppl. S12), S134–S136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Fang, W.; Wang, F. Injectable fillers: Current status, physicochemical properties, function mechanism, and perspectives. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 23841–23858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollina, U.; Wetzker, R.; Abdel-Naser, M.B.; Kruglikov, I.L. Role of adipose tissue in facial aging. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchkonia, T.; Morbeck, D.E.; Von Zglinicki, T.; Van Deursen, J.; Lustgarten, J.; Scrable, H.; Khosla, S.; Jensen, M.D.; Kirkland, J.L. Fat tissue, aging, and cellular senescence. Aging Cell 2010, 9, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, T. Human Skin Aging and the Anti-Aging Properties of Retinol. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Shelbayeh, O.; Arroum, T.; Morris, S.; Busch, K.B. PGC-1α Is a Master Regulator of Mitochondrial Lifecycle and ROS Stress Response. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.-X.; Yin, X.-M. Mitophagy: Mechanisms, pathophysiological roles, and analysis. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Yang, G.; Hägg, D.; Sun, G.; Jiang, N.; Ricupero, C.L.; Wu, J.; Rodhe, C.H.; Ascherman, J.A.; Chen, L.; et al. IGF1 Promotes Adipogenesis by a Lineage Bias of Endogenous Adipose Stem/Progenitor Cells. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 2483–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hattab, M.Y.; Nagumo, Y.; Gourronc, F.A.; Klingelhutz, A.J.; Ankrum, J.A.; Sander, E.A. Human Adipocyte Conditioned Medium Promotes In Vitro Fibroblast Conversion to Myofibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Broadbent, J.A.; Huan, J.; Yang, H. The Effects of Adipose Stem Cell-Conditioned Media on Fibrogenesis of Dermal Fibroblasts Stimulated by Transforming Growth Factor-β1. J. Burn. Care Res. 2018, 39, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjerobabski-Masnec, I.; Situm, M. Skin aging. Acta Clin. Croat. 2010, 49, 515–518. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, M.; Khan, A.; Gupta, M. Skin Ageing: Pathophysiology and Current Market Treatment Approaches. Curr. Aging Sci. 2020, 13, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, S.; Galadari, H.; Vespasiani, G.; Pellacani, G. Skin biostimulation and hyaluronic acid: Current knowledge and new evidence. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024, 23, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röck, K.; Fischer, K.; Fischer, J.W. Hyaluronan Used for Intradermal Injections Is Incorporated into the Pericellular Matrix and Promotes Proliferation in Human Skin Fibroblasts in vitro. Dermatology 2010, 221, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Cao, M.; Liu, H.; He, Y.; Xu, J.; Du, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Cui, L.; Hu, J.; et al. The high and low molecular weight forms of hyaluronan have distinct effects on CD44 clustering. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 43094–43107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Hascall, V.C.; Markwald, R.R.; Ghatak, S. Interactions between Hyaluronan and Its Receptors (CD44, RHAMM) Regulate the Activities of Inflammation and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuneki, M.; Madri, J.A. CD44 Influences Fibroblast Behaviors via Modulation of Cell-Cell and Cell-Matrix Interactions, Affecting Survivin and Hippo Pathways. J. Cell Physiol. 2016, 231, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, P.S.; Majumdar, S.; Jacob, M.; Hayden, J.; Mrass, P.; Weninger, W.; Assoian, R.K.; Puré, E. Fibroblast migration is mediated by CD44-dependent TGFβ activation. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ives, S.J.; Zaleski, K.S.; Slocum, C.; Escudero, D.; Sheridan, C.; Legesse, S.; Vidal, K.; Lagalwar, S.; Reynolds, T.H. The effect of succinic acid on the metabolic profile in high-fat diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Physiol. Rep. 2020, 8, e14630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretter, L.; Szabados, G.; Andó, A.; Horváth, I. Effect of succinate on mitochondrial lipid peroxidation. The protective effect of succinate against functional and structural changes induced by lipid peroxidation. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1987, 19, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzak, G.; Willis, C.M.; Smith, J.A.; Pluchino, S.; Peruzzotti-Jametti, L. Succinate Receptor 1: An Emerging Regulator of Myeloid Cell Function in Inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2021, 42, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, M.R.; Hannawa, O.M.; Yaldo, M.M.; Nageeb, E.M.; Chaiyasate, K. The rise of “Ozempic Face”: Analyzing trends and treatment challenges associated with rapid facial weight loss induced by GLP-1 agonists. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2024, 96, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, C.D.; Lawrence, A.C. Implications of Ozempic and Other Semaglutide Medications for Facial Plastic Surgeons. Facial Plast. Surg. 2023, 39, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullard, N.; Wordsworth, J.; Welsh, C.; Maltman, V.; Bascom, C.; Tasseff, R.; Isfort, R.; Costello, L.; Scanlan, R.-L.; Przyborski, S.; et al. Cell Senescence-Independent Changes of Human Skin Fibroblasts with Age. Cells 2024, 13, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papurina, T.; Barsukov, O.; Zabuga, O.; Krasnienkov, D.; Denis, E. Effects of succinic acid on dermal fibroblasts during cultivation under extremely hypoxic conditions. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2023, 33, 101429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, J.V.; Holtz, R.; Riemer, J. Hyaluronic acid (HA) stimulates the in vitro expression of CD44 proteins but not HAS1 proteins in normal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHEKs) and is HA molecular weight dependent. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Gutiérrez, A.; Fernández-Duran, I.; Marazuela-Duque, A.; Simonet, N.G.; Yousef, I.; Martínez-Rovira, I.; Martínez-Hoyos, J.; Vaquero, A. Shikimic acid protects skin cells from UV-induced senescence through activation of the NAD+-dependent deacetylase SIRT1. Aging 2021, 13, 12308–12333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phipps, S.M.; Berletch, J.B.; Andrews, L.G.; Tollefsbol, T.O. Aging cell culture: Methods and observations. Methods Mol. Biol. 2007, 371, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishad, A.; Naseem, A.; Rani, S.; Malik, S. Automated qualitative batch measurement of lipid droplets in the liver of bird using ImageJ. STAR Protoc. 2023, 4, 102466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | No UVB | UVB | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Control | HA | Succ | ||
| Extracellular matrix | COL1A1 | 1.00 | 1.26 (±0.11) * | 1.36 (±0.04) | 2.36 (±0.09) *** |
| CTGF | 1.00 | 1.49 (±0.27) * | 1.62 (±0.23) | 2.32 (±0.44) * | |
| ELN | 1.00 | 1.26 (±0.09) * | 1.34 (±0.05) | 1.19 (±0.1) | |
| FBN1 | 1.00 | 1.64 (±0.1) ** | 1.4 (±0.15) | 2.01 (±0.11) * | |
| TGF-β1 | 1.00 | 0.76 (±0.09) * | 0.80 (±0.05) | 0.88 (±0.08) * | |
| LOXL1 | 1.00 | 1.11 (±0.07) | 1.10 (±0.05) | 1.41 (±0.13) ** | |
| MMP-1 | 1.00 | 2.22 (±0.13) ** | 2.02 (±0.17) | 1.72 (±0.31) * | |
| MMP-3 | 1.00 | 1.60 (±0.11) ** | 1.16 (±0.03) * | 0.84 (±0.07) ** | |
| MMP-14 | 1.00 | 1.64 (±0.12) ** | 1.62 (±0.09) | 1.62 (±0.12) | |
| MME | 1.00 | 2.38 (±0.28) ** | 2.36 (±0.36) | 2.35 (±0.24) | |
| Senescence associated phenotype | c-jun | 1.00 | 1.45 (±0.15) * | 1.59 (±0.02) | 1.51 (±0.04) |
| CXCL10 | 1.00 | 1.79 (±0.14) ** | 1.56 (±0.2) | 1.48 (±0.12) ** | |
| GDF15 | 1.00 | 2.59 (±0.22) ** | 2.40 (±0.04) | 2.41 (±0.10) | |
| IL-6 | 1.00 | 2.44 (±0.18) ** | 2.17 (±0.14) | 1.23 (±0.08) ** | |
| IL-8 | 1.00 | 3.00 (±0.36) ** | 3.78 (±0.41)* | 2.06 (±0.55) * | |
| BCL2 | 1.00 | 1.57 (±0.25) * | 1.80 (±0.12) | 1.66 (±0.15) | |
| Metabolism | PGC1a | 1.00 | 1.45 (±0.12) * | 1.43 (±0.06) | 1.82 (±0.05) * |
| Autophagy | ATG12 | 1.00 | 1.54 (±0.16) * | 1.89 (±0.14) | 1.46 (±0.06) |
| ATG5 | 1.00 | 1.24 (±0.02) ** | 1.50 (±0.04) ** | 1.20 (±0.09) | |
| ATG7 | 1.00 | 1.07 (±0.07) | 1.77 (±0.04) ** | 1.43 (±0.05) * | |
| Beclin1 | 1.00 | 1.35 (±0.08) ** | 1.73 (±0.13) * | 1.21 (±0.08) | |
| LC3 | 1.00 | 1.53 (±0.10) ** | 1.84 (±0.05) * | 1.34 (±0.1) | |
| Gene | Control | Adipocyte-Conditioned Medium | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | HA + Succ | ||
| COL1A1 | 1.00 | 1.07 (±0.05) | 0.81 (±0.07) |
| COL3A1 | 1.00 | 1.70 (±0.11) ** | 1.92 (±0.08) ** |
| FN1 | 1.00 | 1.60 (±0.25) * | 3.30 (±0.24) * |
| ELN | 1.00 | 0.54 (±0.1) *** | 0.35 (±0.1) |
| EGF | 1.00 | 0.42 (±0.04) ** | 1.17 (±0.06) ** |
| FGFB | 1.00 | 0.33 (±0.05) ** | 0.30 (±0.04) |
| TGFB1 | 1.00 | 0.49 (±0.04) *** | 0.68 (±0.11) |
| ACTA2 | 1.00 | 1.39 (±0.17) * | 1.83 (±0.16) * |
| CCN1 | 1.00 | 1.40 (±0.1) * | 1.37 (±0.1) |
| CEMIP | 1.00 | 0.61 (±0.05) ** | 0.60 (±0.07) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinez-Gutierrez, A.; Cami, H.; Noya, T.; Gómez-Escalante, S.; Miró Llosas, A.; González, M.C. Hyaluronic and Succinic Acid: New Biostimulating Combination to Counteract Dermal and Subcutaneous Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157548
Martinez-Gutierrez A, Cami H, Noya T, Gómez-Escalante S, Miró Llosas A, González MC. Hyaluronic and Succinic Acid: New Biostimulating Combination to Counteract Dermal and Subcutaneous Aging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157548
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinez-Gutierrez, Alfredo, Helena Cami, Teresa Noya, Susana Gómez-Escalante, Aina Miró Llosas, and Mari Carmen González. 2025. "Hyaluronic and Succinic Acid: New Biostimulating Combination to Counteract Dermal and Subcutaneous Aging" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157548
APA StyleMartinez-Gutierrez, A., Cami, H., Noya, T., Gómez-Escalante, S., Miró Llosas, A., & González, M. C. (2025). Hyaluronic and Succinic Acid: New Biostimulating Combination to Counteract Dermal and Subcutaneous Aging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157548








