The Complex Etiology of Epilepsy: Genetic Analysis and HLA Association in Patients in the Middle East
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
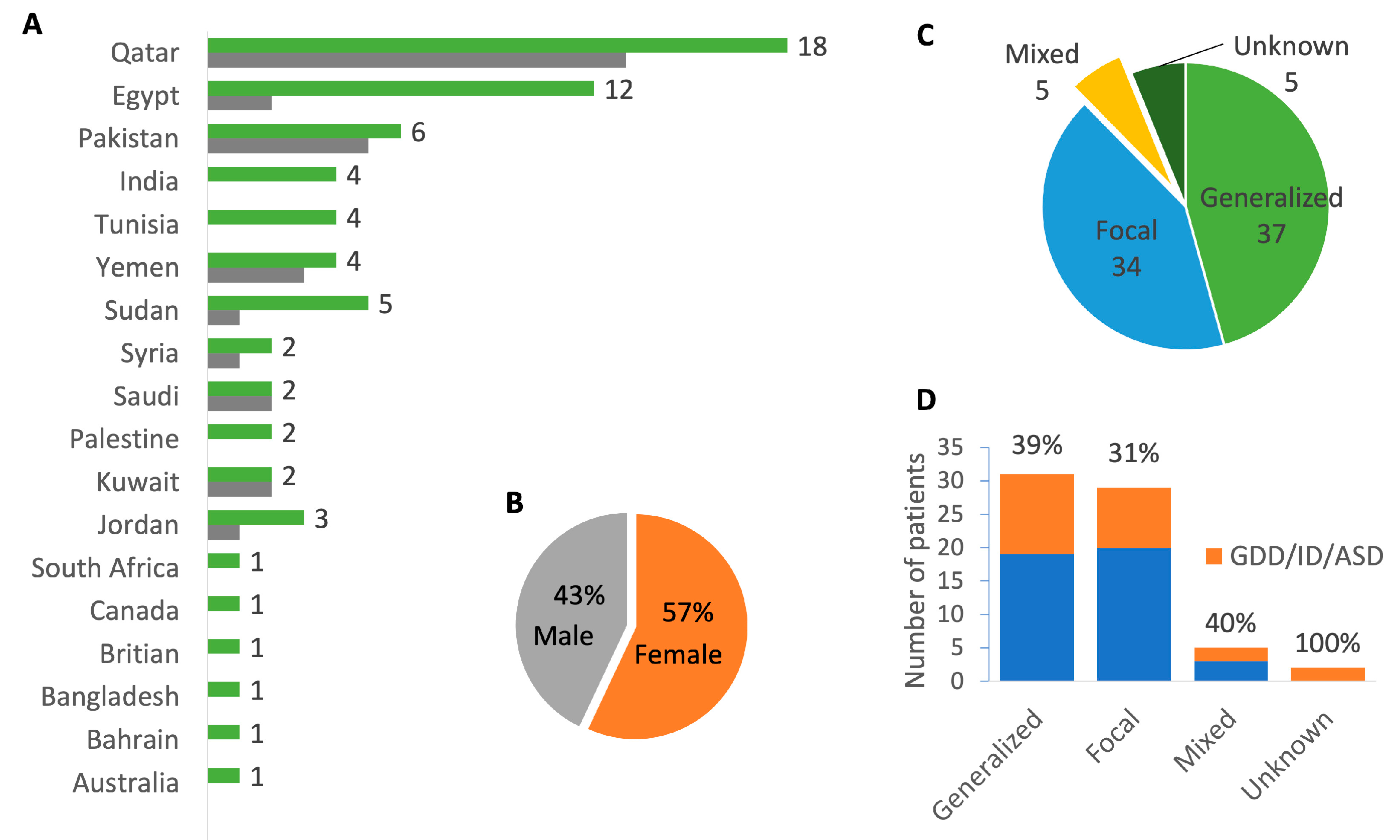
2.1. Cohort Demographics and Phenotype
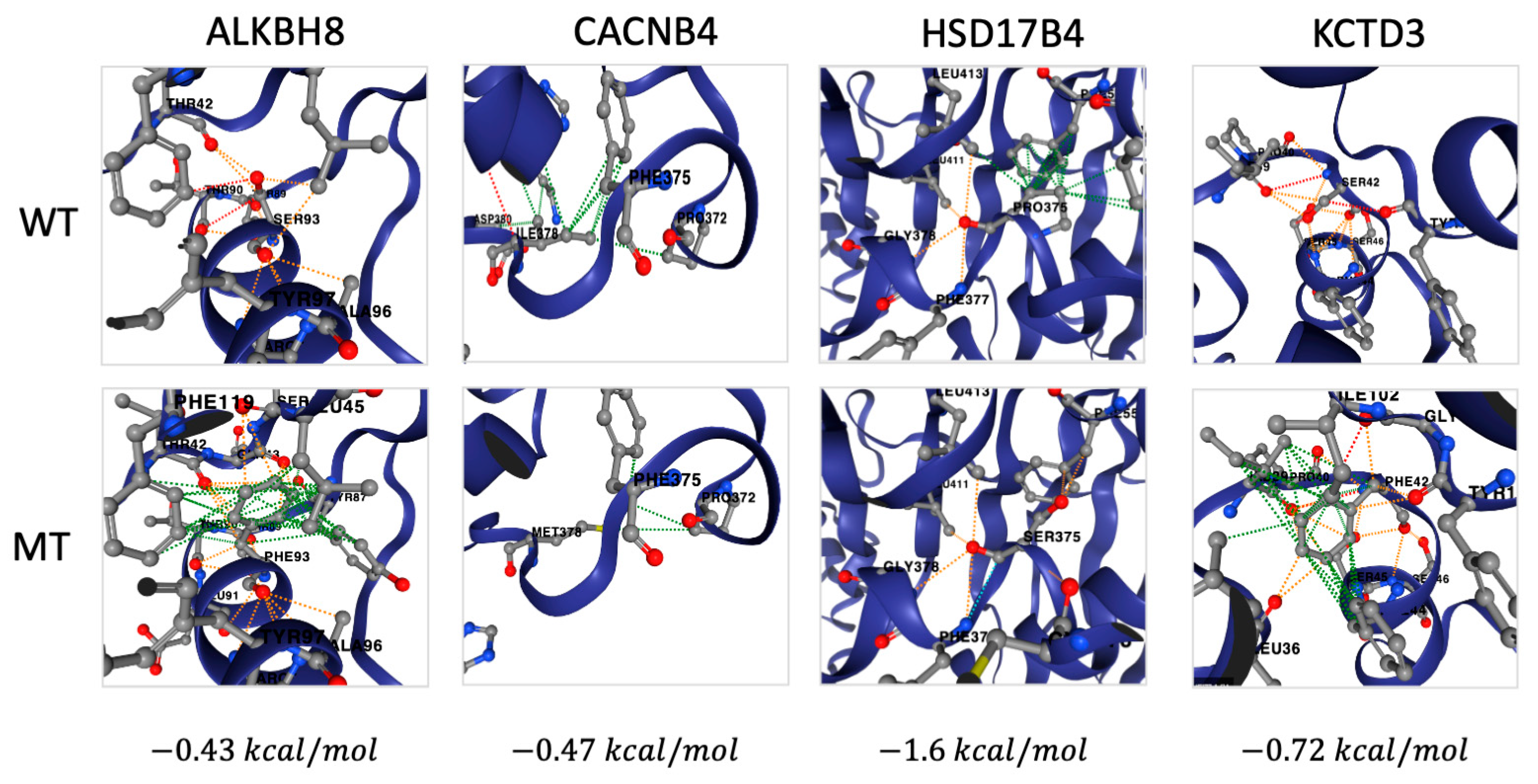
2.2. Identification of Deleterious Variants in High Confidence Genes
2.3. Identification of Deleterious Variants in Low Confidence Genes
2.4. HLA-DRB Is Associated with Epilepsy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and Processing
4.2. Genetic Data Analysis
4.3. HLA Typing and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACMG | American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics |
| ASD | Autism Spectrum Disorder |
| CNV | Copy Number Variant |
| DGV | Database of Genomic Variants |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| GATK | Genome Analysis Toolkit |
| GDD | Global Developmental Delay |
| GWAS | Genome-Wide Association Studies |
| HLA | Human Leukocyte Antigen |
| ID | Intellectual Disability |
| ILAE | International League Against Epilepsy |
| LOH | Loss of Heterozygosity |
| MAF | Minor Allele Frequency |
| MAPQ | Mapping Quality |
| MENA | Middle East and North Africa |
| OCNDS | Okur–Chung Neurodevelopmental Syndrome |
| OMIM | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man |
| P/LP | Pathogenic / Likely Pathogenic |
| PBMC | Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell |
| SNP | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism |
| VUS | Variant of Uncertain Significance |
| WES | Whole Exome Sequencing |
| WGS | Whole Genome Sequencing |
References
- Dunn, P.; Albury, C.L.; Maksemous, N.; Benton, M.C.; Sutherland, H.G.; Smith, R.A.; Haupt, L.M.; Griffiths, L.R. Next Generation Sequencing Methods for Diagnosis of Epilepsy Syndromes. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neligan, A.; Hauser, W.A.; Sander, J.W. The Epidemiology of the Epilepsies. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 107, pp. 113–133. ISBN 978-0-444-52898-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez Fernández, I.; Loddenkemper, T.; Gaínza-Lein, M.; Sheidley, B.R.; Poduri, A. Diagnostic Yield of Genetic Tests in Epilepsy: A Meta-Analysis and Cost-Effectiveness Study. Neurology 2019, 92, E418–E428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenbruch, L.; Bleß, L.; Schulte-Mecklenbeck, A.; Sundermann, B.; Brix, T.; Elger, C.E.; Melzer, N.; Wiendl, H.; Meuth, S.G.; Gross, C.C.; et al. Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid Immune Cell Profiles in Patients with Temporal Lobe Epilepsy of Different Etiologies. Epilepsia 2020, 61, e153–e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, B.; Chaves, J.; Carvalho, C.; Rangel, R.; Santos, A.; Bettencourt, A.; Lopes, J.; Ramalheira, J.; Silva, B.M.; da Silva, A.M.; et al. Brain Expression of Inflammatory Mediators in Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 2017, 313, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, G.C.; Garcia, A.J.; Mochizuki, A.Y.; Chang, J.W.; Reyes, S.D.; Salamon, N.; Prins, R.M.; Mathern, G.W.; Fallah, A. Evidence for Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses in a Cohort of Intractable Pediatric Epilepsy Surgery Patients. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedek, G.; El Latif, M.A.; Miller, K.; Rivkin, M.; Lasu, A.A.R.; Riek, L.P.; Lako, R.; Edvardson, S.; Alon, S.-A.; Galun, E.; et al. Protection or Susceptibility to Devastating Childhood Epilepsy: Nodding Syndrome Associates with Immunogenetic Fingerprints in the HLA Binding Groove. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, J.; Martins-Ferreira, R.; Ferreira, A.M.; Brás, S.; Carvalho, C.; Bettencourt, A.; Samões, R.; Monteiro, F.; Freitas, J.; Chorão, R.; et al. Immunogenetic Protective Factors in Genetic Generalized Epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2020, 166, 106396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, I.E.; Berkovic, S.; Capovilla, G.; Connolly, M.B.; French, J.; Guilhoto, L.; Hirsch, E.; Jain, S.; Mathern, G.W.; Moshé, S.L.; et al. ILAE Classification of the Epilepsies: Position Paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.R.; Williams, E.; Foulger, R.E.; Leigh, S.; Daugherty, L.C.; Niblock, O.; Leong, I.U.S.; Smith, K.R.; Gerasimenko, O.; Haraldsdottir, E.; et al. PanelApp Crowdsources Expert Knowledge to Establish Consensus Diagnostic Gene Panels. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanty, I.; Perez-Palma, E.; Villaman, C.; Stobo, D.; Symonds, J.; Zuberi, S.; Lal, D.; Brunklaus, A. SCN9A Should Not Be Considered an Epilepsy Gene; Refuting a Gene–Disease Association. Epilepsia 2025, epi.18474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Isola, G.B.; Vinti, V.; Fattorusso, A.; Tascini, G.; Mencaroni, E.; Di Cara, G.; Striano, P.; Verrotti, A. The Broad Clinical Spectrum of Epilepsies Associated with Protocadherin 19 Gene Mutation. Front. Neurol. 2022, 12, 780053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimova, P.S.; Kirov, A.; Todorova, A.; Todorov, T.; Mitev, V. A Novel PCDH19 Mutation Inherited from an Unaffected Mother. Pediatr. Neurol. 2012, 46, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, L.-Y.; Subramaniam, S.R.; Tong, T.-Y.T.; Chan, W.-K.; Yau, E.K.-C.; Ching, C.-K. X-Chromosome Inactivation and PCDH19-Associated Epileptic Encephalopathy: A Novel PCDH19 Variant in a Chinese Family. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 521, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.G.; Chance, P.F.; Zou, C.-H.; Spinner, N.B.; Golden, J.A.; Smietana, S. Epilepsy and Mental Retardation Limited to Females: An X-Linked Dominant Disorder with Male Sparing. Nat. Genet. 1997, 17, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaving, L.S.; Christodoulou, J.; Williamson, S.L.; Friend, K.L.; McKenzie, O.L.D.; Archer, H.; Evans, J.; Clarke, A.; Pelka, G.J.; Tam, P.P.L.; et al. Mutations of CDKL5 Cause a Severe Neurodevelopmental Disorder with Infantile Spasms and Mental Retardation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 75, 1079–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Donato, N.; Guerrini, R.; Billington, C.J.; Barkovich, A.J.; Dinkel, P.; Freri, E.; Heide, M.; Gershon, E.S.; Gertler, T.S.; Hopkin, R.J.; et al. Monoallelic and Biallelic Mutations in RELN Underlie a Graded Series of Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Brain 2022, 145, 3274–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyan, A.G.; Dyer, L.M. 3q29 Microduplication Syndrome: Clinical and Molecular Description of Eleven New Cases. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 63, 104083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bögershausen, N.; Krawczyk, H.E.; Jamra, R.A.; Lin, S.; Yigit, G.; Hüning, I.; Polo, A.M.; Vona, B.; Huang, K.; Schmidt, J.; et al. WARS1 and SARS1: Two tRNA Synthetases Implicated in Autosomal Recessive Microcephaly. Hum. Mutat. 2022, 43, 1454–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozarth, X.; Dines, J.N.; Cong, Q.; Mirzaa, G.M.; Foss, K.; Lawrence Merritt, J.; Thies, J.; Mefford, H.C.; Novotny, E. Expanding Clinical Phenotype in CACNA1C Related Disorders: From Neonatal Onset Severe Epileptic Encephalopathy to Late-Onset Epilepsy. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2018, 176, 2733–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco Hernández, A.V.; Caro, A.; Montoya Filardi, A.; Tomás Vila, M.; Monfort, S.; Beseler Soto, B.; Nieto-Barceló, J.J.; Martínez, F. Extending the Clinical Phenotype of SPTAN1: From DEE5 to Migraine, Epilepsy, and Subependymal Heterotopias Without Intellectual Disability. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2022, 188, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appenzeller, S.; Balling, R.; Barisic, N.; Baulac, S.; Caglayan, H.; Craiu, D.; De Jonghe, P.; Depienne, C.; Dimova, P.; Djémié, T.; et al. De Novo Mutations in Synaptic Transmission Genes Including DNM1 Cause Epileptic Encephalopathies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 95, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; He, F.; Chen, C.; Wu, L.; Yang, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.; Chen, C.; et al. Novel West Syndrome Candidate Genes in a Chinese Cohort. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2018, 24, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari Khamirani, H.; Zoghi, S.; Motealleh, A.; Dianatpour, M.; Tabei, S.M.B.; Mohammadi, S.; Dastgheib, S.A. Clinical Features of Okur-Chung Neurodevelopmental Syndrome: Case Report and Literature Review. Mol. Syndromol. 2022, 13, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, K.L.; Scheffer, I.E.; Bennett, M.F.; Grinton, B.E.; Bahlo, M.; Berkovic, S.F. Genes4Epilepsy: An Epilepsy Gene Resource. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Felici, C.; Lambert, L.; De Saint Martin, A.; Abi-Warde, M.; Schaefer, E.; Zix, C.; Zamani, M.; Sadeghian, S.; Zeighami, J.; et al. Putative Founder Effect of Arg338* AP4M1 (SPG50) Variant Causing Severe Intellectual Disability, Epilepsy and Spastic Paraplegia: Report of Three Families. Clin. Genet. 2023, 103, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidahmed, M.Z.; Al-Kindi, A.; Alsaif, H.S.; Miqdad, A.; Alabbad, N.; Alfifi, A.; Abdelbasit, O.B.; Alhussein, K.; Alsamadi, A.; Ibrahim, N.; et al. Recessive Mutations in SCYL2 Cause a Novel Syndromic Form of Arthrogryposis in Humans. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamel, K.; Al-Subaiey, A.A.; Alsabbagh, M.; Fadda, A.; Saeed, A.; Mourao Pacheco, B.; Lo, B.; Benini, R. Novel SCYL2 Mutations and Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita 4: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Hoed, J.; de Boer, E.; Voisin, N.; Dingemans, A.J.M.; Guex, N.; Wiel, L.; Nellaker, C.; Amudhavalli, S.M.; Banka, S.; Bena, F.S.; et al. Mutation-Specific Pathophysiological Mechanisms Define Different Neurodevelopmental Disorders Associated with SATB1 Dysfunction. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 108, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Yao, R. Neurodevelopmental Disorders and Anti-Epileptic Treatment in a Patient with a SATB1 Mutation: A Case Report. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 931667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.G.; Duis, J. Chromosome 15 Imprinting Disorders: Genetic Laboratory Methodology and Approaches. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilthey, A.T.; Mentzer, A.J.; Carapito, R.; Cutland, C.; Cereb, N.; Madhi, S.A.; Rhie, A.; Koren, S.; Bahram, S.; McVean, G.; et al. HLA*LA-HLA Typing from Linearly Projected Graph Alignments. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4394–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, S.; Higasa, K.; Shimizu, M.; Yamada, R.; Matsuda, F. HLA-HD: An Accurate HLA Typing Algorithm for Next-Generation Sequencing Data. Hum. Mutat. 2017, 38, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-J.; Lee, S.-T.; Moon, J.; Sunwoo, J.-S.; Byun, J.-I.; Lim, J.-A.; Shin, Y.-W.; Jun, J.-S.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, W.-J.; et al. Anti-LGI1 Encephalitis Is Associated with Unique HLA Subtypes: HLA Subtypes in Anti-LGI1 Encephalitis. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Vogrig, A.; Honnorat, J. Associations between HLA and Autoimmune Neurological Diseases with Autoantibodies. Auto. Immun. Highlights 2020, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sonderen, A.; Roelen, D.L.; Stoop, J.A.; Verdijk, R.M.; Haasnoot, G.W.; Thijs, R.D.; Wirtz, P.W.; Schreurs, M.W.J.; Claas, F.H.J.; Sillevis Smitt, P.A.E.; et al. Anti-LGI1 Encephalitis Is Strongly Associated with HLA-DR7 and HLA-DRB4. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; French, J.; Bartfai, T.; Baram, T.Z. The Role of Inflammation in Epilepsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, B.; Chaves, J.; Carvalho, C.; Bettencourt, A.; Brito, C.; Boleixa, D.; Freitas, J.; Brás, S.; Lopes, J.; Ramalheira, J.; et al. Immunogenetic Predisposing Factors for Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy with Hippocampal Sclerosis. Int. J. Neurosci. 2018, 128, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto-Santos, J.E.; Kandratavicius, L.; Velasco, T.R.; Assirati, J.A.; Carlotti, C.G.; Scandiuzzi, R.C.; Salmon, C.E.G.; Santos, A.C.D.; Leite, J.P. Individual Hippocampal Subfield Assessment Indicates That Matrix Macromolecules and Gliosis Are Key Elements for the Increased T2 Relaxation Time Seen in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peris Sempere, V.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Ambati, A.; Binks, S.; Pinto, A.-L.; Rogemond, V.; Pittock, S.J.; Dubey, D.; Geschwind, M.D.; Gelfand, J.M.; et al. Human Leukocyte Antigen Association Study Reveals DRB1*04:02 Effects Additional to DRB1*07:01 in Anti-LGI1 Encephalitis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 9, e1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andeweg, S.P.; Keşmir, C.; Dutilh, B.E. Quantifying the Impact of Human Leukocyte Antigen on the Human Gut Microbiota. mSphere 2021, 6, e00476-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, S.K.; Ali, S.; Jaime, C.M.; Guseva, N.V.; Mangalam, A.K. HLA Class II Polymorphisms Modulate Gut Microbiota and Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Phenotype. ImmunoHorizons 2021, 5, 627–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, A.; Fonseca, S.; Carding, S.R. Gut Microbes and Metabolites as Modulators of Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity and Brain Health. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, J.T.; Roesch, L.F.W.; Ördberg, M.; Ilonen, J.; Atkinson, M.A.; Schatz, D.A.; Triplett, E.W.; Ludvigsson, J. Genetic Risk for Autoimmunity Is Associated with Distinct Changes in the Human Gut Microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Galarza, F.F.; McCabe, A.; Santos, E.J.M.D.; Jones, J.; Takeshita, L.; Ortega-Rivera, N.D.; Cid-Pavon, G.M.D.; Ramsbottom, K.; Ghattaoraya, G.; Alfirevic, A.; et al. Allele Frequency Net Database (AFND) 2020 Update: Gold-Standard Data Classification, Open Access Genotype Data and New Query Tools. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2020, 48, D783–D788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International League Against Epilepsy Consortium on Complex Epilepsies; Stevelink, R.; Campbell, C.; Chen, S.; Abou-Khalil, B.; Adesoji, O.M.; Afawi, Z.; Amadori, E.; Anderson, A.; Anderson, J.; et al. GWAS Meta-Analysis of over 29,000 People with Epilepsy Identifies 26 Risk Loci and Subtype-Specific Genetic Architecture. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and Memory-Efficient Alignment of Short DNA Sequences to the Human Genome. Genome. Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce Framework for Analyzing Next-Generation DNA Sequencing Data. Genome. Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Henikoff, S.; Ng, P.C. Predicting the Effects of Coding Non-Synonymous Variants on Protein Function Using the SIFT Algorithm. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I.A.; Schmidt, S.; Peshkin, L.; Ramensky, V.E.; Gerasimova, A.; Bork, P.; Kondrashov, A.S.; Sunyaev, S.R. A Method and Server for Predicting Damaging Missense Mutations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, J.R.; Ziman, R.; Yuen, R.K.C.; Feuk, L.; Scherer, S.W. The Database of Genomic Variants: A Curated Collection of Structural Variation in the Human Genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D986–D992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinnwell, J.P.; Therneau, T.M.; Schaid, D.J. The Kinship2 R Package for Pedigree Data. Hum. Hered. 2014, 78, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Novati, G.; Pan, J.; Bycroft, C.; Žemgulytė, A.; Applebaum, T.; Pritzel, A.; Wong, L.H.; Zielinski, M.; Sargeant, T.; et al. Accurate Proteome-Wide Missense Variant Effect Prediction with AlphaMissense. Science 2023, 381, eadg7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.H.M.; Pires, D.E.V.; Ascher, D.B. DynaMut2: Assessing Changes in Stability and Flexibility upon Single and Multiple Point Missense Mutations. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, S.; Higasa, K.; Yamada, R.; Matsuda, F. Comprehensive HLA Typing from a Current Allele Database Using Next-Generation Sequencing Data. In HLA Typing; Boegel, S., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1802, pp. 225–233. ISBN 978-1-4939-8545-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mbarek, H.; Devadoss Gandhi, G.; Selvaraj, S.; Al-Muftah, W.; Badji, R.; Al-Sarraj, Y.; Saad, C.; Darwish, D.; Alvi, M.; Fadl, T.; et al. Qatar Genome: Insights on Genomics from the Middle East. Hum. Mutat. 2022, 43, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Allelotype | Freq (Count) Controls | Freq (Count) Cases | OR | Confidence Interval | p Adj |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRB1*07:01:01G | 0.20 (622) | 0.31 (34) | 3.2 | 0.6–5.7 | 4.0 × 10−6 |
| DRB3*01:01:02G | 0.49 (2054) | 0.35 (26) | 0.5 | −1.8–2.8 | 2.0 × 10−5 |
| DRB4*01:01:01G | 0.93 (1328) | 1.00 (75) | 3.2 | 0.9–5.6 | 5.1 × 10−9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fadda, A.; Alsabbagh, M.; Vasudeva, D.; Saeed, A.; Aglan Tarek, S.; Hubrack, S.Z.; Benini, R.; Zamel, K.; Lo, B. The Complex Etiology of Epilepsy: Genetic Analysis and HLA Association in Patients in the Middle East. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5815. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125815
Fadda A, Alsabbagh M, Vasudeva D, Saeed A, Aglan Tarek S, Hubrack SZ, Benini R, Zamel K, Lo B. The Complex Etiology of Epilepsy: Genetic Analysis and HLA Association in Patients in the Middle East. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5815. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125815
Chicago/Turabian StyleFadda, Abeer, Mohamed Alsabbagh, Dhanya Vasudeva, Amira Saeed, Sara Aglan Tarek, Satanay Z. Hubrack, Ruba Benini, Khaled Zamel, and Bernice Lo. 2025. "The Complex Etiology of Epilepsy: Genetic Analysis and HLA Association in Patients in the Middle East" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5815. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125815
APA StyleFadda, A., Alsabbagh, M., Vasudeva, D., Saeed, A., Aglan Tarek, S., Hubrack, S. Z., Benini, R., Zamel, K., & Lo, B. (2025). The Complex Etiology of Epilepsy: Genetic Analysis and HLA Association in Patients in the Middle East. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5815. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125815






