In Vivo Neuroprotective Effects of Alpinetin Against Experimental Ischemic Stroke Damage Through Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Alpinetin Alleviated Ischemic Stroke-Induced Cerebral Infarct Volume
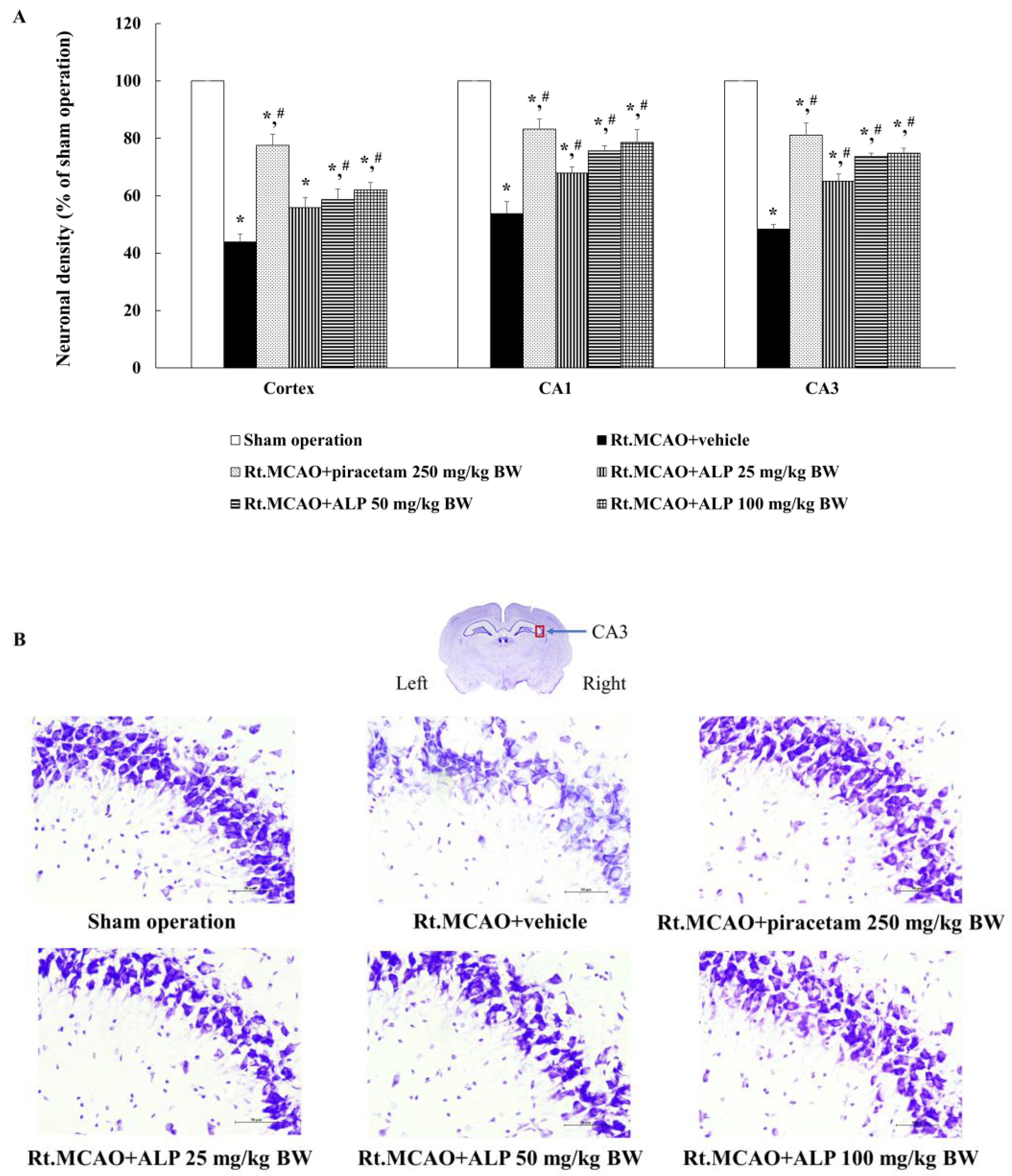
2.2. Alpinetin Improved Ischemic Stroke-Induced Neuronal Loss in the Cortex and Hippocampus
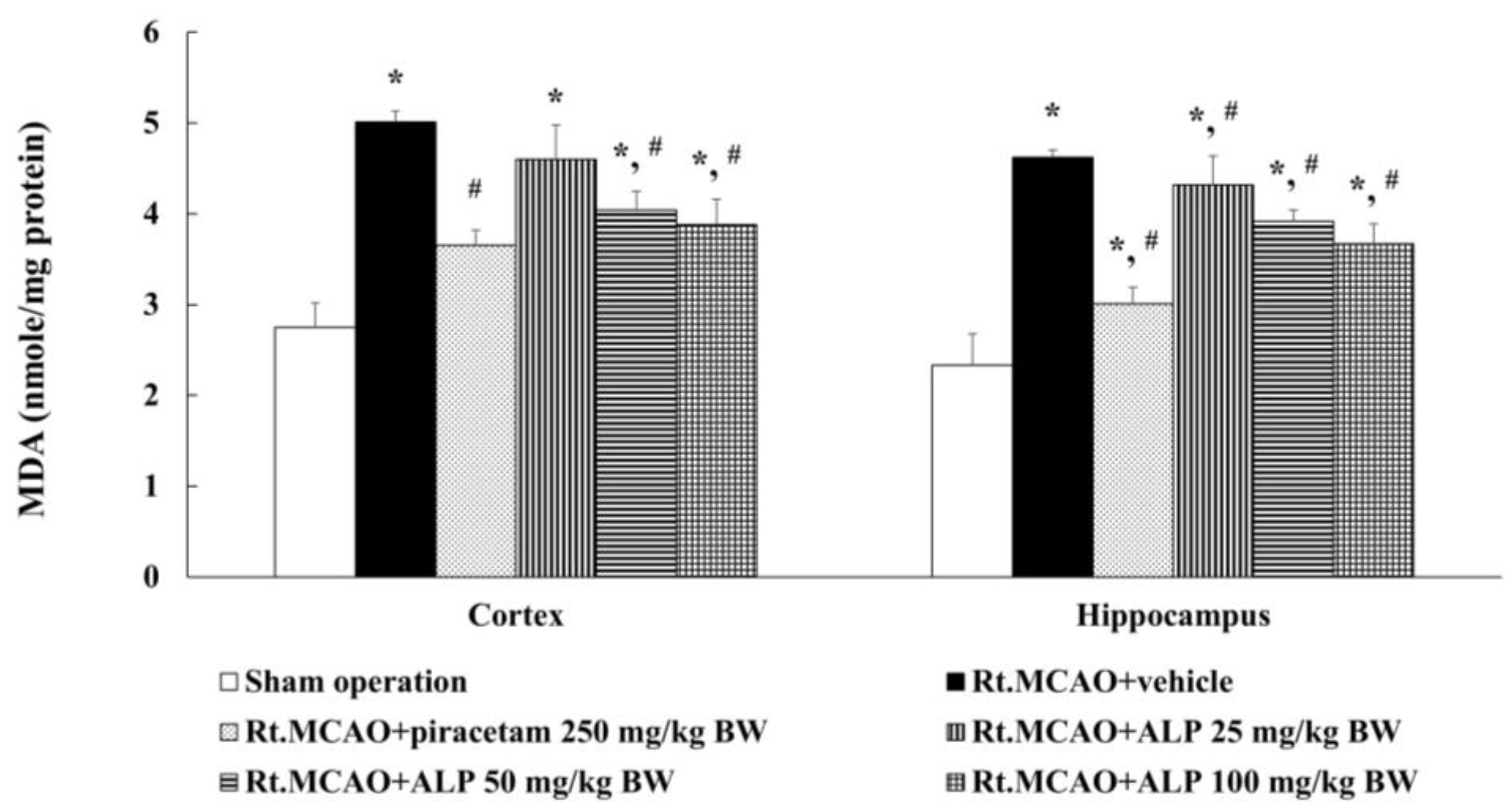
2.3. Alpinetin Ameliorated Ischemic Stroke-Induced Excessive Production of Malondialdehyde (MDA) in the Cortex and Hippocampus
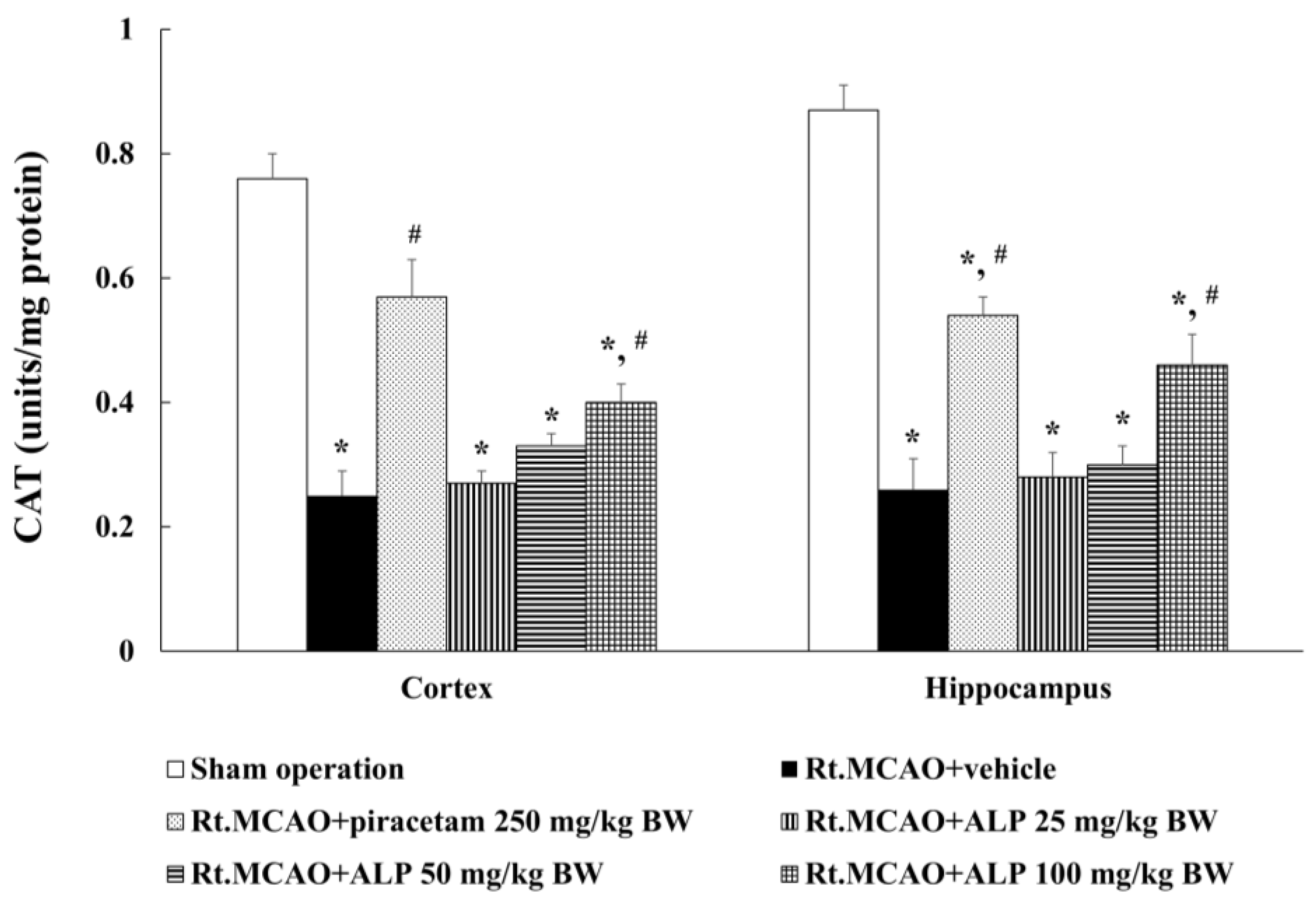
2.4. Alpinetin Increased Catalase (CAT) Activity in the Cortex and Hippocampus
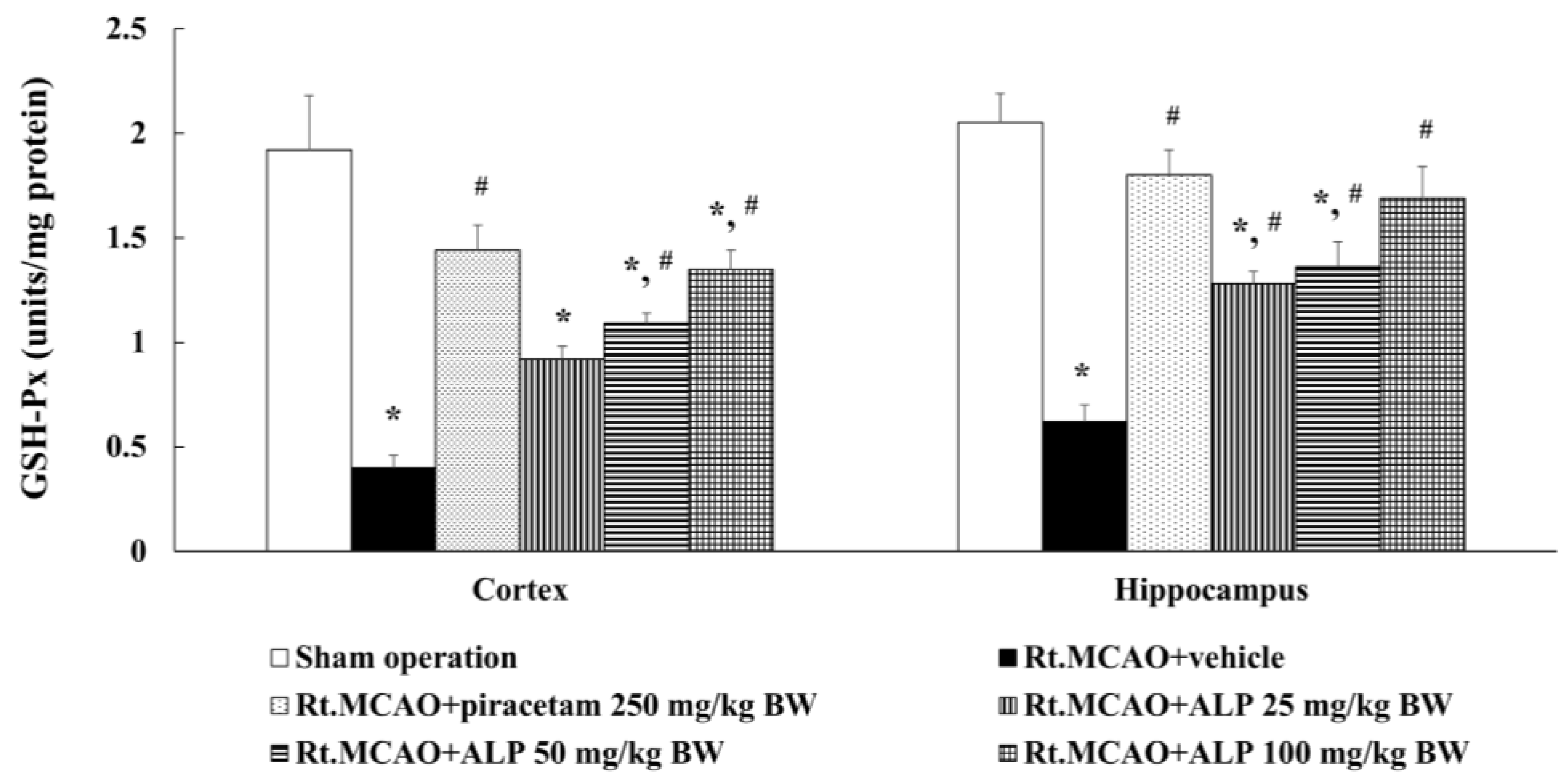
2.5. Alpinetin Enhanced Glutathione Peroxidase (GSH-Px) Levels in the Cortex and Hippocampus
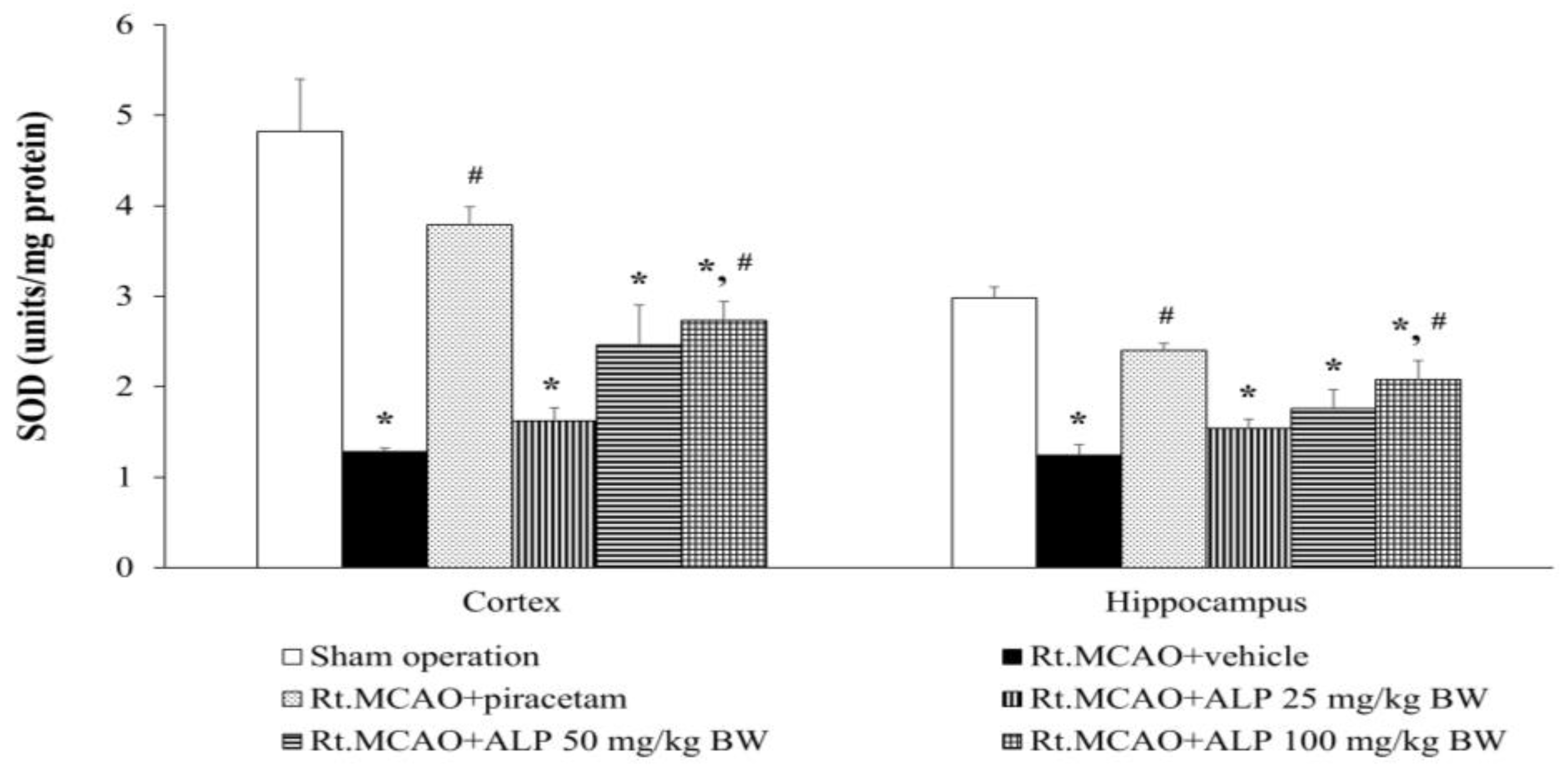
2.6. Alpinetin Improved Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Levels in the Cortex and Hippocampus
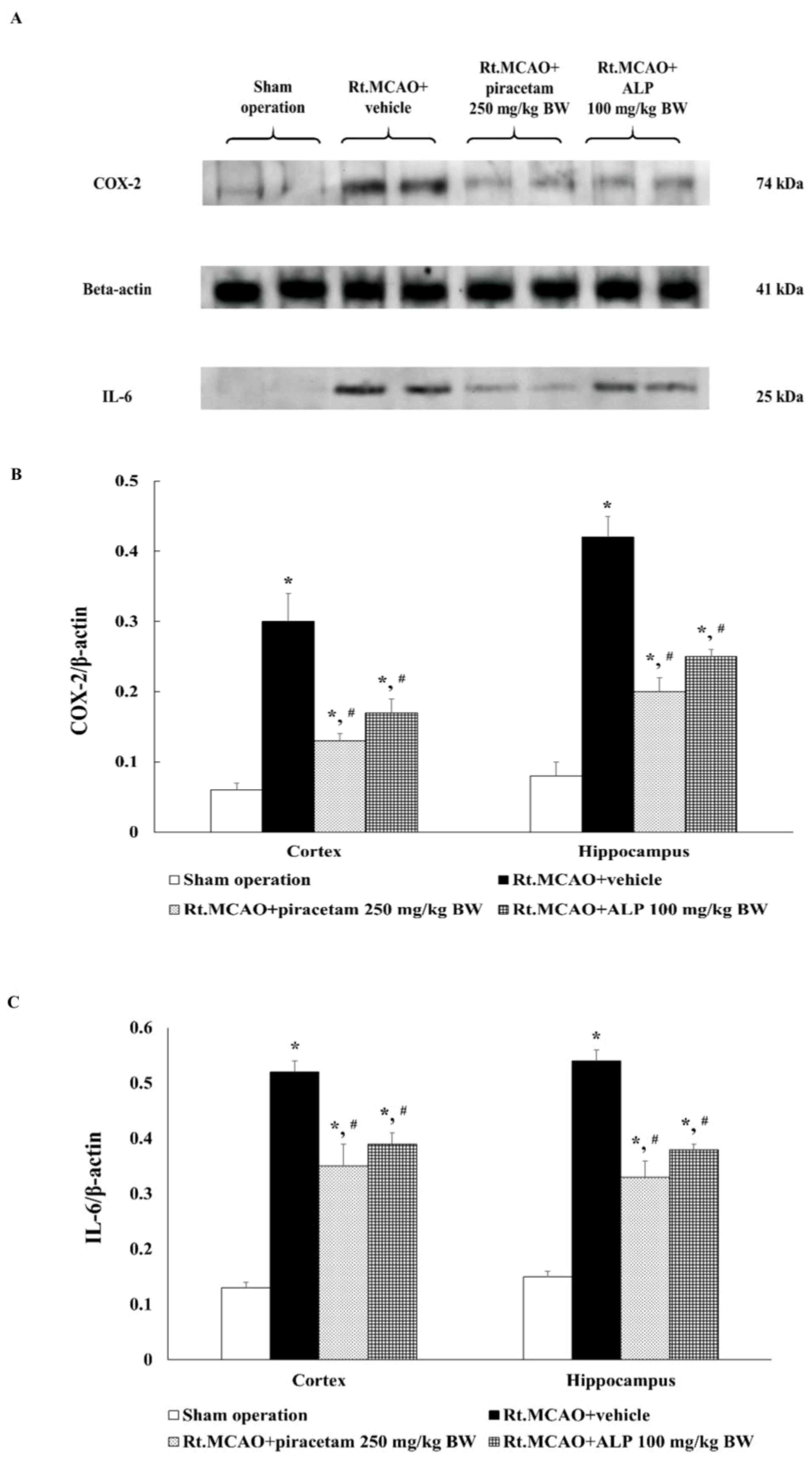
2.7. Alpinetin Regulated the Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and Interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the Cortex and Hippocampus
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
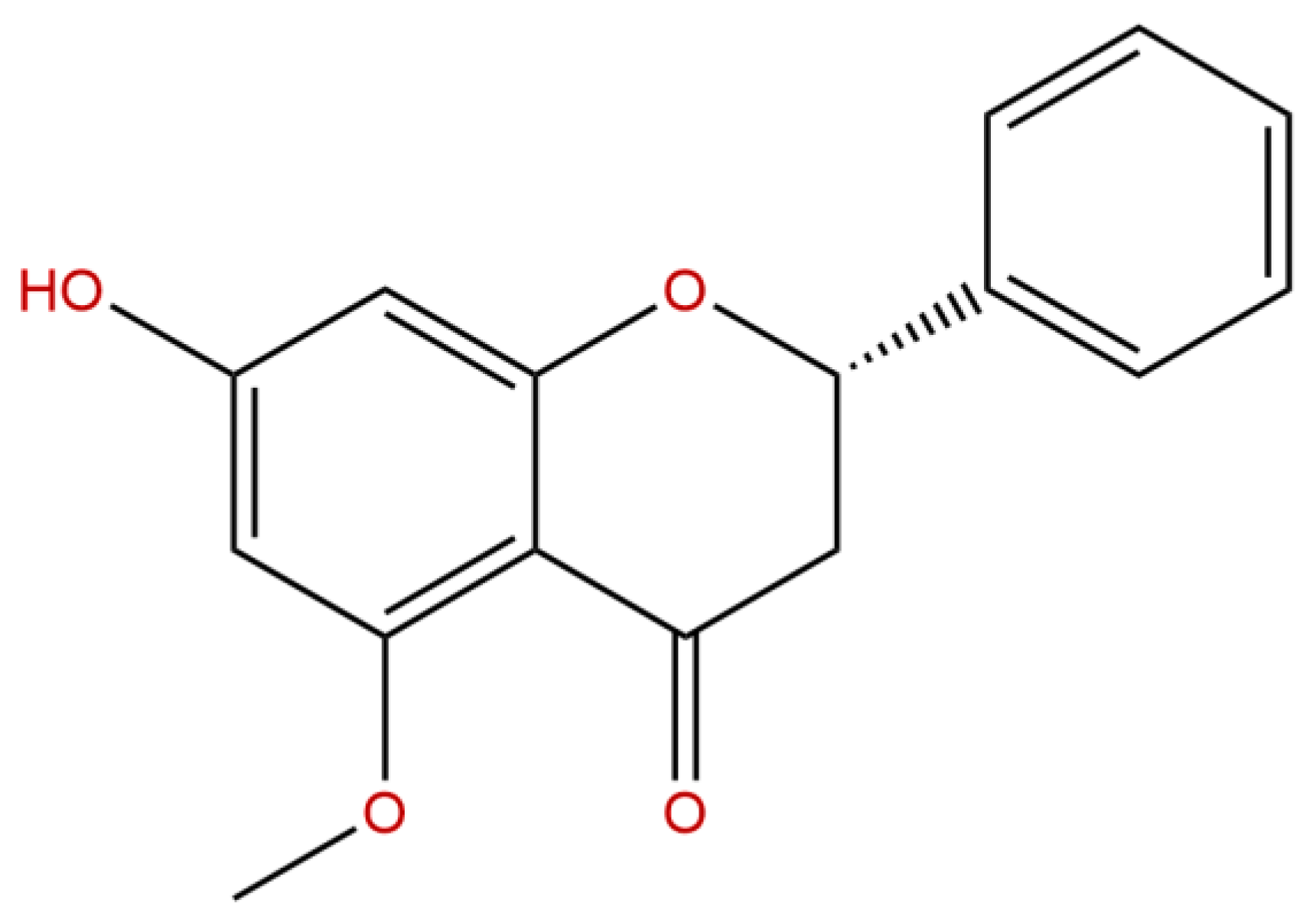
4.1. Treatment Substances
4.2. Animals
4.3. Rt.MACO Model
4.4. Animal Treatment
- Sham operation group: This group underwent sham surgery without insertion of the nylon filament and did not receive any treatment.
- Rt.MCAO+vehicle-treated group: In this group, all animals were subjected to Rt.MCAO by using the same procedure as described above. They received only the vehicle, which in this study was dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), administered i.p. at a volume of 0.5 mL once daily for three consecutive days. This group served as the vehicle control to evaluate the effects of the solvent.
- Rt.MCAO+piracetam 250 mg/kg BW-treated group: All animals in this group were subjected to Rt.MCAO and treated with piracetam at a dose of 250 mg/kg BW, administered i.p. once daily for three consecutive days. This group served as the positive control.
- Rt.MCAO+ALP 25 mg/kg BW-treated group: All animals in this group underwent Rt.MCAO and were treated with alpinetin at a dose of 25 mg/kg BW. The treatment was administered i.p. once daily for three consecutive days.
- Rt.MCAO+ALP 50 mg/kg BW-treated group: All animals in this group underwent Rt.MCAO and were treated with alpinetin at a dose of 50 mg/kg BW. The treatment was administered i.p. once daily for three consecutive days.
- Rt.MCAO+ALP 100 mg/kg BW-treated group: All animals in this group underwent Rt.MCAO and were treated with alpinetin at a dose of 100 mg/kg BW. The treatment was administered i.p. once daily for three consecutive days.
4.5. Assessment of Brain Infarct Volume
4.6. Assessment of Neuronal Density
4.7. Protein Quantification
4.8. Determination of MDA Level
4.9. Determination of CAT Activity
4.10. Determination of GSH-Px Activity
4.11. Determination of SOD Activity
4.12. Western Blot Analysis
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, Z.; Chaudhary, F.; Agrawal, D.K. Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Current Treatment Strategies in Stroke. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 8, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capirossi, C.; Laiso, A.; Renieri, L.; Capasso, F.; Limbucci, N. Epidemiology, organization, diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2023, 11, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MartInez-Coria, H.; Arrieta-Cruz, I.; Cruz, M.E.; Lopez-Valdes, H.E. Physiopathology of ischemic stroke and its modulation using memantine: Evidence from preclinical stroke. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.M.; Pennypacker, K.R. Targeting antioxidant enzyme expression as a therapeutic strategy for ischemic stroke. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 107, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Jung, U.J.; Kim, S.R. Role of Oxidative Stress in Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochhead, J.J.; Ronaldson, P.T.; Davis, T.P. The role of oxidative stress in blood-brain barrier disruption during ischemic stroke: Antioxidants in clinical trials. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 228, 116186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, U.C.; Bhol, N.K.; Swain, S.K.; Samal, R.R.; Nayak, P.K.; Raina, V.; Panda, S.K.; Kerry, R.G.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. Oxidative stress and inflammation in the pathogenesis of neurological disorders: Mechanisms and implications. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2025, 15, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawluk, H.; Tafelska-Kaczmarek, A.; Soponska, M.; Porzych, M.; Modrzejewska, M.; Pawluk, M.; Kurhaluk, N.; Tkaczenko, H.; Kolodziejska, R. The Influence of Oxidative Stress Markers in Patients with Ischemic Stroke. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, F.Z.; Lefter, R.; Jaber, H.; Balmus, I.M.; Ciobica, A.; Iordache, A.C. The Role of Potential Oxidative Biomarkers in the Prognosis of Acute Ischemic Stroke and the Exploration of Antioxidants as Possible Preventive and Treatment Options. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacila, C.I.; Vladoiu, M.G.; Valeanu, M.; Moga, D.F.; Pumnea, P.M. The Role of IL-6 and TNF-Alpha Biomarkers in Predicting Disability Outcomes in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. Life 2025, 15, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluk, H.; Woźniak, A.; Tafelska-Kaczmarek, A.; Kosinska, A.; Pawluk, M.; Sergot, K.; Grochowalska, R.; Kołodziejska, R. The Role of IL-6 in Ischemic Stroke. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, P.J.; Lemmens, R.; Tsivgoulis, G. Inflammation and Stroke Risk: A New Target for Prevention. Stroke 2021, 52, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Dar, N.J.; Bhat, Z.S.; Hussain, A.; Shah, A.; Liu, H.; Graham, S.H. Inflammation in ischemic stroke: Mechanisms, consequences and possible drug targets. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 1378–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palachai, N.; Supawat, A.; Kongsui, R.; Klimaschewski, L.; Jittiwat, J. Galangin’s Neuroprotective Role: Targeting Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Ischemic Stroke in a Rat Model of Permanent Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongsui, R.; Jittiwat, J. Ameliorative effects of 6-gingerol in cerebral ischemia are mediated via the activation of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways. Biomed. Rep. 2023, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, S.; Dong, S.; Jin, S.; Li, Q. Flavonoids Derived from Chinese Medicine: Potential Neuroprotective Agents. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2024, 52, 1613–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Alomar, S.Y.; Valko, R.; Liska, J.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Flavonoids and their role in oxidative stress, inflammation, and human diseases. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2025, 413, 111489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauzour, D.; Vafeiadou, K.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Rendeiro, C.; Spencer, J.P. The neuroprotective potential of flavonoids: A multiplicity of effects. Genes. Nutr. 2008, 3, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Chhabra, V.; Shenoy, S.; Daksh, R.; Ravichandiran, V.; Swamy, R.S.; Kumar, N. Role of Flavonoids in Modulation of Mitochondria Dynamics during Oxidative Stress. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2024, 24, 908–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidfar, M.; Garcez, M.L.; Askari, G.; Bagherniya, M.; Khorvash, F.; Golpour-Hamedani, S.; de Oliveira, J. Role of BDNF Signaling in the Neuroprotective and Memory-enhancing Effects of Flavonoids in Alzheimer’s Disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2024, 23, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, J.N.; Mumtaz, S. Prunin: An Emerging Anticancer Flavonoid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Shen, Y.J.; Chen, M.; Zhao, J.Y.; Chen, S.H.; Zhang, W.; Song, J.K.; Li, L.; Du, G.H. Quercetin attenuates ischemia reperfusion injury by protecting the blood-brain barrier through Sirt1 in MCAO rats. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 24, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, S.; Jonecova, Z.; Curgali, K.; Maretta, M.; Soltes, J.; Svana, M.; Kalpadikis, T.; Caprnda, M.; Adamek, M.; Rodrigo, L.; et al. Quercetin attenuates the ischemia reperfusion induced COX-2 and MPO expression in the small intestine mucosa. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Men, W.; Shan, X.; Zhai, H.; Qiao, X.; Geng, L.; Li, C. Baicalein exerts neuroprotective effect against ischaemic/reperfusion injury via alteration of NF-kB and LOX and AMPK/Nrf2 pathway. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 1327–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Tong, Y.; Luan, F.; Zhu, W.; Zhan, C.; Qin, T.; An, W.; Zeng, N. Alpinetin: A Review of Its Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 814370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radosavljevic, T.; Brankovic, M.; Djuretic, J.; Grujic-Milanovic, J.; Kovacic, M.; Jevtic, J.; Stankovic, S.; Samardzic, J.; Vucevic, D.; Jakovljevic, V. Alpinetin Exhibits Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in C57BL/6 Mice with Alcoholic Liver Disease Induced by the Lieber-DeCarli Ethanol Liquid Diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 26, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, S.; He, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, L. Alpinetin Protects Chondrocytes and Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory Effects via the NF-kappaB/ERK Pathway for Alleviating Osteoarthritis. Inflammation 2020, 43, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Jiang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhou, E.; Wei, Z.; et al. Alpinetin prevents inflammatory responses in OVA-induced allergic asthma through modulating PI3K/AKT/NF-kappaB and HO-1 signaling pathways in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 89, 107073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Maqbool, M.F.; Zheng, D.; Li, Y.; Khan, M.; Ma, T. Alpinetin: A Dietary Flavonoid with Diverse Anticancer Effects. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 4220–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraj, R.L.; Azimullah, S.; Beiram, R.; Jalal, F.Y.; Rosenberg, G.A. Neuroinflammation: Friend and foe for ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffer, H.; Morris, V.B.; Stewart, D.; Labhasetwar, V. Advances in stroke therapy. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2011, 1, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabih, A.; Tadi, P.; Kumar, A. Stroke Prevention. In StatPearls; Ineligible Companies: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, H.C.; Parziali, M.; Danielsson, A.; Sunnerhagen, K.S. Outcome and upper extremity function within 72 h after first occasion of stroke in an unselected population at a stroke unit. A part of the SALGOT study. BMC Neurol. 2012, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inacio, A.R.; Bucala, R.; Deierborg, T. Lack of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in mice does not affect hallmarks of the inflammatory/immune response during the first week after stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masztalewicz, M.; Nowacki, P.; Turowska-Kowalska, J.; Safranow, K. Peripheral blood indicators of inflammatory response during the first twenty-four hours of ischemic stroke. Ann. Acad. Med. Stetin. 2010, 56, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Shaheryar, Z.A.; Khan, M.A.; Adnan, C.S.; Zaidi, A.A.; Hanggi, D.; Muhammad, S. Neuroinflammatory Triangle Presenting Novel Pharmacological Targets for Ischemic Brain Injury. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 748663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciumarnean, L.; Milaciu, M.V.; Runcan, O.; Vesa, S.C.; Rachisan, A.L.; Negrean, V.; Perne, M.G.; Donca, V.I.; Alexescu, T.G.; Para, I.; et al. The Effects of Flavonoids in Cardiovascular Diseases. Molecules 2020, 25, 4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.T.; Lau, C.W.; Chan, F.L.; Yao, X.; Chen, Z.Y.; He, Z.D.; Huang, Y. Vasorelaxant effects of cardamonin and alpinetin from Alpinia henryi K. Schum. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2001, 37, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaudeen, M.A.; Bello, N.; Danraka, R.N.; Ammani, M.L. Understanding the Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke: The Basis of Current Therapies and Opportunity for New Ones. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dajas, F. Life or death: Neuroprotective and anticancer effects of quercetin. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 143, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.J.; Chen, T.H.; Yang, L.Y.; Shih, C.M. Resveratrol protects astrocytes against traumatic brain injury through inhibiting apoptotic and autophagic cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Simonyi, A.; Lubahn, D.; Sun, G.Y.; Sun, A.Y. Resveratrol protects against global cerebral ischemic injury in gerbils. Brain Res. 2002, 958, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supawat, A.; Palachai, N.; Jittiwat, J. Effect of galangin on oxidative stress, antioxidant defenses and mitochondrial dynamics in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Biomed. Rep. 2025, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yue, H.; Jiang, N.; Qiao, L. Diet, oxidative stress and MAFLD: A mini review. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1539578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, V.; Duennwald, M.L. Nrf2 and Oxidative Stress: A General Overview of Mechanisms and Implications in Human Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, R.; Fernandez-Gajardo, R.; Gutierrez, R.; Matamala, J.M.; Carrasco, R.; Miranda-Merchak, A.; Feuerhake, W. Oxidative stress and pathophysiology of ischemic stroke: Novel therapeutic opportunities. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 12, 698–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yoshioka, H.; Kim, G.S.; Jung, J.E.; Okami, N.; Sakata, H.; Maier, C.M.; Narasimhan, P.; Goeders, C.E.; Chan, P.H. Oxidative stress in ischemic brain damage: Mechanisms of cell death and potential molecular targets for neuroprotection. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2011, 14, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Hu, R.; Li, J.; Xing, X.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, J. Alpinetin exerts anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative and anti-angiogenic effects through activating the Nrf2 pathway and inhibiting NLRP3 pathway in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dessouki, A.M.; Alzokaky, A.A.; Raslan, N.A.; Ibrahim, S.; Salama, L.A.; Yousef, E.H. Piracetam mitigates nephrotoxicity induced by cisplatin via the AMPK-mediated PI3K/Akt and MAPK/JNK/ERK signaling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 137, 112511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheble, P.C.; Sena, E.S.; Macleod, M.R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy of piracetam and piracetam-like compounds in experimental stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2008, 25, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortiglione, A.; Minale, M.; Pignataro, G.; Amoroso, S.; DiRenzo, G.; Annunziato, L. The 2-oxopyrrolidinacetamide piracetam reduces infarct brain volume induced by permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in male rats. Neuropharmacology 2002, 43, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jittiwat, J.; Suksamrarn, A.; Tocharus, C.; Tocharus, J. Dihydrocapsaicin effectively mitigates cerebral ischemia-induced pathological changes in vivo, partly via antioxidant and anti-apoptotic pathways. Life Sci. 2021, 283, 119842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Dhapola, R.; Sharma, P.; Nagar, P.; Medhi, B.; HariKrishnaReddy, D. The impact of cytokines in neuroinflammation-mediated stroke. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2024, 78, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.H.; Pei, K.; Zhao, T.T.; Li, H.C.; Li, Q.Q.; Zhou, W.J.; He, W.B.; Zhang, J.L. Protective effect of Liujing Toutong Tablets on rats with permanent cerebral ischemia via NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2023, 48, 5871–5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, D.; Yin, T.; Smalstig, E.B.; Hsu, M.A.; Panetta, J.; Little, S.; Clemens, J. Transcription factor nuclear factor-kappa B is activated in neurons after focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2000, 20, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietzau, G.; Sienkiewicz, W.; Karwacki, Z.; Dziewiatkowski, J.; Kaleczyc, J.; Kowianski, P. The Effect of Simvastatin on the Dynamics of NF-kappaB-Regulated Neurodegenerative and Neuroprotective Processes in the Acute Phase of Ischemic Stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 4935–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmi, A.; Lindsberg, P.J.; Koistinaho, M.; Zhang, W.; Juettler, E.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.L.; Weih, F.; Frank, N.; Schwaninger, M.; Koistinaho, J. Nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to infarction after permanent focal ischemia. Stroke 2004, 35, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotgiu, S.; Zanda, B.; Marchetti, B.; Fois, M.L.; Arru, G.; Pes, G.M.; Salaris, F.S.; Arru, A.; Pirisi, A.; Rosati, G. Inflammatory biomarkers in blood of patients with acute brain ischemia. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, A.; Tong, W.; Xiong, X.; Nie, J.; Zhong, N.; Zhu, G.; Liu, J.; et al. Alpinetin inhibits neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis via targeting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in spinal cord injury. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotelle, N. Role of flavonoids in oxidative stress. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2001, 1, 569–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MohanKumar, S.M.J.; Murugan, A.; Palaniyappan, A.; MohanKumar, P.S. Role of cytokines and reactive oxygen species in brain aging. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2023, 214, 111855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, D.; Mao, Q.; Xia, H. Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegeneration development. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Du, G.H. Effects of alpinetin on rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2004, 6, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Tao, X.; Xu, J. Protective effect of Alpinetin on rats with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 6603–6611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Shi, C.; Qiao, S.; Cao, N.; Guan, C.; Dai, Y.; Wei, Z. Alpinetin exerts anti-colitis efficacy by activating AhR, regulating miR-302/DNMT-1/CREB signals, and therefore promoting Treg differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, J.; Kou, J.; Liu, W.; Fu, Y.; Yang, Z. Alpinetin attenuates inflammatory responses by suppressing TLR4 and NLRP3 signaling pathways in DSS-induced acute colitis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jittiwat, J. Baihui Point Laser Acupuncture Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment, Motor Deficit, and Neuronal Loss Partly via Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in an Animal Model of Focal Ischemic Stroke. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2019, 2019, 1204709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanathorn, J.; Jittiwat, J.; Tongun, T.; Muchimapura, S.; Ingkaninan, K. Zingiber officinale Mitigates Brain Damage and Improves Memory Impairment in Focal Cerebral Ischemic Rat. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2011, 2011, 429505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxide in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblith, S.A.; Proctor, B.E. Photometric determination of catalase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1950, 187, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group Number | Group Name | Treatment | Dose (mg/kg BW) | Route of Administration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sham operation group | - | - | - |
| 2 | Rt.MCAO+vehicle-treated group | vehicle | 1% DMSO | i.p. |
| 3 | Rt.MCAO+piracetam 250 mg/kg BW-treated group | piracetam | 250 mg/kg BW | i.p. |
| 4 | Rt.MCAO+ALP 25 mg/kg BW-treated group | alpinetin | 25 mg/kg BW | i.p. |
| 5 | Rt.MCAO+ALP 50 mg/kg BW-treated group | alpinetin | 50 mg/kg BW | i.p. |
| 6 | Rt.MCAO+ALP 100 mg/kg BW-treated group | alpinetin | 100 mg/kg BW | i.p. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kongsui, R.; Thongrong, S.; Jittiwat, J. In Vivo Neuroprotective Effects of Alpinetin Against Experimental Ischemic Stroke Damage Through Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115093
Kongsui R, Thongrong S, Jittiwat J. In Vivo Neuroprotective Effects of Alpinetin Against Experimental Ischemic Stroke Damage Through Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115093
Chicago/Turabian StyleKongsui, Ratchaniporn, Sitthisak Thongrong, and Jinatta Jittiwat. 2025. "In Vivo Neuroprotective Effects of Alpinetin Against Experimental Ischemic Stroke Damage Through Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115093
APA StyleKongsui, R., Thongrong, S., & Jittiwat, J. (2025). In Vivo Neuroprotective Effects of Alpinetin Against Experimental Ischemic Stroke Damage Through Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115093







