Dermatophagoides farinae Extract Induces Interleukin 33-Mediated Atopic Skin Inflammation via Activation of RIP1
Abstract
1. Introduction
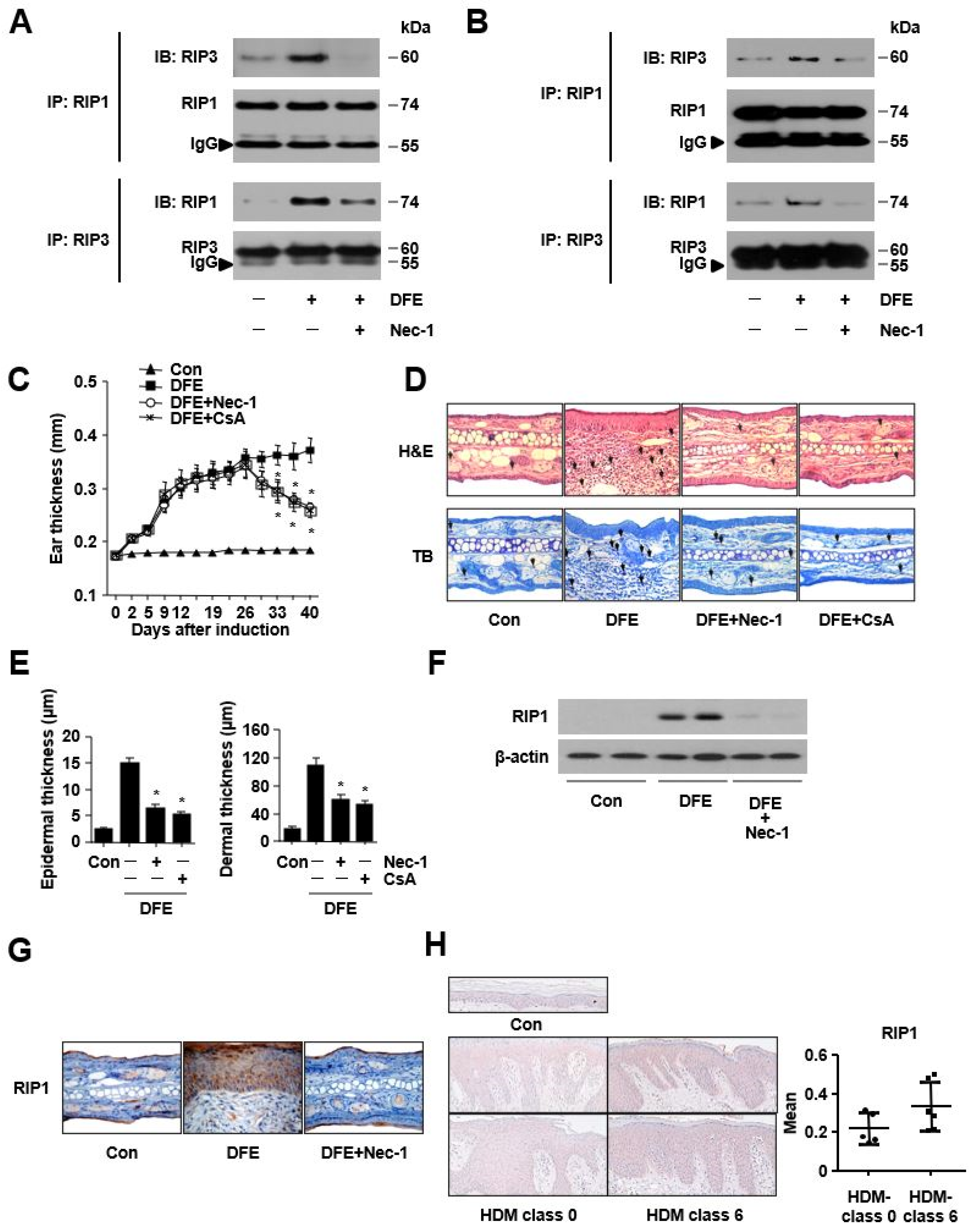
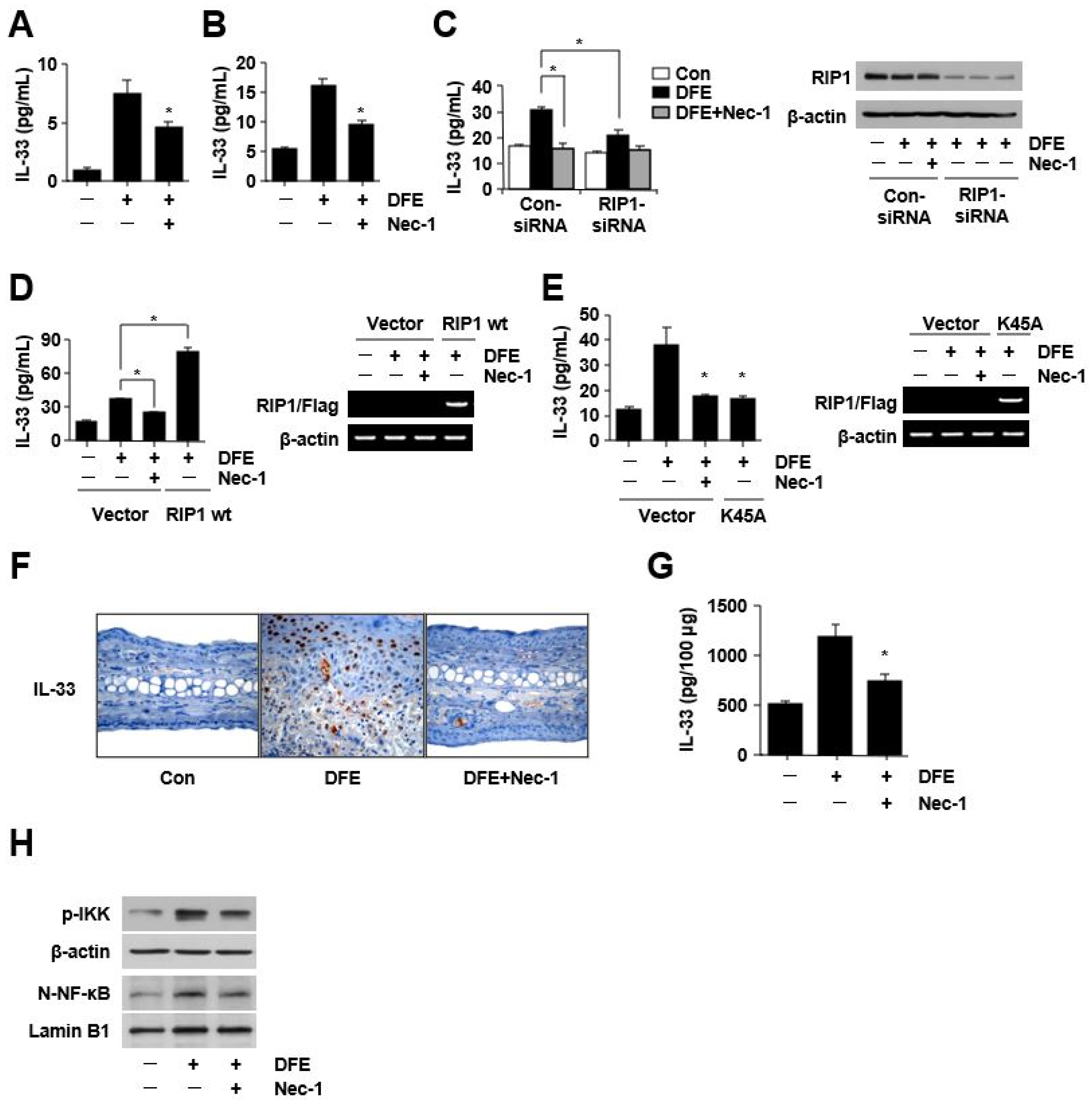
2. Results
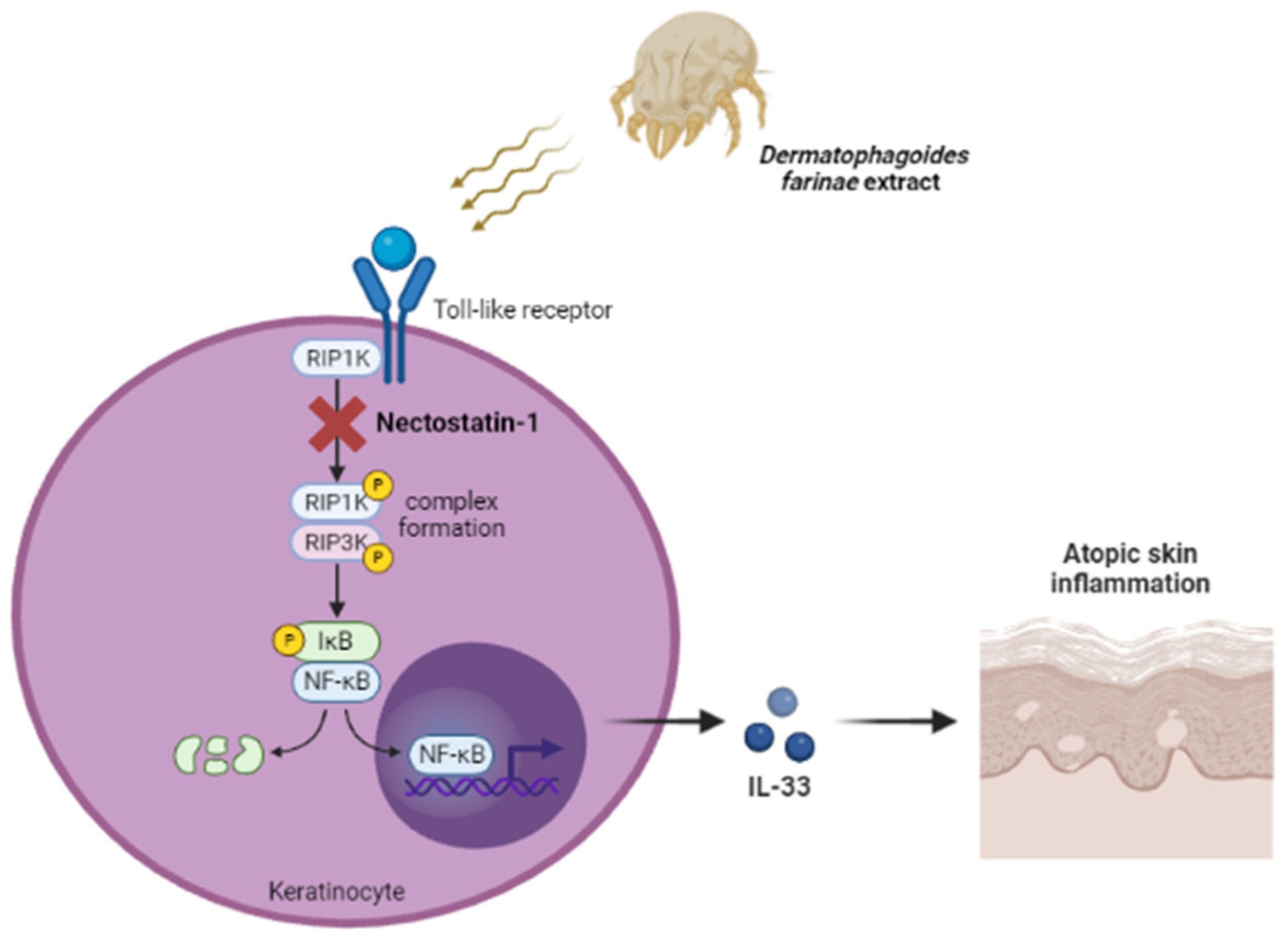
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Animals
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Human Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Skin
4.5. Development of DFE-Induced Atopic Skin Inflammation in Mouse Ear
4.6. Immunoprecipitation and Immunoblotting
4.7. Histological Analysis
4.8. Immunohistochemistry Analysis
4.9. qPCR
4.10. ELISA
4.11. Transfection of Keratinocytes with Small Interfering RNA (siRNA)
4.12. Transfection
4.13. Histamine Assay
4.14. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.15. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humphries, F.; Yang, S.; Wang, B.; Moynagh, P.N. RIP kinases: Key decision makers in cell death and innate immunity. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinlich, R.; Oberst, A.; Beere, H.M.; Green, D.R. Necroptosis in development, inflammation and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofengeim, D.; Yuan, J. Regulation of RIP1 kinase signalling at the crossroads of inflammation and cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, I.H.; Yoshida, T.; De Benedetto, A.; Beck, L.A. The cutaneous innate immune response in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trautmann, A.; Akdis, M.; Schmid-Grendelmeier, P.; Disch, R.; Brocker, E.B.; Blaser, K.; Blaser, K.; Akdis, C.A. Targeting keratinocyte apoptosis in the treatment of atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. IL-33: An alarmin cytokine with crucial roles in innate immunity, inflammation and allergy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 31, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.H.; Choi, J.K.; Jin, M.; Choi, Y.A.; Ryoo, Z.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Park, P.-H.; Kim, S.-U.; Kwon, T.K.; Jang, M.H.; et al. House Dust Mite Increases pro-Th2 Cytokines IL-25 and IL-33 via the Activation of TLR1/6 Signaling. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2354–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Fuente, M.; MacDonald, T.T.; Hermoso, M.A. The IL-33/ST2 axis: Role in health and disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Rape, M. Building ubiquitin chains: E2 enzymes at work. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhuriya, Y.K.; Sharma, D. Necroptosis: A regulated inflammatory mode of cell death. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Berger, S.B.; Jeong, J.U.; Nagilla, R.; Bandyopadhyay, D.; Campobasso, N.; Capriotti, C.; Cox, J.; Dare, L.; Dong, X.; et al. Discovery of a First-in-Class Receptor Interacting Protein 1 (RIP1) Kinase Specific Clinical Candidate (GSK2982772) for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1247–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Tang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yang, S.; Wang, D. Role of necroptosis in infection-related, immune-mediated, and autoimmune skin diseases. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Mu, W. Necrostatin-1 and necroptosis inhibition: Pathophysiology and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 163, 105297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquet, A. Innate immune responses in house dust mite allergy. ISRN Allergy 2013, 2013, 735031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roan, F.; Obata-Ninomiya, K.; Ziegler, S.F. Epithelial cell-derived cytokines: More than just signaling the alarm. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallrapp, A.; Riesenfeld, S.J.; Burkett, P.R.; Kuchroo, V.K. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells in the induction and resolution of tissue inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 286, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Tohyama, M.; Murakami, M.; Shiraishi, K.; Liu, S.; Mori, H.; Utsunomiya, R.; Maeyama, K.; Sayama, K. House dust mite allergens induce interleukin 33 (IL-33) synthesis and release from keratinocytes via ATP-mediated extracellular signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aasen, T.; Izpisua Belmonte, J.C. Isolation and cultivation of human keratinocytes from skin or plucked hair for the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Choi, J.K.; Choi, Y.A.; Kim, Y.Y.; Baek, M.C.; Lee, B.H.; Jang, Y.H.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, D.W. 1,2,4,5-Tetramethoxybenzene Suppresses House Dust Mite-Induced Allergic Inflammation in BALB/c Mice. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 170, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, M.; Bang, J.S.; Ha, D.-L.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, K.D.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, S.-J.; Choi, J.K.; Choi, Y.-A.; Jang, Y.H.; et al. Dermatophagoides farinae Extract Induces Interleukin 33-Mediated Atopic Skin Inflammation via Activation of RIP1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065228
Jin M, Bang JS, Ha D-L, Kim JY, Park KD, Lee WJ, Lee S-J, Choi JK, Choi Y-A, Jang YH, et al. Dermatophagoides farinae Extract Induces Interleukin 33-Mediated Atopic Skin Inflammation via Activation of RIP1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(6):5228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065228
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Meiling, Jin Seon Bang, Dae-Lyong Ha, Jun Young Kim, Kyung Duck Park, Weon Ju Lee, Seok-Jong Lee, Jin Kyeong Choi, Young-Ae Choi, Yong Hyun Jang, and et al. 2023. "Dermatophagoides farinae Extract Induces Interleukin 33-Mediated Atopic Skin Inflammation via Activation of RIP1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 6: 5228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065228
APA StyleJin, M., Bang, J. S., Ha, D.-L., Kim, J. Y., Park, K. D., Lee, W. J., Lee, S.-J., Choi, J. K., Choi, Y.-A., Jang, Y. H., & Kim, S.-H. (2023). Dermatophagoides farinae Extract Induces Interleukin 33-Mediated Atopic Skin Inflammation via Activation of RIP1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 5228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065228






