Chronic Voluntary Alcohol Consumption Alters Promoter Methylation and Expression of Fgf-2 and Fgfr1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
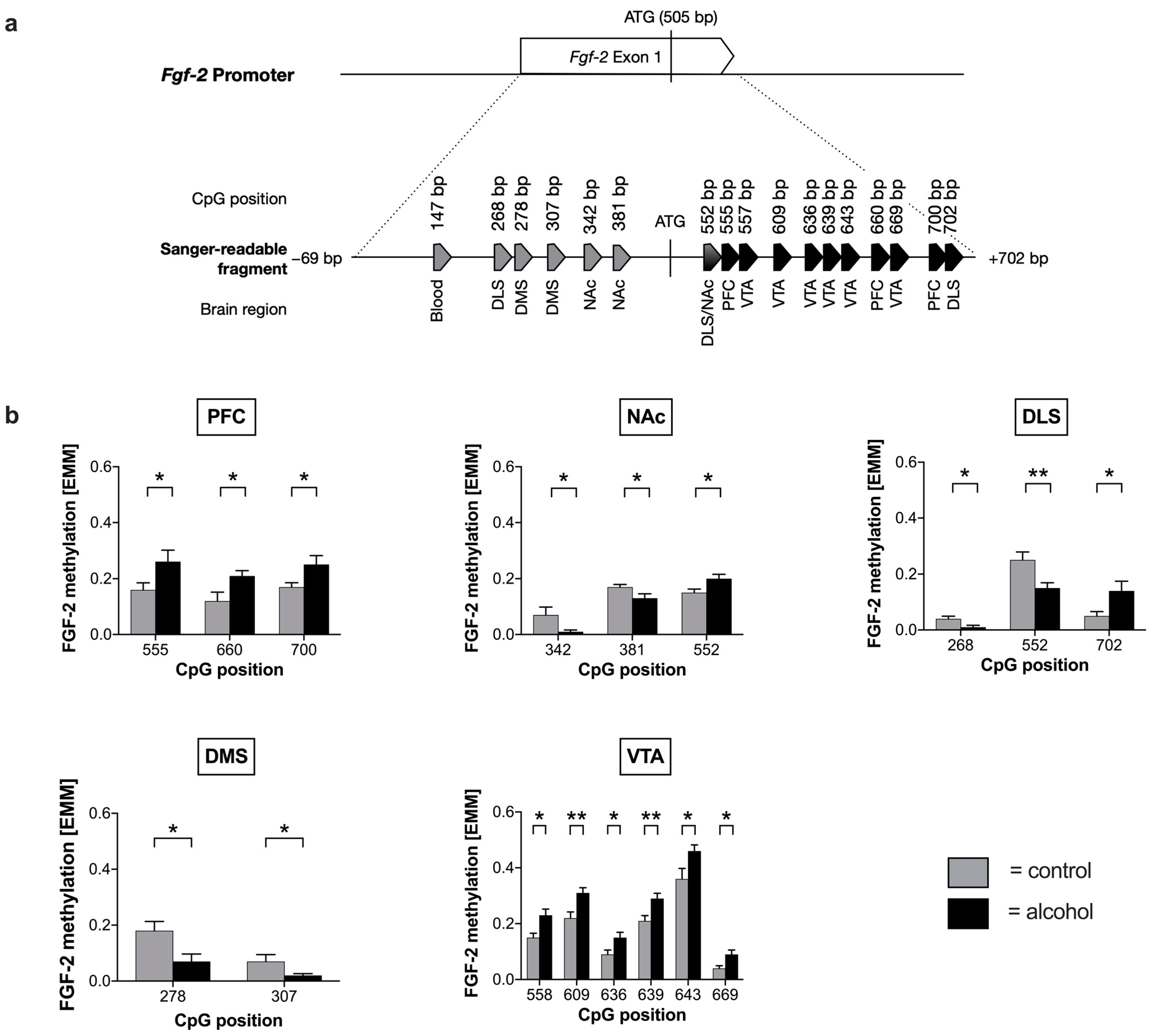
2.1. Voluntary Alcohol Drinking Alters Promoter Methylation and Expression of Fgf-2 in a Brain Region-Specific Manner
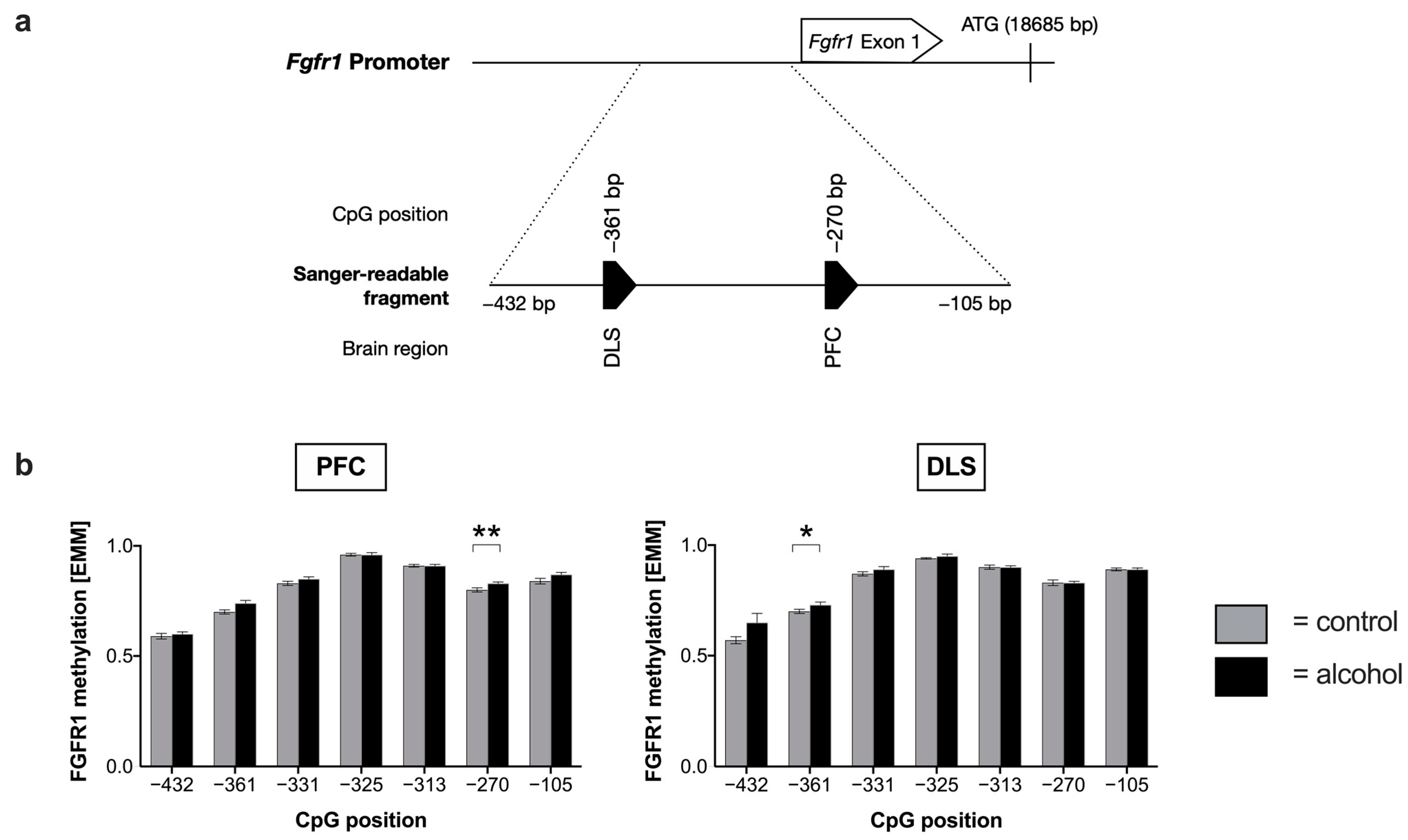
2.2. Effects of Chronic Alcohol Consumption of Fgfr1 Promotor Methylation and Expression
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Animals
4.3. Intermittent Access to 20% (v/v) Alcohol in Two-Bottle Choice (IA2BC)
4.4. Tissue Processing
4.5. Bisulfite Conversion of DNA, PCR Strategy, and Sequencing
4.6. Transcription Factor Analysis
4.7. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2018; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fuster, D.; Samet, J.H. Alcohol Use in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koob, G.F. The dark side of emotion: The addiction perspective. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 753, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ron, D.; Barak, S. Molecular mechanisms underlying alcohol-drinking behaviours. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koob, G.F.; Volkow, N.D. Neurocircuitry of Addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, R.A. Roles for nigrostriatal—Not just mesocorticolimbic—Dopamine in reward and addiction. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.F.; Heilig, M.; Perez, A.; Probst, C.; Rehm, J. Alcohol use disorders. Lancet 2019, 394, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, B.J.; Robbins, T.W. From the ventral to the dorsal striatum: Devolving views of their roles in drug addiction. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.; Sinha, R. The neurobiology of alcohol craving and relapse. Handb. Clin. Neurobiol. 2014, 125, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahao, K.P.; Salinas, A.G.; Lovinger, D.M. Alcohol and the Brain: Neuronal Molecular Targets, Synapses, and Circuits. Neuron 2017, 96, 1223–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, M.; Müller-Ostermeyer, F.; Kloth, V.; Winkler, C.; Grothe, C.; Nikkhah, G. Enhanced survival, reinnervation, and functional recovery of intrastriatal dopamine grafts co-transplanted with Schwann cells overexpressing high molecular weight FGF-2 isoforms. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 187, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, M.; Cesnulevicius, K.; Winkler, C.; Kolb, J.; Lipokatic-Takacs, E.; Jungnickel, J.; Grothe, C. Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF)-2 and FGF Receptor 3 Are Required for the Development of the Substantia Nigra, and FGF-2 Plays a Crucial Role for the Rescue of Dopaminergic Neurons after 6-Hydroxydopamine Lesion. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grothe, C.; Timmer, M. The physiological and pharmacological role of basic fibroblast growth factor in the dopaminergic nigrostriatal system. Brain Res. Rev. 2007, 54, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimaschewski, L.; Claus, P. Fibroblast Growth Factor Signalling in the Diseased Nervous System. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 3884–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratzka, A.; Baron, O.; Stachowiak, M.K.; Grothe, C. Fibroblast growth factor 2 regulates dopaminergic neuron development in vivo. J. Neurochem. 2012, 122, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, O.; Ratzka, A.; Grothe, C. Fibroblast growth factor 2 regulates adequate nigrostriatal pathway formation in mice. J. Comp. Neurol. 2012, 520, 3949–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpel, R.; Baron, O.; Ratzka, A.; Schröder, M.-L.; Hohmann, M.; Effenberg, A.; Claus, P.; Grothe, C. Increased innervation of forebrain targets by midbrain dopaminergic neurons in the absence of FGF-2. Neuroscience 2016, 314, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.M.; Berry, M.; Maher, P.A.; Logan, A.; Baird, A. A comprehensive analysis of the distribution of FGF-2 and FGFR1 in the rat brain. Brain Res. 1995, 701, 201–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuss, B.; Unsicker, K. Survival and Differentiation of Dopaminergic Mesencephalic Neurons Are Promoted by Dopamine-Mediated Induction of FGF-2 in Striatal Astroglial Cells. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2000, 16, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Hövel, F.F.; Kefalakes, E.; Grothe, C. What Can We Learn from FGF-2 Isoform-Specific Mouse Mutants? Differential Insights into FGF-2 Physiology In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Chen, Y. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors (FGFRs): Structures and Small Molecule Inhibitors. Cells 2019, 8, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beenken, A.; Mohammadi, M. The FGF family: Biology, pathophysiology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numakawa, T.; Suzuki, S.; Kumamaru, E.; Adachi, N.; Richards, M.; Kunugi, H. BDNF function and intracellular signaling in neurons. Histol. Histopathol. 2010, 25, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuss, B.; Halbach, O.V.B.U. Fibroblast growth factors and their receptors in the central nervous system. Cell Tissue Res. 2003, 313, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornitz, D.M.; Itoh, N. The Fibroblast Growth Factor signaling pathway. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2015, 4, 215–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Even-Chen, O.; Barak, S. Inhibition of FGF Receptor-1 Suppresses Alcohol Consumption: Role of PI3 Kinase Signaling in Dorsomedial Striatum. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 7947–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Even-Chen, O.; Sadot-Sogrin, Y.; Shaham, O.; Barak, S. Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 in the Dorsomedial Striatum Is a Novel Positive Regulator of Alcohol Consumption. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 8742–8754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisano, M.; Pandey, S.C. Epigenetic mechanisms of alcoholism and stress-related disorders. Alcohol 2017, 60, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberlein, A.; Muschler, M.; Frieling, H.; Behr, M.; Eberlein, C.; Wilhelm, J.; Gröschl, M.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S.; Hillemacher, T. Epigenetic down regulation of nerve growth factor during alcohol withdrawal. Addict. Biol. 2011, 18, 508–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberlein, A.; Büscher, P.; Schuster, R.; Kleimann, A.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Rhein, M.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S.; Frieling, H.; Hillemacher, T. Do changes in the BDNF promoter methylation indicate the risk of alcohol relapse. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 1892–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillemacher, T.; Frieling, H.; Hartl, T.; Wilhelm, J.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S. Promoter specific methylation of the dopamine transporter gene is altered in alcohol dependence and associated with craving. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2009, 43, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnicella, S.; Ron, D.; Barak, S. Intermittent ethanol access schedule in rats as a preclinical model of alcohol abuse. Alcohol 2014, 48, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Even-Chen, O.; Herburg, L.; Kefalakes, E.; Urshansky, N.; Grothe, C.; Barak, S. FGF2 is an endogenous regulator of alcohol reward and consumption. Addict. Biol. 2021, 27, e13115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodbury, M.E.; Ikezu, T. Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 Signaling in Neurogenesis and Neurodegeneration. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwa, L.S.; Chu, A.; Levinson, S.A.; Kayyali, T.M.; DeBold, J.F.; Miczek, K.A. Persistent Escalation of Alcohol Drinking in C57BL/6J Mice With Intermittent Access to 20% Ethanol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 1938–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.F.; Le Moal, M. Drug Abuse: Hedonic Homeostatic Dysregulation. Science 1997, 278, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.A. Functions of DNA methylation: Islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciafrè, S.; Carito, V.; Ferraguti, G.; Greco, A.; Chaldakov, G.N.; Fiore, M.; Ceccanti, M. How alcohol drinking affects our genes: An epigenetic point of view. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponomarev, I.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Harris, R.A.; Mayfield, R.D. Gene Coexpression Networks in Human Brain Identify Epigenetic Modifications in Alcohol Dependence. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 1884–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangra, A.; Sriram, C.S.; Pandey, S.; Choubey, P.; Rajput, P.; Saroha, B.; Bezbaruah, B.K.; Lahkar, M. Epigenetic Modifications, Alcoholic Brain and Potential Drug Targets. Ann. Neurosci. 2016, 23, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenisch, R.; Bird, A. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: How the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.B.; Neyazi, M.; Neyazi, A.; Hillemacher, T.; Pathak, H.; Rhein, M.; Bleich, S.; Goltseker, K.; Sadot-Sogrin, Y.; Even-Chen, O.; et al. Alcohol consumption alters Gdnf promoter methylation and expression in rats. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 121, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, S.J.; Haile, C.N.; Quave, C.B.; Harding, M.J.; Nielsen, D.A.; Meisch, R.A.; Kosten, T.A. Paternal alcohol exposure reduces acquisition of operant alcohol self-administration and affects Bdnf DNA methylation in male and female offspring. Addict. Biol. 2022, 27, e13078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duclot, F.; Kabbaj, M. The Role of Early Growth Response 1 (EGR1) in Brain Plasticity and Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Xu, X.; He, J.; Murray, A.; Sun, M.-A.; Wei, X.; Wang, X.; McCoig, E.; Xie, E.; Jiang, X.; et al. EGR1 recruits TET1 to shape the brain methylome during development and upon neuronal activity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biesiada, E.; Razandi, M.; Levin, E.R. Egr-1 activates basic fibroblast growth factor transcription: Mechanistic implications for astrocyte proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 18576–18581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasumarthi, K.; Jin, Y.; Cattini, P.A. Cloning of the Rat Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 Promoter Region and Its Response to Mitogenic Stimuli in Glioma C6 Cells. J. Neurochem. 1997, 68, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florkiewicz, R.Z.; Shibata, F.; Barankiewicz, T.; Baird, A.; Gonzalez, A.-M.; Florkiewicz, E.; Shah, N. Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Gene Expression. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1991, 638, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, S.K.; Detillieux, K.A.; Dhaliwal, J.; Kardami, E.; Sheikh, F.; Jin, Y.; Cattini, P.A. Transcriptional regulation of FGF-2 gene expression in cardiac myocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 62, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xu, Y.; Ayrapetov, M.K.; Moreau, L.A.; Whetstine, J.R.; Price, B.D. Histone H3 methylation links DNA damage detection to activation of the tumour suppressor Tip60. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1376–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Calame, K. An analysis of genes regulated by the multi-functional transcriptional regulator Yin Yang-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 5151–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Song, E.H.; Park, K.J.; Kim, G.H.; Jeong, E.A.; Lee, Y.J.; Go, M.J.; Kim, D.J.; et al. Chronic Ethanol Consumption Inhibits Glucokinase Transcriptional Activity by Atf3 and Triggers Metabolic Syndrome in Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27065–27079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assiri, M.A.; Ali, H.R.; Marentette, J.O.; Yun, Y.; Liu, J.; Hirschey, M.D.; Saba, L.M.; Harris, P.S.; Fritz, K.S. Investigating RNA expression profiles altered by nicotinamide mononucleotide therapy in a chronic model of alcoholic liver disease. Hum. Genom. 2019, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadiantehrani, S.; Barak, S.; Ron, R. GDNF is a novel ethanol-responsive gene in the VTA: Implications for the development and persistence of excessive drinking. Addict. Biol. 2014, 19, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbit, L.H.; Nie, H.; Janak, P.H. Habitual Alcohol Seeking: Time Course and the Contribution of Subregions of the Dorsal Striatum. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 72, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbit, L.H.; Janak, P.H. Habitual Alcohol Seeking: Neural Bases and Possible Relations to Alcohol Use Disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Steketee, J.D.; Sharp, B.M. Upregulation of Ionotropic Glutamate Receptor Subunits within Specific Mesocorticolimbic Regions during Chronic Nicotine Self-Administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Hamida, S.; Darcq, E.; Wang, J.; Wu, S.; Phamluong, K.; Kharazia, V.; Ron, D. Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase in the Dorsomedial Striatum Promotes Excessive Ethanol-Drinking Behaviors. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 14369–14378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logrip, M.L.; Barak, S.; Warnault, V.; Ron, D. Corticostriatal BDNF and alcohol addiction. Brain Res. 2015, 1628, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liran, M.; Rahamim, N.; Ron, D.; Barak, S. Growth Factors and Alcohol Use Disorder. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2020, 10, a039271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dono, R.; Texido, G.; Dussel, R.; Ehmke, H.; Zeller, R. Impaired cerebral cortex development and blood pressure regulation in FGF-2-deficient mice. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 4213–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mähler Convenor, M.; Berard, M.; Feinstein, R.; Gallagher, A.; Illgen-Wilcke, B.; Pritchett-Corning, K.; Raspa, M. FELASA recommendations for the health monitoring of mouse, rat, hamster, guinea pig and rabbit colonies in breeding and experimental units. Lab. Anim. 2014, 48, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziv, Y.; Rahamim, N.; Lezmy, N.; Even-Chen, O.; Shaham, O.; Malishkevich, A.; Giladi, E.; Elkon, R.; Gozes, I.; Barak, S. Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) is an alcohol-responsive gene and negative regulator of alcohol consumption in female mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peregud, D.; Stepanichev, M.; Gulyaeva, N. Drinking Pattern in Intermittent Access Two-Bottle-Choice Paradigm in Male Wistar Rats Is Associated with Exon-Specific BDNF Expression in the Hippocampus During Early Abstinence. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 71, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewin, J.; Schmitt, A.O.; Adorján, P.; Hildmann, T.; Piepenbrock, C. Quantitative DNA methylation analysis based on four-dye trace data from direct sequencing of PCR amplificates. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 3005–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Transcription Factor | Brain Region (CpG Position) | Consensus Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Activating Transcription Factor 3 (ATF3) | DMS (+307 bp) VTA (+639 bp) | 5′-GTGACGT[AC][AG]-3′ |
| Early Growth Response 1 (EGR1) | DLS (+268 bp; +702 bp) VTA (+588 bp) PFC (+660 bp; +700 bp) | 5′-GCG(T/G)GGGCG-3′ |
| E2F Transcription Factor 1 (E2F1) | DLS (+268 bp) NAc (+342 bp) VTA (+636 bp) PFC (+700 bp) | 5′-TTTC[CG]CGC-3′ |
| Specificity Protein 1 (SP1) | DMS (+278 bp) | 5′-CCCCGCCCCC-3′ |
| Transcriptional Repressor Protein YY1 (YY1) | DLS/NAc (+552 bp) VTA (+558 bp, +609 bp) | 5′-CCGCCATNTT-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herburg, L.; Rhein, M.; Kubinski, S.; Kefalakes, E.; Levin Greenwald, M.; Gielman, S.; Barak, S.; Frieling, H.; Grothe, C. Chronic Voluntary Alcohol Consumption Alters Promoter Methylation and Expression of Fgf-2 and Fgfr1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043336
Herburg L, Rhein M, Kubinski S, Kefalakes E, Levin Greenwald M, Gielman S, Barak S, Frieling H, Grothe C. Chronic Voluntary Alcohol Consumption Alters Promoter Methylation and Expression of Fgf-2 and Fgfr1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(4):3336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043336
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerburg, Leonie, Mathias Rhein, Sabrina Kubinski, Ekaterini Kefalakes, Matar Levin Greenwald, Simona Gielman, Segev Barak, Helge Frieling, and Claudia Grothe. 2023. "Chronic Voluntary Alcohol Consumption Alters Promoter Methylation and Expression of Fgf-2 and Fgfr1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 4: 3336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043336
APA StyleHerburg, L., Rhein, M., Kubinski, S., Kefalakes, E., Levin Greenwald, M., Gielman, S., Barak, S., Frieling, H., & Grothe, C. (2023). Chronic Voluntary Alcohol Consumption Alters Promoter Methylation and Expression of Fgf-2 and Fgfr1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 3336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043336






