Post-Translational Protein Deimination Signatures in Serum and Serum-Extracellular Vesicles of Bos taurus Reveal Immune, Anti-Pathogenic, Anti-Viral, Metabolic and Cancer-Related Pathways for Deimination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
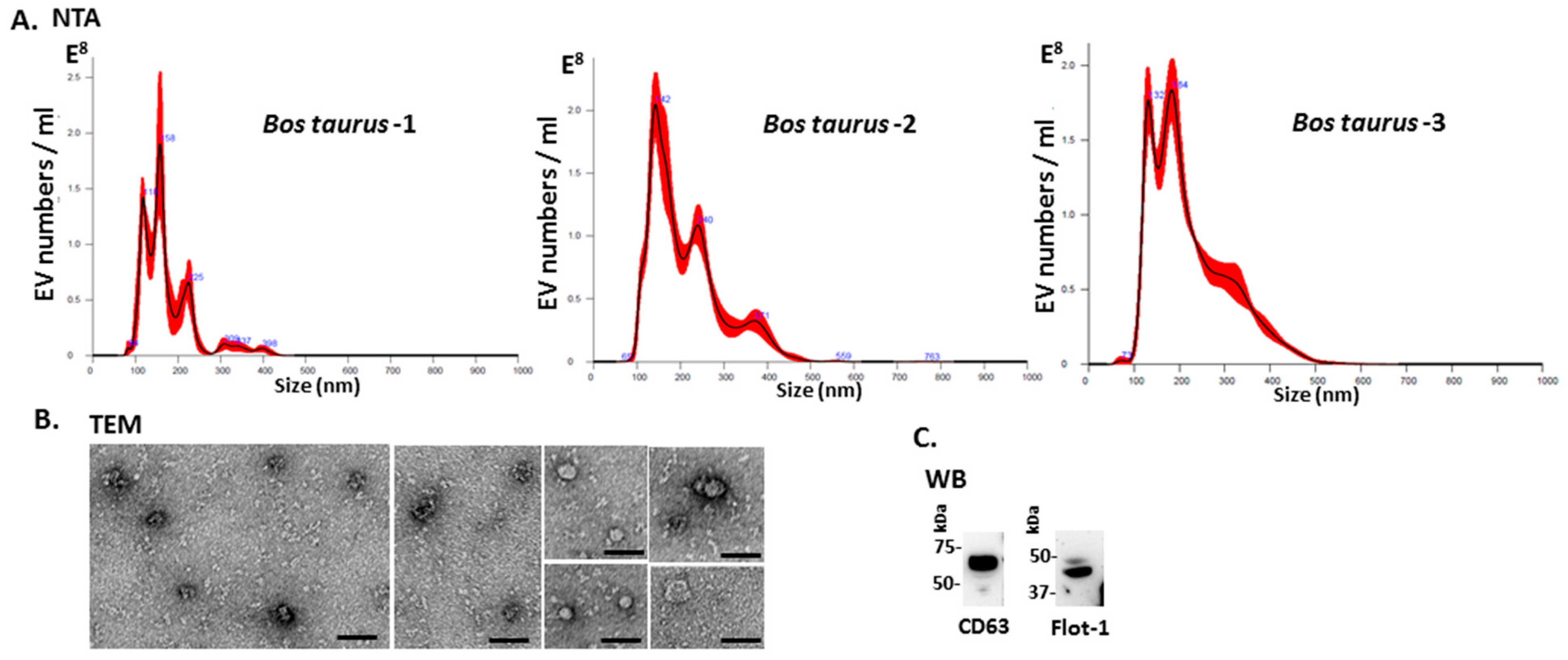
2.1. Characterisation of Bovine Serum-EVs
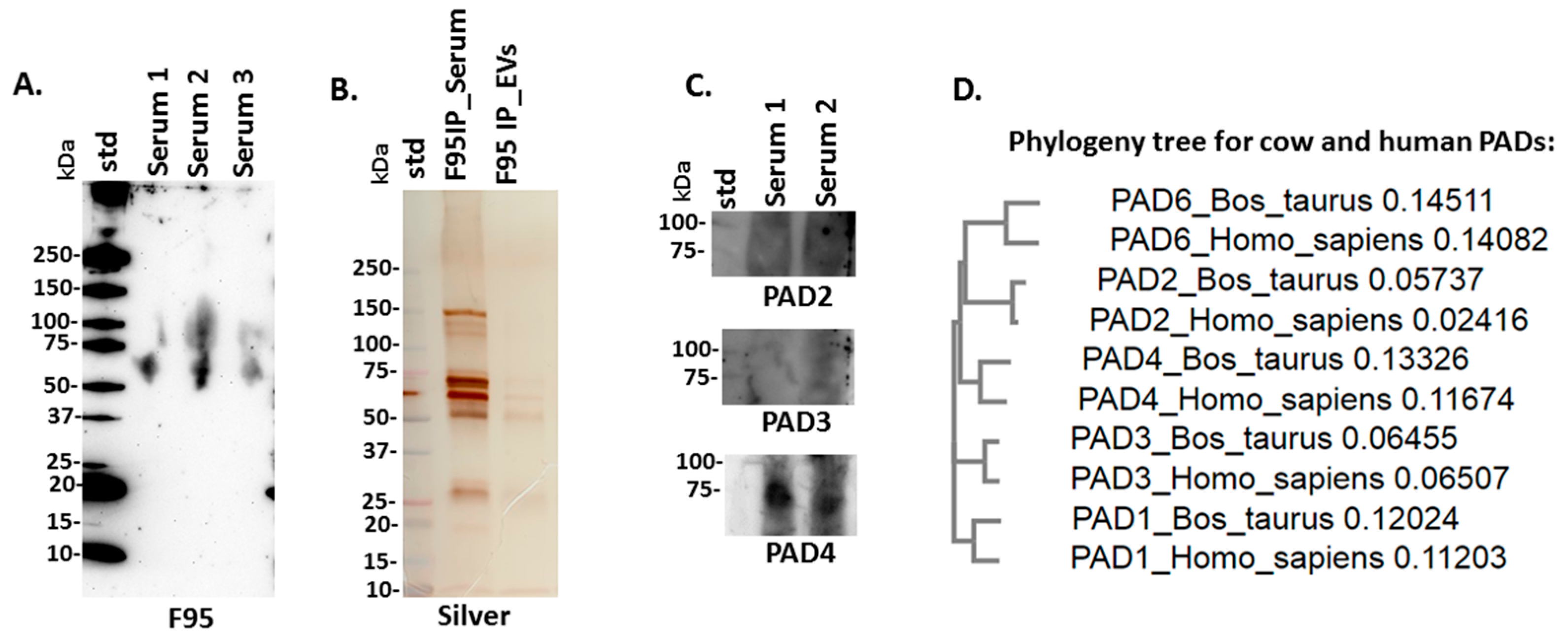
2.2. PAD Protein Homologues and Deiminated Proteins in Bovine Serum and Serum-EVs
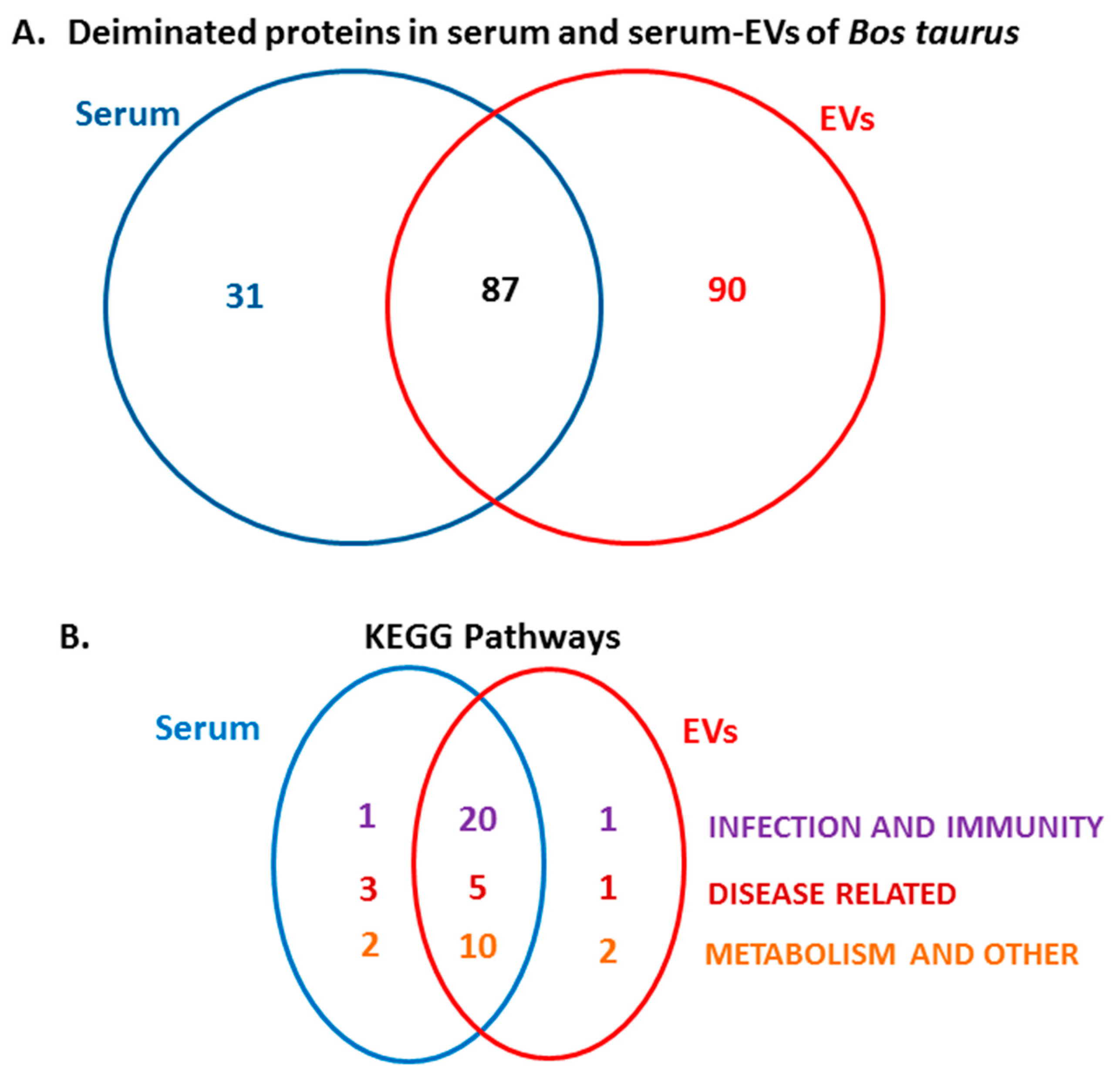
2.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis of Deiminated Proteins in Bovine Serum and Serum-EVs
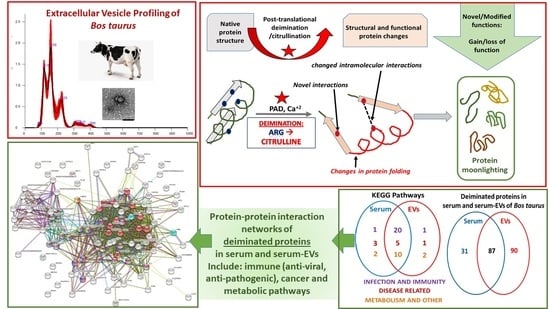
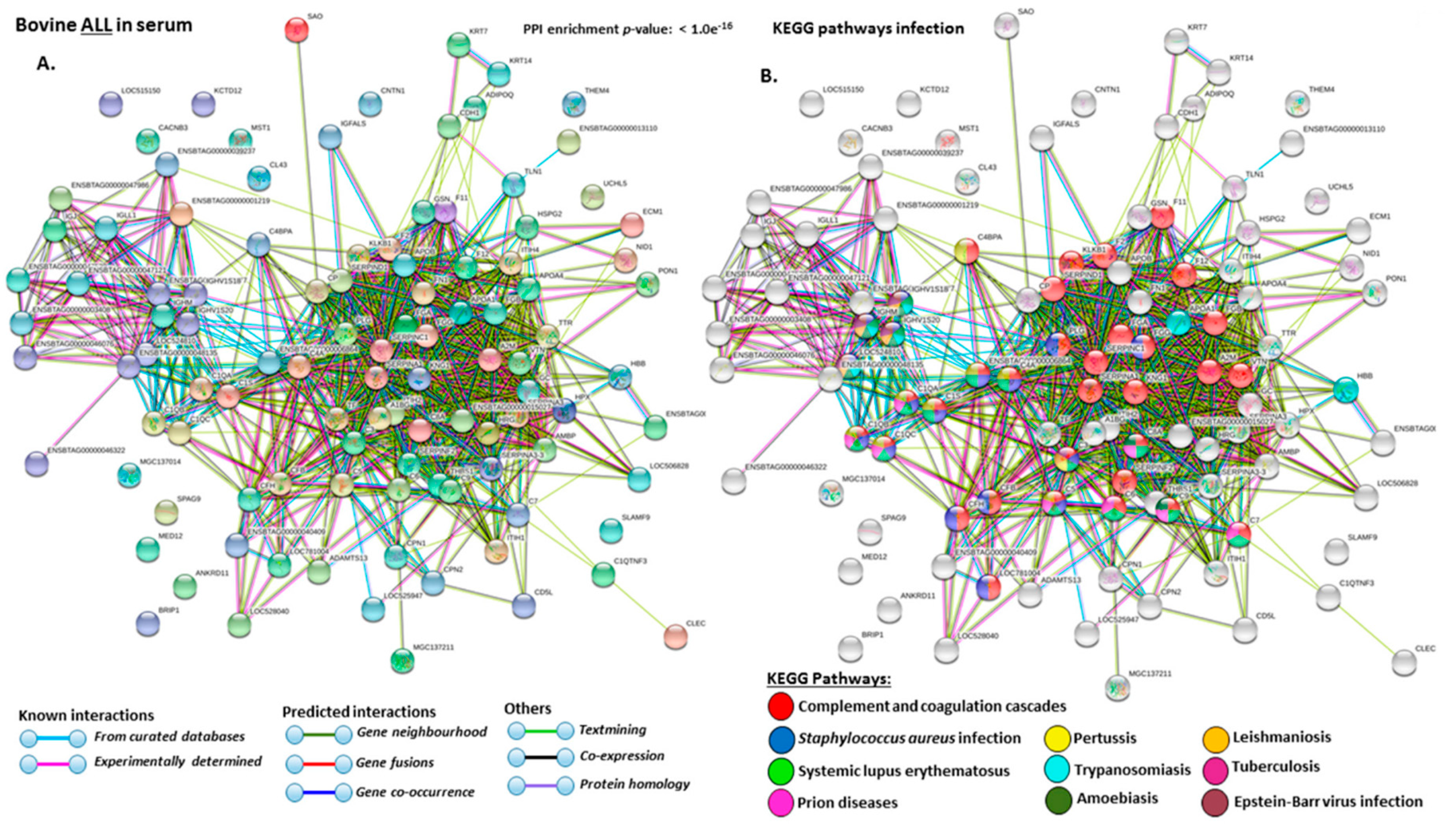
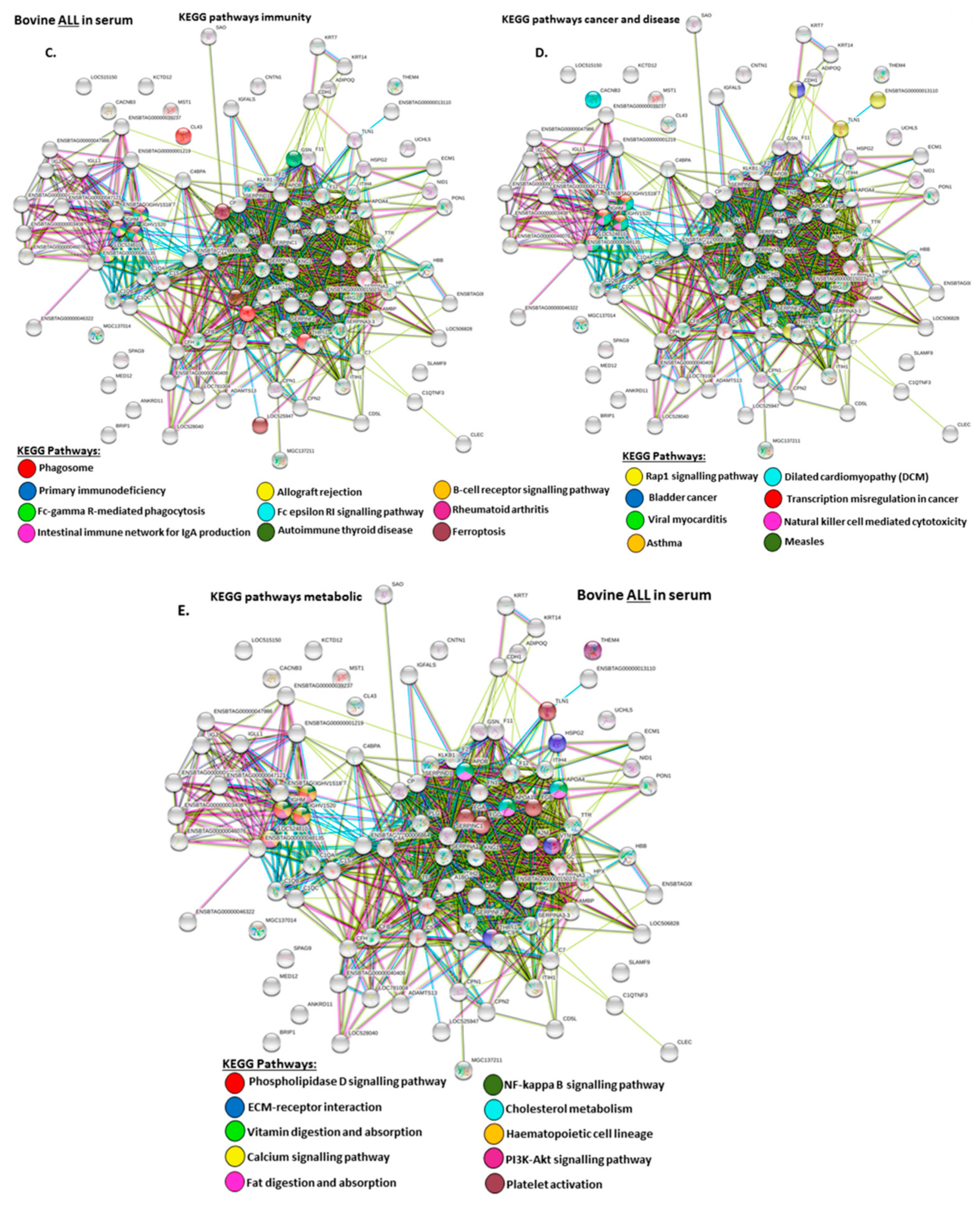
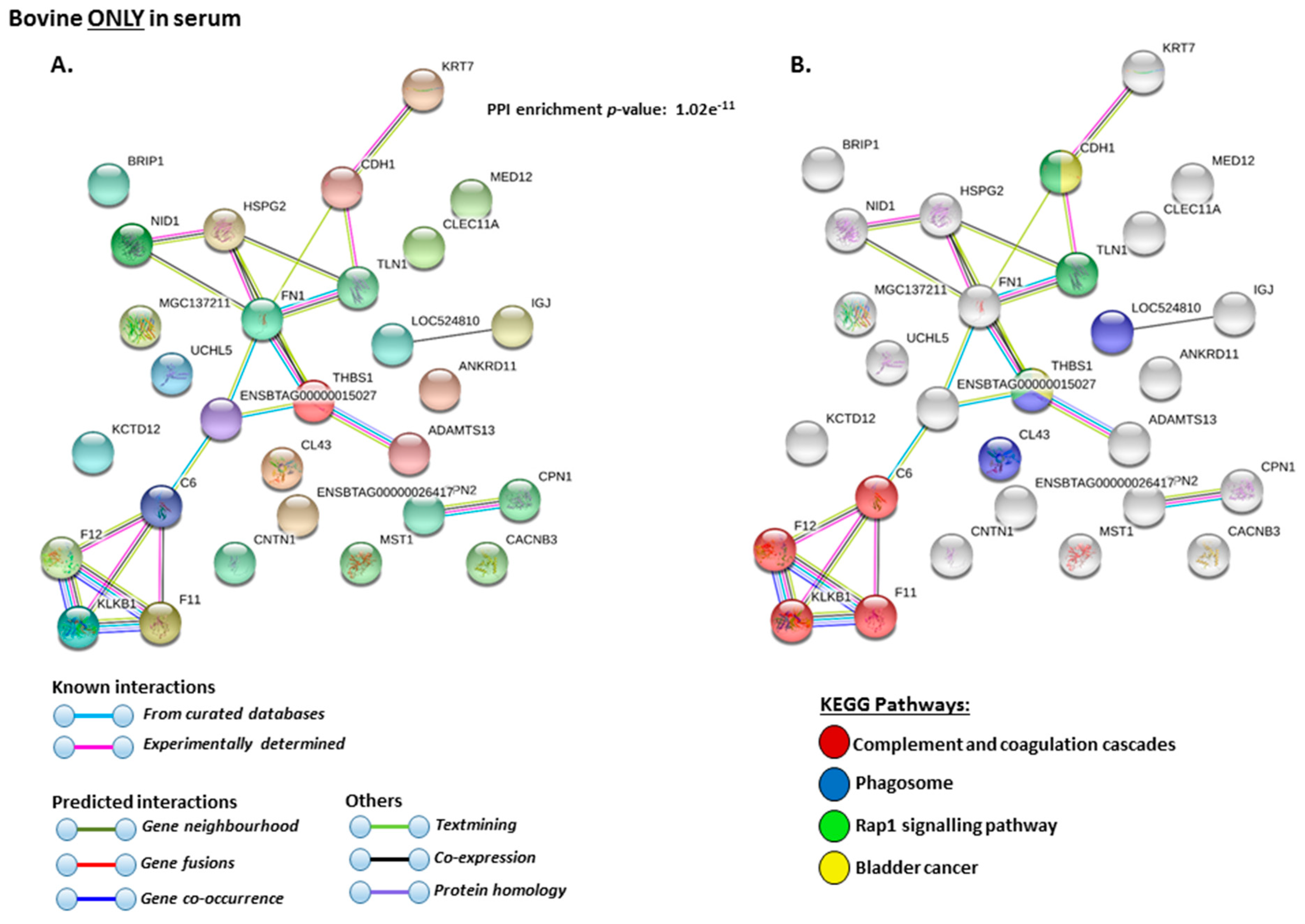
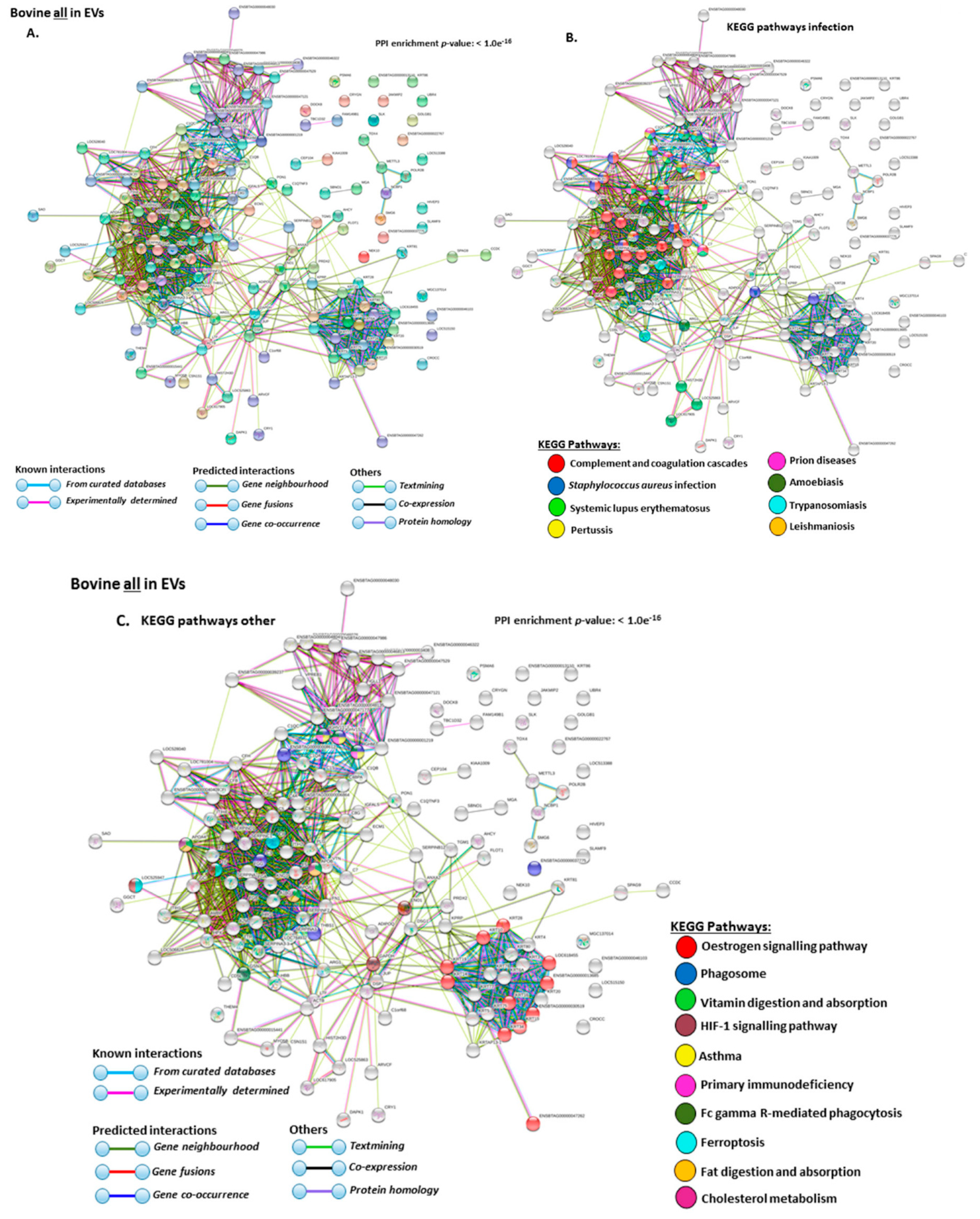
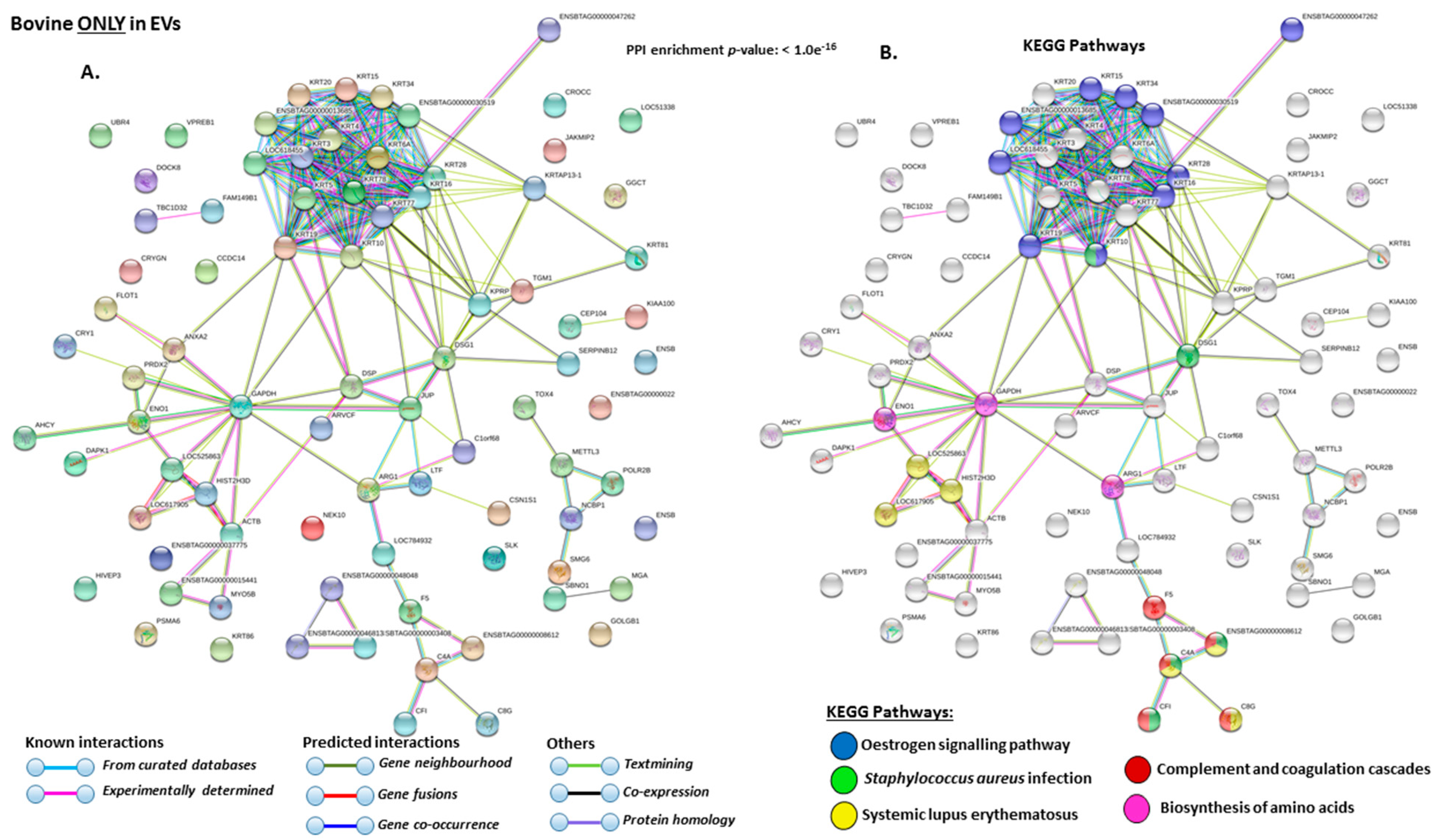
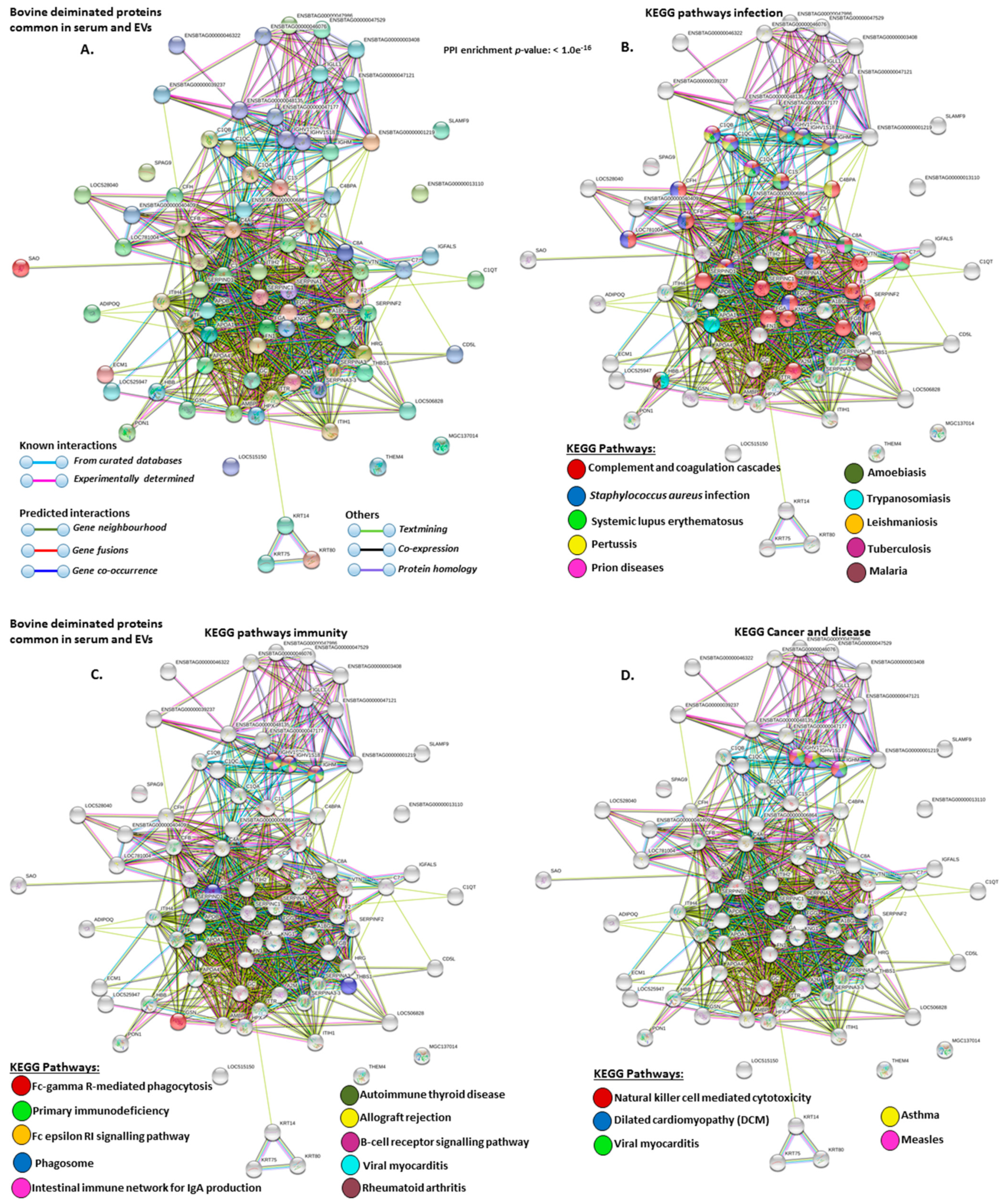
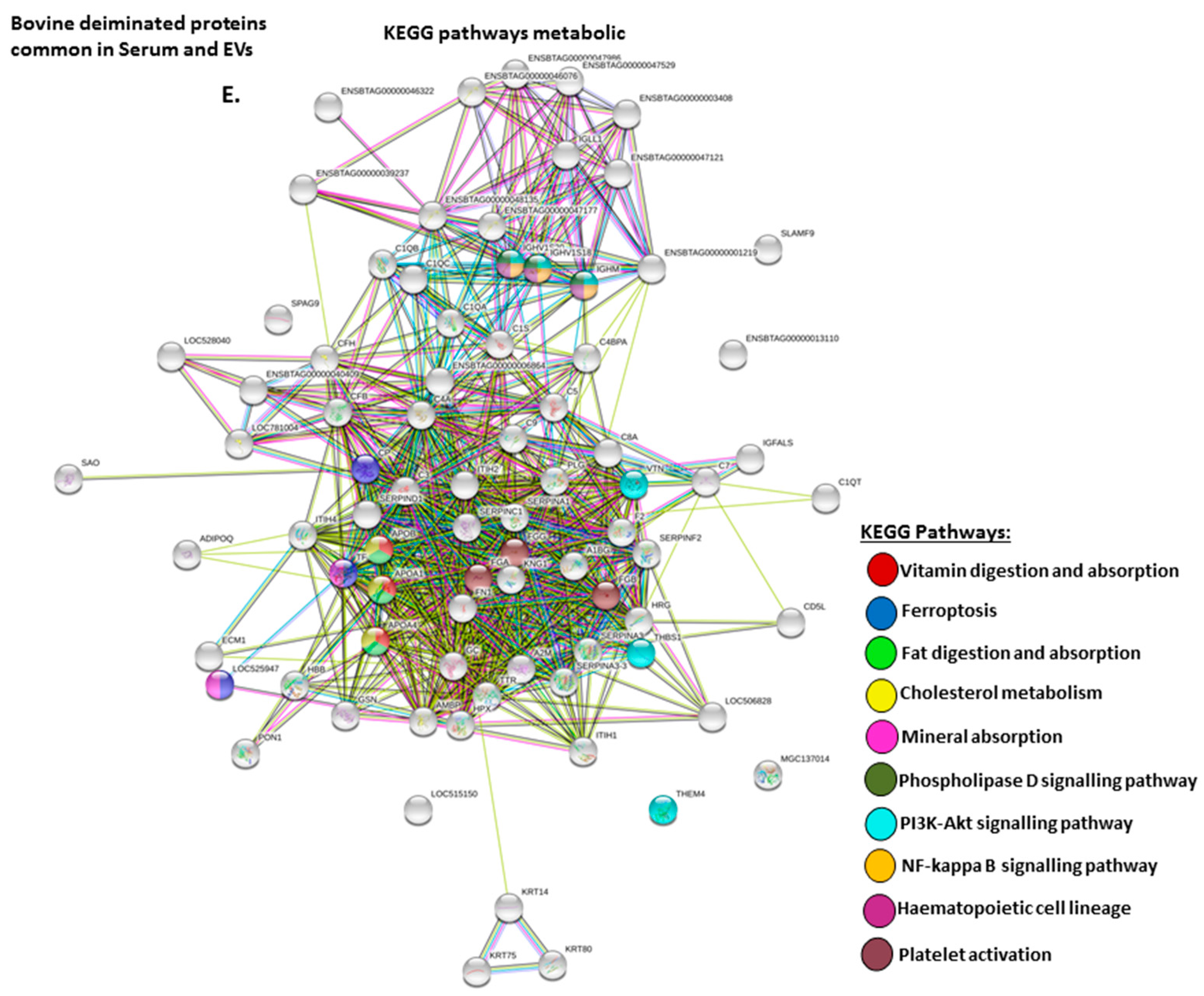
2.4. Protein–Protein Interaction Network Identification of Deiminated Proteins in Bovine Serum and Serum-EVs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Serum Sampling from Cow
4.2. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles and Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
4.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.4. Isolation of Deiminated Proteins in Serum and EVs Using F95-enrichment
4.5. Western Blotting Analysis
4.6. Silver Staining
4.7. Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) Analysis of Deiminated Protein Candidates
4.8. Protein–Protein Interaction Network Analysis
4.9. Phylogenetic Comparison of Bos PADs with Human PADs
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| CD63 | CD63 antigen; granulophysin; lysosomal-associated membrane protein 3 |
| CoV | Coronavirus |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| ECL | Enhanced chemiluminescence |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EVs | Extracellular vesicles |
| F95 | Pan-deimination/citrullination antibody |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| Flot-1 | Flotillin-1 |
| HIF | Hypoxia inducible factor |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin |
| KEGG | Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography mass spectrometry |
| NETosis | Neutrophil extracellular trap formation |
| NTA | Nanoparticle tracking analysis |
| PAD | Peptidylarginine deiminase |
| RAP1 | Ras-related protein 1 |
| SARS | Severe acute respiratory syndrome |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| TBS | Tris buffered saline |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| WB | Western blotting |
References
- Grubb, P.B. Mammal Species of the World. A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, 3rd ed.; online edition; Wilson, D.E., Reeder, D.M., Eds.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005; ISBN 9780801882210. [Google Scholar]
- Seluanov, A.; Gladyshev, V.N.; Vijg, J.; Gorbunova, V. Mechanisms of cancer resistance in long-lived mammals. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sok, D.; Le, K.M.; Vadnais, M.; Saye-Francisco, K.L.; Jardine, J.G.; Torres, J.L.; Berndsen, Z.T.; Kong, L.; Stanfield, R.; Ruiz, J.; et al. Rapid elicitation of broadly neutralizing antibodies to HIV by immunization in cows. Nature 2017, 548, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanfield, R.L.; Haakenson, J.; Deiss, T.C.; Criscitiello, M.F.; Wilson, I.A.; Smider, V.V. The Unusual Genetics and Biochemistry of Bovine Immunoglobulins. Adv. Immunol. 2018, 137, 135–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deiss, T.C.; Vadnais, M.; Wang, F.; Chen, P.L.; Torkamani, A.; Mwangi, W.; Lefranc, M.P.; Criscitiello, M.F.; Smider, V.V. Immunogenetic factors driving formation of ultralong VH CDR3 in Bos taurus antibodies. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossenaar, E.R.; Zendman, A.J.; van Venrooij, W.J.; Pruijn, G.J. PAD, a growing family of citrullinating enzymes: Genes, features and involvement in disease. Bioessays 2003, 25, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- György, B.; Toth, E.; Tarcsa, E.; Falus, A.; Buzas, E.I. Citrullination: A posttranslational modification in health and disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 1662–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicker, K.L.; Thompson, P.R. The protein arginine deiminases: Structure, function, inhibition, and disease. Biopolymers 2013, 99, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Peptidylarginine deiminases in citrullination, gene regulation, health and pathogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1829, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witalison, E.E.; Thompson, P.R.; Hofseth, L.J. Protein Arginine Deiminases and Associated Citrullination: Physiological Functions and Diseases Associated with Dysregulation. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Gallagher, M.; Kholia, S.; Kosgodage, U.S.; Hristova, M.; Hardy, J.; Inal, J.M. Peptidylarginine Deiminases-Roles in Cancer and Neurodegeneration and Possible Avenues for Therapeutic Intervention via Modulation of Exosome and Microvesicle (EMV) Release? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, B.; Martin, A.C. Protein moonlighting: A new factor in biology and medicine. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffrey, C.J. Protein moonlighting: What is it, and why is it important? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20160523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebl, A.; Köllner, B.; Anders, E.; Wimmers, K.; Goldammer, T. Peptidylarginine deiminase gene is differentially expressed in freshwater and brackish water rainbow trout. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 2333–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnadottir, B.; Hayes, P.; Hristova, M.; Bragason, B.T.; Nicholas, A.P.; Dodds, A.W.; Guðmundsdóttir, S.; Lange, S. Post-translational Protein Deimination in Cod (Gadus morhua L.) Ontogeny–Novel Roles in Tissue Remodelling and Mucosal Immune Defences? Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 87, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnadottir, B.; Bragason, B.T.; Bricknell, I.R.; Bowden, T.; Nicholas, A.P.; Hristova, M.; Guðmundsdóttir, S.; Dodds, A.W.; Lange, S. Peptidylarginine Deiminase and Deiminated Proteins are detected throughout Early Halibut Ontogeny-Complement Components C3 and C4 are post-translationally Deiminated in Halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.). Dev. Comp Immunol. 2019, 92, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscitiello, M.F.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Deiminated proteins in extracellular vesicles and plasma of nurse shark (Ginglymostoma cirratum)—Novel insights into shark immunity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 92, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavinho, B.; Rossi, I.V.; Evans-Osses, I.; Lange, S.; Ramirez, M.I. Peptidylarginine deiminase inhibition abolishes the production of large extracellular vesicles from Giardia intestinalis, affecting host-pathogen interactions by hindering adhesion to host cells. BioRxiv 2019, 586438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.S.A.; Shindia, A.A.; AbouZaid, A.A.; Yassin, A.M.; Ali, G.S.; Sitohy, M.Z. Biochemical characterization of peptidylarginine deiminase-like orthologs from thermotolerant Emericella dentata and Aspergillus nidulans. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2019, 124, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielecka, E.; Scavenius, C.; Kantyka, T.; Jusko, M.; Mizgalska, D.; Szmigielski, B.; Potempa, B.; Enghild, J.J.; Prossnitz, E.R.; Blom, A.M.; et al. Peptidyl arginine deiminase from Porphyromonas gingivalis abolishes anaphylatoxin C5a activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 32481–32487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosgodage, U.S.; Matewele, P.; Mastroianni, G.; Kraev, I.; Brotherton, D.; Awamaria, B.; Nicholas, A.P.; Lange, S.; Inal, J.M. Peptidylarginine Deiminase Inhibitors Reduce Bacterial Membrane Vesicle Release and Sensitize Bacteria to Antibiotic Treatment. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamensa, J.W.; Moscarello, M.A. Deimination of human myelin basic protein by a peptidylarginine deiminase from bovine brain. J. Neurochem. 1993, 61, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritzker, L.B.; Moscarello, M.A. A novel microtubule independent effect of paclitaxel: The inhibition of peptidylarginine deiminase from bovine brain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1388, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanan, S.; Cherrington, B.D.; Horibata, S.; McElwee, J.L.; Thompson, P.R.; Coonrod, S.A. Potential role of peptidylarginine deiminase enzymes and protein citrullination in cancer pathogenesis. Biochem. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 895343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, S.; Gögel, S.; Leung, K.Y.; Vernay, B.; Nicholas, A.P.; Causey, C.P.; Thompson, P.R.; Greene, N.D.; Ferretti, P. Protein deiminases: New players in the developmentally regulated loss of neural regenerative ability. Dev. Biol. 2011, 355, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, S.; Rocha-Ferreira, E.; Thei, L.; Mawjee, P.; Bennett, K.; Thompson, P.R.; Subramanian, V.; Nicholas, A.P.; Peebles, D.; Hristova, M.; et al. Peptidylarginine deiminases: Novel drug targets for prevention of neuronal damage following hypoxic ischemic insult (HI) in neonates. J. Neurochem. 2014, 130, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, S. Peptidylarginine Deiminases as Drug Targets in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sase, T.; Arito, M.; Onodera, H.; Omoteyama, K.; Kurokawa, M.S.; Kagami, Y.; Ishigami, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Kato, T. Hypoxia-induced production of peptidylarginine deiminases and citrullinated proteins in malignant glioma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Li, C.; Sun, L.; Jian, L.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X. Hypoxia induces production of citrullinated proteins in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes through regulating HIF1α. Scand. J. Immunol. 2018, 87, e12654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Enriquez-Algeciras, M.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Bonilha, V.L. Protein Deimination in Aging and Age-Related Diseases with Ocular Manifestations. In Protein Deimination in Human Health and Disease; Nicholas, A., Bhattacharya, S., Thompson, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, S.L.; Wagner, D.D. Peptidylarginine deiminase 4: A nuclear button triggering neutrophil extracellular traps in inflammatory diseases and aging. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 6358–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Alam, H.B.; Chong, W.; Mobley, J.; Liu, B.; Deng, Q.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, E.; Wang, T.; et al. CitH3: A reliable blood biomarker for diagnosis and treatment of endotoxic shock. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, B.M.; Chung, C.S.; Chen, Y.; Wilson, Z.; Fallon, E.A.; Reichner, J.S.; Ayala, A. PAD4 deficiency leads to decreased organ dysfunction and improved survival in a dual insult model of hemorrhagic shock and sepsis. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 1817–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claushuis, T.A.M.; van der Donk, L.E.H.; Luitse, A.L.; van Veen, H.A.; van der Wel, N.N.; van Vught, L.A.; Roelofs, J.J.T.H.; de Boer, O.J.; Lankelma, J.M.; Boon, L.; et al. Role of Peptidylarginine Deiminase 4 in Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation and Host Defense during Klebsiella pneumoniae-Induced Pneumonia-Derived Sepsis. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, N.A.; Gut, A.L.; Azevedo, P.S.; Polegato, B.F.; Magalhães, E.S.; Ishikawa, L.L.W.; Bruder, R.C.S.; Silva, E.A.D.; Gonçalves, R.B.; Tanni, S.E.; et al. Peptidylarginine deiminase 4 concentration, but not PADI4 polymorphisms, is associated with ICU mortality in septic shock patients. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 4732–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Pan, B.; Alam, H.B.; Deng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, E.; Liu, B.; Tian, Y.; Williams, A.M.; Duan, X.; et al. Inhibition of peptidylarginine deiminase alleviates LPS-induced pulmonary dysfunction and improves survival in a mouse model of lethal endotoxemia. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 833, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraro, S.P.; De Souza, G.F.; Gallo, S.W.; Da Silva, B.K.; De Oliveira, S.D.; Vinolo, M.A.R.; Saraiva, E.M.; Porto, B.N. Respiratory Syncytial Virus induces the classical ROS-dependent NETosis through PAD-4 and necroptosis pathways activation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobernack, T.; du Teil Espina, M.; Mulder, L.M.; Palma Medina, L.M.; Piebenga, D.R.; Gabarrini, G.; Zhao, X.; Janssen, K.M.J.; Hulzebos, J.; Brouwer, E.; et al. A Secreted Bacterial Peptidylarginine Deiminase Can Neutralize Human Innate Immune Defenses. MBio 2018, 9, e01704-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Yeoh, B.S.; Xiao, X.; Golonka, R.M.; Singh, V.; Wang, Y.; Vijay-Kumar, M. PAD4-dependent NETs generation are indispensable for intestinal clearance of Citrobacter rodentium. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struyf, S.; Noppen, S.; Loos, T.; Mortier, A.; Gouwy, M.; Verbeke, H.; Huskens, D.; Luangsay, S.; Parmentier, M.; Geboes, K.; et al. Citrullination of CXCL12 differentially reduces CXCR4 and CXCR7 binding with loss of inflammatory and anti-HIV-1 activity via CXCR4. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, V.; Sousa, F.H.; Shakamuri, P.; Svoboda, P.; Buch, C.; D’Acremont, M.; Christophorou, M.A.; Pohl, J.; Stevens, C.; Barlow, P.G. Citrullination Alters the Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Activities of the Human Cathelicidin LL-37 during Rhinovirus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortjens, B.; de Boer, O.J.; de Jong, R.; Antonis, A.F.; Sabogal Piñeros, Y.S.; Lutter, R.; van Woensel, J.B.; Bem, R.A. Neutrophil extracellular traps cause airway obstruction during respiratory syncytial virus disease. J. Pathol. 2016, 238, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnadottir, B.; Hayes, P.; Gísladóttir, B.; Bragason, B.Þ.; Hristova, M.; Nicholas, A.P.; Guðmundsdóttir, S.; Lange, S. Pentraxins CRP-I and CRP-II are post-translationally deiminated and differ in tissue specificity in cod (Gadus morhua L.) ontogeny. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 87, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholia, S.; Jorfi, S.; Thompson, P.R.; Causey, C.P.; Nicholas, A.P.; Inal, J.M.; Lange, S. A Novel Role for Peptidylarginine Deiminases (PADs) in Microvesicle Release: A Therapeutic Potential for PAD Inhibitors to Sensitize Prostate Cancer Cells to Chemotherapy. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2015, 4, 26192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosgodage, U.S.; Trindade, R.P.; Thompson, P.T.; Inal, J.M.; Lange, S. Chloramidine/Bisindolylmaleimide-I-Mediated Inhibition of Exosome and Microvesicle Release and Enhanced Efficacy of Cancer Chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosgodage, U.S.; Onganer, P.U.; Maclatchy, A.; Nicholas, A.P.; Inal, J.M.; Lange, S. Peptidylarginine Deiminases Post-translationally Deiminate Prohibitin and Modulate Extracellular Vesicle Release and miRNAs 21 and 126 in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.; Kovacs, D.; Finding, E.; Ulfelder, E.; Luis-Fuentes, V. Extracellular Vesicles: Evolutionarily Conserved Mediators of Intercellular Communication. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2017, 90, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inal, J.M.; Ansa-Addo, E.A.; Lange, S. Interplay of host-pathogen microvesicles and their role in infectious disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Théry, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchinovich, A.; Drapkina, O.; Tonevitsky, A. Transcriptome of Extracellular Vesicles: State-of-the-Art. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagner, T.; Chin, A.; Mariscal, J.; Bannykh, S.; Engman, D.M.; Di Vizio, D. Protein Composition Reflects Extracellular Vesicle Heterogeneity. Proteomics 2019, 19, e1800167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słomka, A.; Urban, S.K.; Lukacs-Kornek, V.; Żekanowska, E.; Kornek, M. Large Extracellular Vesicles: Have We Found the Holy Grail of Inflammation? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, B.M.; Hill, A.F. Extracellular vesicles--Their role in the packaging and spread of misfolded proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 40, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, Y.Q.; Peiris, H.N.; Vaswani, K.; Meier, S.; Burke, C.R.; Macdonald, K.A.; Roche, J.R.; Almughlliq, F.; Arachchige, B.J.; Reed, S.; et al. Characterization of exosomes from body fluids of dairy cows. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 3893–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatien, J.; Mermillod, P.; Tsikis, G.; Bernardi, O.; Janati Idrissi, S.; Uzbekov, R.; Le Bourhis, D.; Salvetti, P.; Almiñana, C.; Saint-Dizier, M. Metabolomic Profile of Oviductal Extracellular Vesicles across the Estrous Cycle in Cattle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinlapadeelerdkul, T.; Sonoda, H.; Uchida, K.; Kitahara, G.; Ikeda, M. Release of urinary aquaporin-2-bearing extracellular vesicles is decreased in pregnant Japanese Black cattle. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 1609–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huson, K.M.; Morphew, R.M.; Allen, N.R.; Hegarty, M.J.; Worgan, H.J.; Girdwood, S.E.; Jones, E.L.; Phillips, H.C.; Vickers, M.; Swain, M.; et al. Polyomic tools for an emerging livestock parasite, the rumen fluke Calicophoron daubneyi; identifying shifts in rumen functionality. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gong, P.; Tai, L.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Neospora caninum Are Recognized by Toll-Like Receptor 2 and Modulate Host Cell Innate Immunity Through the MAPK Signaling Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, N.R.; Breyne, K.; Meyer, E.; Cauty, C.; Jardin, J.; Chrétien, D.; Dupont, A.; Demeyere, K.; Berkova, N.; Azevedo, V.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Extracellular Vesicles Elicit an Immunostimulatory Response in vivo on the Murine Mammary Gland. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Gillan, V.; Simpson, D.M.; Kinnaird, J.; Maitland, K.; Shiels, B.; Devaney, E. Characterisation of infection associated microRNA and protein cargo in extracellular vesicles of Theileria annulata infected leukocytes. Cell. Microbiol. 2019, 21, e12969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez Rico, G.; Martínez-Castillo, M.; González-Ruíz, C.; Luna-Castro, S.; de la Garza, M. Mannheimia haemolytica A2 secretes different proteases into the culture medium and in outer membrane vesicles. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 113, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confer, A.W.; Ayalew, S. Mannheimia haemolytica in bovine respiratory disease: Immunogens, potential immunogens, and vaccines. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2018, 19, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Aswath, K.; Schroeder, S.G.; Lippolis, J.D.; Reinhardt, T.A.; Sonstegard, T.S. MicroRNA expression profiles of bovine milk exosomes in response to Staphylococcus aureus infection. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almughlliq, F.B.; Koh, Y.Q.; Peiris, H.N.; Vaswani, K.; McDougall, S.; Graham, E.M.; Burke, C.R.; Arachchige, B.J.; Reed, S.; Mitchell, M.D. Proteomic content of circulating exosomes in dairy cows with or without uterine infection. Theriogenology 2018, 114, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gassart, A.; Trentin, B.; Martin, M.; Hocquellet, A.; Bette-Bobillo, P.; Mamoun, R.; Vidal, M. Exosomal sorting of the cytoplasmic domain of bovine leukemia virus TM Env protein. Cell Biol. Int. 2009, 33, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, E.C.; Charles, P.D.; Hester, S.S.; Thomas, B.; Trudgian, D.; Martínez-Alonso, M.; Fodor, E. Conserved and host-specific features of influenza virion architecture. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, N.A.; Sampey, G.C.; Lepene, B.; Akpamagbo, Y.; Barclay, R.A.; Iordanskiy, S.; Hakami, R.M.; Kashanchi, F. Presence of Viral RNA and Proteins in Exosomes from Cellular Clones Resistant to Rift Valley Fever Virus Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.D.; Scholz-Romero, K.; Reed, S.; Peiris, H.N.; Koh, Y.Q.; Meier, S.; Walker, C.G.; Burke, C.R.; Roche, J.R.; Rice, G.; et al. Plasma exosome profiles from dairy cows with divergent fertility phenotypes. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 7590–7601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.T.; Navakanitworakul, R.; Khan, T.; Zhang, P.; Davis, J.S.; McGinnis, L.K.; Christenson, L.K. Stage-specific follicular extracellular vesicle uptake and regulation of bovine granulosa cell proliferation. Biol. Reprod. 2017, 97, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almiñana, C.; Tsikis, G.; Labas, V.; Uzbekov, R.; da Silveira, J.C.; Bauersachs, S.; Mermillod, P. Deciphering the oviductal extracellular vesicles content across the estrous cycle: Implications for the gametes-oviduct interactions and the environment of the potential embryo. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Kusama, K.; Ideta, A.; Kimura, K.; Hori, M.; Imakawa, K. Effects of miR-98 in intrauterine extracellular vesicles on maternal immune regulation during the peri-implantation period in cattle. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Guo, S.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, T.; Wu, H.; Qiu, C.; Deng, G. MiRNA profiling of plasma-derived exosomes from dairy cows during gestation. Theriogenology 2019, 130, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ávila, A.C.F.C.M.; Bridi, A.; Andrade, G.M.; Del Collado, M.; Sangalli, J.R.; Nociti, R.P.; da Silva Junior, W.A.; Bastien, A.; Robert, C.; Meirelles, F.V.; et al. Estrous cycle impacts microRNA content in extracellular vesicles that modulate bovine cumulus cell transcripts during in vitro maturation†. Biol Reprod. 2020, 102, 362–375. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, G.M.; Bomfim, M.M.; Del Collado, M.; Meirelles, F.V.; Perecin, F.; da Silveira, J.C. Oxygen tension modulates extracellular vesicles and its miRNA contents in bovine embryo culture medium. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2019, 86, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomini, E.; Alleva, E.; Fornelli, G.; Quartucci, A.; Privitera, L.; Vanni, V.S.; Viganò, P. Embryonic extracellular vesicles as informers to the immune cells at the maternal-fetal interface. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 198, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellisho, E.A.; Briones, M.A.; Velásquez, A.E.; Cabezas, J.; Castro, F.O.; Rodríguez-Álvarez, L. Extracellular vesicles secreted during blastulation show viability of bovine embryos. Reproduction 2019, 158, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauersachs, S.; Mermillod, P.; Almiñana, C. The Oviductal Extracellular Vesicles’ RNA Cargo Regulates the Bovine Embryonic Transcriptome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blans, K.; Hansen, M.S.; Sørensen, L.V.; Hvam, M.L.; Howard, K.A.; Möller, A.; Wiking, L.; Larsen, L.B.; Rasmussen, J.T. Pellet-free isolation of human and bovine milk extracellular vesicles by size-exclusion chromatography. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1294340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zempleni, J.; Aguilar-Lozano, A.; Sadri, M.; Sukreet, S.; Manca, S.; Wu, D.; Zhou, F.; Mutai, E. Biological Activities of Extracellular Vesicles and Their Cargos from Bovine and Human Milk in Humans and Implications for Infants. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordgren, T.M.; Heires, A.J.; Zempleni, J.; Swanson, B.J.; Wichman, C.; Romberger, D.J. Bovine milk-derived extracellular vesicles enhance inflammation and promote M1 polarization following agricultural dust exposure in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 64, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, B.C.; Schmitz, G. Exosomes of pasteurized milk: Potential pathogens of Western diseases. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmoussa, A.; Laugier, J.; Beauparlant, C.J.; Lambert, M.; Droit, A.; Provost, P. Complexity of the microRNA transcriptome of cow milk and milk-derived extracellular vesicles isolated via differential ultracentrifugation. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munagala, R.; Aqil, F.; Jeyabalan, J.; Gupta, R.C. Bovine milk-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Cancer Lett. 2016, 371, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqil, F.; Munagala, R.; Jeyabalan, J.; Agrawal, A.K.; Kyakulaga, A.H.; Wilcher, S.A.; Gupta, R.C. Milk exosomes—Natural nanoparticles for siRNA delivery. Cancer Lett. 2019, 449, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, A.; Moirangthem, A.; Angom, R.S.; Ishiguro, K.; Driscoll, J.; Yan, I.K.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Patel, T. Safety of bovine milk derived extracellular vesicles used for delivery of RNA therapeutics in zebrafish and mice. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Shigemura, H.; Ishiguro, N.; Inoshima, Y. Cell Infectivity in relation to bovine leukemia virus gp51 and p24 in bovine milk exosomes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arntz, O.J.; Pieters, B.C.; Oliveira, M.C.; Broeren, M.G.; Bennink, M.B.; de Vries, M.; van Lent, P.L.; Koenders, M.I.; van den Berg, W.B.; van der Kraan, P.M.; et al. Oral administration of bovine milk derived extracellular vesicles attenuates arthritis in two mouse models. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokarizadeh, A.; Hassanzadeh, K.; Abdi, M.; Soraya, H.; Faryabi, M.R.; Mohammadi, E.; Ahmadi, A. Transdermal delivery of bovine milk vesicles in patients with multiple sclerosis: A novel strategy to induce MOG-specific tolerance. Med. Hypotheses 2015, 85, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Hock, A.; Wu, R.Y.; Minich, A.; Botts, S.R.; Lee, C.; Antounians, L.; Miyake, H.; Koike, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Bovine milk-derived exosomes enhance goblet cell activity and prevent the development of experimental necrotizing enterocolitis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Kraev, I.; Magnadóttir, B.; Dodds, A.W. Complement component C4-like protein in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.)—Detection in ontogeny and identification of post-translational deimination in serum and extracellular vesicles. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 101, 103437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscitiello, M.F.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Deiminated proteins in extracellular vesicles and serum of llama (Lama glama)-Novel insights into camelid immunity. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 117, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscitiello, M.F.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Deimination Protein Profiles in Alligator mississippiensis Reveal Plasma and Extracellular Vesicle-specific Signatures Relating to Immunity, Metabolic Function and Gene Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnadottir, B.; Kraev, I.; Guðmundsdóttir, S.; Dodds, A.W.; Lange, S. Extracellular vesicles from cod (Gadus morhua L.) mucus contain innate immune factors and deiminated protein cargo. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 99, 103397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnadottir, B.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Kraev, I.; Dodds, A.W.; Gudmundsdottir, S.; Lange, S. Extracellular vesicles, deiminated protein cargo and microRNAs are novel serum biomarkers for environmental rearing temperature in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Aquacult. Rep. 2020, 16, 100245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnadottir, B.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Kraev, I.; Svansson, V.; Hayes, P.; Lange, S. Deiminated Proteins and Extracellular Vesicles—Novel Serum Biomarkers in Whales and Orca. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2020, 34, 100676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnadóttir, B.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Kraev, I.; Svansson, V.; Skírnisson, K.; Lange, S. Deiminated proteins and extracellular vesicles as novel biomarkers in pinnipeds: Grey seal (Halichoerus gryptus) and harbour seal (Phoca vitulina). Biochimie 2020, 171–172, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamenter, M.E.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Huynh, K.W.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Post-translational Deimination of Immunological and Metabolic Protein Markers in Plasma and Extracellular Vesicles of Naked Mole-Rat (Heterocephalus glaber). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, R.A.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Protein Deimination and Extracellular Vesicle Profiles in Antarctic Seabirds. Biology 2020, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal-Onganer, P.; MacLatchy, A.; Mahmoud, R.; Kraev, I.; Thompson, P.R.; Inal, J.; Lange, S. Peptidylarginine deiminase isozyme-specific PAD2, PAD3 and PAD4 inhibitors differentially modulate extracellular vesicle signatures and cell invasion in two glioblastoma multiforme cell lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S.; Vranic, S.; Cyprian, F.S.; Al Moustafa, A.E. Epstein-Barr Virus in Gliomas: Cause, Association, or Artifact? Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limam, S.; Missaoui, N.; Mestiri, S.; Yacoubi, M.T.; Krifa, H.; Selmi, B.; Mokni, M. Epstein-Barr virus infection in gliomas. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2019, 67, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knottenbelt, D.C. Cancer-blame it all on viruses! Bladder tumours in cattle and sarcoids in horses may help us understand the relationship between some cancers and viruses. Vet. J. 2007, 174, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borzacchiello, G.; Roperto, F. Bovine papillomaviruses, papillomas and cancer in cattle. Vet. Res. 2008, 39, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez Cuesta, L.; Lendez, P.A.; Nieto Farias, M.V.; Dolcini, G.L.; Ceriani, M.C. Can Bovine Leukemia Virus Be Related to Human Breast Cancer? A Review of the Evidence. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2018, 23, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuddington, B.P.; Mossman, K.L. Oncolytic bovine herpesvirus type 1 as a broad spectrum cancer therapeutic. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 13, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascella, M.; Rajnik, M.; Cuomo, A.; Dulebohn, S.C.; Di Napoli, R. Features, Evaluation and Treatment Coronavirus (COVID-19) [Updated 2020 Mar 20]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554776/ (accessed on 6 April 2020).
- Wang, F.; Ekiert, D.C.; Ahmad, I.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Bazirgan, O.; Torkamani, A.; Raudsepp, T.; Mwangi, W.; Criscitiello, M.F.; et al. Reshaping antibody diversity. Cell 2013, 153, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenbrand, K.M.; Forsythe, K.M.; Rivera-Rivas, J.J.; Czuprynski, C.J.; Aulik, N.A. Histophilus somni causes extracellular trap formation by bovine neutrophils and macrophages. Microb. Pathog. 2013, 54, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méric de Bellefon, L.; Épée, H.; Langhendries, J.P.; De Wit, S.; Corazza, F.; Di Romana, S. Increase in the prevalence of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in the serum of 185 patients infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Joint Bone Spine 2015, 82, 467–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, I.; Santiago, M. Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptides in infectious diseases--a systematic review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 29, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M.; Nishitsuji, H.; Kurihara, K.; Hayashi, T.; Masuda, T.; Kannagi, M. Suppression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by arginine deiminase of Mycoplasma arginini. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87 Pt 6, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driggin, E.; Madhavan, M.V.; Bikdeli, B.; Chuich, T.; Laracy, J.; Bondi-Zoccai, G.; Brown, T.S.; Nigoghossian, C.; Zidar, D.A.; Haythe, J.; et al. Cardiovascular Considerations for Patients, Health Care Workers, and Health Systems During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Pandemic. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020. pii: S0735-1097(20)34637-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, S.; Kawashima, S.; Kanazawa, K.; Hirata, K.; Katayama, Y.; Hotta, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Ito, H.; Yokoyama, M. Expression of nitric oxide synthase in a murine model of viral myocarditis induced by coxsackievirus B3. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 220, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, A.W.; Law, S.K. The phylogeny and evolution of the thioester bond-containing proteins C3, C4 and alpha 2-macroglobulin. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 166, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishelson, Z.; Attali, G.; Mevorach, D. Complement and apoptosis. Mol. Immunol. 2001, 38, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.P.; Smith, J.R.; Dransfield, I. Phagocytosis of opsonized apoptotic cells: Roles for ‘old-fashioned’ receptors for antibody and complement. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 135, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, M.V.; Sim, R.B. Complement in health and disease. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, B.P.; Walters, D.; Serna, M.; Bubeck, D. Terminal complexes of the complement system: New structural insights and their relevance to function. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 274, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder-Braunstein, J.; Kirschfink, M. Complement deficiencies and dysregulation: Pathophysiological consequences, modern analysis, and clinical management. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 114, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Bambir, S.; Dodds, A.W.; Magnadottir, B. The ontogeny of complement component C3 in Atlantic Cod (Gadus morhua L.)—An immunohistochemical study. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2004, 16, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Bambir, S.; Dodds, A.W.; Magnadottir, B. An immunohistochemical study on complement component C3 in juvenile Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Dodds, A.W.; Gudmundsdóttir, S.; Bambir, S.H.; Magnadottir, B. The ontogenic transcription of complement component C3 and Apolipoprotein A-I tRNA in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.)—A role in development and homeostasis? Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2005, 29, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Bambir, S.H.; Dodds, A.W.; Bowden, T.; Bricknell, I.; Espelid, S.; Magnadottir, B. Complement component C3 transcription in Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.) larvae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 20, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Madhavan, M.; Call, M.K.; Santiago, W.; Tsonis, P.A.; Lambris, J.D.; Del Rio-Tsonis, K. Expression of complement 3 and complement 5 in newt limb and lens regeneration. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 2331–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linscott, W.D.; Triglia, R.P. The bovine complement system. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1981, 137, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soler-Rodríguez, A.M.; Romano, E.; Aranguren, Y.; Soyano, A. A new hemolytic assay for bovine serum complement and its application during experimental bovine anaplasmosis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1990, 24, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, S.; Tian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, H.; Zheng, N.; Wang, J. Plasma-based proteomics reveals immune response, complement and coagulation cascades pathway shifts in heat-stressed lactating dairy cows. J. Proteomics 2016, 146, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postma, G.C.; Minatel, L.; Olivares, R.W.; Schapira, A.; Dallorso, M.E.; Carfagnini, J.C. Bactericidal activity of lachrymal secretion and complement system in copper deficient bovines. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 153, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.N.; Pyaram, K.; Ahmad, M.; Sahu, A. Species selectivity in poxviral complement regulators is dictated by the charge reversal in the central complement control protein modules. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostachuk, A. Bovine viral diarrhea virus structural protein E2 as a complement regulatory protein. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 1769–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Liang, L.; Cui, S.; Zhang, Y. RNA-Seq based transcriptome analysis during bovine viral diarrhoea virus (BVDV) infection. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levings, R.L.; Roth, J.A. Immunity to bovine herpesvirus 1: I. Viral lifecycle and innate immunity. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2013, 14, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.R.; Jiang, F.; Wang, Z.H.; Wu, W.X. Antibodies Specific to Membrane Proteins Are Effective in Complement-Mediated Killing of Mycoplasma bovis. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00740-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boshra, H.; Li, J.; Sunyer, J.O. Recent advances on the complement system of teleost fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 20, 239–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunyer, J.O.; Lambris, J.D. Evolution and diversity of the complement system of poikilothermic vertebrates. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 166, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, M.; Kato-Unoki, Y.; Nakahara, M.; Mutsuro, J.; Somamoto, T. Diversified components of the bony fish complement system: More genes for robuster innate defense? Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2006, 586, 121–138. [Google Scholar]
- Nakao, M.; Tsujikura, M.; Ichiki, S.; Vo, T.K.; Somamoto, T. The complement system in teleost fish: Progress of post-homolog-hunting researches. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1296–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forn-Cuní, G.; Reis, E.S.; Dios, S.; Posada, D.; Lambris, J.D.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B. The evolution and appearance of C3 duplications in fish originate an exclusive teleost c3 gene form with anti-inflammatory activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, P.B.; Quigley, J.P. Alpha2-macroglobulin: An evolutionarily conserved arm of the innate immune system. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1999, 23, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.G.; Sim, R.B. Intramolecular general acid catalysis in the binding reactions of alpha 2-macroglobulin and complement components C3 and C4. Biosci. Rep. 1981, 1, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sottrup-Jensen, L.; Stepanik, T.M.; Kristensen, T.; Lønblad, P.B.; Jones, C.M.; Wierzbicki, D.M.; Magnusson, S.; Domdey, H.; Wetsel, R.A.; Lundwall, A.; et al. Common evolutionary origin of alpha 2-macroglobulin and complement components C3 and C4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feige, J.J.; Negoescu, A.; Keramidas, M.; Souchelnitskiy, S.; Chambaz, E.M. Alpha 2-macroglobulin: A binding protein for transforming growth factor-beta and various cytokines. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 1996, 45, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomme, P.T.; McCann, K.B.; Bertolini, J. Transferrin: Structure, function and potential therapeutic actions. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, H. Transferrin and transferrin receptors update. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezkorovainy, A. Antimicrobial properties of iron-binding proteins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1981, 135, 139–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ratledge, C.; Dover, L.G. Iron metabolism in pathogenic bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2000, 54, 881–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, J.A.; Carrasco-Medina, L.; Hodgins, D.C.; Shewen, P.E. Mannheimia haemolytica and bovine respiratory disease. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2007, 8, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, M.F.; Elde, N.C. Buried Treasure: Evolutionary Perspectives on Microbial Iron Piracy. Trends Genet. 2015, 31, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarute, N.; Ross, S.R. New World Arenavirus Biology. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2017, 4, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessling-Resnick, M. Crossing the Iron Gate: Why and How Transferrin Receptors Mediate Viral Entry. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2018, 38, 431–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, M.R.; Lashua, L.P.; Fischer, D.K.; Flitter, B.A.; Eichinger, K.M.; Durbin, J.E.; Sarkar, S.N.; Coyne, C.B.; Empey, K.M.; Bomberger, J.M. Respiratory syncytial virus infection enhances Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm growth through dysregulation of nutritional immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1642–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gommerman, J.L.; Rojas, O.L.; Fritz, J.H. Re-thinking the functions of IgA(+) plasma cells. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 262–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, C.; Kaushik, R.S. Mucosal Immune System of Cattle: All Immune Responses Begin Here. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2019, 35, 431–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, E.A.; Buterbaugh, R.E.; Rinehart, C.L.; Ensley, D.; Perry, G.A.; Abdelsalam, K.W.; Chase, C.C.L. Protection against bovine respiratory syncytial virus in calves vaccinated with adjuvanted modified live vaccine administered in the face of maternal antibody. Vaccine 2020, 38, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, D.; Clarke, A.; Heesom, K.; Murphy, D.; Eggleton, P. Carbamylation/citrullination of IgG Fc in bronchiectasis, established RA with bronchiectasis and RA smokers: A potential risk factor for disease. ERJ Open Res. 2017, 3, 00018–02017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundqvist, M.L.; Middleton, D.L.; Radford, C.; Warr, G.W.; Magor, K.E. Immunoglobulins of the non-galliform birds: Antibody expression and repertoire in the duck. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de los Rios, M.; Criscitiello, M.F.; Smider, V.V. Structural and genetic diversity in antibody repertoires from diverse species. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 33, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Takizawa, F.; Casadei, E.; Shibasaki, Y.; Ding, Y.; Sauters, T.J.C.; Yu, Y.; Salinas, I.; Sunyer, J.O. Specialization of mucosal immunoglobulins in pathogen control and microbiota homeostasis occurred early in vertebrate evolution. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaay3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akula, S.; Hellman, L. The Appearance and Diversification of Receptors for IgM during Vertebrate Evolution. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 408, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Calvert, R.A.; Sutton, B.J.; Doré, K.A. IgY: A key isotype in antibody evolution. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2017, 92, 2144–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magadan, S.; Krasnov, A.; Hadi-Saljoqi, S.; Afanasyev, S.; Mondot, S.; Lallias, D.; Castro, R.; Salinas, I.; Sunyer, O.; Hansen, J.; et al. Standardized IMGT® Nomenclature of Salmonidae IGH Genes, the Paradigm of Atlantic Salmon and Rainbow Trout: From Genomics to Repertoires. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragg, H. The role of serpins in the surveillance of the secretory pathway. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 2763–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporte, M.; Naesens, L. Airway proteases: An emerging drug target for influenza and other respiratory virus infections. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 24, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menou, A.; Duitman, J.; Flajolet, P.; Sallenave, J.M.; Mailleux, A.A.; Crestani, B. Human airway trypsin-like protease, a serine protease involved in respiratory diseases. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 312, L657–L668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagaoua, M.; Hafid, K.; Boudida, Y.; Becila, S.; Ouali, A.; Picard, B.; Boudjellal, A.; Sentandreu, M.A. Caspases and Thrombin Activity Regulation by Specific Serpin Inhibitors in Bovine Skeletal Muscle. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 177, 279–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florin-Christensen, M.; Schnittger, L.; Dominguez, M.; Mesplet, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Ferreri, L.; Asenzo, G.; Wilkowsky, S.; Farber, M.; Echaide, I.; et al. Search for Babesia bovis vaccine candidates. Parassitologia 2007, 49 (Suppl. 1), 9–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barksdale, S.M.; Hrifko, E.J.; Chung, E.M.; van Hoek, M.L. Peptides from American alligator plasma are antimicrobial against multi-drug resistant bacterial pathogens including Acinetobacter baumannii. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilvawala, R.; Nguyen, S.H.; Maurais, A.J.; Nemmara, V.V.; Nagar, M.; Salinger, A.J.; Nagpal, S.; Weerapana, E.; Thompson, P.R. The Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Citrullinome. Cell. Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 691–704.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Minokoshi, Y.; Ito, Y.; Waki, H.; Uchida, S.; Yamashita, S.; Noda, M.; Kita, S.; Ueki, K.; et al. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almabouada, F.; Diaz-Ruiz, A.; Rabanal-Ruiz, Y.; Peinado, J.R.; Vazquez-Martinez, R.; Malagon, M.M. Adiponectin receptors form homomers and heteromers exhibiting distinct ligand binding and intracellular signaling properties. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 3112–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiaschi, T. Mechanisms of Adiponectin Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenberg, A.D.V.; Reis, A.F.; Gerchman, F. Relationships between adiponectin levels, the metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes: A literature review. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 61, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamberi, T.; Magherini, F.; Fiaschi, T. Adiponectin in Myopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parida, S.; Siddharth, S.; Sharma, D. Adiponectin, obesity, and cancer: Clash of the bigwigs in health and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.L.; Tao, J.; Zhao, P.J.; Tang, W.; Xu, J.P.; Zhang, K.Q.; Zou, C.G. Adiponectin receptor PAQR-2 signaling senses low temperature to promote C. elegans longevity by regulating autophagy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiaschi, T.; Magherini, F.; Gamberi, T.; Modesti, P.A.; Modesti, A. Adiponectin as a tissue regenerating hormone: More than a metabolic function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauerwein, H.; Häußler, S. Endogenous and exogenous factors influencing the concentrations of adiponectin in body fluids and tissues in the bovine. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2016, 56, S33–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.; Bae, H.; Lim, W.; Bazer, F.W.; Song, G. Adiponectin: A prosurvival and proproliferation signal that increases bovine mammary epithelial cell numbers and protects them from endoplasmic reticulum stress responses. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 5278–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, N. Relevance of apolipoproteins in the development of fatty liver and fatty liver-related peripartum diseases in dairy cows. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2002, 64, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedzka-Sarek, M.; Metso, J.; Kateifides, A.; Meri, T.; Jokiranta, T.S.; Muszyński, A.; Radziejewska-Lebrecht, J.; Zannis, V.; Skurnik, M.; Jauhiainen, M. Apolipoprotein A-I exerts bactericidal activity against Yersinia enterocolitica Serotype O:3. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 38211–38219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigel, S.; Bunk, S.; Meergans, T.; Doninger, B.; Stich, K.; Stulnig, T.; Derfler, K.; Hoffmann, J.; Deininger, S.; von Aulock, S.; et al. Apolipoprotein B100 is a suppressor of Staphylococcus aureus-induced innate immune responses in humans and mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 2983–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, L.D.; Brown, G.; Gauthier, D.; Reece, K.; Kator, H.; Van Veld, P. Apolipoprotein A-I from striped bass (Morone saxatilis) demonstrates antibacterial activity in vitro. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 151, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Q.; Yang, C.S.; Yang, Y.; Pan, F.; He, L.Y.; Wang, A.M. An apolipoprotein E mimetic peptide with activities against multidrug-resistant bacteria and immunomodulatory effects. J. Pept. Sci. 2013, 19, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghimire, D.; Rai, M.; Gaur, R. Novel host restriction factors implicated in HIV-1 replication. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awadeh, F.T.; Abdelrahman, M.M.; Kincaid, R.L.; Finley, J.W. Effect of selenium supplements on the distribution of selenium among serum proteins in cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostert, V. Selenoprotein P: Properties, functions, and regulation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 376, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, R.F.; Hill, K.E. Selenoprotein P-expression, functions, and roles in mammals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzelius, K.; Hoac, T.; Sundler, R.; Onning, G.; Akesson, B. Occurrence of selenoprotein enzyme activities and mRNA in bovine mammary tissue. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, S.; Shoji, Y.; Sakurai, A.; Yuasa, K.; Himeno, S.; Imura, N. Effects of selenium deficiency on expression of selenoproteins in bovine arterial endothelial cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 24, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ogawa, S.K.; Shin, M.C.; Hirashima, M.; Akaike, N.; Ito, Y. Effects of selenoprotein P on the contraction and relaxation of the airway smooth muscle. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2013, 32, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bao, Y.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Yun, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Ren, Y.; Jia, Y. Transcriptome profiling revealed multiple genes and ECM-receptor interaction pathways that may be associated with breast cancer. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2019, 24, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardpour, S.; Hamidieh, A.A.; Taleahmad, S.; Sharifzad, F.; Taghikhani, A.; Baharvand, H. Interaction between mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles and immune cells by distinct protein content. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8249–8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Jang, M.; Kim, H.; Kwak, W.; Park, W.; Hwang, J.Y.; Lee, C.K.; Jang, G.W.; Park, M.N.; Kim, H.C.; et al. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Adipose Tissues Reveals that ECM-Receptor Interaction Is Involved in the Depot-Specific Adipogenesis in Cattle. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66267. [Google Scholar]
- Stafuzza, N.B.; Zerlotini, A.; Lobo, F.P.; Yamagishi, M.E.; Chud, T.C.; Caetano, A.R.; Munari, D.P.; Garrick, D.J.; Machado, M.A.; Martins, M.F.; et al. Single nucleotide variants and InDels identified from whole-genome re-sequencing of Guzerat, Gyr, Girolando and Holstein cattle breeds. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, B.I.; Santiago, K.G.; Lee, D.; Ha, S.; Seo, K. RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) Based Transcriptome Analysis in Immune Response of Holstein Cattle to Killed Vaccine against Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus Type I. Animals 2020, 10, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, H.; Fan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, M.; Mao, Y.; Karrow, N.A.; Loor, J.J.; Moore, S.; Yang, Z. Transcriptomics and iTRAQ-Proteomics Analyses of Bovine Mammary Tissue with Streptococcus agalactiae-Induced Mastitis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11188–11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, S.; Patergnani, S.; Missiroli, S.; Morciano, G.; Rimessi, A.; Wieckowski, M.R.; Giorgi, C.; Pinton, P. Mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum calcium homeostasis and cell death. Cell Calcium 2018, 69, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paupe, V.; Prudent, J. New insights into the role of mitochondrial calcium homeostasis in cell migration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.M.; Kayastha, B.B.; Franklin, M.J.; Patrauchan, M.A. Calcium Regulation of Bacterial Virulence. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1131, 827–855. [Google Scholar]
- Puri, B.K. Calcium Signaling and Gene Expression. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1131, 537–545. [Google Scholar]
- Granatiero, V.; De Stefani, D.; Rizzuto, R. Mitochondrial Calcium Handling in Physiology and Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 982, 25–47. [Google Scholar]
- Mustaly-Kalimi, S.; Littlefield, A.M.; Stutzmann, G.E. Calcium Signaling Deficits in Glia and Autophagic Pathways Contributing to Neurodegenerative Disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 1158–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorvin, C.M. Molecular and clinical insights from studies of calcium-sensing receptor mutations. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2019, 63, R1–R16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, M.; Alasmari, D.; Assiri, A.; Mattar, E.; Aljaddawi, A.A.; Alattas, S.G.; Redwan, E.M. An Overview of the Intrinsic Role of Citrullination in Autoimmune Disorders. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 7592851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.; Thompson, P.R. Protein Arginine Deiminases (PADs): Biochemistry and Chemical Biology of Protein Citrullination. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 818–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méchin, M.C.; Takahara, H.; Simon, M. Deimination and Peptidylarginine Deiminases in Skin Physiology and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgos, R.A.; Conejeros, I.; Hidalgo, M.A.; Werling, D.; Hermosilla, C. Calcium influx, a new potential therapeutic target in the control of neutrophil-dependent inflammatory diseases in bovines. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 143, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Huang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhu, G. Calcium signaling involved in bovine herpesvirus 1 replication in MDBK cells. Acta Virol. 2017, 61, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadhawan, M.; Tiwari, S.; Sharma, S.; Rathaur, S. Identification and characterization of a novel prolyl oligopeptidase in filarial parasite Setaria cervi. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 2235–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justet, C.; Chifflet, S.; Hernandez, J.A. Calcium Oscillatory Behavior and Its Possible Role during Wound Healing in Bovine Corneal Endothelial Cells in Culture. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8647121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.F.; Bowdridge, E.; McDermott, E.L.; Richardson, S.; Scheidler, J.; Syed, Q.; Bush, T.; Inskeep, E.K.; Flores, J.A. Mechanisms of intracellular calcium homeostasis in developing and mature bovine corpora lutea. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 90, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, F.M.; Dietsch, G.O.; Peñagaricano, F. Genetic dissection of bull fertility in US Jersey dairy cattle. Anim. Genet. 2018, 49, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Félix-Martínez, G.J.; Gil, A.; Segura, J.; Villanueva, J.; Gutíerrez, L.M. Modeling the influence of co-localized intracellular calcium stores on the secretory response of bovine chromaffin cells. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 100, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, L.L. TRIENNIAL LACTATION SYMPOSIUM/BOLFA: Serotonin and the regulation of calcium transport in dairy cows. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 5711–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Brock, E.J.; Ji, K.; Mattingly, R.R. Ras and Rap1: A tale of two GTPases. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 54, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.; Steinman, L.; Zamvil, S.S. Statin therapy in autoimmunity: From protein prenylation to immunomodulation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 5, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanini, L.; Bergmeier, W. RAP GTPases and platelet integrin signaling. Platelets 2019, 30, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Kandula, V.; Kosuru, R.; Ye, X.; Irwin, M.G.; Xia, Z. Decoding telomere protein Rap1: Its telomeric and nontelomeric functions and potential implications in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrzanowska-Wodnicka, M. Rap1 in endothelial biology. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2017, 24, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, R.C.; Cheng, K.; Ring, B.Z.; Su, L. Roles of Rap1 signaling in tumor cell migration and invasion. Cancer Biol. Med. 2017, 14, 90–99. [Google Scholar]
- Bögershausen, N.; Tsai, I.C.; Pohl, E.; Kiper, P.Ö.; Beleggia, F.; Percin, E.F.; Keupp, K.; Matchan, A.; Milz, E.; Alanay, Y.; et al. RAP1-mediated MEK/ERK pathway defects in Kabuki syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3585–3599. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison, M.R.; White, P.C. Prostacyclin regulates bone growth via the Epac/Rap1 pathway. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaśkiewicz, A.; Pająk, B.; Orzechowski, A. The Many Faces of Rap1 GTPase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munson, L.; Moresco, A. Comparative pathology of mammary gland cancers in domestic and wild animals. Breast Dis. 2007, 28, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.S. Bovine and human papillomaviruses: A comparative review. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roperto, S.; Munday, J.S.; Corrado, F.; Goria, M.; Roperto, F. Detection of bovine papillomavirus type 14 DNA sequences in urinary bladder tumors in cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 190, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wu, C.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Pei, Z.; Tao, L.; Gong, Y.; Pan, Y.; Bai, H.; et al. Detection and genomic characterization of Bovine papillomavirus isolated from Chinese native cattle. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmatzadeh, F.; Keyvanfar, H.; Hasan, N.H.; Niap, F.; Bani Hassan, E.; Hematzade, A.; Ebrahimie, E.; McWhorter, A.; Ignjatovic, J. Interaction between Bovine leukemia virus (BLV) infection and age on telomerase misregulation. Vet. Res. Commun. 2015, 39, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, J.; Thompson, P.R. Protein Arginine Methylation and Citrullination in Epigenetic Regulation. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 654–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuzhalin, A.E. Citrullination in cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beato, M.; Sharma, P. Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase 2 (PADI2)-Mediated Arginine Citrullination Modulates Transcription in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentville, V.A.; Vankemmelbeke, M.; Metheringham, R.L.; Durrant, L.G. Post-translational modifications such as citrullination are excellent targets for cancer therapy. Semin. Immunol. 2020, 47, 101393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devraj, G.; Beerlage, C.; Brüne, B.; Kempf, V.A. Hypoxia and HIF-1 activation in bacterial infections. Microbes Infect. 2017, 19, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, K. HIF-1 at the crossroads of hypoxia, inflammation, and cancer. Int. J. Cancer. 2016, 138, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzuto, A.; Carico, E. Role of HIF-1 in Cancer Progression: Novel Insights. A Review. Curr. Mol. Med. 2018, 18, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Wei, F.; Cai, Q. Hostile takeover: Manipulation of HIF-1 signaling in pathogen-associated cancers (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Metheni, M.; Lombès, A.; Bouillaud, F.; Batteux, F.; Langsley, G. HIF-1α induction, proliferation and glycolysis of Theileria-infected leukocytes. Cell Microbiol. 2015, 17, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berisha, B.; Schams, D.; Rodler, D.; Pfaffl, M.W. Angiogenesis in the Ovary—The Most Important Regulatory Event for Follicle and Corpus Luteum Development and Function in Cow—An Overview. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2016, 45, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.; Liu, X.; Yang, T.; Huang, Z.; Hanif, Q.; Asif, M.; Khan, Q.M.; Mansoor, S. Genomic variants identified from whole-genome resequencing of indicine cattle breeds from Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.; Carter, J.F. Stable carbon isotope diagnostics of mammalian metabolism, a high-resolution isotomics approach using amino acid carboxyl groups. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, C.G.; Broderick, G.A. A 100-Year Review: Protein and amino acid nutrition in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 10094–10112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamam, H.J.; Palaniyar, N. Post-Translational Modifications in NETosis and NETs-Mediated Diseases. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, K.; Gokpinar, S.; Gazyagci, A.N.; Babur, C.; Sursal, N.; Azkur, A.K. Role of NETs in the difference in host susceptibility to Toxoplasma gondii between sheep and cattle. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2017, 189, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villagra-Blanco, R.; Silva, L.M.R.; Muñoz-Caro, T.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Gärtner, U.; Taubert, A.; Zhang, X.; Hermosilla, C. Bovine Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils Cast Neutrophil Extracellular Traps against the Abortive Parasite Neospora caninum. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, J.; Sun, D.; Tuo, W.; Xiao, Z. Bovine neutrophils form extracellular traps in response to the gastrointestinal parasite Ostertagia ostertagi. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerjomiceva, N.; Seri, H.; Völlger, L.; Wang, Y.; Zeitouni, N.; Naim, H.Y.; von Köckritz-Blickwede, M. Enrofloxacin enhances the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps in bovine granulocytes. J. Innate Immun. 2014, 6, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, H.N.; Lai, E.T.; Havugimana, P.C.; White, C.; Emili, A.; Sakac, D.; Binnington, B.; Neschadim, A.; McCarthy, S.D.; Branch, D.R. Extracellular histones identified in crocodile blood inhibit in-vitro HIV-1 infection. AIDS 2016, 30, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.M.; Kemp, G.D.; Molle, M.G.; Smith, V.J. Anti-microbial properties of histone H2A from skin secretions of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Biochem. J. 2002, 368 Pt 2, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas, A.P.; Whitaker, J.N. Preparation of a monoclonal antibody to citrullinated epitopes: Its characterization and some applications to immunohistochemistry in human brain. Glia 2002, 37, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Protein Name | Symbol | Sequences | Total Score (p < 0.05) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serotransferrin | G3X6N3 | 76 | 5712 |
| Serotransferrin | Q29443 | 76 | 5711 |
| Complement factor H | Q28085 | 77 | 5123 |
| Alpha-2-macroglobulin | Q7SIH1 | 77 | 5079 |
| Serum albumin | A0A140T897 | 59 | 3944 |
| Uncharacterised protein [complement factor H] | F1MC45 | 54 | 3745 |
| Complement C3 | Q2UVX4 | 68 | 3483 |
| Uncharacterised protein [ceruloplasmin] | F1N076 | 44 | 2712 |
| Embryo-specific fibronectin 1 | B8Y9S9 | 37 | 2263 |
| Hemopexin | Q3SZV7 | 30 | 2019 |
| Uncharacterised protein [complement C4A] | E1BH06 | 34 | 1997 |
| C4b-binding protein alpha chain | Q28065 | 33 | 1841 |
| Kininogen-1 | A0A140T8C8 | 23 | 1505 |
| Kininogen-1 | P01044 | 22 | 1449 |
| Histidine-rich glycoprotein | F1MKS5 | 26 | 1432 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | F1MJK3 | 26 | 1291 |
| Kininogen-2 | P01045 | 19 | 1271 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3X7F3 | 16 | 1259 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3N0V0 | 19 | 1186 |
| Apolipoprotein A-I preproprotein | V6F9A2 | 19 | 1122 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | F1MVK1 | 17 | 953 |
| SERPIND1 protein | A6QPP2 | 16 | 865 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | F1MZ96 | 13 | 837 |
| Uncharacterised protein [Bos taurus immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 1 (IGLL1)] | F1MLW7 | 10 | 815 |
| Uncharacterised protein [Bos taurus immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 1 (IGLL1)] | F1MCF8 | 10 | 796 |
| Uncharacterised protein [Immunoglobulin heavy constant mu] | G5E5T5 | 12 | 784 |
| Uncharacterised protein [Immunoglobulin heavy constant mu] | G5E513 | 10 | 732 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3N0S9 | 12 | 648 |
| Histidine-rich glycoprotein | P33433 | 12 | 623 |
| Alpha-2-antiplasmin | P28800 | 11 | 531 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | F1MLW8 | 5 | 434 |
| Hemoglobin subunit beta | P02070 | 6 | 422 |
| Vitamin D-binding protein | F1N5M2 | 9 | 420 |
| Alpha-1-antiproteinase | P34955 | 8 | 418 |
| Adiponectin | Q3Y5Z3 | 6 | 411 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | F1MW79 | 7 | 403 |
| ECM1 protein | A5PJT7 | 8 | 395 |
| Complement C1q subcomponent subunit B | Q2KIV9 | 8 | 390 |
| Plasma kallikrein | Q2KJ63 | 8 | 385 |
| Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4 | F1MMD7 | 6 | 367 |
| C1QC protein | Q1RMH5 | 5 | 347 |
| Uncharacterised protein [Serpin A3-5; Serine protease inhibitor] | G8JKW7 | 6 | 338 |
| Apolipoprotein A-IV | F1N3Q7 | 7 | 338 |
| Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H2 | F1MNW4 | 6 | 338 |
| Selenoprotein P | P49907 | 6 | 323 |
| Plasminogen | E1B726 | 6 | 302 |
| Complement C1q subcomponent subunit A | Q5E9E3 | 5 | 300 |
| Uncharacterised protein [Bos taurus insulin-like growth factor binding protein, acid labile subunit (IGFALS)] | F1MJZ4 | 6 | 277 |
| Thrombospondin-1 | F1N3A1 | 7 | 273 |
| Serpin A3-3 | G3N1U4 | 5 | 271 |
| Protein HP-20 homolog | Q2KIT0 | 5 | 269 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G5E604 | 4 | 234 |
| Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H1 | Q0VCM5 | 4 | 234 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | E1B805 | 5 | 232 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3MXD9 | 3 | 209 |
| Uncharacterised protein [Bos taurus immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 1 (IGLL1)] | G3N2D7 | 3 | 204 |
| Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 7 | Q29S21 | 4 | 199 |
| Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 | F1MC11 | 4 | 199 |
| Uncharacterised protein [Heparan sulfate proteoglycan 2] | F1MER7 | 4 | 195 |
| Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein | cRAPR1|FETUA_BOVIN | 4 | 190 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3N1H5 | 2 | 187 |
| Serpin A3-8 | A0A0A0MP89 | 3 | 184 |
| Complement factor B | P81187 | 4 | 183 |
| Protein AMBP | F1MMK9 | 5 | 181 |
| Serpin A3-2 | A2I7M9 | 4 | 180 |
| Antithrombin-III | F1MSZ6 | 5 | 176 |
| Paraoxonase 1 | Q2KIW1 | 4 | 174 |
| Gelsolin | F1MJH1 | 3 | 171 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3N3Q3 | 2 | 168 |
| Complement C5a anaphylatoxin | F1MY85 | 3 | 166 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G5E5H2 | 3 | 162 |
| Serpin A3-7 | A0A0A0MP92 | 4 | 160 |
| C1QTNF3 protein | A7MB82 | 3 | 160 |
| Uncharacterised protein [Bos taurus serotransferrin-like] | E1BI82 | 4 | 157 |
| Uncharacterised protein [Apolipoprotein B] | E1BNR0 | 4 | 150 |
| Primary amine oxidase, liver isozyme | Q29437 | 3 | 137 |
| Coagulation factor XI | F1MUT4 | 2 | 127 |
| Hepatocyte growth factor-like protein | E1BDW7 | 2 | 121 |
| Fibrinogen beta chain | F1MAV0 | 3 | 108 |
| Immunoglobulin J chain | Q3SYR8 | 2 | 107 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3MXB5 | 2 | 100 |
| Uncharacterised protein [CD5 molecule-like] | F1N514 | 2 | 94 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3MXG6 | 2 | 94 |
| Complement component C9 | Q3MHN2 | 2 | 87 |
| Complement component C6 | F1MM86 | 3 | 86 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G5E5V1 | 2 | 86 |
| Hemoglobin subunit alpha | P01966 | 2 | 85 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3N028 | 2 | 75 |
| Fibrinogen alpha chain | A5PJE3 | 1 | 74 |
| Vitronectin | Q3ZBS7 | 2 | 73 |
| Alpha-1B-glycoprotein | Q2KJF1 | 1 | 66 |
| Coagulation factor XII | F1MTT3 | 1 | 65 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | F1MSF0 | 2 | 63 |
| Prothrombin | P00735 | 1 | 61 |
| Uncharacterised protein [Nidogen 1] | F1MWN3 | 1 | 57 |
| Protein HP-25 homolog 2 | Q2KIU3 | 1 | 57 |
| Clusterin | F1MWI1 | 1 | 55 |
| Contactin-1 | F1MVI0 | 1 | 54 |
| Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor | F1MR22 | 2 | 51 |
| Uncharacterised protein [Sperm associated antigen 9] | F1MZ69 | 2 | 51 |
| Uncharacterised protein [Ankyrin repeat domain 11] | E1BAT5 | 2 | 51 |
| Beta-2-glycoprotein 1 | A0A140T843 | 1 | 50 |
| Carboxypeptidase N catalytic chain | Q2KJ83 | 1 | 49 |
| Uncharacterised protein [complement component 8, alpha polypeptide (C8A)] | F1MX87 | 1 | 48 |
| Fibrinogen gamma-B chain | F1MGU7 | 1 | 48 |
| Uncharacterised protein [ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 13] | F1MVP0 | 1 | 47 |
| Uncharacterised protein [Talin 1] | F1MDH3 | 1 | 46 |
| Complement C1s subcomponent | Q0VCX1 | 1 | 46 |
| Uncharacterised protein [CL43—Collectin-43] | F1MFY6 | 1 | 45 |
| Complement component C7 | F1N045 | 1 | 44 |
| CLEC11A protein | A5D7L1 | 1 | 43 |
| Uncharacterised protein [KCTD12—Potassium channel tetramerization domain containing 12] | G3N3D4 | 1 | 43 |
| Uncharacterised protein [BRIP1—BRCA1 interacting protein C-terminal helicase 1] | E1BNG9 | 1 | 39 |
| Cadherin-1 | F1N619 | 1 | 39 |
| Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L5 | Q9XSJ0 | 1 | 38 |
| CPN2 protein | A6QP30 | 1 | 37 |
| Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase THEM4 | A1A4L1 | 1 | 37 |
| Uncharacterised protein [SLAMF9—SLAM family member 9] | E1BNF9 | 1 | 36 |
| Uncharacterised protein [MED12; Mediator complex subunit 12] | F1MZ95 | 1 | 35 |
| Transthyretin | O46375 | 1 | 33 |
| Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-3 | Q9MZL3 | 1 | 33 |
| Protein Name | Symbol | Sequences | Total Score (p < 0.05) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serotransferrin | G3X6N3 | 75 | 4958 |
| Serotransferrin | Q29443 | 74 | 4941 |
| Complement factor H | Q28085 | 85 | 4700 |
| Alpha-2-macroglobulin | Q7SIH1 | 77 | 4633 |
| Serum albumin | A0A140T897 | 76 | 4604 |
| Complement C3 | Q2UVX4 | 83 | 4258 |
| Uncharacterised protein (CFH—Complement factor H) | F1MC45 | 61 | 3469 |
| Fibronectin | G5E5A9 | 56 | 2492 |
| Uncharacterised protein (Ceruloplasmin) | F1N076 | 37 | 1994 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | F1MJK3 | 38 | 1870 |
| Uncharacterised protein (C4A—Complement C4) | E1BH06 | 35 | 1840 |
| C4b-binding protein alpha chain | Q28065 | 36 | 1761 |
| Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5 | M0QVZ6 | 35 | 1750 |
| Hemopexin | Q3SZV7 | 30 | 1594 |
| Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 | F1MC11 | 29 | 1592 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3N0V0 | 25 | 1542 |
| Histidine-rich glycoprotein | F1MKS5 | 26 | 1407 |
| Uncharacterised protein (keratin 33A (KRT33A)) | F1MXG6 | 22 | 1311 |
| KRT33A protein | A5PJJ1 | 22 | 1306 |
| Keratin 31 | Q148I8 | 22 | 1291 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3X7F3 | 20 | 1288 |
| Keratin, type II cuticular Hb1 | Q148H4 | 25 | 1225 |
| Uncharacterised protein (keratin 34 (KRT34)) | F1MSA6 | 21 | 1209 |
| Kininogen-1 | A0A140T8C8 | 21 | 1188 |
| Kininogen-1 | P01044 | 21 | 1164 |
| Uncharacterised protein (Desmoplakin) | E1BKT9 | 27 | 1156 |
| Uncharacterised protein (keratin 86 (KRT86)) | E1B898 | 22 | 1104 |
| Apolipoprotein A-I preproprotein | V6F9A2 | 22 | 1101 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | F1MVK1 | 20 | 1066 |
| Uncharacterised protein (KRT6A—Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 59 kDa, component IV) | M0QVY0 | 21 | 1049 |
| Kininogen-2 | P01045 | 19 | 1042 |
| Uncharacterised protein (KRT3—Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 68 kDa, component IB) | G3MXL3 | 21 | 1034 |
| Junction plakoglobin | Q8SPJ1 | 21 | 987 |
| Keratin, type II cytoskeletal | Q08D91 | 19 | 971 |
| Uncharacterised protein (Immunoglobulin heavy constant mu) | G5E5T5 | 16 | 938 |
| Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 17 | A0A140T867 | 17 | 890 |
| Uncharacterised protein (IGLL1—immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 1) | F1MCF8 | 12 | 886 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | F1MH40 | 13 | 872 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | F1MZ96 | 14 | 863 |
| Keratin 10 (Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis; keratosis palmaris et plantaris) | A6QNZ7 | 15 | 854 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | F1MLW7 | 10 | 849 |
| Complement C4 | P01030 | 16 | 826 |
| Uncharacterised protein (Immunoglobulin heavy constant mu) | G5E513 | 15 | 810 |
| KRT15 protein | Q17QL7 | 13 | 734 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3N0S9 | 14 | 631 |
| Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 19 | P08728 | 12 | 625 |
| KRT4 protein | A4IFP2 | 12 | 623 |
| SERPIND1 protein | A6QPP2 | 12 | 606 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | F1MLW8 | 7 | 588 |
| Histidine-rich glycoprotein | P33433 | 9 | 566 |
| Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H2 | F1MNW4 | 12 | 554 |
| Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4 | F1MMD7 | 10 | 521 |
| Vitamin D-binding protein | F1N5M2 | 12 | 517 |
| Antithrombin-III | F1MSZ6 | 11 | 492 |
| Plasminogen | P06868 | 14 | 485 |
| Apolipoprotein A-IV | Q32PJ2 | 11 | 475 |
| Serpin A3-3 | G3N1U4 | 9 | 442 |
| Complement factor B | P81187 | 9 | 429 |
| C1QC protein | Q1RMH5 | 8 | 428 |
| Complement C1q subcomponent subunit B | Q2KIV9 | 7 | 413 |
| Uncharacterised protein (serotransferrin-like) | E1BI82 | 8 | 411 |
| Uncharacterised protein (KRT16—Keratin 16) | G3X7W8 | 9 | 407 |
| Complement C1q subcomponent subunit A | Q5E9E3 | 7 | 401 |
| Serpin A3-4 | A2I7N0 | 9 | 383 |
| Alpha-1B-glycoprotein | Q2KJF1 | 7 | 381 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3N3Q3 | 5 | 367 |
| Uncharacterised protein (Serpin A3-5) | G8JKW7 | 7 | 366 |
| Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 78 | A6QNX5 | 7 | 356 |
| Primary amine oxidase, liver isozyme | Q29437 | 8 | 352 |
| Serpin A3-2 | A2I7M9 | 7 | 333 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | F1MW79 | 6 | 330 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3N1H5 | 5 | 325 |
| Uncharacterised protein (KRT77—Keratin 77) | G3MYU2 | 6 | 310 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | E1B805 | 7 | 309 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3MXG6 | 4 | 305 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3MXD9 | 5 | 300 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3N2P6 | 5 | 292 |
| Uncharacterised protein (insulin-like growth factor binding protein, acid labile subunit (IGFALS)) | F1MJZ4 | 5 | 286 |
| Adiponectin | Q3Y5Z3 | 5 | 282 |
| Alpha-2-antiplasmin | P28800 | 7 | 271 |
| Protein AMBP | F1MMK9 | 6 | 268 |
| Vitronectin | Q3ZBS7 | 5 | 264 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G5E604 | 5 | 254 |
| Desmoglein-1 | F1MIW8 | 7 | 252 |
| Fibrinogen gamma-B chain | F1MGU7 | 5 | 252 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3MY71 | 5 | 251 |
| Annexin A2 | P04272 | 5 | 244 |
| Fibrinogen alpha chain | A5PJE3 | 5 | 243 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3MWT1 | 3 | 241 |
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | P10096 | 6 | 238 |
| Serpin A3-7 | A0A0A0MP92 | 5 | 218 |
| Plakophilin-1 | Q28161 | 4 | 216 |
| Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H1 | Q0VCM5 | 5 | 213 |
| Hemoglobin subunit beta | P02070 | 4 | 212 |
| Alpha-1-antiproteinase | P34955 | 4 | 209 |
| Keratin, type II | A0JND2 | 4 | 198 |
| Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | F1MRD0 | 5 | 197 |
| Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 28 | Q148H6 | 4 | 194 |
| Thrombospondin-1 | F1N3A1 | 6 | 192 |
| Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 20 | F1MPK1 | 4 | 191 |
| ECM1 protein | A5PJT7 | 5 | 188 |
| Uncharacterised protein (Bos taurus immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 1 (IGLL1)) | G3N2D7 | 3 | 186 |
| Selenoprotein P | P49907 | 5 | 184 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | A0A0A0MPA0 | 4 | 176 |
| Gelsolin | F1MJH1 | 4 | 175 |
| Lactotransferrin | P24627 | 4 | 169 |
| Fibrinogen beta chain | F1MAV0 | 5 | 162 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G5E5H2 | 3 | 156 |
| Protein HP-20 homolog | Q2KIT0 | 3 | 151 |
| Uncharacterised protein (TGM1—Transglutaminase 1) | F1MBB7 | 2 | 143 |
| Actin, gamma-enteric smooth muscle | F1MKC4 | 4 | 143 |
| Uncharacterised protein (CD5L—CD5 molecule-like) | F1N514 | 4 | 131 |
| Complement component C7 | F1N045 | 4 | 128 |
| Uncharacterised protein (APOB—Apolipoprotein B) | E1BNR0 | 4 | 119 |
| Arginase-1 | Q2KJ64 | 3 | 119 |
| Alpha-S1-casein | CASA1_BOVIN | 2 | 115 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3N028 | 2 | 114 |
| Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein | cRAPR1|FETUA_BOVIN | 2 | 106 |
| Paraoxonase 1 | Q2KIW1 | 3 | 106 |
| Beta-2-glycoprotein 1 | A0A140T843 | 2 | 97 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G5E5V1 | 2 | 89 |
| Uncharacterised protein (Histone H2B family) | E1B7N8 | 2 | 88 |
| Complement component 1, r subcomponent | A5D9E9 | 3 | 83 |
| Histone H2A | A0A0A0MP90 | 2 | 80 |
| Uncharacterised protein (SLK-STE20-like kinase) | G3X696 | 3 | 80 |
| Prothrombin | P00735 | 2 | 79 |
| Peroxiredoxin-2 | Q9BGI3 | 3 | 79 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | G3MZE0 | 1 | 69 |
| Uncharacterised protein (complement component 8, alpha polypeptide (C8A)) | F1MX87 | 1 | 69 |
| Uncharacterised protein (C1orf68—Chromosome 1 open reading frame 68) | G3N3D3 | 2 | 68 |
| Complement C5a anaphylatoxin | F1MY85 | 2 | 63 |
| Uncharacterised protein (complement factor I (CFI)) | F1N4M7 | 1 | 61 |
| Uncharacterised protein (armadillo repeat gene deleted in velocardiofacial syndrome (ARVCF)) | E1BPV1 | 2 | 59 |
| Uncharacterised protein (NEK10-Uncharacterised protein; NIMA-related kinase 10) | E1BHZ1 | 2 | 58 |
| Keratin associated protein 13-1 | A1A4M9 | 2 | 57 |
| Uncharacterised protein (uncharacterised) | F1MSF0 | 2 | 57 |
| Histone H4 | E1B9M9 | 1 | 56 |
| Gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase | Q32LE4 | 1 | 55 |
| Uncharacterised protein (JAKMIP2—Janus kinase and microtubule interacting protein 2) | G5E551 | 2 | 54 |
| TOX high mobility group box family member 4 | Q0P5K4 | 1 | 53 |
| Uncharacterised protein (TBC1D32—TBC1 domain family, member 32) | F1N7V1 | 2 | 51 |
| Proteasome subunit alpha type-6 | Q2YDE4 | 1 | 50 |
| Uncharacterised protein (KIAA1009 ortholog) | F1MZ01 | 2 | 50 |
| Uncharacterised protein (MYO5B—Myosin VB) | F1MMQ6 | 2 | 50 |
| Uncharacterised protein (Phospholipid phosphatase related 4) | F1MJ26 | 2 | 49 |
| Uncharacterised protein (MGA—MGA, MAX dimerization protein) | E1BKB7 | 2 | 49 |
| Uncharacterised protein (GOLGB1—Golgin B1) | E1BKZ5 | 2 | 47 |
| Histone H3 | E1BGN3 | 1 | 46 |
| Uncharacterised protein (CROCC—Ciliary rootlet coiled-coil, rootletin) | E1BBS9 | 3 | 46 |
| Protein FAM149B1 | A0JNF3 | 2 | 45 |
| Alpha-enolase | F1MB08 | 2 | 45 |
| Uncharacterised protein (UBR4—Ubiquitin protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 4) | E1BHT5 | 3 | 45 |
| Complement component C9 | Q3MHN2 | 1 | 44 |
| Uncharacterised protein (DOCK8—Bos taurus dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (DOCK8)) | E1BNA6 | 2 | 44 |
| Uncharacterised protein (KPRP—Keratinocyte proline-rich protein) | E1BLN6 | 1 | 44 |
| Uncharacterised protein (CCDC14—Coiled-coil domain containing 14) | F1MS02 | 2 | 43 |
| Uncharacterised protein (Strawberry notch homolog 1(Drosophila)) | E1BMP8 | 3 | 42 |
| DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta | A5PJW8 | 1 | 42 |
| Uncharacterised protein (CRYGN-Crystallin, gamma N) | E1BDQ1 | 1 | 42 |
| Flotillin-1 | Q08DN8 | 1 | 41 |
| Uncharacterised protein (SMG6—Uncharacterised protein; Bos taurus smg-6 homolog, nonsense mediated mRNA decay factor (C. elegans) (SMG6)) | E1BFK4 | 2 | 41 |
| C1QTNF3 protein | A7MB82 | 1 | 41 |
| Uncharacterised protein (Protocadherin gamma subfamily B, 1) | F1MCA2 | 1 | 40 |
| Uncharacterised protein (Death-associated protein kinase 1) | F1MRL0 | 1 | 39 |
| Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase THEM4 | A1A4L1 | 1 | 37 |
| Uncharacterised protein (Centrosomal protein 104kDa) | E1BND2 | 1 | 37 |
| C8G protein | A8YXZ2 | 1 | 36 |
| Uncharacterised protein (SERPINB12—Serpin family B member 12) | E1BDF5 | 1 | 36 |
| Uncharacterised protein (SLAMF9 SLAM family member 9) | E1BNF9 | 1 | 36 |
| Complement C1s subcomponent | Q0VCX1 | 1 | 36 |
| Uncharacterised protein (methyltransferase like 3 (METTL3)) | F1MX80 | 1 | 35 |
| Uncharacterised protein (SPAG9—Sperm associated antigen 9) | F1MZ69 | 1 | 35 |
| Adenosylhomocysteinase | Q3MHL4 | 1 | 35 |
| Uncharacterised protein (HIVEP3—Human immunodeficiency virus type I enhancer binding protein 3) | F1MBK6 | 1 | 34 |
| Coagulation factor V | F1N0I3 | 1 | 33 |
| Uncharacterised protein (VPREB1—Uncharacterised protein) | F1N160 | 1 | 33 |
| Uncharacterised protein (SERPING1) | E1BMJ0 | 1 | 33 |
| PPARD protein | A4IFL4 | 32 | |
| Uncharacterised protein | F1MZ93 | 1 | 32 |
| Uncharacterised protein (NCBP1—Nuclear cap binding protein subunit 1) | E1BMM0 | 1 | 32 |
| Transthyretin | O46375 | 1 | 32 |
| Uncharacterised protein (Cryptochrome-1) | F1MXB2 | 1 | 32 |
| Tubulin alpha chain | F1MNF8 | 1 | 31 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Criscitiello, M.F.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Post-Translational Protein Deimination Signatures in Serum and Serum-Extracellular Vesicles of Bos taurus Reveal Immune, Anti-Pathogenic, Anti-Viral, Metabolic and Cancer-Related Pathways for Deimination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082861
Criscitiello MF, Kraev I, Lange S. Post-Translational Protein Deimination Signatures in Serum and Serum-Extracellular Vesicles of Bos taurus Reveal Immune, Anti-Pathogenic, Anti-Viral, Metabolic and Cancer-Related Pathways for Deimination. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(8):2861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082861
Chicago/Turabian StyleCriscitiello, Michael F., Igor Kraev, and Sigrun Lange. 2020. "Post-Translational Protein Deimination Signatures in Serum and Serum-Extracellular Vesicles of Bos taurus Reveal Immune, Anti-Pathogenic, Anti-Viral, Metabolic and Cancer-Related Pathways for Deimination" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 8: 2861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082861
APA StyleCriscitiello, M. F., Kraev, I., & Lange, S. (2020). Post-Translational Protein Deimination Signatures in Serum and Serum-Extracellular Vesicles of Bos taurus Reveal Immune, Anti-Pathogenic, Anti-Viral, Metabolic and Cancer-Related Pathways for Deimination. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(8), 2861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082861