Abstract
An imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and anti-oxidant capacity results in oxidative injury to cellular components and molecules, which in turn disturbs the homeostasis of cells and organs. Although retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a hereditary disease, non-genetic biological factors including oxidative stress also modulate or contribute to the disease progression. In animal models of RP, the degenerating retina exhibits marked oxidative damage in the nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids, and anti-oxidant treatments substantially suppress photoreceptor cell death and microgliosis. Although the mechanisms by which oxidative stress mediates retinal degeneration have not been fully elucidated, our group has shown that oxidative DNA damage and its defense system are key regulators of microglial activation and photoreceptor degeneration in RP. In this review, we summarize the current evidence regarding oxidative stress in animal models and patients with RP. The clinical efficacy of anti-oxidant treatments for RP has not been fully established. Nevertheless, elucidating key biological processes that underlie oxidative damage in RP will be pivotal to understanding the pathology and developing a potent anti-oxidant strategy that targets specific cell types or molecules under oxidative stress.
1. Introduction
The cellular organelles and molecules of the human body are always at risk of being oxidized by reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are produced as a regular part of the body’s activity. ROS such as superoxide (1O2), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals (•OH) are generated in the process of oxidative phosphorylation and ATP synthesis in the mitochondria [1]. Alternatively, ROS can be produced by NADPH oxidases (NOXs), which are transmembrane enzymes that form a 1O2-producing protein complex upon activation [2]. NOXs are critical for the body’s immune defense against infected bacteria as well as for health and fighting disease in a variety of tissues including the retina.
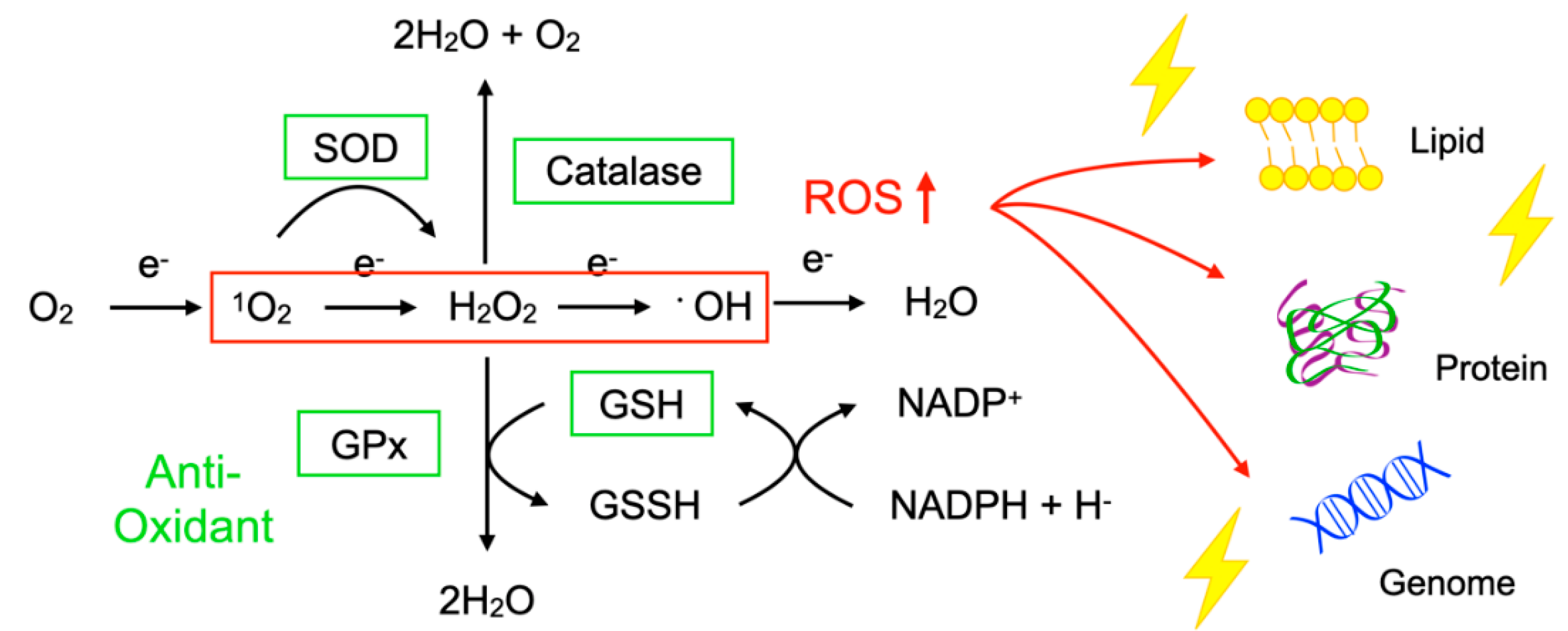
To protect the organelles and molecules against ROS, the cells have an elaborate defense system to neutralize or catalyze ROS and repair ROS-induced damage (Figure 1). For example, superoxide dismutase (SOD) catalyzes the dismutation of 1O2 into oxygen (O2) and H2O2. Catalase breaks down •OH into O2 and water (H2O). Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) catalyzes H2O2 into H2O, with the conversion of glutathione (GSH) to its oxidized disulfide form (GSSG) [3].
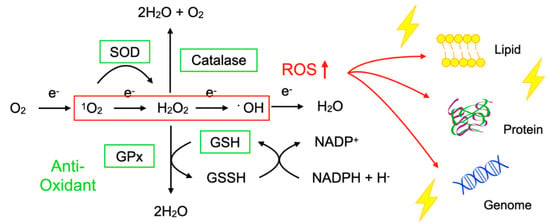
Figure 1.
Imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and anti-oxidants impairs the function of macromolecules. ROS including superoxide (1O2), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals (•OH) are generated during oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) catalyzes the 1O2 into oxygen (O2) and H2O2. Catalase breaks down •OH into O2 and water (H2O). Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) catalyzes H2O2 into H2O, with the conversion of glutathione (GSH) to its oxidized disulfide form (GSSG). An imbalance between ROS production (red box) and anti-oxidant capacity (green box) results in the accumulation of oxidative insults (lightning symbol) to the cellular lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ↑, increase.
Oxidative stress is a state in which the balance between the production of ROS and the anti-oxidant defense system is impaired. The production of ROS is markedly increased in various disease conditions including inflammation, metabolic dysfunction, cancer, and neurodegeneration. Excessive ROS insults the cellular macromolecules such as nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids (Figure 1), leading to cellular dysfunction, transdifferentiation, or death. Accordingly, oxidative stress is generally deemed to be detrimental to human health; however, it should be noted that, in some conditions, ROS are required to mediate the body’s protection against infection and tissue injury [4].
2. Retinitis Pigmentosa and Oxidative Stress
2.1. Etiology of Retinitis Pigmentosa
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) comprises a group of inherited retinal degeneration states that, without effective treatment, lead to blindness [5,6]. Genetic mutations associated with RP have been identified in more than 90 genes, most of which are related to the function and maintenance of rod photoreceptor cells. Rod cells are responsible for vision in dim light, and the symptoms of RP typically start with night blindness due to the dysfunction and death of rod cells. Ring scotoma at the mid-peripheral retina, which corresponds to the region containing the highest rod density, is also associated with RP. At this early stage of the disease, the daily lives and activity levels of patients are usually not severely affected. However, following rod cell loss, the remaining cone photoreceptor cells are gradually but progressively impaired, leading to constriction of the visual field and eventually the loss of central vision. This impairment of cone-mediated daylight vision is the most debilitating aspect of RP. Based on these clinical features, RP is also categorized as rod-cone dystrophy [7].
As can be seen from the variety of causal genes, RP patients show diverse heterogeneity in their phenotype. For example, the onset age of night blindness or other symptoms ranges from early childhood to the mid-30s or even later. The central visual function and its progression also have significant inter-individual variability among patients with mutations in the same gene or even among family members with the same mutation. Recent advances in genotype–phenotype technology have led to a better characterization of each causal gene in RP, but there are still significant gaps between genetic results and clinical findings [8].
Despite the heterogeneity in disease progression, there are shared clinical characteristics in RP, including the appearance of the fundus. It has been suggested that some disease-modifying factors may underlie the disease as a common etiology of RP. For example, following the rod cell loss, the degenerative retina, which largely reduces the O2 consumption, is exposed to higher levels of O2 and thereby damaged by ROS, suggesting that oxidative stress may promote rod and cone degeneration in RP [9]. Other biological factors such as inflammation, autophagy, and metabolic dysfunction have been suggested to modify the disease progression of RP [10,11,12]. Elucidation of the biological mechanisms underlying the rod and cone degeneration in RP will be important for gaining a better understanding of the disease and for the development of novel therapies targeting specific biological pathways.
2.2. Oxidative Damage in Animal Models of RP
2.2.1. Evidence of Increased Oxidative Damage in the RP Retina
Increased ROS in the tissue can be experimentally detected by probes such as dihydroethidium (DHE) and CellROX™, which react with ROS to produce a fluorescent signal. After an in vivo administration of DHE, the red fluorescent signal can be detected in the outer retina of rd1 mice, a murine model of RP that have a mutation in Pde6b and a confounding mutation in Gpr179 [13,14]. This ROS signal is not observed in the normal retina, indicating that the production of ROS is markedly increased in the degenerative loci of RP.
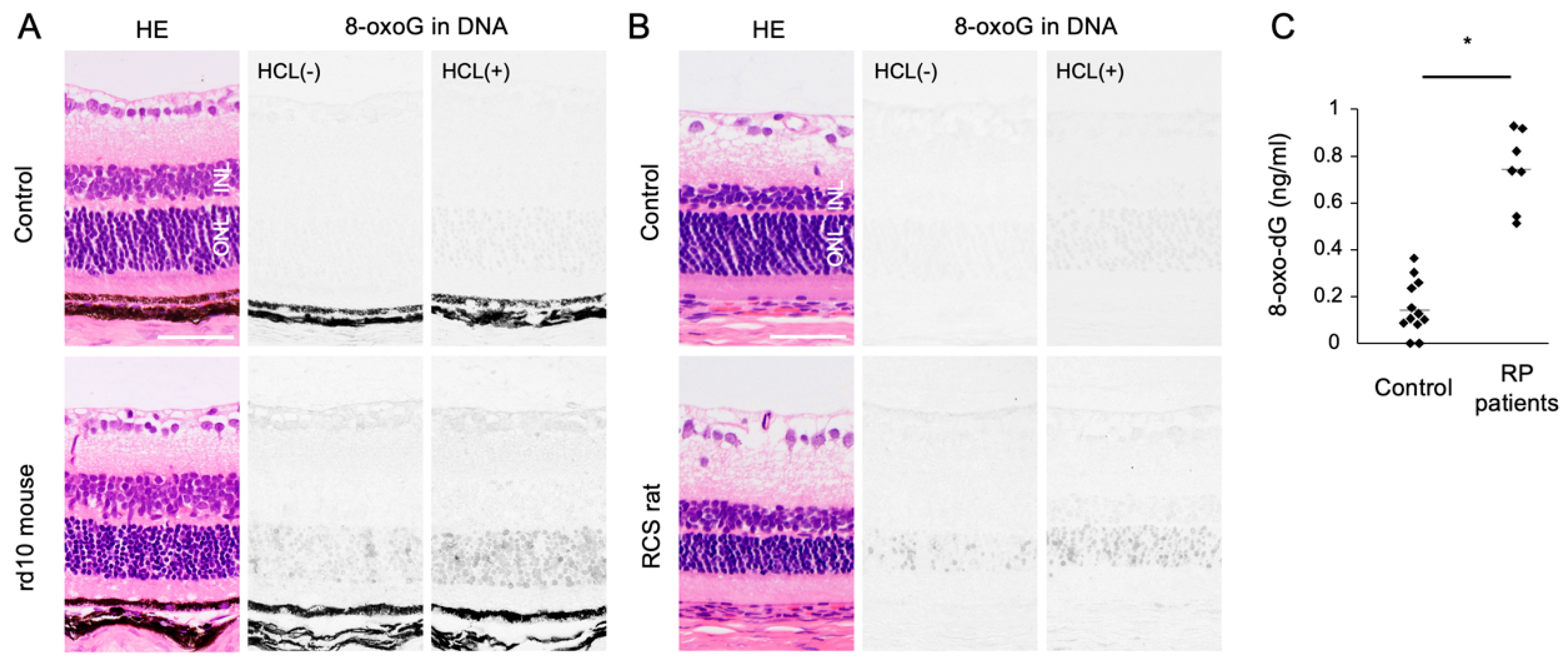
Oxidized lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids can also be visualized by the specific antibodies against the oxidized residue of each molecule. For example, malondialdehyde (MDA) and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) are byproducts of lipid peroxidation; protein carbonyls and nitrotyrosine are markers of protein oxidation; and 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguannine (8-oxoguanine, or 8-oxoG) is a major form of oxidized nucleic acids. In several models of RP, it was shown that oxidized lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids are substantially increased in the degenerative retina, especially in the photoreceptor layer (Figure 2A,B) [15,16].
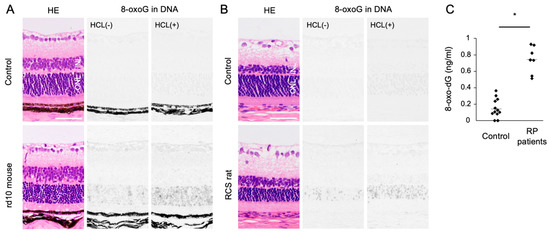
Figure 2.
The Figure is reproduced from [16] with copyright permission. Accumulation of oxidative DNA damage in retinitis pigmentosa (RP). (A,B) Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining and immunohistochemical staining of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguannine (8-oxoG) in the retina of rd10 mice (A) and Royal College of Surgeons (RCS) rats (B), two genetically different models of retinitis pigmentosa. Per staining, HCl pretreatment was used to denature the nuclear DNA, thereby enhancing the detection of 8-oxoG in the nuclear DNA. Note that 8-oxo-G accumulation is substantially increased in the outer nuclear layer (ONL) of RP mice. Scale bar, 50 μm. INL: inner nuclear layer. (C) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for 8-oxo-dG in the vitreous of RP patients and controls (patients with idiopathic epiretinal membrane). The vitreous levels of 8-oxo-dG are increased in RP patients. * p = 0.0003
In addition to the photoreceptor cells, immune cells such as microglial cells or macrophages extensively infiltrate these outer retinal regions and express oxidative molecules such as NOX2, suggesting that these inflammatory cells may be an alternative source of ROS in the RP retina [13].
2.2.2. Role of Oxidative Damage in RP
Although oxidative stress has bidirectional roles (alternately beneficial and detrimental), laboratory findings suggest that oxidative stress acts to promote the retinal degeneration in RP. Yamada et al. showed that mice placed in 75% O2 for 2 weeks exhibited significant degeneration of photoreceptor cells, supporting the notion that a higher O2 supply may be deleterious to the retina [17].
In rd1 mice, Komeima et al. tested a cocktail of four anti-oxidants (vitamin E, a SOD mimetic, vitamin C, and a-lipoic acid), and they demonstrated that this anti-oxidant treatment substantially reduced the accumulation of oxidized lipids and protected cone cells against death. rd10 mice with a Pde6b mutation are another model of RP, and exhibit a slower progression of retinal degeneration [18]. Lee et al. treated rd10 mice with oral N-acetylcysteine (NAC), which replenishes intracellular GSH, and found that NAC substantially protected rod and cone photoreceptor cells [19]. We also assessed oral NAC for rd10 mice, and we found that NAC exerted neuroprotective as well as immunosuppressive effects [20]. The therapeutic effects of anti-oxidants have been observed in several animal models with different genetic mutations, suggesting that oxidative stress may be a common important pathology of the retinal degeneration in RP.
One limitation of these laboratory studies is that, in most of the experiments, the dosage of anti-oxidant drugs was far higher than that used in human medicine or dietary supplements. In addition, the treatment was often initiated at the very early phase in experimental models. Given that RP patients are usually referred to a hospital at the mid-phase or even late phase of the disease, the efficacy of a treatment in experimental models should be carefully interpreted.
2.2.3. Modification of Anti-Oxidant Genes in RP
Gene modification to enhance the body’s anti-oxidant capacity is another approach to combat oxidative stress. Usui et al. showed that transgenic overexpressions of SOD1 and GPx4, which catalyze 1O2 and H2O2, delay the cone degeneration in rd1 mice [21]. Although transgenic overexpression is not applicable to humans, Xiong et al. demonstrated that the viral vector-mediated retinal gene transfer of an anti-oxidant gene had therapeutic potential in RP models. In rd1, rd10, and Rhodopsin−/− mice, the adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector-mediated delivery of nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2 (NRF2), a transcription factor that boosts detoxifying and anti-oxidant genes on oxidative stimulation, is effective for cone survival [22]. Because gene therapy using AAV vector has been approved for Leber’s congenital amaurosis and has been widely tested in clinical trials for inherited retinal degeneration and other retinal diseases, local and long-lasting anti-oxidant therapy may be an alternative strategy for chronic retinal degenerative disorders including RP [23,24].
2.3. Clinical Evidence of Oxidative Stress in RP
Since human retinal samples are rarely obtained with an immediate sample preparation to prevent post-mortem oxidation, oxidative stress in RP patients has been analyzed using the aqueous humor, vitreous body, and peripheral blood samples. In ocular samples, we showed that 8-oxo-7,8-dyhydro-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-dG), a marker of oxidative DNA damage, is increased more than 5-fold in the vitreous of RP patients compared to controls without retinal degeneration (Figure 2C) [16]. Consistent with this finding, Campochiaro et al. demonstrated an approximately 2-fold increase of protein carbonyl contents in the aqueous humor of RP patients [25]. On the other hand, anti-oxidant molecules such as GSH and SOD3 were decreased in the aqueous humor of RP patients [26]. These findings suggest that an oxidative imbalance occurs in the eyes of RP patients, which is consistent with findings in experimental models.
The oxidant and anti-oxidant profiles in the peripheral blood of RP patients have shown some conflicting results. Martínez-Fernández de la Cámara et al. reported increased oxidative markers (e.g., nitrotyrosine and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances) but decreased anti-oxidant SOD3 in RP patients [26]. In contrast, Campochiaro et al. demonstrated no differences in protein carbonyls, the GSH/GSSH ratio, or SOD3 in the serum of RP patients [25]. In our cohort of 52 RP patients, we investigated an oxidant marker (hexanoyl-lysine (HEL)) and three anti-oxidant markers (SOD3, GPx, and potential anti-oxidant (PAO)). We observed no significant difference in these four markers between RP patients and healthy controls; however, a subgroup analysis showed that the serum SOD3 activity was significantly lower in the RP patients with severe degeneration involving the macula [27]. In addition, the lower serum SOD3 activity in the RP patients was related to worse visual acuity and macular retinal sensitivity [27]. These data suggest that the decline of serum SOD3 activity is associated with the loss of cone-mediated central vision.
There are two possible interpretations for the lower serum SOD3 in patients with advanced RP. One possibility is that the serum SOD3 level falls in response to retinal degeneration and increased ocular ROS in RP. Another possibility is that RP patients with a lower baseline anti-oxidant capacity have a faster disease progression. This point should be addressed in future studies by directly comparing oxidant/anti-oxidant molecules between aqueous and serum samples as well as by following up the patients to determine the longitudinal changes of the serum SOD3 activity and central vision.
3. Clinical Outcomes of Anti-oxidant Treatments
3.1. Anti-oxidant Supplements for Systemic Diseases
Vitamins and minerals have potent anti-oxidant ability, and they are commonly taken as dietary supplements to promote good health. Vitamin E is located within the phospholipid layer of the cell membrane and prevents lipid peroxidation. Vitamin C can restore the oxidized vitamin E to the reduced form. Carotenoids (e.g., β-carotene, lutein, zeaxanthin) and polyphenols (e.g., anthocyanidins, catechins, resveratrol) scavenge or reduce the ROS in a direct or indirect manner [28].
The Physicians’ Health Study II (PHS-II) and the SUpplementation in VItamins and Mineral AntioXidants Study (SU.VI.MAX) are two large trials investigating the health outcomes afforded by multivitamin supplements. The PHS-II study included 14,641 male U.S. physicians, and a multivitamin containing 30 formulations was used as an intervention for a 11.2-year follow-up period. The SU.VI.MAX study was conducted in 13,017 French individuals of both sexes with a 7.5-year follow-up, and an intervention group was supplemented with a five-ingredient multivitamin (vitamin C, vitamin E, β-carotene, selenium, and zinc). Both of these studies reported a lower cancer incidence in the men who were taking the multivitamin supplements, whereas no difference in the incidence was revealed in the women [29,30]. This benefit in men was relatively small with borderline significance, and a meta-analysis including more than 100,000 individuals did not show any effects on cancer incidence from the multivitamins. In addition, there were no significant differences in cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality due to anti-oxidant supplements [31]. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) concluded that there is insufficient evidence to recommend for or against the use of anti-oxidant supplements to prevent cardiovascular disease or cancer.
In addition, β-carotene has been shown to increase the risk of lung cancer in individuals who smoke tobacco or have an exposure to asbestos. This was shown in two large trials [32,33] and confirmed in a meta-analysis with an odds ratio of 1.24 in current smokers [34]. These findings suggest that anti-oxidants may not necessarily be beneficial, as expected from the diverse biological functions of ROS.
3.2. Anti-oxidant Supplements for Ocular Disorders
3.2.1. Anti-oxidant Supplements for Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
The Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS) investigated the clinical course of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and cataracts and assessed the impact of anti-oxidants on these eye diseases. For the AMD trial, 3640 participants with AMD regions in the fundus were randomly divided into the following four treatment arms: (1) antioxidants (vitamin C, vitamin E, and β-carotene), (2) zinc, (3) anti-oxidants and zinc, or (4) placebo. In a mean 6.3-year follow-up, the data showed that the use of anti-oxidants plus zinc reduced the risk of developing advanced AMD, with an odds ratio of 0.72 [35].
The AREDS2 assessed whether the addition of lutein/zeaxanthin and/or omega-3 fatty acids to the original AREDS formulation further reduces the risk of AMD progression. For this study, 4203 participants were primarily randomized to the following four treatment arms: (1) lutein/zeaxanthin, (2) omega-3 fatty acids, (3) lutein/zeaxanthin plus omega-3 fatty acids, or (4) placebo. Among the participants, 3036 agreed to the secondary randomization of the AREDS formulation into the following four categories: (1) the original AREDS formulation (vitamin C, vitamin E, β-carotene, and zinc), (2) the AREDS formulation without β-carotene, (3) the AREDS formulation with a lower zinc dose, and (4) the AREDS formulation with no β-carotene and a lower zinc dose. In a mean 5-year follow-up, lutein/zeaxanthin and/or omega-3 fatty acids did not show a clear benefit against AMD progression. However, a secondary analysis of the results demonstrated that the lutein/zeaxanthin-containing AREDS supplements reduced the risk of AMD progression (odds ratio: 0.82) compared to the β-carotene-containing AREDS supplements. Given the potential risk for increasing the incidence of lung cancer, the AREDS Study Group recommended that lutein/zeaxanthin could be a safer carotenoid substitute for β-carotene in the AREDS formulation [36].
The PHS-II study also evaluated the incidence of AMD as well as those of cardiovascular diseases and cancer; 14,236 male U.S. physicians who did not have a diagnosis of AMD at baseline were randomized to treatment groups with a multivitamin, vitamin C, vitamin E, and a placebo. After an 8-year follow-up, the results indicated that neither vitamin C nor vitamin E had significant beneficial or harmful effects on the incidence of AMD [37]. The multivitamin supplement also did not show any benefit or harm regarding the risk of AMD in a mean 11.2-year follow-up [38]. The subjects included in the PHS-II study were associated with a lower risk of AMD compared to the AREDS subjects, and there appears to be insufficient evidence to conclude that an anti-oxidant supplement can prevent AMD in general populations without high-risk profiles.
3.2.2. Anti-oxidant Supplements for RP
Because RP is a relatively rare disease, a large randomized trial to assess the effects of anti-oxidant supplements may not be practical. Vitamin A has been traditionally used for RP, based on the results of a randomized trial showing that vitamin A slowed down the decline of a cone-derived 30-Hz ERG response among 601 subjects with RP. However, it should be noted that there were no significant changes in the rate of the decline of the visual field or visual acuity [39].
Berson et al. conducted a post hoc analysis assessing whether omega-3 intake could affect the visual outcome among 357 RP patients who received daily vitamin A in three clinical trials [40]. A slower rate of decline of visual acuity was observed in the patients with high omega-3 intake, whereas there was no significant difference in the cone ERG response between the patients with a high or low omega-3 intake [40].
In another trial, Hoffman et al. addressed whether docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a major omega-3 fatty acid, could slow the progression of X-linked RP (the DHAX Trial); 78 patients were randomized to treatment with (1) DHA and a multivitamin or (2) the multivitamin alone [41]. The cone ERG response, the primary outcome of that trial, was not significantly different between the groups [41]. However, in ancillary outcome analyses, the rate of the decline of visual field sensitivity was reduced with the DHA supplementation [42].
There have been additional trials assessing the effects of lutein or β-carotene on the progression of RP, and their outcomes are not consistent with respect to the ERG response, visual acuity, or retinal sensitivity, as in the trials described above [43,44].
Given the lack of effects on the incidence of cancer or cardiovascular diseases and the modest impact on AMD progression in a limited population, establishing clear evidence of the merits and demerits of supplement therapy for RP may require larger sample sizes and longer follow-ups. The results of clinical trials of vitamins and minerals for systemic and eye diseases are summarized in Table 1 and Table 2. Note that this review focuses mainly on retinal degeneration and oxidative stress, and we did not introduce all of the trials assessing anti-oxidant supplements.

Table 1.
Treatment outcomes of anti-oxidant supplements in cardiovascular disease (CVD), cancer, and age-related macular degeneration (AMD).

Table 2.
Treatment outcomes of anti-oxidant supplements in retinitis pigmentosa.
3.3. Oral NAC Treatments for RP
Campochiaro et al. recently conducted a Phase 1 clinical trial of the anti-oxidant NAC for RP patients, based on its safety and efficacy in RP model mice [45]. Thirty RP patients were subjected to a dose escalation study with 600 mg (cohort 1), 1200 mg (cohort 2), and 1800 mg NAC (cohort 3) 2×/day for 12 weeks and thereafter 3×/day for 12 weeks. Visual acuity was significantly improved by 0.4, 0.5, and 0.2 letters/month in cohorts 1, 2, and 3, respectively. Retinal sensitivity in the macula was also improved by 0.15 dB/month in cohort 3. The drug-related gastrointestinal adverse events were mild and resolved spontaneously [45]. The efficacy of NAC for RP patients should be addressed in a future trial involving more patients.
4. Oxidative DNA Damage and its Repair System
4.1. Mechanisms by Which Oxidative Stress Mediates Retinal Degeneration
Although the biological actions of anti-oxidant supplements are evident, their clinical benefits have been relatively modest or unclear. Does this mean oxidative stress does not have a major role in these diseases? Accumulated evidence from experimental and clinical studies supports the role of oxidative stress in various disorders including RP. Alternatively, oral anti-oxidant supplements may not be sufficient to detoxify excessive ROS in the diseased loci. In this scenario, a stronger inactivation of ROS would be required; however, because ROS mediate both pro-survival and detrimental functions, an indiscriminate suppression of oxidative stress may not be feasible for human health. An ideal approach could therefore be the targeting of harmful oxidation in the diseased loci or within the specific cellular compartment, with enhanced efficacy and a reduction of adverse effects.
However, the mechanisms by which oxidative stress mediates retinal degeneration remain largely unexplored. In the sections below, we focus on oxidative DNA damage and its related signaling as a mechanism of harmful oxidation. Other oxidative insults such as those on proteins and lipids may also contribute to the harmful effects, but a comprehensive coverage of oxidative insult mechanisms is beyond the scope of this review and can be found in other excellent reviews [46,47,48].
4.2. DNA Oxidation and Mismatched Base Pair Formation
DNA carries the genetic information that produces the RNA and proteins required for cellular homeostasis and life itself. Oxidative damage to nucleic acids is thus hazardous because it can cause significant alterations or the destruction of gene structures. Guanine is the most susceptible nucleobase, and 8-oxoG is frequently used as a marker of oxidative DNA damage. There are two sources of oxidized DNA—one is from the direct oxidation of genomic DNA by ROS and the other is from the incorporation of oxidized bases in the nucleotide pool. It has been shown that guanine in the nucleotide pools tends to be more oxidized than that in the genomic DNA [49,50]. During DNA replication, 8-oxoG can mispair with adenine, resulting in the formation of somatic mutations [49,50].
4.3. Counter-Mechanisms against Oxidative DNA Damage
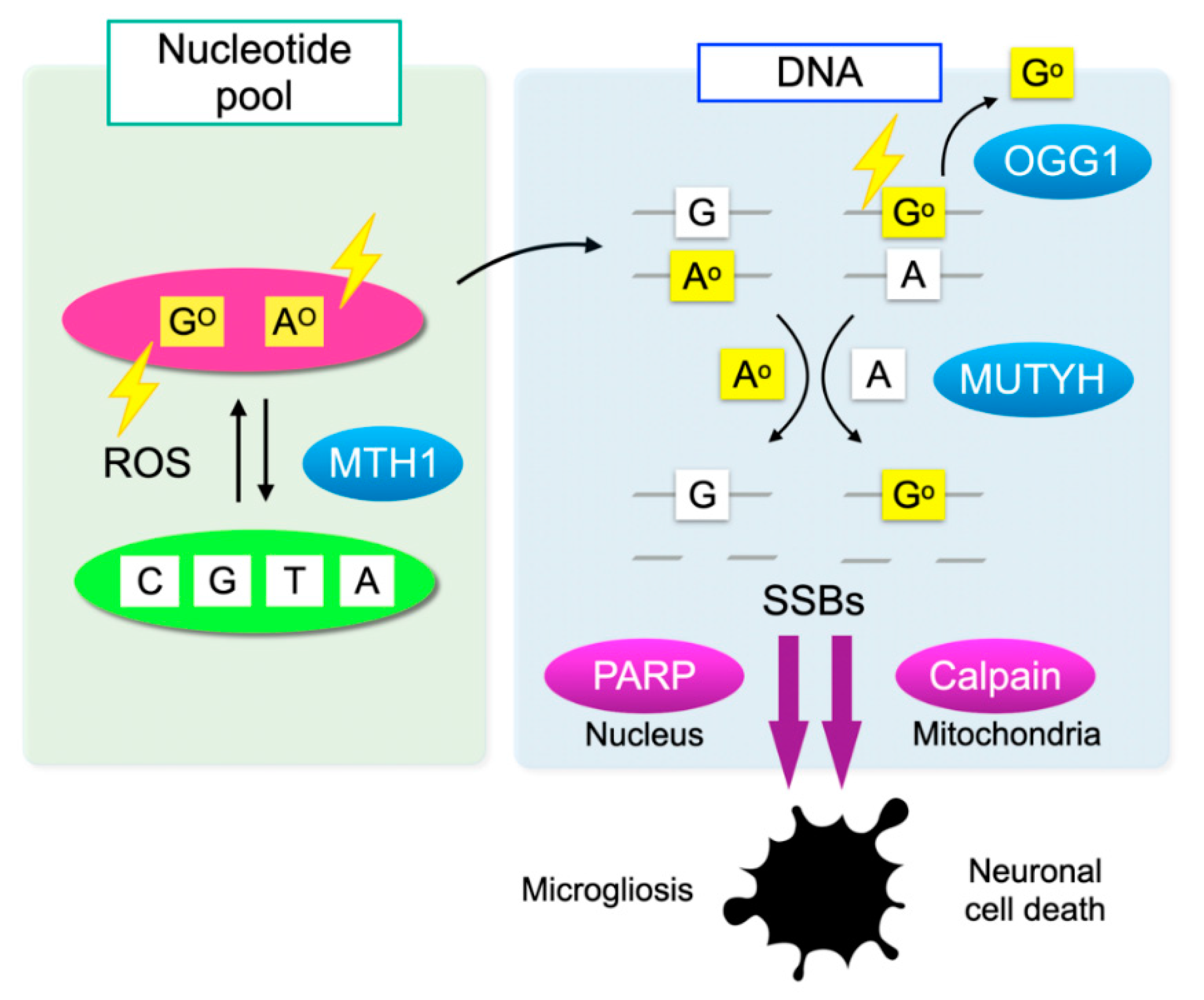
Cells have defense mechanisms to counter oxidative DNA damage. MutT homolog-1 (MTH1), also known as nudix hydrolase 1 (NUDT1), hydrolyzes oxidized purine nucleoside triphosphates, such as 8-oxo-7,8-dihydrro-2′-deoxyguanosine 5′-triphosphate (8-oxo-dGTP) and 1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-2′-deoxyadenosine 5′-triphosphate (2-oxo-dATP) to the monophosphate forms. MTH1 sanitizes the oxidized nucleotides in the nucleotide pool, thereby preventing their incorporation into DNA (Figure 3) [51].
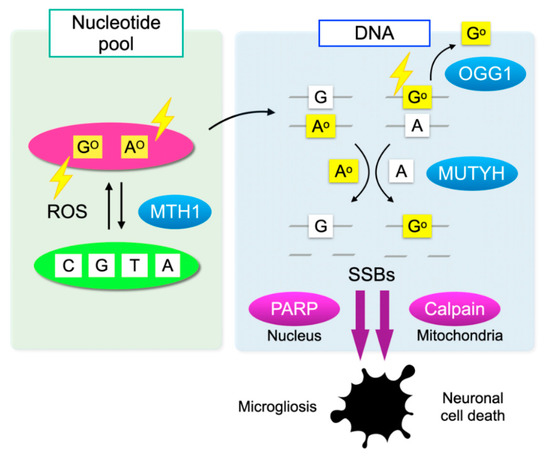
Figure 3.
Oxidative DNA damage and its repair system. Oxidation of DNA occurs via two processes: one is the direct oxidation by reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the other is the incorporation of oxidized bases from the nucleotide pool. Oxidative insults are shown in lightning symbols. During DNA replication, 8-oxoG can mispair with adenine, resulting in the formation of somatic mutations. Mut T homolog-1 (MTH1) hydrolyzes oxidized purine nucleoside triphosphates, such as 8-oxo-7,8-dihydrro-2′-deoxyguanosine 5′-triphosphate (8-oxo-dGTP) and 1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-2′-deoxyadenosine 5′-triphosphate (2-oxo-dATP) in the nucleotide pool, thereby preventing the incorporation of oxidized nucleotides into DNA. On the one hand, 8-oxoG in DNA is excised by 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase-1 (OGG1). On the other hand, the Mut Y homolog (MUTYH) excises the mismatched adenine opposite 8-oxoG, and 2-oxoA opposite guanine. MUTYH can suppress mutagenesis caused by oxidative DNA damage; however, under severe oxidative DNA damage, MUTYH-mediated BER leads to accumulation of single-strand breaks (SSBs) in DNA. SSBs in the nuclear DNA activates poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and SSBs in mitochondrial DNA results in calpain activation through mitochondrial dysfunction, which in turn induces microgliosis and neuronal cell death during neurodegeneration, respectively.
On the one hand, 8-oxoG in DNA is excised by 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase-1 (OGG1) and then replaced with guanine through base excision repair (BER). On the other hand, the Mut Y homolog (MUTYH) excises the mismatched adenine opposite 8-oxoG, and 1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-adenine (2-oxoA) opposite guanine. MUTYH-mediated BER can repair the somatic mutations induced by oxidative DNA damage; however, under severe oxidative DNA damage, the excessive activation of MUTYH leads to the formation of single-strand breaks (SSBs) of DNA, leading to disturbed homeostasis and cell death (Figure 3) [52].
Deficiency in Mth1, Ogg1, or Mutyh in mice increases the spontaneous mutation frequency in DNA, resulting in the increased incidence of cancer [53]. In neurodegenerative conditions, MTH1 and OGG1 exhibit a neuroprotective function by preventing the accumulation of 8-oxoG. The neurodegeneration induced by 3-NP is markedly enhanced in Mth1/Ogg1 double-knockout mice, accompanied by an increase in 8-oxoG accumulation in the degenerating neurons and the activated microglia [54]. In contrast, MUTYH promotes neurodegeneration under oxidative stress. As described above, adenine excision by MUTYH forms SSBs in the nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, which activates the cellular stress response [52]. Neuronal cell loss and microgliosis are attenuated in Mutyh −/− mice in the 3-NP neurodegeneration model [54].
5. DNA Oxidation in Microglia Promotes Inflammation and Degeneration in RP
5.1. Accumulation of 8-oxoG in RP
An accumulation of oxidative DNA damage is associated with neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease [55,56]. In animal models of RP, we previously showed that 8-oxoG accumulation is substantially increased in the outer nuclear layer (ONL) where photoreceptor cells reside. These changes were consistently observed in two RP models with different genetic mutations (Figure 2A,B). In addition, vitreous samples from RP patients contained higher levels of free 8-oxo-dG compared to control subjects without retinal degeneration (Figure 2C) [16]. There findings suggest that oxidative DNA damage may underlie RP as a common pathology.
5.2. Role of Oxidative DNA Damage in RP
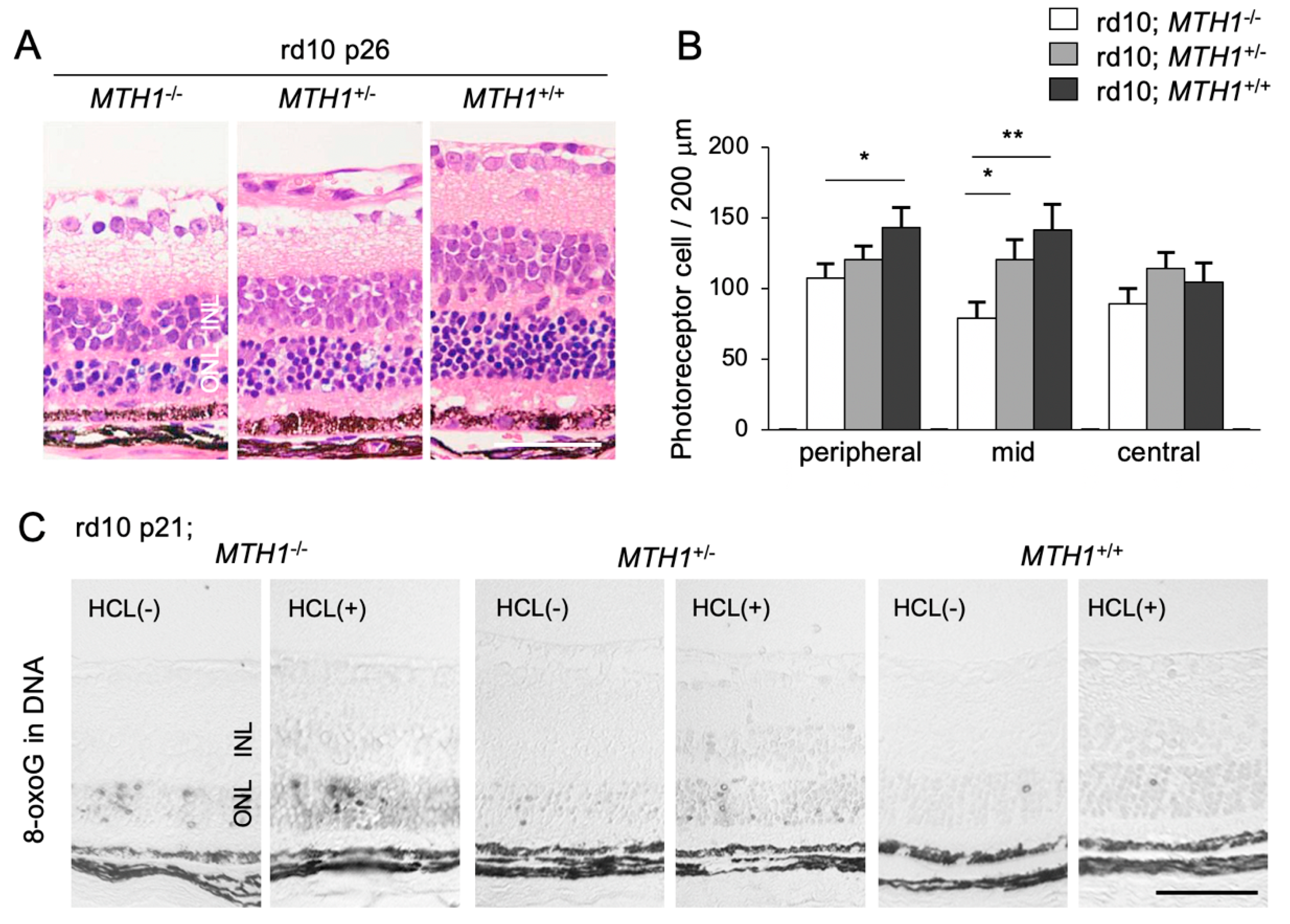
To elucidate the role of oxidative DNA damage in RP, we assessed the effect of a transgenic overexpression of human MTH1 (hMTH1) on retinal degeneration [16]. The accumulation of 8-oxoG in the rd10 mouse retina is attenuated by hMTH1 overexpression, which in turn leads to a suppression of photoreceptor cell death (Figure 4A–C) [16]. These findings suggest that a large proportion of oxidative DNA damage in the ONL of rd10 mice is derived from the oxidized nucleotide pool. This process (i.e., the incorporation of oxidized bases into the nuclear DNA) has been traditionally thought to occur during DNA replication in cell division [49]. However, because photoreceptor cells are post-mitotic neuronal cells, it is less likely that photoreceptors re-enter the cell cycle and replicate their DNA. Alternatively, other non-neuronal proliferating cells in the ONL, such as microglia, may incorporate oxidized nucleic acids into their nuclear DNA during retinal degeneration.
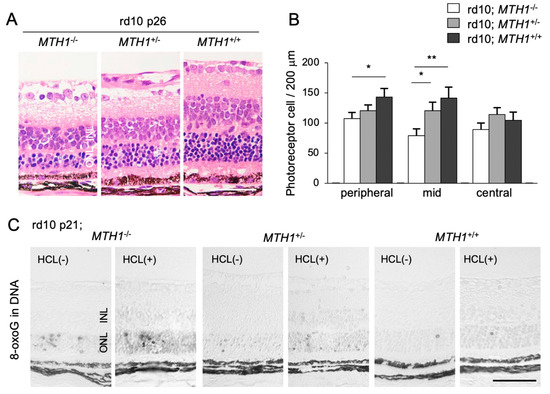
Figure 4.
The Figure is reproduced from [16] with copyright permission. Transgenic overexpression of human Mut T homolog-1 attenuates oxidative DNA damage and suppresses retinal degeneration. (A) Histological examination of rd10 mice, rd10 mice with hemizygous human MutT homolog-1 (hMTH1) expression (rd10; hMTH1-Tg+/−), or rd10 mice with homozygous hMTH1 expression (rd10; hMTH1-Tg+/+). Scale bar, 50 μm. INL: inner nuclear layer. ONL: outer nuclear layer. (B) Quantitative analysis of the number of photoreceptor cells in the ONL. Note that transgenic overexpression of hMTH1 significantly suppresses photoreceptor cell loss in rd10 mice. (C) Immunohistochemical staining of 8-oxoG in the retina of rd10, rd10; hMTH1-Tg+/−, or rd10; hMTH1-Tg+/+ mice. 8-oxo-G accumulation in rd10 mice is attenuated by transgenic hMTH1 expression. Scale bar, 50 μm. * p < 0.05. ** p < 0.01.
5.3. Oxidative DNA Damage Mediates Microglial Activation through MUTYH-mediated SSB Formation, Thereby Promoting Retinal Degeneration
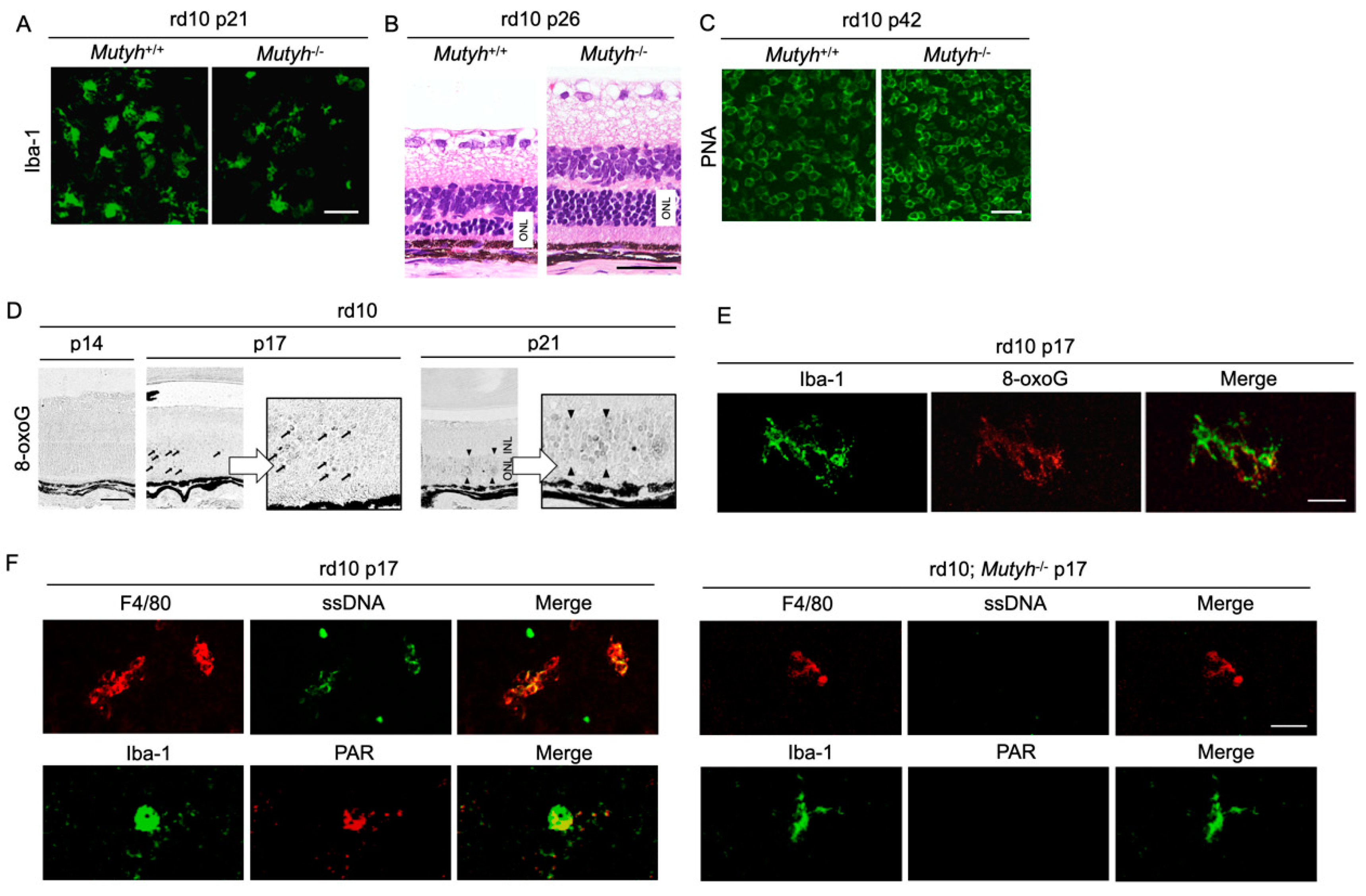
To further determine the mechanisms by which oxidative DNA damage promotes retinal degeneration, we employed rd10 mice to assess the function of MUTYH, which excises adenine mispaired with 8-oxoG [57]. As described above, previous studies demonstrated that MUTYH deficiency prevents SSB formation and cell death under oxidative stress [58,59]. Consistently, our study showed that MUTYH deficiency substantially suppresses the formation of SSBs and attenuates rod and cone photoreceptor cell death as well as microgliosis in rd10 mice (Figure 5A–C) [57]. These findings suggest that MUTYH-mediated BER is critical to promote retinal degeneration and inflammation in RP.
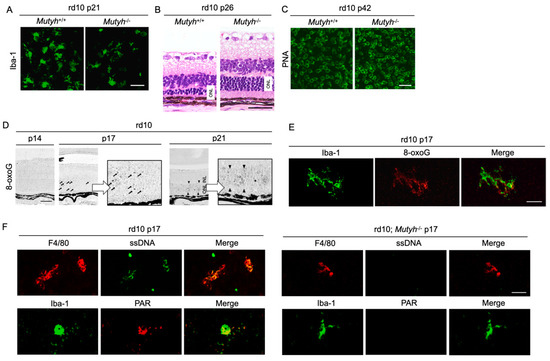
Figure 5.
The Figure is reproduced from [59] with copyright permission. Oxidative DNA damage in microglia mediates retinal inflammation and degeneration through Mut Y homolog activation. (A–C) Immunohistochemical staining of microglial marker Iba-1 (A), hematoxylin and eosin staining (B), and peanut agglutin (PNA) staining, which labels the cone inner and outer segments (C) in rd10 mice or rd10 mice deficient for Mut Y homolog (Mutyh) (rd10; Mutyh−/−). Note that microgliosis and rod as well as cone degeneration are suppressed by Mutyh deficiency. ONL: outer nuclear layer. Scale bar, 50 μm (A,B), 20 μm (C,D). Time-dependent changes of oxidative DNA damage in rd10 mice. Scattered 8-oxoG accumulation is observed at early phase of retinal degeneration (postnatal day 17: P17), and thereafter 8-oxo-G accumulation expands to the ONL diffusely at P21 in rd10 mice. Scale bar, 50 μm. (E) Part of scattered 8-oxo-G staining in the P17 rd10 retinas are colocalized with Iba-1-positive microglial cells, suggesting that 8-oxo-G accumulation in microglia precedes the peak of photoreceptor cell death in rd10 mice. Scale bar, 20 μm. (F) Immunohistochemical staining of single-strand DNA (ssDNA) to detect single-strand breaks (SSBs) and poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) for the marker of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) activation in rd10 or rd10; Mutyh−/− mice. Microglia in rd10 mice are associated with SSB formation and PARP activation, which is reversed by Mutyh deficiency. Scale bar, 20 μm.
Neuronal cells and microglia closely interact during neurodegeneration [60], and it has not been determined which cells are the primary target of oxidative stress. Our analysis of time-dependent changes of oxidative DNA damage in rd10 mice showed that a nuclear accumulation of 8-oxoG in microglia occurs before the peak of photoreceptor degeneration, and thereafter the 8-oxoG accumulation expands to the photoreceptor nuclei along with microglial activation (Figure 5D,E) [57]. These findings suggest that the microglia may be a key target of oxidative stress in RP, and oxidative microglial activation may trigger the vicious cycle of non-resolved neuroinflammation and degeneration in RP. In accord with this idea, anti-oxidant treatments have been shown to robustly suppress the microglial activation and prevent the production of pro-inflammatory molecules in models of retinal degeneration [20,61].
Oka et al. demonstrated that SSBs formed by MUTYH-mediated BER trigger two distinct pathways—nuclear SSBs induce poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) activation and mitochondrial SSBs mediate calpain activation [58]. Consistent with these findings, we observed that nuclear DNA oxidation in the microglia of rd10 mice is associated with PARP activation, and this PARP activation is reversed by MUTYH deficiency (Figure 5F) [57]. In addition, systemic treatment with a PARP inhibitor dampens retinal degeneration in rd10 mice, suggesting that PARP activation in microglia may be an alternative target in RP [16]. Because systemic and long-term PARP inhibition may be associated with non-negligible adverse events, the selective targeting of retinal oxidized microglia may be an attractive strategy to combat detrimental oxidative stress in RP and neurodegeneration.
6. Conclusions
Although RP is a hereditary disease, non-genetic environmental factors such as oxidative stress modulate the disease progression. Oxidative damage is markedly increased in the outer retina of animal RP models as well as in the ocular samples of RP patients. Anti-oxidant interventions, by either pharmacological or genetic approaches, substantially delay photoreceptor cell death in experimental RP, suggesting that oxidative stress is a key contributor to retinal degeneration in RP.
Contrary to these experimental findings, the clinical evidence that anti-oxidant supplements retard the progression of RP has not been fully established. Because anti-oxidant agents are frequently used at extremely high doses in experimental models, stronger ROS inactivation may be required to achieve clinical efficacy in RP patients. To avoid the systemic adverse effects due to long-term anti-oxidant treatment, the targeting of harmful oxidation in the retina would be a more feasible approach. To realize this strategy, a further clarification of the mechanisms by which oxidative stress mediates retinal degeneration in RP is necessary. For example, our research revealed an intimate link between oxidative DNA damage and neuroinflammation, and we identified a MUTYH-SSBs-PARP pathway in microglial cells as a therapeutic target for RP. The elucidation of the key biological processes that underlie oxidative retinal damage will lead to a better understanding of the disease and to the development of novel anti-oxidant therapies for RP.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.M.; methodology, validation, and formal analysis, Y.M. and Y.N.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.M.; writing—review and editing, Y.N. and K.-H.S.; supervision, Y.N. and K.-H.S.; project administration, Y.M.; funding acquisition, Y.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from KAKENHI, #JP19K09952 (to Y.M.), the Center for Clinical and Translational Research of Kyushu University Hospital (to Y.M.), a Kaibara Morikazu Medical Science Promotion Foundation grant (to Y.M.), and a Takeda Science Foundation grant (to Y.M.).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bratic, A.; Larsson, N.G. The role of mitochondria in aging. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeya, R.; Sumimoto, H. Molecular mechanism for activation of superoxide-producing NADPH oxidases. Mol. Cells 2003, 16, 271–277. [Google Scholar]
- Weydert, C.J.; Cullen, J.J. Measurement of superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase in cultured cells and tissue. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeger, G.; Quiney, C.; Cotter, T.G. Hydrogen peroxide as a cell-survival signaling molecule. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 2655–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morizane, Y.; Morimoto, N.; Fujiwara, A.; Kawasaki, R.; Yamashita, H.; Ogura, Y.; Shiraga, F. Incidence and causes of visual impairment in Japan: The first nation-wide complete enumeration survey of newly certified visually impaired individuals. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 63, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Nakatake, S.; Funatsu, J.; Fujiwara, K.; Tachibana, T.; Murakami, Y.; Hisatomi, T.; Yoshida, S.; Enaida, H.; Ishibashi, T.; et al. Night-vision aid using see-through display for patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 63, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartong, D.T.; Berson, E.L.; Dryja, T.P. Retinitis pigmentosa. Lancet 2006, 368, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbakel, S.K.; van Huet, R.A.C.; Boon, C.J.F.; den Hollander, A.I.; Collin, R.W.J.; Klaver, C.C.W.; Hoyng, C.B.; Roepman, R.; Klevering, B.J. Non-syndromic retinitis pigmentosa. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 66, 157–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campochiaro, P.A.; Mir, T.A. The mechanism of cone cell death in Retinitis Pigmentosa. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 62, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Ishikawa, K.; Nakao, S.; Sonoda, K.H. Innate immune response in retinal homeostasis and inflammatory disorders. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2020, 74, 100778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punzo, C.; Kornacker, K.; Cepko, C.L. Stimulation of the insulin/mTOR pathway delays cone death in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, L.; Ma, S.; Cipi, J.; Cheng, S.Y.; Zieger, M.; Hay, N.; Punzo, C. Aerobic glycolysis is essential for normal rod function and controls secondary cone death in retinitis pigmentosa. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 2629–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, S.; Oveson, B.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Jo, Y.J.; Yoshida, T.; Miki, A.; Miki, K.; Iwase, T.; Lu, L.; Campochiaro, P.A. NADPH oxidase plays a central role in cone cell death in retinitis pigmentosa. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiguchi, K.M.; Carvalho, L.S.; Rizzi, M.; Powell, K.; Holthaus, S.M.; Azam, S.A.; Duran, Y.; Ribeiro, J.; Luhmann, U.F.; Bainbridge, J.W.; et al. Gene therapy restores vision in rd1 mice after removal of a confounding mutation in Gpr179. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yang, X.; Dong, A.; Petters, R.M.; Peng, Y.W.; Wong, F.; Campochiaro, P.A. Oxidative damage is a potential cause of cone cell death in retinitis pigmentosa. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 203, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Notomi, S.; Hisatomi, T.; Oka, S.; De Luca, G.; Yonemitsu, Y.; Bignami, M.; Nakabeppu, Y.; et al. MutT homolog-1 attenuates oxidative DNA damage and delays photoreceptor cell death in inherited retinal degeneration. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Yamada, E.; Hackett, S.F.; Ozaki, H.; Okamoto, N.; Campochiaro, P.A. Hyperoxia causes decreased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and endothelial cell apoptosis in adult retina. J. Cell. Physiol. 1999, 179, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komeima, K.; Rogers, B.S.; Lu, L.; Campochiaro, P.A. Antioxidants reduce cone cell death in a model of retinitis pigmentosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11300–11305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Usui, S.; Zafar, A.B.; Oveson, B.C.; Jo, Y.J.; Lu, L.; Masoudi, S.; Campochiaro, P.A. N-Acetylcysteine promotes long-term survival of cones in a model of retinitis pigmentosa. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N.; Ikeda, Y.; Notomi, S.; Ishikawa, K.; Murakami, Y.; Hisatomi, T.; Enaida, H.; Ishibashi, T. Laboratory evidence of sustained chronic inflammatory reaction in retinitis pigmentosa. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, e5–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, S.; Oveson, B.C.; Iwase, T.; Lu, L.; Lee, S.Y.; Jo, Y.J.; Wu, Z.; Choi, E.Y.; Samulski, R.J.; Campochiaro, P.A. Overexpression of SOD in retina: Need for increase in H2O2-detoxifying enzyme in same cellular compartment. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; MacColl Garfinkel, A.E.; Li, Y.; Benowitz, L.I.; Cepko, C.L. NRF2 promotes neuronal survival in neurodegeneration and acute nerve damage. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1433–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, A.M.; Russell, S.; Wellman, J.A.; Chung, D.C.; Yu, Z.F.; Tillman, A.; Wittes, J.; Pappas, J.; Elci, O.; Marshall, K.A.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and durability of voretigene neparvovec-rzyl in rpe65 mutation-associated inherited retinal dystrophy: Results of phase 1 and 3 trials. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garafalo, A.V.; Cideciyan, A.V.; Heon, E.; Sheplock, R.; Pearson, A.; WeiYang Yu, C.; Sumaroka, A.; Aguirre, G.D.; Jacobson, S.G. Progress in treating inherited retinal diseases: Early subretinal gene therapy clinical trials and candidates for future initiatives. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2019, 100827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campochiaro, P.A.; Strauss, R.W.; Lu, L.; Hafiz, G.; Wolfson, Y.; Shah, S.M.; Sophie, R.; Mir, T.A.; Scholl, H.P. Is there excess oxidative stress and damage in eyes of patients with retinitis pigmentosa? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 23, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cámara, C.M.F.; Salom, D.; Sequedo, M.D.; Hervas, D.; Marin-Lambies, C.; Aller, E.; Jaijo, T.; Diaz-Llopis, M.; Millan, J.M.; Rodrigo, R. Altered antioxidant-oxidant status in the aqueous humor and peripheral blood of patients with retinitis pigmentosa. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizu, M.; Murakami, Y.; Fujiwara, K.; Funatsu, J.; Shimokawa, S.; Nakatake, S.; Tachibana, T.; Hisatomi, T.; Koyanagi, Y.; Akiyama, M.; et al. Relationships between serum antioxidant and oxidant statuses and visual function in retinitis pigmentosa. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 4462–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkara, A.; Raizner, A. Supplemental vitamins and minerals for cardiovascular disease prevention and treatment. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc. J. 2019, 15, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Gaziano, J.M.; Sesso, H.D.; Christen, W.G.; Bubes, V.; Smith, J.P.; MacFadyen, J.; Schvartz, M.; Manson, J.E.; Glynn, R.J.; Buring, J.E. Multivitamins in the prevention of cancer in men: The Physicians’ Health Study II randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2012, 308, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hercberg, S.; Galan, P.; Preziosi, P.; Bertrais, S.; Mennen, L.; Malvy, D.; Roussel, A.M.; Favier, A.; Briancon, S. The SU.VI.MAX Study: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of the health effects of antioxidant vitamins and minerals. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004, 164, 2335–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortmann, S.P.; Burda, B.U.; Senger, C.A.; Lin, J.S.; Whitlock, E.P. Vitamin and mineral supplements in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer: An updated systematic evidence review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 159, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpha-Tocopherol Beta Carotene Cancer Prevention Study Group. The effect of vitamin E and beta carotene on the incidence of lung cancer and other cancers in male smokers. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Omenn, G.S.; Goodman, G.E.; Thornquist, M.D.; Balmes, J.; Cullen, M.R.; Glass, A.; Keogh, J.P.; Meyskens, F.L.; Valanis, B.; Williams, J.H.; et al. Effects of a combination of beta carotene and vitamin A on lung cancer and cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvetyanon, T.; Bepler, G. Beta-carotene in multivitamins and the possible risk of lung cancer among smokers versus former smokers: A meta-analysis and evaluation of national brands. Cancer 2008, 113, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, E.Y.; Clemons, T.E.; Agron, E.; Sperduto, R.D.; Sangiovanni, J.P.; Kurinij, N.; Davis, M.D. Age-Related Eye Disease Study Research, G. Long-term effects of vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and zinc on age-related macular degeneration: AREDS report no. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, E.Y.; Clemons, T.E.; Agron, E.; Launer, L.J.; Grodstein, F.; Bernstein, P.S.; Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS2) Research Group. Effect of omega-3 fatty acids, lutein/zeaxanthin, or other nutrient supplementation on cognitive function: The AREDS2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2015, 314, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, W.G.; Glynn, R.J.; Sesso, H.D.; Kurth, T.; Macfadyen, J.; Bubes, V.; Buring, J.E.; Manson, J.E.; Gaziano, J.M. Vitamins E and C and medical record-confirmed age-related macular degeneration in a randomized trial of male physicians. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 1642–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, W.G.; Glynn, R.J.; Manson, J.E.; MacFadyen, J.; Bubes, V.; Schvartz, M.; Buring, J.E.; Sesso, H.D.; Gaziano, J.M. Effects of multivitamin supplement on cataract and age-related macular degeneration in a randomized trial of male physicians. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berson, E.L.; Rosner, B.; Sandberg, M.A.; Hayes, K.C.; Nicholson, B.W.; Weigel-DiFranco, C.; Willett, W. A randomized trial of vitamin A and vitamin E supplementation for retinitis pigmentosa. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1993, 111, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berson, E.L.; Rosner, B.; Sandberg, M.A.; Weigel-DiFranco, C.; Willett, W.C. Omega-3 intake and visual acuity in patients with retinitis pigmentosa receiving vitamin A. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2012, 130, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, D.R.; Hughbanks-Wheaton, D.K.; Pearson, N.S.; Fish, G.E.; Spencer, R.; Takacs, A.; Klein, M.; Locke, K.G.; Birch, D.G. Four-year placebo-controlled trial of docosahexaenoic acid in X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (DHAX trial): A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014, 132, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, D.R.; Hughbanks-Wheaton, D.K.; Spencer, R.; Fish, G.E.; Pearson, N.S.; Wang, Y.Z.; Klein, M.; Takacs, A.; Locke, K.G.; Birch, D.G. Docosahexaenoic acid slows visual field progression in X-linked retinitis pigmentosa: Ancillary outcomes of the DHAX Trial. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 6646–6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berson, E.L.; Rosner, B.; Sandberg, M.A.; Weigel-DiFranco, C.; Brockhurst, R.J.; Hayes, K.C.; Johnson, E.J.; Anderson, E.J.; Johnson, C.A.; Gaudio, A.R.; et al. Clinical trial of lutein in patients with retinitis pigmentosa receiving vitamin A. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2010, 128, 403–411. [Google Scholar]
- Rotenstreich, Y.; Belkin, M.; Sadetzki, S.; Chetrit, A.; Ferman-Attar, G.; Sher, I.; Harari, A.; Shaish, A.; Harats, D. Treatment with 9-cis beta-carotene-rich powder in patients with retinitis pigmentosa: A randomized crossover trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2013, 131, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campochiaro, P.A.; Iftikhar, M.; Hafiz, G.; Akhlaq, A.; Tsai, G.; Wehling, D.; Lu, L.; Wall, G.M.; Singh, M.S.; Kong, X. Oral N-acetylcysteine improves cone function in retinitis pigmentosa patients in phase I trial. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1527–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasuri, K.; Zhang, L.; Keller, J.N. Oxidative stress, neurodegeneration, and the balance of protein degradation and protein synthesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Halliwell, B. Oxidative stress, dysfunctional glucose metabolism and Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative stress: A key modulator in neurodegenerative diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, H.; Kasai, H. Formation of 2-hydroxydeoxyadenosine triphosphate, an oxidatively damaged nucleotide, and its incorporation by DNA polymerases. Steady-state kinetics of the incorporation. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 19446–19450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakabeppu, Y. Cellular levels of 8-oxoguanine in either DNA or the nucleotide pool play pivotal roles in carcinogenesis and survival of cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 12543–12557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakabeppu, Y.; Ohta, E.; Abolhassani, N. MTH1 as a nucleotide pool sanitizing enzyme: Friend or foe? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 107, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, S.; Nakabeppu, Y. DNA glycosylase encoded by MUTYH functions as a molecular switch for programmed cell death under oxidative stress to suppress tumorigenesis. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Tominaga, Y.; Yamauchi, K.; Nakatsu, Y.; Sakumi, K.; Yoshiyama, K.; Egashira, A.; Kura, S.; Yao, T.; Tsuneyoshi, M.; et al. MUTYH-null mice are susceptible to spontaneous and oxidative stress induced intestinal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6599–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Oka, S.; Tsuchimoto, D.; Abolhassani, N.; Nomaru, H.; Sakumi, K.; Yamada, H.; Nakabeppu, Y. 8-Oxoguanine causes neurodegeneration during MUTYH-mediated DNA base excision repair. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4344–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunomura, A.; Perry, G.; Aliev, G.; Hirai, K.; Takeda, A.; Balraj, E.K.; Jones, P.K.; Ghanbari, H.; Wataya, T.; Shimohama, S.; et al. Oxidative damage is the earliest event in Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 60, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A.; Robertson, D.; Olson, S.J.; Graham, D.G.; Montine, T.J. Parkinson’s disease is associated with oxidative damage to cytoplasmic DNA and RNA in substantia nigra neurons. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, S.; Ohno, M.; Tsuchimoto, D.; Sakumi, K.; Furuichi, M.; Nakabeppu, Y. Two distinct pathways of cell death triggered by oxidative damage to nuclear and mitochondrial DNAs. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, J.J.; Devadoss, B.; Winkler, J.A.; Collins, J.J.; Walker, G.C. Oxidation of the guanine nucleotide pool underlies cell death by bactericidal antibiotics. Science 2012, 336, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatake, S.; Murakami, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Morioka, N.; Tachibana, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Yoshida, N.; Notomi, S.; Hisatomi, T.; Yoshida, S.; et al. MUTYH promotes oxidative microglial activation and inherited retinal degeneration. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e87781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Herz, J.; Filiano, A.J.; Smith, A.; Yogev, N.; Kipnis, J. Myeloid cells in the central nervous system. Immunity 2017, 46, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, M.I.; Murakami, Y.; Thanos, A.; Vavvas, D.G.; Miller, J.W. Edaravone, an ROS scavenger, ameliorates photoreceptor cell death after experimental retinal detachment. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 3825–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).