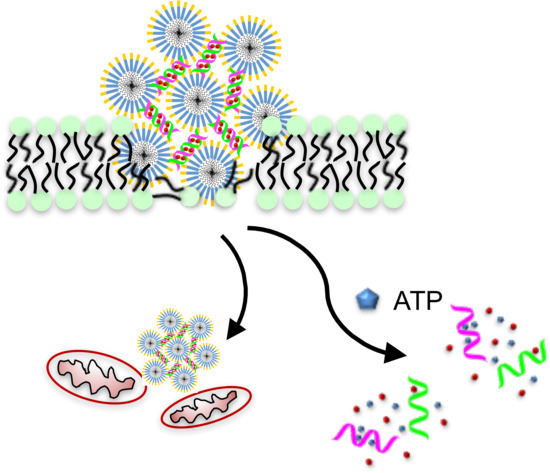
Therapeutic Peptide Amphiphile as a Drug Carrier with ATP-Triggered Release for Synergistic Effect, Improved Therapeutic Index, and Penetration of 3D Cancer Cell Spheroids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
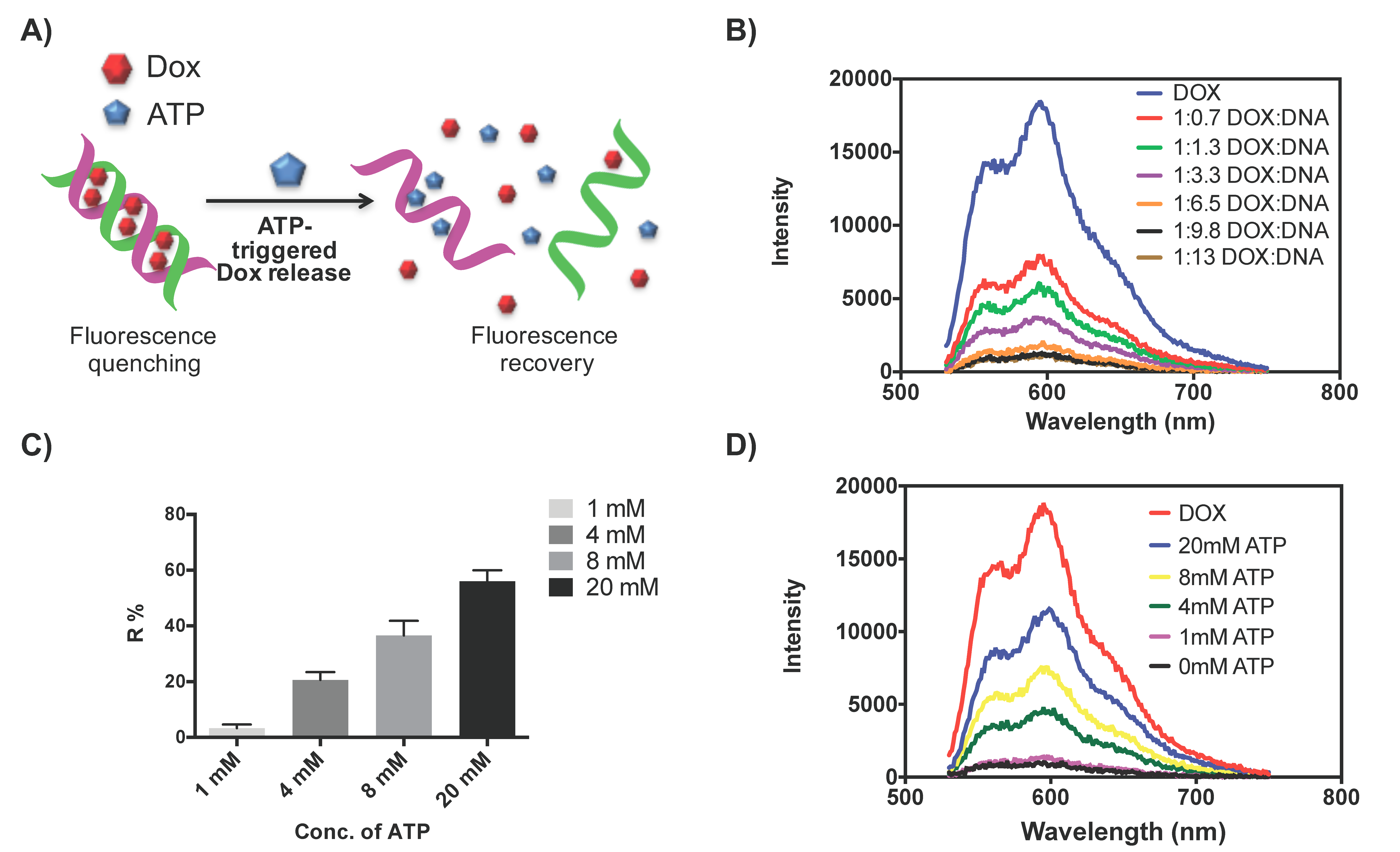
2.1. Dox Loading and Release from DNA Scaffold
2.2. Characterization of the Dox-DNA/PAH6 Nanocomplex
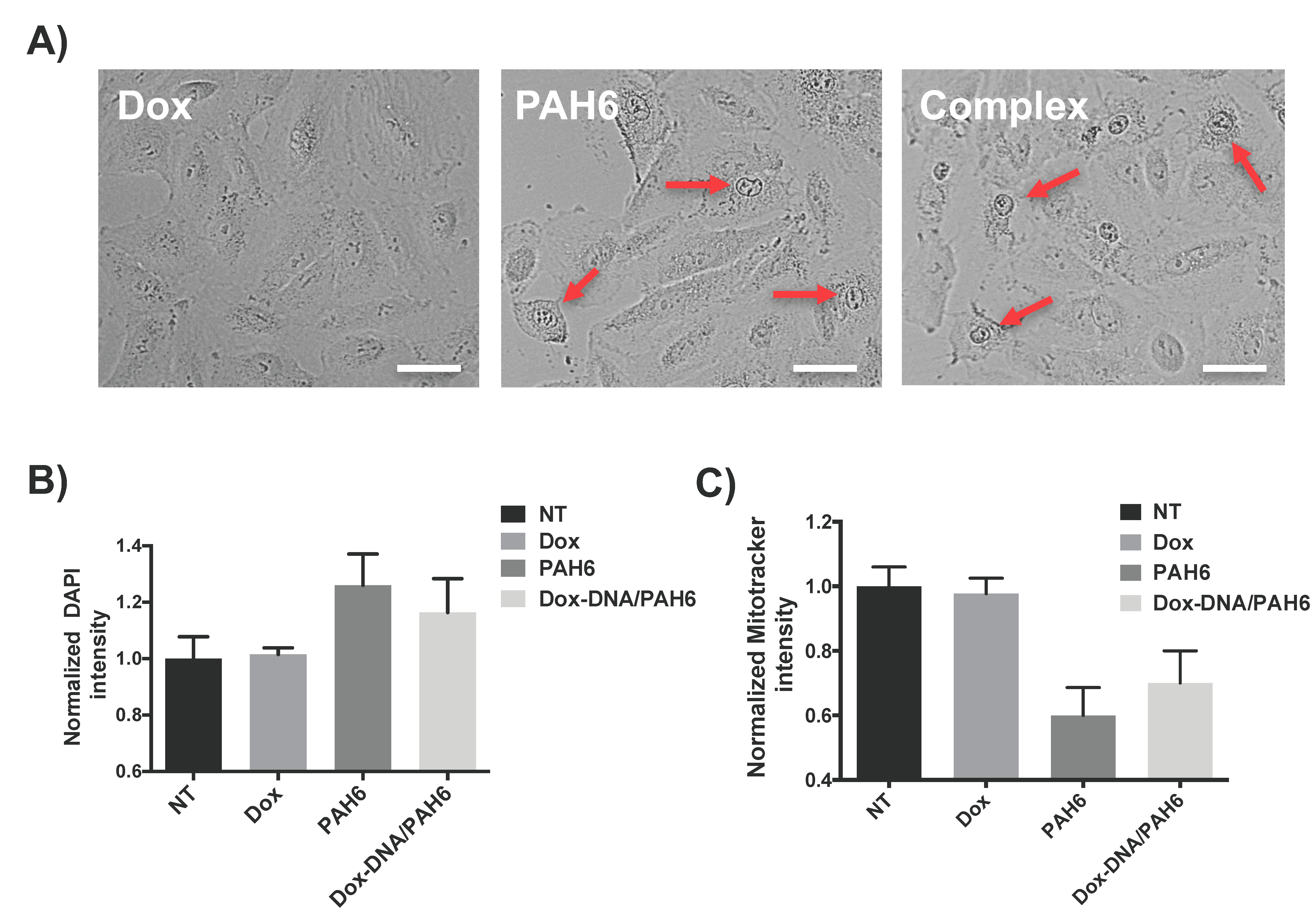
2.3. Membrane Permeabilization and Mitochondrial Depolarization Induced by PAH6
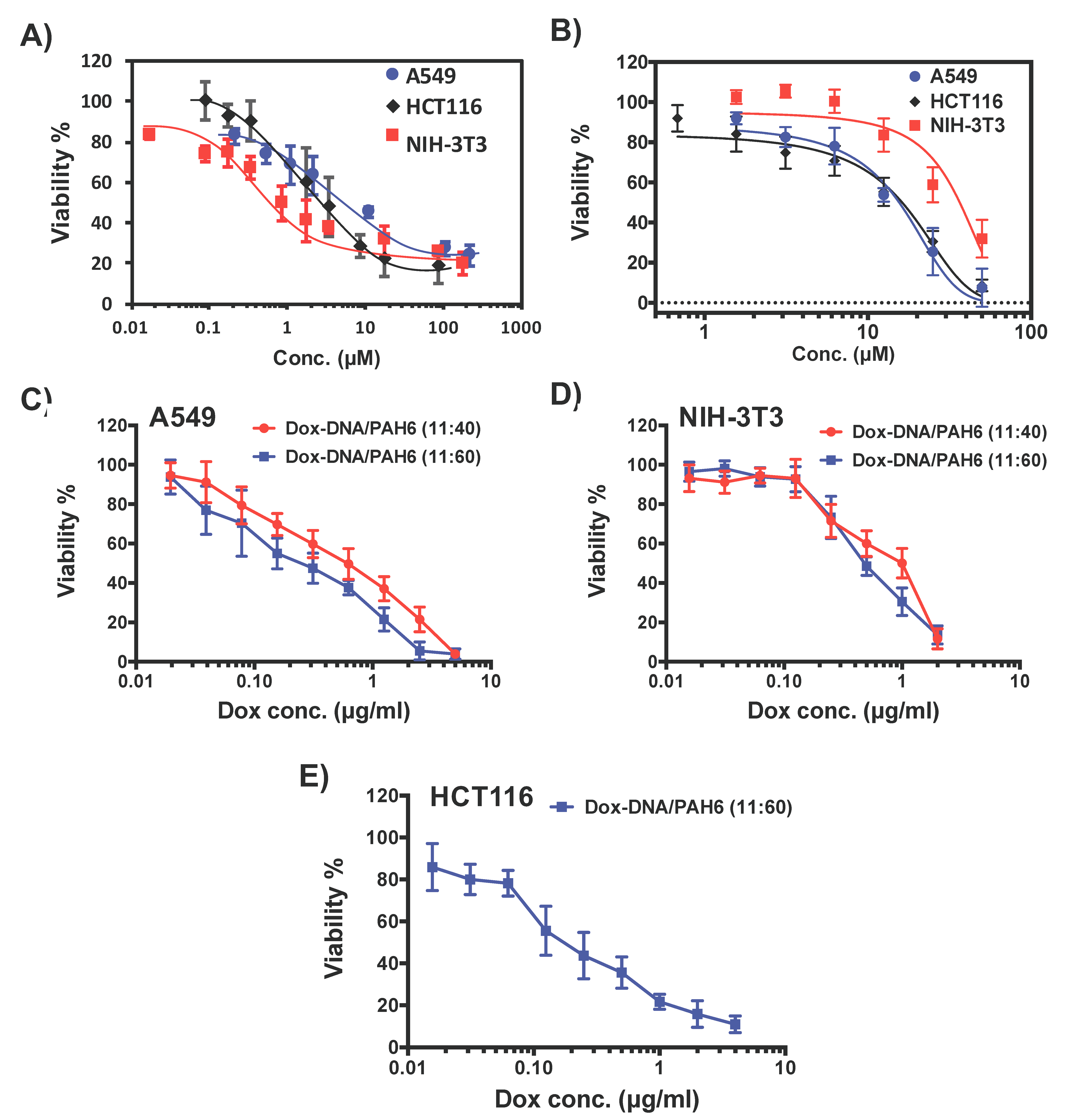
2.4. Synergistic Effect and Selectivity of the Dox-DNA/PAH6 Nanocomplex
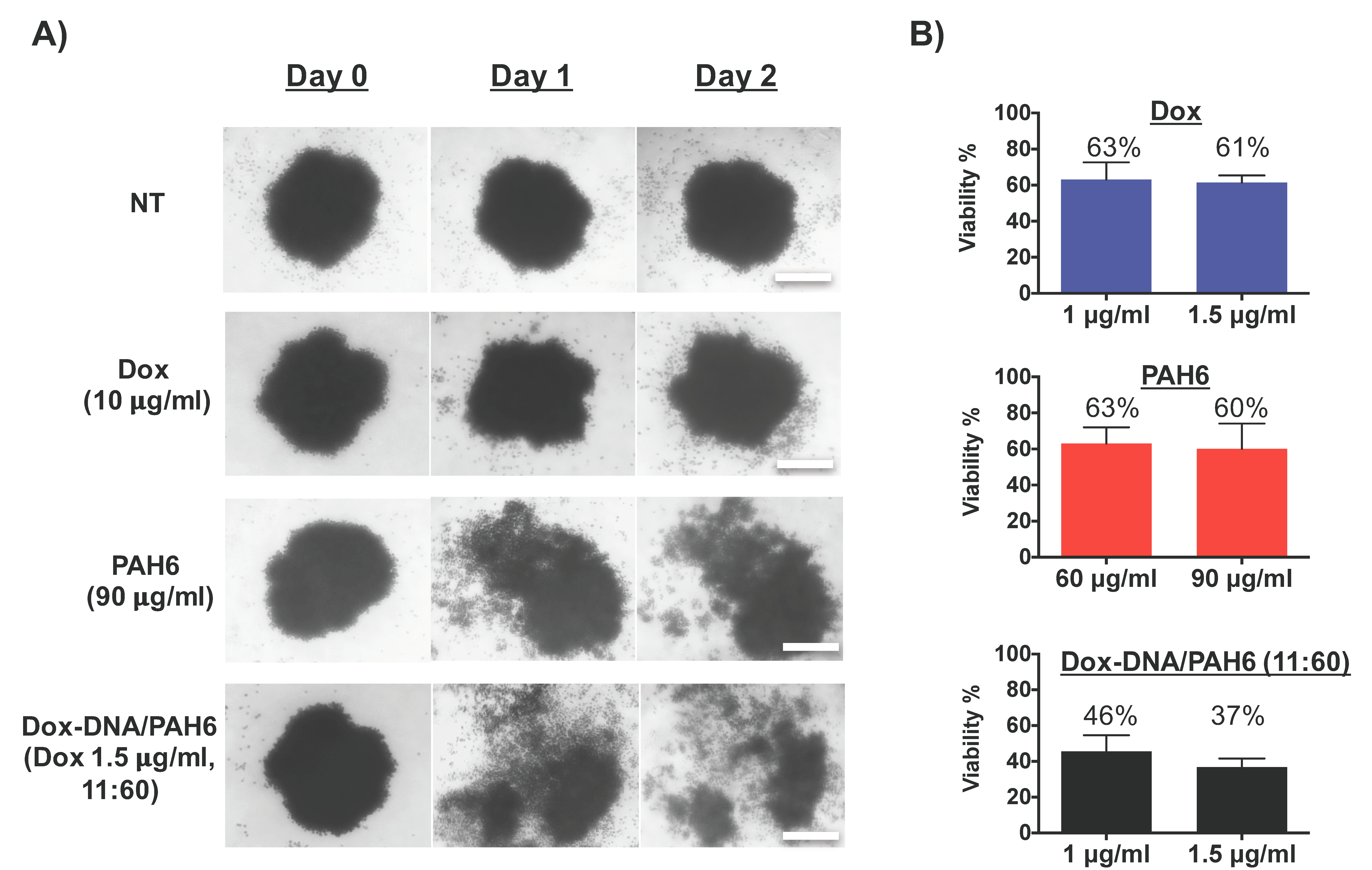
2.5. Anticancer Activity Against Lung Cancer Cell Spheroids
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation and Characterization of Dox-Loaded DNA and the Dox-DNA/PAH6 Nanocomplex
4.3. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
4.4. In Vitro ATP-Triggered Dox Release
4.5. Monolayer Cell Culture
4.6. Cell Morphology Imaging
4.7. Cell Membrane Permeability Assay
4.8. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay
4.9. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Test
4.10. 3D-Cultured A549 Spheroids and Anticancer Activity Test
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, J.; Kantoff, P.W.; Wooster, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Pacardo, D.B.; Wang, C.; Sun, W.; Ligler, F.S.; Dickey, M.D.; Gu, Z. Transformable liquid-metal nanomedicine. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, S.; Glancy, D.; Chan, W.C. DNA-controlled dynamic colloidal nanoparticle systems for mediating cellular interaction. Science 2016, 351, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petros, R.A.; DeSimone, J.M. Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H. Macromolecular therapeutics in cancer treatment: The epr effect and beyond. J. Control. Release 2012, 164, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, V.P.; Stylianopoulos, T.; Martin, J.D.; Popovic, Z.; Chen, O.; Kamoun, W.S.; Bawendi, M.G.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K. Normalization of tumour blood vessels improves the delivery of nanomedicines in a size-dependent manner. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.; Stylianopoulos, T.; Cui, J.; Martin, J.; Chauhan, V.P.; Jiang, W.; Popović, Z.; Jain, R.K.; Bawendi, M.G.; Fukumura, D. Multistage nanoparticle delivery system for deep penetration into tumor tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2426–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, T.J.; Finbloom, J.A.; Chen, F.; Toft, D.J.; Cryns, V.L.; Stupp, S.I. Ph and amphiphilic structure direct supramolecular behavior in biofunctional assemblies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14746–14752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chithrani, B.D.; Ghazani, A.A.; Chan, W.C.W. Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, S.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Bennett, W.F.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, H.Y.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, T.; Ouyang, P.K.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; et al. Design and characterization of a multifunctional ph-triggered peptide c8 for selective anticancer activity. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 2709–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, R.; Jiang, T.; DiSanto, R.; Tai, W.; Gu, Z. Atp-triggered anticancer drug delivery. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, P.; Dai, Y.; Ma, P.A.; Li, X.; Cheng, Z.; Hou, Z.; Kang, X.; Li, C.; Lin, J. Multifunctional up-converting nanocomposites with smart polymer brushes gated mesopores for cell imaging and thermo/ph dual-responsive drug controlled release. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 4067–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Lai, G.H.; Schmidt, N.W.; Sun, V.Z.; Rodriguez, A.R.; Tong, R.; Tang, L.; Cheng, J.; Deming, T.J.; Kamei, D.T.; et al. Translocation of hiv tat peptide and analogues induced by multiplexed membrane and cytoskeletal interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16883–16888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanzl, E.G.; Trantow, B.M.; Vargas, J.R.; Wender, P.A. Fifteen years of cell-penetrating, guanidinium-rich molecular transporters: Basic science, research tools, and clinical applications. Accounts Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2944–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Perche, F.; Wang, T.; Torchilin, V.P. Matrix metalloproteinase 2-sensitive multifunctional polymeric micelles for tumor-specific co-delivery of sirna and hydrophobic drugs. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4213–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Ding, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, R.; Pan, R.; Wan, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Y.-F.; Chen, P. An amphipathic lytic peptide for enhanced and selective delivery of ellipticine. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 4348–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.M. Ligand-targeted therapeutics in anticancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoi, K.; Tanei, T.; Godin, B.; van de Ven, A.L.; Hanibuchi, M.; Matsunoki, A.; Alexander, J.; Ferrari, M. Serum biomarkers for personalization of nanotherapeutics-based therapy in different tumor and organ microenvironments. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotech. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, T.T.; Olive, P.L.; Pun, S.H. Increased nanoparticle penetration in collagenase-treated multicellular spheroids. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Grantab, R.; Sivananthan, S.; Tannock, I.F. The penetration of anticancer drugs through tumor tissue as a function of cellular adhesion and packing density of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykes, E.A.; Chen, J.; Zheng, G.; Chan, W.C.W. Investigating the impact of nanoparticle size on active and passive tumor targeting efficiency. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5696–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, D. High drug-loading nanomedicines: Progress, current status, and prospects. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 4085–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dissanayake, S.; Denny, W.A.; Gamage, S.; Sarojini, V. Recent developments in anticancer drug delivery using cell penetrating and tumor targeting peptides. J. Control. Release 2017, 250, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruoslahti, E. Tumor penetrating peptides for improved drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 110–111, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, W.; Gao, X. Functional peptides for sirna delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 110–111, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erazo-Oliveras, A.; Muthukrishnan, N.; Baker, R.; Wang, T.-Y.; Pellois, J.-P. Improving the endosomal escape of cell-penetrating peptides and their cargos: Strategies and challenges. Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 1177–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, P.; El-Andaloussi, S.; Sütlü, T.; Johansson, H.; Langel, Ü. Delivery of short interfering rna using endosomolytic cell-penetrating peptides. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 2664–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkachenko, A.G.; Xie, H.; Coleman, D.; Glomm, W.; Ryan, J.; Anderson, M.F.; Franzen, S.; Feldheim, D.L. Multifunctional gold nanoparticle-peptide complexes for nuclear targeting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4700–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.S.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhu, J.Y.; Han, K.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Hong, W.; Li, W.X.; Jia, H.Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhuo, R.X.; et al. Dual-ph sensitive charge-reversal polypeptide micelles for tumor-triggered targeting uptake and nuclear drug delivery. Small 2015, 11, 2543–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellerby, H.M.; Arap, W.; Ellerby, L.M.; Kain, R.; Andrusiak, R.; Rio, G.D.; Krajewski, S.; Lombardo, C.R.; Rao, R.; Ruoslahti, E.; et al. Anti-cancer activity of targeted pro-apoptotic peptides. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoskin, D.W.; Ramamoorthy, A. Studies on anticancer activities of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fjell, C.D.; Hiss, J.A.; Hancock, R.E.; Schneider, G. Designing antimicrobial peptides: Form follows function. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 11, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standley, S.M.; Toft, D.J.; Cheng, H.; Soukasene, S.; Chen, J.; Raja, S.M.; Band, V.; Band, H.; Cryns, V.L.; Stupp, S.I. Induction of cancer cell death by self-assembling nanostructures incorporating a cytotoxic peptide. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3020–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stylianopoulos, T.; Soteriou, K.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K. Cationic nanoparticles have superior transvascular flux into solid tumors: Insights from a mathematical model. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostarelos, K.; Emfietzoglou, D.; Papakostas, A.; Yang, W.-H.; Ballangrud, Å.; Sgouros, G. Binding and interstitial penetration of liposomes within avascular tumor spheroids. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 112, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, H.; Park, S.-J.; Bae, Y.H.; Na, K. Biodegradable cationic nanoparticles loaded with an anticancer drug for deep penetration of heterogeneous tumours. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7674–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, R.; Jiang, T.; Sun, W.; Gu, Z. Atp-responsive DNA-graphene hybrid nanoaggregates for anticancer drug delivery. Biomaterials 2015, 50, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agemy, L.; Friedmann-Morvinski, D.; Kotamraju, V.R.; Roth, L.; Sugahara, K.N.; Girard, O.M.; Mattrey, R.F.; Verma, I.M.; Ruoslahti, E. Targeted nanoparticle enhanced proapoptotic peptide as potential therapy for glioblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17450–17455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaires, J.B.; Herrera, J.; Waring, M. Preferential binding of daunomycin to 5’tacg and 5’tagc sequences revealed by footprinting titration experiments. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 6145–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, X.; Song, S.; Zhang, J.; Pan, D.; Wang, L.; Fan, C. A target-responsive electrochemical aptamer switch (treas) for reagentless detection of nanomolar atp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1042–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chen, T.; Han, D.; You, M.; Peng, L.; Cansiz, S.; Zhu, G.; Li, C.; Xiong, X.; Jimenez, E.; et al. Engineering of switchable aptamer micelle flares for molecular imaging in living cells. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5724–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Ji, C.; Shi, J.; Pridgen, E.M.; Frieder, J.; Wu, J.; Farokhzad, O.C. DNA self-assembly of targeted near-infrared-responsive gold nanoparticles for cancer thermo-chemotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11853–11857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorn, C.F.; Oshiro, C.; Marsh, S.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; McLeod, H.; Klein, T.E.; Altman, R.B. Doxorubicin pathways: Pharmacodynamics and adverse effects. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2011, 21, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leist, M.; Single, B.; Castoldi, A.F.; Kuhnle, S.; Nicotera, P. Intracellular adenosine triphosphate (atp) concentration: A switch in the decision between apoptosis and necrosis. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamay, Y.; Shah, J.; Isik, M.; Mizrachi, A.; Leibold, J.; Tschaharganeh, D.F.; Roxbury, D.; Budhathoki-Uprety, J.; Nawaly, K.; Sugarman, J.L.; et al. Quantitative self-assembly prediction yields targeted nanomedicines. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Cui, W.; Li, J.; Sheng, YB.; Chen, P. Functional control of peptide amphiphile assemblies via modulating internal cohesion and surface chemistry switch. Chem.-Eur. J. 2018. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, N.; Ma, W.; Pei, J.; Ouyang, Q.; Tang, C.; Lai, L. Synergistic and antagonistic drug combinations depend on network topology. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoni, M.; Piccinini, F.; Arienti, C.; Zamagni, A.; Santi, S.; Polico, R.; Bevilacqua, A.; Tesei, A. 3D tumor spheroid models for in vitro therapeutic screening: A systematic approach to enhance the biological relevance of data obtained. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, D.; Yu, S.-c.; Ping, Y.-f.; Wu, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Dai, J.; et al. A three-dimensional collagen scaffold cell culture system for screening anti-glioma therapeutics. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 56904–56914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, S.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, P. Therapeutic Peptide Amphiphile as a Drug Carrier with ATP-Triggered Release for Synergistic Effect, Improved Therapeutic Index, and Penetration of 3D Cancer Cell Spheroids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092773
Lu S, Zhao F, Zhang Q, Chen P. Therapeutic Peptide Amphiphile as a Drug Carrier with ATP-Triggered Release for Synergistic Effect, Improved Therapeutic Index, and Penetration of 3D Cancer Cell Spheroids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092773
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Sheng, Feng Zhao, Qiuxin Zhang, and P. Chen. 2018. "Therapeutic Peptide Amphiphile as a Drug Carrier with ATP-Triggered Release for Synergistic Effect, Improved Therapeutic Index, and Penetration of 3D Cancer Cell Spheroids" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092773
APA StyleLu, S., Zhao, F., Zhang, Q., & Chen, P. (2018). Therapeutic Peptide Amphiphile as a Drug Carrier with ATP-Triggered Release for Synergistic Effect, Improved Therapeutic Index, and Penetration of 3D Cancer Cell Spheroids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092773