Effect of Calcium on Absorption Properties and Thermal Stability of Milk during Microwave Heating
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Basic Components of Milk
2.2. Effects of Calcium on the Dielectric Properties and Microwave Absorption Properties of Milk
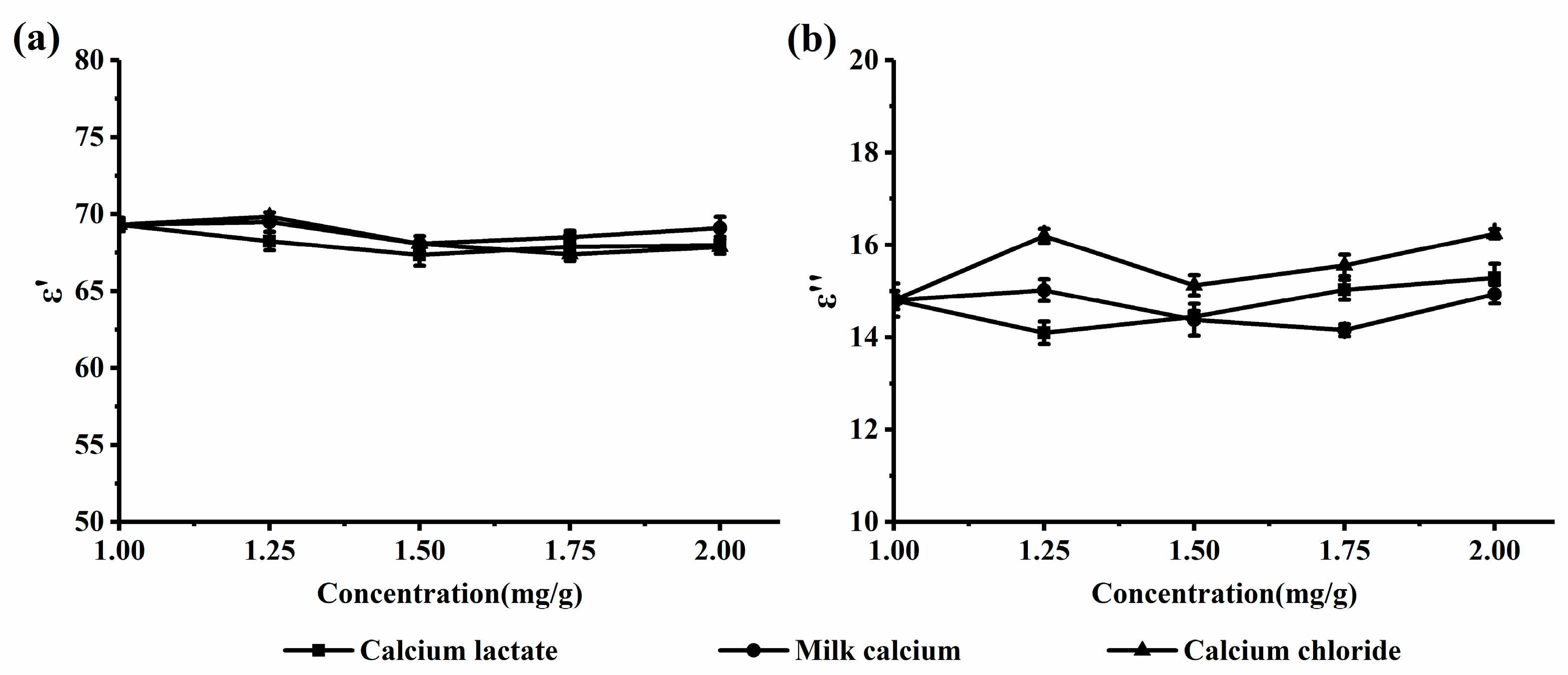
2.2.1. Dielectric Properties of the Calcium-Fortified Milk Systems
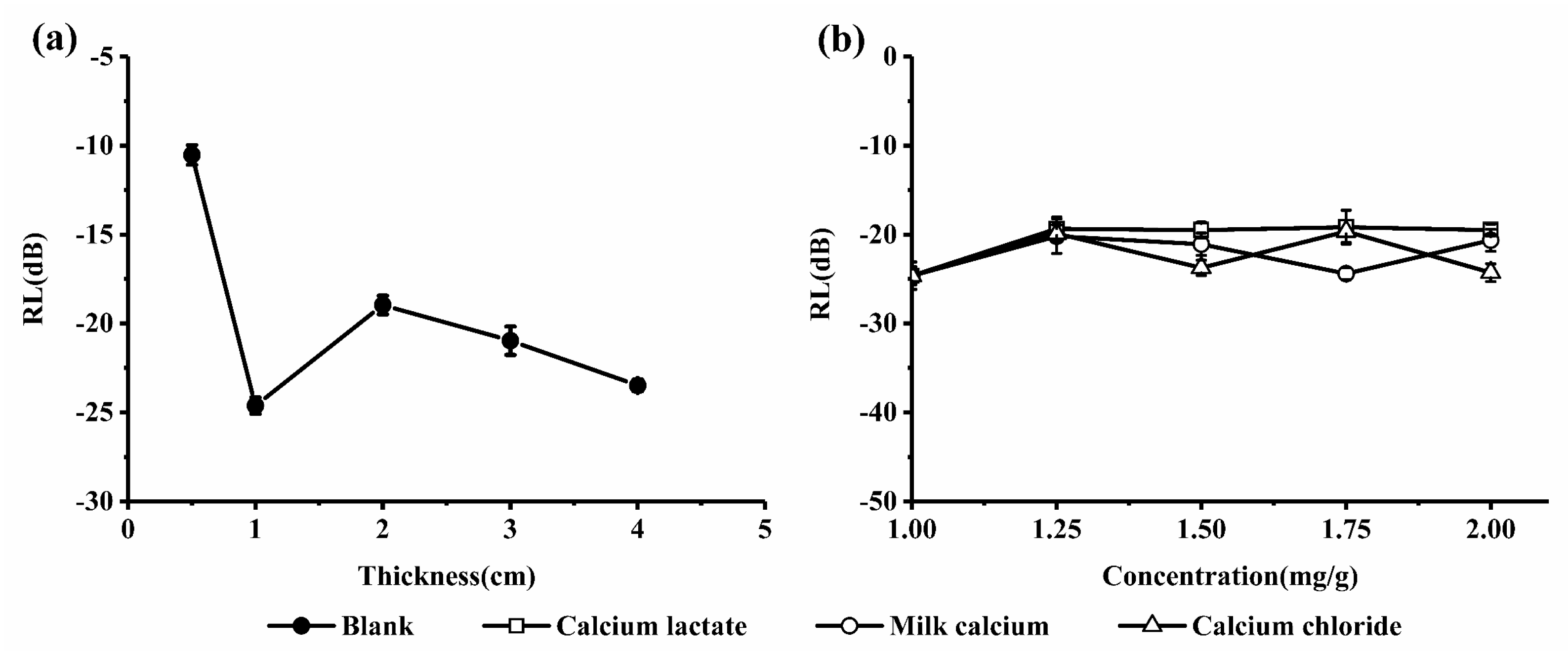
2.2.2. Microwave Absorption Properties of the Calcium-Fortified Milk Systems
2.3. The Thermal Stability of the Calcium-Fortified Milk Systems under the Microwave Field
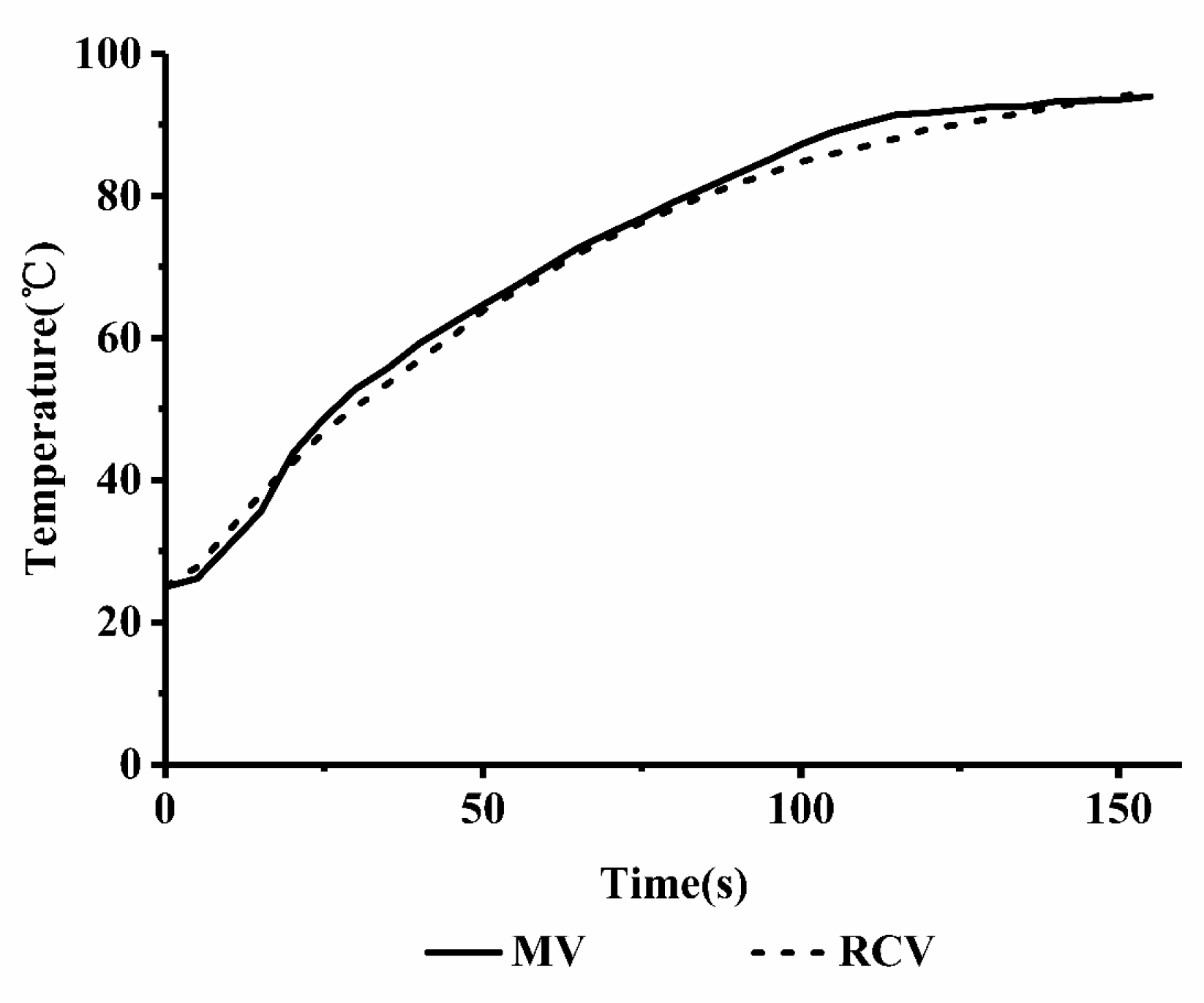
2.3.1. Comparison of the Microwave Heating and Rapid Conventional Heating Curves
2.3.2. The Thermal Stability of the Milk during the Heating Process
2.3.3. The Effects of Different Calcium Forms on the Thermal Stability of Milk
2.3.4. The Effects of Different Calcium Concentrations on the Thermal Stability of Milk
2.3.5. The Effects of Different Heating Methods on the Thermal Stability of Milk
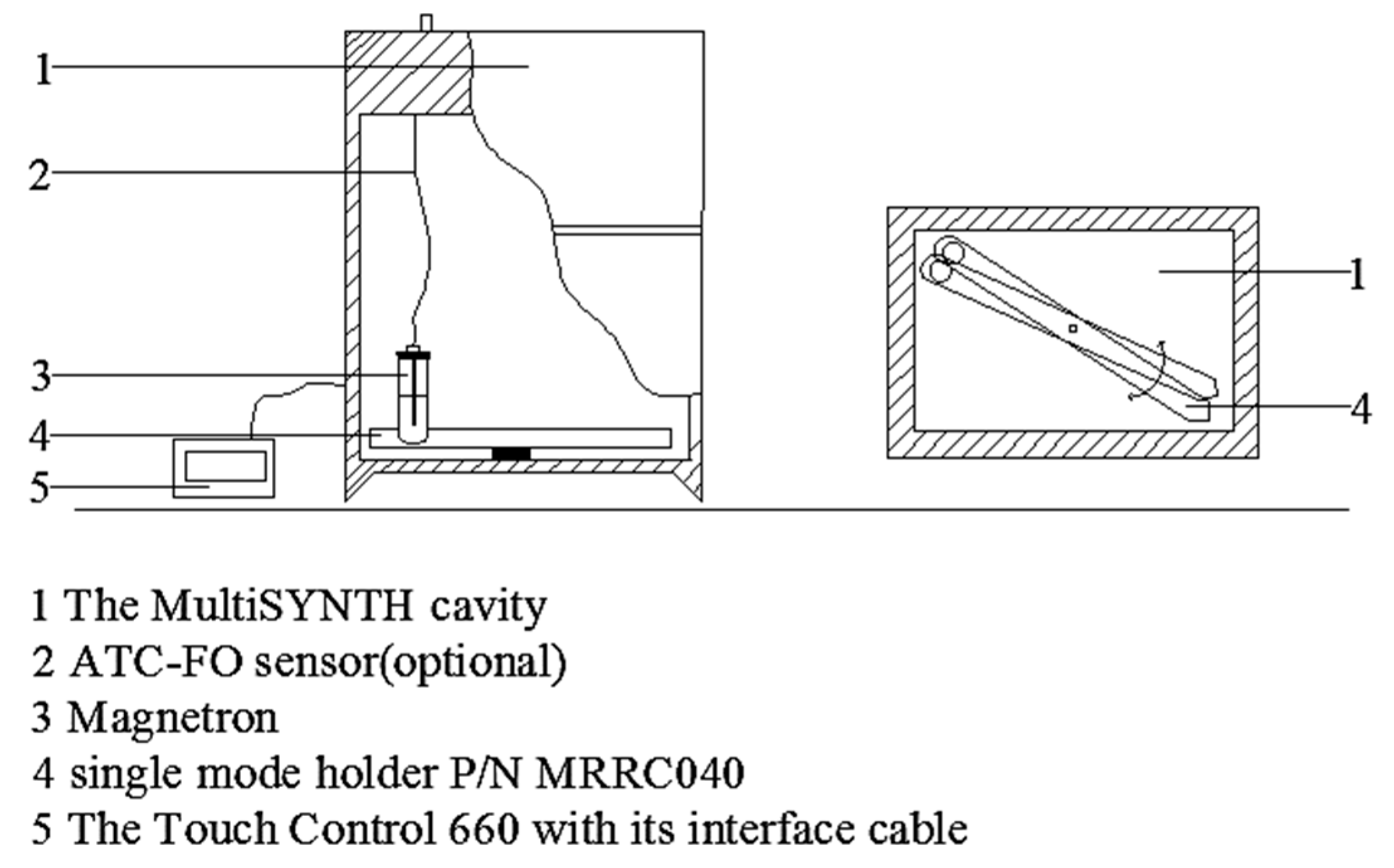
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Calcium-Fortified Milk Systems
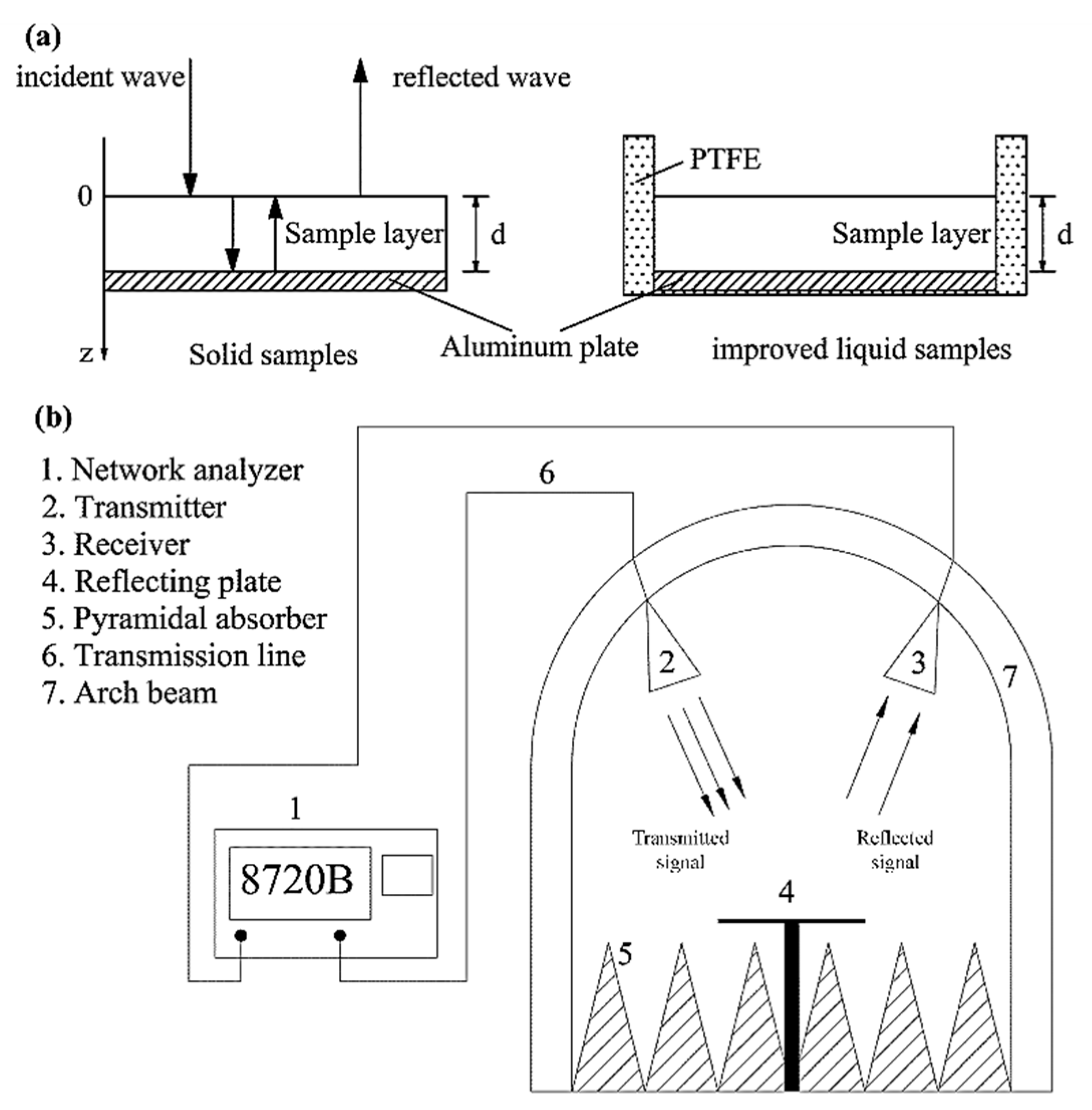
3.3. Determination of Dielectric Properties
3.4. Determination of Reflection Loss (RL)
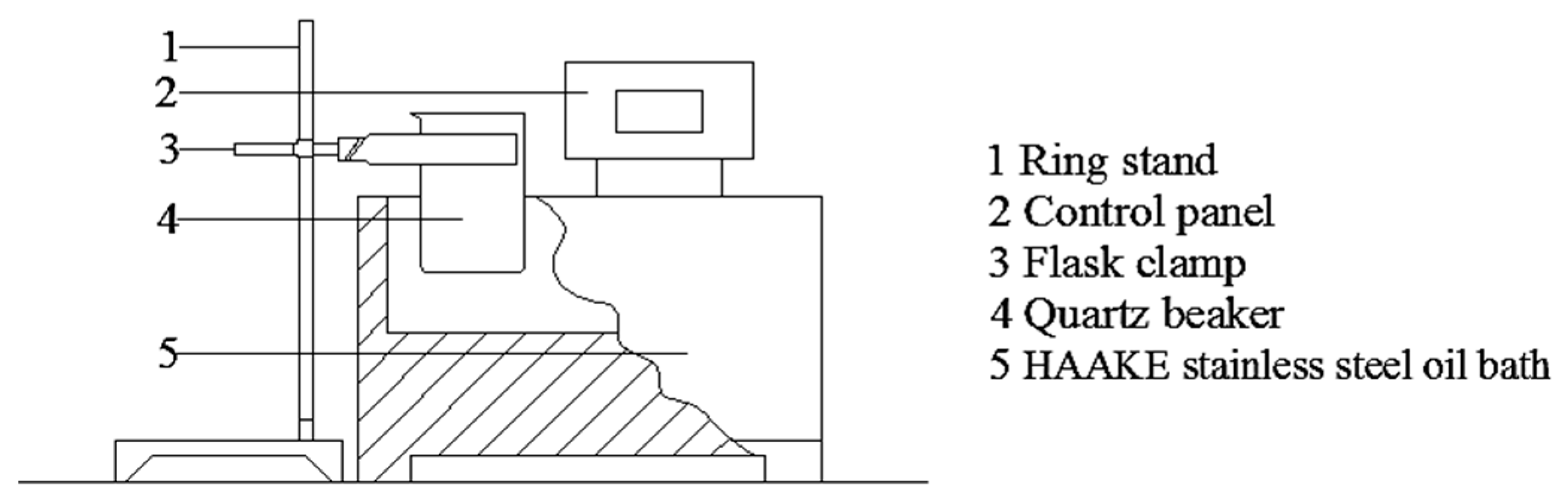
3.5. Rapid Conventional Heating Method
3.6. Microwave Heating Method
3.7. Analysis of Milk Composition
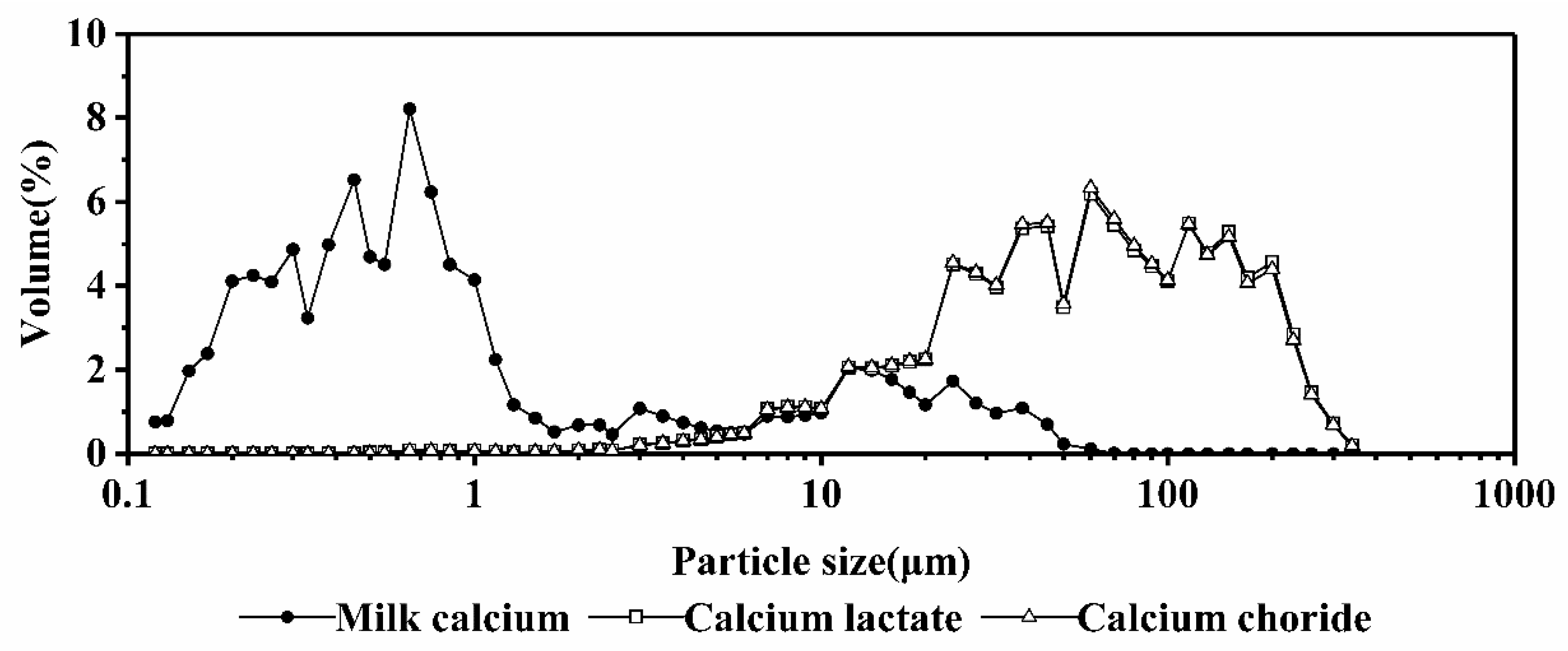
3.8. Analysis of Particle Size
3.9. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, H.; Waungana, A. Influence of Heat Treatment of Milk on Cheesemaking Properties. Int. Dairy J. 2001, 11, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, R.J. Thermal denaturation of whey protein. Bull. Int. Dairy Fed. 1989, 238, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G.; Arora, S.; Sharma, G.S.; Sindhu, J.S.; Kansal, V.K.; Sangwan, R.B. Heat Stability and Calcium Bioavailability of Calcium-fortified Milk. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anema, S.G. Role of Colloidal Calcium Phosphate in the Acid Gelation Properties of Heated Skim Milk. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, C.; Muir, D.D. Inorganic constitutes of milk 1.Correlation of soluble calcium with citrate in bovine milk. J. Dairy Res. 1979, 46, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, C.; Labella, C.; Elshafie, H.S.; Camele, I.; Musto, M.; Paolino, R.; D’adamo, C.; Freschi, P. Effects of different heat treatments on lysozyme quantity and antimicrobial activity of jenny milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5173–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villamiel, M.; Corzo, N.; Martínez-Castro, I.; Olano, A. Chemical changes during microwave treatment of milk. Food Chem. 1996, 56, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westergaard, V. Milk Powder Technology; Niro A/S: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, J. Determination of the influence of homogenizing conditions on the stability of buffalo milk by particle size analysis. China Dairy Ind. 2009, 37, 42–44. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, H.; Regier, M. Microwave Processing of Foods; China Light Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Monzon, M.; Johnson, J.A.; Mitcham, E.J.; Tang, J. Industrial-scale radio frequency treatments for insect control in walnuts: I: Heating uniformity and energy efficiency. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2007, 45, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacilik, K.; Colak, A. Determination of dielectric properties of corn seeds from 1 to 100 MHz. Powder Technol. 2010, 203, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Zhang, L.; Yin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, L.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, L. Dielectric and microwave-absorption properties of SiC nanoparticle/SiBCN composite ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, C. Technique of Microwave Measurements; McGraw-Hill Book Co.: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.B.; Qiu, T.; Shen, C.Y. Absorbing properties and structural design of microwave absorbers based on carbonyl iron and barium ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 318, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, T.; Yu, R.; Jau, Y. Synthesis and microwave absorption characteristics of polyaniline/NiZn ferrite composites in 2–40 GHz. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 126, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, R.; Bedane, T.F.; Erdogdu, F.; Palazoglu, T.; Farag, K. Radio-frequency thawing of food products-A computational study. J. Food Eng. 2015, 146, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, L.; Ren, L.; Gong, G. Study on the Stability of High-calcium Milk. J. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2009, 32, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Jian, X. Study on mid-experiment processing of the high calcium liquid milk. China Dairy Ind. 2006, 34, 60–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Gao, Y.; Wang, C.; Ni, K.; Ge, Z.; Ma, F. A Method to Make High Quality Calcium, Iron and Zinc Fortified Milk. China CN201310660634.5, 26 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, N.; Yagihara, S.; Mashimo, S. Microwave dielectric properties of solid and liquid foods investigated by time-domain reflectometry. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motwani, T.; Seetharaman, K.; Anantheswaran, R.C. Dielectric properties of starch slurries as influenced by starch concentration and gelatinization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 67, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Shen, H.; Huang, L.; Gao, Y.; Lian, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Microwave-Absorbing Properties of Rice Starch. Polymers 2015, 7, 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Ma, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Effect of microwave heating on optical and thermal properties of rice starch. Starch-Stärke 2012, 64, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Mallikarjunan, P. Thermal and dielectric properties of shucked oysters. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 38, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Fan, D.; Huang, L.; Gao, Y.; Lian, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H. Effects of microwaves on molecular arrangements in potato starch. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14348–14353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

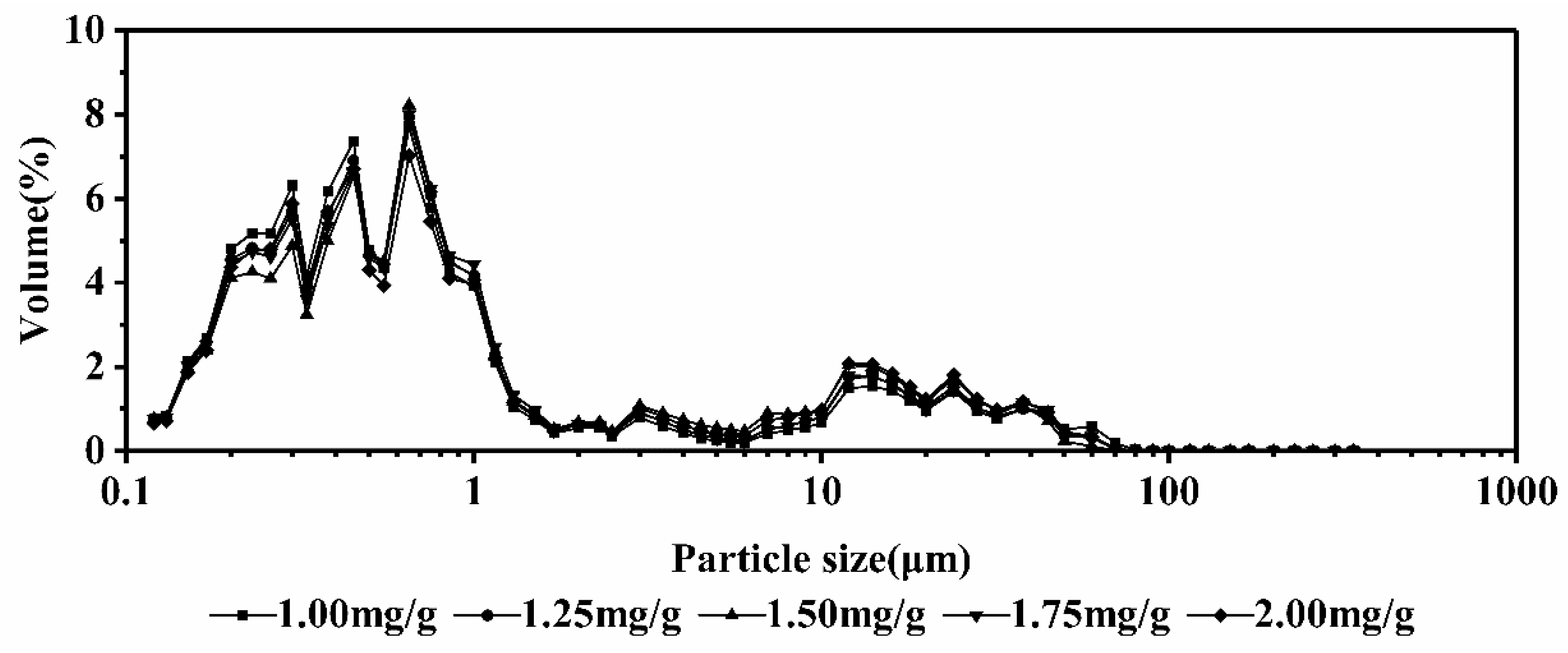
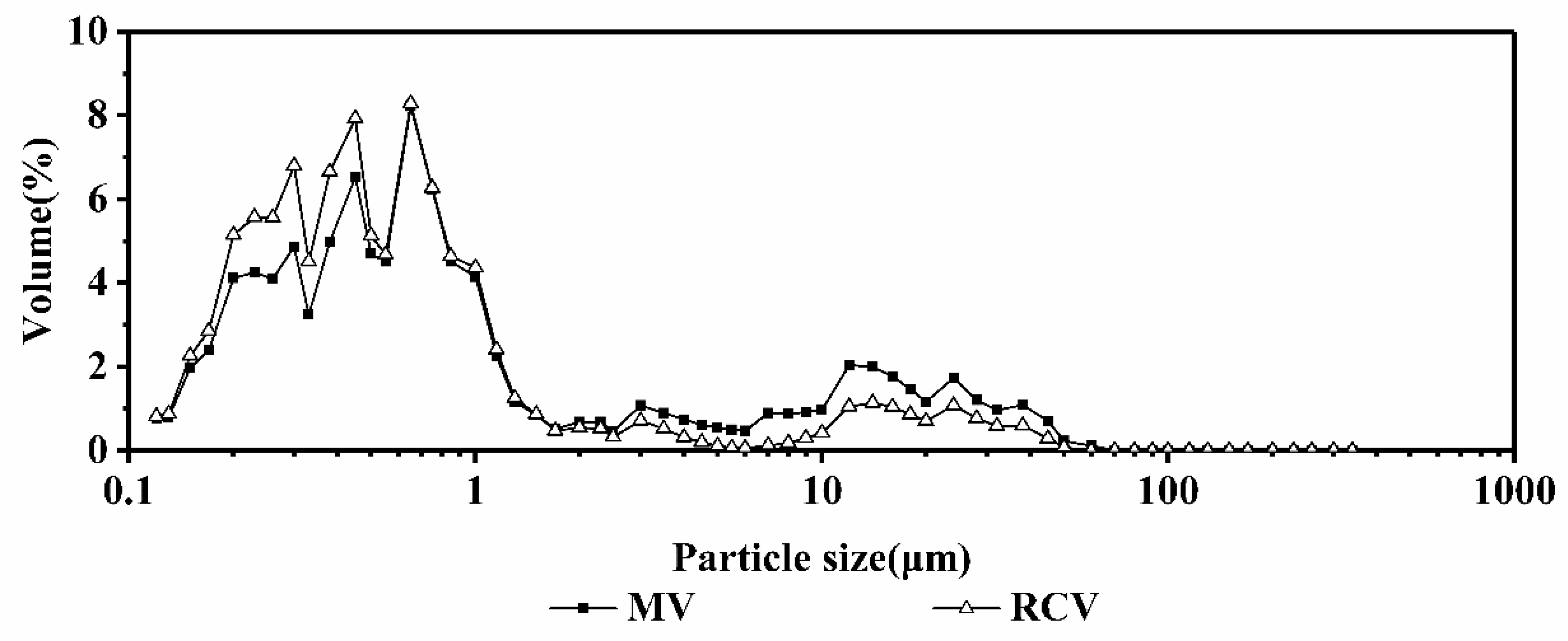
| Sample | Fat/% | Cru.Protein 1/% | Tru.Protein 2/% | Lactose/% | SnF 3/% | Ts 4/% | FPT 5/°C | Calcium/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank milk | 3.50 ± 0.19 | 3.07 ± 0.30 | 2.91 ± 0.21 | 4.62 ± 0.11 | 8.54 ± 0.31 | 12.08 ± 0.30 | 0.495 ± 0.14 | 0.10 ± 0.03 |
| Sample | The Percentage of Particles in Different Distribution/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1–1 μm | 1–10 μm | 10–100 μm | |
| Blank milk | 90.95 ± 0.23 | 5.55 ± 0.31 | 3.50 ± 0.56 |
| Samples | Temperature | 0–1 μm | 1–10 μm | 10–100 μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank milk systems | 25 °C | 90.95 ± 0.23 | 5.55 ± 0.31 | 3.50 ± 0.56 |
| 45 °C | 82.28 ± 0.59 | 7.28 ± 0.42 | 9.44 ± 0.60 | |
| 65 °C | 76.33 ± 0.88 | 10.66 ± 0.74 | 13.01 ± 0.62 | |
| 95 °C | 71.69 ± 0.45 | 12.59 ± 0.51 | 15.72 ± 0.54 | |
| milk calcium-fortified systems | 45 °C | 69.84 ± 0.69 | 15.62 ± 0.51 | 14.54 ± 0.72 |
| 65 °C | 69.83 ± 0.54 | 15.65 ± 0.72 | 14.52 ± 0.49 | |
| 95 °C | 70.35 ± 0.73 | 15.14 ± 0.93 | 14.51 ± 1.21 |
| Calcium Content | Calcium Chloride | Calcium Lactate | Milk Calcium |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.00 mg/g | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1.25 mg/g | 0.0694 g ± 0.0002 | 0.1927 g ± 0.0001 | 0.0975 g ± 0.0002 |
| 1.50 mg/g | 0.1387 g ± 0.0003 | 0.3854 g ± 0.0000 | 0.1951 g ± 0.0002 |
| 1.75 mg/g | 0.2081 g ± 0.0001 | 0.5781 g ± 0.0002 | 0.2926 g ± 0.0000 |
| 2.00 mg/g | 0.2775 g ± 0.0001 | 0.7708 g ± 0.0003 | 0.3902 g ± 0.0001 |
| Heating Stages | Power/W | Time/s |
|---|---|---|
| First stage | 72 | 15 |
| Second stage | 39 | 50 |
| Third stage | 33 | 45 |
| Fourth stage | 31 | 45 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Fan, D.; Hang, F.; Yan, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Effect of Calcium on Absorption Properties and Thermal Stability of Milk during Microwave Heating. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061747
Wu Y, Fan D, Hang F, Yan B, Zhao J, Zhang H, Chen W. Effect of Calcium on Absorption Properties and Thermal Stability of Milk during Microwave Heating. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(6):1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061747
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yejun, Daming Fan, Feng Hang, Bowen Yan, Jianxin Zhao, Hao Zhang, and Wei Chen. 2018. "Effect of Calcium on Absorption Properties and Thermal Stability of Milk during Microwave Heating" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 6: 1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061747
APA StyleWu, Y., Fan, D., Hang, F., Yan, B., Zhao, J., Zhang, H., & Chen, W. (2018). Effect of Calcium on Absorption Properties and Thermal Stability of Milk during Microwave Heating. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(6), 1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061747






