A Recombinant Affinity Reagent Specific for a Phosphoepitope of Akt1
Abstract
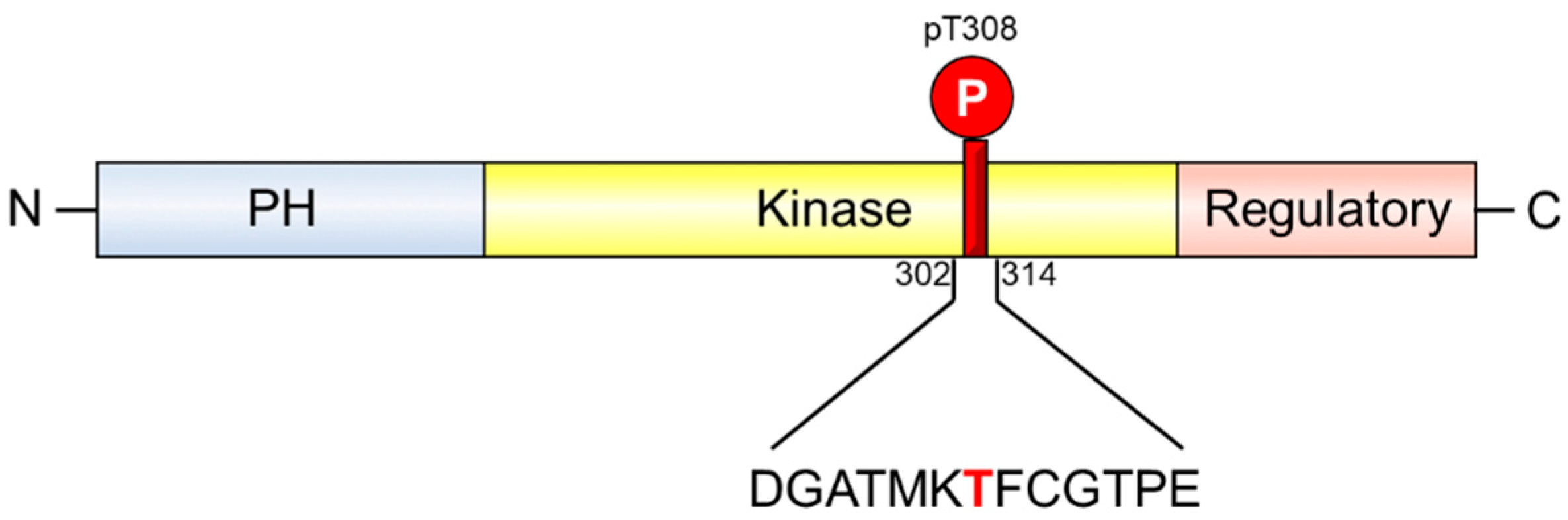
1. Introduction
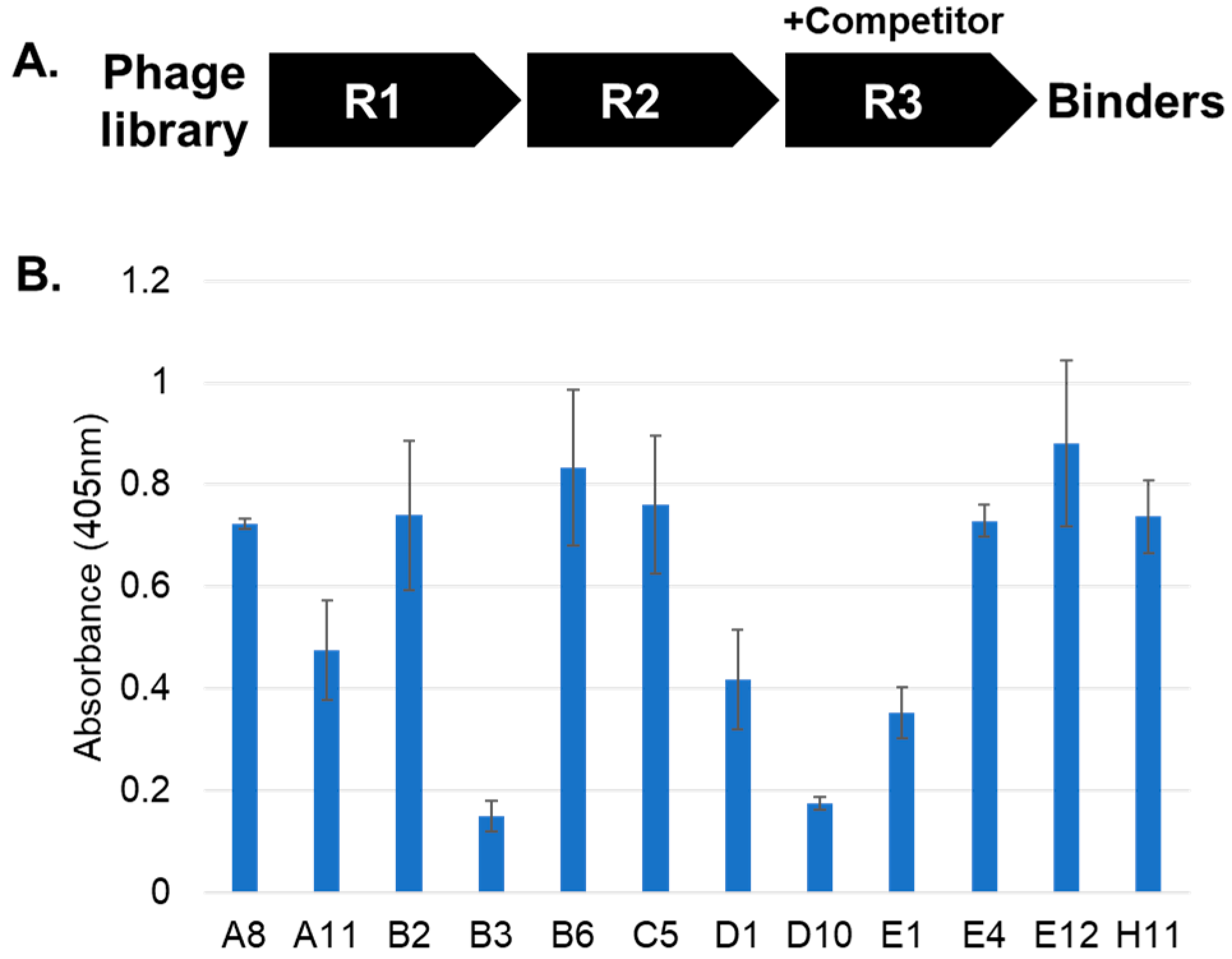
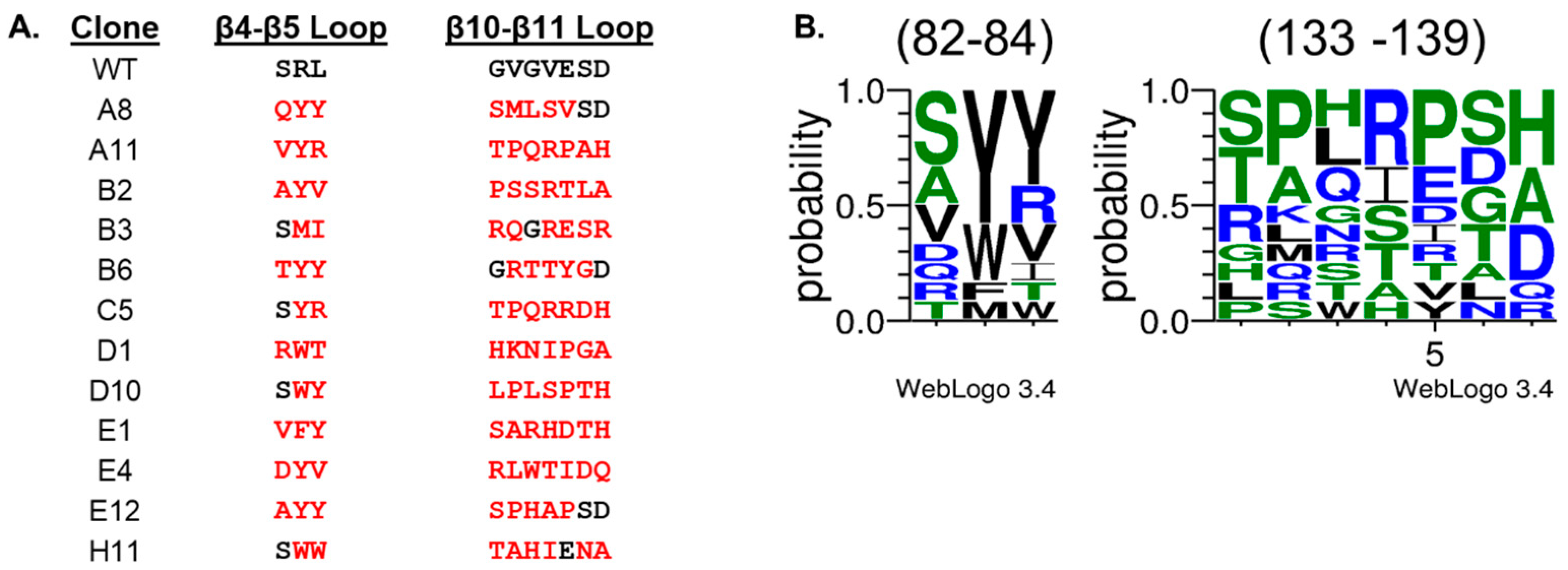
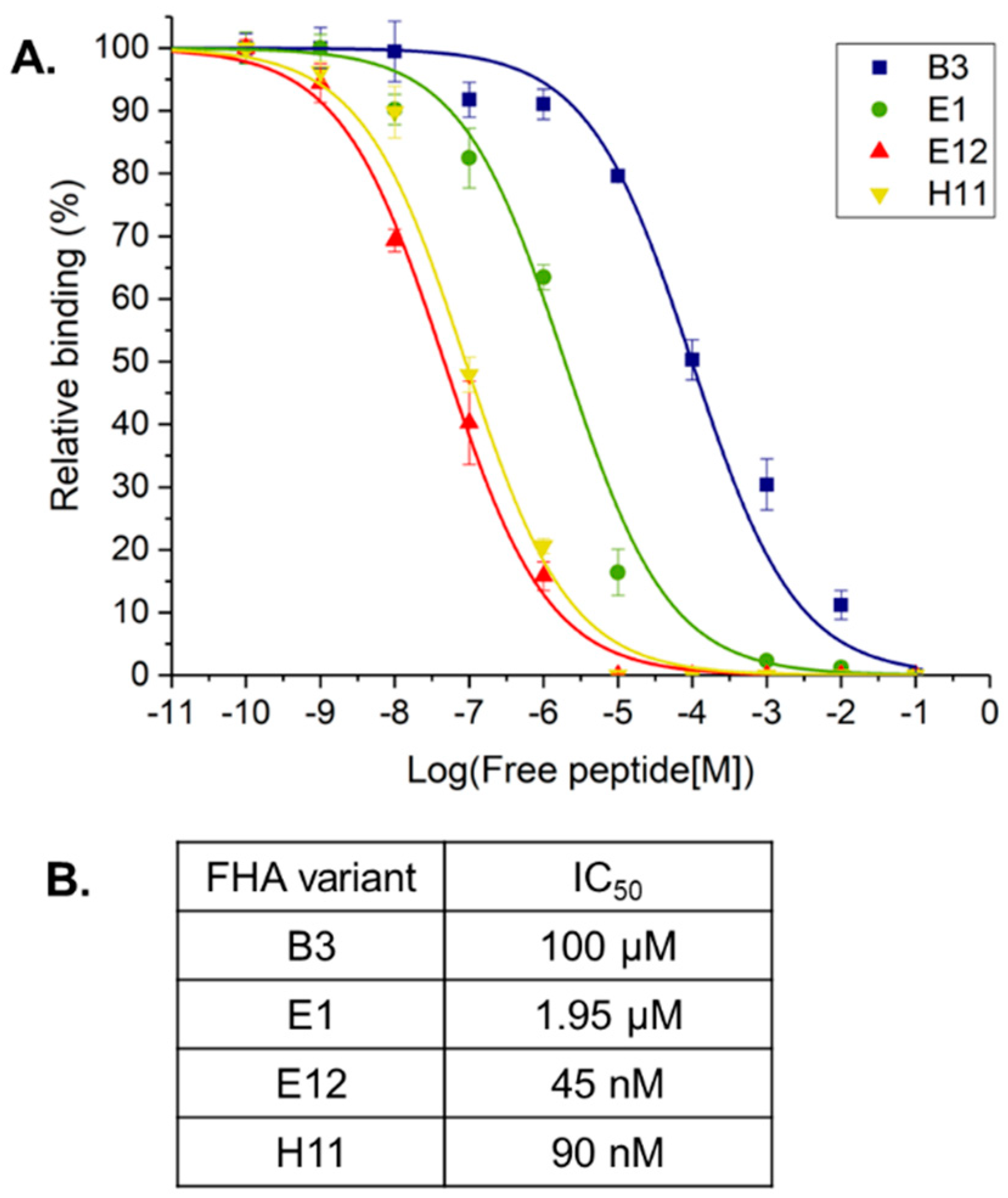
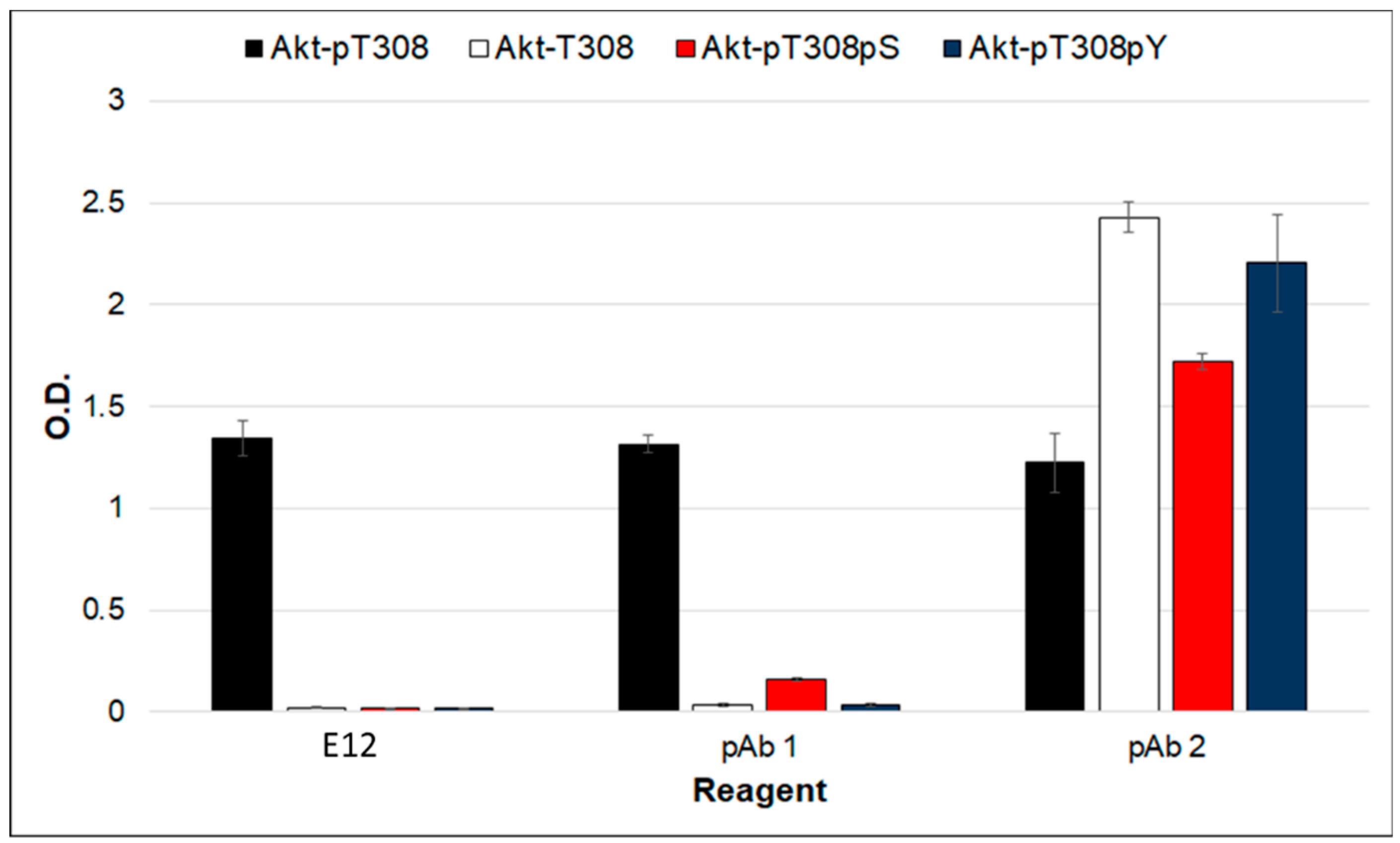
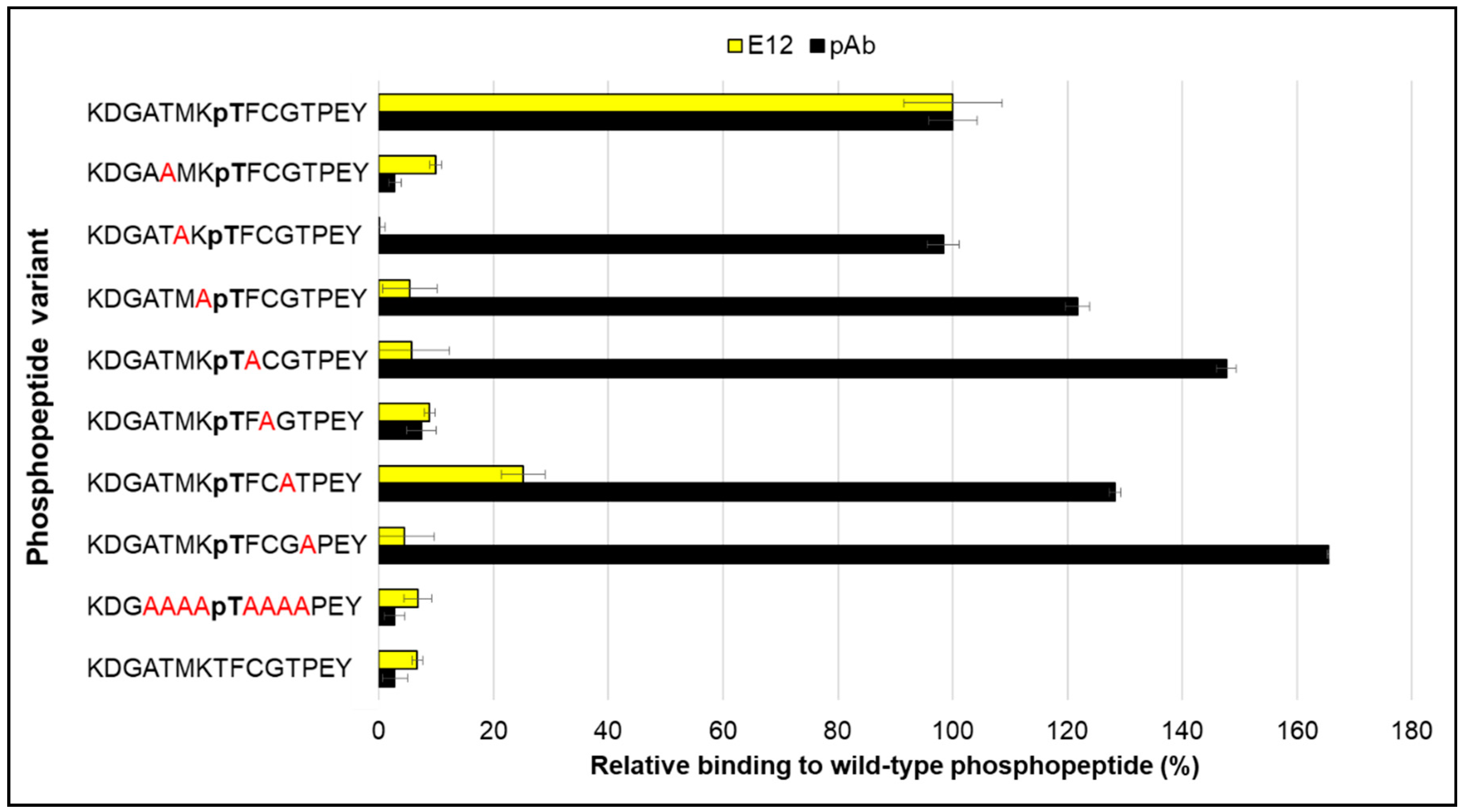
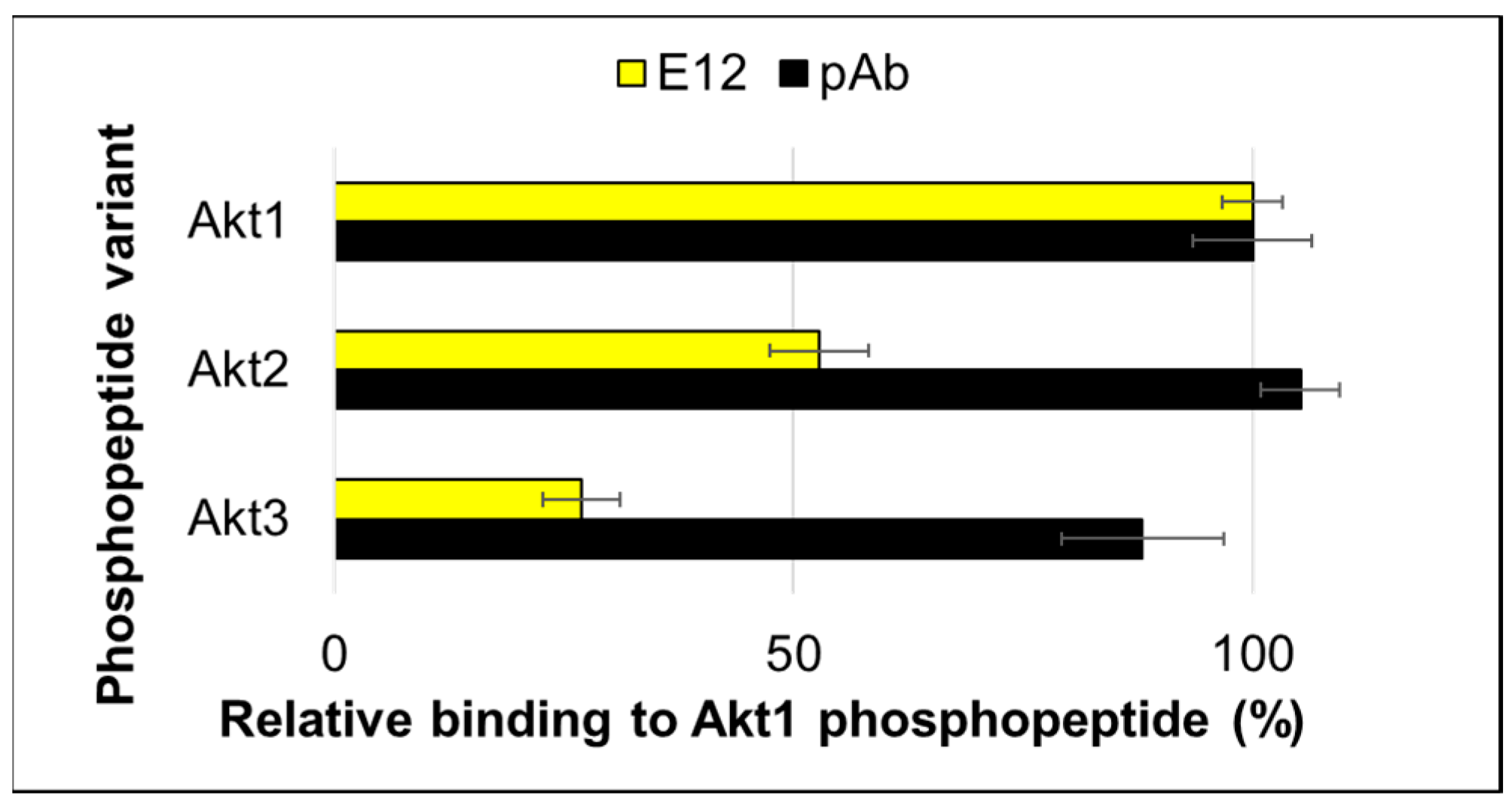
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Peptides
3.2. Cloning and Bacterial Expression of Proteins
3.3. Affinity Selections
3.4. ELISA
3.5. Surface Plasmon Resonance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, P.; Wang, Z.; Wei, W. Phosphorylation of Akt at the C-terminal tail triggers Akt Activation. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 2162–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, B.D.; Toker, A. AKT/PKB Signaling: Navigating the Network. Cell 2017, 169, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, L.; Anderson, K.; Stokoe, D.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Painter, G.F.; Holmes, A.B.; Gaffeny, P.R.J.; Reese, C.B.; McCormick, F.; Tempst, P.; et al. Protein kinase B kinases that mediate phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent activation of protein kinase B. Science 1998, 279, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.X.; Kim, H.Y. Interdomain conformational changes in Akt activation revealed by chemical cross-linking and tandem mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2006, 5, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarbassov, D.D.; Guertin, D.A.; Ali, S.M.; Sabatini, D.M. Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science 2005, 307, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessi, D.R.; Andjelkovic, M.; Caudwell, B.; Cron, P.; Morrice, N.; Cohen, P.; Hemmings, B.A. Mechanism of activation of protein kinase B by insulin and IGF-1. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 6541–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, B.D.; Cantley, L.C. AKT/PKB Signaling: Navigating Downstream. Cell 2007, 129, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.C.; Huang, K.Y.; Yang, C.H.; Yang, Y.S.; Lee, W.Y.; Chiang, C.W. Regulation of phosphorylation of Thr-308 of Akt, cell proliferation, and survival by the B55α regulatory subunit targeting of the protein phosphatase 2A holoenzyme to Akt. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 1882–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, W.; Guo, L.; Bao, W.; Jin, N.; Liu, R.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Chen, B. Gambogic acid suppresses hypoxia-induced hypoxia-inducible factor-1α/vascular endothelial growth factor expression via inhibiting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target protein of rapamycin pathway in multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatani, K.; Thompson, D.A.; Barthel, A.; Sakaue, H.; Liu, W.; Weigel, R.J.; Roth, R.A. Up-regulation of Akt3 in estrogen receptor-deficient breast cancers and androgen-independent prostate cancer lines. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 21528–21532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.Q.; Sun, M.; Feldman, R.I.; Wang, G.; Ma, X.; Jiang, C.; Coppola, D.; Nicosia, S.V.; Cheng, J.Q. Frequent activation of AKT2 and induction of apoptosis by inhibition of phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase/Akt pathway in human ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2324–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altomare, D.A.; Tanno, S.; Rienzo, A.D.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.; Tanno, S.; Skele, K.L.; Hoffman, J.P.; Testa, J.R. Frequent activation of AKT2 kinase in human pancreatic carcinomas. J. Cell. Biochem. 2002, 87, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, E.E.; Elder, D.J.E.; Thomas, E.C.; Phillips, L.; Morgan, C.; Pawade, J.; Sohail, M.; May, M.T.; Hetzel, M.R.; Tavare, J.M. Akt phosphorylation on Thr308 but not on Ser473 correlates with Akt protein kinase activity in human non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradbury, A.; Pluckthun, A. Reproducibility: Standardize antibodies used in research. Nature 2015, 518, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, C.A.; Liao, H.; Sun, R.; Roberts, R.W. mRNA display selection of a high-affinity, modification-specific phospho-IκBα-binding fibronectin. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kummer, L.; Paruzek, P.; Rube, P.; Millgramm, B.; Prinz, A.; Mittl, P.R.E.; Kaufholz, M.; Zimmermann, B.; Herberg, F.W.; Pluckthun, A. Structural and functional analysis of phosphorylation specific binders of the kinase ERK from designed ankyrin repeat protein libraries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2248–E2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, T.; Kaneko, T.; Huang, H.; Cao, X.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Voss, C.; Sidhu, S.S.; Li, S.S.C. Superbinder SH2 domains act as antagonists of cell signaling. Sci. Signal 2012, 5, ra68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vielemeyer, O.; Yuan, H.; Moutel, S.; Saint-Fort, R.; Tang, D.; Nizak, C.; Goud, B.; Wang, Y.; Perez, F. Direct selection of monoclonal phosphospecific antibodies without prior phosphoamino acid mapping. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 20791–20795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, H.H.; Tu, C.; Cao, W.; Klein, A.; Ramsey, R.; Fennell, B.J.; Lambert, M.; Shuilleabhain, D.N.; Autin, B.; Kouranova, E.; et al. An ultra-specific avian antibody to phosphorylated tau protein reveals a unique mechanism for phosphoepitope recognition. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 44425–44434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pershad, K.; Wypisniak, K.; Kay, B.K. Directed evolution of the forkhead-associated domain to generate anti-phosphospecific reagents by phage-display. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 424, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venegas, L.A.; Pershad, K.; Bankole, O.; Shah, N.; Kay, B.K. A comparison of phosphospecific affinity reagents reveals the utility of recombinant Forkhead-associated domains in recognizing phosphothreonine-containing peptides. N. Biotechnol. 2016, 33, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.M.; Chang, C.E. Mechanism of PhosphoThreonine/Serine Recognition and Specificity for Modular Domains from All-atom Molecular Dynamics. BMC Biophys. 2011, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinnis, J.E.; Kay, B.K. Generation of recombinant affinity reagents against a two-phosphosite epitope of ATF2. N Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A Sequence Logo Generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, T.D.; Stephens, R.M. Sequence logos: A new way to display consensus sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 6097–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durocher, D.; Taylor, I.A.; Sarbassova, D.; Haire, L.F.; Westcott, S.L.; Jackson, S.P.; Smerdon, S.J.; Yaffe, M.B. The molecular basis of FHA domain:phosphopeptide binding specificity and implications for phospho-dependent signaling mechanisms. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venegas, L.A.; Kall, S.L.; Bankole, O.; Lavie, A.; Kay, B.K. Generating a recombinant phosphothreonine-binding domain for a phosphopeptide of the human transcription factor, c-Myc. New Biotechnol. 2018, 45, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Cron, P.; Good, V.M.; Thompson, V.; Hemmings, B.A.; Barford, D. Crystal structure of an activated Akt/Protein Kinase B ternary complex with GSK3-peptide and AMP-PNP. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2002, 9, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peri, C.; Morra, G.; Colombo, G. Surface energetics and protein-protein interactions: Analysis and mechanistic implications. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pershad, K.; Sullivan, M.A.; Kay, B.K. Drop-out phagemid vector for switching from phage displayed affinity reagents to expression formats. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 412, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goletz, S.; Christensen, P.A.; Kristensen, P.; Blohm, D.; Tomlinson, I.; Winter, G.; Karsten, U. Selection of large diversities of antiidiotypic antibody fragments by phage display. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 315, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Yuan, C.; Hammet, A.; Mahajan, A.; Chen, E.S.W.; Wu, M.R.; Su, M.I.; Heierhorst, J.; Tsai, M.D. Diphosphothreonine-specific interaction between an SQ/TQ cluster and an FHA domain in the Rad53-Dun1 kinase cascade. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| FHA Variant | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E12 | H11 | |||||
| Peptide Target | Ka (M−1 s−1) | Kd (s−1) | KD (nM) | Ka (M−1 s−1) | Kd (s−1) | KD (nM) |
| Akt1-pT308 | 4.830 × 104 | 7.821 × 10−3 | 162 ± 12 | 4.157 × 104 | 7.401 × 10−3 | 178 ± 8 |
| Akt1-T308 | 2.302 | 2.144 × 10−3 | 9.31 × 105 | 2.165 | 1.0108 × 10−2 | 5.002 × 106 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McGinnis, J.E.; Venegas, L.A.; Lopez, H.; Kay, B.K. A Recombinant Affinity Reagent Specific for a Phosphoepitope of Akt1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3305. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113305
McGinnis JE, Venegas LA, Lopez H, Kay BK. A Recombinant Affinity Reagent Specific for a Phosphoepitope of Akt1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3305. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113305
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcGinnis, Jennifer E., Leon A. Venegas, Hector Lopez, and Brian K. Kay. 2018. "A Recombinant Affinity Reagent Specific for a Phosphoepitope of Akt1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3305. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113305
APA StyleMcGinnis, J. E., Venegas, L. A., Lopez, H., & Kay, B. K. (2018). A Recombinant Affinity Reagent Specific for a Phosphoepitope of Akt1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3305. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113305





