Efficient Hydrogen Production from Ammonia Using Ru Nanoparticles on Ce-Based Metal–Organic Framework (MOF)-Derived CeO2 with Oxygen Vacancies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
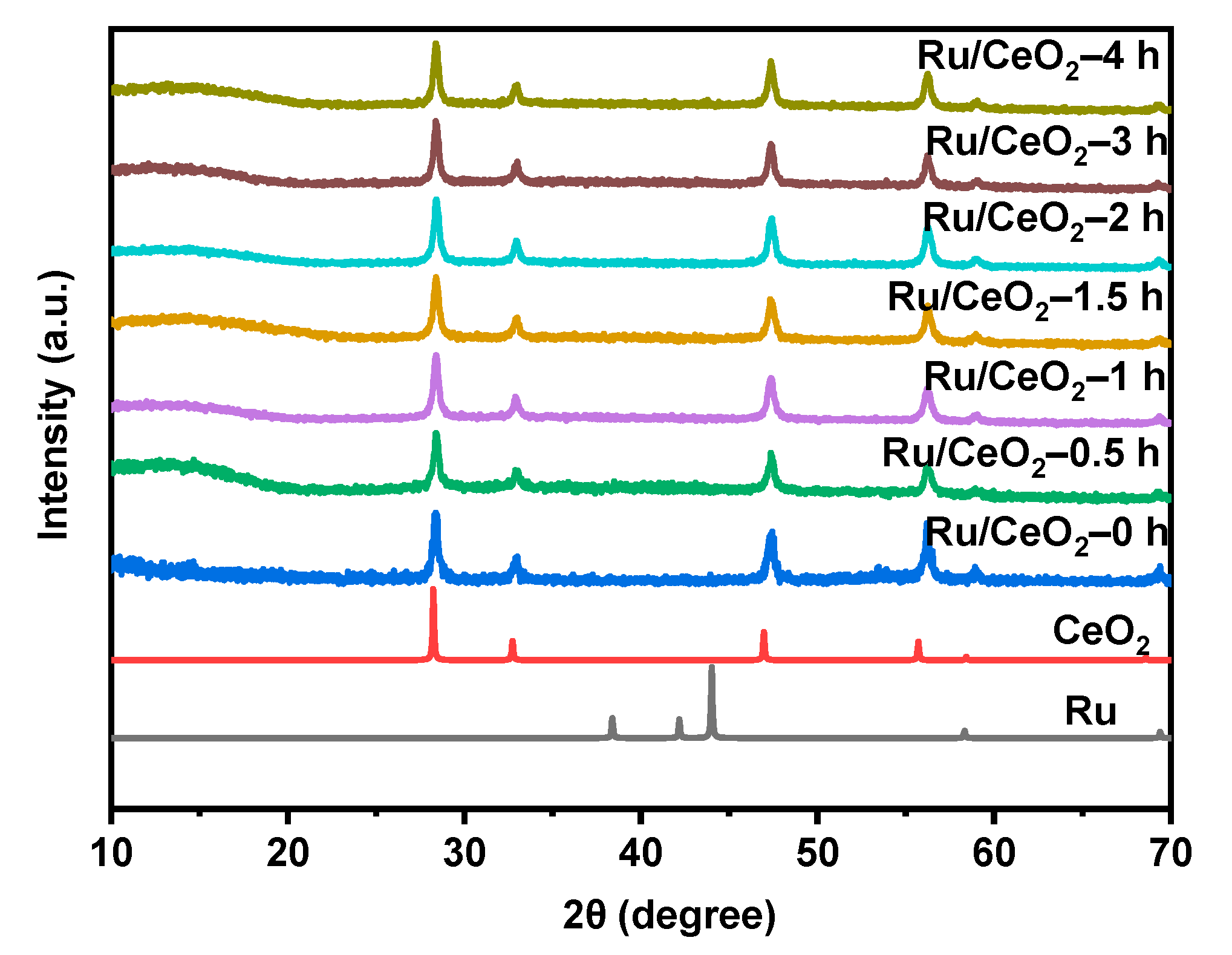
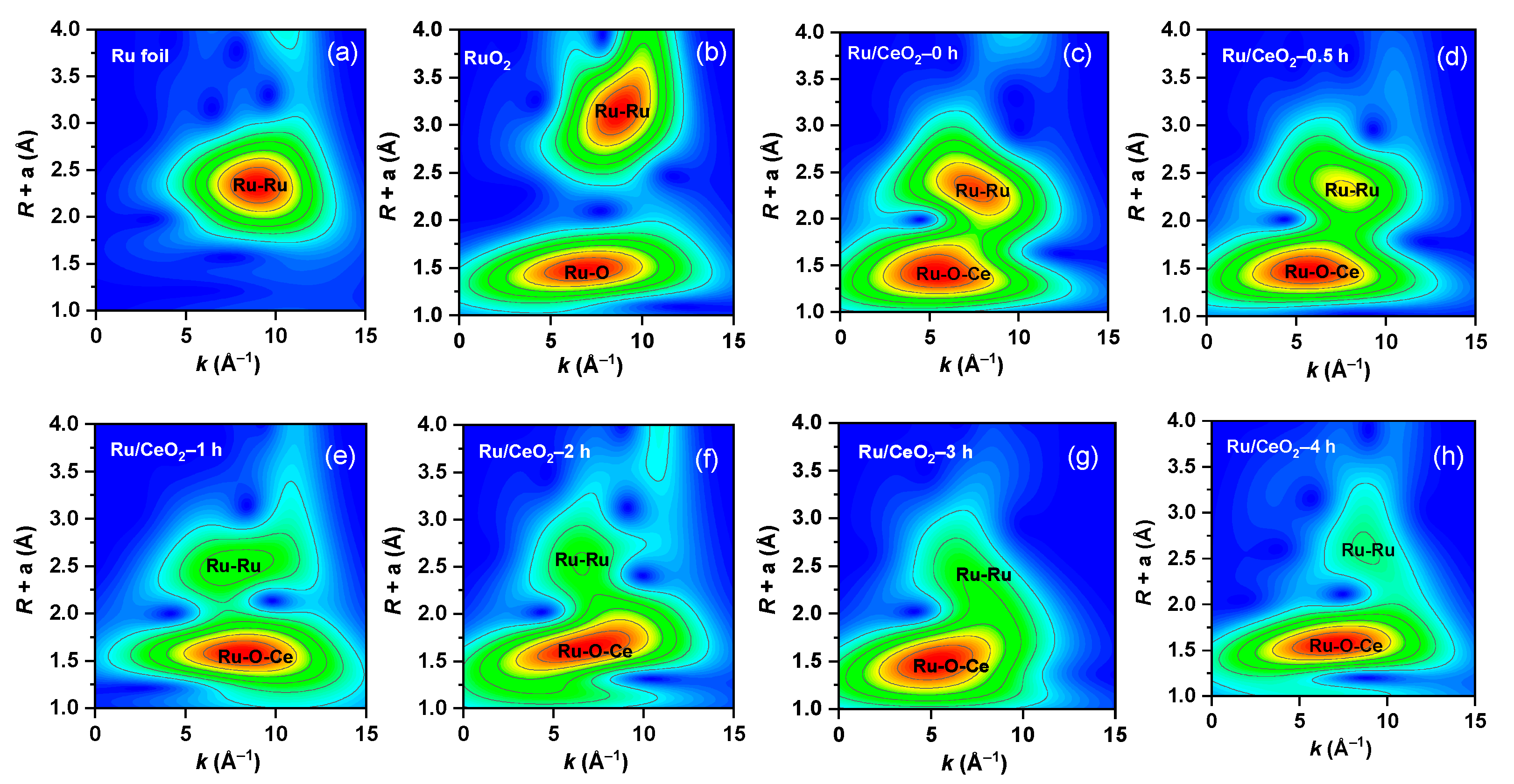
2.1. Structural Characterization of Carrier and Catalyst
2.2. Comparison of Catalytic Performance of Ammonia Decomposition to Hydrogen
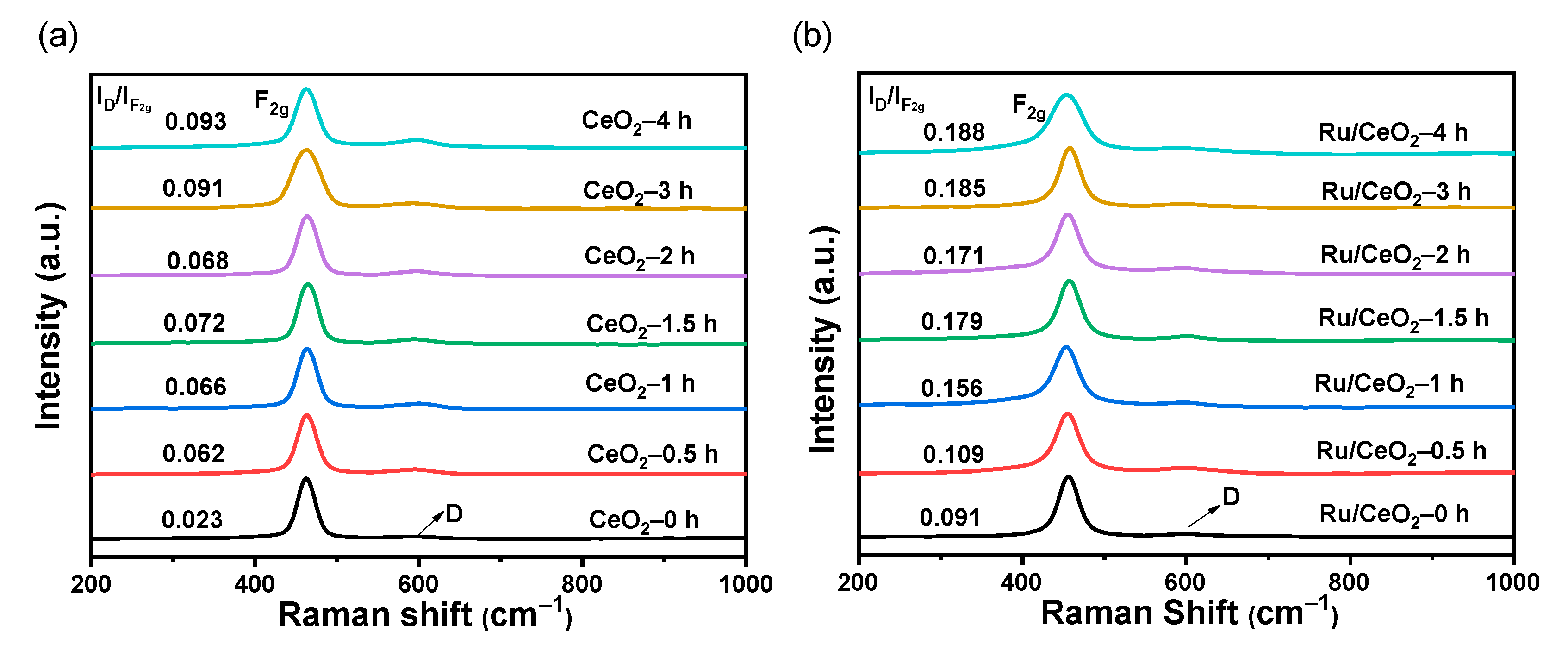
2.3. Surface Chemical State of the Carrier and the Catalyst
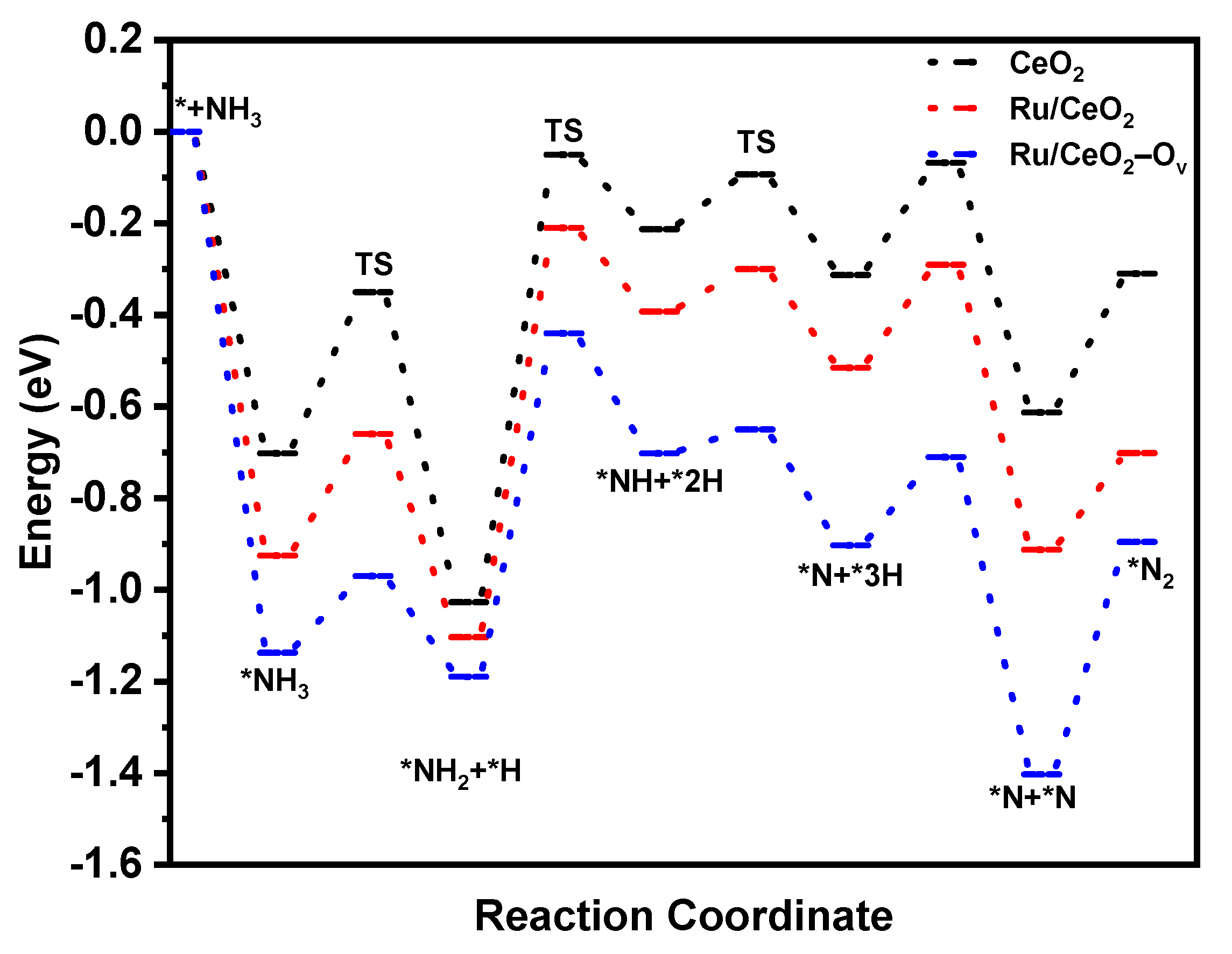
2.4. Reaction Mechanism
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Catalyst Preparation
3.3. Catalyst Activity Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, S.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, D.; Cao, T.; Sha, H.; Zhang, C.; Song, H.; Da, Z. Ammonia as hydrogen carrier: Advances in ammonia decomposition catalysts for promising hydrogen production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 169, 112918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Devaguptapu, S.V.; Sviripa, A.; Lund, C.R.F.; Wu, G. Low-temperature ammonia decomposition catalysts for hydrogen generation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 226, 162–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.; Grönkvist, S. Large-scale storage of hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 11901–11919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Ju, X.; Chen, P. Applications of rare earth oxides in catalytic ammonia synthesis and decomposition. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 6330–6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlane, N.; Katikaneni, S.P.; Paglieri, S.N.; Harale, A.; Solami, B.; Sarathy, S.M.; Gascon, J. A technological roadmap to the ammonia energy economy: Current state and missing technologies. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Tao, Y.; Shao, J.; Zhang, Y.; You, H. Ammonia as an effective hydrogen carrier and a clean fuel for solid oxide fuel cells. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 228, 113729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.E.; Torrente-Murciano, L. H2 production via ammonia decomposition using non-noble metal catalysts: A review. Top. Catal. 2016, 59, 1438–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongil, A.B. Recent progress on transition metal nitrides nanoparticles as heterogeneous catalysts. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.; Lee, T.; Lee, Y.-J.; Jeong, H.; Jo, Y.S.; Kim, Y.; Nam, S.W.; Han, J.; Lee, K.B.; Yoon, C.W.; et al. Highly monodisperse sub-nanometer and nanometer Ru particles confined in alkali-exchanged zeolite Y for ammonia decomposition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 283, 119627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-W.; Li, X.; Qin, Y.-H.; Deng, L.; Wang, C.-W.; Jiang, X. Ammonia decomposition over SiO2-supported Ni-Co bimetallic catalyst for COx-free hydrogen generation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 15263–15269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.P.; Chen, L.; Chen, C. Fe/ZSM-5 catalysts for ammonia decomposition to COx-free hydrogen: Effect of SiO2/Al2O3 ratio. Mol. Catal. 2018, 455, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.F.; Wu, K.; Zhou, C.; Yao, Y.H. Electronic metal-support interaction enhanced ammonia decomposition efficiency of perovskite oxide supported ruthenium. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 257, 117719–117726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, R.; Steiner, R.; Marot, L. Decomposition studies of NH3 and ND3 in presence of H2 and D2 with Pt/Al2O3 and Ru/Al2O3 catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 14130–14140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzón, M.; Avilés-García, O.; Osa, A.R. New catalysts based on reduced graphene oxide for hydrogen production from ammonia decomposition. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 25, 100615–100625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzone, S.; Goklany, T.; Zhang, G. Ruthenium-based catalysts supported on carbon xerogels for hydrogen production via ammonia decomposition. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2022, 632, 118484–118499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.F.; Xu, B.Q.; Wang, S.J.; Ng, C.F.; Au, C.T. Magnesia-Carbon Nanotubes (MgO-CNTs) Nanocomposite: Novel Support of Ru Catalyst for the Generation of COx-Free Hydrogen from Ammonia. Catal. Lett. 2004, 96, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, T.V.; Sivadinarayana, C.; Goodman, D.W. Catalytic ammonia decomposition: COX-free hydrogen production for fuel cell applications. Catal. Lett. 2001, 72, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Wu, S.; Ayvali, T.; Zheng, J.; Fellowes, J.; Ho, P.-L.; Leung, K.C.; Large, A.; Held, G.; Kato, R.; et al. Dispersed surface Ru ensembles on MgO(111) for catalytic ammonia decomposition. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.F.; Zhang, Q.H.; Xu, B.Q.; Zhu, W.X.; Ng, C.F.; Zhou, X.P.; Au, C.T. Carbon nanotubes-supported Ru catalyst for the generationof COx-free hydrogen from ammonia. Catal. Today 2004, 93, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Liu, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; He, T.; Chen, P. Strong metal-support interaction modulatescatalytic activity of Ru nanoparticles on Gd2O3 forefficient ammonia decomposition. iScience 2024, 27, 110931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, H.; Wang, L.; Li, T.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.Q. Promotion of Low-Temperature Catalytic Activity of Ru-Based Catalysts for Ammonia Decomposition via Lanthanum and Cesium Codoping. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 5620–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, Y.; Muroyama, H.; Matsui, T.; Eguchi, K. Investigation on catalytic performance and desorption behaviors of ruthenium catalysts supported on rare-earth oxides for NH3 decomposition. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 32543–32551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, T.; Kuribara, H.; Kimura, K.; Sato, T.; Itoh, N. Development of a Cs-Ru/CeO2 Spherical Catalyst Prepared by Impregnation and Washing Processes for Low-Temperature Decomposition of NH3: Characterization and Kinetic Analysis Results. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 18460–18470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yu, Y.; Tang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ye, C.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, R. Hydrogen generation by ammonia decomposition over Co/CeO2 catalyst: Influence of support morphologies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 532, 147335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucentini, I.; Serrano, I.; Soler, L.; Divins, N.J.; Llorca, J. Ammonia decomposition over 3D-printed CeO2 structures loaded with Ni. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 591, 117382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Liu, L.; Yu, P.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; He, T.; Wu, G.; Chen, P. Mesoporous Ru/MgO prepared by a deposition-precipitation method as highly active catalyst for producing COx-free hydrogen from ammonia decomposition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 211, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Feng, J.; He, T.; Chen, P. Highly Efficient Ru/MgO Catalyst with Surface-Enriched Basic Sites for Production of Hydrogen from Ammonia Decomposition. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 4161–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroyama, H.; Saburi, C.; Matsui, T.; Eguchi, K. Ammonia decomposition over Ni/La2O3 catalyst for on-site generation of hydrogen. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 443–444, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Long, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W. One-pot synthesis of supported Ni@Al2O3 catalysts with uniform small-sized Ni for hydrogen generation via ammonia decomposition. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 4045–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.E.; Ménard, H.; González Carballo, J.M.; Tooze, R.; Torrente-Murciano, L. Hydrogen production from ammonia decomposition using Co/γ-Al2O3 catalysts—Insights into the effect of synthetic method. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 27210–27220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Fu, X.P.; Wang, W.W.; Jin, Z.; Song, Q.S.; Jia, C.J. Promoted porous Co3O4-Al2O3 catalysts for ammonia decomposition. Sci. China Chem. 2018, 61, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.F.; Zhang, Q.H.; Xu, B.Q.; Zhu, W.X.; Ng, C.F.; Au, C.T. Investigation on the catalysis of COx-free hydrogen generation from ammonia. J. Catal. 2004, 224, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzut, B.; Montini, T.; Pavel, C.C.; Comotti, M.; Vizza, F.; Bianchini, C.; Fornasiero, P. Embedded Ru@ZrO2 Catalysts for H2 Production by Ammonia Decomposition. ChemCatChem 2010, 2, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thien, A.L.; Youngmin, K.; Hyun, W.K. Ru-supported lanthania-ceria composite as an efficient catalyst for COx-free H2 production from ammonia decomposition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 285, 119831. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.-C.; Fu, X.-P.; Wang, W.-W.; Wang, X.; Wu, K.; Si, R.; Ma, C.; Jia, C.-J.; Yan, C.-H. Ceria-supported ruthenium clusters transforming from isolated single atoms for hydrogen production via decomposition of ammonia-ScienceDirect. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 268, 118424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouiki, A.; Fatimah, S.; Chafiq, M.; Ryu, J.; Ko, Y.G. State-of-the-art advancements in metal-organic framework nanoarchitectures for catalytic applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 38, 102224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, I.E.; Fonseca, J.; Reithofer, M.R. Tackling orientation of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): The quest to enhance MOF performance. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2023, 481, 21503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivan, S.E.; Kang, K.H.; Han, S.J. Facile MOF-derived one-pot synthetic approach toward Ru single atoms, nanoclusters, and nanoparticles dispersed on CeO2 supports for enhanced ammonia synthesis. J. Catal. 2022, 408, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zheng, X.; Mao, D.; Meng, T.; Mao, H.; Yu, J. Promoting catalytic CO2 methanation using Ru catalyst supported on Ce-MOF-derived CeO2. Renew. Energy 2025, 245, 122834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, E.; Cai, S.; Jia, H.; Chen, J.; Liang, P. In situ pyrolysis of Ce-MOF to prepare CeO2 catalyst with obviously improved catalytic performance for toluene combustion. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 344, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.E.; Khan, M.M.; Cho, M.H. Ce3+-ion, Surface Oxygen Vacancy, and Visible Light-induced Photocatalytic Dye Degradation and Photocapacitive Performance of CeO2-Graphene Nanostructures. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Cullen, D.A. Distribution and Valence State of Ru Species on CeO2 Supports: Support Shape Effect and Its Influence on CO Oxidation. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 11088–11103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zheng, C.; Liu, W.; Wu, X.; Liu, S. Oxidative Redispersion-Derived Single-Site Ru/CeO2 Catalysts with Mobile Ru Complexes Trapped by Surface Hydroxyls Instead of Oxygen Vacancies. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 6028–6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, H. Precision tailoring strategy of oxygen vacancies for electromagnetic pollution regulation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 681, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.Y.; Lu, J.Q.; Luo, M.F. Study of oxygen vacancies in Ce0.9Pr0.1O2-δ solid solution by in situ X-ray diffraction and in situ Raman spectro-scopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 18695–18702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; He, S.; Chen, H. Active site dependent reaction mechanism over Ru/CeO2 catalyst toward CO2 methanation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6298–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, C.J.; Lee, D.W.; Kim, M.S. The synthesis of methanol from CO/CO2/H2 gas over Cu/Ce1-xZrxO2 catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2013, 378, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakpal, T.L.L. Structure-dependent activity of CeO2 supported Ru catalysts for CO2 methanation. J. Catal. 2018, 367, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, K.; Peng, B. Ceria-Based Materials for Thermocatalytic and Photocatalytic Organic Synthesis. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 9618–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Brosnahan, J.T. Ru/CeO2 Catalyst with Optimized CeO2 Support Morphology and Surface Facet for Propane Combustion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5349–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Dai, Q.; Wang, X. Morphology effect of Ru/CeO2 catalysts for the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 158–159, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, X.; Meng, D. Effect of Ceria Crystal Plane on the Physicochemical and Catalytic Properties of Pd/Ceria for CO and Propane Oxidation. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2265–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.A.; Kim, Y.; Han, S.J.; Do, Q.C.; Kim, G.J.; Im, Y.; Chae, H.-J. Ru dispersed on CeO2{100} facets boosting the catalytic NH3 decomposition for green H2 generation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y. Capping experiments reveal multiple surface activesites in CeO2 and their cooperative catalysis. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 15229–15237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Huang, L.; Liu, X. Mixed-Valence Ce-BPyDC Metal-Organic Framework with Dual Enzyme-like Activities for Colorimetric Biosensing. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 11382–11388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöchl, P.E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 17953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montini, T.; Melchionna, M.; Monai, M. Fundamentals and Catalytic Applications of CeO2-Based Materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5987–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ji, W.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Au, C. Ammonia decomposition over Ru and Ni catalysts supported on fumed SiO2, MCM-41, and SBA-15. J. Catal. 2005, 236, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qu, Y.; Shen, X.; Cai, Z. Ruthenium catalyst supported on Ba modified ZrO2 for ammonia decomposition to COx-free hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 7300–7307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Liu, L.; Ju, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; He, T. Highly dispersed ruthenium nanoparticles on Y2O3 as superior catalyst for ammonia decomposition. ChemCatChem 2021, 13, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, N.; Kim, S.; Tayal, A.; Oh, J.; Yoon, W.; Kim, W.B. Y-doped BaCeO3 perovskite-supported Ru catalysts for COx-free hydrogen production from ammonia: Effect of strong metal–support interactions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 15564–15573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, L.; Song, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, J.; Ji, W.; Au, C.T. Core-Shell Structured Microcapsular-like Ru@SiO2 Reactor for Efficient Generation of COx-Free Hydrogen through Ammonia Decomposition. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 5298–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Wei, Z. Highly active ruthenium catalyst supported on barium hexaaluminate for ammonia decomposition to COx-free hydrogen. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 8226–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Liu, H.; Xu, K.; Wang, W.; Jia, C. CeO2 modified Ru/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for ammonia decomposition reaction. J. Rare Earths 2023, 41, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.P.; Zhu, Z. Catalytic ammonia decomposition for CO-free hydrogen generation over Ru/Cr2O3 catalysts. Appl. Catal. A 2013, 467, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucentini, I.; Casanovas, A.; Llorca, J. Catalytic ammonia decomposition for hydrogen production on Ni, Ru and NiRu supported on CeO2. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 12693–12707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucentini, I.; Colli, G.G.; Luzi, C.D.; Serrano, I.; Martínez, O.M.; Llorca, J. Catalytic ammonia decomposition over Ni-Ru supported on CeO2 for hydrogen production: Effect of metal loading and kinetic analysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 286, 119896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Cha, J.; Kim, J.S.; Ahn, C.; Kim, Y.; Jeong, H. Hydrogen production from ammonia decomposition over Ru-rich surface on La2O2CO3-Al2O3 catalyst beads. Catal. Today 2023, 411, 113867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yu, Y.; Yang, J.; Yan, Y.; Wang, D.; Hu, F. Ru/La2O3 catalyst for ammonia decomposition to hydrogen. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 476, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Xu, B.; Ng, C.; Au, C. Nano Ru/CNTs: A highly active and stable catalyst for the generation of COx-free hydrogen in ammonia decomposition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2004, 48, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.B.; Kim, H.Y.; Jeon, M.; Lee, D.H.; Park, H.S.; Choi, S.H. Enhanced ammonia dehydrogenation over Ru/LaxAl2O3 (x = 0-50 mol%): Structural and electronic effects of La doping. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Mahin, J.; Datta, S.; Bell, T.E.; Torrente-Murciano, L. Ru-based catalysts for H2 production from ammonia: Effect of 1D support. Top. Catal. 2019, 62, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, Z.H.; Yan, Z.F.; Lu, G.Q.; Rintoul, L. Catalytic ammonia decomposition over Ru/carbon catalysts: The importance of the structure of carbon support. Appl. Catal. A 2007, 320, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocer, T.; Oztuna, F.E.S.; Kurtoğlu, S.F.; Unal, U.; Uzun, A. Graphene aerogel-supported ruthenium nanoparticles for COx-free hydrogen production from ammonia. Appl. Catal. A 2021, 610, 117969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| T °C | 375 | 400 | 425 | 450 | 475 | 500 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH3 Conv./% a | |||||||
| Ru/CeO2-C | 7.87 | 16.86 | 33.47 | 52.66 | 73.75 | 85.16 | |
| Ru/CeO2-0 h | 23.41 | 45.26 | 64.44 | 78.95 | 91.88 | 95.95 | |
| Ru/CeO2-0.5 h | 30.24 | 55.79 | 73.53 | 86.24 | 92.95 | 96.99 | |
| Ru/CeO2-1 h | 34.92 | 57.94 | 75.56 | 87.79 | 95.7 | 97.72 | |
| Ru/CeO2-1.5 h | 38.85 | 61.37 | 78.57 | 89.77 | 97.11 | 99.01 | |
| Ru/CeO2-2 h | 37.98 | 58.97 | 76 | 87.84 | 96.63 | 98.13 | |
| Ru/CeO2-3 h | 42.86 | 64.91 | 81.04 | 92.19 | 98.22 | 99.90 | |
| Ru/CeO2-4 h | 43.58 | 65.10 | 81.74 | 92.39 | 98.38 | 100.00 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.; Yao, W.; Liu, Y.; Xi, S.; Zhang, T. Efficient Hydrogen Production from Ammonia Using Ru Nanoparticles on Ce-Based Metal–Organic Framework (MOF)-Derived CeO2 with Oxygen Vacancies. Molecules 2025, 30, 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112301
Wu W, Yao W, Liu Y, Xi S, Zhang T. Efficient Hydrogen Production from Ammonia Using Ru Nanoparticles on Ce-Based Metal–Organic Framework (MOF)-Derived CeO2 with Oxygen Vacancies. Molecules. 2025; 30(11):2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112301
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wenying, Wenhao Yao, Yitong Liu, Senliang Xi, and Teng Zhang. 2025. "Efficient Hydrogen Production from Ammonia Using Ru Nanoparticles on Ce-Based Metal–Organic Framework (MOF)-Derived CeO2 with Oxygen Vacancies" Molecules 30, no. 11: 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112301
APA StyleWu, W., Yao, W., Liu, Y., Xi, S., & Zhang, T. (2025). Efficient Hydrogen Production from Ammonia Using Ru Nanoparticles on Ce-Based Metal–Organic Framework (MOF)-Derived CeO2 with Oxygen Vacancies. Molecules, 30(11), 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112301







