Novel Magnetically Recoverable Amino-Functionalized MIL-101(Fe) Composite with Enhanced Adsorption Capacity for Pb(II) and Cd(II) Ions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
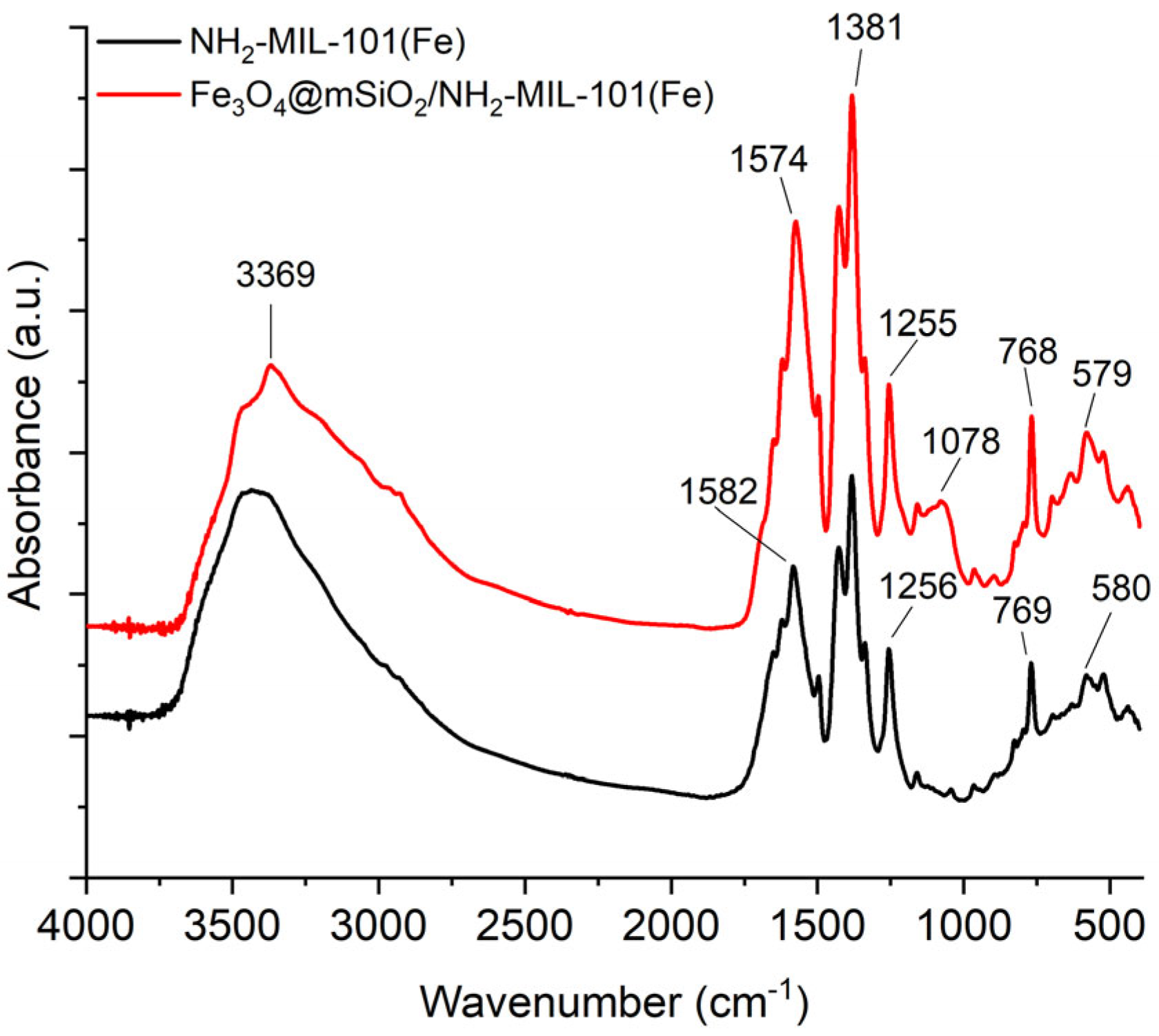
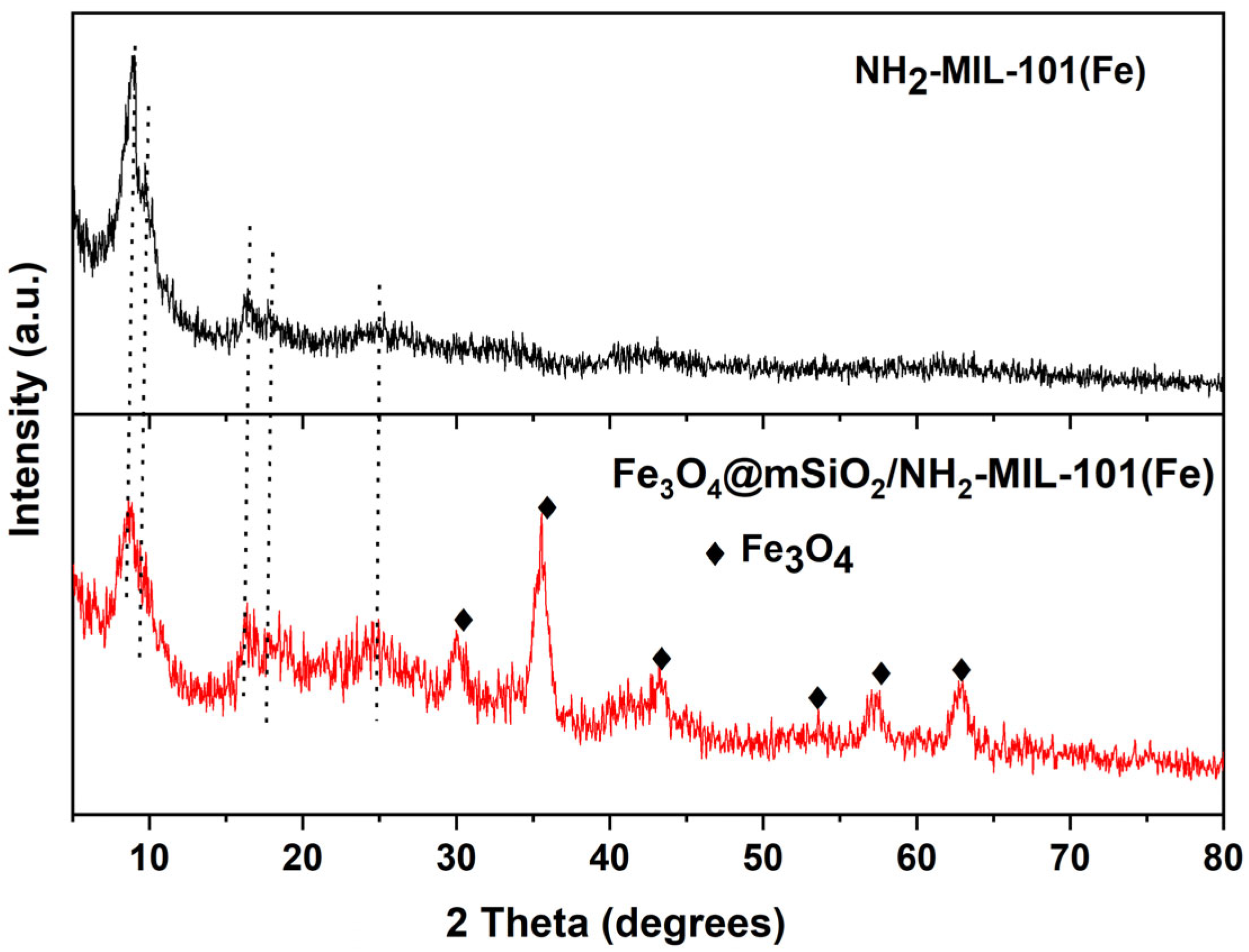
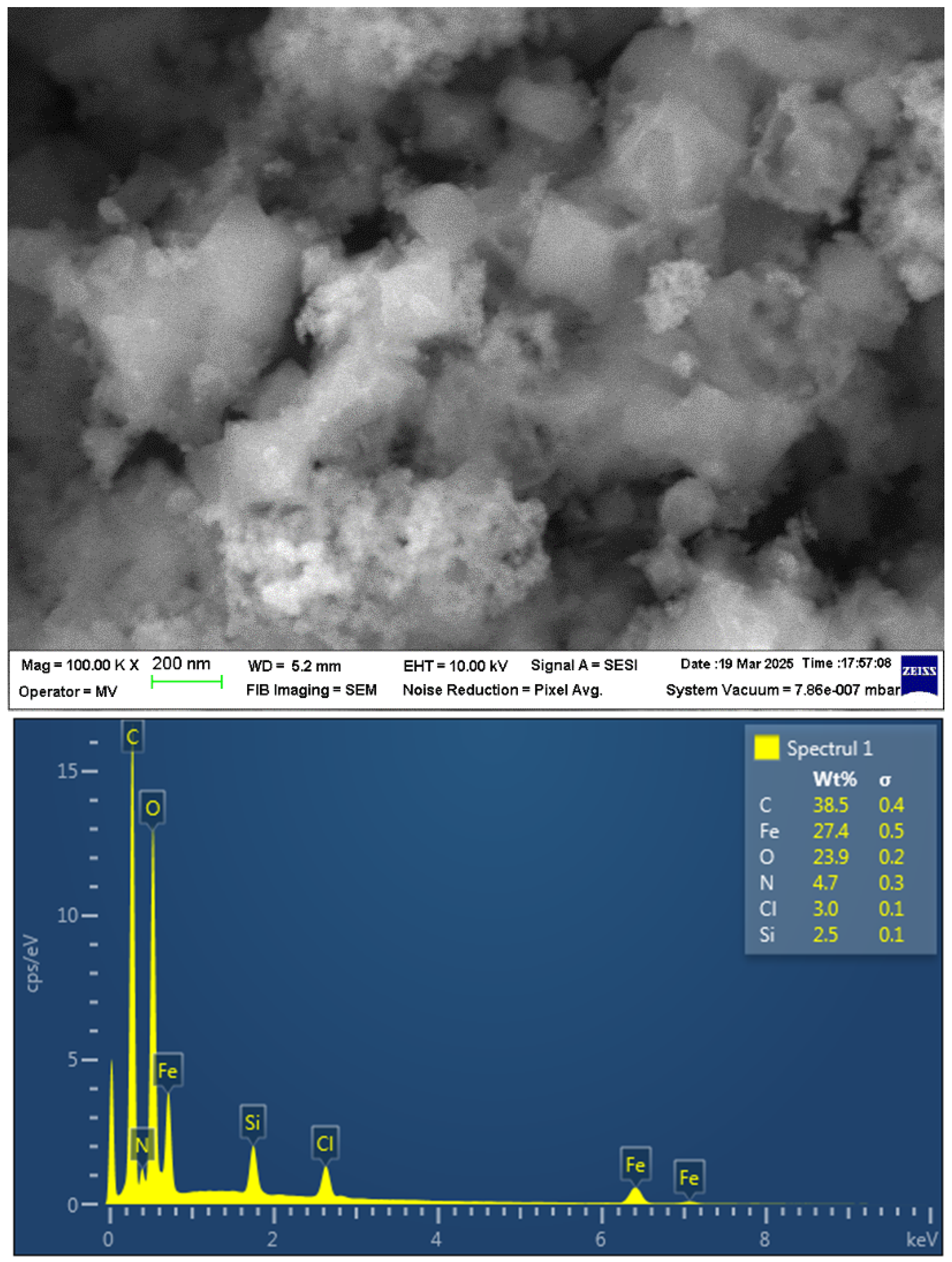
2.1. Characterization of the Materials
2.2. Adsorption Studies
2.2.1. Effect of pH and Adsorption Mechanism
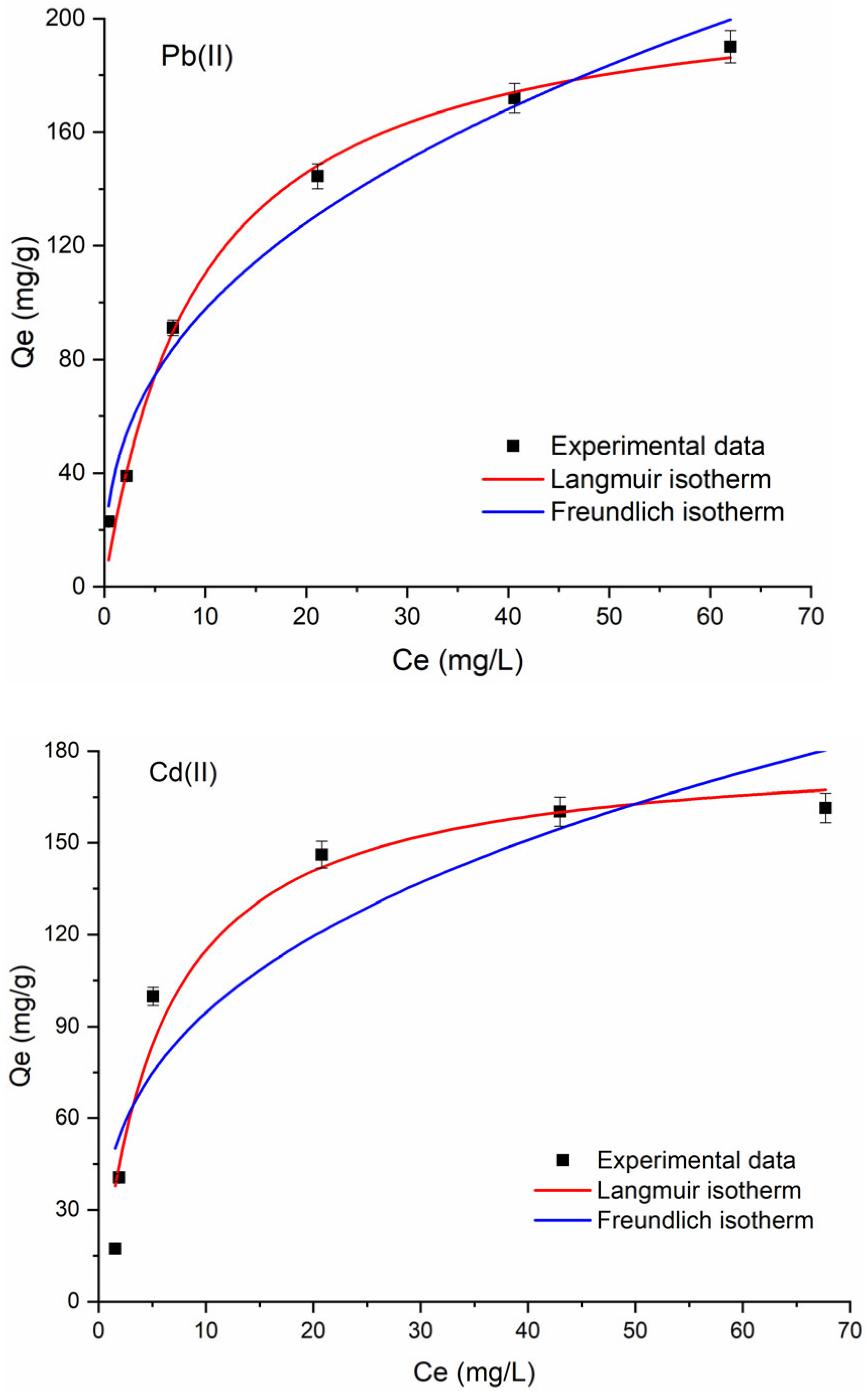
2.2.2. Equilibrium Adsorption Isotherms
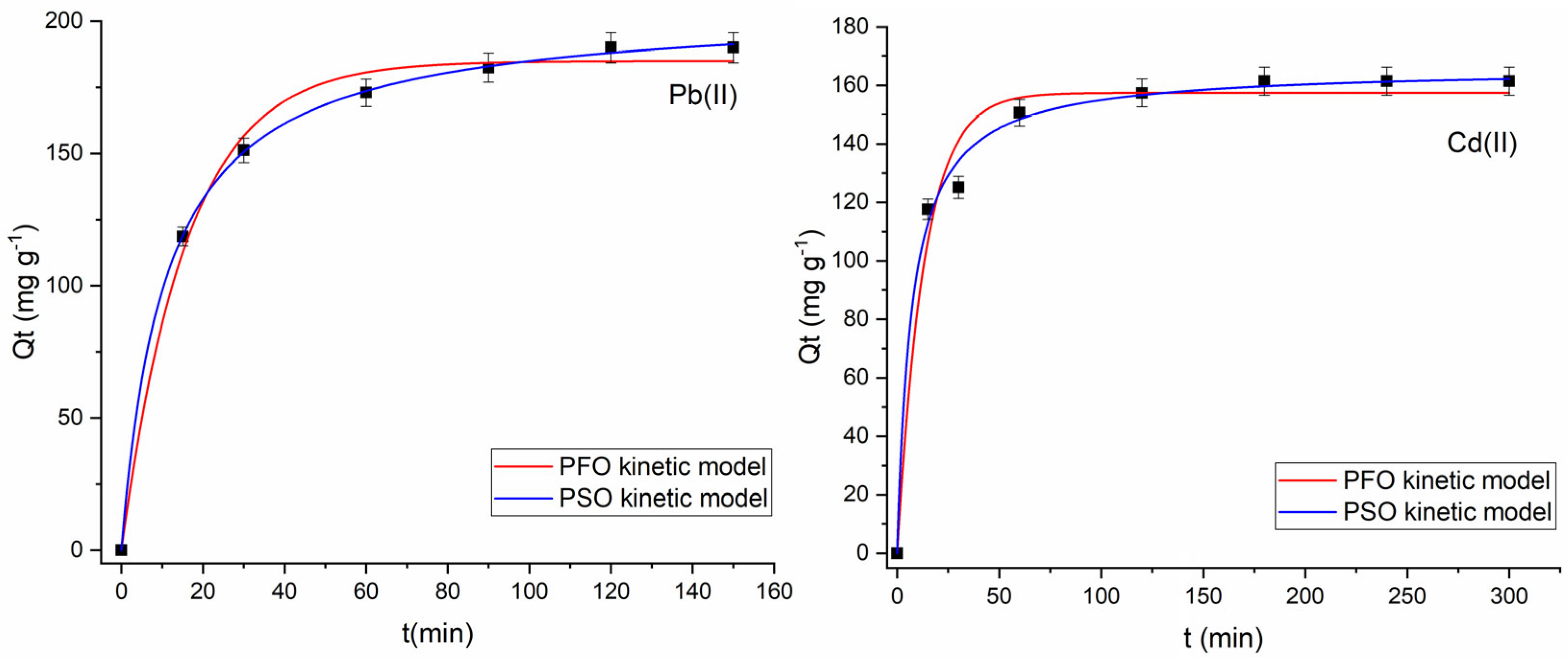
2.2.3. Effect of Contact Time
2.2.4. Kinetic Analysis
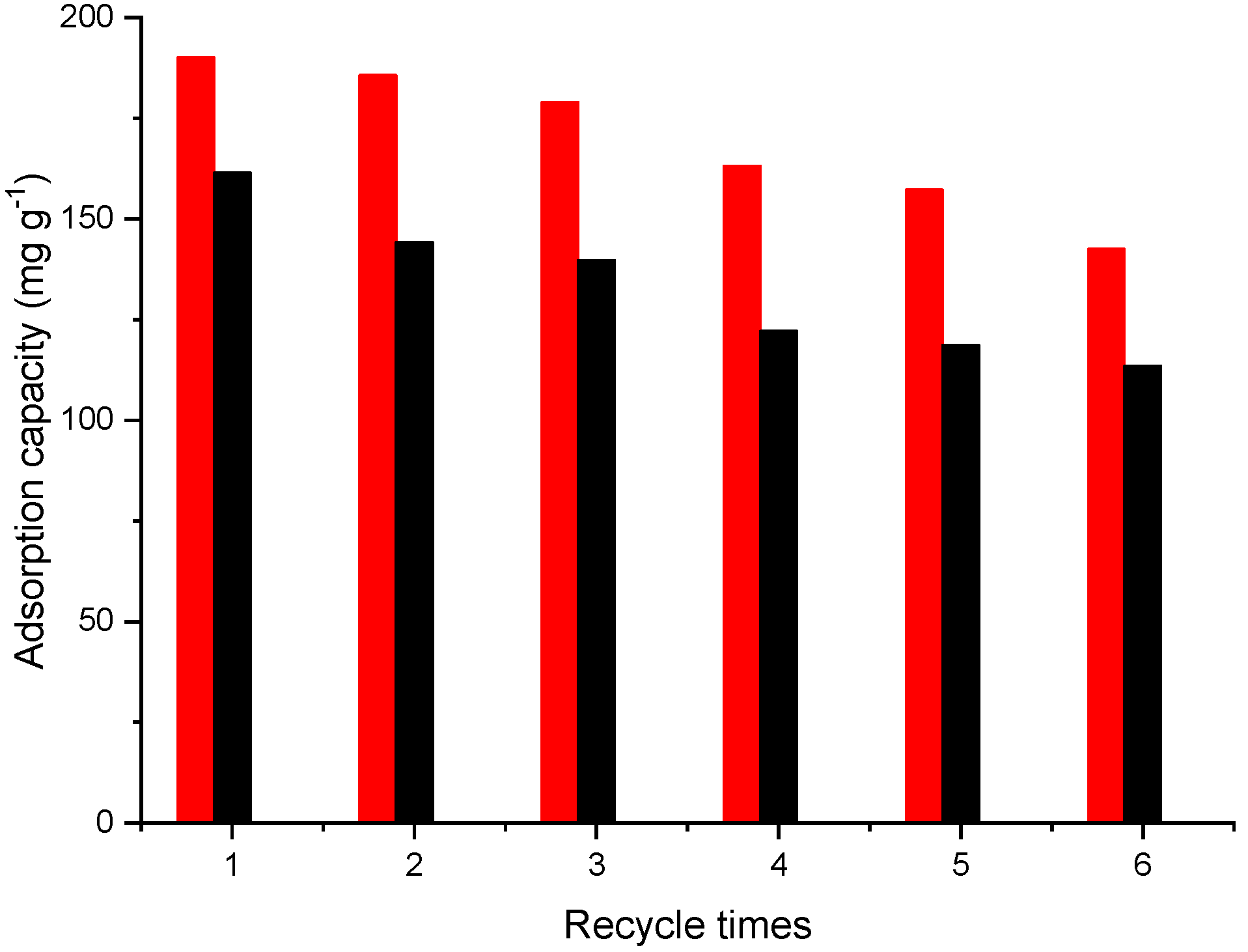
2.2.5. Reusability Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
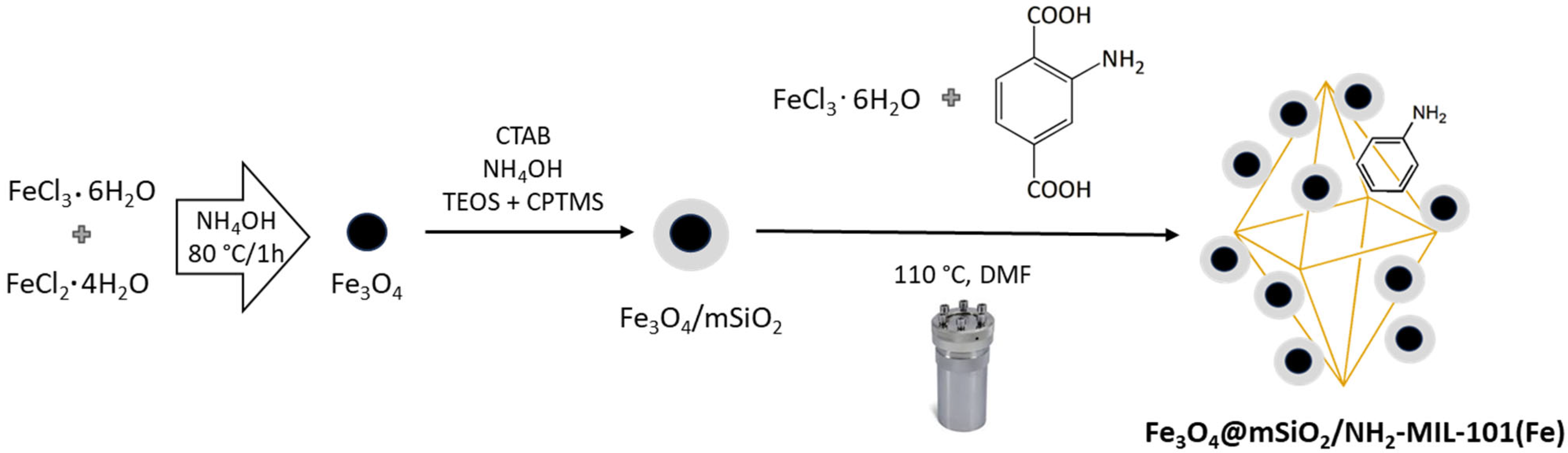
3.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4@mSiO2
3.3. Synthesis of Fe3O4@mSiO2/NH2-MIL-101(Fe)
3.4. Characterization Methods
3.5. Adsorption and Desorption Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Chen, C. Biosorbents for Heavy Metals Removal and Their Future. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 195–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy Metal Pollution in the Environment and Their Toxicological Effects on Humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, S. Low-Cost Adsorbents for Heavy Metals Uptake from Contaminated Water: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, M.A. New Trends in Removing Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater. Arabian J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T.; Moheb, A.; Sadrzadeh, M.; Razmi, A. Modeling of Metal Ion Removal from Wastewater by Electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 41, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, A. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water and Wastewaters by Sulfur-Containing Precipitation Agents. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbych, S.; Hilal, N.; Sorokin, G.; Leaper, M. Ion Exchange Extraction of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 39, 2031–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qodah, Z.; Al-Shannag, M. Heavy Metal Ions Removal from Wastewater Using Electrocoagulation Processes: A Comprehensive Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 52, 2649–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, R.K.; Agrawal, K.; Shah, M.P.; Verma, P. Bioremediation of Heavy Metals from Wastewater: A Current Perspective on Microalgae-Based Future. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 75, 701–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Sajad, M.A. Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals—Concepts and Applications. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Matis, K.A. Nanoadsorbents for Pollutants Removal: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 203, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culita, D.C.; Simonescu, C.M.; Patescu, R.E.; Preda, S.; Stanica, N.; Munteanu, C.; Oprea, O. Polyamine Functionalized Magnetite Nanoparticles as Novel Adsorbents for Cu(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2017, 27, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowsell, J.L.C.; Yaghi, O.M. Metal–Organic Frameworks: A New Class of Porous Materials. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2004, 73, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.; Ansari, M.Z.; Hakeem Anwer, A.; Kim, S.-H.; Nasar, A.; Shoeb, M.; Mashkoor, F. A Review on Metal-Organic Frameworks for the Removal of Hazardous Environmental Contaminants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 305, 122416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefayathullah, M.; Singh, S.; Ganesan, V.; Maduraiveeran, G. Metal-Organic Frameworks for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 331, 103210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatou, M.-A.; Vagena, I.-A.; Lagopati, N.; Pippa, N.; Gazouli, M.; Pavlatou, E.A. Functional MOF-Based Materials for Environmental and Biomedical Applications: A Critical Review. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yao, J. Tailoring the Structure and Function of Metal Organic Framework by Chemical Etching for Diverse Applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 470, 214699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, H.; Zhu, J.; Duan, L.; Ding, Y.; Liang, F.; Li, Y.; Peng, X.; Jiang, R.; Yu, J.; et al. A Fluorine-Functionalized Tb(III)–Organic Framework for Ba2+ Detection. Molecules 2024, 29, 5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Chen, C.; Chen, M.; Zhu, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L. A Hydrostable Cadmium–Organic Framework for Highly Selective and Sensitive Luminescence Sensing of Al3+ Ion. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2019, 29, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Jhung, S.H. Composites of Metal–Organic Frameworks: Preparation and Application in Adsorption. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andani, A.M.; Tabatabaie, T.; Farhadi, S.; Ramavandi, B. MIL-101(Cr)–Cobalt Ferrite Magnetic Nanocomposite: Synthesis, Characterization and Applications for the Sonocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dye Pollutants. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 32845–32855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.-L.; Ma, X.; Fang, Y.-L. Preparation of Magnetic Amine Functionalized MIL-101(Fe) Composites and Their Adsorption Properties. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2025, 35, 2721–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Ding, W.-Q.; Liu, P.; Xu, L.; Fu, M.-L.; Yuan, B. Magnetic Fe3O4/MIL-101 Composite as a Robust Adsorbent for Removal of p-Arsanilic Acid and Roxarsenic in the Aqueous Solution. Colloids Surfaces A 2023, 662, 131014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geranmayeh, S.; Mastali, S.; Mohammadnejad, M. Functionalized Iron Oxide/MOF Nanocomposite Exhibiting Excellent Performance for Methylene Blue Adsorption. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 162, 112222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maan, O.; Song, P.; Chen, N.; Lu, Q. An In Situ Procedure for the Preparation of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 Polyacrylamide Hydrogel for Adsorption of Aqueous Pollutants. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1801895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Jiang, L.; Yang, J.; Hu, T.; Shan, S.; Su, H.; Wu, F. MOF/Hydrogel Composite-Based Adsorbents for Water Treatment: A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 50, 103348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.D.; Tran, H.-V.; Xu, S.; Lee, T.R. Fe3O4 Nanoparticles: Structures, Synthesis, Magnetic Properties, Surface Functionalization, and Emerging Applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, G.; Gao, M.; Huang, X.; Xu, D. Recent Advances and Applications of Magnetic Metal-Organic Frameworks in Adsorption and Enrichment Removal of Food and Environmental Pollutants. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 50, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Jiao, Z.; Yao, W. A Simple Solvothermal Process for Fabrication of a Metal-Organic Framework with an Iron Oxide Enclosure for the Determination of Organophosphorus Pesticides in Biological Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1371, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghian, S.; Pourfakhar, H.; Baghdadi, M.; Aminzadeh, B. Application of Sand Particles Modified with NH2-MIL-101(Fe) as an Efficient Visible-Light Photocatalyst for Cr(VI) Reduction. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 129365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xie, Y.; Cui, K.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y. Adsorption Behavior and Adsorption Mechanism of Glyphosate in Water by Amino-MIL-101(Fe). J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2022, 161, 110403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi, M.M.; Movahedi, F. Fe3O4/MIL-101(Fe) Nanocomposite as an Efficient and Recyclable Catalyst for Strecker Reaction. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboori, A. A Nanoparticle Sorbent Composed of MIL-101(Fe) and Dithiocarbamate-Modified Magnetite Nanoparticles for Speciation of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) Prior to Their Determination by Electrothermal AAS. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enache, D.F.; Vasile, E.; Simonescu, C.M.; Culita, D.; Vasile, E.; Oprea, O.; Pandele, A.M.; Razvan, A.; Dumitru, F.; Nechifor, G. Schiff Base-Functionalized Mesoporous Silicas (MCM-41, HMS) as Pb(II) Adsorbents. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chircov, C.; Ștefan, R.-E.; Dolete, G.; Andrei, A.; Holban, A.M.; Oprea, O.-C.; Vasile, B.S.; Neacșu, I.A.; Tihăuan, B. Dextran-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Loaded with Curcumin for Antimicrobial Therapies. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherasim, O.; Popescu, R.C.; Grumezescu, V.; Mogoșanu, G.D.; Mogoantă, L.; Iordache, F.; Holban, A.M.; Vasile, B.Ș.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Oprea, O.-C.; et al. MAPLE Coatings Embedded with Essential Oil-Conjugated Magnetite for Anti-Biofilm Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.; Chen, G.; Wang, H. Degradation of Orange G Using PMS Triggered by NH2-MIL-101(Fe): An Amino-Functionalized Metal–Organic Framework. Molecules 2024, 29, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Su, R. Preparation of NH2-MIL-101(Fe) Metal Organic Framework and Its Performance in Adsorbing and Removing Tetracycline. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larasati, L.; Dendy, D.; Nugroho, R.A.; Lestari, W.W.; Sukowati, C.; Firdaus, M.; Masykur, A.; Wibowo, F.R. Facile and Rapid One-Pot Electrosynthesis of Curcumin Modified MIL-101(Fe)–NH2 and the Release and Biological Studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2025, 340, 130832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajevardi, A.; Hossaini Sadr, M.; Badiei, A.; Armaghan, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Fe3O4@SiO2@MIL-100(Fe) Nanocomposite: A Nanocarrier for Loading and Release of Celecoxib. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 307, 112996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaiwi, F.A.; Sirkecioglu, A. Amine-Functionalized Metal Organic Frameworks MIL-101(Cr) Adsorbent for Copper and Cadmium Ions in Single and Binary Solution. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 3362–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malash, G.F.; El-Khaiary, M.I. Piecewise Linear Regression: A Statistical Method for the Analysis of Experimental Adsorption Data by the Intraparticle-Diffusion Models. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 163, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh Thanh, H.T.; Thu Phuong, T.T.; Le Hang, P.T.; Tam Toan, T.T.; Tuyen, T.N.; Mau, T.X.; Khieu, D.Q. Comparative Study of Pb(II) Adsorption onto MIL–101 and Fe–MIL–101 from Aqueous Solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4093–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Ding, L.; Luo, J. Adsorptive Removal of Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Samples with Amino-Functionalization of Metal–Organic Frameworks MIL-101(Cr). J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 1732–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Wang, C.-C.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Gao, S. Defective SO3H-MIL-101(Cr) for Capturing Different Cationic Metal Ions: Performances and Mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, X.; Sun, Z.; Meng, H.; Han, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X. Surface Functionalization of MIL-101(Cr) by Aminated Mesoporous Silica and Improved Adsorption Selectivity toward Special Metal Ions. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 5384–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Gu, J.; Yin, N. Efficient Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) Using NH2 -Functionalized Zr-MOFs via Rapid Microwave-Promoted Synthesis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 1880–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.F. Synthesis of Carbon Nano-Onion Embedded Metal–Organic Frameworks as an Efficient Adsorbent for Cadmium Ions: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 24099–24111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roushani, M.; Saedi, Z.; Baghelani, Y.M. Removal of Cadmium Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using TMU-16-NH 2 Metal Organic Framework. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2017, 7, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonescu, C.M.; Tatatrus, A.; Culita, D.C.; Stanica, N.; Butoi, B.; Kuncser, A. Facile Synthesis of Cobalt Ferrite (CoFe2O4) Nanoparticles in the Presence of Sodium Bis (2-Ethyl-Hexyl) Sulfosuccinate and Their Application in Dyes Removal from Single and Binary Aqueous Solutions. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culita, D.C.; Simonescu, C.M.; Patescu, R.-E.; Dragne, M.; Stanica, N.; Oprea, O. O-Vanillin Functionalized Mesoporous Silica–Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Pb(II) from Water. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 238, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

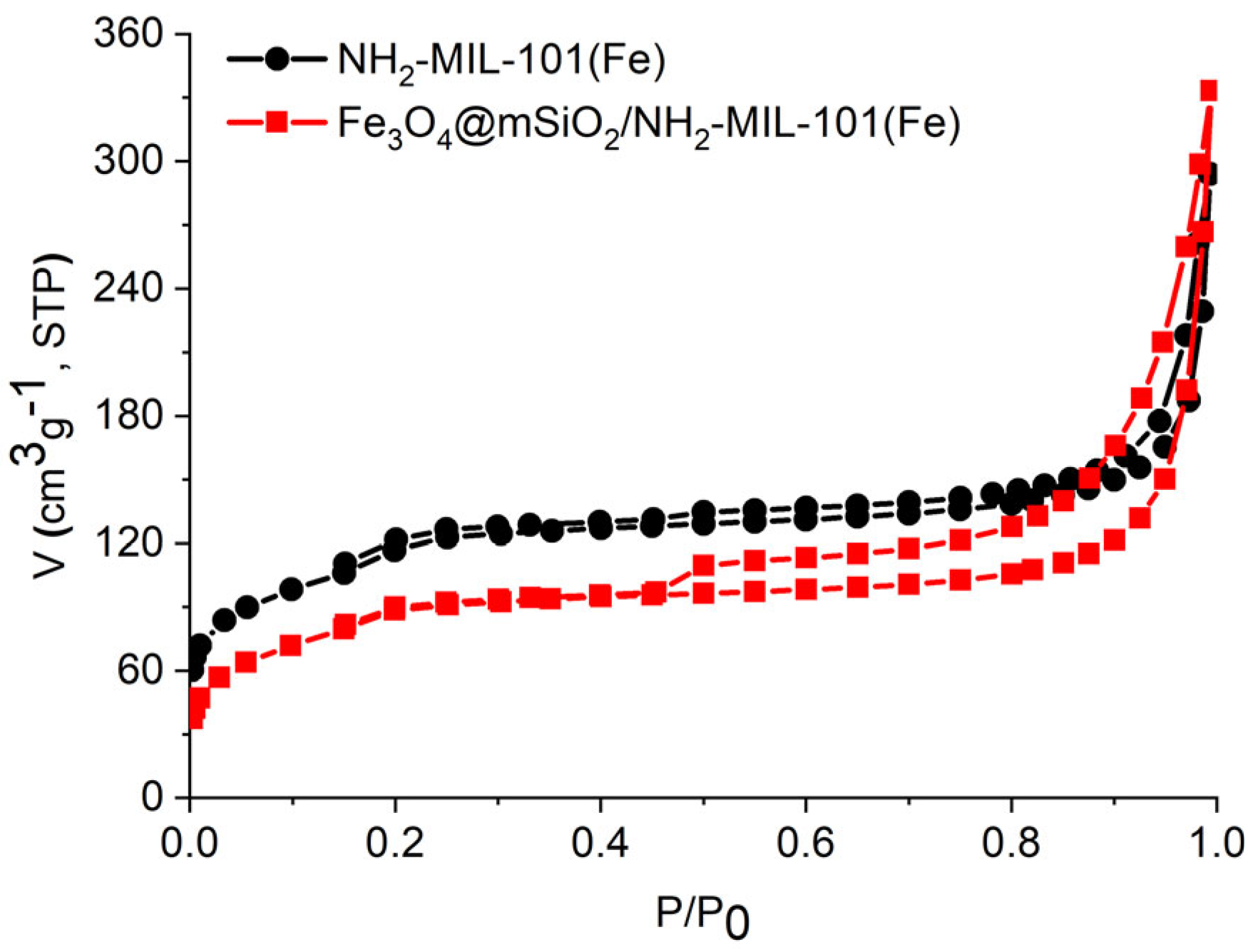
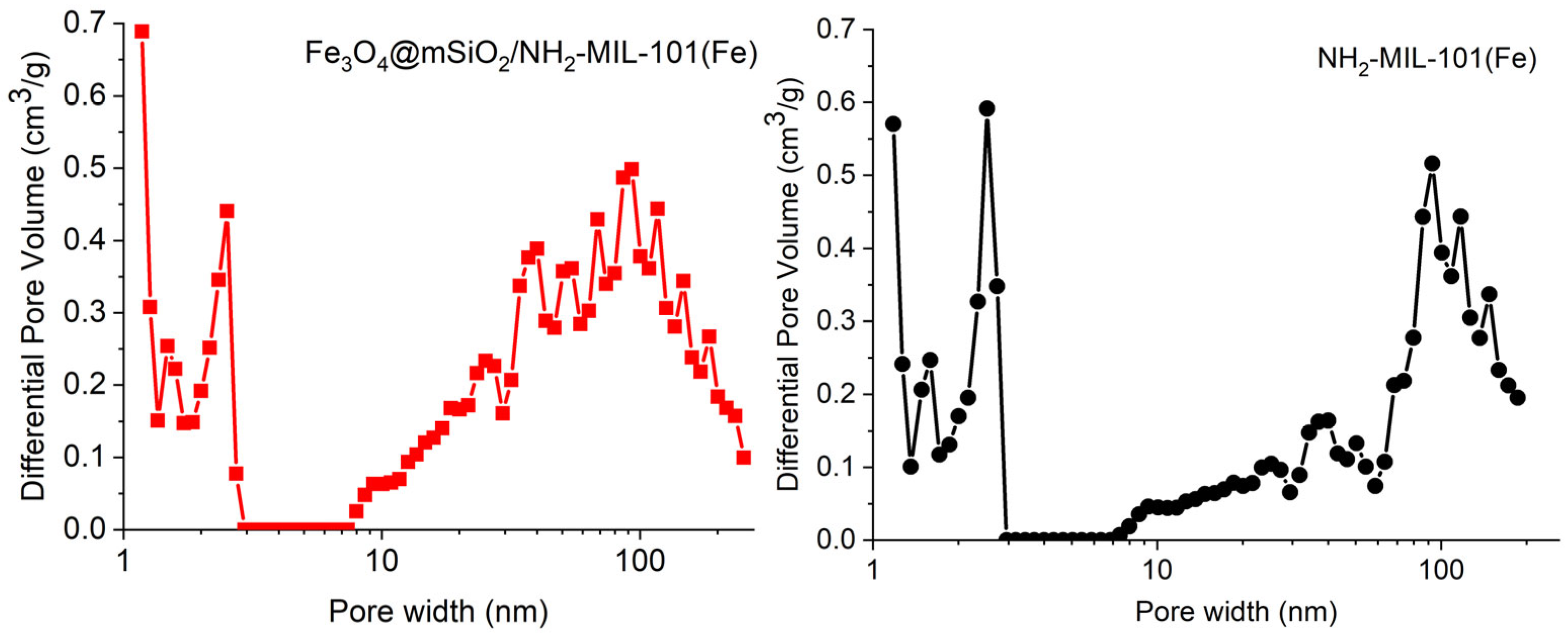
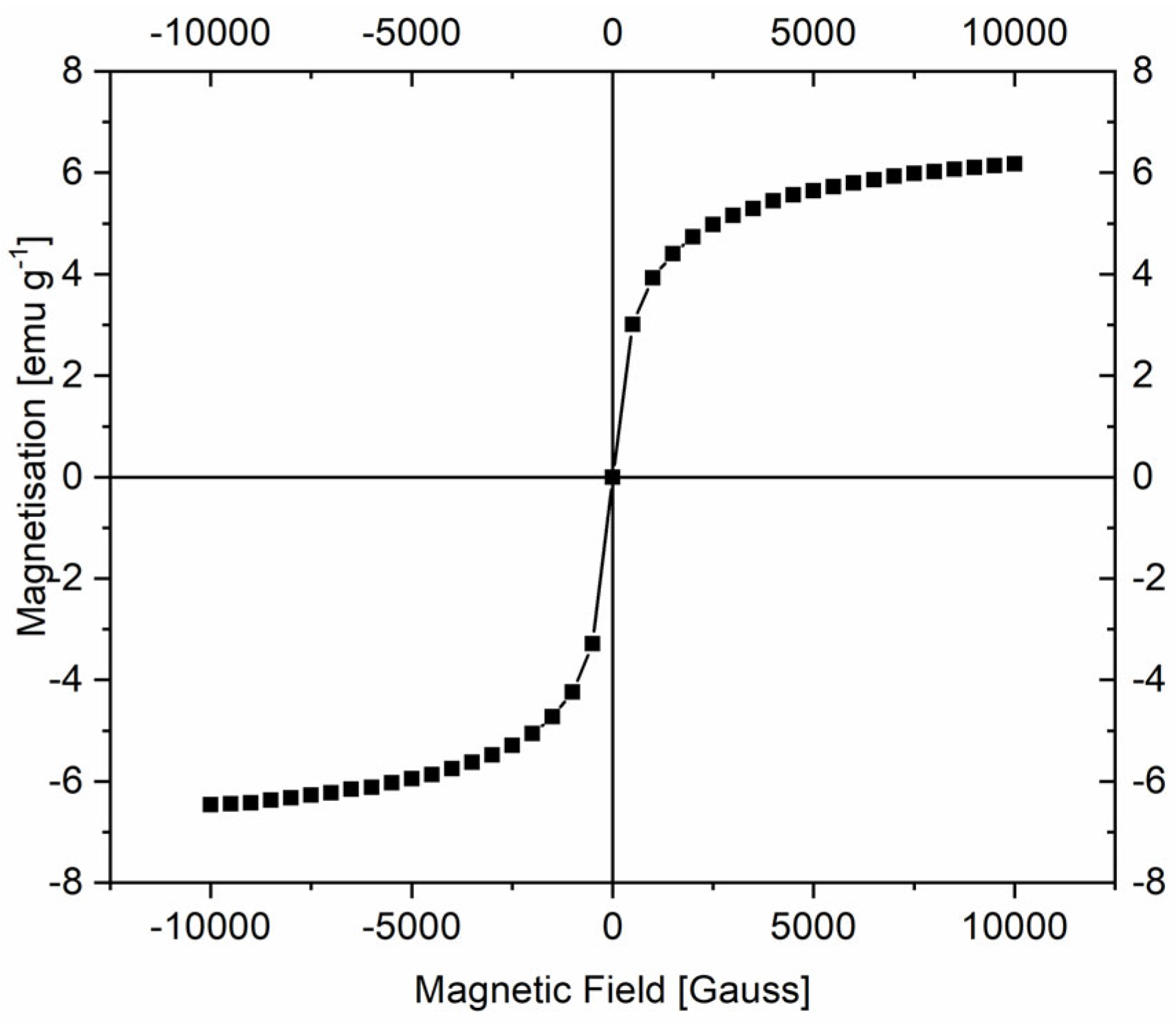
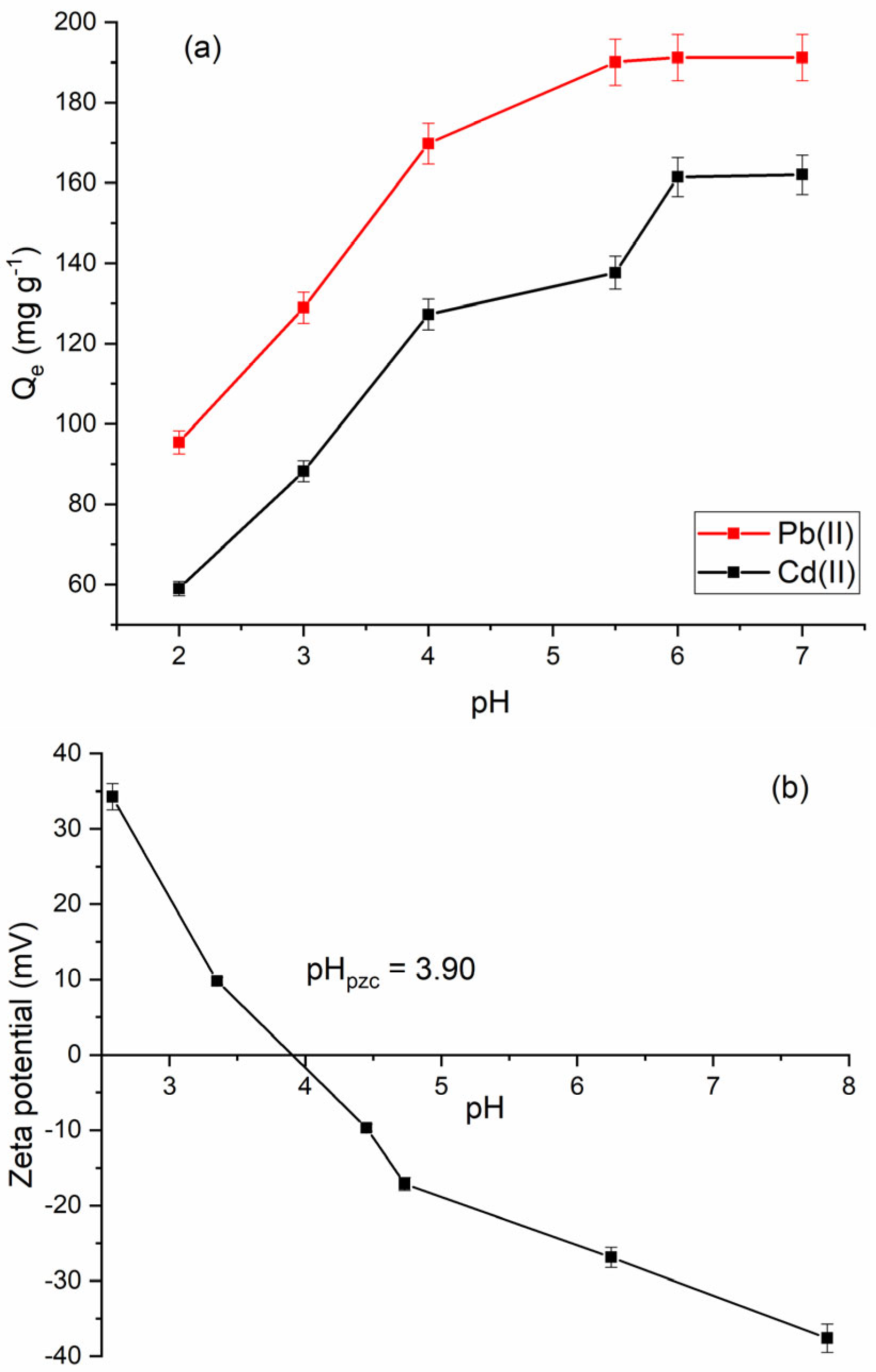

| Sample | SBET (m2/g) | Smicro (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4@mSiO2/NH2-MIL-101(Fe) | 324.4 | 26.7 | 0.515 |
| NH2-MIL-101(Fe) | 418.5 | 33.8 | 0.454 |
| Langmuir Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm (mg g−1) | KL (L mg−1) | R2 | AIC | RL | |
| Pb2+ | 214.6 | 0.1055 | 0.9887 | 39.6358 | 0.0865 |
| Cd2+ | 181.6 | 0.1723 | 0.9541 | 46.7816 | 0.0548 |
| Freundlich Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KF (mg g−1) | 1/n | R2 | AIC | |
| Pb2+ | 50.2054 | 0.3328 | 0.9483 | 45.5727 |
| Cd2+ | 43.4725 | 0.3374 | 0.8175 | 55.0602 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorption Capacity for Pb(II) (mg g−1) | Adsorption Capacity for Cd(II) (mg g−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe–MIL–101 | 86.20 | - | [44] |
| MIL-101 | 57.96 | - | [44] |
| ED-MIL-101(5 mmol) | 81.09 | - | [45] |
| ED-MIL-101(Cr) | 63.15 | [42] | |
| SS-SO3H-MIL-101(Cr)-3 | 183.4 | 98.7 | [46] |
| NH2-mSiO2@MIL-101(Cr) | 161.3 | - | [47] |
| UiO-66-NH2 | 135.0 | - | [48] |
| CMOF-199 | - | 92.4 | [49] |
| TMU-16-NH2 | - | 126.6 | [50] |
| Fe3O4@mSiO2/NH2-MIL-101(Fe) | 214.6 | 181.6 | This work |
| Sample | Pb(II) | Cd(II) |
|---|---|---|
| Qe exp (mg·g−1) | 190.05 | 161.45 |
| Pseudo-first-order model | ||
| Qe cal (mg·g−1) | 185.01 ± 3.19 | 157.46 ± 3.90 |
| k1 (min−1) | 0.0624 ± 0.0050 | 0.0753 ± 0.0106 |
| R2 adjusted | 0.9922 | 0.9753 |
| AIC | 36.76 | 44.20 |
| Pseudo-second-order model | ||
| Qe cal (mg·g−1) | 205.11 ± 0.99 | 165.99 ± 2.62 |
| k2 (10−4 g·mg−1·min−1) | 4.4839 ± 1.3909 | 8.4634 ± 1.1834 |
| R2 adjusted | 0.9997 | 0.9936 |
| AIC | 13.47 | 33.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simonescu, C.M.; Culita, D.C.; Marinescu, G.; Atkinson, I.; Marinescu, V.; Oprea, O.; Stanica, N. Novel Magnetically Recoverable Amino-Functionalized MIL-101(Fe) Composite with Enhanced Adsorption Capacity for Pb(II) and Cd(II) Ions. Molecules 2025, 30, 2879. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132879
Simonescu CM, Culita DC, Marinescu G, Atkinson I, Marinescu V, Oprea O, Stanica N. Novel Magnetically Recoverable Amino-Functionalized MIL-101(Fe) Composite with Enhanced Adsorption Capacity for Pb(II) and Cd(II) Ions. Molecules. 2025; 30(13):2879. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132879
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimonescu, Claudia Maria, Daniela C. Culita, Gabriela Marinescu, Irina Atkinson, Virgil Marinescu, Ovidiu Oprea, and Nicolae Stanica. 2025. "Novel Magnetically Recoverable Amino-Functionalized MIL-101(Fe) Composite with Enhanced Adsorption Capacity for Pb(II) and Cd(II) Ions" Molecules 30, no. 13: 2879. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132879
APA StyleSimonescu, C. M., Culita, D. C., Marinescu, G., Atkinson, I., Marinescu, V., Oprea, O., & Stanica, N. (2025). Novel Magnetically Recoverable Amino-Functionalized MIL-101(Fe) Composite with Enhanced Adsorption Capacity for Pb(II) and Cd(II) Ions. Molecules, 30(13), 2879. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132879








