Diselenide-Bridged Doxorubicin Dimeric Prodrug: Synthesis and Redox-Triggered Drug Release
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
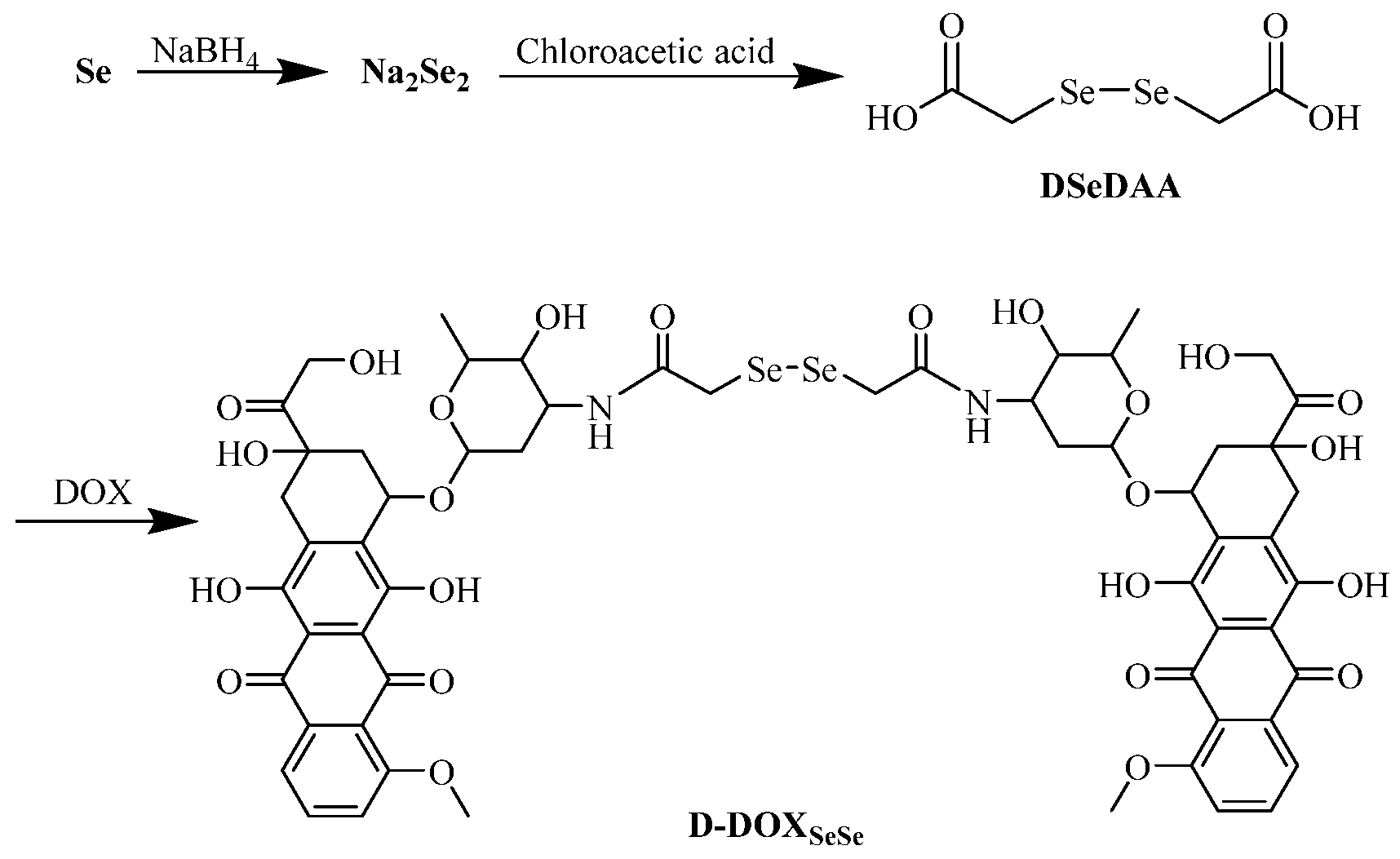
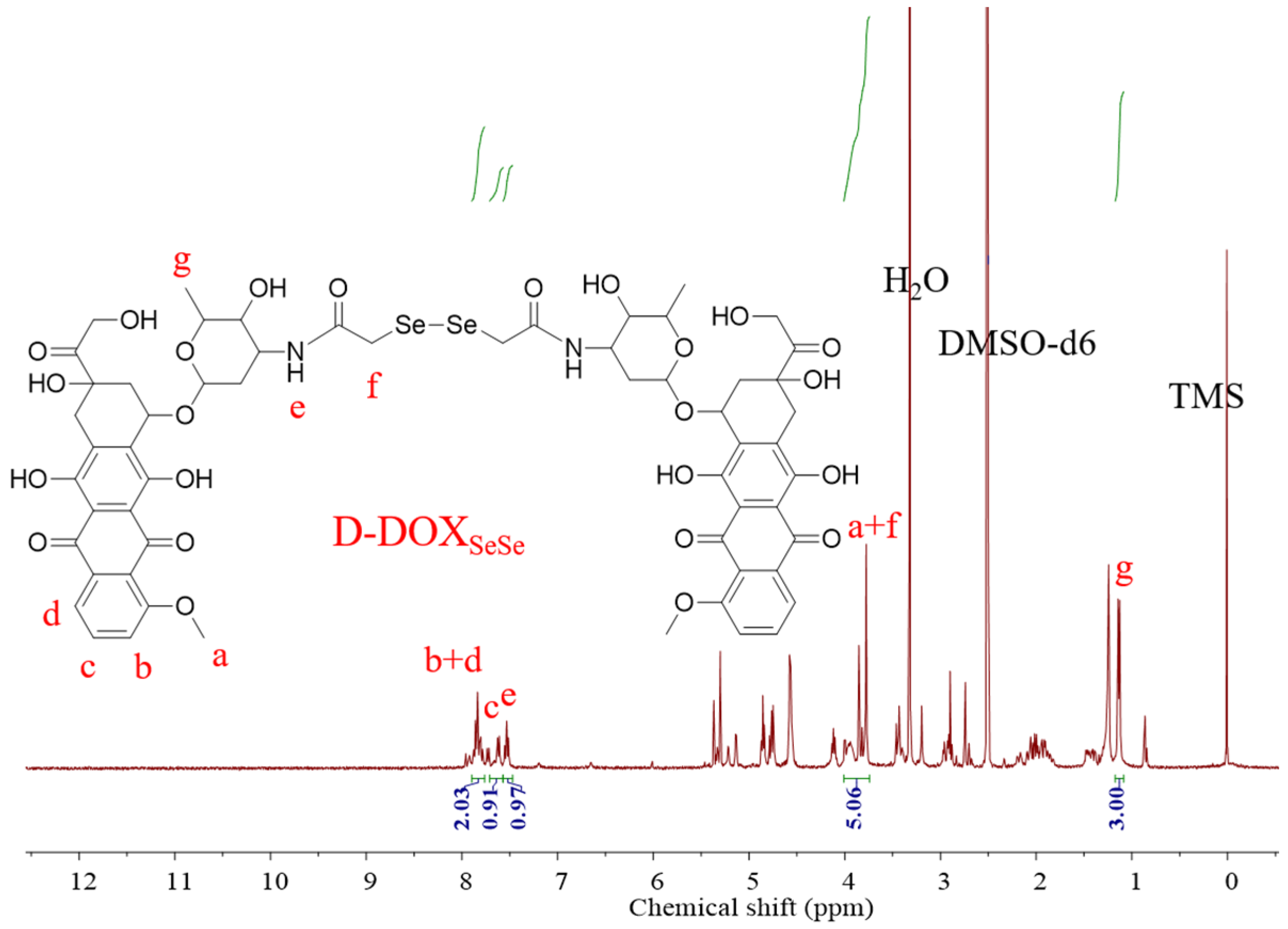
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Diselenide-Bridged Doxorubicin Dimeric Prodrug
2.2. The Fabrication and Characterization of Diselenide-Bridged Dimeric Prodrug Nanoparticles
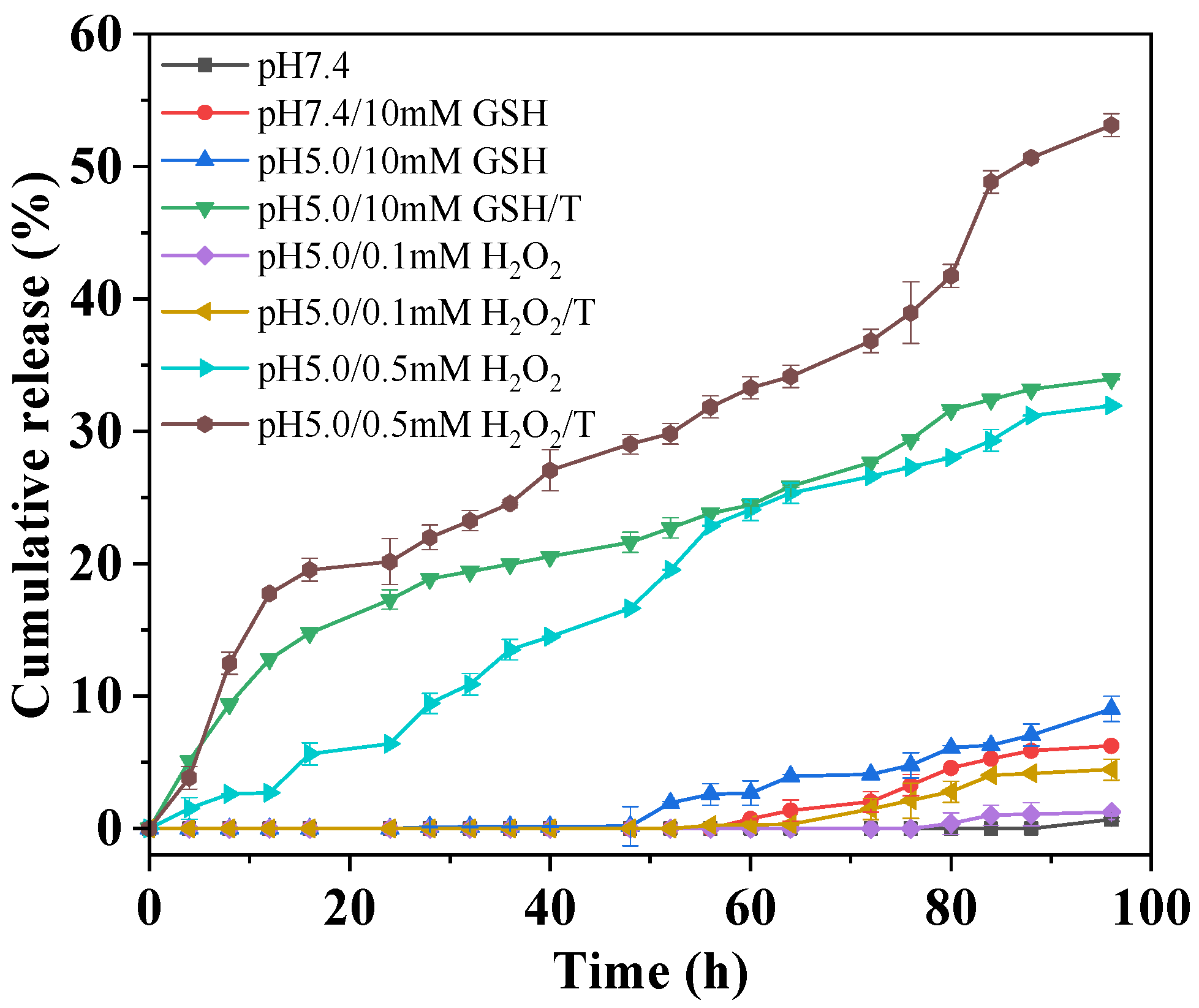
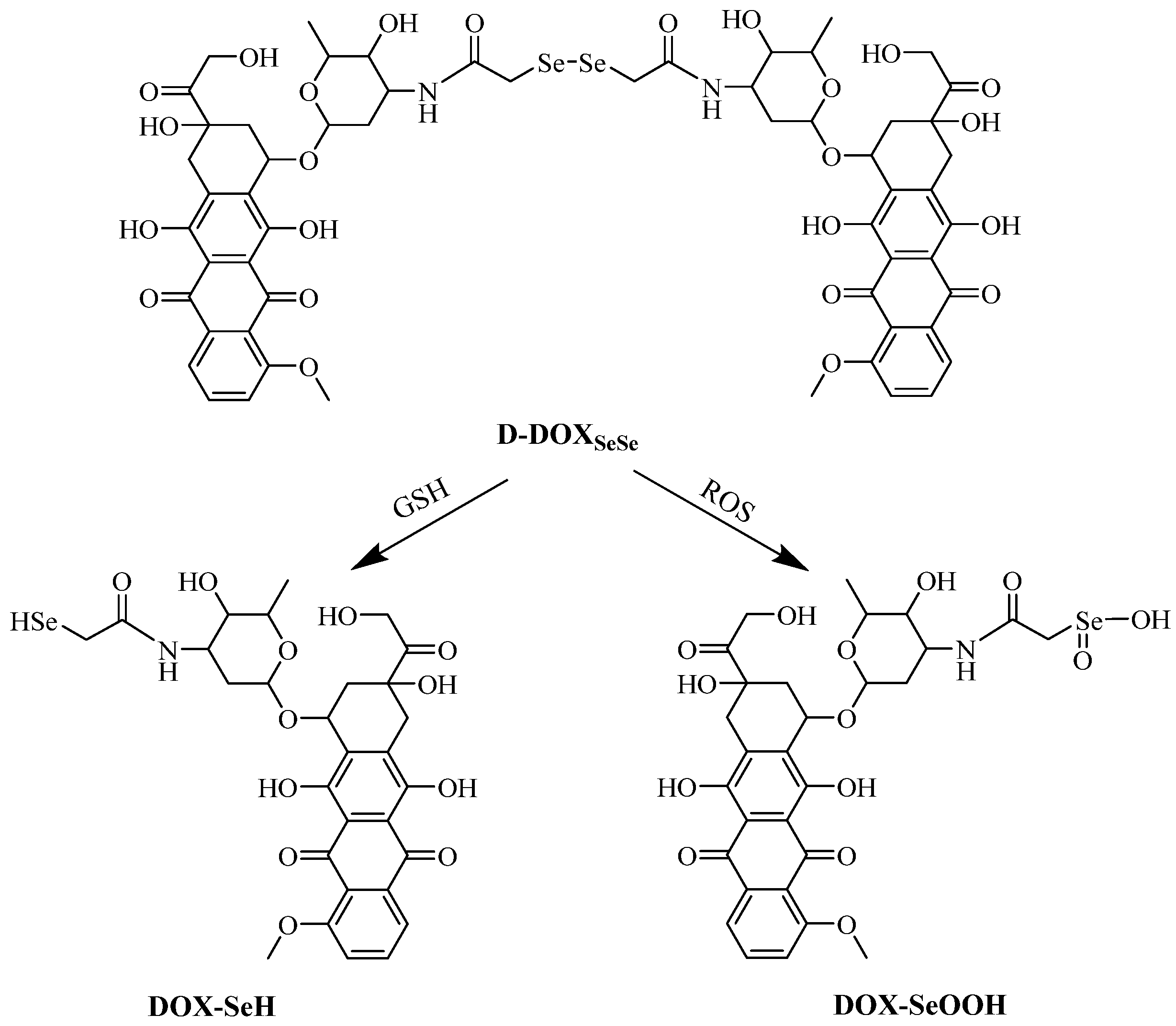
2.3. Redox-Triggered Drug Release from Diselenide-Bridged Dimeric Prodrug Nanoparticles
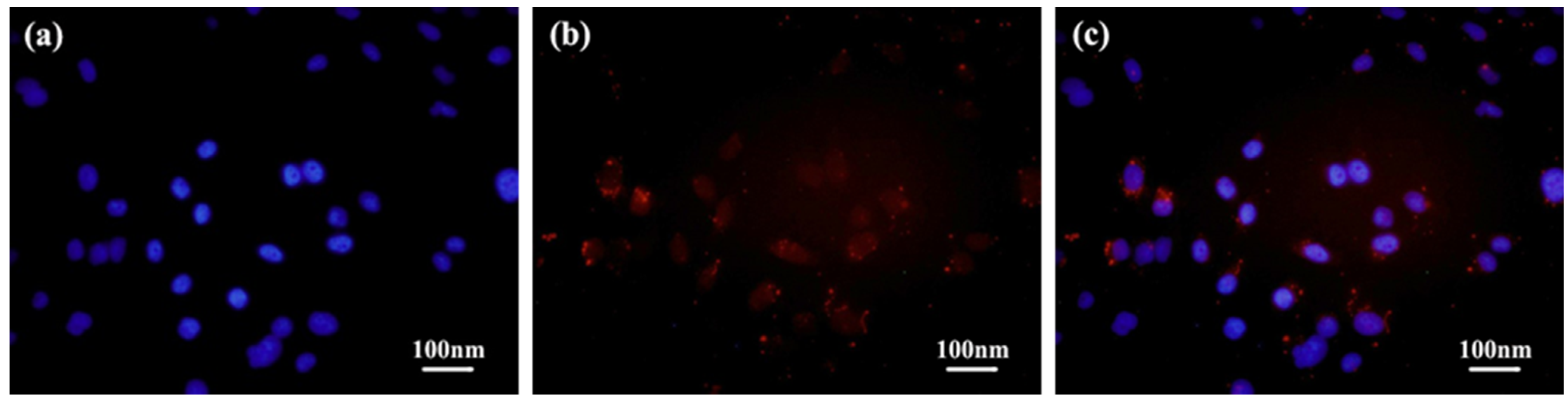
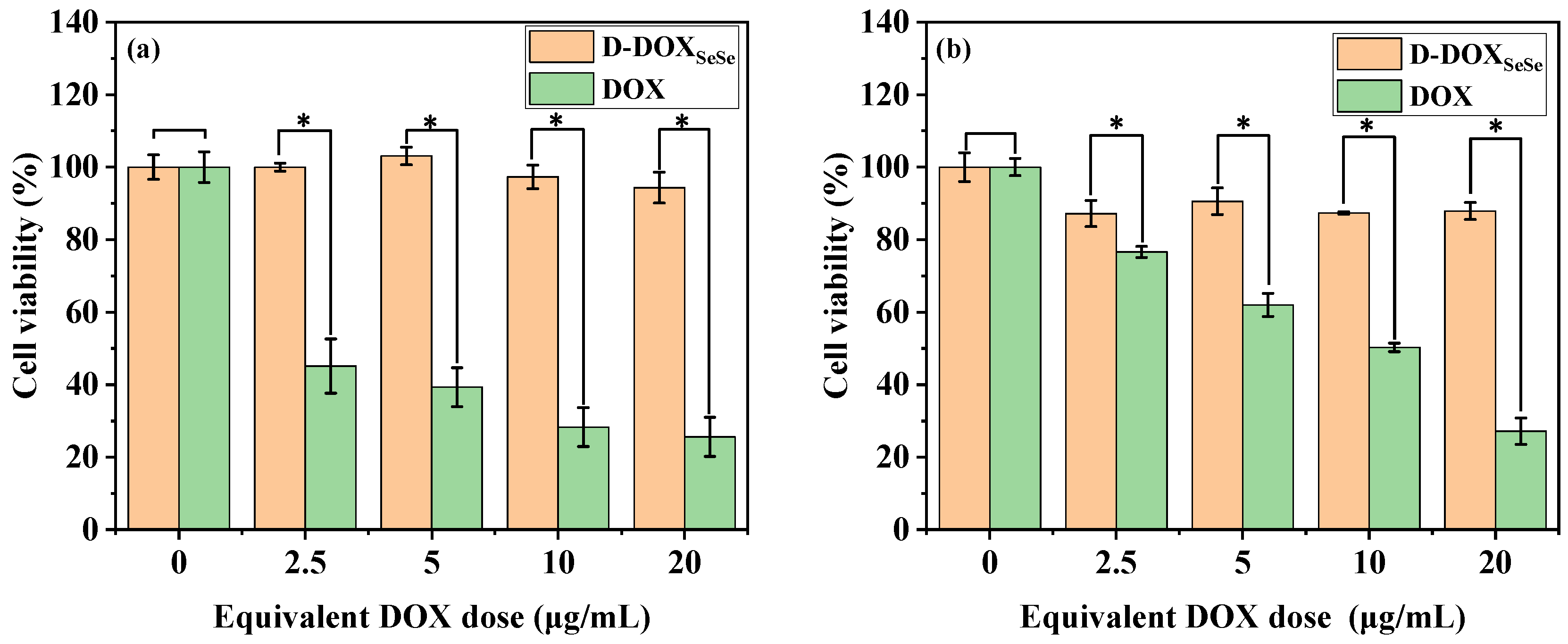
2.4. Cellular Uptake and Tumor-Selective Cytotoxicity of Diselenide-Bridged Dimeric Prodrug Nanoparticles
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Analysis and Characterization
4.3. Synthesis Procedure
4.4. Redox-Triggered Drug Release
4.5. Redox-Triggered Drug Release
4.6. In Vitro Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalyane, D.; Raval, N.; Maheshwari, R.; Tambe, V.; Kalia, K.; Tekade, R.K. Employment of enhanced permeability and retention effect (EPR): Nanoparticle-based precision tools for targeting of therapeutic and diagnostic agent in cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 1252–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.-D.; Zhang, X.-N. Advances in receptor modulation strategies for flexible, efficient, and enhanced antitumor efficacy. J. Control. Release 2021, 333, 418–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Jiang, C. Stimuli-responsive drug delivery systems triggered by intracellular or subcellular microenvironments. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 196, 114773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhadi, E.; Mashreghi, M.; Maleki, M.F.; Alavizadeh, S.H.; Arabi, L.; Badiee, A.; Jaafari, M.R. Redox-sensitive nanoscale drug delivery systems for cancer treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Pérez, M.; Ali, W.; Marć, M.A.; Handzlik, J.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E. Selenides and Diselenides: A Review of Their Anticancer and Chemopreventive Activity. Molecules 2018, 23, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Q.; Xu, J.Y.; Lin, A.J.; Wu, X.M.; Wu, L.; Xie, W.J. Recent Advances for the Synthesis of Selenium-containing Small Molecules as Potent Antitumor Agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 2009–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.F.; Liu, J.F.; Tian, L.; Li, J.Y.; Gao, Y.; Xing, Y.; Yan, W.J.; Hua, C.Y.; Xie, X.L.; Liu, C.; et al. Insights into stimuli-responsive diselenide bonds utilized in drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollazadeh, S.; Mackiewicz, M.; Yazdimamaghani, M. Recent advances in the redox-responsive drug delivery nanoplatforms: A chemical structure and physical property perspective. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2022, 118, 111536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, H.F.; Abuwatfa, W.H.; Husseini, G.A. Redox-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems: A Chemical Perspective. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Ramesh, K.; Reddy, O.S.; Karthika, V.; Kumar, P.; Jo, S.H.; Yoo, S.I.; Park, S.H.; Lim, K.T. Redox-Responsive Comparison of Diselenide and Disulfide Core-Cross-Linked Micelles for Drug Delivery Application. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Lu, D.Q.; Chen, L.J.; Yang, R.J.; Liu, D.H.; Zhang, B. Diselenide-crosslinked carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles for doxorubicin delivery: Preparation and in vivo evaluation. Crabohydr. Polym. 2022, 292, 119699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.G.; Robby, A.I.; Lee, B.C.; Lee, G.; Park, S.Y. Mitochondria-targeted ROS- and GSH-responsive diselenide-crosslinked polymer dots for programmable paclitaxel release. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 99, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birhan, Y.S.; Darge, H.F.; Hanurry, E.Y.; Andrgie, A.T.; Mekonnen, T.W.; Chou, H.Y.; Lai, J.Y.; Tsai, H.C. Fabrication of Core Crosslinked Polymeric Micelles as Nanocarriers for Doxorubicin Delivery: Self-Assembly, In Situ Diselenide Metathesis and Redox-Responsive Drug Release. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.F.; Lei, M.; Yan, L.K.; An, F.F. Diselenide-crosslinked zwitterionic nanogels with dual redox-labile properties for controlled drug release. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 2360–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.X.; Li, Q.Y.; Hou, W.; Zhang, J.N.; Ye, H.M.; Li, H.A.; Zeng, D.P.; Bai, J. A redox-sensitive core-crosslinked nanosystem combined with ultrasound for enhanced deep penetration of nanodiamonds into tumors. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 15252–15263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.L.; Hwang, S.C.; Nah, J.W.; Kim, J.; Cha, B.; Kang, D.H.; Jeong, Y.I. Redox- and pH-Responsive Nanoparticles Release Piperlongumine in a Stimuli-Sensitive Manner to Inhibit Pulmonary Metastasis of Colorectal Carcinoma Cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 2702–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.D.; Hu, X.L.; Hu, Y.J.; Wu, B.Y.; Xing, D. Visible light-induced crosslinking and physiological stabilization of diselenide-rich nanoparticles for redox-responsive drug release and combination chemotherapy. Biomaterials 2017, 121, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepagan, V.G.; Kwon, S.; You, D.G.; Nguyen, V.Q.; Um, W.; Ko, H.; Lee, H.; Jo, D.G.; Kang, Y.M.; Park, J.H. In situ diselenide-crosslinked polymeric micelles for ROS-mediated anticancer drug delivery. Biomaterials 2016, 103, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.T.; Huang, W.; Zhou, L.Z.; Huang, P.; Pang, Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Yan, D.Y. PEGylated poly(diselenide-phosphate) nanogel as efficient self-delivery nanomedicine for cancer therapy. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 6498–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, W.G.; Zhang, N.; Yang, C.S.; Xu, H.W.; Wang, Z.T.; Li, B.S.; Ding, J.X.; Chen, X.S. X-ray-responsive polypeptide nanogel for concurrent chemoradiotherapy. J. Control. Release 2021, 332, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Zhang, F.; Chen, F.M.; Zheng, X.; Hu, H.Z.; Yang, C.; Tu, Z.X.; Wang, Z.; Chang, Z.M.; Lu, J.N.; et al. Biomimetic Diselenide-Bridged Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles as an X-ray-Responsive Biodegradable Carrier for Chemo-Immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 202004385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.X.; Zhang, S.T.; Xu, J.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; He, J.L.; Yang, Y.; Huynh, T.; Ni, P.H.; Duan, G.X.; Yang, Z.X.; et al. Low-Dose X-ray-Responsive Diselenide Nanocarriers for Effective Delivery of Anticancer Agents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 43398–43407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhang, X.; Miao, X.; Yang, Z.; Xu, H. gamma-Ray-responsive supramolecular hydrogel based on a diselenide-containing polymer and a peptide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 6233–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, A.; Gulfam, M.; Jo, S.-H.; Seo, J.-W.; Ali, I.; Vu, T.T.; Joo, S.-B.; Park, S.-H.; Lim, K.T. Gelatin-based NIR and reduction-responsive injectable hydrogels cross-linked through IEDDA click chemistry for drug delivery application. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 191, 112019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; He, Q.; Li, Z.L.; Ren, Y.H.; Liao, Y.X.; Zhang, Z.J.; Dai, Q.; Wan, C.Y.; Long, S.H.; Kong, L.Y.; et al. ROS-cleavable diselenide nanomedicine for NIR-controlled drug release and on-demand synergistic chemo-photodynamic therapy. Acta Biomater. 2022, 153, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, F.; Rong, G.; Wang, W.; Kang, X.; et al. Breaking the intracellular redox balance with diselenium nanoparticles for maximizing chemotherapy efficacy on patient-derived xenograft models. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 16984–16996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, K.L.; Tian, H.L.; Zhang, T.T.; Gao, Y.J.; Nice, E.C.; Huang, C.H.; Xie, N.; Ye, G.L.; Zhou, Y.P. Chemo-photothermal nanoplatform with diselenide as the key for ferroptosis in colorectal cancer. J. Control. Release 2024, 366, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.M.; Shan, X.Z.; Wang, Y.Q.; Chen, Q.; Sun, J.; He, Z.G.; Sun, B.J.; Luo, C. Dimeric prodrug-based nanomedicines for cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Pan, J.X.; Wang, T.T.; Lai, Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Chen, F.M.; Xu, L.M.; Qu, X.W.; Hu, X.L.; Yu, H.J. Sequentially Activatable Polypeptide Nanoparticles for Combinatory Photodynamic Chemotherapy of Breast Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 39787–39798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.J.; Xia, R.; Wang, J.; Pei, Q.; Xie, Z.G.; Jing, X.B. Engineering paclitaxel prodrug nanoparticles via redox-activatable linkage and effective carriers for enhanced chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 46291–46302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.Y.; Sun, B.J.; Yang, Y.X.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, M.R.; Sun, M.C.; Luo, C.; He, Z.G.; Sun, J. Probing the Superiority of Diselenium Bond on Docetaxel Dimeric Prodrug Nanoassemblies: Small Roles Taking Big Responsibilities. Small 2020, 12, 2005039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.X.; Wang, J.L.; Pan, H.; Sang, Y.L.; Wang, D.Z.; Wang, Z.Y.; Ai, J.; Lin, B.; Chen, L.J. pH-redox responsive polymer-doxorubicin prodrug micelles studied by molecular dynamics, dissipative particle dynamics simulations and experiments. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 69, 103136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P. Polyprodrugs for tumor chemotherapy: From molecular structure to drug release performance. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 9565–9571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.M.; Liu, P. Synthesis and self-assembly of an acid/reduction co-triggered degradable amphiphilic copolyprodrug as a tumor-selective drug self-delivery system. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 2926–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.Q.; Liang, Y.Q.; Zhou, Y.X.; Song, X.N.; He, B.; Zhang, H.; Dai, W.B.; Wang, X.Q.; et al. Reduction Responsive Self-Assembled Nanoparticles Based on Disulfide-Linked Drug–Drug Conjugate with High Drug Loading and Antitumor Efficacy. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolinsky, J.B.; Colson, Y.L.; Grinstaff, M.W. Local drug delivery strategies for cancer treatment: Gels, nanoparticles, polymeric films, rods, and wafers. J. Control. Release 2012, 159, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Zhang, J.X.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, L.S.; Ruan, C.H.; Chen, Q.J.; Chen, X.L.; et al. Enhanced bioreduction-responsive diselenide-based dimeric prodrug nanoparticles for triple negative breast cancer therapy. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4884–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.T.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhong, M.; Xu, Q.H.; Li, X.M.; Chang, B.B.; Fang, J.G. Integration of a Diselenide Unit Generates Fluorogenic Camptothecin Prodrugs with Improved Cytotoxicity to Cancer Cells. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 17979–17991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, M.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.F.; Lu, C. Diselenium-linked dimeric prodrug nanomedicine breaking the intracellular redox balance for triple-negative breast cancer targeted therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2023, 193, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.J.; Luo, C.; Zhang, X.B.; Guo, M.C.; Sun, M.C.; Yu, H.; Chen, Q.; Yang, W.Q.; Wang, M.L.; Zuo, S.Y.; et al. Probing the impact of sulfur/selenium/carbon linkages on prodrug nanoassemblies for cancer therapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.X.; Zuo, S.Y.; Dong, F.D.; Liu, T.; Gao, Y.L.; Yang, Y.X.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Sun, B.J.; He, Z.G. Small changes in the length of diselenide bond-containing linkages exert great influences on the antitumor activity of docetaxel homodimeric prodrug nanoassemblies. Asia J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Liu, P. Diselenide-Bridged Doxorubicin Dimeric Prodrug: Synthesis and Redox-Triggered Drug Release. Molecules 2024, 29, 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081709
Hu Y, Liu P. Diselenide-Bridged Doxorubicin Dimeric Prodrug: Synthesis and Redox-Triggered Drug Release. Molecules. 2024; 29(8):1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081709
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yanru, and Peng Liu. 2024. "Diselenide-Bridged Doxorubicin Dimeric Prodrug: Synthesis and Redox-Triggered Drug Release" Molecules 29, no. 8: 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081709
APA StyleHu, Y., & Liu, P. (2024). Diselenide-Bridged Doxorubicin Dimeric Prodrug: Synthesis and Redox-Triggered Drug Release. Molecules, 29(8), 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081709




