Spondias sp: Shedding Light on Its Vast Pharmaceutical Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Socioeconomic Importance
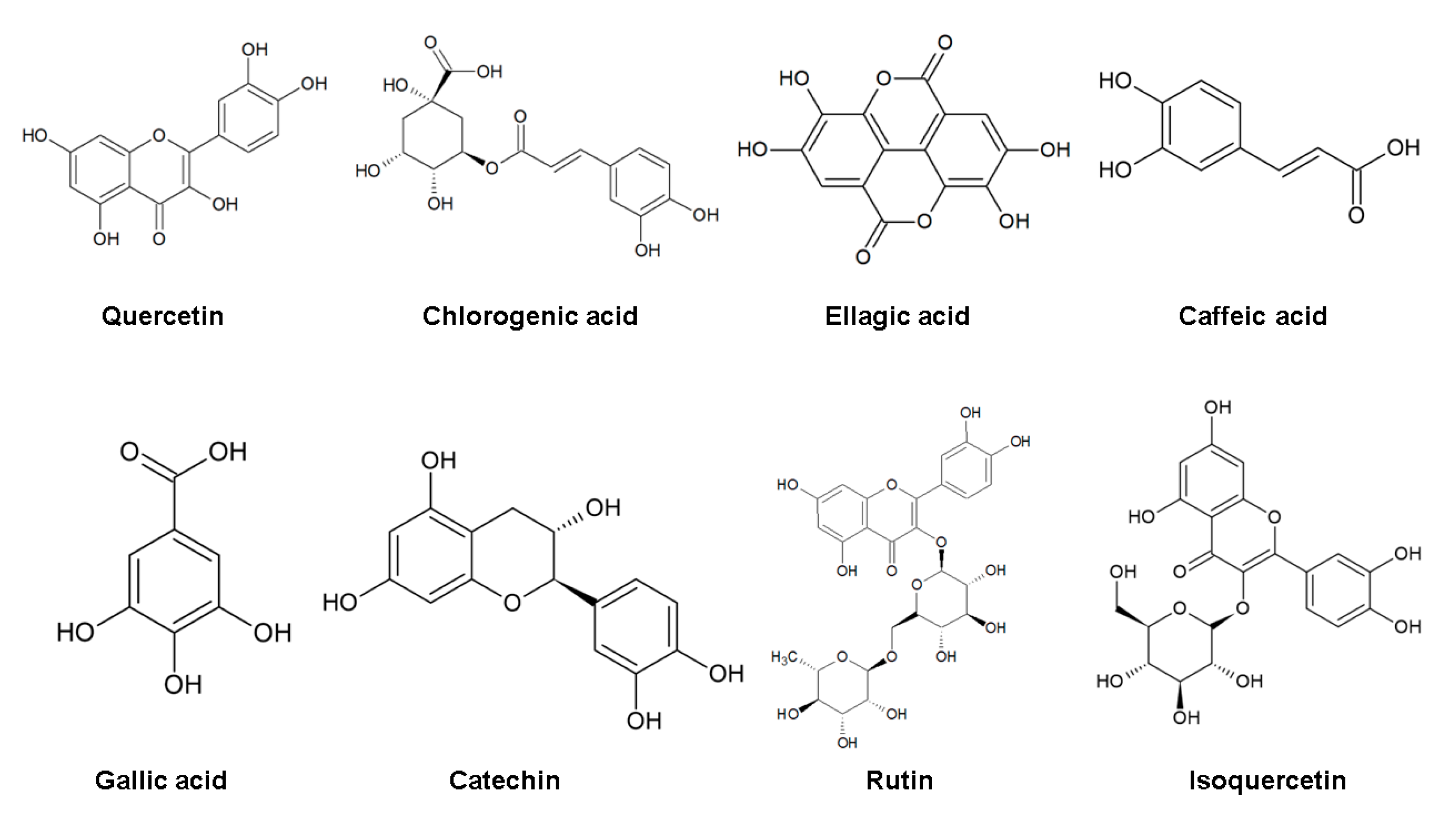
4. Bioactive Compounds
5. Pharmacological Activity
5.1. S. mombin L.
| Species | Activity | Part of the Plant Evaluated | References |
|---|---|---|---|
 Spondias mombin L. | Antibacterial | Bark | [13] |
| Plant | [14] | ||
| Root, leaf, and stem bark | [15] | ||
| Antidepressant | Leaf | [42] | |
| Anti-inflammatory | Leaf | [40,44] | |
| Antifungal | Root, leaf, and stem bark | [15] | |
| Antioxidant | Leaf | [37,40] | |
| Crude fruit juice | [38] | ||
| Antiviral | Leaf and branches | [35] | |
| Anxiolytic | Leaf | [45] | |
| Molluscicidal | Leaf | [46] | |
| Sedative, anti-epileptic, and antipsychotic | Leaf | [41] |
5.2. S. dulcis or S. cytherea Parkinson
| Species | Activity | Part of the Plant Evaluated | References |
|---|---|---|---|
 Spondias dulcis or Spondias cytherea Parkinson | Anticancer | Fruit | [53] |
| Antimicrobial | Fruit | [49] | |
| Leaf | [49,54] | ||
| Peel | [55] | ||
| Antimutagenic and antigenotoxic | Stem bark | [56] | |
| Antioxidant | Fruit | [49,52] | |
| Leaf | [26,49,51,57] | ||
| Stem bark | [26,56] | ||
| Enzymatic inhibition | Fruit | [52] | |
| Leaf | [26,51] | ||
| Pomace | [58] | ||
| Stem bark | [26] | ||
| Immunomodulation | Pulp | [59] | |
| Thrombolytic | Fruit | [49] | |
| Leaf | [49] |
5.3. S. purpurea L.
| Species | Activity | Part of the Plant Evaluated | References |
|---|---|---|---|
 Spondias purpurea L. | Antidiabetic | Seed | [67] |
| Antihyperlipidemic | Seed | [67] | |
| Antimicrobial | Leaf | [68] | |
| Antioxidant | Fruit | [69] | |
| Leaf | [65] | ||
| Peel | [62,63] | ||
| Pomace | [70] | ||
| Pulp | [63,71,72] | ||
| Anti-ulcer | Leaf | [61,73] | |
| Photoprotective | Peel | [65] |
5.4. S. tuberosa Arr. Câmara
5.5. S. pinnata
| Species | Activity | Part of the Plant Evaluated | References |
|---|---|---|---|
 Spondias pinnata | Anti-inflammatory | Bark | [90] |
| Antioxidant | Bark | [91] | |
| Antimicrobial | Resin | [92] | |
| Cellular immunity and phagocytosis | Leaf | [93] | |
| Hepatoprotective | Bark | [91] |
5.6. S. mombin × S. tuberosa
| Species | Activity | Part of the Plant Evaluated | References |
|---|---|---|---|
 Spondia tuberosa Arruda × Spondia mombin | Anti-acetylcholinesterase | Pulp | [83] |
| Antibacterial | Leaf | [37] | |
| Antidiabetic | Pulp | [81] | |
| Bark | [80] | ||
| Antifungal | Leaf | [9] | |
| Antioxidant | Pulp | [71,78,79] | |
| Cytotoxic | Bark | [94] | |
| Seed | [95] | ||
| Peel, pulp, and seeds | [77] | ||
| Gastroprotective | Leaf | [84] |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Sameh, S.; Al-Sayed, E.; Labib, R.M.; Singab, A.N. Genus Spondias: A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 5382904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of Spondias pinnata Kurz. Leaves. Eur. J. Med. Plants 2014, 4, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.C.; Carvalho, P.C.L.; van den Berg, C. Domestication, hybridization, speciation, and the origins of an economically important tree crop of Spondias (Anacardiaceae) from the Brazilian Caatinga dry forest. Neodiversity 2015, 8, 8–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.D.; Daly, D.C. A revision of Spondias L. (Anacardiaceae) in the Neotropics. PhytoKeys 2015, 55, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Junior, J.F.; Fernandes Bezerra, J.E.; Lederman, I.E.; Alves, M.A.; Melo Neto, M.L. Collecting, ex situ conservation and characterization of “cajá-umbu” (Spondias mombin × Spondias tuberosa) germplasm in Pernambuco State, Brazil. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2004, 51, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.A.M.; Giffony, P.S.; dos Santos, S.B.; Guedes, J.A.; Ribeiro, M.E.N.; Araújo, T.G.d.; da Silva, L.M.; Zocolo, G.J.; Ricardo, N.M. Spondias purpurea L. Stem Bark Extract: Antioxidant and in vitro Photoprotective Activities. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2021, 32, 1918–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, L.A.; Reis, L.C.B.; Dias, Ê.R.; Camilloto, G.P.; Branco, A. Characterization of a flavonol-rich antioxidant fraction from Spondias purpurea L. pulp and the effect of its incorporation on cellulose acetate-based film. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 3270–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.L.; Mazzutti, S.; de Souza, J.A.; Ferreira, S.R.; Soares, L.A.; Stragevitch, L.; Danielski, L. Extraction of umbu (Spondias tuberosa) seed oil using CO2, ultrasound and conventional methods: Evaluations of composition profiles and antioxidant activities. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 145, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Cordeiro, B.M.P.; de Lima Santos, N.D.; Ferreira, M.R.A.; de Araújo, L.C.C.; Junior, A.R.C.; da Conceição Santos, A.D.; de Oliveira, A.P.; da Silva, A.G.; da Silva Falcão, E.P.; dos Santos Correia, M.T. Hexane extract from Spondias tuberosa (Anacardiaceae) leaves has antioxidant activity and is an anti-Candida agent by causing mitochondrial and lysosomal damages. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameh, S.; Al-Sayed, E.; Labib, R.M.; Singab, A.N.B. Comparative metabolic profiling of essential oils from Spondias pinnata (Linn. F.) Kurz and characterization of their antibacterial activities. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 137, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narain, N.; Galvão, M.d.S.; Madruga, M.S. Volatile compounds captured through purge and trap technique in caja-umbu (Spondias sp.) fruits during maturation. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, R.T.; Borges, K.C.; Medeiros, M.F.; Genovese, M.I. Bioactive compounds and phenolic-linked functionality of powdered tropical fruit residues. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2012, 18, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olugbuyiro, J.A.; Moody, J.O.; Hamann, M.T. Phytosterols from Spondias mombin Linn with Antimycobacterial Activities. Afr. J. Biomed. Res. 2013, 16, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olugbuyiro, J.; Moody, J.; Hamann, M. AntiMtb activity of triterpenoid-rich fractions from Spondias mombin L. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 8, 1807–1809. [Google Scholar]
- Osuntokun, O.T.; Idowu, T.; Gamberini, M.C. Antibacterial and Antifungal Efficacy of Partially Partitioned Fractions of Spondias mombin (Linn) Extracts (Root, Leaf and Stem Bark) against Clinical and Environmental Isolates. Med. Chem. 2018, 8, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, F.X.d. Spondias agroindustriais e os seus métodos de propagação. Embrapa Agroindústria Trop. 1998, 28, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- de Freitas Lins Neto, E.M.; Peroni, N.; de Albuquerque, U.P. Traditional Knowledge and Management of Umbu (Spondias tuberosa, Anacardiaceae): An Endemic Species from the Semi–Arid Region of Northeastern Brazil. Econ. Bot. 2010, 64, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, E.d. Capítulo IV. In Os sertões, 3rd ed.; Universidade de São Paulo; A Biblioteca Virtual do Estudante Brasileiro: São Paulo, Brazil, 1984; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Fruticultura Tropical: Espécies Regionais e Exóticas. Available online: http://livimagens.sct.embrapa.br/amostras/00083730.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2022).
- Cavalcanti, N.d.B.; Resende, G.M.; Brito, L.T.d.L.; Lima, J.B. Extrativismo do imbuzeiro (Spondias tuberosa Arr. Cam.) como fonte alternativa de renda para pequenos produtores no semi-arido nordestino: Um estudo de caso. Ciência E Agrotecnologia 1996, 20, 529–533. [Google Scholar]
- de Carvalho, J.E.U.; do Nascimento, W.M.O. Cajá. Rev. Bras. De Frutic. 2020, 42, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rice-Evans, C.A.; Miller, N.J.; Paganga, G. Structure-antioxidant activity relationships of flavonoids and phenolic acids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 933–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Rosa, L.; Alvarez-Parrilla, E.; Aguilar, G. Fruit and Vegetable Phytochemicals: Chemistry, Nutritional Value, and Stability; Chapter 2. Phenolic Compounds: Chemistry and Occurrence in Fruits and Vegetables; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 53–88. [Google Scholar]
- Heim, K.E.; Tagliaferro, A.R.; Bobilya, D.J. Flavonoid antioxidants: Chemistry, metabolism and structure-activity relationships. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.; Oliveira, L.L.D.; Gonçalves, R.; Amaral, A.C.F.; Kuster, R.M.; Sakuragui, C.M. Phytochemical and phylogenetic analysis of Spondias(Anacardiaceae). Química Nova 2015, 38, 813–816. [Google Scholar]
- Sinan, K.I.; Zengin, G.; Zheleva-Dimitrova, D.; Gevrenova, R.; Picot-Allain, M.C.N.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Behl, T.; Goh, B.H.; Ying, P.T.S.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Exploring the Chemical Profiles and Biological Values of Two Spondias Species (S. dulcis and S. mombin): Valuable Sources of Bioactive Natural Products. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Assis, R.C.; Soares, R.d.L.G.; Siqueira, A.C.P.; de Rosso, V.V.; de Sousa, P.H.M.; Mendes, A.E.P.; de Alencar Costa, E.; de Góes Carneiro, A.P.; Maia, C.S.C. Determination of water-soluble vitamins and carotenoids in Brazilian tropical fruits by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, E.Q.D.; Ferreira, C.F.D.S.L.; Oliveira, E.D.; Costa, V.C.D.O.; Dantas, M.K.L. Phytochemical characterization of Spondias sp. and Spondias tuberosa Arruda Câmera extracts of occurrence in Paraiba semiarid. J. Exp. Biol. Agric. Sci. 2017, 5, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiburski, J.H.; Rosenthal, A.; Deliza, R.; de Oliveira Godoy, R.L.; Pacheco, S. Nutritional properties of yellow mombin (Spondias mombin L.) pulp. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2326–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, S.A.; Barbosa, I.S.; de Almeida, C.L.F.; de Medeiros, J.W.; Silva Neto, J.C.; Rolim, L.A.; da Silva, T.G.; Ximenes, R.M.; de Menezes, I.R.A.; Caldas, G.F.R.; et al. Evaluation of gastroprotective and ulcer healing activities of yellow mombin juice from Spondias mombin L. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa Gomes, M.; Diógenes Alves Uchoa Lins, R.; Zucolotto Langassner, S.M.; Dantas da Silveira É, J.; Gomes de Carvalho, T.; Diniz de Sousa Lopes, M.L.; de Souza Araújo, L.; Addison Carvalho Xavier de Medeiros, C.; Ferreira de Carvalho Leitão, R.; Coelho Bernardo Guerra, G.; et al. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity of hydroethanolic extract of Spondias mombin leaf in an oral mucositis experimental model. Arch. Oral Biol. 2020, 111, 104664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, L.; Santos, P.; Riatto, V.; David, J.; David, J. New alkyl phenols and fatty acid profile from oils of pulped spondias mombin L. seed wastes. Química Nova 2018, 41, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.H.A.; Boylan, F.; Salgado, H.R.N. Quality standardization of herbal medicines of Spondias dulcis Parkinson using analytical and microbiological analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 134, 1923–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, J.C.R.; Salgado, H.R.N. Atividade inseticida das plantas e aplicações: Revisão. Rev. Bras. De Plantas Med. 2011, 13, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, E.; Lima, T.L.C.; Boff, L.; Lima, S.G.M.; Lourenço, E.M.G.; Ferreira É, G.; Barbosa, E.G.; Machado, P.R.L.; Farias, K.J.S.; Ferreira, L.S.; et al. Antiviral Potential of Spondias mombin L. Leaves Extract Against Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1 Replication Using In Vitro and In Silico Approaches. Planta Med. 2020, 86, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, T.S.J.d.; Soares, A.A.; Rocha, T.M.; Pimenta, A.T.Á.; Miron, D.; Silva, R.J.F.; Viana, G.S.B.; Leal, L.K.A.M. Spondias mombin: Quality control and anti-inflammatory activity in human neutrophils. J. Herb. Med. 2020, 24, 100393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.R.A.d.; Morais, S.M.d.; Marques, M.M.M.; Oliveira, D.F.d.; Barros, C.C.; Almeida, R.R.d.; Vieira, Í.G.P.; Guesdes, M.I.F. Chemical composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of two Spondias species from Northeastern Brazil. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coolborn, A.F.; Esther, B.B.; Akinsola, A.F.; Afolabi, O.B. Antioxidant, physicochemical and mineral evaluations of Spondias mombin crude fruit juice. Acta Biol. Szeged. 2016, 60, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- de Carvalho, J.M.; Maia, G.A.; da Fonseca, A.V.V.; de Sousa, P.H.M.; Rodrigues, S. Effect of processing on physicochemical composition, bioactive compounds and enzymatic activity of yellow mombin (Spondias mombin L.) tropical juice. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, B.; Siqueira, E.M.S.; Bitencourt, M.A.O.; Lima, M.C.J.S.; Lima, A.K.; Ortmann, C.F.; Chaves, V.C.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F.; Rocha, H.A.O.; Scortecci, K.C.; et al. Phytochemical study and anti-inflammatory and antioxidant potential of Spondias mombin leaves. Rev. Bras. De Farmacogn. 2016, 26, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoka, A.O.; Akomolafe, R.O.; Iwalewa, E.O.; Akanmu, M.A.; Ukponmwan, O.E. Sedative, antiepileptic and antipsychotic effects of Spondias mombin L. (Anacardiaceae) in mice and rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 103, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Sampaio, T.I.; de Melo, N.C.; de Freitas Paiva, B.T.; da Silva Aleluia, G.A.; da Silva Neto, F.L.P.; da Silva, H.R.; Keita, H.; Cruz, R.A.S.; Sánchez-Ortiz, B.L.; Pineda-Peña, E.A.; et al. Leaves of Spondias mombin L. a traditional anxiolytic and antidepressant: Pharmacological evaluation on zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 224, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, O. Comparative Study of Aqueous and Ethanolic Leaf Extracts of Spondias Mombin on Neurobehaviour in Male Rats. IOSR J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2013, 5, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.S.; Linsa, R.D.A.U.; Langassner, S.M.Z.; Silveira, É.J.D.d.; Carvalho, T.G.d.; Lopes, M.L.D.d.S.; Araújo, L.d.S.; Medeiros, C.A.C.X.d.; Leitão, R.F.d.C.; Guerra, G.C.B.; et al. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity of hydroethanolic extract of Spondias mombin leaf in an oral mucositis experimental model. Arch. Oral Biol. 2020, 111, 104664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoka, A.O.; Akomolafe, R.O.; Iwalewa, E.O.; Ukponmwan, O.E. Studies on the Anxiolytic Effect of Spondias mombin L. (Anacardiaceae) Extracts. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2005, 2, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corthout, J.; Pieters, L.; Claeys, M.; Geerts, S.; Vanden Berghe, D.; Vlietinck, A. Antibacterial and molluscicidal phenolic acids from Spondias mombin. Planta Med. 1994, 60, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prescott, T.A.K.; Briggs, M.; Kiapranis, R.; Simmonds, M.S.J. Medicinal plants of Papua New Guinea’s Miu speaking population and a focus on their use of plant–slaked lime mixtures. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 174, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmatullah, M.; Ferdausi, D.; Mollik, M.A.H.; Azam, M.N.K.; Taufiq-Ur-Rahman, M.; Jahan, R. Ethnomedicinal survey of Bheramara area in Kushtia district, Bangladesh. Am.-Eurasian J. Sustain. Agric. 2009, 3, 534–541. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, S.M.A.; Ahmed, K.T.; Manik, M.K.; Wahid, M.A.; Kamal, C.S.I. A comparative study of the antioxidant, antimicrobial, cytotoxic and thrombolytic potential of the fruits and leaves of Spondias dulcis. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, S.; Akhter, R.; Tithi, N.; Wadud, M.; Narjish, S.; Shahriar, M.; Bhuiyan, M. Biological investigations of the leaf extract of Spondias pinnata. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2015, 6, 3351–3358. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, P.L.; Fauzi, N.A.; Mohamed Yunus, S.N.; Abdul Hamid, N.A.; Abd Ghafar, S.Z.; Azizan, A.; Zolkeflee, N.K.Z.; Abas, F. Biological Activities of Selected Plants and Detection of Bioactive Compounds from Ardisia elliptica Using UHPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2020, 25, 3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Yunus, S.N.; Abas, F.; Jaafar, A.H.; Azizan, A.; Zolkeflee, N.K.Z.; Abd Ghafar, S.Z. Antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of eight neglected fruit extracts and UHPLC-MS/MS profile of the active extracts. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolande, F.N.; Sayantan, B.; Paramita, G.; Deblina, S.; Simplice, M.R.; Christopher, T.B.; Murmu, N. Cytotoxic Effect of Spondias cytherea Fruit Extract in Murine Melanoma Model In Vivo and In Vitro. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2018, 37, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Manjunath, H.; Selvaraj, R. Antibacterial and dye degradation potential of zero-valent silver nanoparticles synthesised using the leaf extract of Spondias dulcis. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 13, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zofou, D.; Shu, G.L.; Foba-Tendo, J.; Tabouguia, M.O.; Assob, J.-C.N. In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Salmonella Evaluation of Pectin Extracts and Hydrolysates from “Cas Mango” (Spondias dulcis). Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 3578402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, C.d.S.; Brito, L.D.; Tarifa, M.O.; Silva, N.J.F.d.; Rodrigues, K.S.; Cavalcante, D.G.S.M.; Gomes, A.S.; Zocoler, M.A.; Yoshihara, E.; Camparoto, M.L.; et al. Protective effects of bark ethanolic extract from Spondias dulcis Forst F. against DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene and cyclophosphamide. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2019, 42, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manik, M.K.; Islam, S.; Wahid, M.; Morshed, M.M.; Kamal, S.; Islam, M.; Ahmed, K.T. Investigation of in vitro Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Thrombolytic Activity of the Exocarp of Spondias pinnata (Anacardiaceae). Can. Chem. Trans. 2013, 1, 191–201. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Chauhan, G.S. Extraction and characterization of pectin from apple pomace and its evaluation as lipase (steapsin) inhibitor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacomini, M.; Serrato, R.V.; Sassaki, G.L.; Lopes, L.; Buchi, D.F.; Gorin, P.A.J. Isolation and partial characterization of a pectic polysaccharide from the fruit pulp of Spondias cytherea and its effect on peritoneal macrophage activation. Fitoterapia 2005, 76, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Abreu, D.J.M.; de Moraes, I.A.; Asquieri, E.R.; Damiani, C. Red mombin (Spondias purpurea L.) seed flour as a functional component in chocolate brownies. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.A.M.; Dos Santos, S.B.F.; Lopes, M.M.A.; Guimaraes, D.J.S.; de Oliveira Silva, E.; de Souza Filho, M.S.M.; Mattos, A.L.A.; da Silva, L.M.R.; de Azeredo, H.M.C.; Ricardo, N. Antioxidant films and coatings based on starch and phenolics from Spondias purpurea L. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.V.; Costa, S.C.C.; Branco, C.R.C.; Branco, A. In vitro photoprotective activity of the Spondias purpurea L. peel crude extract and its incorporation in a pharmaceutical formulation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 83, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa-Hernández, J.M.; Mendoza-Cardoso, G.; Mendoza-Espinoza, J.A.; Vela-Hinojosa, C.; Díaz de León-Sánchez, F.; Rivera-Cabrera, F.; Alia-Tejacal, I.; Pérez-Flores, L.J. Antioxidant Capacity In Vitro and In Vivo of Various Ecotypes of Mexican Plum (Spondias purpurea L.). J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2576–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollano-Mendieta, X.C.; Meza-Márquez, O.G.; Osorio-Revilla, G.; Téllez-Medina, D.I. Effect of In Vitro Digestion on the Antioxidant Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity of 12 Plum (Spondias purpurea L.) Ecotypes. Foods 2021, 10, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, C.L.F.; Brito, S.A.; de Santana, T.I.; Costa, H.B.A.; de Carvalho Júnior, C.H.R.; da Silva, M.V.; de Almeida, L.L.; Rolim, L.A.; Dos Santos, V.L.; Wanderley, A.G.; et al. Spondias purpurea L. (Anacardiaceae): Antioxidant and Antiulcer Activities of the Leaf Hexane Extract. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 6593073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñiz, A.; Garcia, E.; Gonzalez, D.; Zuñiga, L. Antioxidant Activity and In Vitro Antiglycation of the Fruit of Spondias purpurea. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 5613704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz-Ramirez, A.; Garcia-Campoy, A.H.; Pérez Gutiérrez, R.M.; Garcia Báez, E.V.; Mota Flores, J.M. Evaluation of the Antidiabetic and Antihyperlipidemic Activity of Spondias purpurea Seeds in a Diabetic Zebrafish Model. Plants 2021, 10, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uc-Cachón, A.H.; Dzul-Beh, A.d.J.; Palma-Pech, G.A.; Jiménez-Delgadillo, B.; Flores-Guido, J.S.; Gracida-Osorno, C.; Molina-Salinas, G.M. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of Mayan medicinal plants against Methicillin-susceptible and -resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 114369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoris, E.; Pereira Lima, G.P.; Fabris, S.; Bertelle, M.; Sicari, M.; Stevanato, R. Antioxidant properties of Brazilian tropical fruits by correlation between different assays. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 132759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, L.C.B.; Carneiro, L.M.; Branco, C.R.C.; Branco, A. Comparison of Conventional Microwave and Focused Microwave-assisted Extraction to Enhance the Efficiency of the Extraction of Antioxidant Flavonols from Jocote Pomace (Spondias purpurea L.). Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2015, 70, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, A.A.F.; Ávila, S.; Ito, V.; Nogueira, A.; Wosiacki, G.; Haminiuk, C.W.I. The association between chromaticity, phenolics, carotenoids, and in vitro antioxidant activity of frozen fruit pulp in Brazil: An application of chemometrics. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, C510–C516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutra, R.L.T.; Dantas, A.M.; Marques, D.d.A.; Batista, J.D.F.; Meireles, B.R.L.d.A.; de Magalhães Cordeiro, Â.M.T.; Magnani, M.; Borges, G.d.S.C. Bioaccessibility and antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds in frozen pulps of Brazilian exotic fruits exposed to simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, L.D.; Araujo, C.d.S.; Cavalcante, D.G.S.M.; Gomes, A.S.; Zocoler, M.A.; Yoshihara, E.; Job, A.E.; Kerche, L.E. In vivo assessment of antioxidant, antigenotoxic, and antimutagenic effects of bark ethanolic extract from Spondias purpurea L. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2022, 85, 336–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, H.J.; Bacher, L.B.; de Lacerda, M.T.C. Frutas no Brasil: Nativas e Exóticas (de Consumo in Natura); Instituto Plantarum de Estudos da Flora Ldta: Nova Odessa, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, E.; Pereira, E.; Mendes, D.; Paraizo, E.; Duarte, A.; Pessoa, H.; Figueiredo, J. Extension of umbu (Spondias tuberosa Arruda) postharvest life using a cassava starch-based coating Prolongación de la vida poscosecha del umbú (Spondias tuberosa Arruda) mediante recubrimiento a base de almidón de yuca. Agron. Colomb. 2021, 39, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, F.H.; de Almeida, J.S. Avaliação da germinação de sementes de Spondias tuberosa Arr. dispersas por caprinos. J. Environ. Anal. Prog. 2020, 5, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omena, C.M.B.; Valentim, I.B.; Guedes, G.d.S.; Rabelo, L.A.; Mano, C.M.; Bechara, E.J.H.; Sawaya, A.C.; Trevisan, M.T.S.; da Costa, J.G.; Ferreira, R.C.S. Antioxidant, anti-acetylcholinesterase and cytotoxic activities of ethanol extracts of peel, pulp and seeds of exotic Brazilian fruits: Antioxidant, anti-acetylcholinesterase and cytotoxic activities in fruits. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiros, M.; de Jesus, R.; Barreiros, A.; Sandes, T.; Ramalho, S.; Narain, N. Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of eight tropical fruits by DPPH method. In Proceedings of the III International Symposium on Medicinal and Nutraceutical Plants and III Conference of National Institute of Science and Technology for Tropical Fruits, ISHS Acta Horticulturae 1198, Aracaju, Brazil, 14–19 October 2012; pp. 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Gualberto, N.C.; de Oliveira, C.S.; Nogueira, J.P.; de Jesus, M.S.; Araujo, H.C.S.; Rajan, M.; Neta, M.T.S.L.; Narain, N. Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activities in the agro-industrial residues of acerola (Malpighia emarginata L.), guava (Psidium guajava L.), genipap (Genipa americana L.) and umbu (Spondias tuberosa L.) fruits assisted by ultrasonic or shaker extraction. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110538. [Google Scholar]
- de Moura Barbosa, H.; Amaral, D.; do Nascimento, J.N.; Machado, D.C.; de Sousa Araújo, T.A.; de Albuquerque, U.P.; da Silva Almeida, J.R.G.; Rolim, L.A.; Lopes, N.P.; Gomes, D.A. Spondias tuberosa inner bark extract exert antidiabetic effects in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 227, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza Schmidt Goncalves, A.E.; Lajolo, F.M.; Genovese, M.I. Chemical composition and antioxidant/antidiabetic potential of Brazilian native fruits and commercial frozen pulps. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4666–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, M.; Da Silva Pinto, M.; De Souza Schmidt Gonçalves, A.; Lajolo, F. Bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacity of exotic fruits and commercial frozen pulps from Brazil. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2008, 14, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Zeraik, M.L.; Queiroz, E.F.; Marcourt, L.; Ciclet, O.; Castro-Gamboa, I.; Silva, D.H.S.; Cuendet, M.; da Silva Bolzani, V.; Wolfender, J.-L. Antioxidants, quinone reductase inducers and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from Spondias tuberosa fruits. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, A.D.; Feitoza, G.S.; da Silva Oliveira, F.G.; de Veras, B.O.; Lacerda, F.F.; da Silva, N.H.; Harand, W.; Paz, S.T.; de Melo-Júnior, M.R.; Guedes, J.R. Natural gastroprotective remedy from the branches of Spondias tuberosa arruda. Pharmacogn. Res. 2020, 12, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, R.G.C.; Pereira, U.C.; Andrade, J.K.S.; de Oliveira, C.S.; Vasconcelos, S.V.; Narain, N. In vitro gastrointestinal digestion and probiotics fermentation impact on bioaccessbility of phenolics compounds and antioxidant capacity of some native and exotic fruit residues with potential antidiabetic effects. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewa ayu, S. Biological activity of Spondias pinnata: A review. Indones. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 13, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Hazra, B.; Biswas, S.; Mandal, N. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activity of Spondias pinnata. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2008, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yang, J.J.; Song, X.Z.; Wang, Y.F.; Corlett, R.T.; Xu, Y.K.; Hu, H.B. Chemical Composition and the Cytotoxic, Antimicrobial, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Fruit Peel Essential Oil from Spondias pinnata (Anacardiaceae) in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. Molecules 2020, 25, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghate, N.B.; Hazra, B.; Sarkar, R.; Mandal, N. In vitro anticancer activity of Spondias pinnata bark on human lung and breast carcinoma. Cytotechnology 2014, 66, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marathe, A.; Rao, G.M.; Chakrapani, M. Spondias pinnata bark extract- an ameliorator of inflammatory derangement in etoposide induced mucositis: An experimental approach. Vet. World 2021, 14, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.S.; Mujahid, M.; Kashif, S.M.; Khalid, M.; Badruddeen; Arif, M.; Bagga, P.; Akhtar, J.; Rahman, M.A. Protection of hepatotoxicity using Spondias pinnata by prevention of ethanol-induced oxidative stress, DNA-damage and altered biochemical markers in Wistar rats. Integr. Med. Res. 2016, 5, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Roy, A.; Nigam, V.; Mukherjee, K. Antimicrobial activity of Spondias pinnata resin. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 1656–1661. [Google Scholar]
- Sri Laksemi, D.A.A.; Arijana, I.G.K.; Sudarmaja, I.M.; Ariwati, N.L.; Tunas, K.; Damayanti, P.A.A.; Diarthini, N.L.P.E.; Swastika, I.K.; Wiryantini, I.A.D. Ethanol Extract of Spondias pinnata Leaves Reduce Parasite Number and Increase Macrophage Phagocytosis Capacity of Mice Infected by Plasmodium berghei. Indones. Biomed. J. 2021, 13, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, H.M.; Nascimento, J.N.; Araujo, T.A.; Duarte, F.S.; Albuquerque, U.P.; Vieira, J.R.; Santana, E.R.D.; Yara, R.; Lima, C.S.; Gomes, D.A. Acute toxicity and cytotoxicity effect of ethanolic extract of Spondias tuberosa Arruda bark: Hematological, biochemical and histopathological evaluation. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências 2016, 88, 1993–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.A.; de Rezende, L.C.; Oliveira, J.C.S.d.; David, J.M.; David, J.P. Chemical Study, Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activities of Oil Seeds of Spondias tuberosa (Anacardiaceae). Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2019, 19, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, É.M.d.; Ataide, J.A.; Coco, J.C.; Fava, A.L.M.; Silvério, L.A.L.; Sueiro, A.C.; Silva, J.R.A.; Lopes, A.M.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Mazzola, P.G. Spondias sp: Shedding Light on Its Vast Pharmaceutical Potential. Molecules 2023, 28, 1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041862
Santos ÉMd, Ataide JA, Coco JC, Fava ALM, Silvério LAL, Sueiro AC, Silva JRA, Lopes AM, Paiva-Santos AC, Mazzola PG. Spondias sp: Shedding Light on Its Vast Pharmaceutical Potential. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041862
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Érica Mendes dos, Janaína Artem Ataide, Julia Cedran Coco, Ana Laura Masquetti Fava, Luiza Aparecida Luna Silvério, Ana Claudia Sueiro, Jéssica Ribeiro Alves Silva, André Moreni Lopes, Ana Cláudia Paiva-Santos, and Priscila Gava Mazzola. 2023. "Spondias sp: Shedding Light on Its Vast Pharmaceutical Potential" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041862
APA StyleSantos, É. M. d., Ataide, J. A., Coco, J. C., Fava, A. L. M., Silvério, L. A. L., Sueiro, A. C., Silva, J. R. A., Lopes, A. M., Paiva-Santos, A. C., & Mazzola, P. G. (2023). Spondias sp: Shedding Light on Its Vast Pharmaceutical Potential. Molecules, 28(4), 1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041862












