Identification and Distribution of Novel Metabolites of Lolitrem B in Mice by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
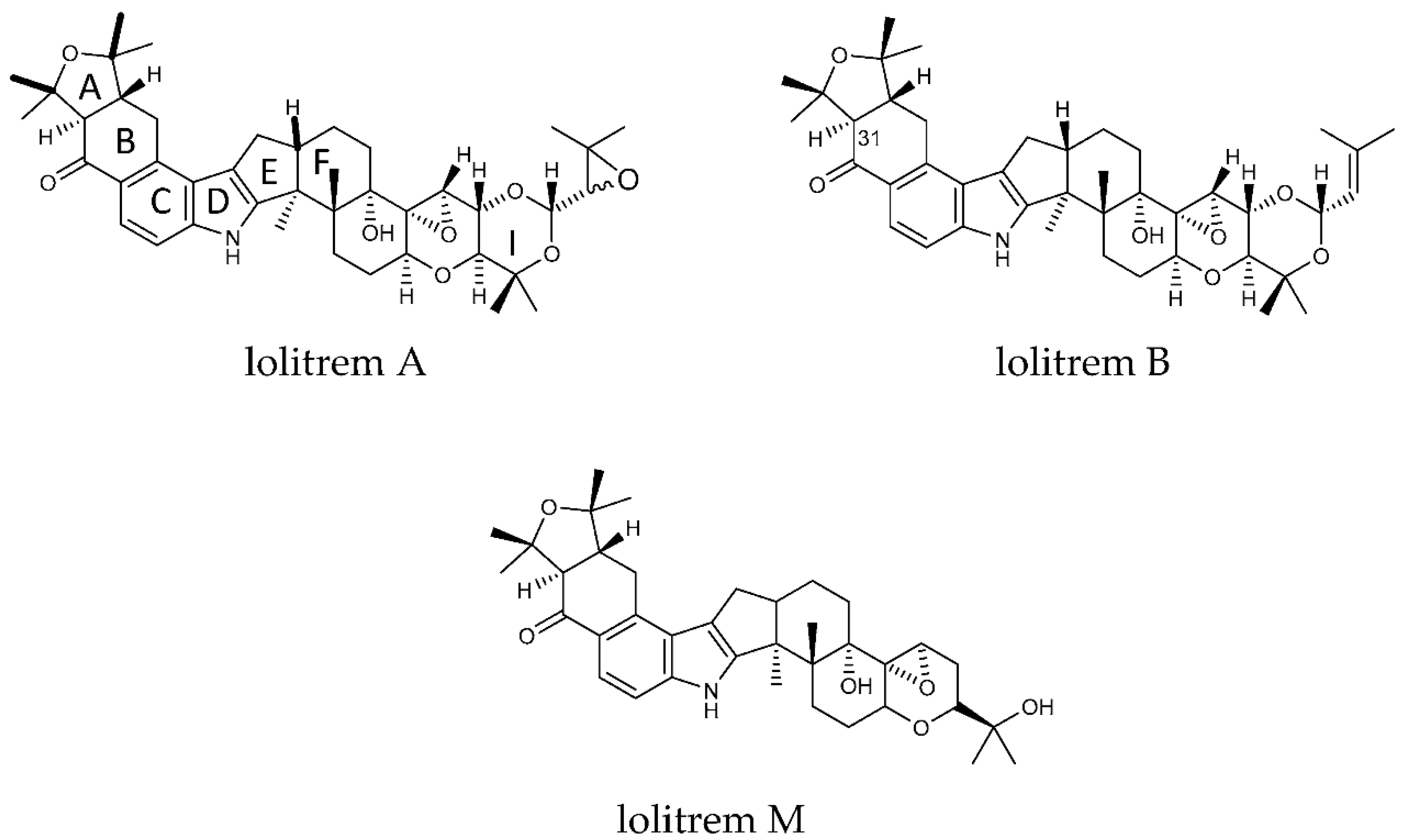
1. Introduction
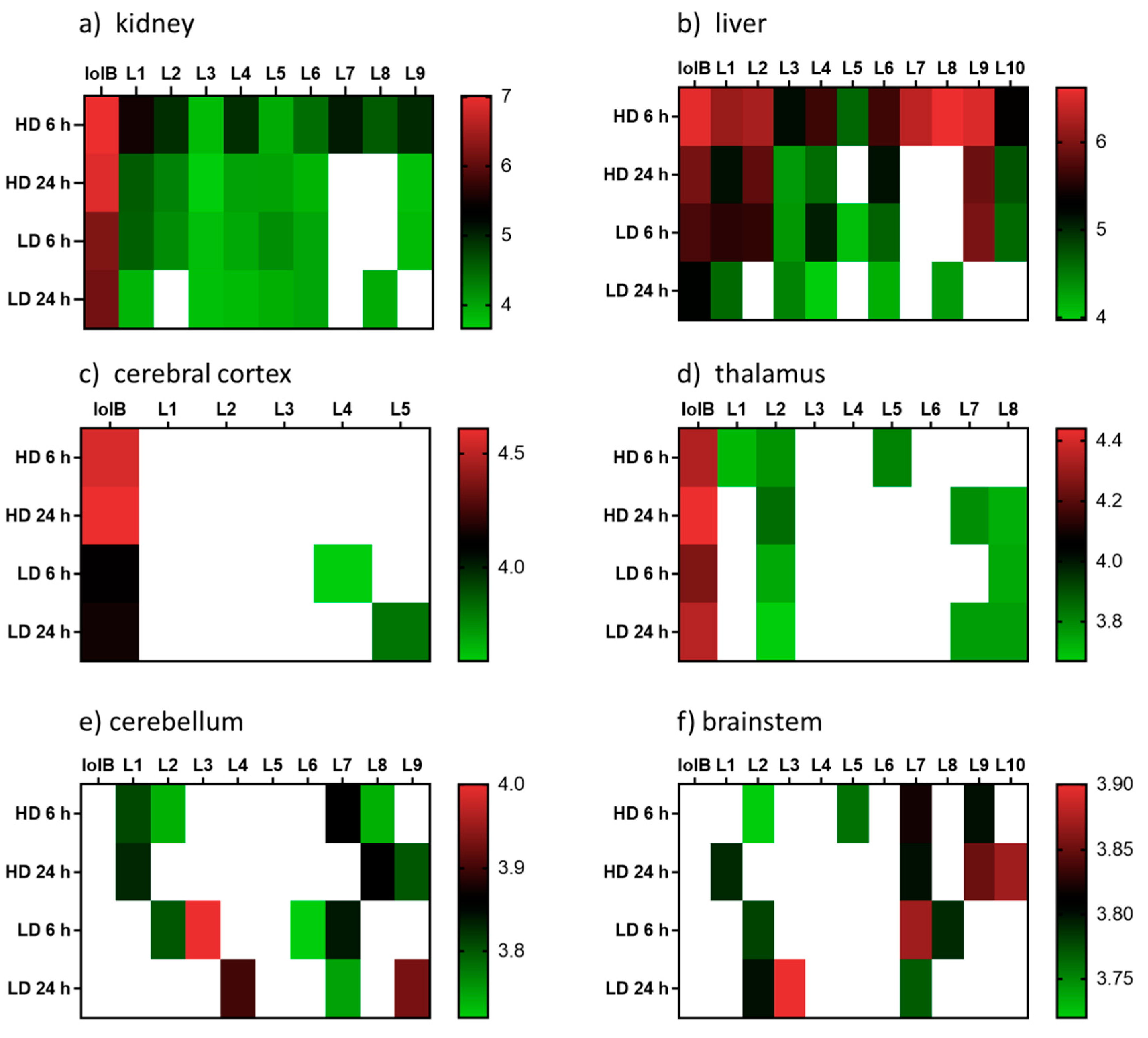
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Ethical Approval
3.2. Tissue Extracts
3.3. Liquid Chromatography–High-Resolution Tandem Mass Spectrometry Parameters
3.4. Metabolite Identification
3.5. Metabolite Distribution
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, L.; Catherine, T.; Bernadette, F.; Anne, A.; Jean-Denis, T.; Stéphanie, G.; Michel, D. Dysregulation of energy balance by trichothecene mycotoxins: Mechanisms and prospects. Neurotoxicology 2015, 49, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, G.J.; Boermans, H.J. Fumonisin toxicosis in domestic animals: A review. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 1994, 36, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gaigé, S.; Djelloul, M.; Tardivel, C.; Airault, C.; Félix, B.; Jean, A.; Lebrun, B.; Troadec, J.D.; Dallaporta, M. Modification of energy balance induced by the food contaminant T-2 toxin: A multimodal gut-to-brain connection. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 37, 54–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montella, P.G.; Reddy, C.S. Neurotoxic effects of secalonic acid D in mice during subchronic postnatal exposure. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1991, 40, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes, J.J.; Cameron, J.E.; Cole, R.J. Aflatrem: A tremorgenic mycotoxin with acute neurotoxic effects. Environ. Health Perspect. 1985, 62, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.; Guthridge, K.; Vassiliadis, S.; Hemsworth, J.; Hettiarachchige, I.; Spangenberg, G.; Rochfort, S. Tremorgenic Mycotoxins: Structure Diversity and Biological Activity. Toxins 2019, 11, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zijll de Jong, E. Global Genetic Diversity of the Perennial Ryegrass Fungal Endophyte Neotyphodium lolii. Crop Sci. 2008, 48, 1487–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, M.D.; Edwards, S.H.; Scherpenhuizen, J.M.; Narayan, E.J.; Kessell, A.E.; Piltz, J.; Raidal, S.R.; Ramsay, J.; Quinn, J.C. Development of a model for investigation of perennial ryegrass toxicosis in sheep. N. Z. Vet. J. 2018, 66, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.M.; Blythe, L.L.; Duringer, J.M. The role of the oregon state university endophyte service laboratory in diagnosing clinical cases of endophyte toxicoses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7376–7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Ishizaki, I.; Ishizaka, M.; Kanbara, T.; Ishiguro-Takeda, Y. Lolitrem B residue in fat tissues of cattle consuming endophyte-infected perennial ryegrass straw. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2004, 16, 340–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finch, S.C.; Fletcher, L.R.; Babu, J.V. The evaluation of endophyte toxin residues in sheep fat. N. Z. Vet. J. 2011, 60, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.; Rochfort, S.; Read, E.; Deseo, M.; Jaehne, E.; Van Den Buuse, M.; Guthridge, K.; Combs, M.; Spangenberg, G.; Quinn, J. Tremorgenic effects and functional metabolomics analysis of lolitrem B and its biosynthetic intermediates. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finch, S.C.; Thom, E.R.; Babu, J.V.; Hawkes, A.D.; Waugh, C.D. The evaluation of fungal endophyte toxin residues in milk. N. Z. Vet. J. 2013, 61, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motoyama, T.; Hayashi, T.; Hirota, H.; Ueki, M.; Osada, H. Terpendole E, a kinesin Eg5 inhibitor, is a key biosynthetic intermediate of indole-diterpenes in the producing fungus Chaunopycnis alba. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludlow, E.J.; Vassiliadis, S.; Ekanayake, P.N.; Hettiarachchige, I.K.; Reddy, P.; Sawbridge, T.I.; Rochfort, S.J.; Spangenberg, G.C.; Guthridge, K.M. Analysis of the Indole Diterpene Gene Cluster for Biosynthesis of the Epoxy-Janthitrems in Epichloe Endophytes. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, P.J.; Smith, C.C.T.; de Belleroche, J.; Bradford, H.F.; Mantle, P.G.; Thomas, A.J.; Penny, R.H. Actions of tremorgenic fungal toxins on neurotransmitter release. J. Neurochem. 1980, 34, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, L.R. Managing Ryegrass-Endophyte Toxicoses. In Neotyphodium in Cool-Season Grasses; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, L.R.; Sutherland, B.L. Sheep responses to grazing ryegrass with AR37 endophyte. In Proceedings of the New Zealand Grassland Association, Dunedin; New Zealand Grassland Association: Wellington, New Zealand, 2018; pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Imlach, W.L.; Finch, S.C.; Dunlop, J.; Meredith, A.L.; Aldrich, R.W.; Dalziel, J.E. The molecular mechanism of “ryegrass staggers,” a neurological disorder of K+ channels. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 327, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirono, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Misono, K.; Zollinger, D.R.; Trimmer, J.S.; Rasband, M.N.; Misonou, H. BK channels localize to the paranodal junction and regulate action potentials in myelinated axons of cerebellar Purkinje cells. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 7082–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, U.S.; Cui, J. BK channel activation: Structural and functional insights. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, R.T.; Hawkes, A.D. The potent tremorgenic neurotoxins lolitrem B and aflatrem: A comparison of the tremor response in mice. Experientia 1986, 42, 823–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalziel, J.E.; Finch, S.C.; Dunlop, J. The fungal neurotoxin lolitrem B inhibits the function of human large conductance calcium-activated potassium channels. Toxicol. Lett. 2005, 155, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday-Finch, S.C. Aspects of the Chemistry and Toxicology of Indole-Diterpenoid Mycotoxins Involved in Tremorgenic Disorders in Livestock. Mycotoxin Res. 1997, 13, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imlach, W.L.; Finch, S.C.; Dunlop, J.; Dalziel, J.E. Structural determinants of lolitrems for inhibition of BK large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 605, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Gallagher, R.T.; Hawkes, A.D.; Munday, S.C.; Towers, N.R. Synthesis and tremorgenicity of paxitriols and lolitriol: Possible biosynthetic precursors of lolitrem B. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlier, J.; Diao, X.; Scheidweiler, K.B.; Huestis, M.A. Distinguishing intake of new synthetic cannabinoids ADB-PINACA and 5F-ADB-PINACA with human hepatocyte metabolites and high-resolution mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 1008–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrobel, I.; Friedecký, D.; Faber, E.; Najdekr, L.; Mičová, K.; Karlíková, R.; Adam, T. Novel sulphur-containing imatinib metabolites found by untargeted LC-HRMS analysis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 104, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlfarth, A.; Roman, M.; Andersson, M.; Kugelberg, F.C.; Diao, X.; Carlier, J.; Eriksson, C.; Wu, X.; Konradsson, P.; Josefsson, M.; et al. 25C-NBOMe and 25I-NBOMe metabolite studies in human hepatocytes, in vivo mouse and human urine with high-resolution mass spectrometry. Drug Test. Anal. 2017, 9, 680–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, K.F.M.; Leonforte, A.; Cunningham, P.J.; Walsh, J.R.; Allen, D.I.; Johnstone, G.R.; Kearney, G. Incidence of ryegrass endophyte (Neotyphodium lolii) and diversity of associated alkaloid concentrations among naturalised populations of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2000, 51, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.; Deseo, M.A.; Ezernieks, V.; Guthridge, K.; Spangenberg, G.; Rochfort, S. Toxic Indole Diterpenes from Endophyte-Infected Perennial Ryegrass Lolium perenne L.: Isolation and Stability. Toxins 2019, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
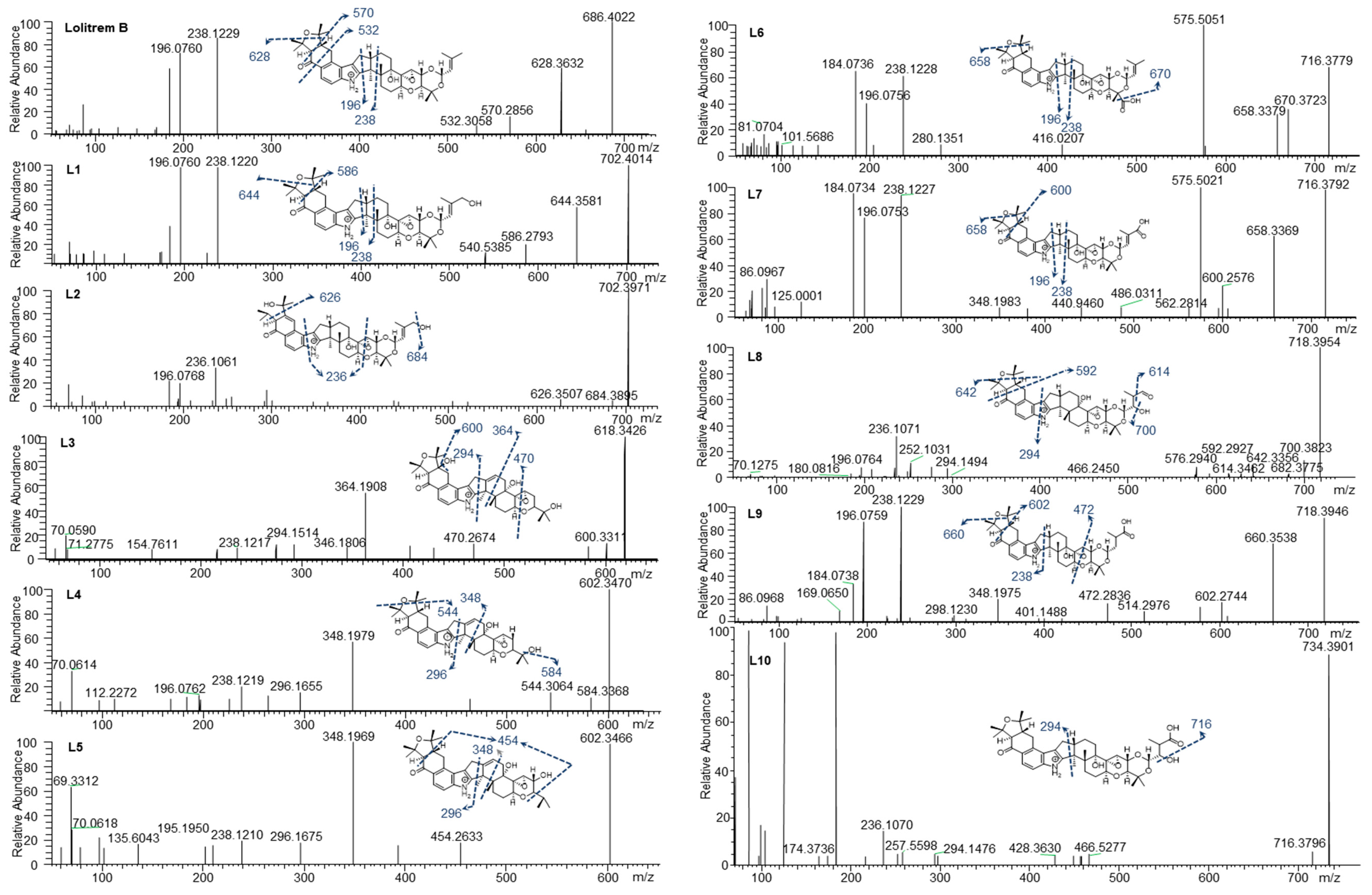
| Metabolite | Biotransformation | [M + H]+ m/z | Retention Time, Min | Mass Error, ppm | Diagnostic Product Ions, m/z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lolitrem B | C42H56NO7 | 686.4036 | 8.56 | −4.239 | 628.3632 570.2856, 532.3058, 238.1229, 196.0760 |
| L1 | C42H56NO8 | 702.4014 | 7.34 | 1.888 | 644.3581, 586.2793, 540.5385, 238.1220, 196.0760 |
| L2 | C42H56NO8 | 702.3971 | 7.83 | −0.718 | 684.3895, 626.3507, 236.1061, 196.0768 |
| L3 | C37H48NO7 | 618.3426 | 6.46 | 0.098 | 600.3311, 470.2674, 364.1908, 294.1514, 238.1217 |
| L4 | C37H48NO6 | 602.3470 | 7.38 | −0.738 | 584.3368, 544.3064, 348.1979, 296.1655, 238.1219, 196.0762 |
| L5 | C37H48NO6 | 602.3466 | 7.72 | 0.275 | 454.2633, 348.1969, 296.1675, 238.1210, 195.1950 |
| L6 | C42H54NO9 | 716.3779 | 7.77 | −1.817 | 670.3723, 658.3379, 238.1228, 196.0756 |
| L7 | C42H54NO9 | 716.3792 | 7.66 | −0.221 | 658.3369, 600.2576, 238.1227, 196.0753 |
| L8 | C42H56NO9 | 718.3954 | 6.45 | −0.346 | 700.3823, 642.3355, 592.2927, 236.1069, 196.0764 |
| L9 | C42H56NO9 | 718.3946 | 7.73 | −0.513 | 660.3538, 602.2744, 472.2836, 348.1975, 238.1229, 196.0759 |
| L10 | C42H56NO10 | 734.3923 | 6.89 | 0.281 | 716.3796, 236.1070, 294.1476, 236.1070 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reddy, P.; Elkins, A.; Hemsworth, J.; Guthridge, K.; Vassiliadis, S.; Read, E.; Spangenberg, G.; Rochfort, S. Identification and Distribution of Novel Metabolites of Lolitrem B in Mice by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2020, 25, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020372
Reddy P, Elkins A, Hemsworth J, Guthridge K, Vassiliadis S, Read E, Spangenberg G, Rochfort S. Identification and Distribution of Novel Metabolites of Lolitrem B in Mice by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2020; 25(2):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020372
Chicago/Turabian StyleReddy, Priyanka, Aaron Elkins, Joanne Hemsworth, Kathryn Guthridge, Simone Vassiliadis, Elizabeth Read, German Spangenberg, and Simone Rochfort. 2020. "Identification and Distribution of Novel Metabolites of Lolitrem B in Mice by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry" Molecules 25, no. 2: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020372
APA StyleReddy, P., Elkins, A., Hemsworth, J., Guthridge, K., Vassiliadis, S., Read, E., Spangenberg, G., & Rochfort, S. (2020). Identification and Distribution of Novel Metabolites of Lolitrem B in Mice by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Molecules, 25(2), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020372







