Emerging Techniques for Differentiation of Fresh and Frozen–Thawed Seafoods: Highlighting the Potential of Spectroscopic Techniques
Abstract
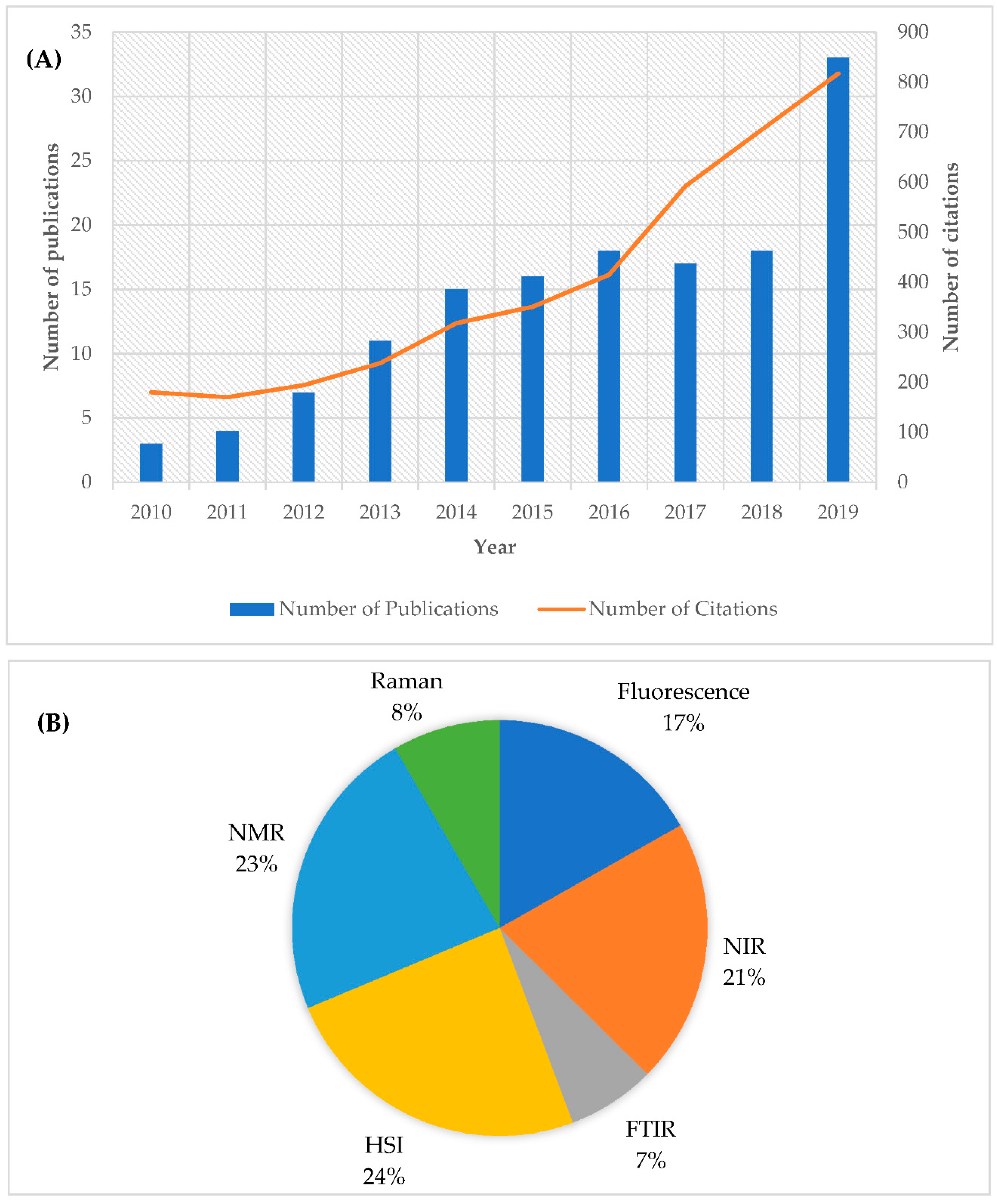
1. Introduction
2. Quality Change Occurring during Freezing, Frozen Storage, and Thawing of Seafoods
3. Analytical Methods Used to Detect Frozen–Thawed Seafoods
3.1. Enzymatic and Electrophoresis Methods
3.2. Histological Measurements: Changes in Muscle Structure and Microstructure
3.3. Other Detection Approaches
4. Detection of Frozen–Thawed Seafoods by Spectroscopic Techniques
4.1. UV-Vis and Fluorescence Spectroscopy
4.2. Infrared Spectroscopy and Hyperspectral Imaging
4.3. Raman Spectroscopy
4.4. NMR Spectroscopy
4.5. Impedance Spectroscopy
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, D.; Wu, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, F.; Xu, Y.; Xia, W. Recent advances in quality retention of non-frozen fish and fishery products: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, P.K.; Vatsa, S.; Srivastav, P.P.; Pathak, S.S. A comprehensive review on freshness of fish and assessment: Analytical methods and recent innovations. Food Res. Int. 2020, 133, 109157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozogul, Y. Innovative Technologies in Seafood Processing; Ozogul, Y., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; ISBN 9780815366447. [Google Scholar]
- Commission, E. Commission Regulation (EU) No1276/2011 of 8 December 2011 Amending Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards the Treatment to Kill Viable Parasites in Fishery Products for Human Consumption. Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, 50, 39–41. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.-W. Hyperspectral imaging technique for evaluating food quality and safety during various processes: A review of recent applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.F.; Zhang, M.; Adhikari, B.; Sun, J. Recent developments in novel freezing and thawing technologies applied to foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3620–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Sun, D.W.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Q.J. Improving the quality and safety of frozen muscle foods by emerging freezing technologies: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2925–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidini, S.; Varrà, M.O.; Zanardi, E. Approaching Authenticity Issues in Fish and Seafood Products by Qualitative Spectroscopy and Approaching Authenticity Issues in Fish and Seafood Products by Qualitative Spectroscopy and Chemometrics Products by Qualitative Spectroscopy and Chemomet. Molecules 2019, 24, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrez-Bagnis, V.; Sotelo, C.G.; Mendes, R.; Silva, H.; Kappel, K.; Schröder, U. Methods for Seafood Authenticity Testing in Europe. In Bioactive Molecules in Food Reference Series in Phytochemistry; Mérillon, J.-M., Ramawat, K.G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–55. ISBN 9783319545288. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament and Council of the European Union. Regulation (EU) No 1379/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 December 2013 on the common organization of the markets in fishery and aquaculture products, amending Council Regulations (EC) No 1184/2006 and (EC) No 1224/2009 and repealin. Off. J. Eur. Union 2013, L354, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bozzetta, E.; Pezzolato, M.; Cencetti, E.; Varello, K.; Abramo, F.; Mutinelli, F.; Ingravalle, F.; Teneggi, E. Histology as a valid and reliable tool to differentiate fresh from frozen-thawed fish. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 1536–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinacci, L.; Armani, A.; Guidi, A.; Nucera, D.; Shvartzman, D.; Miragliotta, V.; Coli, A.; Giannessi, E.; Stornelli, M.R.; Fronte, B.; et al. Histological discrimination of fresh and frozen/thawed fish meat: European hake (Merluccius merluccius) as a possible model for white meat fish species. Food Control 2018, 92, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzolato, M.; Baioni, E.; Maurella, C.; Varello, K.; Meistro, S.; Balsano, A.; Bozzetta, E. Distinguishing between fresh and frozen-thawed smoked salmon: Histology to detect food adulteration in high-value products. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, W.; Hu, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Xie, J. Effect of the number of freeze-thaw cycles number on the quality of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei): An emphasis on moisture migration and microstructure by LF-NMR and SEM. Aquac. Fish. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethuin, P.; Marlard, S.; Delosière, M.; Carapito, C.; Delalande, F.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Dehaut, A.; Lencel, V.; Duflos, G.; Grard, T. Differentiation between fresh and frozen-thawed sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fillets using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diop, M.; Watier, D.; Masson, P.-Y.; Diouf, A.; Amara, R.; Grard, T.; Lencel, P. Assessment of freshness and freeze-thawing of sea bream fillets (Sparus aurata) by a cytosolic enzyme: Lactate dehydrogenase. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlard, S.; Doyen, P.; Grard, T. Rapid Multiparameters Approach to Differentiate Fresh Skinless Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Fillets from Frozen-Thawed Ones. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2019, 28, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duflos, G.; Le Fur, B.; Mulak, V.; Becel, P.; Malle, P. Comparison of methods of differentiating between fresh and frozen-thawed fish or fillets. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2002, 82, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmetti, C.; Manfredi, M.; Brusadore, S.; Sciuto, S.; Esposito, G.; Ubaldi, P.G.; Magnani, L.; Gili, S.; Marengo, E.; Acutis, P.L.; et al. Two-dimensional gel and shotgun proteomics approaches to distinguish fresh and frozen-thawed curled octopus (Eledone cirrhosa). J. Proteom. 2018, 186, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H.; Shen, H.; Yu, X.; Luo, Y. Protein and lipid changes of mud shrimp (Solenocera melantho) during frozen storage: Chemical properties and their prediction. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 2043–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Karoui, R. Quality evaluation of fish and other seafood by traditional and nondestructive instrumental methods: Advantages and limitations. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1976–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y. Effects of frozen storage on physicochemical characteristics of bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) fillets. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Liang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, J.; Zou, X.; Zuo, M.; Guo, Z. Rapid detection of Atlantic salmon multi-quality based on impedance properties. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, A.; Masot, R.; Fernández-Segovia, I.; Ruiz-Rico, M.; Alcañiz, M.; Barat, J.M. Differentiation between fresh and frozen-thawed sea bream (Sparus aurata) using impedance spectroscopy techniques. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 19, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Segovia, I.; Fuentes, A.; Aliño, M.; Masot, R.; Alcañiz, M.; Barat, J.M. Detection of frozen-thawed salmon (Salmo salar) by a rapid low-cost method. J. Food Eng. 2012, 113, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shen, H.; Luo, Y. Study on the electric conduction properties of fresh and frozen-thawed grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) and tilapia(Oreochromis niloticus). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 2560–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidaček, S.; Medić, H.; Botka-Petrak, K.; Nežak, J.; Petrak, T. Bioelectrical impedance analysis of frozen sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). J. Food Eng. 2008, 88, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, K.E.; Stormo, S.K.; Skjelvareid, M.H.; Heia, K. Non-invasive assessment of packaged cod freeze-thaw history by hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Eng. 2017, 205, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimiya, T.; Sivertsen, A.H.; Heia, K. VIS/NIR spectroscopy for non-destructive freshness assessment of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fillets. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivertsen, A.H.; Kimiya, T.; Heia, K. Automatic freshness assessment of cod (Gadus morhua) fillets by Vis/Nir spectroscopy. J. Food Eng. 2011, 103, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderssen, K.E.; Stormo, S.K.; Skåra, T.; Skjelvareid, M.H.; Heia, K. Predicting liquid loss of frozen and thawed cod from hyperspectral imaging. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 135577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Heia, K.; Lindberg, S.; Nilsen, H. Spectroscopic Techniques for Monitoring Thermal Treatments in Fish and Other Seafood: A Review of Recent Developments and Applications. Foods 2020, 6, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Chen, W.H.; Tian, H.Y.; Liu, Y. Detection of Frozen-Thawed Cycles for Frozen Tilapia (Oreochromis) Fillets Using Near Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2018, 27, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamprese, C.; Casiraghi, E. Application of FT-NIR and FT-IR spectroscopy to fish fillet authentication. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoui, R.; Lefur, B.; Grondin, C.; Thomas, E.; Demeulemester, C.; De Baerdemaeker, J.; Guillard, A.S. Mid-infrared spectroscopy as a new tool for the evaluation of fish freshness. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velioğlu, H.M.; Temiz, H.T.; Boyaci, I.H. Differentiation of fresh and frozen-thawed fish samples using Raman spectroscopy coupled with chemometric analysis. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.-H.; Makino, Y.; Oshita, S.; García Martín, J.F. Hyperspectral imaging and multispectral imaging as the novel techniques for detecting defects in raw and processed meat products: Current state-of-the-art research advances. Food Control 2018, 84, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, D.-W.; Pu, H.; Zeng, X.-A.; Xiong, Z. Potential of visible/near-infrared hyperspectral imaging for rapid detection of freshness in unfrozen and frozen prawns. J. Food Eng. 2015, 149, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoui, R.; Hassoun, A.; Ethuin, P. Front face fluorescence spectroscopy enables rapid differentiation of fresh and frozen-thawed sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fillets. J. Food Eng. 2017, 202, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoui, R.; Thomas, E.; Dufour, E. Utilisation of a rapid technique based on front-face fluorescence spectroscopy for differentiating between fresh and frozen-thawed fish fillets. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, É.; Frencia, J.P.; Kane, E. Development of a rapid method based on front-face fluorescence spectroscopy for the monitoring of fish freshness. Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumilina, E.; Møller, I.A.; Dikiy, A. Differentiation of fresh and thawed Atlantic salmon using NMR metabolomics. Food Chem. 2020, 314, 126227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Sahar, A.; Lakhal, L.; Aït-Kaddour, A. Fluorescence spectroscopy as a rapid and non-destructive method for monitoring quality and authenticity of fish and meat products: Impact of different preservation conditions. LWT 2019, 103, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, D.-W. Hyperspectral imaging as an effective tool for quality analysis and control of fish and other seafoods: Current research and potential applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 37, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Måge, I.; Schmidt, W.F.; Temiz, H.T.; Li, L.; Kim, H.-Y.; Nilsen, H.; Biancolillo, A.; Aït-Kaddour, A.; Sikorski, M.; et al. Fraud in Animal Origin Food Products: Advances in Emerging Spectroscopic Detection Methods over the Past Five Years. Foods 2020, 9, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Bao, Y.; Lu, H.; Shen, H. Effects of different freezing treatments on the biogenic amine and quality changes of bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) heads during ice storage. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballin, N.Z.; Lametsch, R. Analytical methods for authentication of fresh vs. thawed meat—A review. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leygonie, C.; Britz, T.J.; Hoffman, L.C. Impact of freezing and thawing on the quality of meat: Review. Meat Sci. 2012, 91, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, Y.K.S. Theories of protein denaturation during frozen storage of fish flesh. In Advances in Food Research; Chichesters, C.O., Mrak, E.M., Stewart, G.F., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 275–311. ISBN 9780120164264. [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa, N.; Okazaki, E. Recent research on factors influencing the quality of frozen seafood. Fish. Sci. 2020, 86, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, D.W. Measuring and controlling ice crystallization in frozen foods: A review of recent developments. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 90, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstorebrov, I.; Eikevik, T.M.; Bantle, M. Effect of low and ultra-low temperature applications during freezing and frozen storage on quality parameters for fish. Int. J. Refrig. 2016, 63, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Okazaki, E.; Zheng, J.; Que, T.; Chen, S.; Hu, Y. Structure of northern snakehead (Channa argus) meat: Effects of freezing method and frozen storage. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 1166–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesvadba, P. Thermal Properties and Ice Crystal Development in Frozen Foods. In Frozen Food Science and Technology; Evans, J.A., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Estévez, M. Protein carbonyls in meat systems: A review. Meat Sci. 2011, 89, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, S.; Ahn, D.U. Protein Oxidation: Basic Principles and Implications for Meat Quality. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Okazaki, E.; Turza, S.; Yumiko, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Fukuda, Y. Non-destructive visible/NIR spectroscopy for differentiation of fresh and frozen-thawed fish. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, c506–c510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff-Lonergan, E.; Lonergan, S.M. Mechanisms of water-holding capacity of meat: The role of postmortem biochemical and structural changes. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, A.B.; Solva, M.V.D.; Lannes, S.C.D.S. Lipid oxidation in meat: Mechanisms and protective factors—A review. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 38, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M. Differentiation of fresh and frozen-thawed fish. In Handbook of Seafood and Seafood Products Analysis; Nollet, L.M.L., Toldrá, F., Eds.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 735–750. [Google Scholar]
- Muela, E.; Sañudo, C.; Campo, M.M.; Medel, I.; Beltrán, J.A. Effect of freezing method and frozen storage duration on instrumental quality of lamb throughout display. Meat Sci. 2010, 84, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Tan, M. Influence of multiple freeze-thaw cycles on quality characteristics of beef semimembranous muscle: With emphasis on water status and distribution by LF-NMR and MRI. Meat Sci. 2019, 147, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, F.; Krzewinski, F.; Le Fur, B.; N’Guessan, A.; Malle, P.; Kol, O.; Duflos, G. Differentiation of fresh and frozen/thawed fish, European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax), gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata), cod (Gadus morhua) and salmon (Salmo salar), using volatile compounds by SPME/GC/MS. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 2560–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasolato, L.; Balzan, S.; Riovanto, R.; Berzaghi, P.; Mirisola, M.; Ferlito, J.C.; Serva, L.; Benozzo, F.; Passera, R.; Tepedino, V.; et al. Comparison of visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy to authenticate fresh and frozen-thawed swordfish (xiphias gladius L). J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2012, 21, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberio, G.R.A.; Barbagallo, R.N.; Todaro, A.; Bono, G.; Spagna, G. Effect of freezing/thawing process in different sizes of blue fish in the Mediterranean through lysosomal enzymatic tests. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, A. Changes in the meat from aquaculture species during storage at low temperature and attempts for differentiation between thawed-frozen and fresh chilled meat. A review. Bulg. J. Vet. Med. 2007, 10, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Dalvi-Isfahan, M.; Jha, P.K.; Tavakoli, J.; Daraei-Garmakhany, A.; Xanthakis, E.; Le-Bail, A. Review on identification, underlying mechanisms and evaluation of freezing damage. J. Food Eng. 2019, 255, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurgisladottir, S.; Ingvarsdottir, H.; Torrissen, O.J.; Cardinal, M.; Hafsteinsson, H. Effects of freezing/thawing on the microstructure and the texture of smoked atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Food Res. Int. 2000, 33, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meistro, S.; Pezzolato, M.; Muscolino, D.; Giarratana, F.; Baioni, E.; Panebianco, A.; Bozzetta, E. Histology as a valid tool to differentiate fresh from frozen-thawed marinated fish. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 1457–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Grandois, J.; Ruas, M.; Kalisa, P.; Jolissaint, M.; Marchioni, E.; Aoudé-Werner, D.; Le Fur, B.; Ennahar, S. Detection of cold chain abuse in frozen and chilled salmon using the comet assay. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 54, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popelka, P.; Nagy, J.; Pipová, M.; Marcinčák, S.; Lenhardt, L. Comparison of chemical, microbiological and histological changes in fresh, frozen and double frozen rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Acta Vet. Brno 2014, 83, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, M.H. Basic Principles of Spectroscopy. In Food Analysis; Nielsen, S.S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, J.; Nørgaard, L.; Bro, R.; Engelsen, S.B. Multivariate autofluorescence of intact food systems. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1979–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElMasry, G.; Nakazawa, N.; Okazaki, E.; Nakauchi, S. Non-invasive sensing of freshness indices of frozen fish and fillets using pretreated excitation–emission matrices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Kondo, N.; Ogawa, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kanamori, K. Determination of K value for fish flesh with ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy and interval partial least squares (iPLS) regression method. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 141, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Shibata, M.; ElMasry, G.; Nakazawa, N.; Nakauchi, S.; Hagiwara, T.; Osako, K.; Okazaki, E. Expeditious prediction of post-mortem changes in frozen fish meat using three-dimensional fluorescence fingerprints. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; ElMasry, G.; Moriya, K.; Rahman, M.M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Ito, K.; Nakazawa, N.; Nakauchi, S.; Okazaki, E. Smart technique for accurate monitoring of ATP content in frozen fish fillets using fluorescence fingerprint. LWT 2018, 92, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Karoui, R. Front-face fluorescence spectroscopy coupled with chemometric tools for monitoring fish freshness stored under different refrigerated conditions. Food Control 2015, 54, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Suzuki, T.; Shirataki, Y.; Kuramoto, M.; Kondo, N. Freshness related fluorescent compound changes in Japanese dace fish (Tribolodon hakonensis) eye fluid during storage. Eng. Agric. Environ. Food 2018, 11, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omwange, K.A.; Al Riza, D.F.; Sen, N.; Shiigi, T.; Kuramoto, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Kondo, N.; Suzuki, T. Fish freshness monitoring using UV-fluorescence imaging on Japanese dace (Tribolodon hakonensis) fisheye. J. Food Eng. 2020, 287, 110111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Kondo, N.; Ogawa, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Shirataki, Y.; Wakita, Y. Classification of fresh and spoiled Japanese dace (Tribolodon hakonensis) fish using ultraviolet-visible spectra of eye fluid with multivariate analysis. Eng. Agric. Environ. Food 2016, 9, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M.M.; Martínez, E.; Saitua, E.; Rodríguez, R.; Pérez, I.; Olabarrieta, I. Non-invasive differentiation between fresh and frozen/thawed tuna fillets using near infrared spectroscopy (Vis-NIRS). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 78, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Okazaki, E. Classification of fresh and frozen-thawed fish by near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, C665–C668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, D.-W.; Pu, H.-B.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.-L. Integration of classifiers analysis and hyperspectral imaging for rapid discrimination of fresh from cold-stored and frozen-thawed fish fillets. J. Food Eng. 2015, 161, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottavian, M.; Fasolato, L.; Facco, P.; Barolo, M. Foodstuff authentication from spectral data: Toward a species-independent discrimination between fresh and frozen–thawed fish samples. J. Food Eng. 2013, 119, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottavian, M.; Fasolato, L.; Serva, L.; Facco, P.; Barolo, M. Data Fusion for Food Authentication: Fresh/Frozen-Thawed Discrimination in West African Goatfish (Pseudupeneus prayensis) Fillets. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Careche, M.; Sánchez-Alonso, I.; Martinez, I. Estimation of Quality in Frozen Fish by Low Field NMR. In Modern Magnetic Resonance, 2nd ed.; Webb, G.A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1901–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumilina, E.; Ciampa, A.; Capozzi, F.; Rustad, T.; Dikiy, A. NMR approach for monitoring post-mortem changes in Atlantic salmon fillets stored at 0 and 4 °C. Food Chem. 2015, 184, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Alonso, I.; Moreno, P.; Careche, M. Low field nuclear magnetic resonance (LF-NMR) relaxometry in hake (Merluccius merluccius, L.) muscle after different freezing and storage conditions. Food Chem. 2014, 153, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Alonso, I.; Martinez, I.; Sánchez-Valencia, J.; Careche, M. Estimation of freezing storage time and quality changes in hake (Merluccius merluccius, L.) by low field NMR. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancolillo, A.; Marini, F. Chapter Four—Chemometrics Applied to Plant Spectral Analysis. In Vibrational Spectroscopy for Plant Varieties and Cultivars Characterization Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry, Volume 80; Lopes, J., Sousa, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 53, pp. 69–104. ISBN 9788578110796. [Google Scholar]
- Sannia, M.; Serva, L.; Balzan, S.; Segato, S.; Novelli, E.; Fasolato, L. Application of near-infrared spectroscopy for frozen-thawed characterization of cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4437–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amigo, J.M. Carolina Santos Preprocessing of hyperspectral and multispectral images. In Data Handling in Science and Technology; Amigo, J.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 32, pp. 37–53. ISBN 9788578110796. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, J.; Wang, X.; Russel, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y. Comparisons of Fish Morphology for Fresh and Frozen-Thawed Crucian Carp Quality Assessment by Hyperspectral Imaging Technology. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zhang, D.; He, Y.; Liu, F.; Sun, D.W. Application of Visible and Near Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging to Differentiate Between Fresh and Frozen-Thawed Fish Fillets. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 2931–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maléchaux, A.; Le Dréau, Y.; Artaud, J.; Dupuy, N. Control chart and data fusion for varietal origin discrimination: Application to olive oil. Talanta 2020, 217, 121115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Reina, R.; Callejón, R.M.; Savorani, F.; Amigo, J.M.; Cocchi, M. Data fusion approaches in spectroscopic characterization and classification of PDO wine vinegars. Talanta 2019, 198, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, K.M.; Andrade, M.V.O.; Santos Filho, A.M.P.; Lasmar, M.C.; Sena, M.M. Detection and characterisation of frauds in bovine meat in natura by non-meat ingredient additions using data fusion of chemical parameters and ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2016, 205, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhao, B.; He, L. Raman instruments for food quality evaluation. In Evaluation Technologies for Food Quality; Zhong, J., Wang, X., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 119–143. ISBN 9780128142189. [Google Scholar]
- Rygula, A.; Majzner, K.; Marzec, K.M.; Kaczor, A.; Pilarczyk, M.; Baranska, M. Raman spectroscopy of proteins: A review. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 1061–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Vasefi, F.; Hellberg, R.S.; Akhbardeh, A.; Isaacs, R.B.; Yilmaz, A.G.; Hwang, C.; Baek, I.; Schmidt, W.F.; Kim, M.S. Detection of fish fillet substitution and mislabeling using multimode hyperspectral imaging techniques. Food Control 2020, 114, 107234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerath, F. Basic Principles of NMR. In Magnetism and Superconductivity in Iron-Based Superconductors as Probed by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance; Vieweg+Teubner Verlag: Dresden, Germany, 2012; Volume 9783834824, pp. 3–30. ISBN 9783834824233. [Google Scholar]
- Bertram, H.C. 1H NMR Relaxometry in Meat Science. In Modern Magnetic Resonance; Webb, G.A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1449–1462. [Google Scholar]
- Duflot, M.; Sánchez-Alonso, I.; Duflos, G.; Careche, M. LF 1H NMR T2 relaxation rate as affected by water addition, NaCl and pH in fresh, frozen and cooked minced hake. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, J.R.; Barsoukov, E. Impedance Spectroscopy Theory, Experiment, and Applications, 2nd ed.; Barsoukov, E., Macdonald, J.R., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 125, ISBN 9786468600. [Google Scholar]
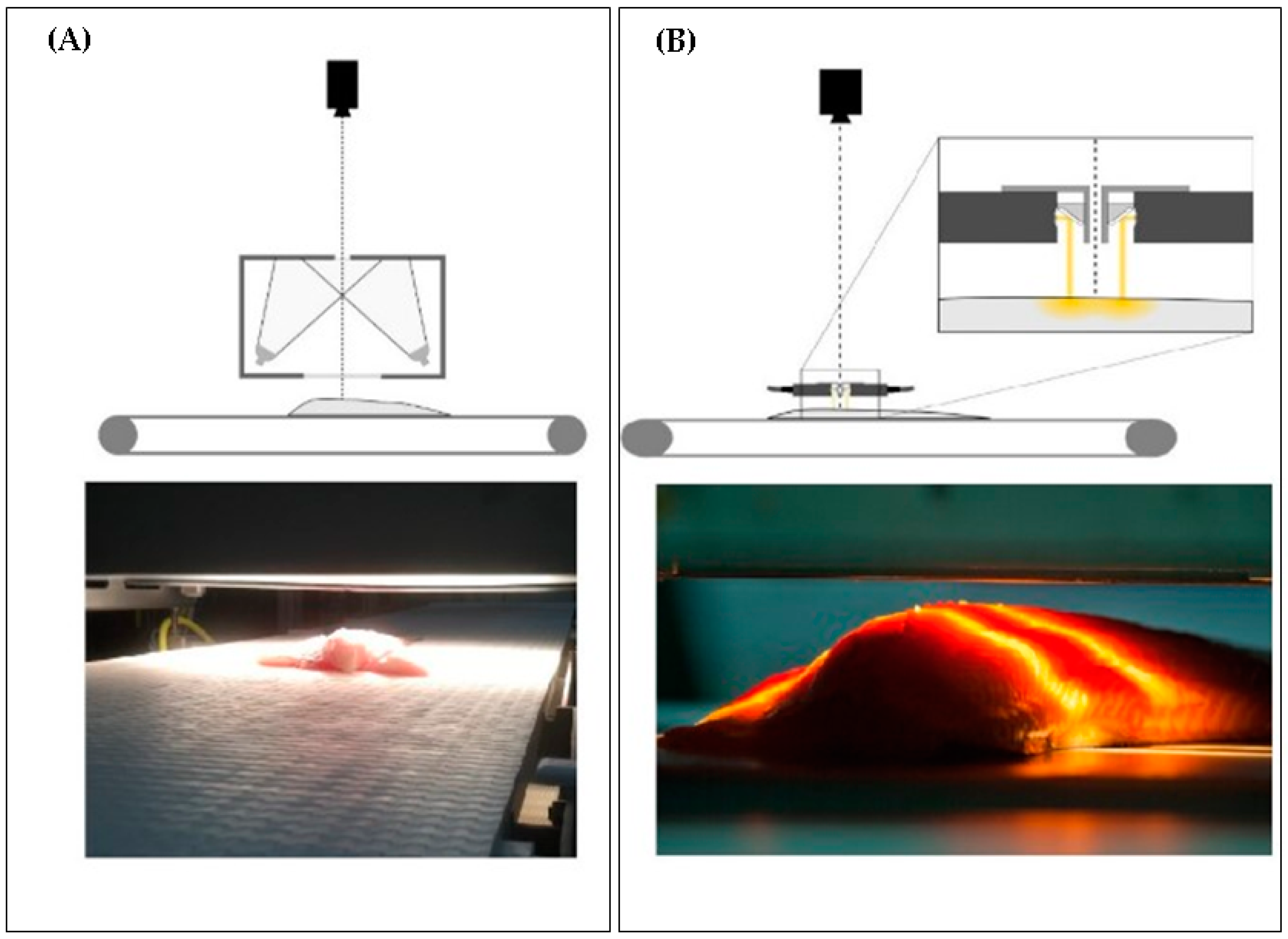
| Type of Spectroscopy | Wavelength Region | Wavelength Limits | Type of Transition | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorption, emission, and fluorescence | Ultraviolet | 10–380 nm | Bonding electrons in molecules | Accuracy, sensitivity/sample preparation |
| Absorption, emission, and fluorescence | Visible | 380–750 nm | Bonding electrons in molecules | Accuracy, sensitivity/limited range |
| Absorption | Near-infrared | 13,000–4000 cm−1 | Vibrational position of atoms in molecular bonds | Fast, no sample preparation/non-specific, water interferes, calibration |
| Mid-infrared | 4000–200 cm−1 | Fast, specific for functional groups/water interferes | ||
| Far-infrared | 200–10 cm−1 | Suitable for studying the anion–cation interaction/complex spectrum, difficult interpretation | ||
| Nuclear magnetic resonance | Radio wave | 1–1000 m | Nuclei orientation into a magnetic field | Accuracy/sample preparation, costs |
| Type of Food | Authenticity Issue | Analytical Technique | Modelling Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UV-Vis and Fluorescence Spectroscopy | ||||
| Whiting fillets | Fresh/frozen–thawed | FFFS | PCA, FDA | [40] |
| Cod, Mackerel, Salmon and Whiting fillets | Monitoring of fish freshness | FFFS | PCA, Mahalanobis distance method | [41] |
| Horse mackerel fillet | Prediction of post-mortem changes in frozen fish | EEM | PLSR | [76] |
| Horse mackerel fillet | Prediction ATP content in early stages post-mortem fish | EEM | PLSR | [77] |
| Whiting fillets | Monitoring fish freshness under different refrigerated conditions | FFFS | PCA, FDA | [78] |
| Japanese dace fish | Monitoring fish freshness during storage | EEM | Linear/exponential regression | [79] |
| Japanese dace fisheye | Prediction standard freshness index of k-value | EEM | PLSR | [80] |
| Japanese dace fish | freshness | UV-Vis | SVM, LDA, SIMCA | [81] |
| Infrared Spectroscopy and Hyperspectral Imaging | ||||
| Cod | Freezing history | Vis/NIR HSI | PCA | [28] |
| Cod | Fresh/frozen–thawed | Vis/NIR HSI | PCA + Rosenblatts perceptron | [30] |
| Swordfish | Fresh/frozen–thawed | NIR/Vis-NIR | PCA + multivariate binary logistic regression | [64] |
| Tuna | Fresh/frozen–thawed | Vis/NIR | PLS-DA | [82] |
| Horse mackerel | Fresh/frozen–thawed | NIR | PCA, MLR | [83] |
| Red sea bream | Fresh/frozen–thawed | Vis/NIR | PCA-LDA, SIMCA | [57] |
| Grass carp | Fresh/frozen–thawed | Vis/NIR HSI | SIMCA, LS-SVM, PNN | [84] |
| Several species | Fresh/frozen–thawed | NIR | PLS-DA | [85] |
| Goatfish | Fresh/frozen–thawed | Vis/NIR | PLS-DA; Multi-block PLS-DA | [86] |
| Atlantic salmon | Fresh/frozen–thawed | Vis/NIR Vis/NIR HSI | PLSR, kNN classifier | [29] |
| NMR Spectroscopy | ||||
| Several species (fish) | Effects of freezing, thawing, storage time and interaction between temperature, time, and freezing rate | LF 1H NMR | Several techniques | [87] |
| Atlantic salmon fillets | Monitoring of metabolites during cold storage and estimation of freshness indices | High-resolution NMR | - | [88] |
| Hake fillets | Monitoring of consequences of different freezing and storage conditions | Low-field NMR T2 relaxometry | - | [89] |
| Hake fillets | Quality changes and estimation of freezing storage time | Low-field NMR T2 relaxometry | PCA, PLSR | [90] |
| Impedance Spectroscopy | ||||
| Sea bream | Fresh/frozen samples, discrimination between different storage time and number of freezing cycles | Impedance spectroscopy | PCA-Stepwise LDA | [24] |
| Salmon | Fresh/frozen–thawed, effect of freezing storage times and number of freezing cycles | Impedance spectroscopy | PCA-Stepwise LDA | [25] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassoun, A.; Shumilina, E.; Di Donato, F.; Foschi, M.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Biancolillo, A. Emerging Techniques for Differentiation of Fresh and Frozen–Thawed Seafoods: Highlighting the Potential of Spectroscopic Techniques. Molecules 2020, 25, 4472. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194472
Hassoun A, Shumilina E, Di Donato F, Foschi M, Simal-Gandara J, Biancolillo A. Emerging Techniques for Differentiation of Fresh and Frozen–Thawed Seafoods: Highlighting the Potential of Spectroscopic Techniques. Molecules. 2020; 25(19):4472. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194472
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassoun, Abdo, Elena Shumilina, Francesca Di Donato, Martina Foschi, Jesus Simal-Gandara, and Alessandra Biancolillo. 2020. "Emerging Techniques for Differentiation of Fresh and Frozen–Thawed Seafoods: Highlighting the Potential of Spectroscopic Techniques" Molecules 25, no. 19: 4472. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194472
APA StyleHassoun, A., Shumilina, E., Di Donato, F., Foschi, M., Simal-Gandara, J., & Biancolillo, A. (2020). Emerging Techniques for Differentiation of Fresh and Frozen–Thawed Seafoods: Highlighting the Potential of Spectroscopic Techniques. Molecules, 25(19), 4472. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194472








