Abstract
In this paper, the microwave (MW)-assisted catalyst-free and mostly solvent-free Kabachnik–Fields reaction of amino alcohols, paraformaldehyde, and various >P(O)H reagents (dialkyl phosphites, ethyl phenyl-H-phosphinate, and secondary phosphine oxides) is reported. The synthesis of N-2-hydroxyethyl-α-aminophosphonate derivatives was optimized in respect of the temperature, the reaction time, and the molar ratio of the starting materials. A few by-products were also identified. N,N-Bis(phosphinoylmethyl)amines containing a hydroxyethyl group were also prepared by the double Kabachnik–Fields reaction of ethanolamine with an excess of paraformaldehyde and secondary phosphine oxides. The crystal structure of a 2-hydroxyethyl-α-aminophosphine oxide and a bis(phosphinoylmethyl)ethanolamine was studied by X-ray analysis.
1. Introduction
α-Aminophosphonate derivatives are among the most important organophosphorus compounds [1]. Due to the P–C–N moiety in the α-aminophosphonic skeleton, these compounds can be considered as the P-analogues of natural α-amino acids, which may mean a potential biological activity [2].
α-Aminophosphonates and α-aminophosphine oxides containing a reactive group may show special properties as compared to regular derivatives. In case of the closely related α-aminophosphines [3], a -COOH function on the molecule made possible further transformations and ensured a linkage for a polymer support [4,5].
Several reactive end groups can be easily built on the α-aminophosphonate skeleton. A possible reactive function is the hydroxyl group, which can be alkylated, acylated, or even phosphorylated [6]. Another option is the carboxylic function, which may also mean a possibility for further functionalizations [7]. α-Aminophosphonates containing a carboxylic group may be synthesized starting from amino acids [8,9].
The conventional preparations of α-aminophosphonates and related derivatives are the Kabachnik–Fields (phospha-Mannich) reaction, in which an amine, an oxo-compound, and a >P(O)H derivative react with each other [10,11], and the aza-Pudovik reaction, in which a >P(O)H reagent is added on the C=N double bond of an imine [12].
Over the seven decades from its discovery, several exotic catalysts and/or solvents have been tried out in the Kabachnik–Fields reaction [13,14]. However, in most cases, catalyst-free and often solvent-free approaches could be performed applying the microwave (MW) technique [9,13,15,16,17,18].
The Kabachnik–Fields condensation of amino alcohols is a less studied area. The condensation of ethanolamine was investigated with oxo compounds (e.g., paraformaldehyde [19], benzaldehyde [20], or acetone [19]) and dialkyl phosphites. A MW-assisted, Al2O3-catalyzed variation was also reported; however, the reactions were carried out in a kitchen MW oven [21]. Using a non-professional MW device, the precise measurement of the reaction parameters is practically impossible [22]. The phospha-Mannich reaction of propanolamine was performed in toluene [23]. In two instances, N-alkylamino alcohols served as the amine component, and the reactions were carried out in a solvent for a long reaction time [24,25]. A few special amino alcohols, such as 2-amino-2-methylpropanole [26] or (R)-2-phenylglycinol [27] were also tried out in the condensation.
The double Kabachnik–Fields reaction of an amino alcohol was mentioned in only one example [28]. The reaction was carried out for 12 h in THF.
The utilization of secondary phosphine oxides as the P-component was reported in one instance [29]. In this example, the conventional heating and the MW technique were compared, and the latter was found to be more efficient. However, it should be noted that the MW-assisted reactions were performed in a kitchen MW oven.
In this paper, we introduce the synthesis of 2-hydroxyethyl-α-aminophosphonates and 2-hydroxyethyl-α-aminophoshine oxides by the MW-assisted Kabachnik–Fields condensation of amino alcohols, paraformaldehyde, and >P(O)H reagents, such as dialkyl phosphites, ethyl phenyl-H-phosphinate, and secondary phosphine oxides. We also aimed at developing a green, catalyst-free and mostly solvent-free synthesis, as well as at the preparation of new derivatives.
2. Results and Discussion
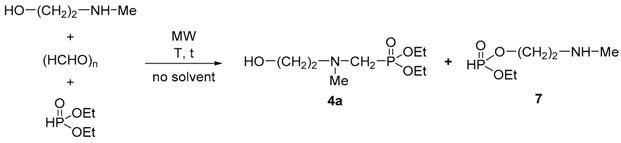
In the first step, the Kabachnik–Fields reaction of ethanolamine, paraformaldehyde, and diethyl phosphite was studied at 80 °C for 20 min in the absence of a solvent and a catalyst (Scheme 1). Although full conversion was achieved, beside the expected α-aminophosphonate (3), the mixture comprised 9% of the N-methylated-α-aminophosphonate (4a) and 3% of the N-ethylated-α-aminophosphonate (5a), as well as 34% of the 2-aminoethyl ethyl phosphite (6) based on 31P NMR.
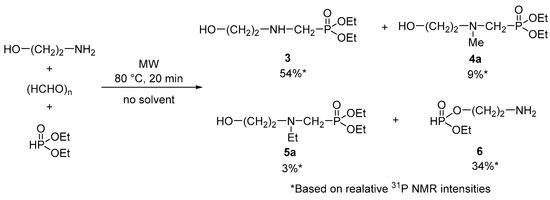
Scheme 1.
Condensation of ethanolamine, paraformaldehyde, and diethyl phosphite.
Formation of the N-methyl-α-aminophosphonate (4a) may be explained with the methylation by the paraformaldehyde, which side reaction was also observed in similar Kabachnik–Fields reactions of ethyl octyl phosphite [18] or alkyl phenyl-H-phosphinates [16]. The N-ethylated by-product (5a) may have formed in the alkylation of compound 3 by diethyl phosphite, which is also a known side reaction during similar transformations [30]. The 2-aminoethyl ethyl phosphite (6), which was present in the highest proportion of 34%, is probably the product of the alcoholysis of diethyl phosphite by ethanolamine [31,32].
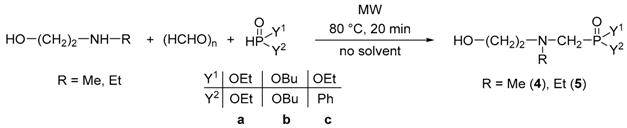
In the next series of experiments, the condensation of N-methylethanolamine, paraformaldehyde, and diethyl phosphite was investigated (Table 1). Carrying out the reaction at 60 °C for 20 min, the conversion was 85%, and the mixture comprised 96% of the desired N-hydroxyethyl-N-methyl-α-aminophosphonate (4a) and 4% of H-phosphonate 7 formed in the alcoholysis of diethyl phosphite by N-methylethanolamine (Table 1, Entry 1). In accordance to our previous experiences [32], the N-methyl-ethanolamine was much less active in the alcoholysis than the ethanolamine. Repeating the experiment at 80 °C, the reaction reached a full conversion, and the ratio of products 4a and 7 was 95:5, respectively (Table 1, Entry 2). The comparative thermal experiment under similar conditions was less selective, since 81% of the desired product (4a) and 19% of compound 7 were present in the mixture (Table 1, Entry 3). At 100 °C for 10 min, the ratio of the by-product (7) increased (Table 1, Entry 4). Based on the results obtained, the temperature of 80 °C and the reaction time of 20 min were found to be the optimum conditions (Table 1, Entry 2).

Table 1.
Optimization of the condensation of N-methylethanolamine, paraformaldehyde, and diethyl phosphite.
Next, the condensation of N-alkylethanolamines, paraformaldehyde, and dialkyl phosphites or ethyl phenyl-H-phosphinate was studied under the optimized conditions (80 °C and 20 min). The reactions were complete in all the cases. Using N-methylethanolamine, the diethyl (N-2-hydroxyethyl)(N-methyl)aminomethylphosphonate (4a) was isolated in a yield of 78% (Table 2, Entry 1). Changing for dibutyl phosphite, the desired product (4b) was obtained in a yield of 87% after column chromatography (Table 2, Entry 2). The ethyl phenyl-H-phosphinate was also tried out as the phosphorus reagent; however, the α-aminophosphinate (4c) could be prepared in a slightly lower yield (67%) as compared to the α-aminophosphonates (Table 2, Entry 3). Carrying out the experiments starting from N-ethylethanolamine, the condensations took place similarly (Table 2, Entries 4-6). The diethyl (5a) and the dibutyl 2-ethyl-2-hydroxyethyl-α-aminophoshhonate (5b) were prepared in yields of 72% and 79%, respectively; while using ethyl phenyl H-phosphinate as the P-reagent, product 5c was isolated in a yield of 64%.

Table 2.
Condensation of N-alkylethanolamines, paraformaldehyde, and dialkyl phosphites or ethyl phenyl-H-phosphinate.
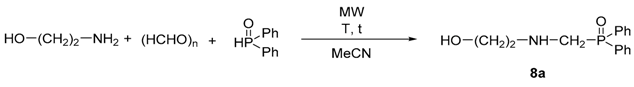
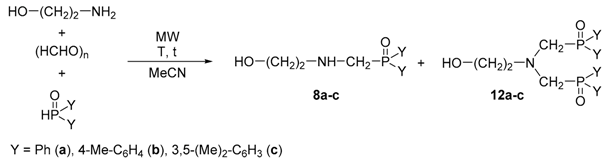
The transformations were also performed using secondary phosphine oxides (Table 3 and Table 4). In these reactions, some acetonitrile had to be used to overcome the heterogeneity. First, the condensation of ethanolamine, paraformaldehyde, and diphenylphosphine oxide was investigated (Table 3). In these experiments, only the desired product (8a) was formed, and no by-product was observed. Carrying out the reaction at 80 °C for 20 min, the α-aminophosphine oxide (8a) was obtained in a conversion of 58% (Table 3, Entry 1). Prolonging the irradiation to 30 min, a significantly higher conversion (86%) could be reached (Table 3, Entry 2). Any further increase in the reaction time did not cause a significant change in the conversion (Table 3, Entry 3). Performing the three-component reaction at 100 °C, the conversion was already 92% after 20 min; using a reaction time of 30 min, the condensation was complete (Table 3, entries 4 and 5).

Table 3.
Optimization of the condensation of ethanolamine, paraformaldehyde, and diphenylphosphine oxide.

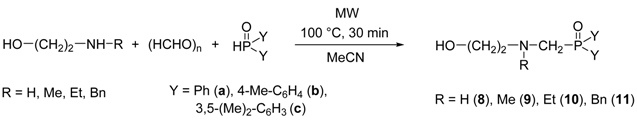
Table 4.
Condensation of amino alcohols, paraformaldehyde, and secondary phosphine oxides.
The condensation of ethanolamine with paraformaldehyde and other secondary phosphine oxides was also carried out (Table 4, entries 1–3). Using the optimized conditions (100 °C, 30 min), the reactions were complete in all the cases. Applying diphenylphosphine oxide as the P-component, the corresponding 2-hydroxyethyl-α-aminophosphine oxide (8a) was obtained in a yield of 96% after column chromatography (Table 4, Entry 1). Changing for bis(p-tolyl)phosphine oxide or bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)phosphine oxide, the reactions took place similarly, and the desired products (8b or 8c) were isolated in yields of 89% and 95%, respectively (Table 4, entries 2 and 3). The condensation was also extended for using N-alkylethanolamines (N-methyl-, N-ethyl-, or N-benzylethanolamine), and the corresponding α-aminophosphine oxide derivatives (9–11a–c) were obtained in high yields (88–96%) (Table 4, entries 4–12).
In the next round, the double Kabachnik–Fields condensation of ethanolamine with an excess of paraformaldehyde and secondary phosphine oxides was studied (Table 5). As the first experiment, the ethanolamine was reacted with two equivalents of the paraformaldehyde and the diphenylphosphine oxide at 100 °C for 1 h (Table 5, Entry 1). It was found that the mono α-aminophosphine oxide (8a) was the main product (75%), while the desired N,N-bis(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)ethanolamine (12a) was present in a proportion of only 25%. Increasing the temperature to 120 °C, the ratio of product 12a increased to 34% (Table 5, Entry 2). Prolonging the reaction time to 1.5 h, the composition did not change significantly (Table 5, Entry 3). As the next step, the effect of the molar ratio of starting materials was investigated (Table 5, entries 4–6). By using 2.5 equivalents of the diphenylphosphine oxide, the ratio of the mono (8a) and the bis product (12a) remained almost unchanged (Table 5, Entry 4). When both reagents (the paraformaldehyde and the diphenylphosphine oxide) were used in 2.5 equivalents quantity, the proportion of product 12a increased significantly (Table 5, Entry 5). Further increase in the molar ratios to three equivalents allowed a full transformation toward the N,N-bis(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)ethanolamine (12a), which was obtained in a yield of 95% after purification (Table 5, Entry 6). The double Kabachnik–Fields reaction was also carried out starting from bis(p-tolyl)phosphine oxide or bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)phosphine oxide using the optimized conditions (Table 5, entries 7 and 8). The p-tolyl-substituted product (12b) was synthesized in a yield of 93%, while product 12c could be isolated in a yield of 91%.

Table 5.
Double Kabachnik–Fields reaction of ethanolamine using excess of the paraformaldehyde and the secondary phosphine oxides.
In addition to the spectroscopic analysis, we have determined the crystal structure of 11a and 12a∙H2O by single-crystal XRD analysis (Figure 1). In the structure of 11a, an intramolecular O–H···O=P hydrogen bond is present between the hydroxy group as the donor and the P=O group as the acceptor. Moreover, intermolecular C–H···O=P interactions enable the formation of hydrogen-bonded chains, which are connected into layers via C–H∙∙∙π interactions (Figure S1, Table S1). In the structure of 12a∙H2O, an O–H···O hydrogen bond is present between the hydroxy group (donor) and the water hydrate molecule (acceptor). The H2O forms two more O–H···O=P hydrogen bonds with P=O groups of two adjacent molecules, resulting in the formation of wavy layers enhanced by C–H∙∙∙O interactions. These layers are connected into a supramolecular structure via additional C–H∙∙∙O interactions (Figure S2, Table S1).
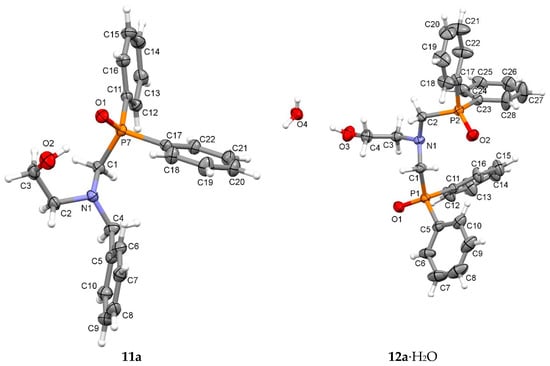
Figure 1.
X-ray structures and atom numbering of compounds 11a and 12a∙H2O. Probability ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% level.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
The reactions were carried out in a 300-W CEM Discover focused microwave reactor (CEM Microwave Technology Ltd., Buckingham, UK) equipped with a pressure controller using 10–50 W irradiation under isothermal conditions.
HPLC-MS measurements were performed with an Agilent 1200 liquid chromatography system coupled with a 6130 quadrupole mass spectrometer equipped with an ESI ion source (Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA, USA). Analysis was performed at 40 °C on a Gemini C18 column (150 mm × 4.6 mm, 3 µm; Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA) with a mobile phase flow rate of 0.6 mL/min. The composition of eluent A was 0.1% (NH4)(HCOO) in water; eluent B was 0.1% (NH4)(HCOO) and 8% water in acetonitrile. 0–3 min. 5% B, 3–13 min. gradient, 13–20 min. 95% B. The injection volume was 5 µL. The chromatographic profile was registered at 254 nm. The MSD operating parameters were as follows: positive ionization mode, scan spectra from m/z 100 to 1000, drying gas temperature 300 °C, nitrogen flow rate 12 L/min, nebulizer pressure 60 psi, and capillary voltage 4000 V.
High-resolution mass spectrometric measurements were performed using a Q-TOF Premier mass spectrometer in positive electrospray mode.
The 31P, 1H, 13C, and NMR spectra were taken in CDCl3 solution on a Bruker AV-300 spectrometer (Bruker AXS GmBH, Karlsruhe, Germany) operating at 121.5 MHz, 75.5 MHz, and 300 MHz, respectively. Chemical shifts are downfield relative to 85% H3PO4 and TMS.
3.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of the 2-Hydroxyethyl-α-aminophosphonates and -α-Aminophosphinates
The mixture of 1.0 mmol of amino alcohol [ethanolamine (0.06 mL), N-methylethanolamine (0.08 mL), or N-ethylethanolamine (0.10 mL)], 1.0 mmol of paraformaldehyde (0.03 g), and 1.0 mmol of >P(O)H reagent [diethyl phosphite (0.13 mL), dibutyl phosphite (0.20 mL), or ethyl phenyl-H-phosphinate (0.17 g)] was irradiated in a sealed tube at 80 °C for 20 min in a CEM Discover Microwave reactor equipped with a pressure controller. The crude product was purified by flash column chromatography using silica gel and dichloromethane–methanol 9:1 as the eluent. Thus, the following products were prepared:
Diethyl (N-2-hydroxyethyl)(N-methyl)aminomethylphosphonate (4a): Yield: 78% (0.18 g), yellow oil; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 26.6; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 16.5 (d, 3JCP = 5.9, OCH2CH3), 44.8 (d, 3JCP = 6.5, NCH3), 52.5 (d, 1JCP = 165.6, CH2P), 59.3 (HOCH2), 60.9 (d, 3JCP = 10.9, CH2CH2N), 62.2 (d, 2JCP = 7.1, OCH2CH3); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 1.34 (t, JHH = 7.1, 6H, OCH2CH3), 2.48 (s, 3H, NCH3), 2.69 (t, JHH = 5.2, 2H, CH2N), 2.87 (d, JHP = 10.6, 2H, CH2P), 3.62 (t, JHH = 5.2, 2H, HOCH2), 4.06–4.25 (m, 4H, OCH2CH3); [M + H]+found = 226.1201, C8H21NO4P requires 226.1208.
Dibutyl (N-2-hydroxyethyl)(N-methyl)aminomethylphosphonate (4b): Yield: 84% (0.24 g), yellow oil; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 25.7; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 13.6 (CH2CH3), 18.7 (CH2CH3), 32.6 (d, 3JCP = 5.8, CH2CH2CH3), 44.7 (d, 3JCP = 6.5, NCH3), 52.3 (d, 1JCP = 165.2, CH2P), 59.2 (HOCH2), 60.9 (d, 3JCP = 10.5, CH2CH2N) 65.9 (d, 2JCP = 7.1, OCH2CH2CH2); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 0.94 (t, JHH = 7.4, 6H, CH2CH3), 1.33-1.47 (m, 4H, CH2CH3), 1.62–1.72 (m, 4H, CH2CH2CH3), 2.48 (s, 3H, NCH3), 2.68 (t, JHH = 5.1, 2H, CH2N), 2.87 (d, JHP = 10.7, 2H, CH2P), 3.61 (t, JHH = 5.1, 2H, HOCH2), 4.02–4.14 (m, 4H, OCH2CH2CH2); [M + H]+found = 282.1814, C12H29NO4P requires 282.1834.
Ethyl ([N-2-hydroxyethyl][N-methyl]aminomethyl)(phenyl)phosphinate (4c): Yield: 67% (0.17 g), yellow oil; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 39.5; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 16.6 (d, 3JCP = 6.1, OCH2CH3), 45.1 (d, 3JCP = 5.3, NCH3), 55.9 (d, 1JCP = 122.5, CH2P), 59.3 (HOCH2) 61.1 (d, 2JCP = 6.8, OCH2CH2), 61.5 (d, 3JCP = 10.2, CH2N), 128.8 (d, 3JCP = 12.3, C3), 130.2 (d, 1JCP = 122.3, C1), 132.0 (d, 2JCP = 9.6, C2), 132.6 (d, JCP = 2.7, C4); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 1.32 (t, JHH = 7.0, 3H, OCH2CH3), 2.93 (s, 3H, NCH3), 2.56-2.69 (m, 2H, CH2N), 2.95-3.06 (m, 2H, CH2P), 3.43–3.58 (m, 2H, HOCH2), 3.89–3.95 (m, 1H, CHA, OCH2CH3), 4.09–4.19 (m, 1H, CHB, OCH2CH3), 7.47–7.54 (m, 2H, C2H), 7.55–7.61 (m, 1H, C4H), 7.78–7.86 (m, 2H, C3H); [M + H]+found = 258.1247, C12H21NO3P requires 258.1259.
Diethyl (N-ethyl)(N-2-hydroxyethyl)aminomethylphosphonate (5a): Yield: 72% (0.17 g), pale yellow oil; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 26.4; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 11.4 (NCH2CH3), 16.5 (d, 3JCP = 5.7, OCH2CH3), 49.1 (d, 1JCP = 168.1, CH2P), 50.5 (d, 3JCP = 7.7, NCH2CH3), 57.4 (d, 3JCP = 8.2, CH2CH2N), 59.8 (HOCH2), 62.2 (d, 2JCP = 7.0, OCH2CH3); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 1.05 (t, JHH = 7.0, 3H, NCH2CH3), 1.34 (t, JHH = 7.0, 6H, OCH2CH3), 2.69–2.81 (m, 4H, NCH2CH3, CH2CH2N), 2.91 (d, JHP = 10.2, 2H, CH2P), 3.58–3.63 (m, 2H, HOCH2), 4.11–4.21 (m, 4H, OCH2CH3); [M + H]+found = 240.1353, C9H23NO4P requires 240.1365.
Dibutyl (N-ethyl)(N-2-hydroxyethyl)aminomethylphosphonate (5b): Yield: 79% (0.23 g), pale yellow oil; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 26.5; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 11.5 (NCH2CH3), 13.6 (CH2CH2CH3), 18.7 (CH2CH2CH3), 32.7 (d, 3JCP = 5.8, OCH2CH2CH2), 49.0 (d, 1JCP = 167.5, CH2P), 50.4 (d, 3JCP = 7.6, NCH2CH3), 57.4 (d, 3JCP = 8.2, CH2CH2N), 59.7 (HOCH2), 66.0 (d, 2JCP = 7.3, OCH2CH3); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 0.94 (t, JHH = 7.4, 6H, CH2CH2CH3), 1.05 (t, JHH = 7.1, 3H, NCH2CH3), 1.32–1.49 (m, 4H, CH2CH2CH3), 1.58–1.73 (m, 4H, CH2CH2CH3), 2.66–2.82 (m, 4H, CH2CH2N, NCH2CH3), 2.91 (d, JHH = 10.3, 2H, CH2P), 3.60 (t, JHH = 5.1, 2H, HOCH2) 3.98–4.16 (m, 4H, OCH2CH3); [M + H]+found = 296.1976, C13H31NO4P requires 296.1991.
Ethyl ([N-ethyl][N-2-hydroxyethyl]aminomethyl)(phenyl)phosphinate (5c): Yield: 64% (0.17 g), pale yellow oil; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 40.1; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 11.2 (NCH2CH3), 16.5 (d, 3JCP = 6.1, OCH2CH3), 50.7 (d, 3JCP = 6.2, NCH2CH3), 52.8 (d, 1JCP = 124.0, CH2P), 57.7 (d, 3JCP = 7.8, CH2CH2N), 59.9 (HOCH2), 61.1 (d, 2JCP = 7.0, OCH2CH3), 128.7 (d, 3JCP = 12.2, C3), 130.1 (d, 1JCP = 121.8, C1), 132.0 (d, 2JCP = 9.6, C2) 132.5 (d, JCP = 2.8, C4); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 0.86 (t, JHH = 7.1, 3H, NCH2CH3), 1.32 (t, JHH = 7.1, 3H, OCH2CH3), 2.51–2.62 (m, 2H, CH2CH2N), 2.62-2.74 (m, 2H, NCH2CH3), 2.95–3.10 (m, 2H, CH2P), 3.48–3.59 (m, 2H, HOCH2) 3.88–3.98 (m, 1H, CHA, OCH2CH3) 4.10–4.19 (m, 1H, CHB, OCH2CH3) 7.47–7.53 (m, 2H, C2H), 7.55–7.61 (m, 1H, C4H), 7.78–7.84 (m, 2H, C3H); [M + H]+found = 272.1405, C13H23NO3P requires 272.1416.
3.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of the 2-Hydroxyethyl-α-aminophosphine oxides
The mixture of 1.0 mmol of amino alcohol [ethanolamine (0.06 mL), N-methylethanolamine (0.08 mL), N-ethylethanolamine (0.10 mL), or N-benzylethanolamine (0.14 mL)], 1.0 mmol of paraformaldehyde (0.03 g) and 1.0 mmol of secondary phosphine oxide [diphenylphosphine oxide (0.20 g), bis(p-tolyl)phosphine oxide (0.23 g), or bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)phosphine oxide (0.26 g)] in 2 mL of acetonitrile was irradiated in a sealed tube at 100 °C for 30 min in a CEM Discover Microwave reactor equipped with a pressure controller. The crude product was purified by flash column chromatography using silica gel and dichloromethane–methanol 9:1 as the eluent. Thus, the following products were prepared:
(2-Hydroxyethylaminomethyl)diphenylphosphine oxide (8a): Yield: 96% (0.27 g), white crystal; Mp: 84–85 °C; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 30.1; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 48.6 (d, 1JCP = 80.2, CH2P), 53.0 (d, 3JCP = 11.6, CH2N), 60.6 (HOCH2), 128.7 (d, 3JCP = 11.6, C3), 131.1 (d, 2JCP = 9.3, C2), 131.6 (d, 1JCP = 97.8, C1), 132.1 (d, JCP = 2.8, C4); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 2.76 (brs, 1H, NH), 2.84 (t, JHH = 5.1, 2H, CH2N), 3.53 (d, JHP = 6.9, 2H, CH2P), 3.61 (t, JHH = 5.0, 2H, OCH2), 7.38–7.60 (m, 6H, C2H, C4H), 7.68–7.86 (m, 4H, C3H); [M + H]+found = 276.1146, C15H19NO2P requires 276.1153.
(2-Hydroxyethylaminomethyl)bis(p-tolyl)phosphine oxide (8b): Yield: 89% (0.27 g), pale yellow viscous oil; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 30.8; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 21.6 (C4CH3), 48.6 (d, 1JCP = 79.7, CH2P), 53.0 (d, 1JCP = 11.7, CH2N), 60.5 (HOCH2), 128.2 (d, 1JCP = 100.6, C1), 129.5 (d, 3JCP = 11.9, C3), 131.1 (d, 2JCP = 9.6, C2), 142.6 (d, JCP = 2.7, C4); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 2.30 (s, 6H, C4CH3), 2.75 (t, JHH = 5.1, 2H, CH2N), 2.86 (brs, 1H, NH), 3.40 (d, JHP = 6.8, 2H, CH2P), 3.51 (t, JHH = 5.0, 2H, OCH2), 7.12–7.26 (m, 4H, C2H), 7.46–7.64 (m, 2H, C3H); [M + H]+found = 304.1456, C17H23NO2P requires 304.1466.
(2-Hydroxyethylaminomethyl)bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)phosphine oxide (8c): Yield: 95% (0.31 g), pale yellow viscous oil; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 30.5; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 21.4 (C3CH3), 48.3 (d, 1JCP = 78.1, CH2P), 52.8 (d, 3JCP = 10.5, CH2N), 60.5 (HOCH2), 128.5 (d, 2JCP = 9.2, C2), 131.4 (d, 1JCP = 97.0, C1), 133.9 (d, JCP = 2.8, C4), 138.5 (d, 3JCP = 12.3, C3); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 2.34 (s, 12H, C3CH3), 2.52 (brs, 1H, NH), 2.87 (t, JHH = 5.0, 2H, CH2N), 3.49 (d, JHP = 6.3, 2H, CH2P), 3.60 (t, JHH = 4.9, 2H, OCH2), 7.16 (s, 2H, C4H), 7.36 (d, JHH = 11.7, 4H, C2H); [M + H]+found = 332.1771, C19H27NO2P requires 332.1779.
[(N-2-Hydroxyethyl)(N-methyl)aminomethyl]diphenylphosphine oxide (9a): Yield: 95% (0.27 g), pale yellow viscous oil; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 28.5; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 45.6 (d, 3JCP = 5.4, NCH3), 56.9 (d, 1JCP = 89.0, CH2P), 59.5 (HOCH2), 61.9 (d, 3JCP = 8.1 CH2N), 128.7 (d, 3JCP = 11.4, C3), 131.1 (d, 2JCP = 9.0, C2), 131.7 (d, 1JCP = 97.0, C1), 132.0 (d, JCP = 2.7, C4); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 2.35 (s, 3H, NCH3), 2.71 (t, JHH = 5.0, 2H, CH2N), 3.38 (d, JHP = 4.6, 2H, CH2P), 3.59 (t, JHH = 5.0, 2H, OCH2), 7.45–7.52 (m, 4H, C2H), 7.52–7.57 (m, 2H, C4H), 7.75–7.83 (m, 4H, C3H); [M + H]+found = 290.1300, C16H21NO2P requires 290.1310.
[(N-2-Hydroxyethyl)(N-methyl)aminomethyl]bis(p-tolyl)phosphine oxide (9b): Yield: 96% (0.30 g), pale yellow viscous oil; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 29.0; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 21.6 (C4CH3), 45.6 (d, 3JCP = 5.5, NCH3), 57.1 (d, 1JCP = 89.1, CH2P), 59.5 (HOCH2), 61.9 (d, 3JCP = 8.0, CH2N), 128.6 (d, 1JCP = 99.4, C1), 129.4 (d, 3JCP = 11.8, C3), 131.1 (d, 2JCP = 9.3, C2), 142.5 (d, JCP = 2.8, C4); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 2.35 (s, 3H, NCH3), 2.40 (s, 6H, C4CH3), 2.70 (t, JHH = 5.0, 2H, CH2N), 3.33 (d, JHP = 4.8, 2H, CH2P), 3.58 (t, JHH = 5.0, 2H, OCH2), 7.20–7.37 (m, 4H, C4H), 7.58–7.74 (m, 4H, C3H); [M + H]+found = 318.1620, C18H25NO2P requires 318.1623.
(N-2-Hydroxyethyl)(N-methyl)aminomethyl]bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)phosphine oxide (9c): Yield: 93% (0.32 g), pale yellow viscous oil; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 28.9; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 21.3 (C3CH3), 45.7 (d, 3JCP = 5.0, NCH3), 56.8 (d, 1JCP = 88.3, CH2P), 59.4 (OCH2), 62.0 (d, 3JCP = 8.3 CH2N), 128.6 (d, 2JCP = 9.0, C2), 131.7 (d, 1JCP = 96.2, C1), 133.7 (d, JCP = 2.9, C4), 138.4 (d, 3JCP = 12.0, C3); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 2.35 (s, 12H, C3CH3), 2.38 (s, 3H, NCH3), 2.70 (t, JHH = 5.0, 2H, CH2N), 3.34 (d, JHP = 4.7, 2H, CH2P), 3.59 (t, JHH = 5.0, 2H, OCH2), 7.15 (s, 2H, C4H), 7.58–7.74 (d, JHH = 11.4, 4H, C2H), [M + H]+found = 346.1931, C20H29NO2P requires 346.1936.
[(N-Ethyl)(N-2-hydroxyethyl)aminomethyl]diphenylphosphine oxide (10a): Yield: 93% (0.32 g), white crystal; Mp: 81–82 °C; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 28.5; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 11.0 (NCH2CH3), 51.2 (d, 3JCP = 6.2, NCH2CH3), 54.1 (d, 1JCP = 90.2, CH2P), 58.0 (d, 3JCP = 5.9, CH2N), 60.3 (OCH2), 128.6 (d, 3JCP = 11.4, C3), 131.2 (d, 2JCP = 8.9, C2), 131.7 (d, 1JCP = 96.3, C1), 132.0 (d, JCP = 2.8, C4); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 0.83 (t, JHH = 7.1, 3H, NCH2CH3), 2.55 (q, JHH = 7.1, 2H, NCH2CH3), 2.84 (t, JHH = 5.1, 2H, CH2CH2N), 3.53 (d, JHP = 6.9, 2H, CH2P), 3.59 (t, JHH = 5.0, 2H, OCH2), 7.41–7.61 (m, 6H, C2H, C4H), 7.68–7.88 (m, 4H, C3H); [M + H]+found = 304.1457, C17H23NO2P requires 304.1466.
[(N-Ethyl)(N-2-hydroxyethyl)aminomethyl]bis(p-tolyl)phosphine oxide (10b): Yield: 91% (0.30 g), pale yellow viscous oil; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 29.1; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 11.0 (NCH2CH3), 21.6 (C4CH3), 51.2 (d, 3JCP = 6.4, NCH2CH3), 54.1 (d, 1JCP = 90.2, CH2P), 58.0 (d, 3JCP = 5.8, CH2N), 60.3 (OCH2), 128.6 (d, 1JCP = 99.0, C1), 129.4 (d, 3JCP = 11.8, C3), 131.2 (d, 2JCP = 8.9, C2), 142.5 (d, JCP = 2.8, C4); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 0.84 (t, JHH = 7.1, 3H, NCH2CH3), 2.40 (s, 6H, C4CH3), 2.56 (q, JHH = 7.1, 2H, NCH2CH3), 2.77 (t, JHH = 5.0, 2H, CH2CH2N), 3.38 (d, JHP = 4.2, 2H, CH2P), 3.60 (t, JHH = 4.9, 2H, OCH2), 7.21–7.33 (m, 4H, C2H), 7.59–7.71 (m, 4H, C3H); [M + H]+found = 332.1771, C19H27NO2P requires 332.1779.
[(N-Ethyl)(N-2-hydroxyethyl)aminomethyl]bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)phosphine oxide (10c): Yield: 88% (0.32 g), pale yellow viscous oil; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 29.1; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 10.9 (NCH2CH3), 21.3 (C3CH3), 51.1 (d, 3JCP = 6.0, NCH2CH3), 54.0 (d, 1JCP = 89.4, CH2P), 57.9 (d, 3JCP = 6.2, CH2N), 60.1 (OCH2), 128.7 (d, 2JCP = 9.0, C2), 131.6 (d, 1JCP = 95.9, C1), 133.7 (d, JCP = 2.9, C4), 138.3 (d, 3JCP = 12.0, C3); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 0.86 (t, JHH = 7.0, 3H, NCH2CH3), 2.35 (s, 12H, C3CH3), 2.57 (q, JHH = 7.0, 2H, NCH2CH3), 2.76 (t, JHH = 4.9, 2H, CH2CH2N), 3.40 (d, JHP = 4.1, 2H, CH2P), 3.60 (t, JHH = 4.9, 2H, OCH2), 7.15 (s, 2H, C4H) 7.37 (d, JHH = 11.3, 4H, C2H); [M + H]+found = 360.2075, C21H31NO2P requires 360.2092.
[(N-Benzyl)(N-2-hydroxyethyl)aminomethyl]diphenylphosphine oxide (11a): Yield: 90% (0.33 g), white crystal; Mp: 105–106 °C; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 28.9; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 53.9 (d, 1JCP = 87.9, CH2P), 58.5 (d, 3JCP = 4.7, CH2CH2N), 60.4 (OCH2), 61.7 (d, 3JCP = 7.7, C1CH2N), 127.2 (C4), 128.3 (C3), 128.7 (d, 3JCP = 11.5, C3′), 129.0 (C2), 131.1 (d, 2JCP = 9.1, C2′), 131.7 (d, 1JCP = 95.8, C1′), 132.0 (d, JCP = 2.7, C4), 137.9 (C1); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 2.88 (t, JHH = 4.9, 2H, CH2CH2N), 3.51 (d, JHP = 4.3, 2H, CH2P), 3.63 (t, JHH = 5.0, 2H, OCH2), 3.67 (s, 2H, C1CH2N), 6.98–7.11 (m, 2H, C2H), 7.13–7.25 (m, 3H, C3H, C4H), 7.38–7.57 (m, 6H, C2′H, C4′H), 7.61–7.78 (m, 4H, C3′H); [M + H]+found = 366.1615, C22H25NO2P requires 366.1623.
[(N-Benzyl)(N-2-hydroxyethyl)aminomethyl]bis(p-tolyl)phosphine oxide (11b): Yield: 89% (0.35 g), pale yellow viscous oil; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 29.5; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 21.6 (C4′CH3), 54.0 (d, 1JCP = 88.1, CH2P), 58.4 (d, 3JCP = 4.9, CH2CH2N), 60.3 (OCH2), 61.6 (d, 3JCP = 7.5, C1CH2N), 127.2 (C4), 127.8 (C3), 128.3 (C2), 128.5 (d, 1JCP = 99.4, C1′), 129.4 (d, 3JCP = 11.9, C3′), 131.1 (d, 2JCP = 9.4, C2′), 138.0 (C1), 142.4 (d, JCP = 2.8, C4); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 2.38 (s, 6H, C4CH3), 2.87 (t, JHH = 4.8, 2H, CH2CH2N), 3.46 (d, JHP = 4.5, 2H, CH2P), 3.62 (t, JHH = 5.0, 2H, OCH2), 3.67 (s, 2H, C1CH2N), 7.00–7.11 (m, 2H, C2H), 7.13–7.36 (m, 7H, C3H, C4H, C2′H), 7.47–7.66 (m, 4H, C3′H); [M + H]+found = 394.1926, C24H29NO2P requires 394.1936.
[(N-Benzyl)(N-2-hydroxyethyl)aminomethyl]bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)phosphine oxide (11c): Yield: 92% (0.39 g), pale yellow viscous oil; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 29.2; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 21.3 (C3CH3), 53.9 (d, 1JCP = 87.3, CH2P), 58.5 (d, 3JCP = 5.0, CH2CH2N), 60.3 (OCH2), 61.7 (d, 3JCP = 7.1, C1CH2N), 127.1 (C4), 128.2 (C3), 128.6 (d, 2JCP = 9.0, C2′), 128.9 (C2), 131.6 (d, 1JCP = 96.0, C1′), 133.7 (d, JCP = 2.7, C4), 138.2 (C1), 138.4 (d, 3JCP = 12.1, C3′); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 2.32 (s, 12H, C3CH3), 2.87 (t, JHH = 4.7, 2H, CH2CH2N), 3.48 (d, JHP = 4.1, 2H, CH2P), 3.63 (t, JHH = 5.0, 2H, OCH2), 3.67 (s, 2H, C1CH2N), 7.03–7.16 (m, 4H, C2H, C4′H), 7.17–7.24 (m, 3H, C3H, C4H), 7.31 (d, JHH = 11.4, 4H, C2′H); [M + H]+found = 422.2240, C26H33NO2P requires 422.2249.
3.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of the N,N-Bis(diarylphosphinoylmethyl)ethanolamines
The mixture of 1.0 mmol of ethanolamine (0.06 mL), 3.0 mmol of paraformaldehyde (0.09 g), and 3.0 mmol of secondary phosphine oxide [diphenylphosphine oxide (0.61 g), bis(p-tolyl)phosphine oxide (0.69 g), or bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)phosphine oxide (0.77 g)] in 2 mL of acetonitrile was irradiated in a sealed tube at 120 °C for 1 h in a CEM Discover Microwave reactor equipped with a pressure controller. The crude product was purified by flash column chromatography using silica gel and dichloromethane–methanol 9:1 as the eluent. Thus, the following products were prepared:
N,N-Bis(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)ethanolamine (12a): Yield: 95% (0.46 g), white crystal; Mp: 146–147 °C; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 28.9; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 55.5 (dd, 1JCP = 81.2, 3JCP = 5.7, CH2P), 59.9 (HOCH2), 60.3 (t, 3JCP = 5.3, CH2N), 128.6 (m, C3), 131.1 (m, C2), 131.8 (d, 1JCP = 96.3, C1), 132.0 (brs, C4); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 3.05 (t, JHH = 4.9, 2H, CH2N), 3.56 (t, JHH = 4.9, 2H, HOCH2), 3.82 (d, JHP = 3.9, 4H, CH2P), 7.33–7.56 (m, 12H, C2H, C4H) 7.64–7.82 (m, 8H, C3H); [M + H]+found = 490.1685, C28H30NO3P2 requires 490.1701.
N,N-Bis(di-p-tolyl)phosphinoylmethyl)ethanolamine (12b): Yield: 93% (0.51 g), white crystal*; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 29.4; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 21.6 (C4CH3), 55.5 (dd, 1JCP = 81.2, 3JCP = 5.5, CH2P), 59.9 (HOCH2), 60.3 (t, 3JCP = 4.9, CH2N), 128.8 (d, 1JCP = 98.5, C1), 129.3 (m, C3), 131.1 (m, C2), 142.3 (brs, C4); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 2.36 (s, 12H, C4CH3), 3.02 (t, JHH = 5.0, 2H, CH2N), 3.54 (t, JHH = 4.7, 2H, HOCH2), 3.73 (d, JHP = 3.7, 4H, CH2P), 7.07–7.32 (m, 8H, C2H) 7.46–7.70 (m, 8H, C3H); [M + H]+found = 546.2308, C32H38NO3P2 requires 546.2326. *No sharp melting point was observed.
N,N-Bis(3,5-dimethylphenylphosphinoylmethyl)ethanolamine (12c): Yield: 91% (0.55 g), pale yellow crystal; Mp: 128–129 °C; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 28.6; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 21.3 (C3CH3), 55.0 (dd, 1JCP = 78.8, 3JCP = 3.9, CH2P), 59.9 (HOCH2), 60.4 (t, 3JCP = 4.3, CH2N), 128.5 (m, C2), 132.2 (d, 1JCP = 98.1, C1), 133.6 (brs, C4), 138.3 (m, C3); 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 2.29 (s, 24H, C3CH3), 2.99 (t, JHH = 4.8, 2H, CH2N), 3.57 (t, JHH = 4.9, 2H, HOCH2), 3.75 (s, 4H, CH2P), 7.09 (s, 4H, C4H) 7.32 (d, JHH = 11.3, 8H, C2H); [M + H]+found = 602.2926, C36H46NO3P2 requires 602.2952.
3.5. Crystal Structure Determination
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction data of 11a and 12a∙H2O were collected on an Agilent Technologies SuperNova Dual diffractometer using Mo-Kα radiation (λ = 0.71073 Å) at room temperature. The data were processed using CrysAlis Pro [33]. The structures were solved by ShelXT [34] using intrinsic phasing and refined by a full-matrix least-squares procedure based on F2 with ShelXL [35] using Olex2 program suite [36]. All the non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically. Hydrogen atoms were readily located in difference Fourier maps, and were subsequently treated as riding atoms in geometrically idealized positions with C–H = 0.93 Å (aromatic) or 0.97 Å (methylene), O–H = 0.82 Å, and with Uiso(H) = kUeq(C,O), where k = 1.5 for the hydroxyl group and 1.2 for all the H atoms bonded to C atoms, unless otherwise noted. In 12a, H2O H atoms bonded to water solvate molecule O4 were refined restraining the bonding distances with Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq(O). Crystal structure data are deposited with the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre under CCDC 1,906,625 (11a) and 1,906,626 (12a∙H2O), and can be obtained free of charge via http://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/conts/retrieving.html (or from the CCDC, 12 Union Road, Cambridge CB2 1EZ, UK; Fax: +44 1223 336033; E-mail: deposit@ccdc.cam.ac.uk).
4. Conclusions
In summary, we have developed a facile, catalyst-free and mostly solvent-free MW-assisted method for the synthesis of N-2-hydroxyethyl-α-aminophosphonates and N-2-hydroxyethyl-α-aminophosphine oxides, as well as N,N-bis(diarylphosphinoylmethyl)ethanolamines by the three-component reaction of amino alcohols, paraformaldehyde, and dialkyl phosphites or diarylphosphine oxides. This method is a novel approach for the preparation of N-2-hydroxyethyl-α-aminophosphine oxides and N,N-bis(diarylphosphinoylmethyl)ethanolamines. Altogether, 21 derivatives were synthesized and fully characterized, and all of them are new compounds. The crystal structure of [(N-benzyl)(N-2-hydroxyethyl)aminomethyl]diphenylphosphine oxide (11a) and N,N-bis(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)ethanolamine (12a) was studied by single-crystal XRD analysis.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary data associated with this article are available online. X-ray crystallographic data and copies of 31P, 1H, and 13C NMR spectra for all compounds synthesized are presented. Figure S1: (a) Chain formation via C–H∙∙∙O hydrogen bonding in 11a. (b) Layer formation via C–H∙∙∙π interactions. Figure S2: (a) Layer formation via O–H∙∙∙O hydrogen bonding in 12a∙H2O along ab-plane. (b) Packing of layers along c-axis. Table S1: Hydrogen bond geometry for 11a and 12a∙H2O. Table S2: Essential crystallographic data of the 11a and 12a∙H2O single-crystal diffraction experiments and model refinements.
Author Contributions
Á.T. and E.S. performed the experiments. F.P. performed the crystal structure analysis. E.B. and G.K. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools. E.B., Á.T. and G.K. wrote the paper.
Funding
The project was supported by the Hungarian Research Development and Innovation Office (FK123961 and K119202), by the bilateral Hungarian-Slovenian Science and Technology Cooperation project (2018-2.1.11-TÉT-SI-2018-00008). E.B. was supported by the János Bolyai Research Scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences (BO/00278/17/7), and by the ÚNKP-18-4-BME-131 New National Excellence Program of the Ministry of Human Capacities. Á.T. was supported by the ÚNKP-18-3-III-BME-251 New National Excellence Program of the Ministry of Human Capacities.
Acknowledgments
F.P. thanks the EN-FIST Centre of Excellence, Ljubljana, Slovenia, for using the SuperNova diffractometer.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hudson, H.R.; Kukhar, V.P. Aminophosphonic and Aminophosphinic Acids: Chemistry and Biological Activity; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2000; ISBN 978-0-471-89149-9. [Google Scholar]
- Tajti, Á.; Keglevich, G. The Importance of Organophosphorus Compounds as Biologically Active Agents; Organophosphorus Chemistry, Keglevich, G., Eds.; Walter de Gruyter GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 53–65. ISBN 978-3-11-053453-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bálint, E.; Tajti, Á.; Tripolszky, A.; Keglevich, G. Synthesis of platinum, palladium and rhodium complexes of α-aminophosphine ligands. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 4755–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Aroya, B.B.-N.; Portnoy, M. Solid-phase synthesis of an α-aminophosphine library. J. Comb. Chem. 2001, 3, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Aroya, B.B.-N.; Portnoy, M. Preparation of α-aminophosphines on solid support: Model studies and parallel synthesis. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 5147–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patai, S. The Hydroxyl Group; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1971; ISBN 9780471669395. [Google Scholar]
- Patai, S. Carboxylic Acids and Esters; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1969; ISBN 9780471669197. [Google Scholar]
- Bálint, E.; Fazekas, E.; Drahos, L.; Keglevich, G. The Synthesis of N,N-Bis(dialkoxyphosphinoylmethyl)- and N,N-Bis(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)glycine Esters by the Microwave-Assisted Double Kabachnik–Fields Reaction. Heteroatom Chem. 2013, 24, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, E.; Fazekas, E.; Kóti, J.; Keglevich, G. Synthesis of N,N-Bis(dialkoxyphosphinoylmethyl)- and N,N-Bis(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-β- and γ-amino acid Derivatives by the Microwave-Assisted Double Kabachnik–Fields Reaction. Heteroatom Chem. 2015, 26, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabachnik, M.I.; Medved, T.Y. New synthesis of aminophosphonic acids. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1952, 83, 689–692. [Google Scholar]
- Fields, E.K. The synthesis of esters of substituted amino phosphonic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 1528–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudovik, A.N. Addition of dialkyl phosphites to imines. New method of synthesis of esters of amino phosphonic acids. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1952, 83, 865–869. [Google Scholar]
- Keglevich, G.; Szekrenyi, A. Eco-friendly accomplishment of the extended Kabachnik-Fields reaction; a solvent-and catalyst-free microwave-assisted synthesis of α-aminophosphonates and α-aminophosphine oxides. Lett. Org. Chem. 2008, 5, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, E.; Tajti, Á.; Tripolszky, A. Synthesis of α-aminophosphonates by the Kabachnik–Fields Reaction and by the Pudovik Reaction. In Organophosphorus Chemistry; Keglevich, G., Ed.; Walter de Gruyter GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 108–147. ISBN 978-3-11-053453-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bálint, E.; Tóth, R.E.; Keglevich, G. Synthesis of alkyl α-aminomethyl-phenylphosphinates and N,N-bis(alkoxyphenylphosphinylmethyl)amines by the microwave-assisted Kabachnik–Fields reaction. Heteroatom Chem. 2016, 27, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, E.; Tripolszky, A.; Jablonkai, E.; Karaghiosoff, K.; Czugler, M.; Mucsi, Z.; Kollár, L.; Pongrácz, P.; Keglevich, G. Synthesis and use of α-aminophosphine oxides and N,N-bis(phosphinoylmethyl)amines—A study on the related ring platinum complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2016, 801, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajti, Á.; Bálint, E.; Keglevich, G. Synthesis of ethyl octyl α-aminophosphonate derivatives. Curr. Org. Synth. 2016, 13, 638–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, E.; Tajti, Á.; Kalocsai, D.; Mátravölgyi, B.; Konstantin, K.; Czugler, M.; Keglevich, G. Synthesis and utilization of optically active α-aminophosphonate derivatives by Kabachnik-Fields reaction. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 5659–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsukov, A.V.; Zhadanov, B.V.; Matkovskaya, T.A.; Kaslina, N.A.; Polyakova, I.A.; Yaroshenko, G.F.; Kessenikh, A.V.; Dyatlova, N.M. Synthesis of New Complexons of the Aliphatic Series and Investigation of the Mechanism of Acidic Dissociation. Zh. Obshch. Khim. 1985, 55, 1594–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, Z.; Zou, R.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, Y. A Facile and Clean Procedure for Preparation of α-Aminophosphonates via a Rotary Evaporator Equipped with Circulating Water Vacuum Pumps. Phosphorus, Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2010, 185, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboudin, B.; Nazari, R. Microwave-assisted synthesis of 1-aminoalkyl phosphonates under solvent-free conditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 8211–8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, E.; Keglevich, G. The Spread of the Application of the Microwave Technique in Organic Synthesis. In Milestones in Microwave Chemistry; Keglevich, G., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; p. 110. ISBN 978-3-319-30632-2. [Google Scholar]
- Zamorano-Octaviano, J.; Hernández-Martínez, A.; Ortega-Guevara, A.; Linzaga-Elizalde, I.; Höpfl, H. Linear and cyclic aminomethanephosphonic acid esters derived from benzaldehyde derivatives, 3-aminopropanol, and diethyl phosphite. Heteroatom Chem. 2006, 17, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floch, V.; Le Bolc’h, G.; Gable-Guillaume, C.; Le Bris, N.; Yaouanc, J.-J.; des Abbayes, H.; Férec, C.; Clément, J.-C. Phosphonolipids as non-viral vectors for gene therapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 33, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krchová, T.; Herynek, V.; Gálisová, A.; Blahut, J.; Hermann, P.; Kotek, J. Eu (III) Complex with DO3A-amino-phosphonate Ligand as a Concentration-Independent pH-Responsive Contrast Agent for Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS). Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 2078–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, S.; Clément, J.-L.; Muller, A.; Culcasi, M.; Pietri, S. Synthesis and 31P NMR characterization of new low toxic highly sensitive pH probes designed for in vivo acidic pH studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2002, 10, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, A.; Karimian, A.; Ipaktschi, J. Lithium perchlorate/diethylether catalyzed aminophosphonation of aldehydes. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 6729–6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chougrani, K.; Boutevin, B.; David, G.; Boutevin, G. New N,N-amino-diphosphonate-containing methacrylic derivatives, their syntheses and radical copolymerizations with MMA. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkasov, R.A.; Garifzyanov, A.R.; Talan, A.S.; Davletshin, R.R.; Kurnosova, N.V. Synthesis of new liophilic functionalized aminomethylphosphine oxides and their acid-base and membrane-transport properties toward acidic substrates. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2009, 79, 1835–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gancarz, R. Alkylating Properties of Dialkyl Phosphites. Phosphorus, Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 1994, 92, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keglevich, G.; Bálint, E.; Tajti, Á.; MÁtravölgyi, B.; Balogh, G.T.; Bálint, M.; Ilia, G. Microwave-assisted alcoholysis of dialkyl phosphites by ethylene glycol and ethanolamine. Pure Appl. Chem. 2014, 86, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajti, Á.; Keglevich, G.; Bálint, E. Microwave-assisted alcoholysis of dialkyl H-phosphonates by diols and amino alcohols. Phosphorus, Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2017, 192, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CrysAlisPro, version 1.171.39.46e; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction: Yarnton, UK, 2018.
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystalstructure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 4a–c, 5a–c, 8–11a–c and 12a–c are available from the authors. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).