The Effect of Concentration on the Cross-Linking and Gelling of Sodium Carbonate-Soluble Apple Pectins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Monosaccharide Composition and Methylesterification
2.2. Nanostructure
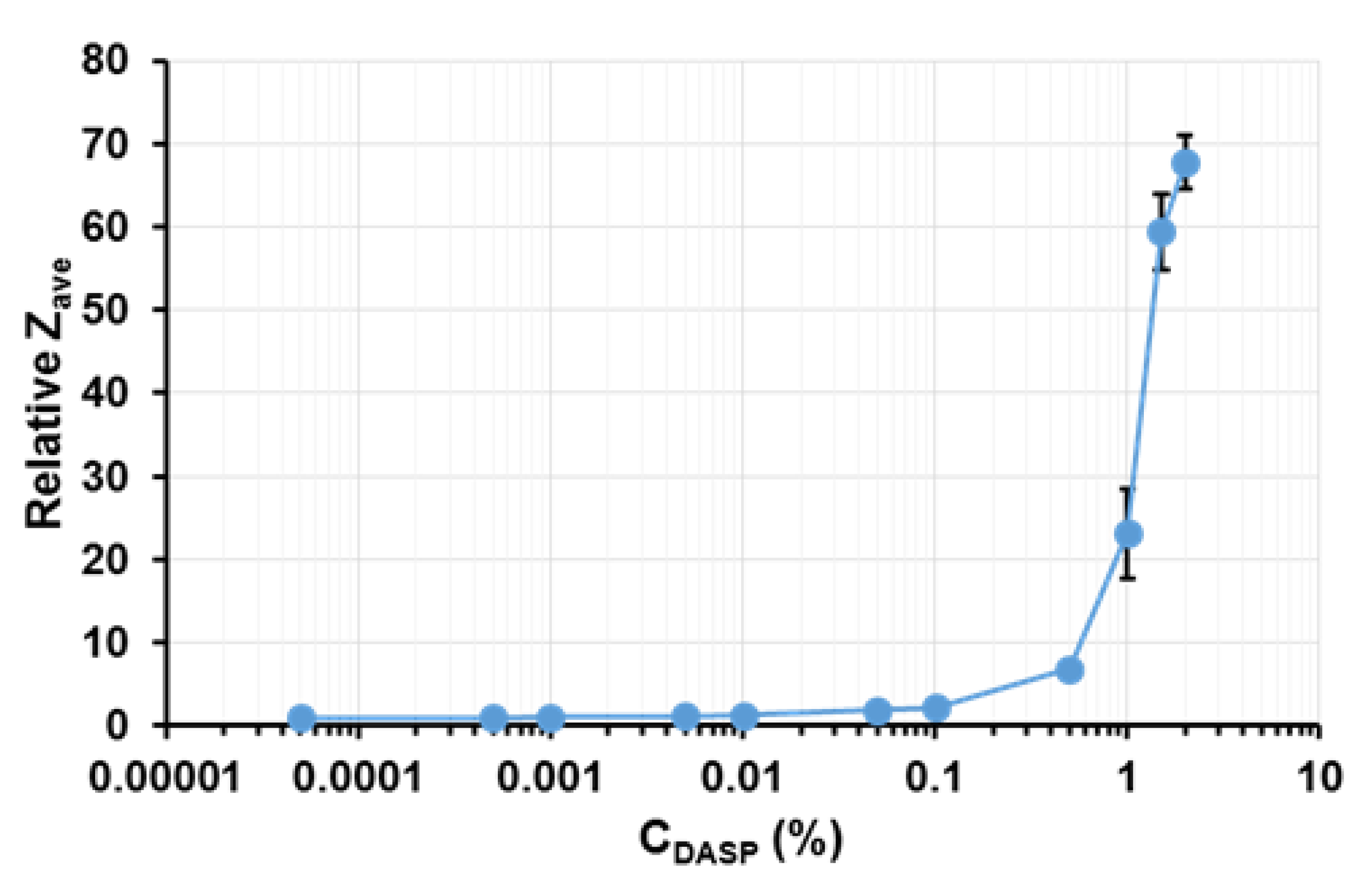
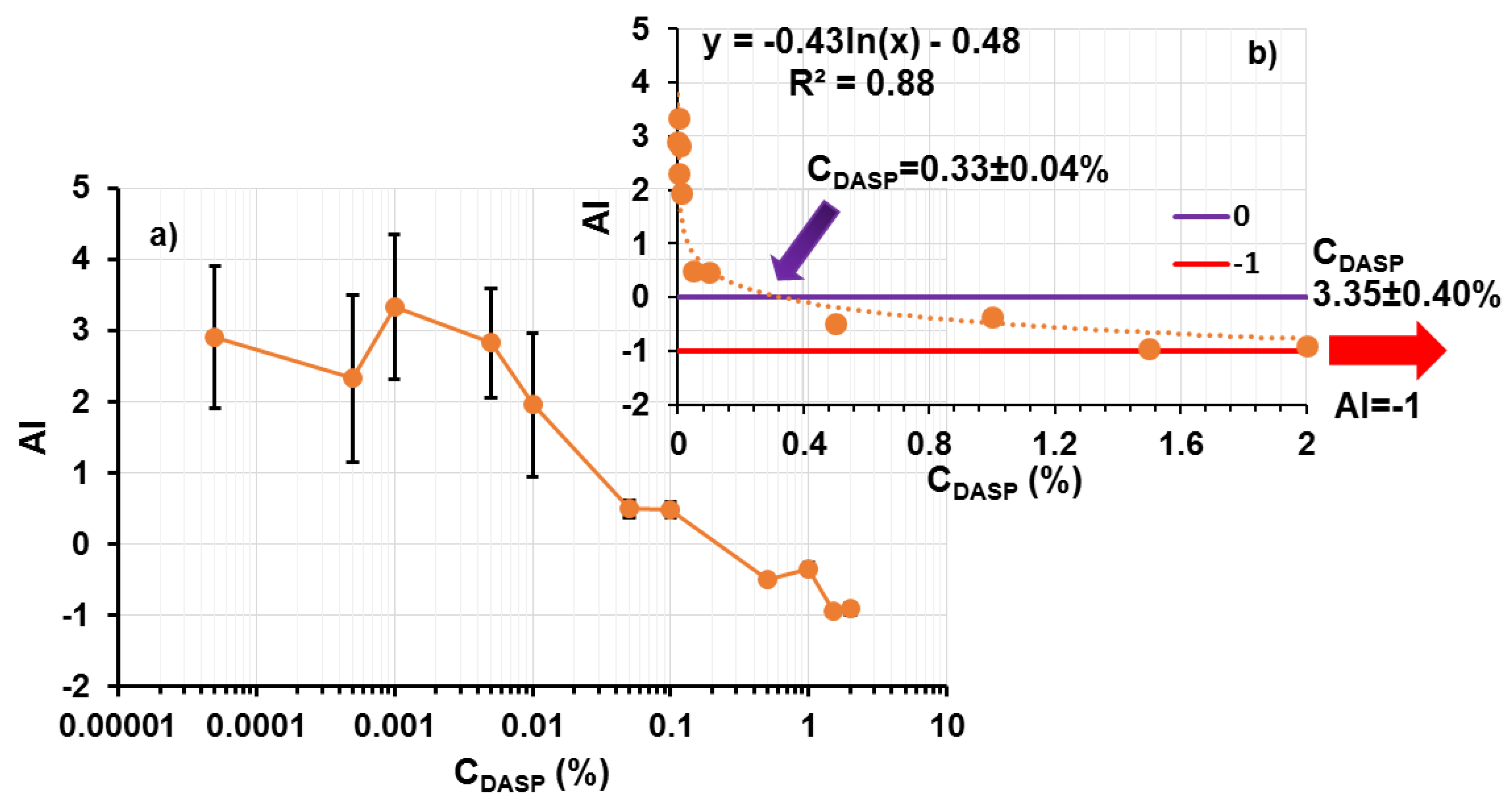
2.3. Particle Size and Aggregation Index (Ability of Light Transmittance)
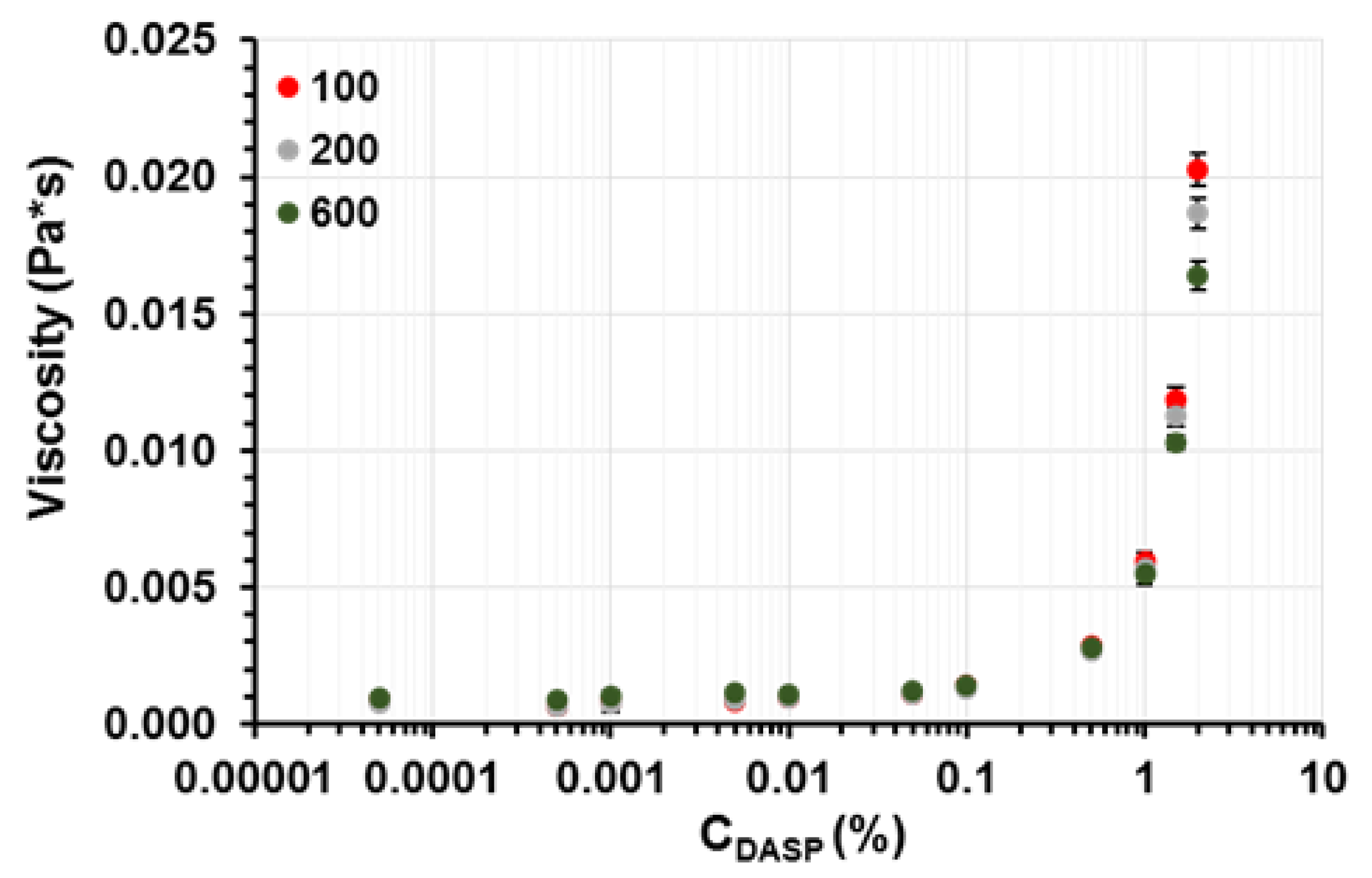
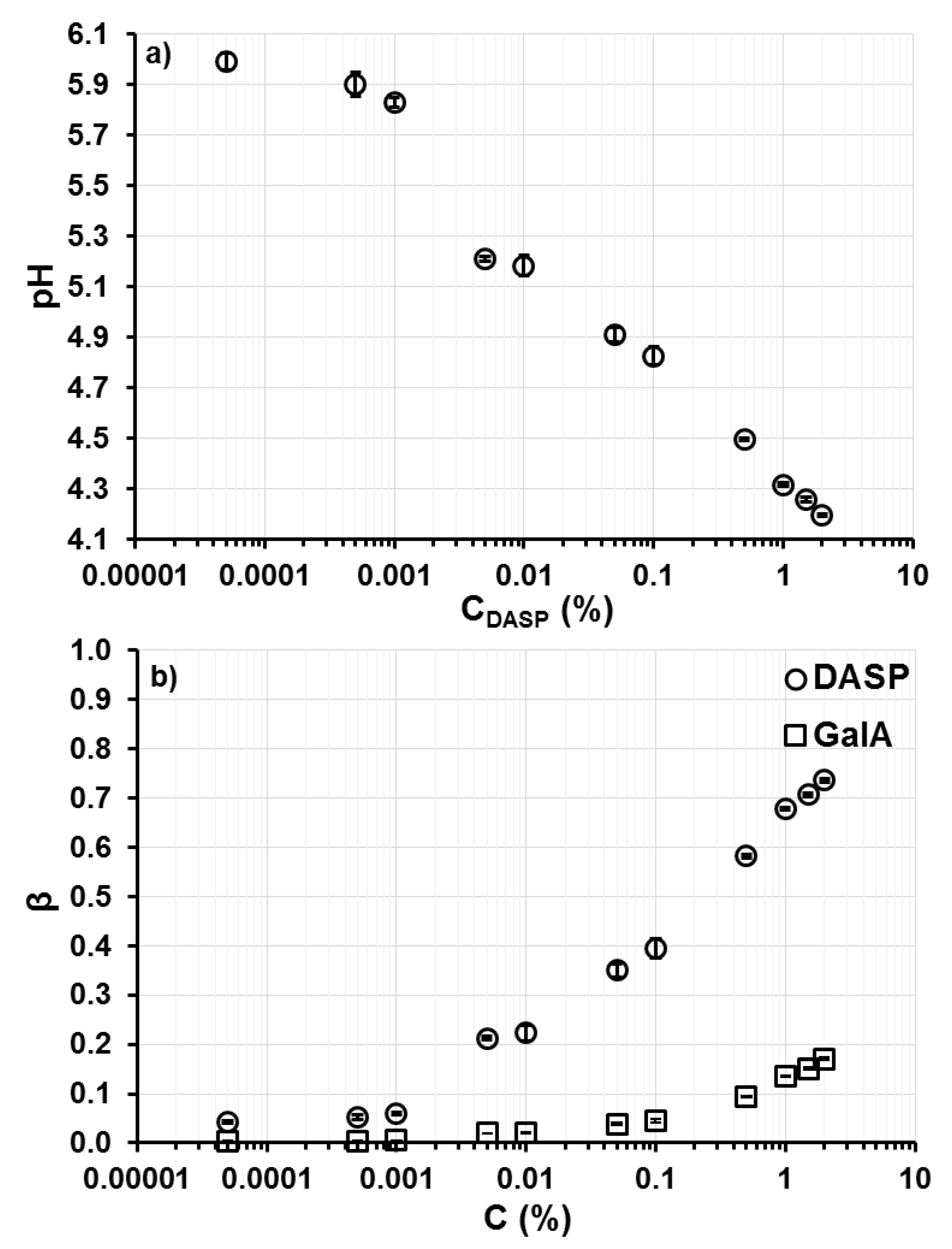
2.4. Viscosity and Degree of Hydrogen Ion Binding
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Isolation of Cell Wall Material and Pectin Fractionation
3.2. Preparation of Samples
3.3. AFM Imaging and Quantitative Analysis
3.4. Particle Size and Aggregation Index Determination in Pectin Solutions
3.5. Viscosity Measurements
3.6. pH Determination and Calculations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McNeil, M.; Darvill, A.G.; Fry, S.C.; Albersheim, P. Structure and function of the primary cell walls of plants. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1984, 53, 625–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, M.P.; Kohn, R. Determination of the esterification degree of carboxyl groups of pectin with methanol by means of infrared spectroscopy. Chem. Zvesti 1975, 29, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Normand, J.; Bonnin, E.; Delavault, P. Cloning and expression in Pichia pastoris of an Irpex lacteus rhamnogalacturonan hydrolase tolerant to acetylated rhamnogalacturonan. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 94, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralet, M.-C.; Cabrera, J.C.; Bonnin, E.; Quéméner, B.; Hellìn, P.; Thibault, J.-F. Mapping sugar beet pectin acetylation pattern. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 1832–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, T.M.I.E.; Nielsen, J.E.; Mikkelsen, J.D. Isolation, characterization and immuno localization of orange fruit acetyl esterase. In Pectins and Pectinases; Visser, J., Voragen, A.G.J., Eds.; Elsevier Science, B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 723–730. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Mort, A. Structure of a rhamnogalacturonan fragment from apple pectin: Implications for pectin architecture. Int. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2014, 2014, 347381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schols, H. Structural Characterization of Pectic Hairy Regions Isolated from Apple Cell Walls. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen Agricultural University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Thibault, J.-F.; Ralet, M.-C. Physico-chemical properties of pectins in the cell walls and after extraction. In Advances in Pectin and Pectinase Research; Voragen, F., Schols, H., Visser, R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 91–105. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Fishman, M.L.; Hicks, K.B. Pectin in controlled drug delivery—A review. Cellulose 2007, 14, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettani, S.R.; de Oliveira Ragazzo, G.; Leal Santos, N.; Kieckbusch, T.G.; Gaspar Bastos, R.; Soares, M.R.; Altenhofen da Silva, M. Sugarcane vinasse and microalgal biomass in the production of pectin particles as an alternative soil fertilizer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Meng, Y.; Hu, C.; Dong, G.; Qu, Y.; Deng, H.; Guo, Y. Mathematical model of Ca2+ concentration, pH, pectin concentration and soluble solids (sucrose) on the gelation of low methoxyl pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 66, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capel, F.; Nicolai, T.; Durand, D.; Boulenguer, P.; Langendorff, V. Calcium and acid induced gelation of (amidated) low methoxyl pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ström, A.; Schuster, E.; Goh, S.M. Rheological characterization of acid pectin samples in the absence and presence of monovalent ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliarti, O.; Hoon, A.L.S.; Chong, S.Y. Influence of pH, pectin and Ca concentration on gelation properties of low-methoxyl pectin extracted from Cyclea barbata Miers. Food Struct. 2017, 11, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierczyńska, J.; Cybulska, J.; Zdunek, A. Rheological and chemical properties of pectin enriched fractions from different sources extracted with citric acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdunek, A.; Kozioł, A.; Pieczywek, P.M.; Cybulska, J. Evaluation of the nanostructure of pectin, hemicellulose and cellulose in the cell walls of pears of different texture and firmness. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2014, 7, 3525–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybulska, J.; Zdunek, A.; Kozioł, A. The self-assembled network and physiological degradation of pectins in carrot cell walls. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, V.J.; Kirby, A.R.; Gunning, A.P. Using atomic force microscopy to probe food biopolymer functionality. Scanning 1999, 21, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjøniksen, A.-L.; Hiorth, M.; Nyström, B. Temperature-induced association and gelation of aqueous solutions of pectin. A dynamic light scattering study. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 2427–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, J.; Deotare, V.W.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Sood, A.K. Gelation of aqueous pectin solutions: A dynamic light scattering study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 245, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Malvern Instruments. Zetasizer Nano Application Note, Enhanced Protein Aggregation Detection Using Dual Angle Dynamic Light Scattering, MRK1441-01; Malvern Instruments Ltd.: Malvern, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gawkowska, D.; Cieśla, J.; Zdunek, A.; Cybulska, J. Cross-linking of diluted alkali-soluble pectin from apple (Malus domestica fruit) in different acid-base conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 92, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawkowska, D.; Cybulska, J.; Zdunek, A. Cross-linking of sodium carbonate-soluble pectins from apple by zinc ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 196, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posé, S.; Kirby, A.R.; Paniagua, C.; Waldron, K.W.; Morris, V.J.; Quesada, M.A.; Mercado, J.A. The nanostructural characterization of strawberry pectins in pectate lyase or polygalacturonase silenced fruits elucidates their role in softening. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Round, A.N.; Rigby, N.M.; MacDougall, A.J.; Ring, S.G.; Morris, V.J. Investigating the nature of branching in pectin by atomic force microscopy and carbohydrate analysis. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 331, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; He, Z.; Liu, Q.; Lai, S.; Yang, H. Effect of exogenous ATP on the postharvest properties and pectin degradation of mung bean sprouts (Vigna radiata). Food Chem. 2018, 251, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paniagua, C.; Kirby, A.R.; Gunning, A.P.; Morris, V.J.; Matas, A.J.; Quesada, M.A.; Mercado, J.A. Unravelling the nanostructure of strawberry fruit pectins by endo-polygalacturonase digestion and atomic force microscopy. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Round, A.N.; Rigby, N.M.; MacDougall, A.J.; Morris, V.J. A new view of pectin structure revealed by acid hydrolysis and atomic force microscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wan, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Zhu, J. Effect of calcium ions on the III steps of self-assembly of SA investigated with atomic force microscopy. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 1995–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareie, M.H.; Gokmen, V.; Javadipour, I. Investigating network, branching, gelation and enzymatic degradation in pectin by atomic force microscopy. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 40, 169–172. [Google Scholar]
- Muthukumar, M. Ordinary–extraordinary transition in dynamics of solutions of charged macromolecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12627–12632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Standard ISO 22412:2017. Particle Size Analysis—Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS); International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Förster, S.; Schmidt, M.; Antonietti, M. Static and dynamic light scattering by aqueous polyelectrolyte solutions: Effect of molecular weight, charge density and added salt. Polymer 1990, 31, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro-da-Cunha, M.G.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Souza, B.W.S.; Teixeira, J.A.; Vicente, A.A. Influence of concentration, ionic strength and pH on zeta potential and mean hydrodynamic diameter of edible polysaccharide solutions envisaged for multinanolayered films production. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 85, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, U.T.D.; Lerbret, A.; Neiers, F.; Chambin, O.; Assifaoui, A. Binding of divalent cations to polygalacturonate: A mechanism driven by the hydration water. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, F.; Arslan, N. Effect of temperature and concentration on viscosity of orange peel pectin solutions and intrinsic viscosity-molecular weight relationship. Carbohydr. Polym. 1999, 40, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Wang, K.; Yang, R.; Kang, J.; Zhang, J. Rheological properties of natural low-methoxyl pectin extracted from sunflower head. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinsky, J.A. Ion binding in charged polymers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1976, 19, 125–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vleugels, L.F.W.; Ricois, S.; Voets, I.K.; Tuinier, R. Determination of the “apparent pKa” of selected food hydrocolloids using ortho-toluidine blue. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaschina, I.G.; Braudo, E.E.; Tolstoguzov, V.B. Circular-dichroism studies of pectin solutions. Carbohydr. Res. 1978, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.L.P.; Martins, R.R.; da Trindade Neto, C.G.; Pereira, M.R.; Fonseca, J.L.C. Characterization of polyelectrolyte effect in poly(acrylic acid) solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkinshaw, M.D.; Arnott, S. Conformations and interactions of pectins. I. X-ray diffraction analyses of sodium pectate in neutral and acidified forms. J. Mol. Biol. 1981, 153, 1055–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assifaoui, A.; Lerbret, A.; Uyen, H.T.D.; Neiers, F.; Chambin, O.; Loupiac, C.; Cousin, F. Structural behaviour differences in low methoxy pectin solutions in the presence of divalent cations (Ca2+ and Zn2+): A process driven by the binding mechanism of the cation with the galacturonate unit. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, H.; Einhorn-Stoll, U.; Senge, B. Structure formation in sugar containing pectin gels—Influence of Ca2+ on the gelation of low-methoxylated pectin at acidic pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, C.M.G.C. Variability in cell wall preparations: Quantification and comparison of common methods. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 60, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redgwell, R.J.; Melton, L.D.; Brasch, D.J. Cell wall dissolution in ripening kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa): Solubilization of the pectic polymers. Plant Physiol. 1992, 98, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbato, G.; Carneiro, K.; Cuppini, D.; Garnaes, J.; Gori, G.; Hughes, G.; Jensen, C.P.; Jørgensen, J.F.; Jusko, O.; Livi, S.; et al. Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Methods for Roughness and Micro Hardness Measurements; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 1995.
- Kohn, R.; Kovác, P. Dissociation constants of D-galacturonic and D-glucuronic acid and their О-methyl derivatives. Chem. Zvesti 1978, 32, 478–485. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Not available. |
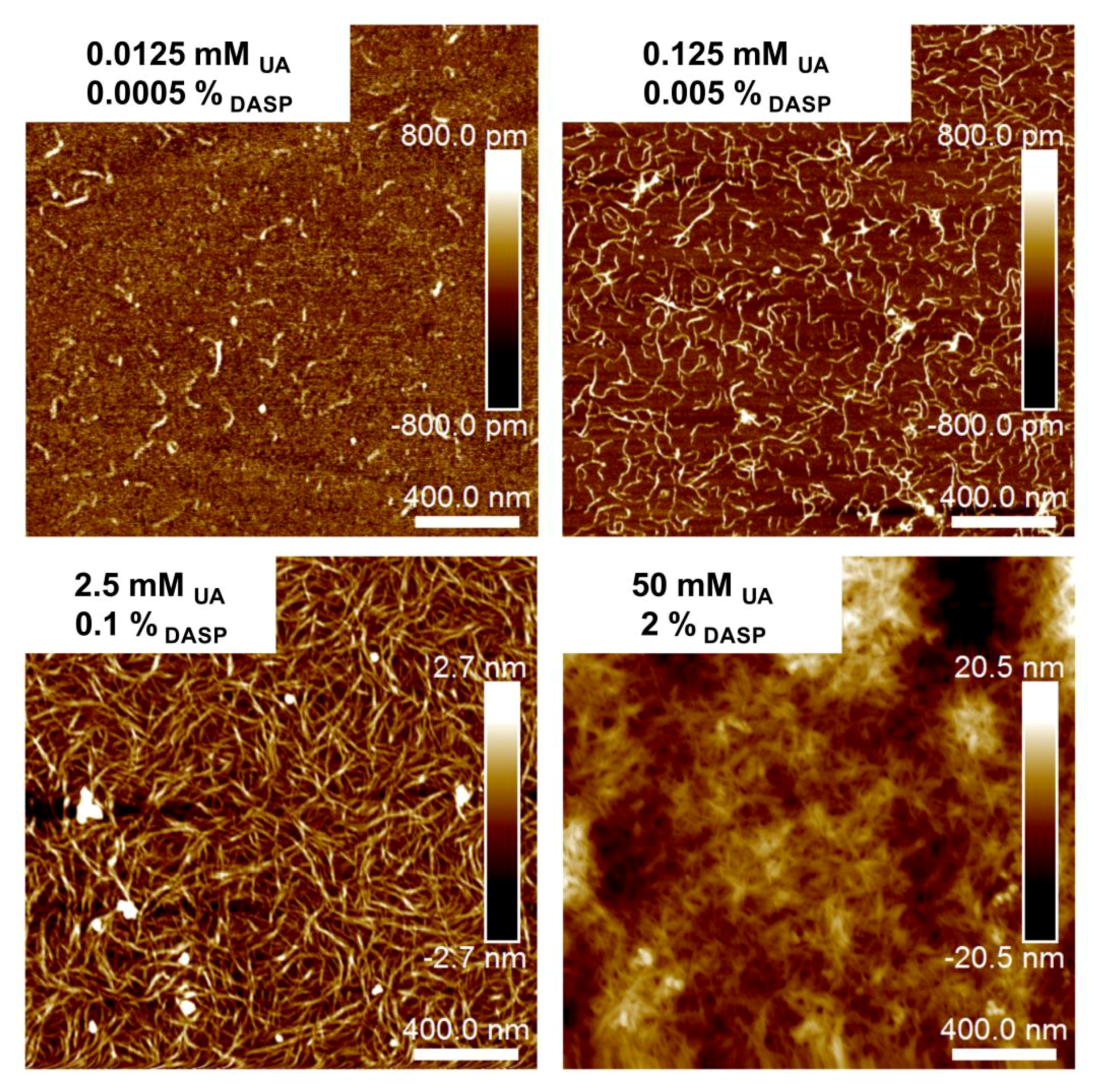
| CDASP (%) | Sa min | Sa max | Sq min | Sq max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00005 | 0.1029 | 0.1092 | 0.1535 | 0.1691 |
| 0.0005 | 0.0919 | 0.1106 | 0.1441 | 0.1500 |
| 0.001 | 0.1487 | 0.2100 | 0.2145 | 0.3630 |
| 0.005 | 0.1182 | 0.1291 | 0.1754 | 0.2155 |
| 0.01 | 0.2021 | 0.2451 | 0.3778 | 0.5186 |
| 0.05 | 0.2107 | 0.2317 | 0.4085 | 0.4957 |
| 0.1 | 0.5425 | 0.5680 | 0.7975 | 0.8733 |
| 0.5 | 1.3817 | 1.4408 | 1.8101 | 2.0064 |
| 1 | 2.0590 | 2.7888 | 2.7928 | 3.9249 |
| 1.5 | 2.4921 | 2.8095 | 3.3201 | 3.7959 |
| 2 | 3.1350 | 3.6414 | 4.1914 | 4.9073 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gawkowska, D.; Cieśla, J.; Zdunek, A.; Cybulska, J. The Effect of Concentration on the Cross-Linking and Gelling of Sodium Carbonate-Soluble Apple Pectins. Molecules 2019, 24, 1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081635
Gawkowska D, Cieśla J, Zdunek A, Cybulska J. The Effect of Concentration on the Cross-Linking and Gelling of Sodium Carbonate-Soluble Apple Pectins. Molecules. 2019; 24(8):1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081635
Chicago/Turabian StyleGawkowska, Diana, Jolanta Cieśla, Artur Zdunek, and Justyna Cybulska. 2019. "The Effect of Concentration on the Cross-Linking and Gelling of Sodium Carbonate-Soluble Apple Pectins" Molecules 24, no. 8: 1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081635
APA StyleGawkowska, D., Cieśla, J., Zdunek, A., & Cybulska, J. (2019). The Effect of Concentration on the Cross-Linking and Gelling of Sodium Carbonate-Soluble Apple Pectins. Molecules, 24(8), 1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081635







