Asperaculanes A and B, Two Sesquiterpenoids from the Fungus Aspergillus aculeatus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
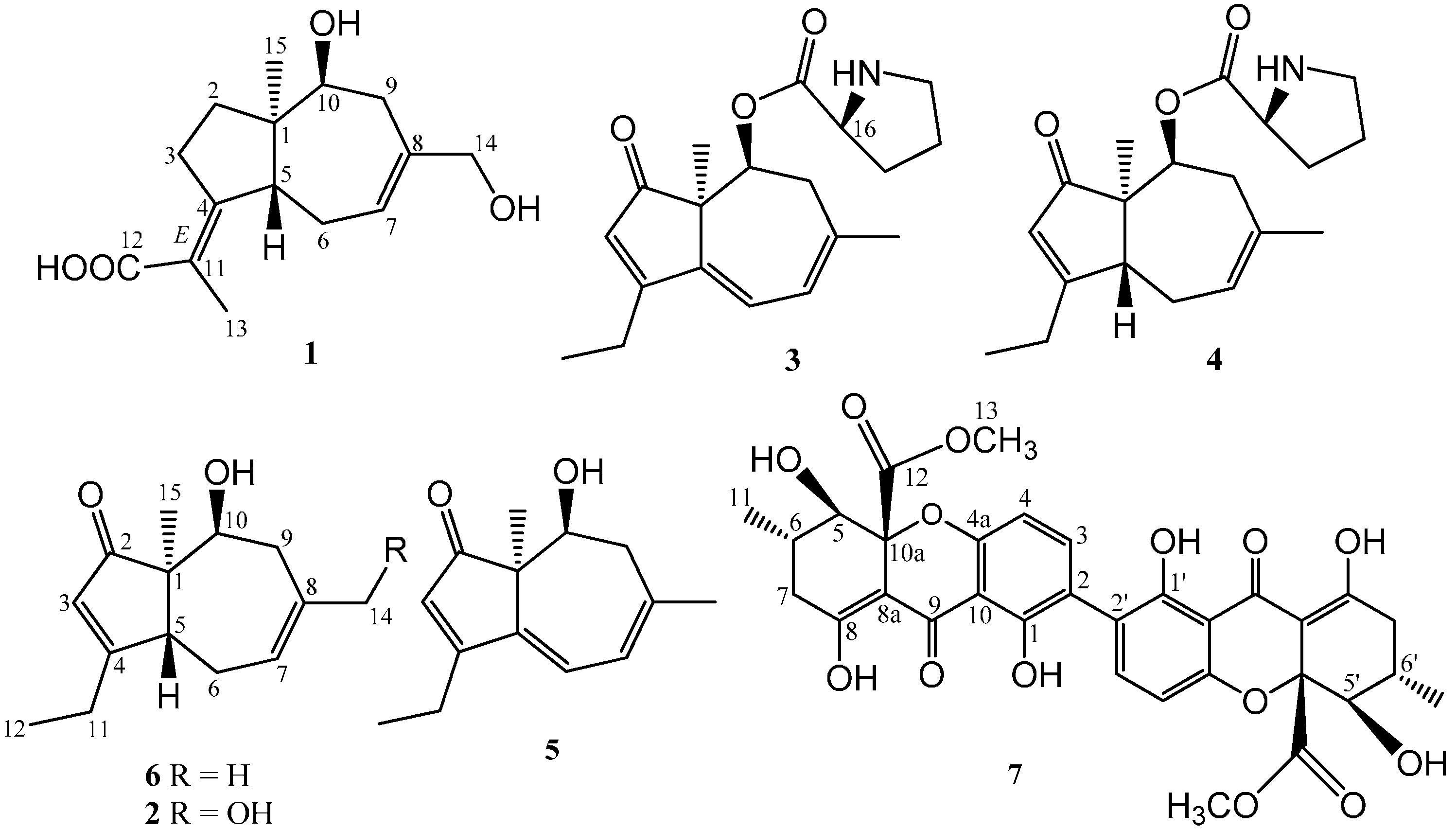
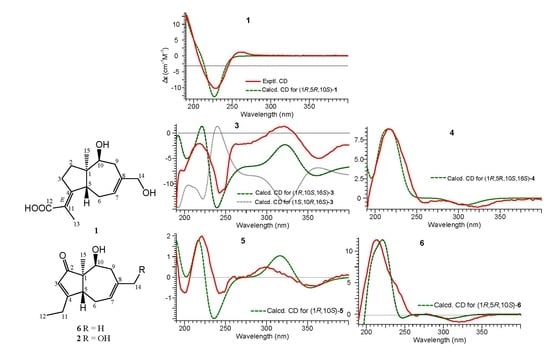
2.1. Structure Elucidation of Compounds 1–2 and Absolute Configurations of 3–6
| No. | 1 a | 6 b | 2 a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | |
| 1 | — | 50.1 | — | 56.8 | — | 56.5 |
| 2 | 1.20, m 1,85 c | 36.7 | — | 213.3 | — | 211.0 |
| 3 | 2.52 c 2.72, dd (17.6, 7.0) | 34.0 | 5.79, s | 123.5 | 5.70, s | 124.0 |
| 4 | — | 162.7 | — | 186.2 | — | 184.1 |
| 5 | 3.04, d (11.7) | 44.8 | 3.52, d (12.6) | 44.3 | 3.40, d (14.4) | 44.0 |
| 6 | 2.91, m 2.52 c | 28.9 | 2.11, d (15.2) 2.53 c | 25.5 | 2.03, d (14.8) 2.52 c | 25.5 |
| 7 | 5.65, d (5.9) | 126.0 | 5.56, br d (5.7) | 122.1 | 5.70 overlapped | 121.3 |
| 8 | — | 137.8 | — | 132.4 | — | 137.4 |
| 9 | 2.34, d (17.0) 2.15, dd (17.0, 2.3) | 36.1 | 2.32, d (18.4) 2.55 c | 39.5 | 2.15, d (18.0) 2.32, ddd (18.4, 10.8, 4.4) | 36.5 |
| 10 | 3.82 br. d (2.3) | 73.8 | 4.15, dd (2.6, 4.9) | 68.8 | 4.00, d (2.4) | 68.0 |
| 11 | — | 122.7 | 2.4, q (7.3) | 23.8 | 2.35, q (7.3) | 24.0 |
| 12 | — | 173.2 | 1.19, t (7.3) | 10.3 | 1.08, t (7.3) | 11.7 |
| 13 | 1.81, s | 16.7 | — | — | — | — |
| 14 | 3.69 br. s | 71.1 | 1.74, s | 28.3 | 3.67, d (4.8) | 68.9 |
| 15 | 0.88, s | 19.6 | 0.97, s | 17.3 | 0.80, s | 18.3 |
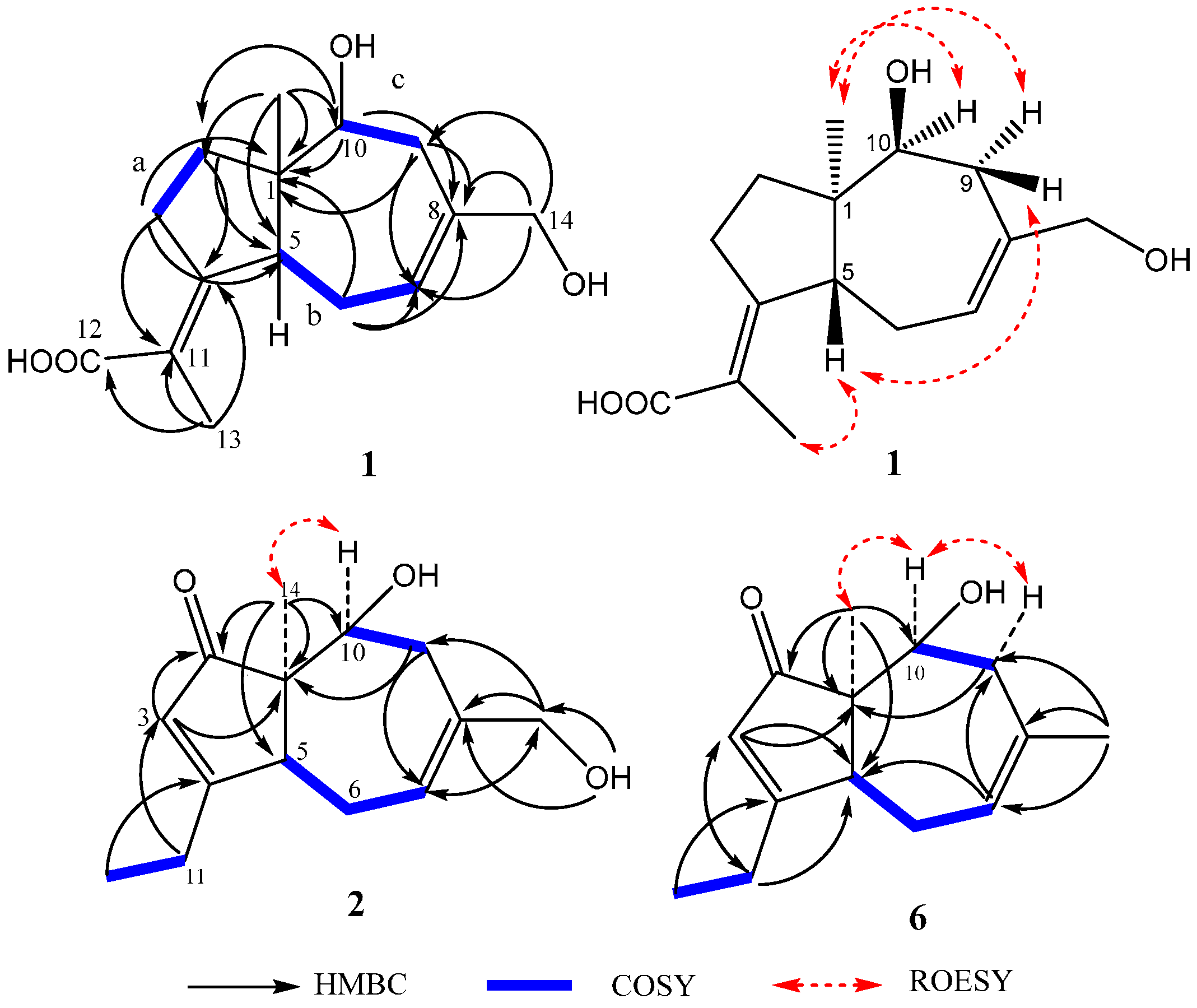
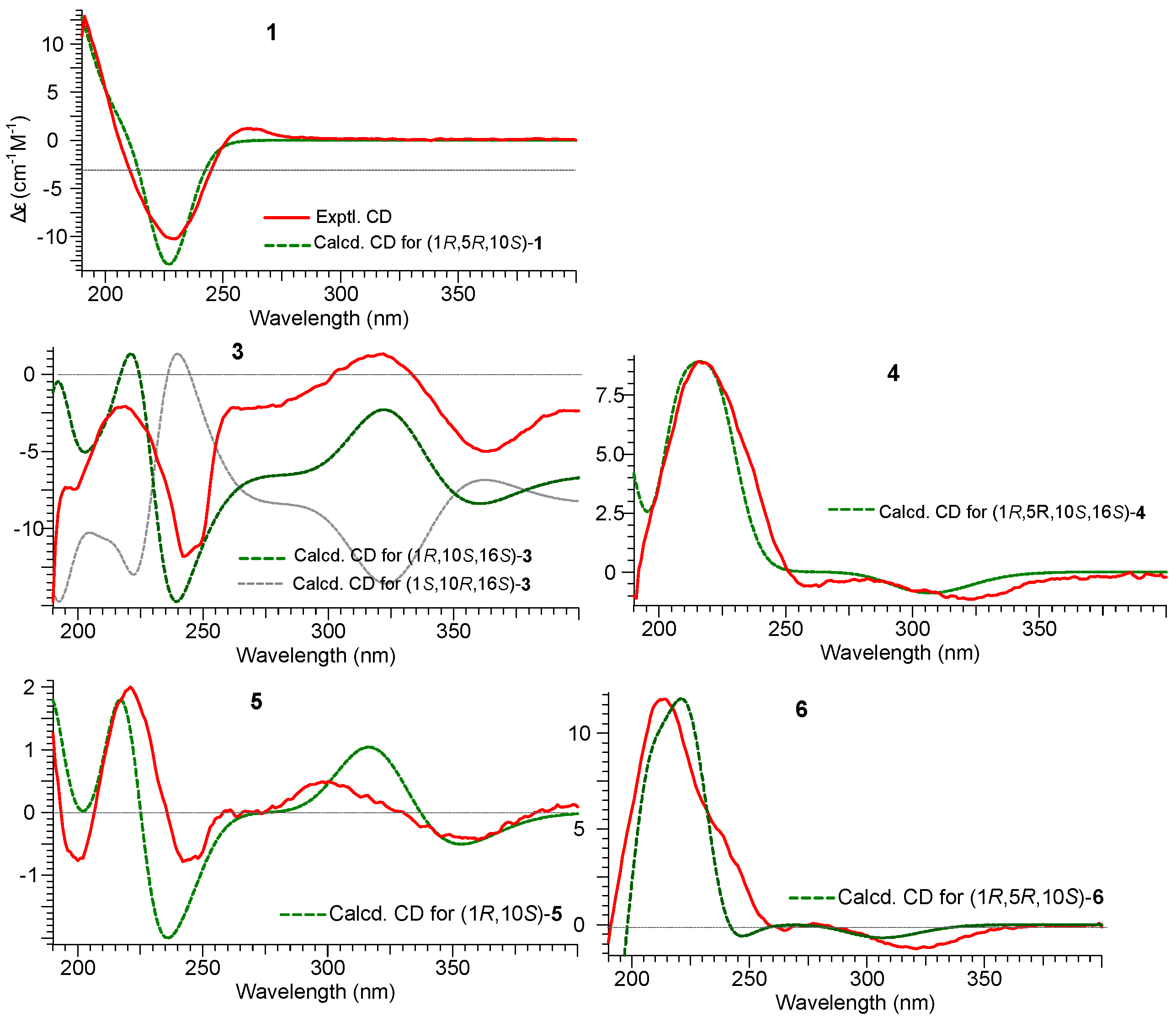
2.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Procedures
3.2. Fungal Material and Fermentation
3.3. Extraction, Isolation and Purification
3.4. Absolute Configuration Determination
3.5. Computational Section
3.6. Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bugni, T.S.; Ireland, C.M. Marine-derived fungi: A chemically and biologically diverse group of microorganisms. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 21, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.M.; Yang, S.X.; Qin, J.C. Azaphilones: Chemistry and biology. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4755–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bérdy, J. Thoughts and facts about antibiotics: Where we are now and where we are heading. J. Antibiot. 2012, 65, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.M. New biologically active metabolites from Chinese higher fungi. Curr. Org. Chem. 2006, 10, 849–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Ali, M.S.; Hussain, S.; Jabbar, A.; Ashraf, M.; Lee, Y.S. Marine natural products of fungal origin. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, T.O.; Smedsgaard, J.; Nielsen, K.F.; Hansen, M.E.; Frisvad, J.C. Phenotypic taxonomy and metabolite profiling in microbial drug discovery. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 672–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Sun, Y.L.; Liu, K.S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Qian, P.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Qi, S.H. Indole alkaloids from marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowii SCSIO 00305. J. Antibiot. 2012, 65, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, A.L.; Gao, J.M. Metabolites from Aspergillus fumigatus, an endophytic fungus associated with Melia azedarach, and their antifungal, antifeedant, and toxic activities. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2012, 60, 3424–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.Q.; Tang, H.Y.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, J.; Gao, Y.Q.; Zhang, A.L.; Gao, J.M. Potential allelopathic indole diketopiperazines produced by the plant endophytic Aspergillusfumigatus using the one strain-many compounds method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11447–11452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Y.Q.; Shi, X.W.; Gao, J.M. Antifungal and antibacterial metabolites from an endophytic Aspergillus sp. associated with Melia azedarach. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, K.; Yagi, A.; Satoi, S.; Takada, M.; Hayashi, M. Studies on aculeacin. I. Isolation and characterization of aculeacin A. J. Antibiot. 1977, 30, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoi, S.; Yagi, A.; Asano, K.; Mizuno, K.; Watanabe, T. Studies on aculeacin. II. Isolation and characterization of aculeacins B, C, D, E, F and G. J. Antibiot. 1977, 30, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Hirai, H.; Ishiguro, M.; Kambara, T.; Kojima, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Nishida, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Sugiura, A.; Harwood, H.J., Jr.; et al. CJ-15,183, a new inhibitor of squalene synthase produced by a fungus, Aspergillus aculeatus. J. Antibiot. 2001, 54, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingavat, N.; Dobereiner, J.; Wiyakrutta, S.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kittakoop, P. Aspergillusol A, an α-glucosidase inhibitor from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus aculeatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 2049–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, A.; George, B.; Brunhilde, K.; Arnold, L.D. Secalonic acids D and F are toxic metabolites of Aspergillus aculeatus. J. Org. Chem. 1977, 42, 352–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingavat, N.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kittakoop, P. Asperaculin A, a sesquiterpenoid from a marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus aculeatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1650–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, W.W.; Zheng, Q.H.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhong, P.; Hu, X.; Fang, Z.X.; Zhang, Q.Q. Aculeatusquinones A-D, novel metabolites from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus aculeatus. Heterocycles 2013, 87, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Furutsuka, K.; Shiono, Y. Okaramines H and I, new okaramine congeners, from Aspergillus aculeatus. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringmann, G.; Bruhn, T.; Maksimenka, K.; Hemberger, Y. The assignment of absolute stereostructures through quantum chemical circular dichroism calculations. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 2717–2727. [Google Scholar]
- Goto, H.; Ohta, K.; Kamakura, T.; Obata, S.; Nakayama, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Ōsawa, E. Conflex Software, Version 6.7; Conflex Corp.: Tokyo Yokohama, Japan, 2010.
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Revision D.01; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Marfey, P. Determination of d-amino acids. II. Use of a bifunctional reagent, 1,5-difluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene. Carlsberg Res. Commun. 1984, 49, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.M.; Hoeck, C.; Frisvad, J.C.; Gotfredsen, C.H.; Larsen, T.O. Dereplication guided discovery of secondary metabolites of mixed biosynthetic origin from Aspergillus aculeatus. Molecules 2014, 19, 10898–108921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dall’Acqua, S.; Linardi, M.A.; Maggi, F.; Nicoletti, M.; Petitto, V.; Innocenti, G.; Basso, G.; Viola, G. Natural daucane sesquiterpenes with antiproliferative and proapoptotic activity against human tumor cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 5876–5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wawrzyn, G.T.; Quin, M.B.; Choudhary, S.; López-Gallego, F.; Schmidt-Dannert, C. Draft genome of Omphalotus olearius provides a predictive framework for sesquiterpenoid natural product biosynthesis in Basidiomycota. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Tang, J.J.; Zhang, C.C.; Tian, J.M.; Guo, J.T.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Gao, J.M. Semisynthesis and in vitro cytotoxic evaluation of new analogues of 1-O-acetylbritannilactone, a sesquiterpene from Inula britannica. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 80, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruhn, T.; Schaumloeffel, A.; Hemberger, Y.; Bringmann, G. SpecDis: Quantifying the comparison of calculated and experimental electronic circular dichroism spectra. Chirality 2013, 25, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.-Q.; Guo, C.-J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, W.-M.; Wang, C.C.C.; Gao, J.-M. Asperaculanes A and B, Two Sesquiterpenoids from the Fungus Aspergillus aculeatus. Molecules 2015, 20, 325-334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20010325
Gao Y-Q, Guo C-J, Zhang Q, Zhou W-M, Wang CCC, Gao J-M. Asperaculanes A and B, Two Sesquiterpenoids from the Fungus Aspergillus aculeatus. Molecules. 2015; 20(1):325-334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20010325
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yu-Qi, Chun-Jun Guo, Qiang Zhang, Wen-Ming Zhou, Clay C. C. Wang, and Jin-Ming Gao. 2015. "Asperaculanes A and B, Two Sesquiterpenoids from the Fungus Aspergillus aculeatus" Molecules 20, no. 1: 325-334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20010325
APA StyleGao, Y.-Q., Guo, C.-J., Zhang, Q., Zhou, W.-M., Wang, C. C. C., & Gao, J.-M. (2015). Asperaculanes A and B, Two Sesquiterpenoids from the Fungus Aspergillus aculeatus. Molecules, 20(1), 325-334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20010325