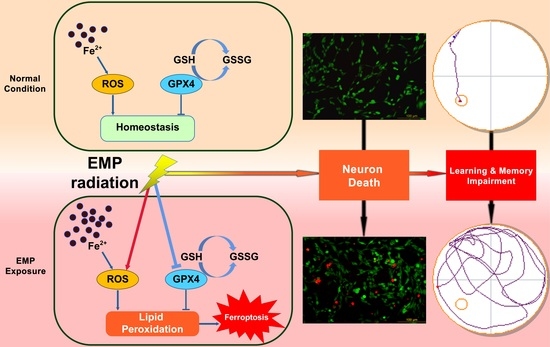
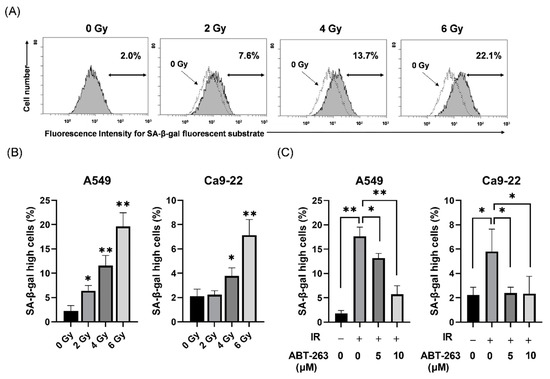
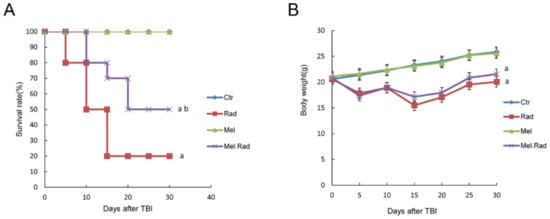
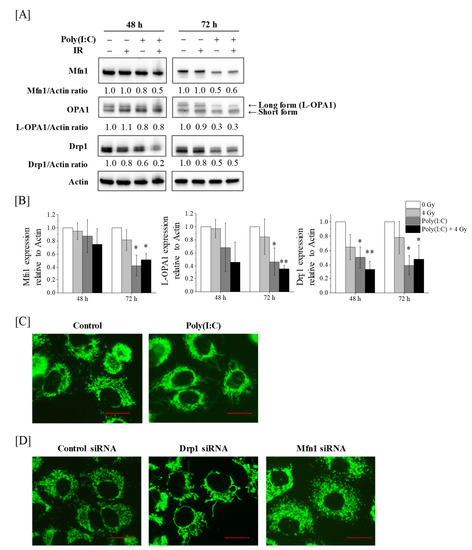
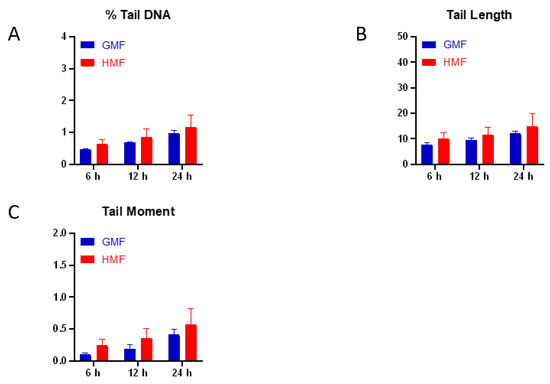
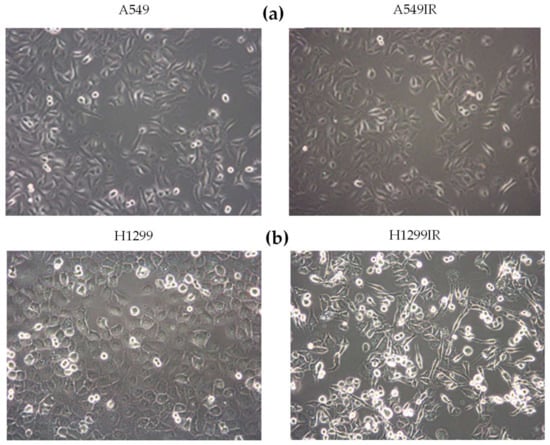
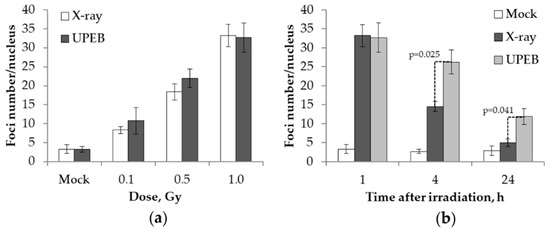
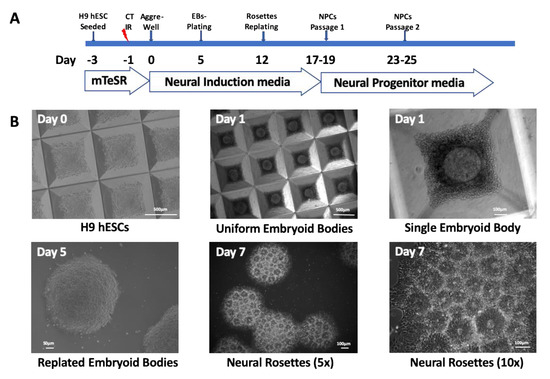
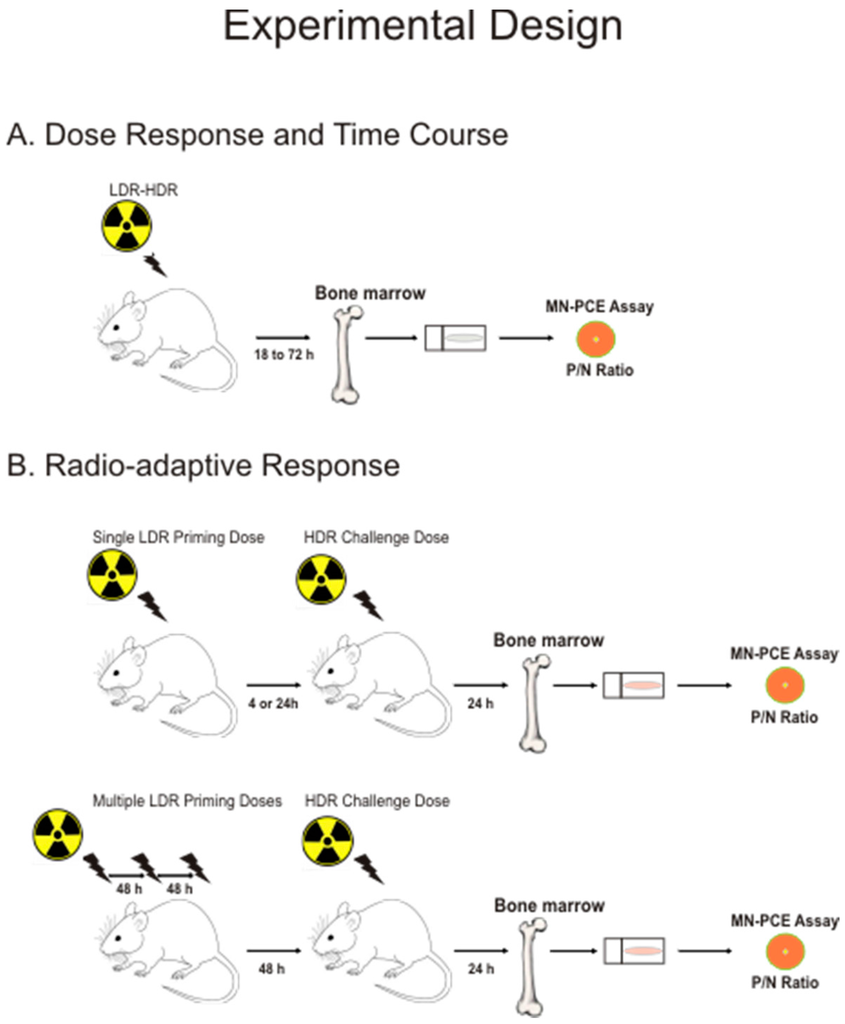
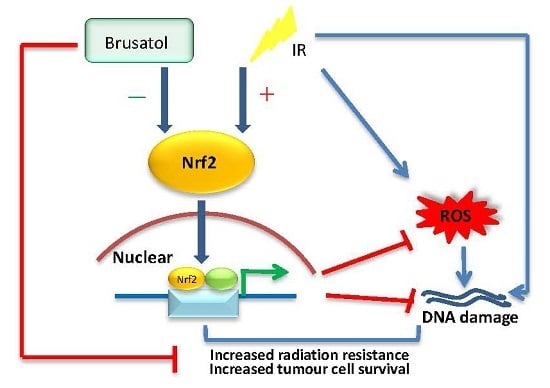
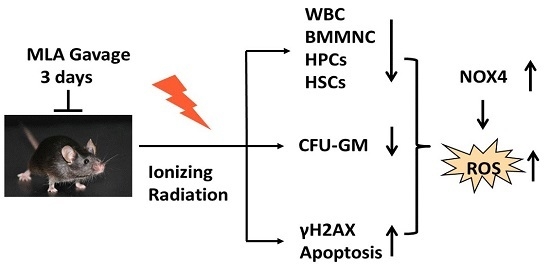
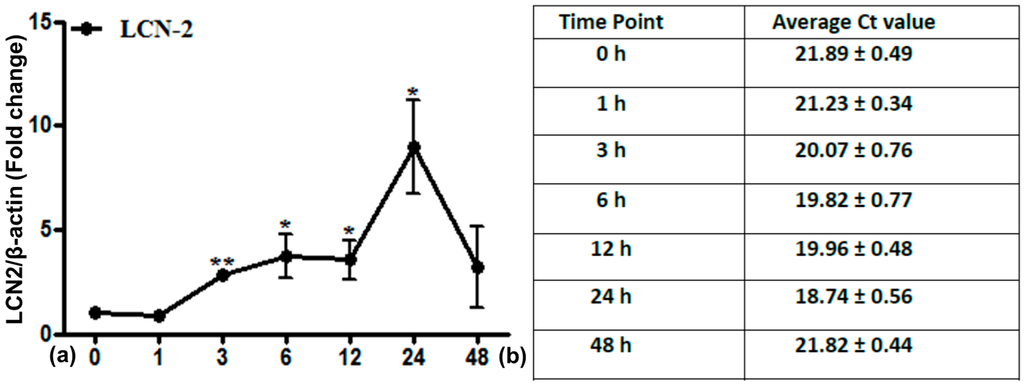
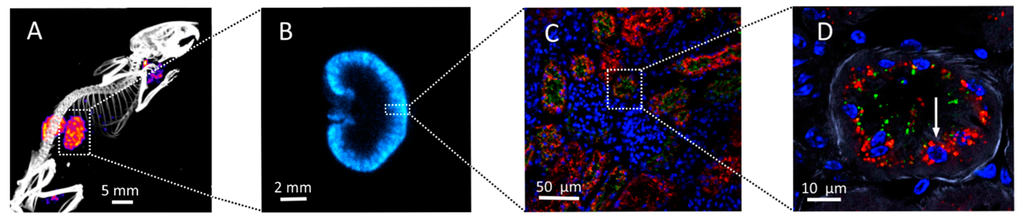
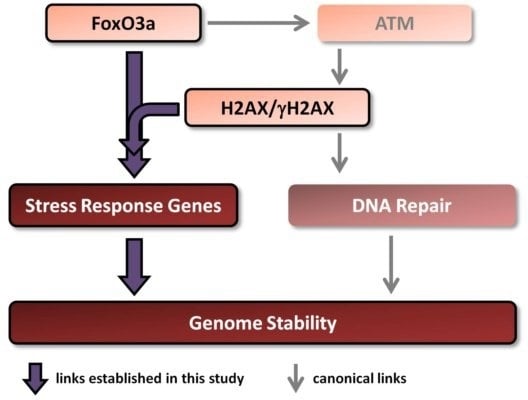
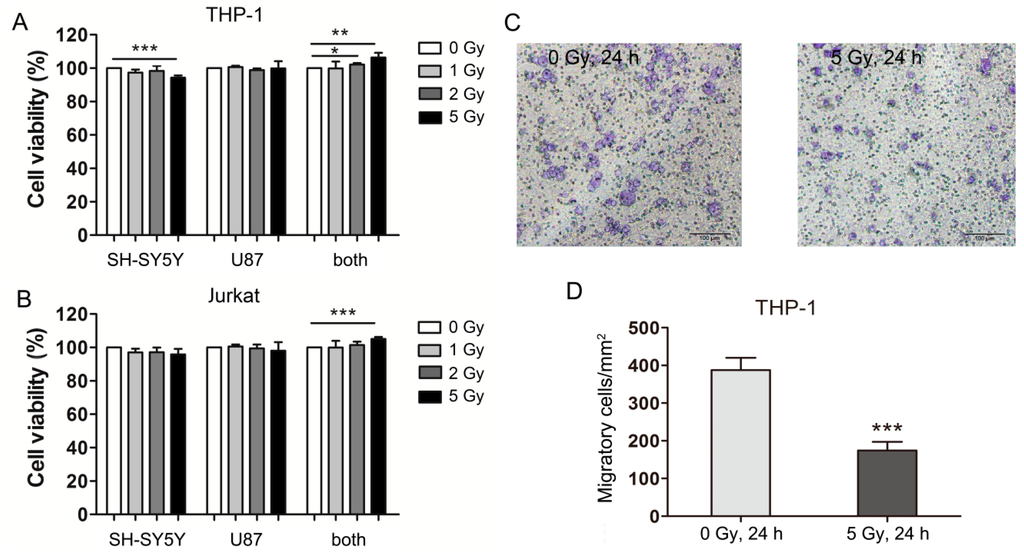
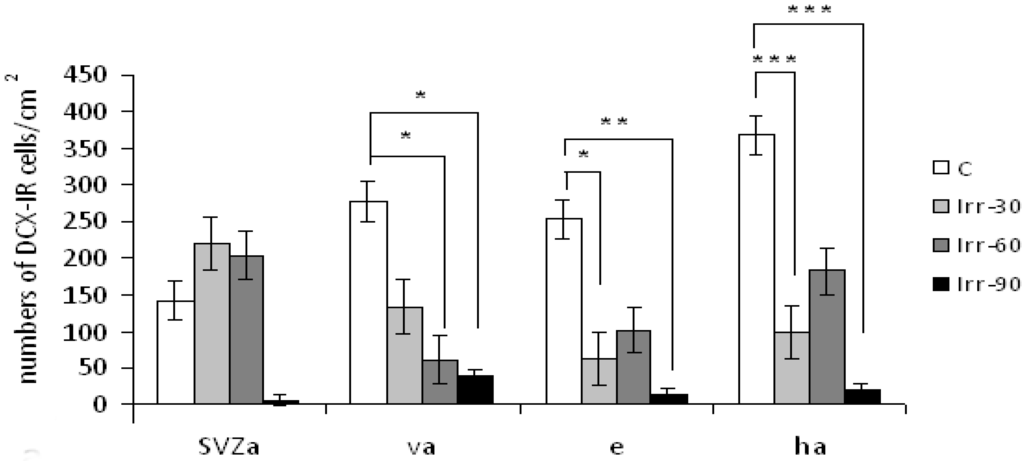
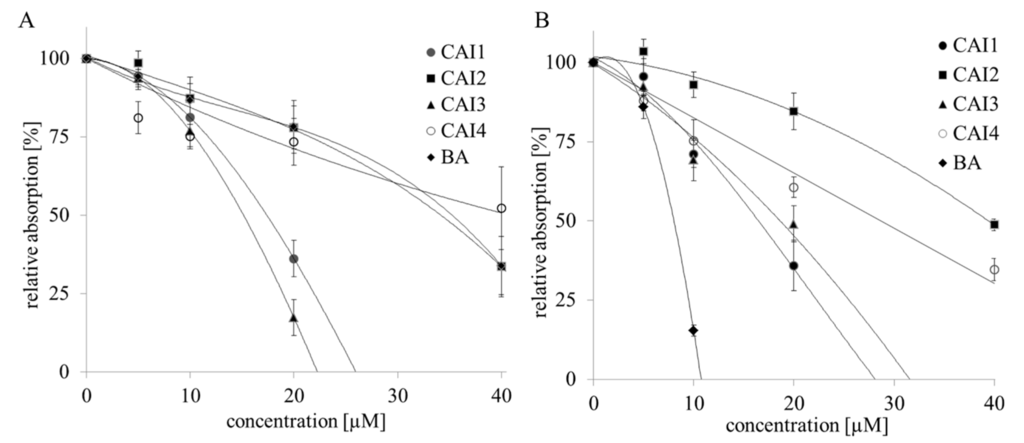
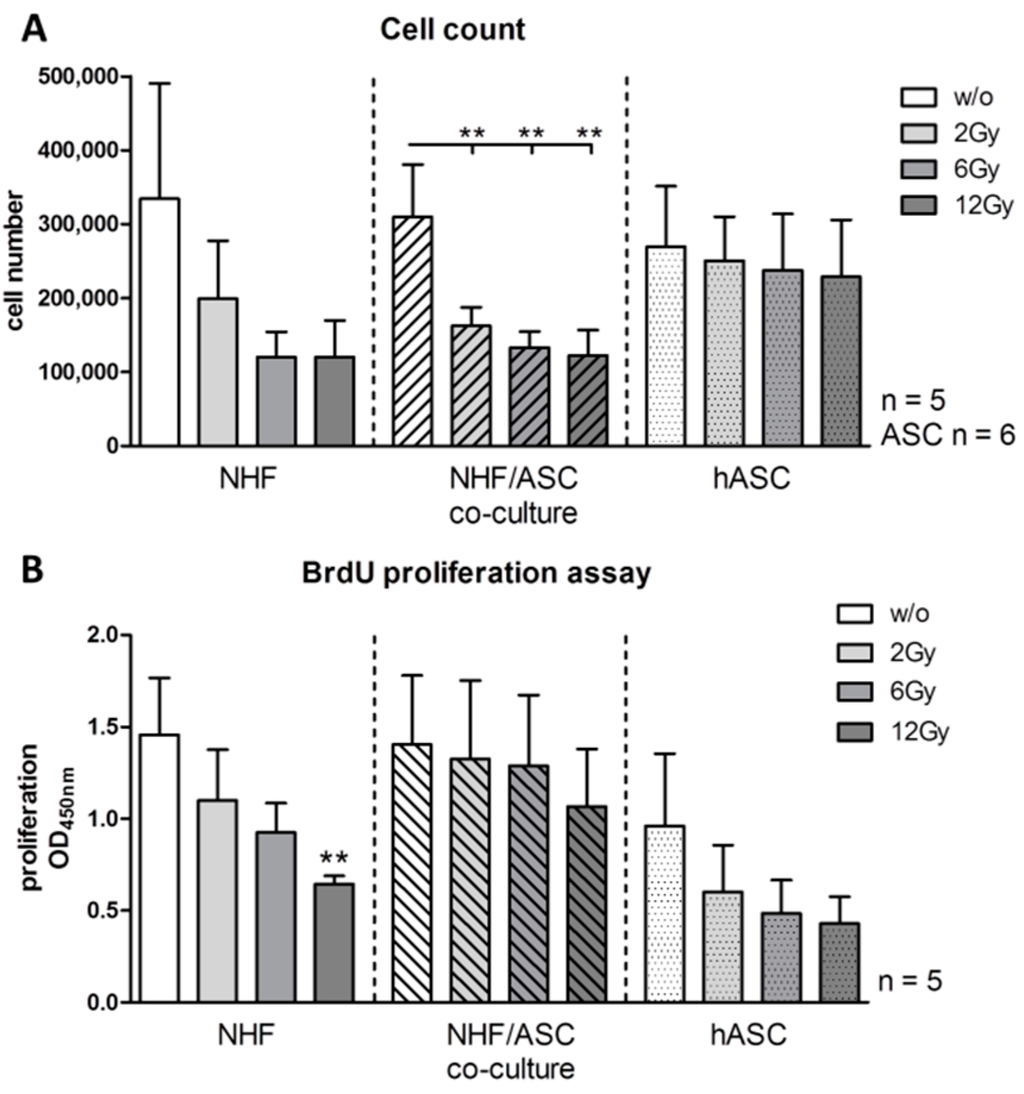
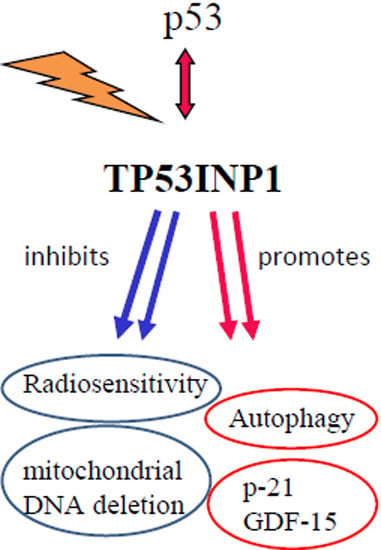
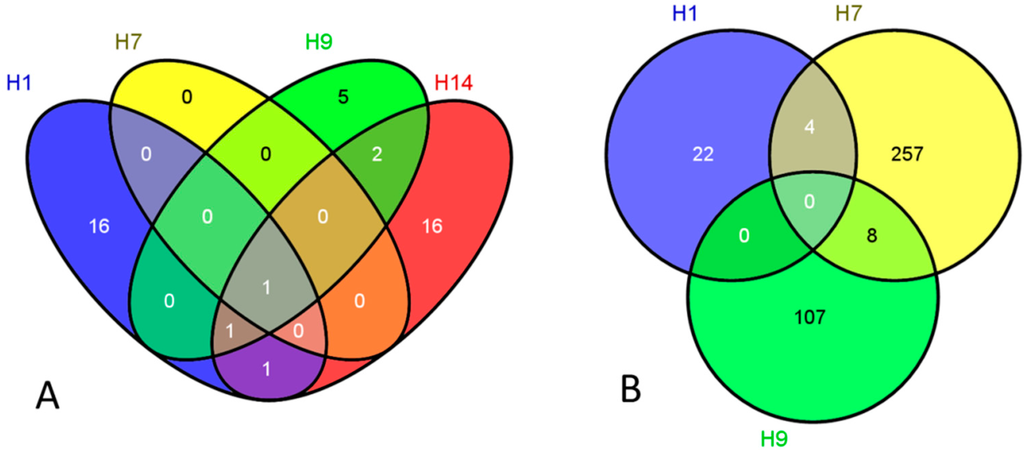
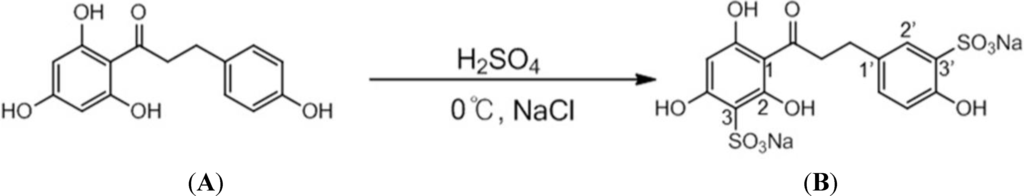
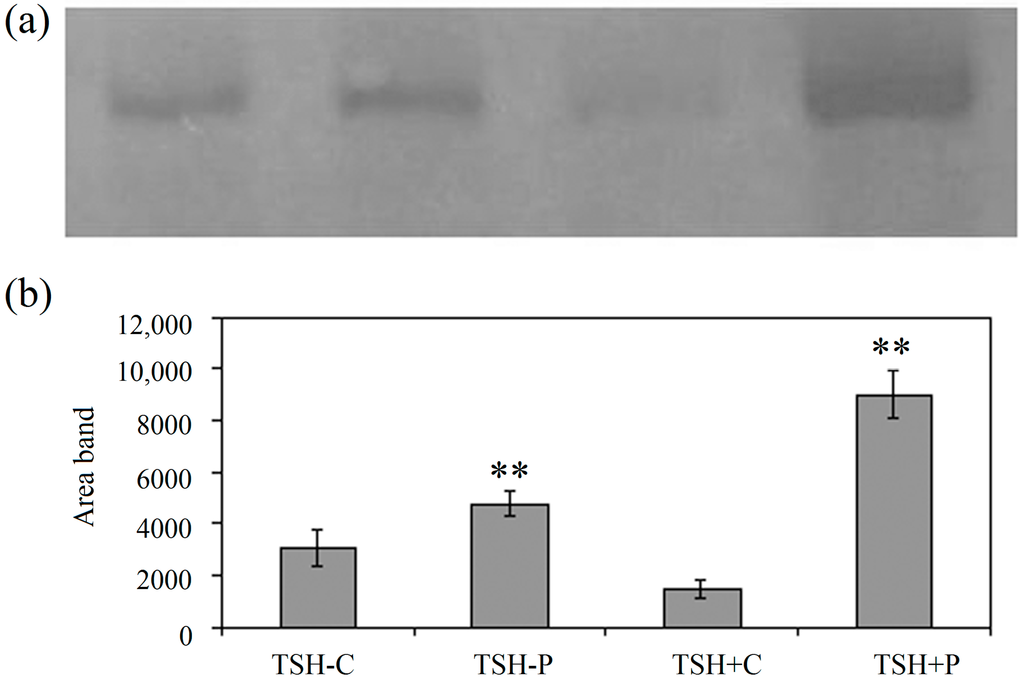
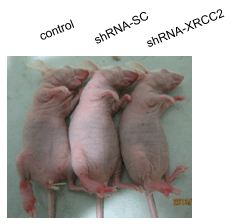
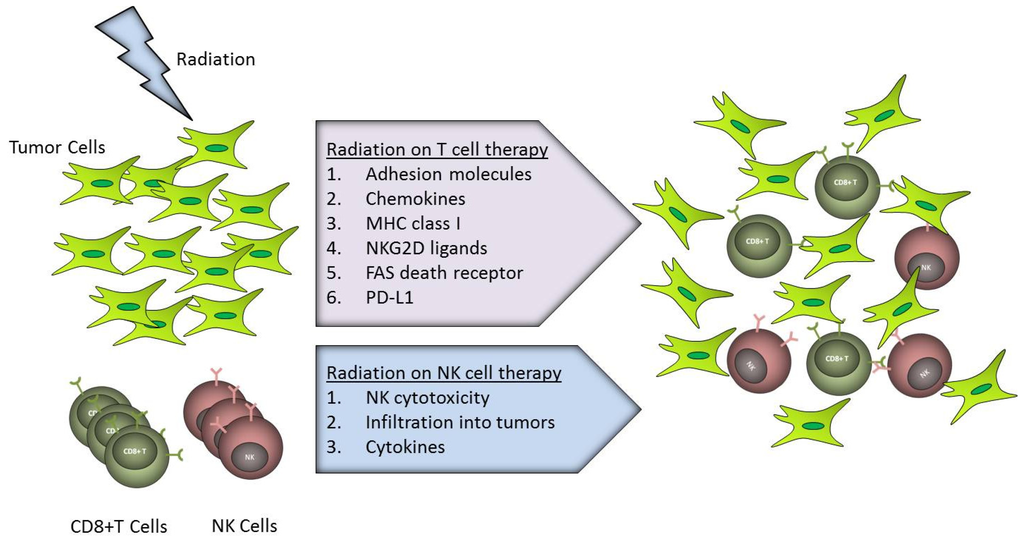
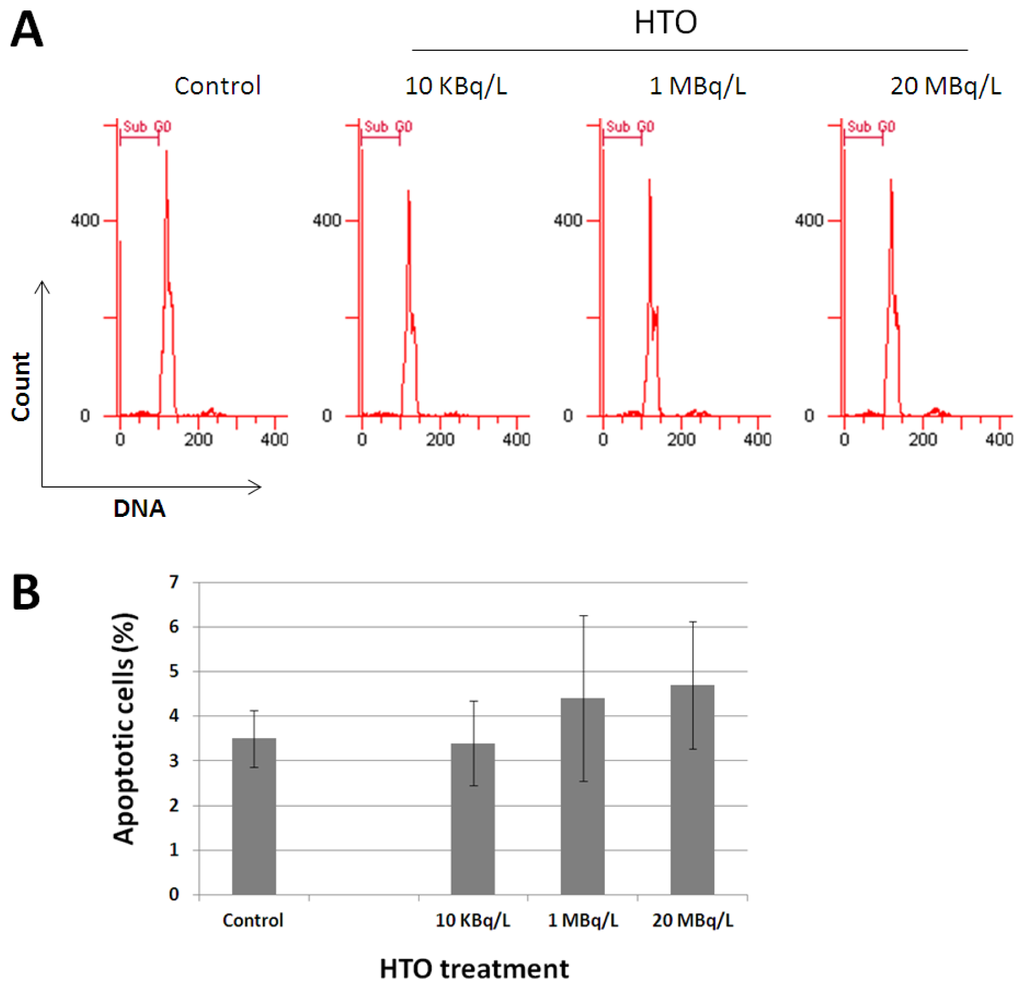
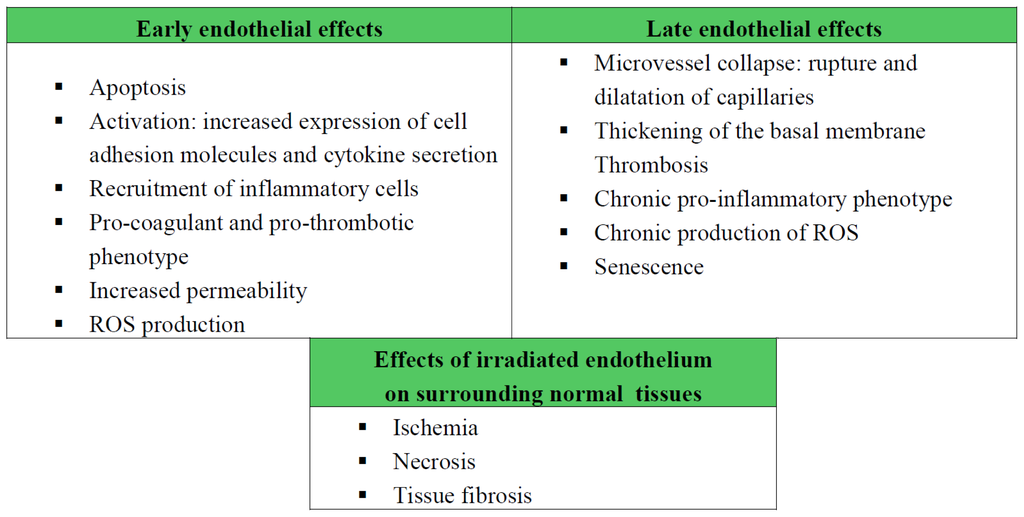
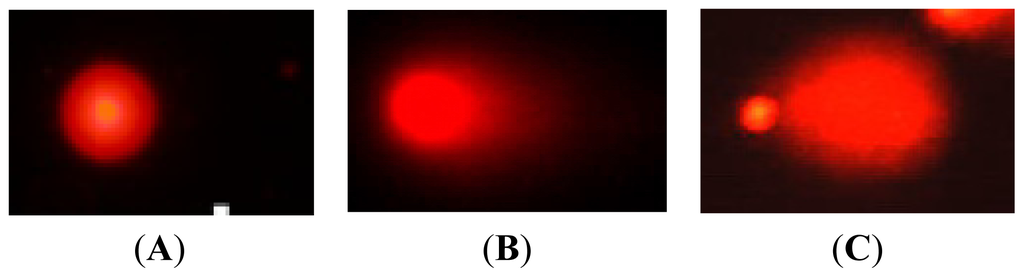
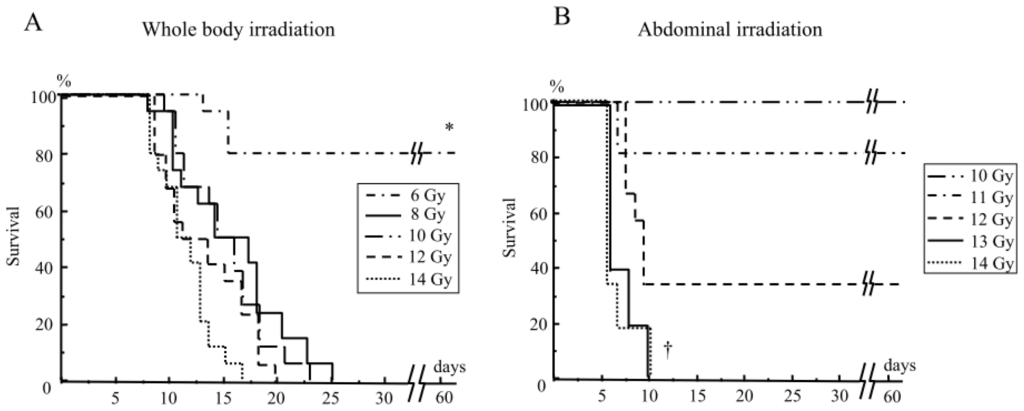
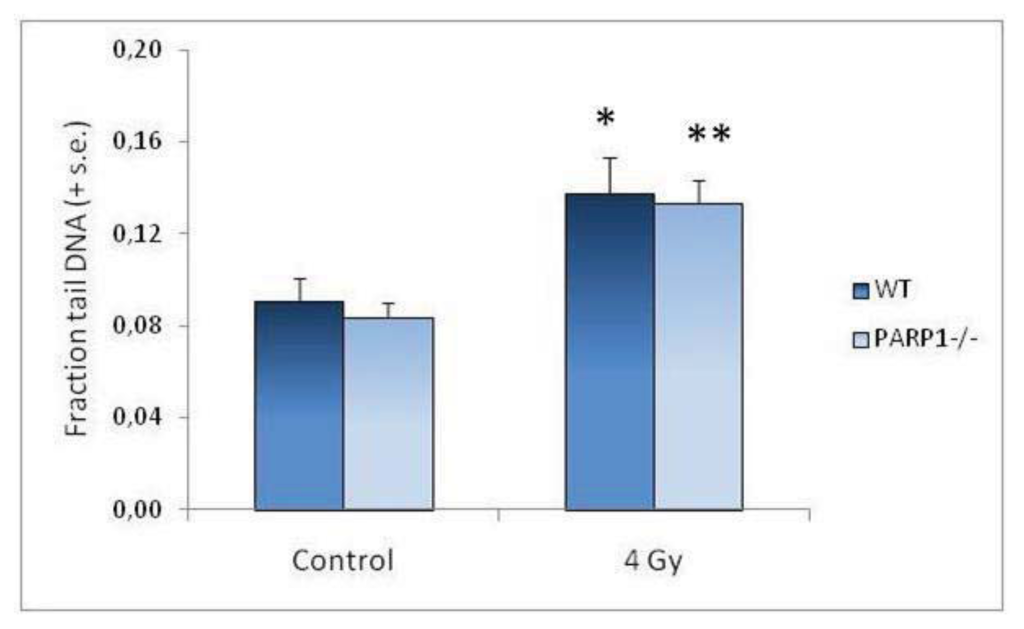
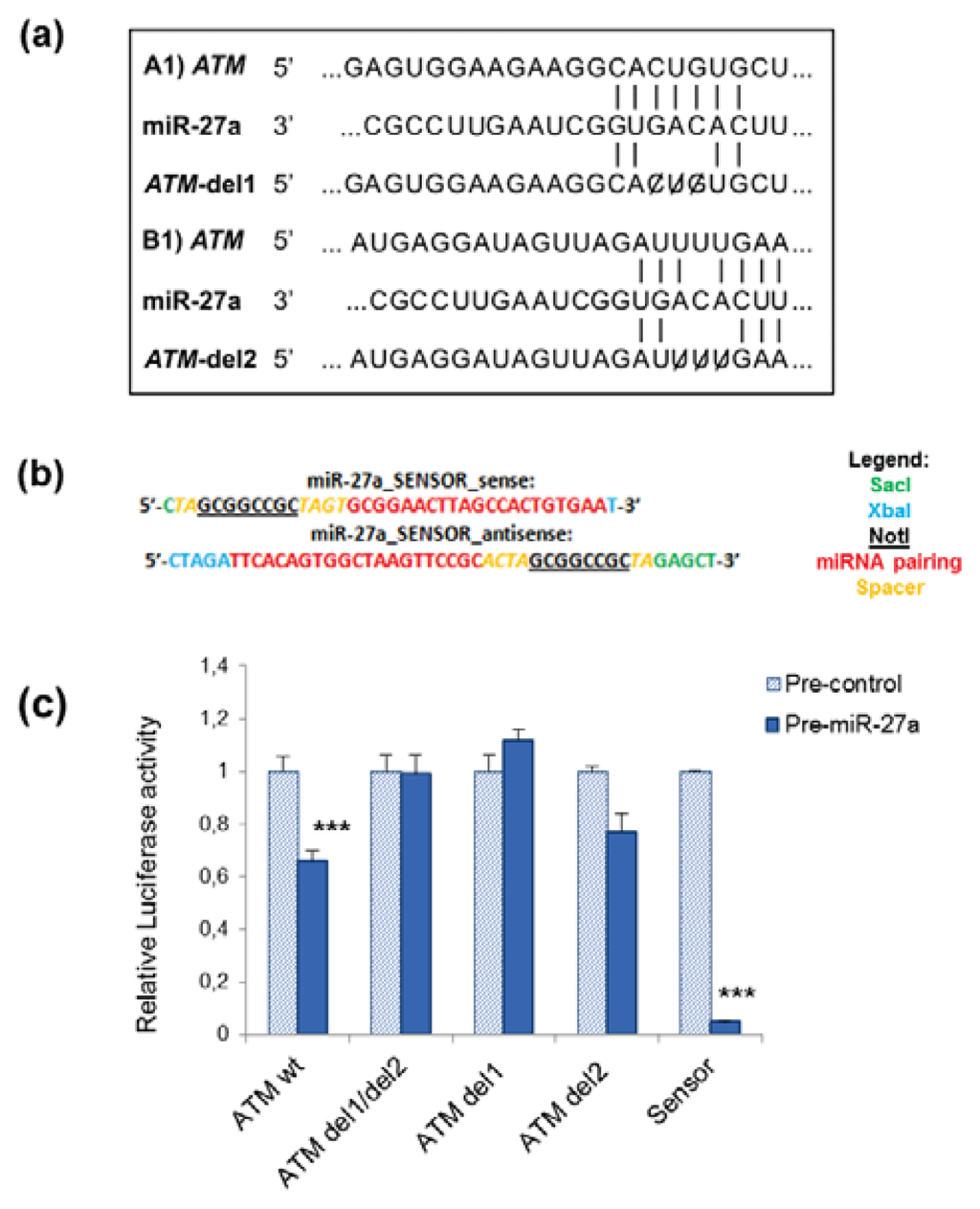
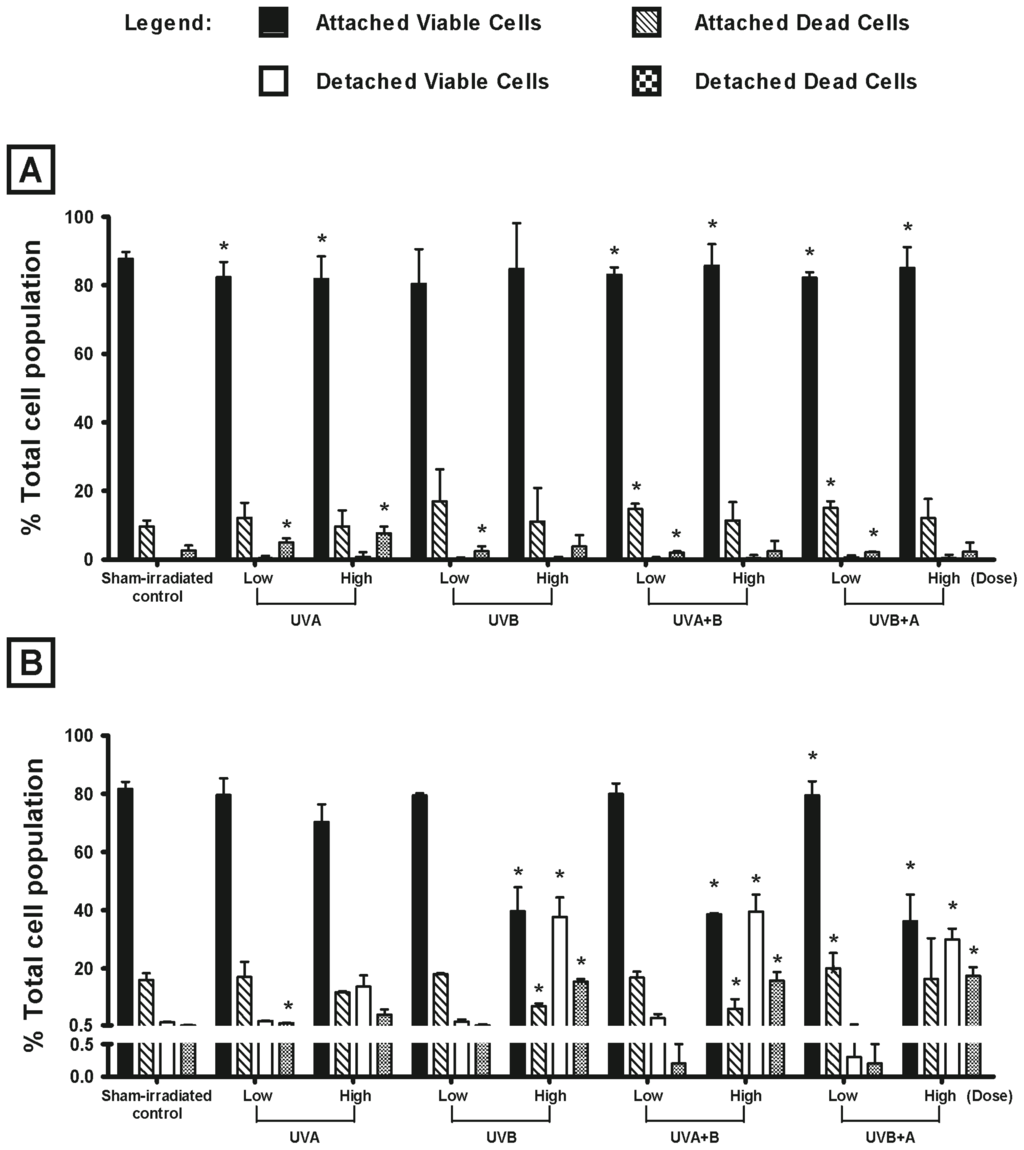
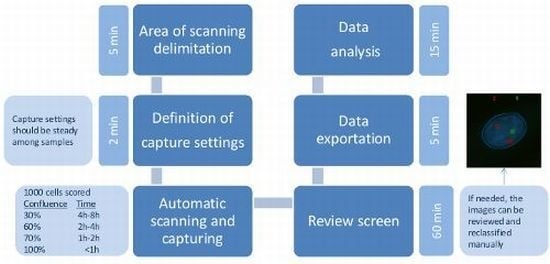
Radiation Toxicity in Cells (Closed)
A topical collection in International Journal of Molecular Sciences (ISSN 1422-0067). This collection belongs to the section "Molecular Toxicology".
Viewed by 683950Editor
Interests: cell signaling; melanoma; photobiology; skin cancer; cell metabolism; melaninognesis; cell motility; ionizing radiation
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
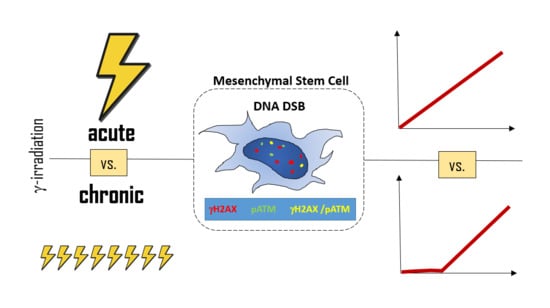
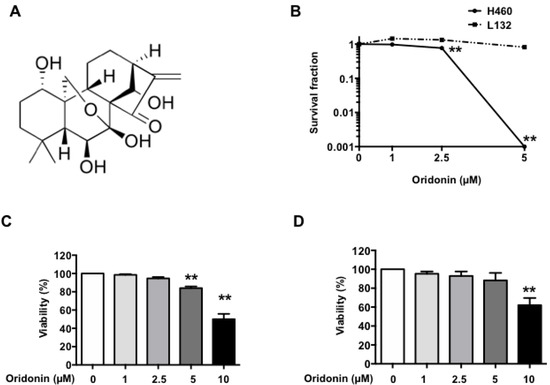
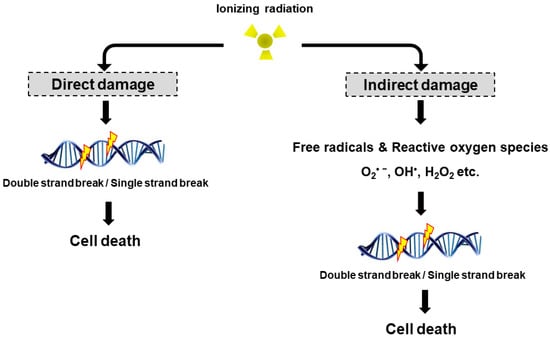
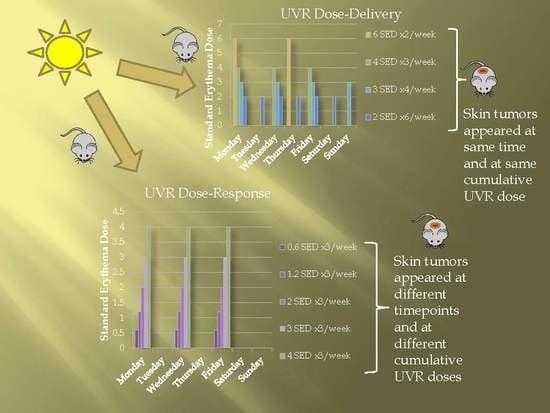
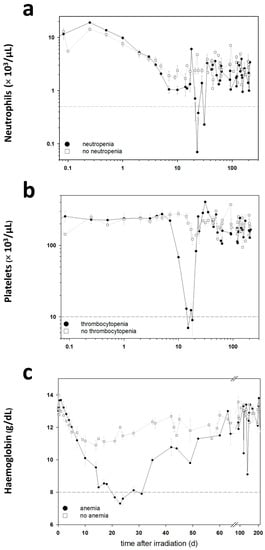
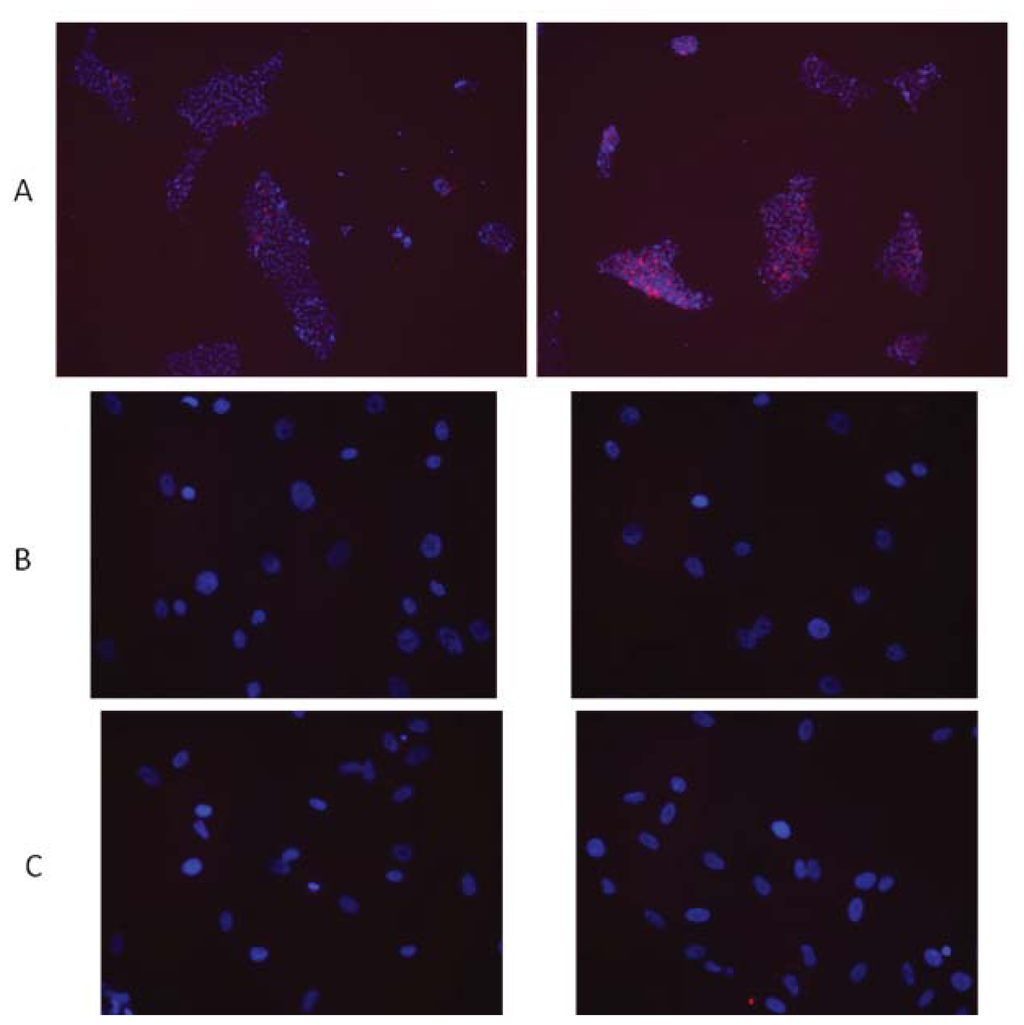
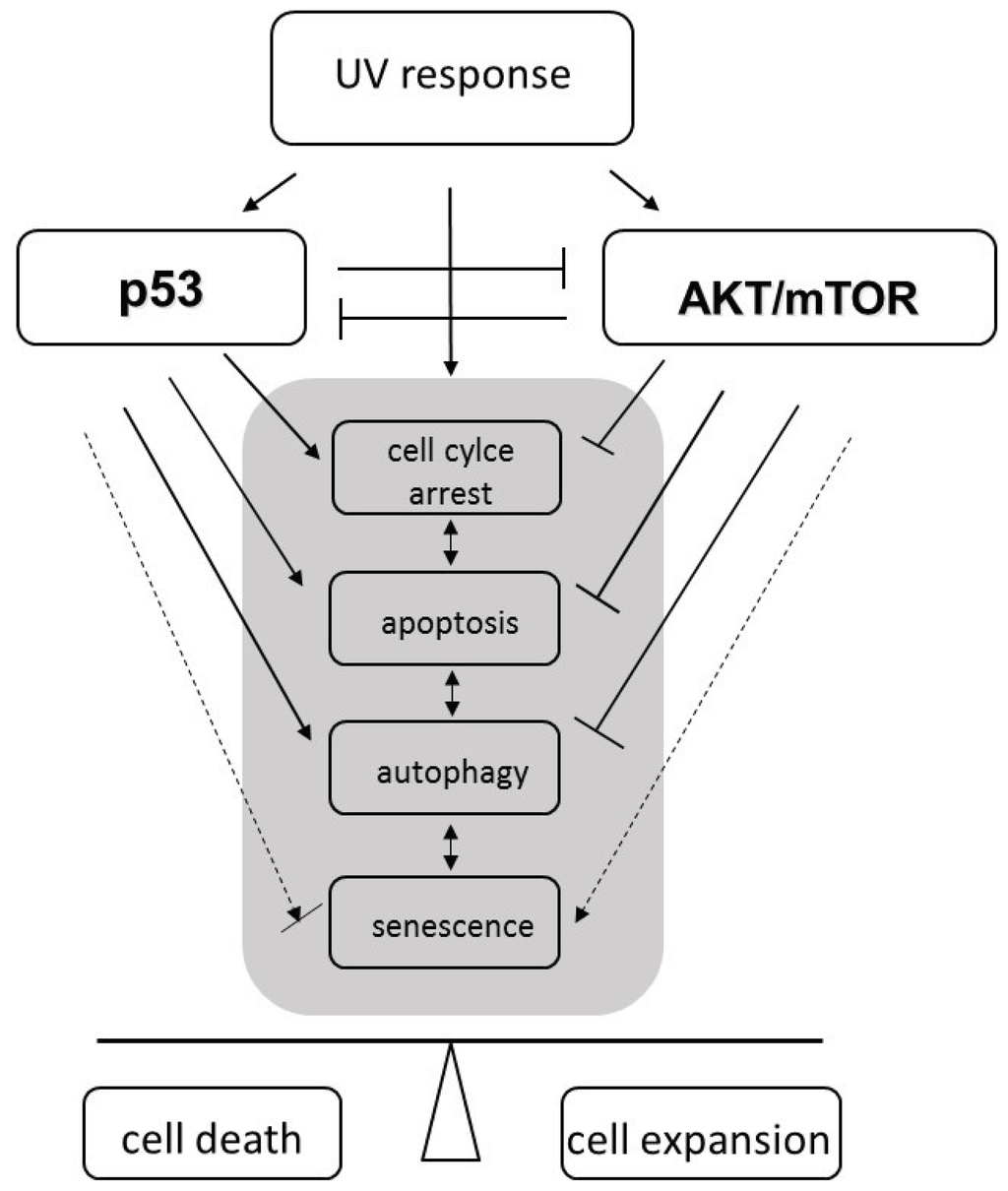
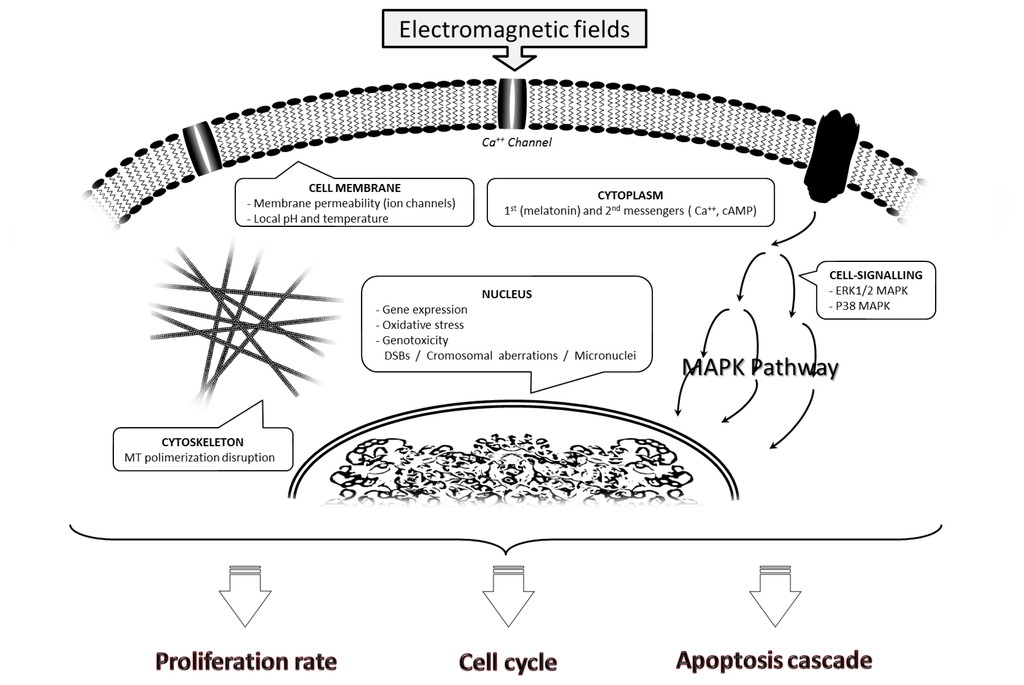
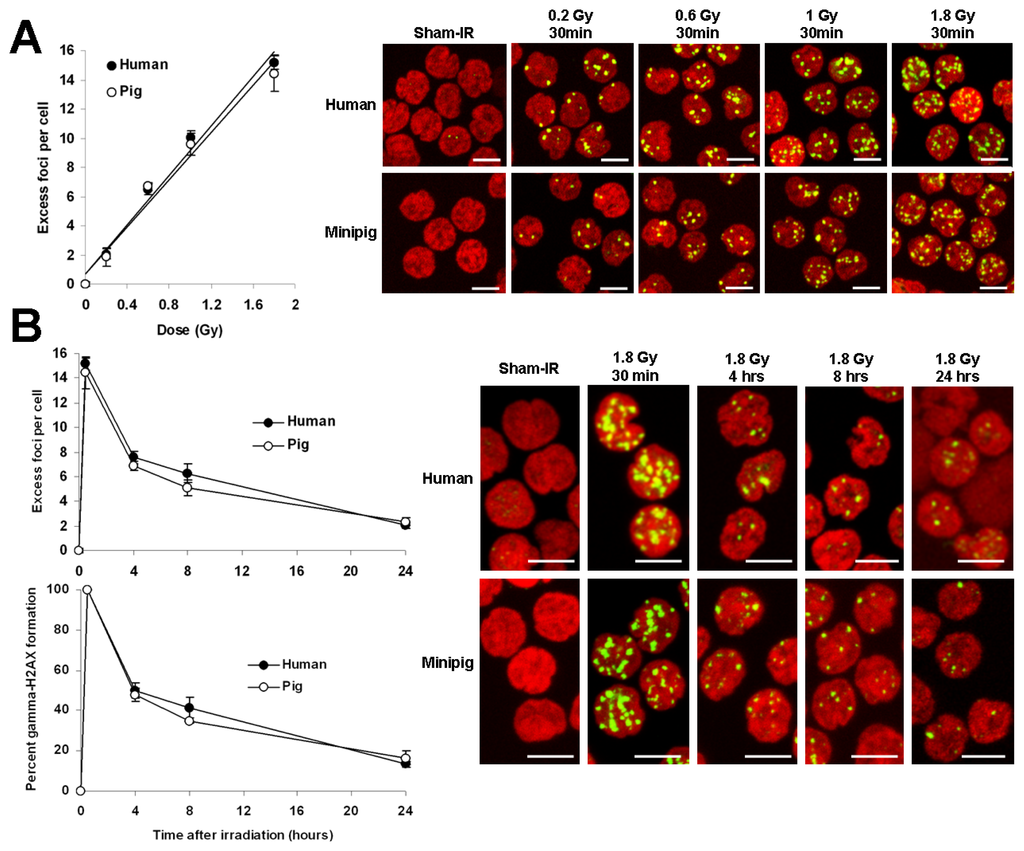
Life forms on the planet are exposed to different forms of radiation. Such radiation may be emitted from the sun, such as X-rays, radio waves, and visible, ultraviolet or infrared light. Radiation may also come from other natural sources, such as α-, β- or γ-radiation. Concern has also been raised about the effects of exposure to microwaves, naturally occurring radioactivity, and heat (thermal radiation). The mechanisms by which these forms of radiation affect cell function differ considerably, but high levels of exposure can result in cell death, and long-term exposure is known to cause a range of cancers.
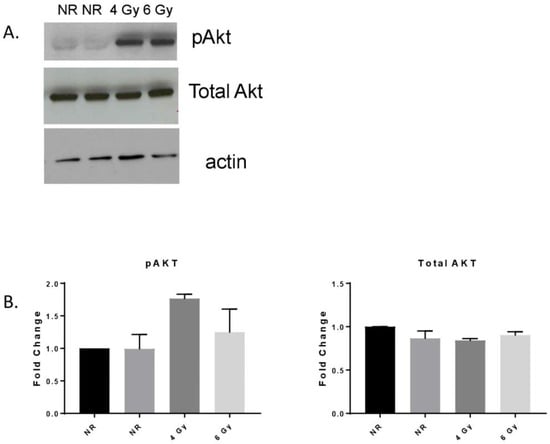
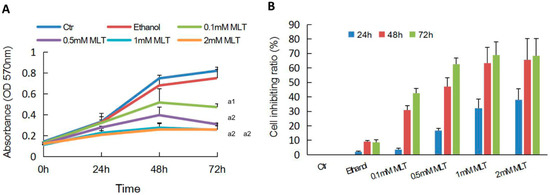
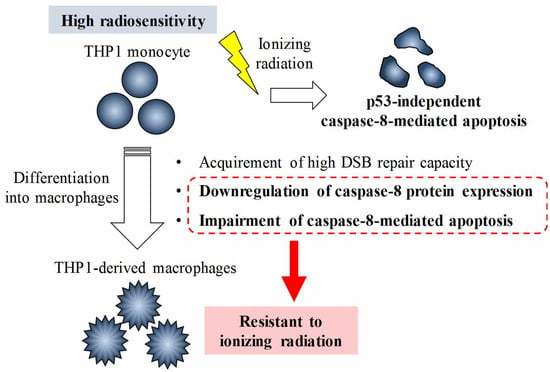
This issue will look at the cytotoxic effects of radiation on living systems; studies will range from those concerning cultured cells to those discussing population and epidemiology. While emphasis will be placed on radiation-induced cytotoxicity, studies discussing radiation’s connections with DNA damage, intracellular signaling pathways, caspase activation, membrane damage, ROS/RNS production, gene activation, organelle dysfunction, and animal and epidemiological studies are also encouraged. Reviews of the mechanisms involved in the cytotoxic effects of electromagnetic radiation are welcomed, as well as studies discussing the effects of long-term human exposure to these forms of radiation. I encourage you to submit a manuscript to this issue so as to help shed further “light” on the lethal effects that radiation has on cells and individuals.
Prof. Dr. Terrence Piva
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts for the topical collection can be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. All papers will be peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on this website. The topical collection considers regular research articles, short communications and review articles. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The article processing charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Keywords
- radiation
- ultraviolet light
- X-rays
- γ radiation
- microwaves
- cell death pathways
- DNA damage
- cell membrane
- ROS
- signaling pathways
- epidemiology studies
- animal studies