Digital Dentistry: State of the Art and Future Perspectives
A topical collection in Oral (ISSN 2673-6373).
Viewed by 16030
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Lucio Lo Russo
Prof. Dr. Lucio Lo Russo
 Prof. Dr. Lucio Lo Russo
Prof. Dr. Lucio Lo Russo
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Periodontology and Oral Implantology, Dental Research Division, Foggia University, 71122 Foggia, Italy
Interests: digital dentistry; implant dentistry; prosthodontics; oral medicine; periodontology
 Dr. Ji-Man Park
Dr. Ji-Man Park
 Dr. Ji-Man Park
Dr. Ji-Man Park
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Prosthodontics and Dental Research Institute, Seoul National University School of Dentistry, Seoul 03080, Republic of Korea
Interests: 3D-printed devices; additive manufacturing; bioprinting; digital dentistry; digital denture manufacturing; intraoral scanner; patient-specific dental implant; robotic surgery system; zirconia 3D printer
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Digital technologies are reshaping dental practice. With new materials, new application procedures, and clinical protocols, they are widening the available options for oral rehabilitation. Digital dentistry is constantly contributing to the standardization and quality improvement of dental treatments, facilitating the effectiveness and efficiency of dental offices and laboratories. Transforming all options made available by digital dental technologies into an opportunity to make oral rehabilitation affordable for patients while keeping profitability in mind for oral healthcare providers may be boosted by the dissemination of the current state of the art and research for future applications. As such, the aim of this topical collection is to promote knowledge sharing regarding what is immediately applicable to clinical practice and the current issues or challenges that ongoing or future research can address.
Prof. Dr. Lucio Lo Russo
Dr. Ji-Man Park
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Oral is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1200 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- digital dentistry
- intraoral scans
- 3D printing
- milling
- clear aligners
- digital dentures
- guided implant surgery
- chairside dentistry
Published Papers (4 papers)
2025
Open AccessReview
The Role of Digital Innovations in Shaping Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics: A Narrative Review
by
Mariya Dimitrova
Viewed by 1982
Abstract
The rapid digitization of dentistry is significantly transforming fixed prosthodontics, a discipline highly dependent on technical precision. This narrative review, incorporating a structured literature search, provides a critical overview of how digital tools—including computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM), intraoral scanners (IOS), and additive
[...] Read more.
The rapid digitization of dentistry is significantly transforming fixed prosthodontics, a discipline highly dependent on technical precision. This narrative review, incorporating a structured literature search, provides a critical overview of how digital tools—including computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM), intraoral scanners (IOS), and additive manufacturing—are influencing clinical protocols and production methods. A database-guided selection process was employed to identify relevant studies published between 2000 and 2024, spanning in vitro research, observational studies, and clinical trials. While digital workflows offer promising benefits, such as increased accuracy, efficiency, and patient comfort, supporting evidence remains preclinical or short-term in nature. The review highlights areas of innovation as well as ongoing limitations in clinical validation, standardization, and adoption. A more cautious interpretation of the current evidence is warranted, especially regarding long-term clinical outcomes and cost-effectiveness. This review aims to inform clinicians, researchers, and educators about both the potential and the present limitations of digital fixed prosthodontics.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
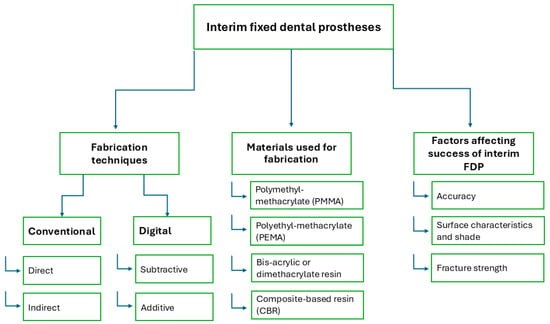
Interim Fixed Dental Prostheses Fabrication Techniques and Factors Affecting Their Success: A Narrative Review
by
Nour Abdelmohsen, Christoph Bourauel and Tarek M. Elshazly
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2255
Abstract
Interim fixed dental prostheses (FDPs) play a crucial role in maintaining oral stability during the construction of final FDPs. Traditionally, interim FDPs were fabricated using conventional methods. However, advancements in digital dentistry have introduced computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) techniques, including milling from prefabricated blanks
[...] Read more.
Interim fixed dental prostheses (FDPs) play a crucial role in maintaining oral stability during the construction of final FDPs. Traditionally, interim FDPs were fabricated using conventional methods. However, advancements in digital dentistry have introduced computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) techniques, including milling from prefabricated blanks and three-dimensional (3D) printing using light-sensitive resins, as common production methods. The aim of this review was to accumulate data on various fabrication techniques for interim FDPs, the materials used in their production, and the impact of each technique on key factors influencing the success of interim FDPs. We concluded that each technique for fabricating interim FDPs has its own advantages and limitations, and all can be effectively utilized for FDP production. However, digital techniques provide superior quality compared to conventional methods, particularly for long-term use.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Three-Dimensional Printing in Dentistry: A Scoping Review of Clinical Applications, Advantages, and Current Limitations
by
Mi-Kyoung Jun, Jong-Woo Kim and Hye-Min Ku
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 9064
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) printing is transforming dentistry by enabling precise and personalized treatments in prosthodontics, orthodontics, and endodontics. However, challenges such as high costs, material limitations, and post-processing requirements hinder its broader adoption. This scoping review aims to explore and map the breadth of
[...] Read more.
Three-dimensional (3D) printing is transforming dentistry by enabling precise and personalized treatments in prosthodontics, orthodontics, and endodontics. However, challenges such as high costs, material limitations, and post-processing requirements hinder its broader adoption. This scoping review aims to explore and map the breadth of evidence regarding the clinical applications, benefits, and limitations of 3D printing in these disciplines, while identifying research gaps and future opportunities. A scoping review was conducted following the PRISMA for scoping reviews framework. Research from PubMed, Google Scholar, and Scopus was systematically searched, covering studies from January 2006 to November 2024. Key topics included applications, material properties, and technological challenges in prosthodontics, orthodontics, and endodontics. Results: In prosthodontics, 3D printing facilitates the fabrication of crowns, bridges, and dentures with high accuracy, though material strength and stability remain challenges. Orthodontics benefits from 3D-printed aligners and diagnostic models, improving patient comfort and treatment precision, but issues with material durability persist. In endodontics, 3D-printed surgical guides and training models enhance procedural accuracy and educational outcomes. Across disciplines, 3D printing reduces production time and enhances customization but incurs high costs and requires significant post-processing. This scoping review highlights the transformative potential of 3D printing in dentistry, providing an overview of current and future advancements and limitations. While 3D printing has improved precision, efficiency, and patient satisfaction, material and cost-related barriers remain. Future research should address these challenges to expand its clinical applicability and enhance personalized dental care.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessTechnical Note
Digital Denture Cast-Free Workflow Merging Concepts and Advantages of Mucostatics and Mucocompressive Philosophies
by
Lucio Lo Russo, Laura Guida, Mauro Lorusso, Alfredo De Lillo, Domenico Ciavarella and Fariba Esperouz
Viewed by 1817
Abstract
Background: Mucostatic impressions have been always indicated in thin, sharp, or flabby ridges, and have been addressed for their beneficial effect on long-term residual ridge stability. Nonetheless, a purely mucostatic impression was not possible until intraoral scans became available. This provides an option
[...] Read more.
Background: Mucostatic impressions have been always indicated in thin, sharp, or flabby ridges, and have been addressed for their beneficial effect on long-term residual ridge stability. Nonetheless, a purely mucostatic impression was not possible until intraoral scans became available. This provides an option for digital removable denture which is biologically sensible but might reduce retention in comparison with a mucocompressive impression with border molding. On the other hand, pressure applied to the mucosa may have harmful effects on the long-term residual ridge stability, causing higher resorption and ultimately reduced denture retention. Hence, the possibility to merge mucostatics and mucocompressive philosophies would be a clinically and biologically sensible option for oral rehabilitation in aging populations where patients will potentially wear dentures for longer periods. This possibility is demonstrated in this technical report with a cast-free digital workflow. Technique: Baseplates for occlusion rims, closely adapted to the mucosa, were designed on intraoral scans of edentulous arches and, once 3D-printed, used to register maxillomandibular relations and information for tooth arrangement, as well as to perform border molding. Occlusion rims were then scanned and, within the 3Shape Dental System 2024 software program, the intaglio surfaces of their baseplates were segmented and inverted to obtain the digital master casts which incorporated the precise reproduction of the molded borders. Then, denture design was performed and manufactured; no limitations regarding manufacturing options are applicable to the presented technique. Conclusions: The potential benefits (i.e., improved retention in the initial period after denture delivery and the preservation of tissues) of the presented digital cast-free workflow, based on merging mucostatic and mucocompressive philosophies to obtain dentures with a mucostatic intaglio surface and functional borders, are sensible clinical outcomes which recommend the clinical application of the technique, although further validation, especially in the long term, is required.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures