Histone Demethylases
A topical collection in Epigenomes (ISSN 2075-4655).
Viewed by 8006Editor
Interests: p53; apoptosis; cancer therapy; cancer biology; cancer cell biology; tumor biology; DNA damage; molecular oncology; clinical oncology; medical oncology
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
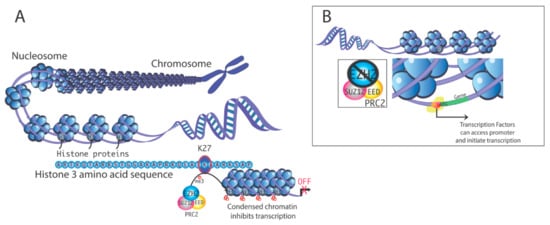
Histone demethylases are an expanding group of epigenetic regulators of chromatin structure and gene expression and play diverse roles in both embryonal development and disease. These histone demethylating enzymes antagonize the activity of histone methyl transferases by removing methyl groups from the specific lysine residue in the histones and in other non-histone target proteins, such as p53.
The first histone demethylase to be discovered was LSD1 (KDM1), an enzyme of critical importance for embryogenesis and embryonic stem cells. Recent evidence indicates that histone demethylases play important roles in tumorigenesis, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, invasion, metastases, and cancer stem cell phenotypes. For instance, Jumonji family histone demethylases collaborate with pathogenic H3K27M mutations in pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas by removing the tri-methylation mark from histone H3 lysine 27, thus triggering global de-repression of genes involved in cancer stemness. Accordingly, overexpression of Jumonji family demethylases has been linked to chemotherapy and radiation resistance, and poor prognosis. Emerging are the functions of histone demethylases in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
The aim of this Topical Collection is to highlight the diverse roles histone demethylases play in embryonic development and human diseases, such as cancer and neurodegenerative disease. We are particularly interested in experimental basic science and translational research studies focusing on pharmacological targeting histone demethylases, as well as review articles that would illuminate recent advances in our understanding of histone demethylase functions in cancer and other diseases.
Dr. Anatoly Nikolaev
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Epigenomes is an international peer-reviewed open access quarterly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- histones
- H3K27
- H3K27M
- methylation
- demethylation
- Jumonji
- LSD1
- KDM1
- embryogenesis
- KDM5
- KDM6
- cancer stem cells
- pediatric glioma
- leukemia
- lymphoma
- multiple myeloma
- neurodegeneration
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s diseases