Differential Expression of STK35L1-Associated Transcription Factors in Plasmodium Infection During the Liver Stage of Malaria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
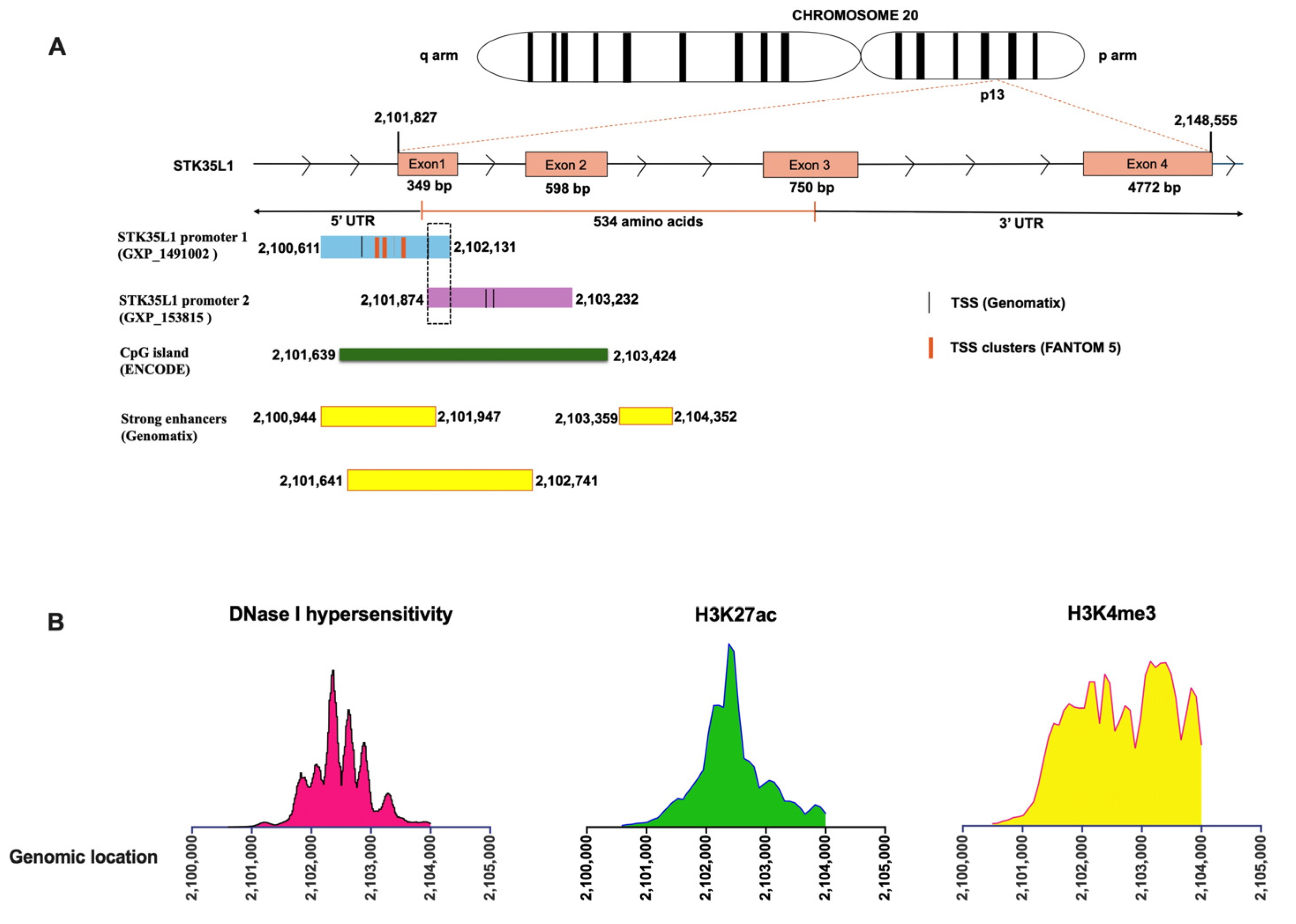
2.1. Identification and Characterization of the Human STK35 Promoter
2.2. Identification of Putative Transcription Factors Binding to the STK35L1 Promoter Region
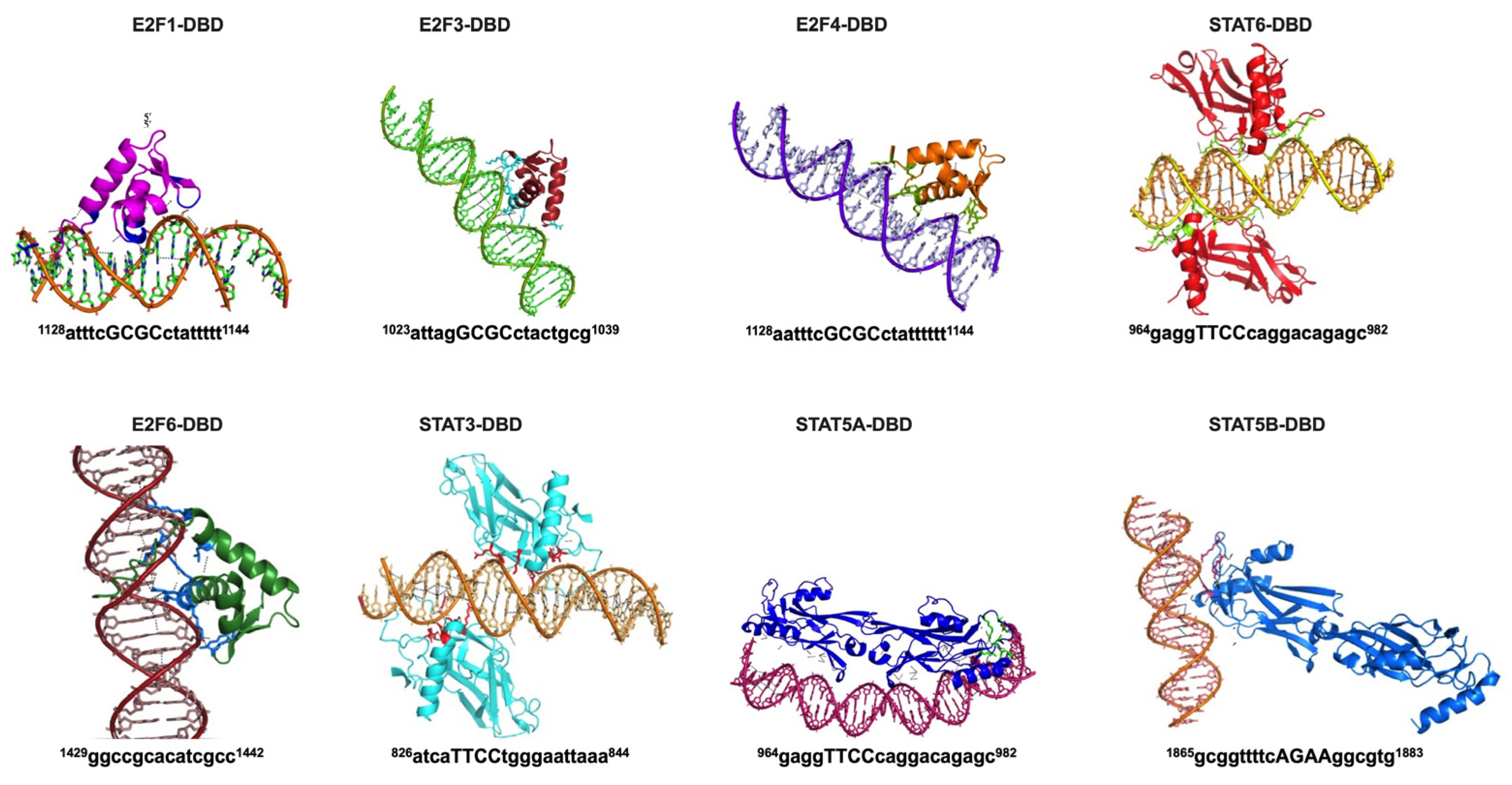
2.3. Identification of Transcription Factors Binding Regions in the Promoter of STK35L1
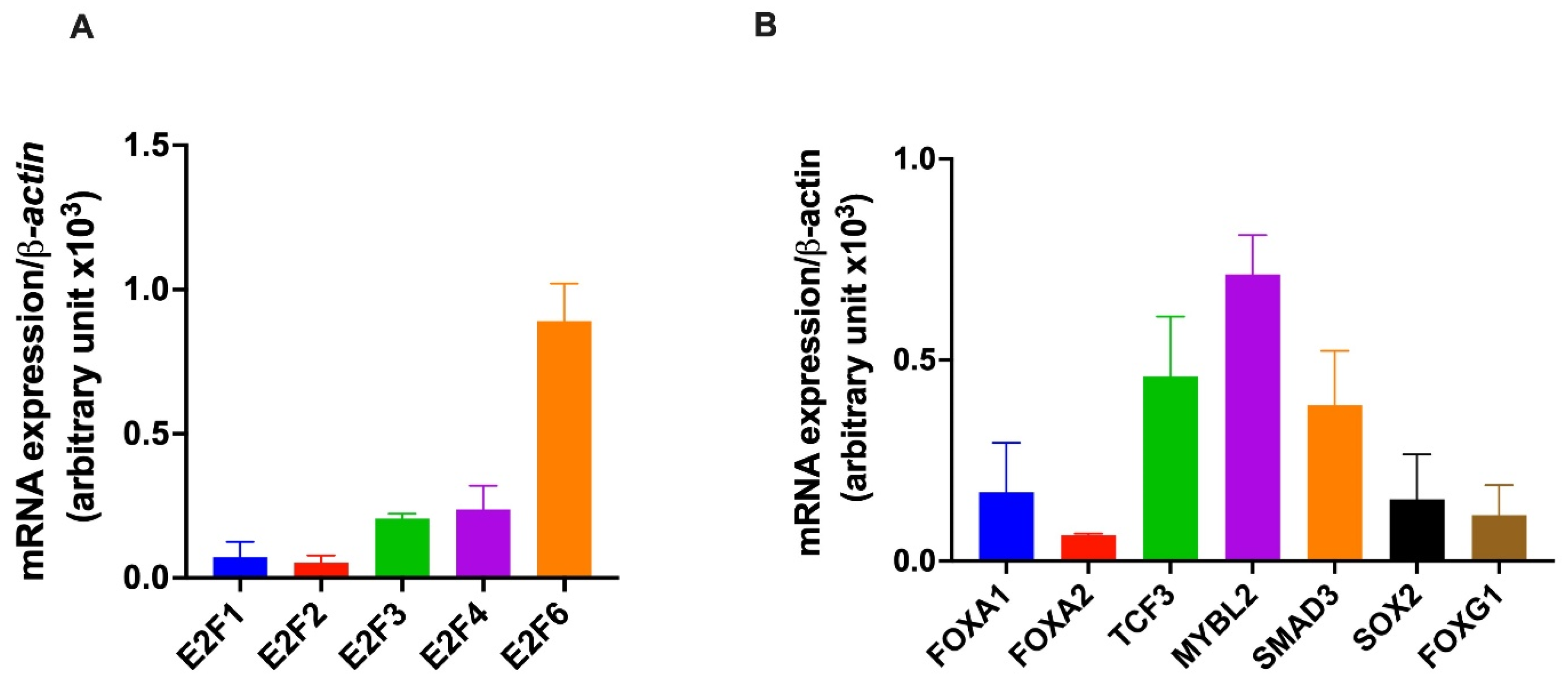
2.4. Expression of Identified Transcription Factors in HepG2 Cells
2.5. STK35L1-Linked TFs Were Differentially Expressed During Plasmodium Sporozoites Infection in HepG2 Cells
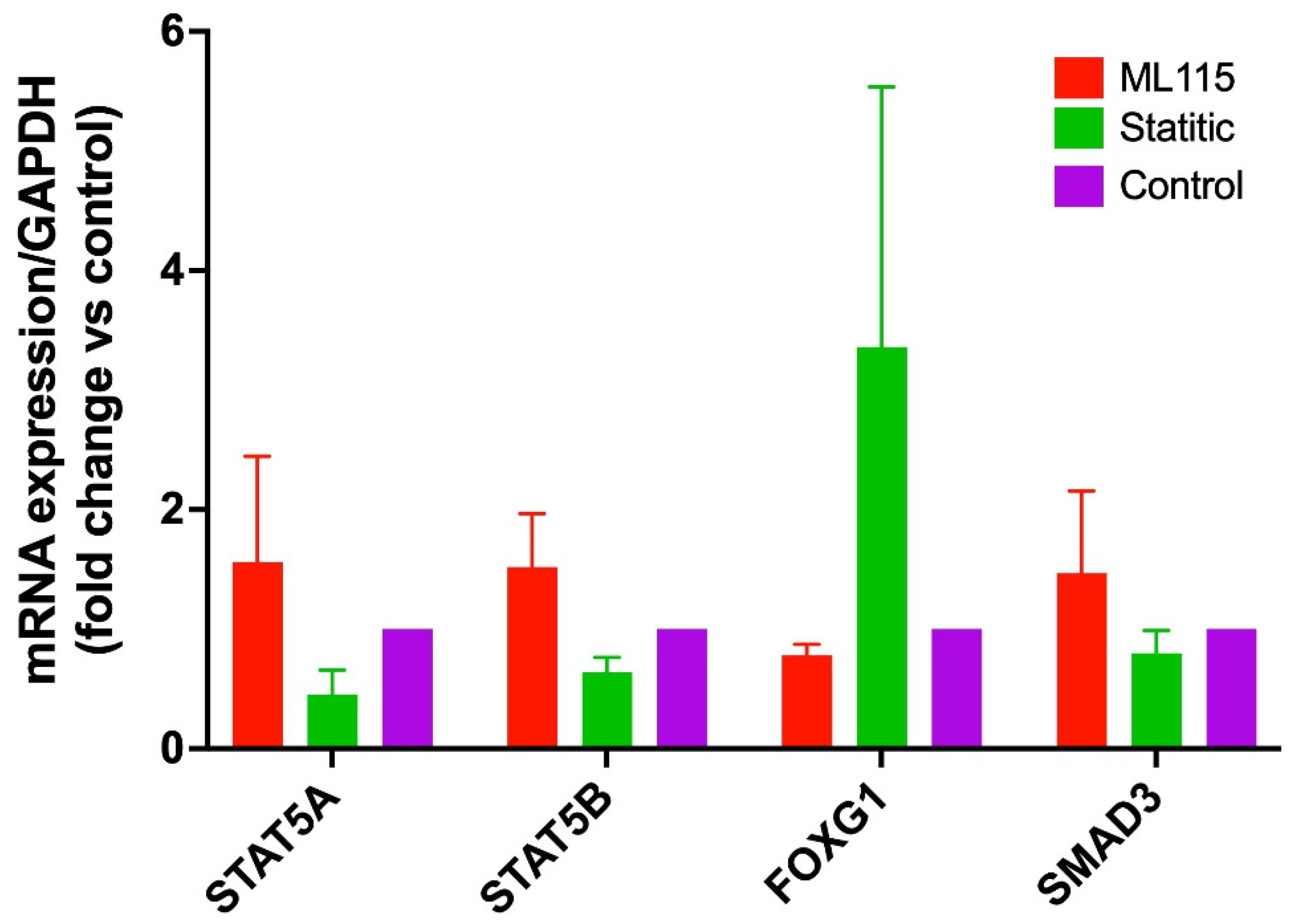
2.6. Upregulation of the Selected TFs Is Independent of STAT3 Activation During the Plasmodium Infection in HepG2 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Mosquito Rearing and Sporozoite Production
4.3. Cell Culture and HepG2 Cell Infection
4.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
4.5. Promoter Prediction
4.6. Protein–DNA Modelling
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| STAT | Signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| SMAD | Suppressor of mothers against decapentaplegic |
| MYBL2 | MYB Proto-Oncogene Like 2 |
| TCF3 | Transcription factor 3 |
| FOX | Forkhead-box |
| TF | Transcription factor |
| AF3 | AlphaFold 3.0 |
References
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2024: Addressing Inequity in the Global Malaria Response; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- von Seidlein, L.; Peto, T.J.; Landier, J.; Nguyen, T.-N.; Tripura, R.; Phommasone, K.; Pongvongsa, T.; Lwin, K.M.; Keereecharoen, L.; Kajeechiwa, L.; et al. The impact of targeted malaria elimination with mass drug administrations on falciparum malaria in Southeast Asia: A cluster randomised trial. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerig, C.; Abdi, A.; Bland, N.; Eschenlauer, S.; Dorin-Semblat, D.; Fennell, C.; Halbert, J.; Holland, Z.; Nivez, M.-P.; Semblat, J.-P.; et al. Malaria: Targeting parasite and host cell kinomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2010, 1804, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arang, N.; Kain, H.S.; Glennon, E.K.; Bello, T.; Dudgeon, D.R.; Walter, E.N.F.; Gujral, T.S.; Kaushansky, A. Identifying host regulators and inhibitors of liver stage malaria infection using kinase activity profiles. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudêncio, M.; Rodrigues, C.D.; Hannus, M.; Martin, C.; Real, E.; Gonçalves, L.A.; Carret, C.; Dorkin, R.; Röhl, I.; Jahn-Hoffmann, K.; et al. Kinome-wide RNAi screen implicates at least 5 host hepatocyte kinases in Plasmodium sporozoite infection. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adderley, J.D.; John von Freyend, S.; Jackson, S.A.; Bird, M.J.; Burns, A.L.; Anar, B.; Metcalf, T.; Semblat, J.-P.; Billker, O.; Wilson, D.W.; et al. Analysis of erythrocyte signalling pathways during Plasmodium falciparum infection identifies targets for host-directed antimalarial intervention. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Kalia, I.; Kaushik, V.; Brünnert, D.; Quadiri, A.; Kashif, M.; Chahar, K.R.; Agrawal, A.; Singh, A.P.; Goyal, P. STK35L1 regulates host cell cycle-related genes and is essential for Plasmodium infection during the liver stage of malaria. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 406, 112764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.; Behring, A.; Kumar, A.; Siess, W. STK35L1 associates with nuclear actin and regulates cell cycle and migration of endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.; Behring, A.; Kumar, A.; Siess, W. Identifying and characterizing a novel protein kinase STK35L1 and deciphering its orthologs and close-homologs in vertebrates. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Whiley, P.A.F.; Goh, H.Y.; Wong, C.; Higgins, G.; Tachibana, T.; McMenamin, P.G.; Mayne, L.; Loveland, K.L. The STK35 locus contributes to normal gametogenesis and encodes a lncRNA responsive to oxidative stress. Biol. Open 2018, 7, bio032631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Bao, Y.; Chen, T.; Xu, P.; Liu, Z.; Ma, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Mapping functional elements of the DNA damage response through base editor screens. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 115047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, Y.; Miyamoto, Y.; Yamashiro, T.; Asally, M.; Masui, A.; Wong, C.; Loveland, K.L.; Yoneda, Y. Nuclear retention of importin α coordinates cell fate through changes in gene expression. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Hu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Li, S. Serine/Threonine kinase 35, a target gene of STAT3, regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, J. STK35 Is ubiquitinated by NEDD4L and promotes glycolysis and inhibits apoptosis through regulating the AKT signaling pathway, influencing chemoresistance of colorectal cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 582695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyanskaya, S.A.; Moreno, R.Y.; Lu, B.; Feng, R.; Yao, Y.; Irani, S.; Klingbeil, O.; Yang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Demerdash, O.E.; et al. SCP4-STK35/PDIK1L complex is a dual phospho-catalytic signaling dependency in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Qin, L.; Liu, G.; Zhao, S.; Peng, N.; Chen, X. Dynamic balance of pSTAT1 and pSTAT3 in C57BL/6 mice infected with lethal Or nonlethal Plasmodium yoelii. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 5, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Amodu, A.S.; Pitts, S.; Patrickson, J.; Hibbert, J.M.; Battle, M.; Ofori-Acquah, S.F.; Stiles, J.K. Heme mediated STAT3 activation in severe malaria. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Jove, R. The STATs of cancer—new molecular targets come of age. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehret, G.B.; Reichenbach, P.; Schindler, U.; Horvath, C.M.; Fritz, S.; Nabholz, M.; Bucher, P. DNA binding specificity of different STAT proteins: Comparison of in vitro specificity with natural target sites. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 6675–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, R.; de la Vega, P.; Paik, S.H.; Murata, Y.; Ferguson, E.W.; Richie, T.L.; Ooi, G.T. Early transcriptional responses of HepG2-A16 liver cells to infection by Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 26396–26405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, S.S.; Carret, C.; Grosso, A.R.; Tarun, A.S.; Peng, X.; Kappe, S.H.I.; Prudêncio, M.; Mota, M.M. Host cell transcriptional profiling during malaria liver stage infection reveals a coordinated and sequential set of biological events. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizio, M.; Harshbarger, J.; Shimoji, H.; Severin, J.; Kasukawa, T.; Sahin, S.; Abugessaisa, I.; Fukuda, S.; Hori, F.; Ishikawa-Kato, S.; et al. Gateways to the FANTOM5 promoter level mammalian expression atlas. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunham, I.; Kundaje, A.; Aldred, S.F.; Collins, P.J.; Davis, C.A.; Doyle, F.; Epstein, C.B.; Frietze, S.; Harrow, J.; Kaul, R.; et al. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012, 489, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartharius, K.; Frech, K.; Grote, K.; Klocke, B.; Haltmeier, M.; Klingenhoff, A.; Frisch, M.; Bayerlein, M.; Werner, T. MatInspector and beyond: Promoter analysis based on transcription factor binding sites. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2933–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’Ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachmann, A.; Xu, H.; Krishnan, J.; Berger, S.I.; Mazloom, A.R.; Ma’ayan, A. ChEA: Transcription factor regulation inferred from integrating genome-wide ChIP-X experiments. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2438–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madoux, F.; Koenig, M.; Nelson, E.; Chowdhury, S.; Cameron, M.; Mercer, B.A.; Roush, W.; Frank, D.; Hodder, P. Modulators of STAT transcription factors for the targeted therapy of cancer (STAT3 activators). In Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]; National centre for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schust, J.; Sperl, B.; Hollis, A.; Mayer, T.U.; Berg, T. Stattic: A small-molecule inhibitor of STAT3 activation and dimerization. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberle, V.; Stark, A. Eukaryotic core promoters and the functional basis of transcription initiation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 621–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraki, T.; Kondo, S.; Katayama, S.; Waki, K.; Kasukawa, T.; Kawaji, H.; Kodzius, R.; Watahiki, A.; Nakamura, M.; Arakawa, T.; et al. Cap analysis gene expression for high-throughput analysis of transcriptional starting point and identification of promoter usage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15776–15781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Hitz, B.C.; Gabdank, I.; Hilton, J.A.; Kagda, M.S.; Lam, B.; Myers, Z.; Sud, P.; Jou, J.; Lin, K.; et al. New developments on the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) data portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D882–D889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaton, A.M.; Bird, A. CpG islands and the regulation of transcription. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Carrozzi, V.R.; Braas, D.; Bhatt, D.M.; Cheng, C.S.; Hong, C.; Doty, K.R.; Black, J.C.; Hoffmann, A.; Carey, M.; Smale, S.T. A unifying model for the selective regulation of inducible transcription by CpG islands and nucleosome remodeling. Cell 2009, 138, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beacon, T.H.; Delcuve, G.P.; López, C.; Nardocci, G.; Kovalchuk, I.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Davie, J.R. The dynamic broad epigenetic (H3K4me3, H3K27ac) domain as a mark of essential genes. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, D.; David, G.J. Distinct and overlapping roles for E2F family members in transcription, proliferation and apoptosis. Curr. Mol. Med. 2006, 6, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bracken, A.P.; Ciro, M.; Cocito, A.; Helin, K. E2F target genes: Unraveling the biology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epiphanio, S.; Mikolajczak, S.A.; Gonçalves, L.A.; Pamplona, A.; Portugal, S.; Albuquerque, S.; Goldberg, M.; Rebelo, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Akinc, A.; et al. Heme oxygenase-1 Is an anti-inflammatory host factor that promotes murine plasmodium liver infection. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesina, A.M.; Nguyen, Y.; Guanaratne, P.; Pulliam, J.; Lopez-Terrada, D.; Margolin, J.; Finegold, M. FOXG1 is overexpressed in hepatoblastoma. Hum. Pathol. 2007, 38, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Shang, L.; Pan, B.-Q.; Wang, X.-M.; Jiang, Y.-Y.; Hao, J.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhan, Q.-M.; et al. Calreticulin promotes migration and invasion of esophageal cancer cells by upregulating neuropilin-1 expression via STAT5A. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6153–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagvadorj, A.; Kirken, R.A.; Leiby, B.; Karras, J.; Nevalainen, M.T. Transcription factor signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 promotes growth of human prostate cancer cells in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicirò, Y.; Sala, A. MYB oncoproteins: Emerging players and potential therapeutic targets in human cancer. Oncogenesis 2021, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Fan, J.; Liu, Z.; Tang, R.; Wang, X.; Bo, H.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, X.; Huang, Z.; Xing, L.; et al. TCF3 regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of human spermatogonial stem cells by targeting PODXL. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 695545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Wu, J.; Pattaradilokrat, S.; Tumas, K.; He, X.; Peng, Y.-C.; Huang, R.; Myers, T.G.; Long, C.A.; Wang, R.; et al. Detection of host pathways universally inhibited after Plasmodium yoelii infection for immune intervention. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, D.; Hüser, L.; Elton, J.J.; Umansky, V.; Altevogt, P.; Utikal, J. SOX2 in development and cancer biology. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 67, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, D.; Bauer, J.; Wise, P.; Krüger, M.; Simonsen, U.; Wehland, M.; Infanger, M.; Corydon, T.J. The role of SOX family members in solid tumours and metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 67, 122–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derynck, R.; Zhang, Y.E. Smad-dependent and smad-independent pathways in TGF-β family signalling. Nature 2003, 425, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, F.M.; de Souza, J.B.; Corran, P.H.; Sultan, A.A.; Riley, E.M. Activation of transforming growth factor β by malaria parasite-derived metalloproteinases and a thrombospondin-like molecule. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Transcription Factor | NCBI Gene IDs | NCBI Protein IDs |
|---|---|---|
| STAT5A | >NM_001288718.1 | NP_001275647.1 |
| STAT5B | >NM_012448.3 | NP_036580.2 |
| STAT6 | >NM_001178078.2 | NP_001171549.1 |
| STAT3 | >NM_139276.2 | NP_644805.1 |
| E2F1 | >NM_005225.2 | NP_005216.1 |
| E2F2 | >NM_004091.3 | NP_004082.1 |
| E2F3 | >NM_001949.4 | NP_001940.1 |
| E2F4 | >NM_001950.3 | NP_001941.2 |
| E2F6 | >NM_198256.4 | NP_937987.2 |
| FOXA1 | >NM_004496.5 | NP_004487.2 |
| FOXA2 | >NM_021784.4 | NP_068556.2 |
| TCF3 | >NM_003200.5 | NP_001129611.1 |
| FOXG1 | >NM_005249.5 | NP_005240.3 |
| MYBL2 | >NM_002466.4 | NP_002457.1 |
| SMAD3 | >NM_005902.4 | NP_005893.1 |
| SOX2 | >NM_003106.4 | NP_003097.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yadav, A.; Sharma, P.K.; Hazarika, M.; Gehlot, P.; Bage, S.; Saini, M.; Gaur, K.; Aswathi, A.P.; Thakur, M.; Sawant, D.M.; et al. Differential Expression of STK35L1-Associated Transcription Factors in Plasmodium Infection During the Liver Stage of Malaria. Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040026
Yadav A, Sharma PK, Hazarika M, Gehlot P, Bage S, Saini M, Gaur K, Aswathi AP, Thakur M, Sawant DM, et al. Differential Expression of STK35L1-Associated Transcription Factors in Plasmodium Infection During the Liver Stage of Malaria. Kinases and Phosphatases. 2025; 3(4):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040026
Chicago/Turabian StyleYadav, Arpana, Phulwanti Kumari Sharma, Mayuree Hazarika, Pragya Gehlot, Saloni Bage, Mahesh Saini, Kritika Gaur, Acham Parambath Aswathi, Malti Thakur, Devesh Madhukar Sawant, and et al. 2025. "Differential Expression of STK35L1-Associated Transcription Factors in Plasmodium Infection During the Liver Stage of Malaria" Kinases and Phosphatases 3, no. 4: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040026
APA StyleYadav, A., Sharma, P. K., Hazarika, M., Gehlot, P., Bage, S., Saini, M., Gaur, K., Aswathi, A. P., Thakur, M., Sawant, D. M., Singh, A. P., Brünnert, D., & Goyal, P. (2025). Differential Expression of STK35L1-Associated Transcription Factors in Plasmodium Infection During the Liver Stage of Malaria. Kinases and Phosphatases, 3(4), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040026







