Abstract
Protein kinase CK2 is a Ser/Thr protein kinase that phosphorylates hundreds of substrates mainly related to survival and proliferation pathways. It has long been considered an anti-cancer drug target. However, during the recent COVID-19 pandemic, CK2 inhibitors have been repurposed as anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs. This was based on the initial finding of CK2 among the proteins of the host cell that interact with the viral proteins and modulate the infection. Since then, several studies have deepened our understanding of the CK2/COVID-19 connection, and we deem it is time to review all the findings. Interestingly, other coronaviruses cross-talk with CK2 as well, with similarities and differences compared to the SARS-CoV-2 case. Therefore, we believe that the analysis of the effects obtained by targeting CK2 in case of coronavirus infections, both at the molecular and phenomenological level, will help in extrapolating information that could be useful not only for COVID-19 (whose pandemic emergency is hopefully turning off) but also for other infections.
1. Introduction
1.1. CK2 General Features, Structure, and Regulation
Protein kinase CK2 is a Ser/Thr kinase expressed in all eukaryotic cells and involved in all cellular processes. It localizes mainly in the nucleus and cytoplasm, but also other sub-cellular compartments [1], such as mitochondria and plasma membrane, where it can be exported to the external side and is therefore considered an ecto-kinase [2]. The acronym CK2 originates from the term “casein kinase 2” since this protein kinase was initially regarded as responsible for the phosphorylation of milk casein [3]. However, it was later clear that casein is physiologically phosphorylated by another kinase (G-CK, or genuine casein kinase, recently identified with Fam20C [3]). At the same time, it is not a physiological substrate of CK2, which in turn phosphorylates hundreds of substrates [4] and is involved in virtually all cellular processes. It is ubiquitously expressed and essential for embryonal development [5], and its levels are particularly high in physiologically and pathologically rapidly proliferating cells [6,7,8]. Indeed, cancer cells are known to be addicted to CK2 [9], which plays essential roles in potentiating cancer hallmarks and tumorigenic signals [10,11,12]. Therefore, CK2 is presently considered a cancer drug target [13,14,15,16,17].
CK2 is constitutively active, meaning that it does not require signaling by second messengers or phosphorylation events to be activated, and its functions are roughly regulated by changes in protein expression. However, several mechanisms have been proposed that might contribute to modulating the activity of this enigmatic kinase, ranging from changes in subcellular localization, substrate availability/accessibility, association to other proteins, composition in subunits/isoforms, and supramolecular polymerization of the kinase holoenzyme [18,19].
From a structural point of view, mammalian CK2 is a tetrameric holoenzyme: it is composed of two catalytic subunits (α or α′, coded by two different genes, CSNK2A1 and CSNK2A2, respectively) and two regulatory subunits β, coded by the CSNK2B gene. Different holoenzyme combinations are possible (α2 β2, α′2 β2, and αα′β2). However, the catalytic subunits are also active as monomers, and the regulatory functions of β are mainly to preserve the enzyme stability and drive the selection of substrates [20]. The actual existence of the isolated CK2 subunits in cells is still uncertain: several pieces of evidence (reviewed in [18]) suggest a role of the monomeric catalytic subunits, not combined with the regulatory ones, in specific pathological conditions, especially in cancer cells. Nevertheless, a direct demonstration of the isolated α or α′ subunits in cells has never been provided.
The two isoforms of the catalytic subunit, α and α′, are supposed to be mainly overlapping in their functions, but a few differential roles have also been reported: they differ mainly for their C-terminal sequences, through which they can bind different partner proteins, what is hypothesized to allow them exerting some isoform-specific functions [21].
1.2. CK2 in Diseases
CK2 activity is implicated in a plethora of diverse human diseases, as recently reviewed [22]. As mentioned above, its pathological functions are mainly documented in cancer. The first connection between CK2 and mammalian tumorigenesis dates back to the late 80s, when Ole-MoiYoi and coworkers, by studying bovine theileriosis (a cattle parasite disease that represents a naturally occurring animal model), provided the earliest evidence of a molecular causative link between CK2 and mammalian lymphoid oncogenesis (as reviewed in [23]). Subsequently, a huge amount of data was collected supporting a tumorigenic role for CK2 in different types of human hematological malignancies and solid cancers, where it is often found overexpressed compared to normal tissues [24,25]. Given the close relationship frequently occurring between viral infections and tumorigenesis, this profound engagement of CK2 in cancer has particular relevance for the topic of this review, as will be discussed below.
For a detailed description of the many other diseases where CK2 has been found involved, we refer the readers to another recent review [22]. Here we can just briefly list the CK2 implication in inflammation and autoimmune disorders [26], diabetes and obesity [27], diverse ophthalmic pathologies [28,29], cardiovascular diseases, such as cardiac ischemia–reperfusion injury, atherosclerosis, and cardiac hypertrophy [30,31,32]. CK2 is also considered an emerging target for neurological and psychiatric disorders [33] and possibly for cystic fibrosis [34]. Moreover, recently, psychiatric disorders and syndromes due to mutations of the genes for the CK2 subunits have been identified [35]. Specifically, they are called Okur-Chung Neurodevelopmental Syndrome or OC-NDS (mutations of the CSNK2A1 gene, coding for CK2 α) and Poirier-Benvenu Neurodevelopmental Syndrome or POBINDS (mutations of the CSNK2B gene, coding for CK2 β).
Notably, other well-known functions of CK2 are in human infections; given the relevance of the topic of this review, they will be dealt with separately in the next paragraph.
1.3. CK2 in Viral Infections
Protein phosphorylation is a widespread and effective way to modulate protein functions, which even viruses exploit for their replication and life cycle. However, they depend on host protein kinases for the catalysis of this process; consistently, the activation of specific cellular kinases in response to the infection has been frequently observed, with the consequent phosphorylation of viral proteins, but also increased phosphorylation level of host cell proteins [36]. CK2 is among the most pleiotropic kinases, with 25 % of the phospho-proteome depending on its activity [3]. Therefore it makes sense that it could also be crucial for viruses. Indeed, its involvement in the phosphorylation of viral proteins has been known for many years, with 40 cases documented in 2003 [4]. One of the first reported cases is the human papillomavirus E7 protein; interestingly, this is the target of CIGB-300, a clinical-grade drug displaying promising anticancer properties [37,38]. Other notable examples (recently reviewed [8,22]) are the HIV-1 Rev protein, hepatitis C and B virus proteins, NSP1 of rotavirus, the nucleocapsid protein of the Hantaan virus, the matrix M protein of the human respiratory syncytial virus, the leader L protein of the encephalomyocarditis virus, the Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF57. Other viruses reported to exploit the activity of CK2 for their infection and propagation are Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) [39], Herpes Simplex Viruses (HSV), Human Cytomegalovirus (CMV) [8], and the list is continuously increasing, now also including coronaviruses, as described below in more details. In many cases, the infection preludes tumor transformation; therefore, the involvement of CK2, a pro-tumor kinase, is not so unexpected.
The mechanisms by which the phosphorylation by CK2 of viral proteins contributes to the infection are largely unknown. In some cases, the classical antiapoptotic mechanism that CK2 exerts by phosphorylating sites near a caspase site and preventing cleavage [40] might also apply to viral proteins, as reported in the case of ORF57 [41]. For the human papillomavirus E1 protein, it has been demonstrated that the phosphorylation by CK2 stabilizes ATP-dependent DNA helicase activity, which is essential for viral replication [42].
Regardless of the phosphorylated protein and the effect produced, it is worth noting that CK2 targeting has been proposed to stimulate host defence against virus infection by increasing IFN-α and IFN-β response, possibly by regulating the RIG-1 dependent signaling pathway [43,44]. This mechanism would not be limited to a specific viral infection.
3. CK2 and SARS-CoV-2
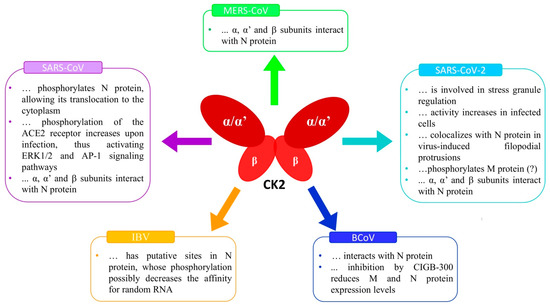
SARS-CoV-2, like the other β-CoVs, exploits the ACE receptor, a CK2 substrate [45], raising the interest in CK2 as an anti-COVID-19 target. But regardless of ACE, as early as the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, two important papers were published that directly correlated CK2 to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Gordon et al. [58] applied an affinity-purification/mass spectrometry approach to identify host proteins exploited by the virus and already targeted by existing drugs. Among the human druggable proteins that physically associate with SARS-CoV-2 proteins, they identified CK2, which was supposed to be involved in stress granule regulation. Consistently, CK2 inhibitors disrupt stress granules. All the CK2 subunits (the α (CSNK2A1) and α’ (CSNK2A2) catalytic isoforms and the β regulatory subunit (CSNK2B)) were found to bind to the N protein [56].
The global phosphorylation landscape of SARS-CoV-2 infection was also published in 2020 [59], reporting that some CK2-dependent phospho-sites (belonging to both viral and host cell proteins) are upregulated in SARS-CoV-2 infected cells. This suggested that SARS-CoV-2 would enhance CK2 activity. They found that CK2 localizes with N protein in filopodia protrusions possessing budding viral particles markedly induced by the infection. Also, employing transcriptome and computational analyses, Shaath and Alajez [60] observed activation of CK2 in Calu-3 infected cells, and Fatoki and coworkers described CK2 as one of the key players in the SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle [61]. As reviewed by Chatterjee and Thakur [36], some of the CK2-dependent phospho-sites found in SARS-CoV-2 infected cells belong to the viral M protein, but the consequences of the phosphorylation remain unknown.
SARS-CoV-2 activates several host cell kinases [36], with the final effect of complex crosstalk between different signaling pathways globally contributing to virus infection and replication. An example of great relevance for this review is the case of the PI3K/Akt pathway: it is deeply interconnected with CK2, which potentiates it by acting at several levels [62]. Since this pathway is instrumental to SARS-CoV-2 biology [63,64], CK2 also contributes to virus replication by boosting it. Another example of the intricate network by which CK2 might sustain the SARS-CoV-2 infection is the ERK1/2 and AP-1 signaling pathway (previously mentioned also for SARS-CoV), in which PAK1, an activator of this pathway and a substrate of CK2, can promote the activation of the transcription nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and STAT3 pathways [65]. Both NF-κB and STAT3 are CK2 substrates, involved in the induction of inflammatory cytokine expressions and polarization of M2 macrophages promoting lung fibrosis in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection, respectively [66,67]. An additional crossing point between CK2 and SARS-CoV-2 is the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which CK2 regulates [68,69] and is crucial in SARS-CoV-2 infection since the treatment of SARS-Cov-2 infected cells with iCRT14t, a specific inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin, decreased the cytopathic effect (changes in cell morphology caused by the virus) and reduced SARS-CoV-2 N protein level [36].
The multiple levels of connections between CK2 and SARS-CoV-2 are summarized in Figure 2.
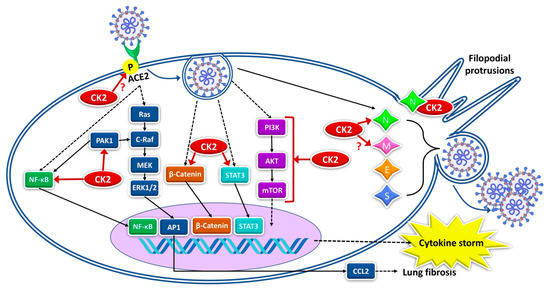
Figure 2.
Different levels of CK2 involvement in SARS-CoV-2 infection. CK2 actions are indicated by the red arrows, with a question mark where data are still speculative, or the effects of the phosphorylation are not known. Dashed arrows refer to signaling pathways not defined. See the text for references.
4. CK2 Targeting as Anti-COVID-19 Strategy
The above-described involvement of CK2 in the SARS-CoV-2 biology, its druggability, and the existence of CK2 inhibitors already in human clinical trials as anticancer drugs (CX-4945 or silmitasertib (https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?cond=&term=CX-4945&cntry=&state=&city=&dist=) (accessed on 15 June 2023) and CIGB-300 (https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?cond=&term=cigb-300&cntry=&state=&city=&dist=) (accessed on 15 June 2023) have promptly sparked interest in CK2 as a possible target for COVID-19 as well, and the repurposing of the compounds.
Apart from the already quoted study on bovine coronaviruses [50], by a computational biology analysis [70], CIGB-300 has been proposed to interfere with the SARS-CoV-2 life cycle in infected human cells: it might affect the immune response to the infection and perturb the virus hijacking of RNA splicing machinery. An exploratory clinical study with CIGB-300 (now called CIGB-325) has been performed to investigate its safety and putative clinical benefit in COVID-19 patients with pneumonia [71]. Despite the small sample size (twenty patients), and the preliminary level of the study, the results were encouraging since CIGB-300 significantly reduced the median number of pulmonary lesions with mild and/or moderate adverse events.
The CX-4945 repurposing was proposed since the beginning [58] when CK2 was found to interact with SARS-CoV-2 N protein and influence stress granule regulation. CX-4945 is presently in a clinical trial for COVID-19 and coronavirus, besides cancer https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04668209?term=CX-4945&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 15 June 2023). Other compounds have been investigated as potential anti-COVID-19 drugs. By studying the network of genes expressed in COVID-19-infected patients, Fatoki et al. [61] tried to predict the drug compounds that could interfere with pathologic signaling pathways. They identified CK2 (along with DNA-PK) as playing a crucial role in the SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle, and, by investigating phytochemicals that could represent therapeutic modulators, suggested emodin, ellagic acid, quercetin, and others as CK2 targeting compounds. They are indeed among the already-known inhibitors of CK2 [13].
5. Conclusions
Protein phosphorylation, elicited from the host kinases, is a well-known mechanism viruses exploit for survival. SARS-CoV-2 is no exception: the viral proteins N, M, S, 3a, and 9b were phosphorylated in about 70 different sites, corresponding to the consensus sequences of several kinases. Moreover, in SARS-CoV-2 infected cells, the phosphorylation of many host cell proteins increases (more than 15,000 phosphorylation sites identified) [36,59], and, at least in part, this is achieved through the activation of host kinases induced by the virus. Despite its constitutive activity, CK2 is among the activated enzymes. This could seem counterintuitive: what is the advantage of activating a kinase that is already catalytically competent? However, while the conformation structure of CK2 perfectly explains its constitutive activity [72], this does not exclude regulation events that can further enhance the phosphorylation of its substrates [18]. Since CK2 is very pleiotropic, being responsible for up to 25% of the phosphoproteome [3], its involvement in phosphorylating substrates instrumental for the virus life cycle is not unexpected. Moreover, its peculiar consensus sequence (S/T-x-x-E/D/pX) [73] is very common and present in several virus proteins.
As the Figure 2 summarises, CK2 and SARS-CoV-2 biology signals have several connecting points. Among them, it is worth pointing out the virus receptor ACE2, which is a substrate of CK2. Although the effects of the ACE2 phosphorylation on SARS-CoV-2 infection have never been described, by similarity with what was observed in the case of SARS-CoV [46], they are expected to be essential for the receptor functions. Other crucial levels of SARS-CoV-2/CK2 integration are the several signaling pathways strongly implicated in the infection and regulated by CK2 at multiple levels, such as PI3K/Akt, NF-κB, STAT3, Wnt/β-catenin, ERK1/2, and AP-1. However, the most significant connection is probably represented by the N protein, which can physically interact with each of the CK2 subunits and stimulate its catalytic activity. Indeed, N proteins of different coronaviruses are crucial for the functions played by CK2 in the infected cells (see Figure 1). Future studies will hopefully define the N protein/CK2 interaction at the molecular level, with exciting implications for our knowledge of CK2 biology, and ideally providing hypotheses on possible interventions to regulate its activity.
Although the COVID-19 outbreak is now less scary, it is important to highlight that identifying new antiviral therapies is still desirable to face the continued virus evolution with the possible emergence of new variants. Inevitably, selective pressure can generate drug-resistant mutants: this is frequent with direct antiviral agents, while cellular proteins exploited by the virus are less likely to be circumvented by viral escape mutants [74]. Also, considering the potential emergence of new β-CoVs, a broad-spectrum drug with activity against a wide range of viruses would be advantageous to prevent rapid viral spread. In this view, data reported so far provide strong evidence for CK2 as an ideal target. The wide availability of CK2 inhibitors and the clinical level of some of them complete the rationale for considering this kinase as a valuable target.
Author Contributions
M.R. conceptualized the manuscript. C.P.Q.M. and M.R. contributed to researching the content for the review, discussing the content, and writing the review. C.P.Q.M. perceived and designed the figures. M.R. critically reviewed the manuscript. C.P.Q.M. edited the manuscript before submission. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work performed in the Authors’ laboratory was supported by Institutional Funding (DOR and SID) to MR.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The Authors thank all the members of their laboratory for the helpful discussion.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Filhol, O.; Cochet, C. Protein Kinase CK2 in Health and Disease: Cellular Functions of Protein Ki-nase CK2: A Dynamic Affair. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2009, 66, 1830–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, F.; Allende, C.C.; Allende, J.E. Protein Kinase Casein Kinase 2 Holoenzyme Produced Ectopi-cally in Human Cells Can Be Exported to the External Side of the Cellular Membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4718–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venerando, A.; Ruzzene, M.; Pinna, L.A. Casein Kinase: The Triple Meaning of a Misnomer. Biochem. J. 2014, 460, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meggio, F.; Pinna, L.A. One-Thousand-and-One Substrates of Protein Kinase CK2? FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2003, 17, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, I.; Degano, I.R.; Chea, K.; Cha, J.; Toselli, P.; Seldin, D.C. CK2α Is Essential for Embryonic Morphogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 356, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, B.; Issinger, O.G. Protein Kinase CK2 and Its Role in Cellular Proliferation, Development and Pathology. Electrophoresis 1999, 20, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issinger, O.G. Casein Kinases: Pleiotropic Mediators of Cellular Regulation. Pharmacol. Ther. 1993, 59, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Denis, N.A.; Litchfield, D.W. Protein Kinase CK2 in Health and Disease: From Birth to Death: The Role of Protein Kinase CK2 in the Regulation of Cell Proliferation and Survival. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2009, 66, 1817–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzzene, M.; Pinna, L.A. Addiction to Protein Kinase CK2: A Common Denominator of Diverse Cancer Cells? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firnau, M.-B.; Brieger, A. CK2 and the Hallmarks of Cancer. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strum, S.W.; Gyenis, L.; Litchfield, D.W. CSNK2 in Cancer: Pathophysiology and Translational Applications. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trembley, J.H.; Kren, B.T.; Afzal, M.; Scaria, G.A.; Klein, M.A.; Ahmed, K. Protein Kinase CK2—Diverse Roles in Cancer Cell Biology and Therapeutic Promise. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2022, 478, 899–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgo, C.; Ruzzene, M. Protein Kinase CK2 Inhibition as a Pharmacological Strategy. In Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Borgo, C.; Ruzzene, M. Role of Protein Kinase CK2 in Antitumor Drug Resistance. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2019, 38, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buontempo, F.; McCubrey, J.A.; Orsini, E.; Ruzzene, M.; Cappellini, A.; Lonetti, A.; Evangelisti, C.; Chiarini, F.; Evangelisti, C.; Barata, J.T.; et al. Therapeutic Targeting of CK2 in Acute and Chronic Leukemias. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, C.; Sachdev, M.; Muthusami, S.; Kapadia, M.; Petrovic-Dovat, L.; Hartman, M.; Ding, Y.; Song, C.; Payne, J.L.; Tan, B.-H.; et al. Casein Kinase II (CK2) as a Therapeutic Target for Hematological Malignancies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trembley, J.H.; Chen, Z.; Unger, G.; Slaton, J.; Kren, B.T.; Van Waes, C.; Ahmed, K. Emergence of Protein Kinase CK2 as a Key Target in Cancer Therapy. BioFactors Oxf. Engl. 2010, 36, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgo, C.; D’Amore, C.; Cesaro, L.; Sarno, S.; Pinna, L.A.; Ruzzene, M.; Salvi, M. How Can a Traffic Light Properly Work If It Is Always Green? The Paradox of CK2 Signaling. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 56, 321–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roffey, S.E.; Litchfield, D.W. CK2 Regulation: Perspectives in 2021. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, L.A. Protein Kinase CK2: A Challenge to Canons. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 3873–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchfield, D.W.; Bosc, D.G.; Canton, D.A.; Saulnier, R.B.; Vilk, G.; Zhang, C. Functional Specialization of CK2 Isoforms and Characterization of Isoform-Specific Binding Partners. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 227, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgo, C.; D’Amore, C.; Sarno, S.; Salvi, M.; Ruzzene, M. Protein Kinase CK2: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Diverse Human Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ole-MoiYoi, O.K. Casein Kinase II in Theileriosis. Science 1995, 267, 834–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, C.E.; Seidner, Y.; Dominguez, I. Mining CK2 in Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, M.M.J.; Lee, M.; Dominguez, I. Cancer-Type Dependent Expression of CK2 Transcripts. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Benveniste, E.N. The Immune Regulatory Role of Protein Kinase CK2 and Its Implications for Treatment of Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ampofo, E.; Nalbach, L.; Menger, M.D.; Montenarh, M.; Götz, C. Protein Kinase CK2-A Putative Target for the Therapy of Diabetes Mellitus? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljubimov, A.V.; Caballero, S.; Aoki, A.M.; Pinna, L.A.; Grant, M.B.; Castellon, R. Involvement of Protein Kinase CK2 in Angiogenesis and Retinal Neovascularization. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 4583–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morooka, S.; Hoshina, M.; Kii, I.; Okabe, T.; Kojima, H.; Inoue, N.; Okuno, Y.; Denawa, M.; Yoshida, S.; Fukuhara, J.; et al. Identification of a Dual Inhibitor of SRPK1 and CK2 That Attenuates Pathological Angiogenesis of Macular Degeneration in Mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 88, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, L.; Harms, C.; An, J.; Rohne, J.; Gertz, K.; Dietz, R.; Endres, M.; von Harsdorf, R. Protein Kinase CK2 Links Extracellular Growth Factor Signaling with the Control of P27 Kip1 Stability in the Heart. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadey, K.S.; Brown, B.A.; Sala-Newby, G.B.; Jayaraman, P.-S.; Gaston, K.; George, S.J. Protein Kinase CK2 Inhibition Suppresses Neointima Formation via a Proline-Rich Homeodomain-Dependent Mechanism. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2017, 99, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhu, P.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Ren, J.; Chen, Y. Pathogenesis of Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Is Associated with CK2α-Disturbed Mitochondrial Homeostasis via Suppression of FUNDC1-Related Mitophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castello, J.; Ragnauth, A.; Friedman, E.; Rebholz, H. CK2-An Emerging Target for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A. Cystic Fibrosis as a Bowel Cancer Syndrome, and the Potential Role of CK2. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 316, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballardin, D.; Cruz-Gamero, J.M.; Bienvenu, T.; Rebholz, H. Comparing Two Neurodevelopmental Disorders Linked to CK2: Okur-Chung Neurodevelopmental Syndrome and Poirier-Bienvenu Neurodevelopmental Syndrome-Two Sides of the Same Coin? Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 850559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, B.; Thakur, S.S. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Triggers Phosphorylation: Potential Target for Anti-COVID-19 Therapeutics. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 829474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottardo, M.F.; Capobianco, C.S.; Sidabra, J.E.; Garona, J.; Perera, Y.; Perea, S.E.; Alonso, D.F.; Farina, H.G. Preclinical Efficacy of CIGB-300, an Anti-CK2 Peptide, on Breast Cancer Metastasic Colonization. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perea, S.E.; Reyes, O.; Baladron, I.; Perera, Y.; Farina, H.; Gil, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Bacardi, D.; Marcelo, J.L.; Cosme, K.; et al. CIGB-300, a Novel Proapoptotic Peptide That Impairs the CK2 Phosphorylation and Exhibits Anticancer Properties Both in Vitro and Vivo. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 316, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenarh, M.; Grässer, F.A.; Götz, C. Protein Kinase CK2 and Epstein-Barr Virus. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, J.S.; Turowec, J.P.; Vilk, G.; Li, S.S.C.; Gloor, G.B.; Litchfield, D.W. Regulation of Cell Proliferation and Survival: Convergence of Protein Kinases and Caspases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majerciak, V.; Pripuzova, N.; Chan, C.; Temkin, N.; Specht, S.I.; Zheng, Z.-M. The Stability of Structured Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus ORF57 Protein Is Regulated by Protein Phosphorylation and Homodimerization. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3256–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piirsoo, A.; Piirsoo, M.; Kala, M.; Sankovski, E.; Lototskaja, E.; Levin, V.; Salvi, M.; Ustav, M. Activity of CK2alpha Protein Kinase Is Required for Efficient Replication of Some HPV Types. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Xie, Y.; Yuan, C.; Xiang, Y.; Sun, B.; Lan, K.; Chen, M.; James, S.J.; et al. Casein Kinase II Controls TBK1/IRF3 Activation in IFN Response against Viral Infection. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 4477–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ren, H.; Liu, Y.; Teeling, J.L.; Gu, J. Phosphorylation of RIG-I by Casein Kinase II Inhibits Its Antiviral Response. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 1036–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlstedt, K.; Shoghi, F.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Busse, R.; Fleming, I. CK2 Phosphorylates the Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and Regulates Its Retention in the Endothelial Cell Plasma Membrane. Circ. Res. 2002, 91, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.-Y.; Chang, S.C.; Wu, H.-Y.; Yu, T.-C.; Wei, W.-C.; Lin, S.; Chien, C.-L.; Chang, M.-F. Upregulation of the Chemokine (C-C Motif) Ligand 2 via a Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Spike-ACE2 Signaling Pathway. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7703–7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Dickmander, R.J.; Bayati, A.; Taft-Benz, S.A.; Smith, J.L.; Wells, C.I.; Madden, E.A.; Brown, J.W.; Lenarcic, E.M.; Yount, B.L.; et al. Host Kinase CSNK2 Is a Target for Inhibition of Pathogenic SARS-like β-Coronaviruses. ACS Chem. Biol. 2022, 17, 1937–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Bound to the ACE2 Receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkard, C.; Verheije, M.H.; Wicht, O.; van Kasteren, S.I.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Haagmans, B.L.; Pelkmans, L.; Rottier, P.J.M.; Bosch, B.J.; Haan, C.A.M. de Coronavirus Cell Entry Occurs through the Endo-/Lysosomal Pathway in a Proteolysis-Dependent Manner. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramón, A.C.; Pérez, G.V.; Caballero, E.; Rosales, M.; Aguilar, D.; Vázquez-Blomquist, D.; Ramos, Y.; Rodríguez-Ulloa, A.; Falcón, V.; Rodríguez-Moltó, M.P.; et al. Targeting of Protein Kinase CK2 Elicits Antiviral Activity on Bovine Coronavirus Infection. Viruses 2022, 14, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea, S.E.; Reyes, O.; Puchades, Y.; Mendoza, O.; Vispo, N.S.; Torrens, I.; Santos, A.; Silva, R.; Acevedo, B.; López, E.; et al. Antitumor Effect of a Novel Proapoptotic Peptide That Impairs the Phosphorylation by the Protein Kinase 2 (Casein Kinase 2). Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7127–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasova, A.N.; Saif, L.J. Bovine Coronavirus and the Associated Diseases. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 643220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Gill, A.; Dove, B.K.; Emmett, S.R.; Kemp, C.F.; Ritchie, M.A.; Dee, M.; Hiscox, J.A. Mass Spectroscopic Characterization of the Coronavirus Infectious Bronchitis Virus Nucleoprotein and Elucidation of the Role of Phosphorylation in RNA Binding by Using Surface Plasmon Resonance. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1164–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Xu, L.; Huang, M.; Qisheng Li, F.; Liu, D.X. Identification of Two ATR-Dependent Phosphorylation Sites on Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein with Nonessential Functions in Viral Replication and Infectivity in Cultured Cells. Virology 2013, 444, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.A.; Ouchi, T. Cellular Commitment to Reentry into the Cell Cycle after Stalled DNA Is Determined by Site-Specific Phosphorylation of Chk1 and PTEN. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2509–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.E.; Hiatt, J.; Bouhaddou, M.; Rezelj, V.V.; Ulferts, S.; Braberg, H.; Jureka, A.S.; Obernier, K.; Guo, J.Z.; Batra, J.; et al. Comparative Host-Coronavirus Protein Interaction Networks Reveal Pan-Viral Disease Mechanisms. Science 2020, 370, eabe9403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surjit, M.; Kumar, R.; Mishra, R.N.; Reddy, M.K.; Chow, V.T.K.; Lal, S.K. The Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein Is Phosphorylated and Localizes in the Cytoplasm by 14-3-3-Mediated Translocation. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11476–11486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.E.; Jang, G.M.; Bouhaddou, M.; Xu, J.; Obernier, K.; White, K.M.; O’Meara, M.J.; Rezelj, V.V.; Guo, J.Z.; Swaney, D.L.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 Protein Interaction Map Reveals Targets for Drug Repurposing. Nature 2020, 583, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouhaddou, M.; Memon, D.; Meyer, B.; White, K.M.; Rezelj, V.V.; Correa Marrero, M.; Polacco, B.J.; Melnyk, J.E.; Ulferts, S.; Kaake, R.M.; et al. The Global Phosphorylation Landscape of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cell 2020, 182, 685–712.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaath, H.; Alajez, N.M. Computational and Transcriptome Analyses Revealed Preferential Induction of Chemotaxis and Lipid Synthesis by SARS-CoV-2. Biology 2020, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatoki, T.H.; Ibraheem, O.; Ogunyemi, I.O.; Akinmoladun, A.C.; Ugboko, H.U.; Adeseko, C.J.; Awofisayo, O.A.; Olusegun, S.J.; Enibukun, J.M. Network Analysis, Sequence and Structure Dynamics of Key Proteins of Coronavirus and Human Host, and Molecular Docking of Selected Phytochemicals of Nine Medicinal Plants. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 39, 6195–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzzene, M.; Bertacchini, J.; Toker, A.; Marmiroli, S. Cross-Talk between the CK2 and AKT Signaling Pathways in Cancer. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2017, 64, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, M.S.; Cavalli, E.; McCubrey, J.; Hernández-Bello, J.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F. The PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway: A Potential Pharmacological Target in COVID-19. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klann, K.; Bojkova, D.; Tascher, G.; Ciesek, S.; Münch, C.; Cinatl, J. Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Inhibition Prevents SARS-CoV-2 Replication. Mol. Cell 2020, 80, 164–174.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berretta, A.A.; Silveira, M.A.D.; Cóndor Captcha, J.M.; De Jong, D. Propolis and Its Potential against SARS-CoV-2 Infection Mechanisms and COVID-19 Disease: Running Title: Propolis against SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-M.; Wang, L.; Yoo, D. Activation of NF-ΚB and Induction of Proinflammatory Cytokines Expressions Mediated by ORF7a Protein of SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarzadeh, A.; Nemati, M.; Jafarzadeh, S. Contribution of STAT3 to the Pathogenesis of COVID-19. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 154, 104836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, D.P.; Yefi, R.; Cabello, P.; Maturana, J.L.; Niechi, I.; Silva, E.; Galindo, M.; Antonelli, M.; Marcelain, K.; Armisen, R.; et al. CK2 Functionally Interacts with AKT/PKB to Promote the β-Catenin-Dependent Expression of Survivin and Enhance Cell Survival. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 356, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.H.; Sussman, D.J.; Seldin, D.C. Endogenous Protein Kinase CK2 Participates in Wnt Signaling in Mammary Epithelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 23790–23797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, J.; Bringas, R.; Fernandez-de-Cossio, J.; Perera-Negrin, Y. Targeting CK2 Mediated Signaling to Impair/Tackle SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Computational Biology Approach. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, L.R.; Baladrón, I.; Rittoles, A.; Díaz, P.A.; Valenzuela, C.; Santana, R.; Vázquez, M.M.; García, A.; Chacón, D.; Thompson, D.; et al. Treatment with an Anti-CK2 Synthetic Peptide Improves Clinical Response in COVID-19 Patients with Pneumonia. A Randomized and Controlled Clinical Trial. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niefind, K.; Guerra, B.; Ermakowa, I.; Issinger, O.G. Crystal Structure of Human Protein Kinase CK2: Insights into Basic Properties of the CK2 Holoenzyme. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 5320–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meggio, F.; Marin, O.; Pinna, L.A. Substrate Specificity of Protein Kinase CK2. Cell. Mol. Biol. Res. 1994, 40, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chitalia, V.C.; Munawar, A.H. A Painful Lesson from the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Need for Broad-Spectrum, Host-Directed Antivirals. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).