Simple Summary
Salmonellosis remains a significant public health concern, with animals such as cattle serving as potential sources of infection. The slaughter of infected animals from contaminated farms is a major contributor to human Salmonella infections. In this review, the various pathways are explored through which Salmonella enters cattle populations and strategies are examined for mitigating or controlling the disease on farms. Ultimately, a comprehensive appeal is made to all stakeholders in cattle production to actively contribute to reducing Salmonella infections on farms.
Abstract
Salmonellosis in humans is a public health threat and cattle are important reservoirs for the pathogen. Cattle products such as ground beef have been linked to human salmonellosis outbreaks, and some disease investigations have been traced back to infected animal herds on farms and animal markets as the origin of infection. It is now common to isolate Salmonella from many cattle operations as the pathogen once introduced onto a farm can establish an undesirable endemic condition among herds. It is, therefore, essential to adopt measures to mitigate or prevent the introduction and spread of zoonotic disease agents like Salmonella in animal populations. With this background, the potential sources and risks of Salmonella infection in cattle, the control of already established infection, and other preventative measures are discussed in this article. We conclude that a holistic approach involving all stakeholders in cattle production is needed to safeguard public health, eventually forestalling human salmonellosis from cattle sources. In achieving this, it will be essential to consider the farm as a critical control point in preventing the introduction of Salmonella into the food chain.
1. Introduction
Salmonella is a zoonotic pathogen of great concern worldwide [1], with food animals remaining significant reservoirs for human infection [2]. Although most human salmonellosis cases are linked to contaminated poultry, pork, and egg products [3], the risk of infection from cattle and their products continues to pose a serious public health threat [4]. Reports worldwide indicate the frequent isolation of Salmonella from retail beef and its products [5,6,7,8], as well as from raw dairy milk and related products [9,10,11,12,13].
Outbreaks of salmonellosis have been repeatedly associated with the consumption of unpasteurized milk [14] and beef products [15]. In the U.S., beef accounted for an estimated 5.7–9.1% of all human foodborne salmonellosis cases between 2012 and 2019, including several outbreaks [5] often linked to ground beef consumption [16]. Similarly, in France, a prolonged outbreak of Salmonella Enteritidis was traced to frozen beef burgers imported from Poland [17]. In the Netherlands, a national outbreak investigation also identified contaminated raw beef as the source of infection [18].
Traceback investigations have often pointed to animal farms and markets as potential sources of infections [19,20]. For instance, a multi-drug-resistant Salmonella Heidelberg outbreak in the U.S. was linked to contact with dairy calves [19]. In the same country, another investigation of an outbreak involving ground beef contamination identified dairy cattle in the state of New Mexico as the source [21]. Among other livestock, during the persistent polyclonal Salmonella Enteritidis outbreak across 18 countries between 2016 and 2020 which was linked to contaminated chicken eggs, farms in Poland and some other packaging centers were implicated [22].
Studies globally have revealed that isolating Salmonella from dairy or beef cattle and their environments is common [23,24,25]. The persistence of Salmonella on cattle farms is attributed to the pathogen’s ability to cycle between host and non-host environments, surviving for extended periods on various surfaces [26]. Traditionally, the beef industry has focused its efforts on interventions at the processing and packaging stages to reduce human exposure to Salmonella [4]. However, in recent years, there has been a shift toward understanding Salmonella ecology in pre-harvest cattle on farms [4]. Ongoing research aims to assess the Salmonella populations present in pre-harvest cattle and their environments [25,27,28], yet the pathogen’s endemicity in cattle farms persists [29].
The introduction of Salmonella to cattle farms often occurs through infected animals, contaminated feed, and vectors such as birds and rodents [30]. Additional sources include contaminated water, other livestock, wildlife, insects, people, equipment, and vehicles [28]. Due to these multiple potential sources, the introduction of the pathogen to a new herd is frequently considered a multi-source event [23].
Given the One Health concept, which emphasizes the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health [31], preventing the introduction and spread of pathogens like Salmonella in cattle populations is crucial for safeguarding public health and minimizing environmental contamination. In this article, the risk factors and potential sources of Salmonella infection in cattle farms, the factors facilitating its persistence, and possible intervention strategies are explored.
2. Common Risk Factors and Sources of Salmonella Infection in Cattle
2.1. Infected Newcomers and Animal Trading
Introducing new cattle into a herd has long been a significant source of Salmonella in cattle operations [32], making it one of the primary pathogen sources. In larger farms, the continual purchase of replacement animals or herd expansion from external sources is often essential and unavoidable for management [23]. Farmers may introduce new cattle for various reasons, such as replacing culled bulls or heifers to prevent inbreeding and maintaining herd size [33]. While some operations raise their own heifers, others continue to purchase replacements [33]. However, this practice can increase the prevalence of Salmonella within the herd, as it heightens the risk of introducing infected animals [23].
Animals already infected with Salmonella may appear healthy but can still shed the pathogen in their feces [34]. Fecal samples from cattle herds may test positive for Salmonella even 14 months after the initial exposure [35]. Although clinically infected animals tend to shed Salmonella at higher rates than asymptomatic ones, both can continue shedding the pathogen for extended periods [36,37]. It is estimated that approximately 10² to 10⁷ colony-forming units (CFUs) of Salmonella can be shed per gram of cattle feces [20]. Studies have indicated that certain Salmonella serovars, such as Salmonella Typhimurium, can persist in large dairy herds for about 3.5 years and in calf units for up to 2 years [38]. Conversely, serovars like Salmonella Dublin can lead to persistently infected cattle that exhibit no clinical signs [39]. The absence of obvious symptoms, such as diarrhea, in apparently healthy yet infected cattle increases the risk of introducing them into uninfected herds. A study on Salmonella Dublin in a Danish dairy production system revealed that, on average, a single infected calf could infect two others when introduced into a fully susceptible population [40].
Animal trading has long been a crucial factor in understanding the epidemiology of salmonellosis in cattle [41]. Simply put, it involves a production farm and a dealer who purchases and sells calves to multiple rearing farms [41]. The buying and selling of animals create opportunities for pathogen transmission, such as Salmonella, as the commingling of animals at sale sites facilitates fecal–oral infection cycles [42,43,44]. Some researchers have even described animal markets as “hubs” for pathogen transmission [45]. A recent multistate salmonellosis outbreak, caused by a multidrug-resistant Salmonella Heidelberg strain, was traced to a livestock market where male dairy calves were auctioned [19]. Essentially, cattle trading forms a network of animal holdings and premises connected through multiple animal movements [46]. These movements, particularly between agricultural premises, contribute significantly to the spread of infectious agents and are regarded as a critical epidemiological factor in several livestock diseases [47].
2.2. Fomites
2.2.1. People, Contaminated Instruments, and Equipment
Despite the growing number of reports highlighting the potential transmission of infections from humans to animals, these occurrences have not been comprehensively explored, and the extent of human contributions to disease outbreaks in affected animal populations remains insufficiently examined [31,48,49].
In the case of salmonellosis in cattle, human movement in and out of farm premises plays a significant role in mechanically transmitting the pathogen among herds [38,45]. Animal traders, such as specialized veal producers, are a prime example of this risk group, as they frequently purchase and raise calves from multiple dairy herds [50]. Although their primary role is to transport purchased animals to slaughterhouses, their interactions with animals from different herds particularly during farm visits can facilitate the spread of pathogens from infected to uninfected flocks [45].
Additionally, the employment of farm workers presents a potential risk for pathogen transmission. Many of these individuals may work on multiple farms while managing their own livestock, inadvertently serving as vectors for disease spread, particularly in the absence of stringent biosecurity measures [45].
Veterinary health facilities also serve as common hotspots for nosocomial infections, including pathogens such as Salmonella spp. [51]. These facilities can become hubs for fomites, especially in the absence of stringent hygiene standards. Common fomites in veterinary clinics from which pathogens have been isolated include burdizzos, doorknobs, drawer handles, fridge handles, hoof cutters, ice chests, kidney bowls, mobile phones, muzzles, pens, record books, surgical instruments, surgical tables, switches, and vials, all of which can play a crucial role in the spread of infectious agents [52]. Animal workers who do not use examination gloves or change into new examination gloves for each animal are highly likely to cause cross-contamination [53,54]. This is typically seen during rectal maneuvers among large herds, usually for pregnancy confirmation or artificial insemination procedures.
2.2.2. Farm Equipment and Vehicles
The sharing of equipment among farmers poses a significant risk for the spread of Salmonella among herds within a common geographic area [33,44,45]. Tractors, trailers, and wagons are the most commonly shared equipment, followed by harvesting and plowing machinery, as well as muck vehicles [45]. Farmers frequently borrow tractors from one another for tasks such as waste handling and feeding [45]. Additionally, animal chutes used for restraint are also commonly shared. The use of shared vehicles and equipment increases the likelihood of pathogen transmission, as they may already be contaminated from previous use. Some researchers have proposed targeted interventions for trailers to reduce Salmonella infections in calves [55], including thorough washing and disinfection of vehicles after use.
2.3. Feed
Animal feed is one of the many potential sources of Salmonella infection in animals [26]. Increasing evidence suggests that Salmonella can spread from feed to food-producing animals [56]. Cattle feed, in particular, not only serves as a potential source of Salmonella transmission but also harbors other significant pathogens, such as Escherichia coli O157:H7 [57]. Several studies have reported the isolation of Salmonella from cattle feed, with some demonstrating its potential transmission to cattle through feed, as summarized in Table 1.
A notable example of feed-related Salmonella infection among other livestock is the 2009 Salmonella Tennessee outbreak in Finland, which affected pigs and hens and was traced back to contamination in a feed mill production line [58]. In countries like Sweden, where Salmonella is well controlled or absent in food-producing animals, contaminated feed is considered a major route of infection for farm animals [58]. A single batch of contaminated feed from a commercial mill can be distributed to multiple farms, potentially leading to widespread infection [59].
It has long been recognized that Salmonella can colonize the cooling systems used for processing pellet or mash feed in animal feed mills, contaminating ingredient intake pits, and out-loading gantries [60]. Additionally, Salmonella present in feed components may survive processing and subsequently infect food-producing animals [59]. For instance, the pathogen can persist in both the dry raw materials used for poultry feed production and in the final dry feed for extended periods [58].

Table 1.
Some reported Salmonella serovars isolated from cattle feed and ingredients.
Table 1.
Some reported Salmonella serovars isolated from cattle feed and ingredients.
| Isolation Source | Serotype Involved | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Dry beef cattle feed | Agona Anatum Barranquilla Cerro Cubana Give Infantis Kentucky Lexington Liverpool Mbandaka Meleagridis Montevideo Muenster Orion var. 15+, 34+ (Thomasville) Senftenberg Soerenga Typhimurium var. O 5- (Copenhagen) | [61] |
| Medicated beef cattle feed | Cerro Cubana Infantis Lexington var. O 15+ (Manila) Liverpool Mbandaka Montevideo Newport Tennessee Typhimurium var. O 5- (Copenhagen) | [61] |
| Dairy cattle feed | 42:z4,z23 Agona Alachua Barranquilla Havana Kentucky Livingstone Mbandaka Meleagridis Rissen Senftenberg | [61] |
| Cattle feed ingredients | Typhimurium ** Mbandaka Cerro Braenderup Meleagridis | [57] |
| Feed mill | Menhaden | [62] |
| Cattle feed | Infantis ** | [63] |
| Animal feed ingredients | Senftenberg Enteritidis Gallinarum Saintpaul Lexington | [64] |
| Animal feed | Mbadanka | [65] |
**: Feed and cattle Salmonella isolates were genetically the same or closely related.
2.4. Non-Production Animals and Production Animals
2.4.1. Wildlife, Rodents, Birds, and Flies
Consumer demands and animal welfare policies have driven the transition of animal production industries from intensive to more extensive farming systems [66,67]. Extensive farming systems follow a natural or semi-natural approach to raising animals [68], providing them with ample space to exercise and engage in natural behaviors such as grazing in open areas like pastures, meadows, and mountains [69,70]. While these practices contribute to improving meat quality [71], they also increase the potential for interactions between farm animals and wildlife. Various wildlife species have been identified as reservoirs of Salmonella, raising concerns about the transmission of infectious agents to free-ranging domestic food animals [2,72,73]. Rodents, wild birds (e.g., wild geese, sparrows, and waterfowl), reptiles, wild boars, and rabbits have all been implicated in transmitting Salmonella to farm animals [37,38,74,75,76,77,78]. Cattle, for instance, may ingest contaminated fecal droppings from these animals while grazing in open fields.
In addition, wild birds can contaminate stored animal feed with their droppings, particularly in cases of inadequate feed storage [74,75]. An investigation into a salmonellosis outbreak in a cattle herd linked the disease to haylage contamination by blackbirds, starlings, and geese [79]. The presence of wild geese around cattle and their feed was significant in establishing clinical salmonellosis within the herd [79]. Molecular studies have identified genetically identical Salmonella serovars in both wildlife and cattle (Table 2), suggesting transmission between the two. Public health concerns are rising due to the epidemiological significance of salmonellosis in wildlife [78], as many wildlife species such as rodents, reptiles, and amphibians can carry Salmonella asymptomatically [80].
Flies and other insects have also been identified as vectors of Salmonella transmission [81], especially those feeding on cattle manure. In some cases, these flies have contributed to the spread of antibiotic-resistant Salmonella on farms [20]. Common flies that may facilitate transmission include horse flies, house flies, horn flies, face flies, stable flies, and deer flies [33].
2.4.2. Pets Animals, Herding Animals, and Stray Animals
Fecal shedding of Salmonella among pet animals, including dogs and cats, has been well-documented even in asymptomatic cases [82,83,84,85]. Some farmers keep these companion animals on-site [74], posing a risk of feed contamination if infected pets have access to storage areas [58]. A study in Denmark found Salmonella in dogs and cats living near infected cattle herds [86].
In some regions, herding dogs are commonly used to manage livestock such as sheep, goats, and cattle [87]. The Old English Sheepdog, for example, was originally bred for herding purposes [88]. However, if these herding animals are infected with Salmonella, they can shed the bacteria in their feces, potentially infecting the herd. A recent study in Southern Bavaria found that some herding dogs were shedding the cattle-adapted serovar Salmonella Dublin [89].
Stray animals, which include unowned, homeless, free-roaming, or abandoned dogs and cats, are frequently found near livestock breeding sites and contribute to the spread of Salmonella among farm animals [90,91]. They can introduce pathogens into the environment through fecal shedding, amplifying the spread of infection. Due to inadequate care and treatment, sick stray animals often remain untreated, leading to persistent environmental contamination with pathogens such as Salmonella [92].
2.4.3. Other Livestock Animals
In farming systems where various livestock species, such as cattle, poultry, sheep, goats, and pigs, are reared together, farmers may adopt a multi-species grazing system on the same land, which can be a more sustainable farming approach [93]. However, this practice increases the risk of inter-species pathogen transmission through the fecal–oral route. Like other livestock, sheep and goats can serve as reservoirs of Salmonella, potentially shedding the pathogen in their feces [91]. The evidence of genetically related Salmonella strains isolated from cattle and other livestock, indicating inter-species transmission, is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Studies showing evidence of possible inter-specie infection of Salmonella between cattle and other production and non-production animals.
Table 2.
Studies showing evidence of possible inter-specie infection of Salmonella between cattle and other production and non-production animals.
| Animal Type | Specie | Serovar | Comparative Methodology | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wildlife | Raccoons Crows | Braenderup, Dublin Montevideo, 4, [5], 12:i:- | PFGE | [94] |
| Wildlife | Hedgehog | Muenster | PFGE | [95] |
| Wildlife | Wild boar | Meleagridis, Anatum | PFGE | [96] |
| Production Animal | Chicken | Enteritidis | ERIC-PCR | [97] |
| Production Animal | Pig | Typhimurium | PFGE | [98] |
PFGE: pulse field gel electrophoresis; ERIC-PCR: enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus–polymerase chain reaction.
2.5. Herd Size
Studies have reported an association between large herd size, Salmonella infection, and fecal shedding in cattle herds [32,99]. Large herd size is considered a key risk factor for the persistent presence of Salmonella on farms [36]. Unfortunately, it is challenging for large herds to transition from a positive to a negative infection status [100]. Several factors contribute to the increased risk of Salmonella infection in large herds, including a higher likelihood of purchasing cattle from external sources, increased herd density that facilitates transmission, stress due to overcrowding, and difficulties in implementing effective interventions [99].
For instance, free-stall housing, which is commonly used in large herds, poses significant challenges in controlling manure-transmitted pathogens like Salmonella. The unrestricted movement of animals in free-stall barns allows direct contact with fecal matter, leading to further contamination of shared feed and water sources [99]. Additionally, it has been observed that larger operations are more likely to move cattle to grazing areas without defined borders, which increases the risk of pathogen spread [33]. Even when borders are in place, nose-to-nose contact across farm boundaries can facilitate the transmission of pathogens between neighboring farms [45].
Furthermore, intensive husbandry systems are not always a reliable solution, as they can create environments conducive to Salmonella shedding. Exposure to pathogen-laden manure in such systems can perpetuate chronic infections within the herd [101,102].
2.6. Communal Pastures and Grazing
The most cost-effective way to feed cattle is by grazing them on pasture, making cattle a popular choice for utilizing pasture lands [33]. Grazing becomes even more efficient and manageable when multiple animals share communal pastures. These communal grazing areas have sometimes been used to temporarily hold cattle before they are transported to other locations [103]. In some regions, pasturing cattle on alpine meadows is a cherished tradition [89], and it is a common practice for farmers to take their animals to shared pastures, particularly during the summer grazing period [104].
However, communal grazing exposes cattle to cross-infection [89]. On pastures, Salmonella Dublin can survive in feces for at least 119 days and remain viable in surface water for approximately 87 days, facilitating the rapid spread of the pathogen among animals [89]. Studies have also shown that Salmonella can persist in cattle fecal pats, especially when moisture levels remain around 80% [105].
In some regions, the practice of agistment where farmers pay to graze their livestock on communal pastures alongside other animals such as sheep is common. Although sheep do not typically transmit many cattle diseases, Salmonella Dublin and certain viruses can spread between the two species [45]. The shedding of Salmonella during these periods can result in extensive environmental contamination, increasing the risk of within-herd transmission and unintentional spread to other herds [99].
Additionally, ponds, rivers, cisterns, and streams are commonly used as drinking water sources for cattle during grazing. For example, many cattle operations in the U.S. rely on ponds for drinking water [33]. However, these water sources can harbor foodborne pathogens such as Salmonella [106], making them potential hotspots for infection [79].
2.7. Animal Waste Handling as Slurry and Manure
Salmonella can persist in manure and slurries for extended periods, even when processed and used as organic fertilizers [107], which are often applied to grazing fields. Consequently, spreading slurry containing Salmonella and other pathogens can facilitate the transmission of disease to farm premises, ultimately infecting animals [108]. A study of U.S. dairy herds found that farms with at least one antibiotic-resistant isolate were more likely to use composted or dried manure for bedding [109]. Similarly, a study conducted in New South Wales, Australia, reported that manure from an old dairy farm had been applied to the pasture of a new dairy farm a few months before a salmonellosis outbreak occurred [38]. Manure from older dairy farms is likely to harbor several pathogens, including Salmonella [110,111], which can survive for several weeks in dry environments and several months in wet environments [80]. Further investigations revealed that in addition to slurry application, the pasture on the new farm was irrigated with water from an effluent pond contaminated with runoff from washings of the old dairy farm [38]. The authors concluded that the improper use of manure and effluent as fertilizer likely contributed to the introduction and persistence of Salmonella Typhimurium in the herd [38]. Additionally, some cattle owners spread poultry manure on adjacent properties, an activity that has also been identified as a potential source of Salmonella infection in cattle [75].
The aerosolized transmission of Salmonella in livestock is also possible [112,113]. Certain farm practices, such as using flush water systems to wash manure, can facilitate the airborne spread of the pathogen [32]. An early experimental study demonstrated that Salmonella Typhimurium could survive in the air long enough to pose a significant airborne transmission hazard [114]. Inhalation of Salmonella Typhimurium by mice caused disease and death, with doses as low as 150 CFU proving infectious [114]. This finding suggests that airborne transmission should be considered a potential route of infection for Salmonella Typhimurium in cattle, particularly in calves [114]. Experimental inoculation of calves with approximately 104 to 106 CFU of Salmonella Typhimurium via ‘mouth and nose only’ or ‘whole body’ aerosol exposure successfully induced infection [114].
2.8. Abortions and Live Births
Abortions can occur in cattle infected with Salmonella [36], with aborted tissues and fluids serving as potential sources of infection for other herds. Abortion due to Salmonella infection typically occurs during the last trimester [23,115]. However, certain serovars, such as Salmonella Dublin, can induce abortion at any stage of pregnancy and may present as the only clinical sign [116,117]. A study investigating abortion in dairy cattle identified Salmonella Brandenburg in placental tissues [115], indicating that cattle exposed to such aborted materials can become infected with Salmonella [118].
Additionally, evidence has suggested that vertical transmission from the dam to the fetus is possible, with viable calves potentially being born already infected without fecal–oral exposure [119]. Vertical transmission of Salmonella has been documented not only in cattle but also in poultry [51].
Clinical signs observed in Salmonella-infected pregnant cows may include intermittent loose stools, acute post-abortion pyrexia, and reduced feed intake [115]. Although the bacterium is rarely shed directly in the milk of infected dams, serovars such as Salmonella Dublin have a higher likelihood of shedding compared to other serovars [30].
2.9. Cattle Shows
A United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) report highlighted instances where some farmers transported their cattle to events such as shows, fairs, and rodeos [33]. Following these events, some farmers reintegrate their animals into their herds without implementing any quarantine measures [33]. Such practices present potential pathways for disease introduction, as the animals come into contact with numerous humans and other animals during these gatherings. Additionally, during such events, animals from different locations may be housed in the same confined spaces or share common feed and water sources, facilitating the potential transmission of pathogens. These events can also induce significant stress in the animals [120], and stress in any form can contribute to the shedding of pathogens.
3. Prevention and Control
Upon confirmation of Salmonella infection in cattle, a series of comprehensive investigations and control measures must be promptly implemented, taking into account all possible sources of infection [23]. It is essential to identify and map out all potentially exposed and infected premises to ensure the rigorous implementation of control measures [103]. Morbidity, mortality, and production losses in newly infected or persistently infected herds are significant concerns [121]. Regardless of the serovar involved, similar control measures can be applied, though specific challenges arise with the host-adapted serovar Salmonella Dublin [23]. The following sections discuss preventative and control measures to mitigate Salmonella in cattle herds, beginning with biosecurity.
3.1. Biosecurity
The OIE (2015) defines biosecurity as “a set of management and physical measures designed to reduce the risk of introduction, establishment and spread of animal diseases, infections or infestations to, from and within an animal population” [122]. Simply put, biosecurity encompasses any practices or systems aimed at preventing the spread of pathogens to susceptible or naïve farm animals and their environment [123]. For cattle farmers, this involves implementing management systems and practices that prevent herd infections [124]. There is no single universal approach to biosecurity; instead, various tools are available to control infections, which can be tailored to the specific needs and objectives of each herd [125]. The primary goal of biosecurity measures is to prevent disease introduction to naïve herds, with other aspects serving as contingency plans in case prevention efforts fail [122]. However, achieving this goal in modern cattle farming is challenging due to various operational constraints, necessitating collaborative efforts among stakeholders to address these challenges [126]. The preventative measures discussed here outline key biosecurity strategies to prevent or control Salmonella on cattle farms.
3.2. Interventions Aimed at Farm Animals and Their Environment
Strategies to reduce cattle exposure to Salmonella while enhancing their disease resistance are crucial for preventing and controlling the pathogen [30]. However, despite their effectiveness, these strategies can be demanding and, in some cases, impractical, especially in large herds. Nevertheless, where feasible, farmers can combine human resources and mechanization to optimize disease prevention and control on their farms.
A key approach is maintaining a strict hygienic environment through periodic disinfection and thorough cleaning of the premises. Additionally, herd owners must assess the risk of introducing new livestock from infected herds. Therefore, maintaining a high level of external biosecurity is essential [100]. Ideally, farmers should source cattle from Salmonella-free herds or ensure all new animals undergo serological testing before integration.
Whenever possible, maintaining a closed herd is recommended [30]. Stressors such as introducing new animals, overcrowding, and inadequate transition space and time should be minimized or avoided [37]. If acquiring new animals is unavoidable, introducing younger cattle is preferable, as they pose a lower risk of carrying Salmonella compared to adults [127]. This is because adult cattle have a higher likelihood of testing positive for Salmonella [34]. Nevertheless, regardless of where the animal is obtained, the quarantining and vaccination of new arrivals will remain important to reduce the chances of introducing Salmonella into a herd [128,129]. However, vaccinations are not a substitute for good management practices [37], as the efficiencies of current vaccines for cattle are still evaluated for improvement [130,131]. just like in other livestock such as poultry [132] and pigs [133].
While larger herd sizes are linked to challenges in Salmonella control, reducing herd size is neither a practical nor an economically viable solution [75]. Instead, farmers should focus on implementing management systems that minimize herd exposure to potential infection sources. For instance, using flooring systems that allow manure to fall into a collection trench can improve hygiene and reduce the risk of fecal–oral disease transmission. Additionally, the periodic testing and culling of infected animals should be carried out [30].
To manage sick animals effectively, particularly in large dairies where the number of cases can be overwhelming, farmers should avoid housing sick, maternity, and recovering animals together for convenience’s sake [23].
Newborn and milk-fed calves require special attention as they are highly susceptible to Salmonella infection [116]. Before calving, cattle that test positive for Salmonella must be housed separately from those testing negative [37]. Maintaining high hygienic standards in calving and calf housing environments is essential. Furthermore, all newborns should be fed colostrum or milk exclusively from Salmonella-negative cattle [37]. In endemic situations where these standards are difficult to meet, heat treatment of colostrum and pasteurization of milk may be beneficial [116].
Providing pre-weaned calves with medicated milk replacers can further lower their risk of Salmonella infection and shedding [75]. Preventing contact between adult cattle and calves, along with implementing an all-in, all-out system in calf and heifer-raising facilities, can significantly reduce Salmonella transmission from infected cattle to young calves [37].
Although no evidence currently exists of Salmonella transmission to cattle through contaminated semen, a recent study reported the isolation of a multi-drug-resistant strain of Salmonella Dublin from the cryopreserved semen of a 17-month-old Holstein bull at a stud facility in the Midwest U.S. [134]. The pathogen was also cultured from various postmortem samples of the euthanized bull, including urine, bile, feces, prostate, seminal vesicles, preputial mucosa, colon, and small intestine [134]. Notably, the antimicrobial resistance pattern of the isolates from the cryopreserved semen was identical to that of the postmortem samples [134].
Therefore, farmers are advised to ensure that bulls brought onto their farms for mating purposes are free from Salmonella infection. Moreover, achieving completely sterile semen during breeding is virtually impossible, as microorganisms are naturally present in every ejaculate [135]. Nevertheless, bulls designated for semen production for artificial insemination should be housed in strictly regulated semen collection centers that adhere to specific protocols. These protocols include regular clinical examinations, pathogen assessments of semen, and routine testing for various diseases, all of which must be conducted and approved by qualified veterinary authorities [135].
However, testing the total volume of the millions of semen doses collected worldwide is both impractical and unsafe. The most reliable and effective approach is to ensure that all bulls used for semen production are pathogen-free. In doing so, it can be reasonably presumed that the semen from these bulls is also pathogen-free [135].
Minimizing fecal contamination of feedstuffs, feeding surfaces, water troughs, and equipment is crucial [37]. In areas where open grazing is practiced, cattle should be restricted from grazing on slurry-treated pastures for at least a month after application [38]. Proper drainage and leveling of water-collecting areas on farms and pastures are essential [37], as stagnant water may attract birds and other animals that could use it as a drinking source.
As previously mentioned, cleaning and disinfecting the farm environment is vital; however, this task can be daunting, particularly in large dairy herds [23]. Removing all visible debris is a critical step in the cleaning and decontamination process, as even the most effective disinfectants may have limited impact in environments containing organic matter such as feces and bedding material [23]. Cleaning helps eliminate most microorganisms, allowing disinfectants to effectively eradicate the remaining microbes. This method is particularly effective in controlling pathogens transmitted via the fecal–oral route, such as Salmonella [23].
However, pressure washing is not recommended for cleaning animal pens and farm premises, as it can aerosolize pathogens and facilitate their spread [23,29]. Additionally, power washing is ineffective in removing microbial biofilms; therefore, the use of handheld foamers to apply alkaline detergents and acid rinses is advised where applicable [23]. Concrete pads should be disinfected after cleaning and exposed to sunlight for several days [29] as Salmonella is susceptible to most disinfectants and ultraviolet radiation [101].
Special attention should be given to cleaning livestock trailers, maternity and calf pens, feeding equipment, and other areas prone to Salmonella contamination [23]. The routine cleaning and disinfection of vehicles and animal market premises are also recommended as essential measures for salmonellosis control [136]. Additionally, veterinarians and farm personnel should frequently clean and disinfect all instruments to reduce the risk of infection spread [52].
3.3. Farm Workers and Other People
Biosecurity measures must be enforced for both employees and visitors. These measures may include washing hands with soap and warm water before and after visiting the animal herd, as well as changing clothes before and after each visit. Employees and individuals who regularly work on the farm must strictly adhere to biosecurity protocols when handling different groups of animals [30]. Visitors should be directed to a designated parking area that is located away from vehicles and equipment that have access to the animals. This precaution helps minimize the risk of disease introduction from external sources. For cases involving sick animals, it is recommended to assign dedicated personnel to handle them exclusively [23]. Additionally, water baths with disinfectants should be strategically placed at key locations on the farm premises, and boot covers must be provided for both workers and visitors while on site.
3.4. Wildlife and Flies
It is crucial to consider rodents and wildlife when implementing biosecurity measures to control Salmonella, as they can act as reservoirs of infection and contaminate animal feed with pathogens [33,58]. To prevent cattle from accessing pond water, other water bodies, and feeding areas shared with birds and wildlife, such as waterfowl, these areas should be fenced off or drained using appropriate channels in the case of water bodies [37]. Rodent control can be achieved through biological methods, such as using cats, or chemical methods, including baits and traps [33].
For effective fly control on farms, both topical and oral treatments, as well as treated ear tags, can be utilized. Additionally, environmental control measures such as fly sprays, foggers, traps, and fly tape should be incorporated into fly management programs. Biological control methods, such as introducing predator wasps to disrupt the fly life cycle and prevent their maturation, can also be employed [33].
Proper feed storage is essential to prevent access by wildlife and potential contamination [137]. Finally, appropriate farm fencing should be installed where necessary to deter wildlife that may serve as disease vectors.
3.5. Animal Feed
The World Organization for Animal Health (OIE), recognizing the critical role of animal feed quality in both human and animal health, has dedicated a chapter in the Terrestrial Animal Health Code to “The control of hazards of animal health and public health importance in animal feed.” This effort is further supported by guidelines from the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) on the “Application of risk assessment for feed” and the “Risk analysis of foodborne antimicrobial resistance” [59].
In as much as during feed preparation, pelleting (which is heat processing), chemical additions, or both help in destroying Salmonella that may be present in the feed [26], in addition, every stage of the feed processing chain must be routinely monitored to prevent potential Salmonella contamination [137]. In Sweden, a Salmonella control program based on the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points (HACCPs) principles was implemented in 1991 [56]. According to this program, if Salmonella is detected before heat treatment, the contaminated section of the production line undergoes thorough cleaning and disinfection. If Salmonella is found after heat treatment, the entire feed mill must be cleaned and disinfected, and production can only resume once environmental sampling results are negative [56].
Certain plant essential oils have also been identified as effective in reducing Salmonella growth [138]. Incorporating such chemical and biological compounds with antibiotic properties can significantly lower bacterial loads in animal feed. For instance, adding probiotics and modifying feed structure such as increasing feed particle size has been shown to reduce the intestinal load of Salmonella in pig herds, thereby decreasing fecal shedding [139]. Further studies are needed to evaluate the impact of similar modifications in pelleted cattle feed.
Additionally, methods such as radiation treatment and the inclusion of organic acids have been identified as effective measures to ensure feed safety [137]. Nonetheless, it is essential to protect all feed ingredients from contamination by wild birds and rodents, while feed transport vehicles should be regularly cleaned and sanitized [26].
3.6. Vehicles, Equipment, and Animal Movements
It is essential to clean and disinfect all equipment between use [30]. Farmers should avoid using the same equipment for both manure handling and feed distribution [23]. Additionally, they must ensure that feed delivery vehicles do not pass through manure or manure-scraping lanes [37]. Vehicles should also be designed for easy cleaning [136]. Currently, no federal regulations in the U.S. mandate the cleaning of trailers between cattle loads. This challenge may be further exacerbated by the lack of trailer washing facilities in the region, making regular cleaning and disinfection difficult [55]. Nevertheless, farmers should adopt the practice of routinely cleaning their animal transport vehicles while public health authorities consider implementing regulations to enhance animal transport hygiene.
3.7. National Control Programs
National control programs in some countries have successfully prevented and eradicated many diseases [140]. For instance, Sweden has implemented an effective yet costly Salmonella control program, which has limited the number of cattle farms infected with Salmonella each year. This program restricts the movement of all infected herds until they are confirmed free of infection, with farmers receiving government compensation for any losses incurred. Additionally, the program treats all Salmonella serovars as undesirable due to their zoonotic potential [74].
Livestock disease control programs have largely relied on restricting animal movements between farms and through high-risk areas. This approach is particularly effective given the complexities of trade networks in animal production [122]. Recently, advancements in technology and infrastructure for tracking livestock movements have gained significant attention, as they provide valuable insights into the potential spread of infections within source populations [141].
A notable example of such stringent control measures is Denmark’s Salmonella Dublin program, aimed at eradicating Salmonella Dublin from the national cattle population [122]. The program mandates that all cattle movements between herds be recorded in the Central Husbandry Registry (CHR), which is closely integrated with the Danish Cattle Database (DCDB) and managed by SEGES, Denmark’s leading agricultural consultancy service. These movement records are rigorously monitored for errors to ensure compliance with the European Union’s cross-compliance standards and regulations [122].
Many governments now mandate the registration of livestock movements in centralized national databases, which facilitate swift access to data during infection investigations. Countries such as the United Kingdom, Argentina, and all European Union member states have adopted this approach [47]. However, others such as the United States currently lack a comprehensive system for tracing and identifying individual animals, their holdings, or livestock shipments, despite previous efforts [47]. The 2018 CattleTrace initiative, however, presents a valuable opportunity to enhance livestock disease control and prevention in the country by enabling the rapid tracing of infected animals [47]. Furthermore, the recently developed U.S. Animal Movement Model (USAMM) shows promise in predicting the size and spatial distribution of cattle shipments [47]. Ensuring traceability from farms to processing facilities and ultimately to consumers is crucial, especially during outbreak investigations [21].
Aside from control programs focused on animal movement, other national initiatives have implemented routine mandatory surveillance exercises, often tailored to achieve specific national objectives [142]. For instance, in the Netherlands, national control programs target six endemic cattle diseases, including salmonellosis, and are designed to address prevailing conditions such as the high exportation of dairy products [142]. As part of this strategy, periodic surveillance through bulk-milk testing for antibodies in dairy cattle has been established as a national control measure [142].
Similarly, the Canadian Integrated Program for Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance (CIPARS) undertakes both active and passive surveillance of Salmonella in beef and dairy cattle, among other responsibilities [143]. These surveillance activities can be extended to breeding centers and animal feed mills to ensure compliance with hygienic standards.
While recognizing the importance of continuous on-farm surveillance and monitoring of animal movement, national efforts should also promote broader stakeholder collaboration at various levels of cattle production. Regulations and policies, to be enforced through national instruments such as laws and bylaws, will ensure that all stakeholders involved in this critical industry contribute to minimizing the presence of Salmonella in cattle production.
4. Conclusions
In this article, common sources and risks of Salmonella infection in cattle herds (Figure 1) are reviewed and summarized and interventions are explored to reduce cattle exposure to the pathogen and contain existing infections within herds. Addressing Salmonella in cattle production requires a coordinated approach involving all stakeholders, including animal industries (such as feed producers and breeding stations), individuals (such as veterinarians, farmers, and animal traders), government regulatory authorities, and the public. A comprehensive approach is essential due to the numerous potential sources of Salmonella introduction to cattle herds. Given the ongoing threat Salmonella poses to public health, it is crucial to strengthen surveillance and control measures, particularly on animal farms where food animals are raised.
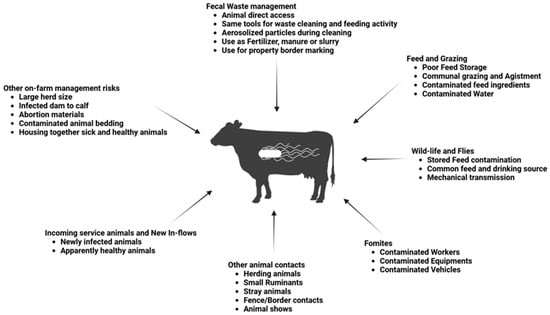
Figure 1.
Sources and risk of Salmonella exposure to cattle.
Author Contributions
K.E.B.: Conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing; E.K., R.N. and V.O.: writing—review and editing, visualization; D.B., S.P., T.S., C.R.J. and W.A.: writing—review and editing, supervision; W.A. and T.S.: funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by grants from National Institute of Food and Agriculture: 2021-38821-34710; 2022-67017-36982; 2022-38821-37362.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to Ruby Perry, Dean, Tuskegee University College of Veterinary Medicine, for supporting graduate research and the Center for Food Animal Health, Food Safety and Defense Laboratory.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Burciaga, S.; Trachsel, J.M.; Sockett, D.; Aulik, N.; Monson, M.S.; Anderson, C.L.; Bearson, S.M.D. Genomic and Phenotypic Comparison of Two Variants of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Enterica Serovar Heidelberg Isolated during the 2015–2017 Multi-State Outbreak in Cattle. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1282832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, A.; Kemal, J.; Alemayehu, H.; Habte Mariam, S. Isolation, Identification, and Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing of Salmonella from Slaughtered Bovines and Ovines in Addis Ababa Abattoir Enterprise, Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 1, 3714785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehuwa, O.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Jaiswal, S. Salmonella, Food Safety and Food Handling Practices. Foods 2021, 10, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.; Dudley, E.; Kittana, H.; Thompson, A.C.; Scott, M.; Norman, K.; Valeris-Chacin, R. Genomic Profiling of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Clinical Salmonella Isolates from Cattle in the Texas Panhandle, USA. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canning, M.; Birhane, M.G.; Dewey-Mattia, D.; Lawinger, H.; Cote, A.; Gieraltowski, L.; Schwensohn, C.; Tagg, K.A.; Francois Watkins, L.K.; Park Robyn, M.; et al. Salmonella Outbreaks Linked to Beef, United States, 2012–2019. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, B.; Cunha-Neto, A.; Castro, V.S.; Carvalho, R.C.T.; Teixeira, L.A.C.; dos Prazeres Rodrigues, D.; de Souza Figueiredo, E.E. Salmonella Schwarzengrund, Akuafo, and O:16 Isolated from Vacuum-Packaged Beef Produced in the State of Mato Grosso, Brazil. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2021, 15, 1876–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, N.; Feng, Y.; Pan, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xue, C.; Zhu, B.; Hu, Y. Genomic Characterization of Salmonella Enterica Isolates From Retail Meat in Beijing, China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 636332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kebede, M.T.; Getu, A.A. Assessment of Bacteriological Quality and Safety of Raw Meat at Slaughterhouse and Butchers’ Shop (Retail Outlets) in Assosa Town, Beneshangul Gumuz Regional State, Western Ethiopia. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañeda-Salazar, R.; Pulido-Villamarín, A.; Ángel-Rodríguez, G.L.; Zafra-Alba, C.A.; Oliver-Espinosa, O. Isolation and Identification of Salmonella spp. In Raw Milk from Dairy Herds in Colombia. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Sci. 2021, 58, e172805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ling, Z.; Sun, N.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, L. Molecular Genetic Characteristics of Mcr-9-Harbouring Salmonella Enterica Serotype Typhimurium Isolated from Raw Milk. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 57, 106332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebeyehu, A.; Taye, M.; Abebe, R. Isolation, Molecular Detection and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile of Salmonella from Raw Cow Milk Collected from Dairy Farms and Households in Southern Ethiopia. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, E.N.; Van Doren, J.M.; Leonard, C.L.; Datta, A.R. Prevalence of Listeria Monocytogenes, Salmonella spp., Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli, and Campylobacter spp. in Raw Milk in the United States between 2000 and 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonça, R.; Furtado, R.; Coelho, A.; Correia, C.B.; Suyarko, E.; Borges, V.; Gomes, J.P.; Pista, A.; Batista, R. Raw Milk Cheeses from Beira Baixa, Portugal—A Contributive Study for the Microbiological Hygiene and Safety Assessment. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 1759–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace, D.; Wu, F.; Havelaar, A.H. MILK Symposium Review: Foodborne Diseases from Milk and Milk Products in Developing Countries—Review of Causes and Health and Economic Implications. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 9715–9729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, Z.; Canning, M.; Rickless, D.; Devine, C.; Buckman, R.; Payne, D.C.; Marshall, K.E. Comparing Individual and Community-Level Characteristics of People with Ground Beef-Associated Salmonellosis and Other Ground Beef Eaters: A Case-Control Analysis. J. Food Prot. 2024, 87, 100303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belk, A.D.; Arnold, A.N.; Sawyer, J.E.; Griffin, D.B.; Taylor, T.M.; Savell, J.W.; Gehring, K.B. Comparison of Salmonella Prevalence Rates in Bovine Lymph Nodes across Feeding Stages. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Pihier, N.; Vanbockstael, C.; Le Hello, S.; Cadel Six, S.; Fournet, N.; Jourdan-Da Silva, N. Outbreak of Salmonella Enteritidis Linked to the Consumption of Frozen Beefburgers Received from a Food Bank and Originating from Poland: Northern France, December 2014 to April 2015. Eurosurveillance 2016, 21, 30363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidl, G.; Schoss, S.; te Wierik, M.; Heck, M.; Tolsma, P.; Urbanus, A.; Slegers-Fitz-James, I.; Friesema, I. Tracing Back the Source of an Outbreak of Salmonella Typhimurium; National Outbreak Linked to the Consumption of Raw and Undercooked Beef Products, the Netherlands, October to December 2015. PLoS Curr. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, M.; Gollarza, L.; Sockett, D.; Aulik, N.; Patton, E.; Francois Watkins, L.K.; Gambino-Shirley, K.J.; Folster, J.P.; Chen, J.C.; Tagg, K.A.; et al. Outbreak of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Heidelberg Infections Linked to Dairy Calf Exposure, United States, 2015-2018. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2022, 19, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tao, S.; Hinkle, N.; Harrison, M.; Chen, J. Salmonella, Including Antibiotic-Resistant Salmonella, from Flies Captured from Cattle Farms in Georgia, U.S.A. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, K.E.H.; Tewell, M.; Tecle, S.; Leeper, M.; Sinatra, J.; Kissler, B.; Fung, A.; Brown, K.; Wagner, D.; Trees, E.; et al. Protracted Outbreak of Salmonella Newport Infections Linked to Ground Beef: Possible Role of Dairy Cows—21 States, 2016–2017. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarno, E.; Pezzutto, D.; Rossi, M.; Liebana, E.; Rizzi, V. A Review of Significant European Foodborne Outbreaks in the Last Decade. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holschbach, C.L.; Peek, S.F. Salmonella in Dairy Cattle. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2017, 34, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasquez-Munoz, A.; Castro-Vargas, R.; Cullens-Nobis, F.M.; Mani, R.; Abuelo, A. Review: Salmonella Dublin in Dairy Cattle. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 10, 1331767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickodem, C.; Arnold, A.N.; Gehring, K.B.; Gill, J.J.; Richeson, J.T.; Samuelson, K.L.; Morgan Scott, H.; Smith, J.K.; Matthew Taylor, T.; Vinasco, J.; et al. A Longitudinal Study on the Dynamics of Salmonella Enterica Prevalence and Serovar Composition in Beef Cattle Feces and Lymph Nodes and Potential Contributing Sources from the Feedlot Environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e00033-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, F.T. A Review of Practical Salmonella Control Measures in Animal Feed. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2011, 20, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, A.N.; Sawyer, J.E.; Gehring, K.B. Longitudinal Evaluation of Salmonella in Environmental Components and Peripheral Lymph Nodes of Fed Cattle From Weaning to Finish in Three Distinct Feeding Locations. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, F.; Ventura, G.; Rosignoli, C.; Rota Nodari, S.; D’incau, M.; Marocchi, L.; Santucci, G.; Boldini, M.; Gradassi, M. Detection and Phenotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Salmonella Enterica Serotypes in Dairy Cattle Farms in the Po Valley, Northern Italy. Animals 2024, 14, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gull, T. Bacterial Causes of Intestinal Disease in Dairy Calves: Acceptable Control Measures. Vet. Clin. N. Am.-Food Anim. Pract. 2022, 38, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeron, L. Prevention and Control of Salmonella in Dairy Cattle. WCDS Adv. Dairy Technol. 2023, 34, 117–119. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, B.D.; Barnes, A.N.; Umar, S.; Guo, X.; Thongthum, T.; Gray, G.C. Reverse Zoonotic Transmission (Zooanthroponosis): An Increasing Threat to Animal Health. In Zoonoses: Infections Affecting Humans and Animals; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–63. ISBN 978-3-030-85877-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kabagambe, E.K.; Wells, S.J.; Garber, L.P.; Salman, M.D.; Wagner, B.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J. Risk Factors for Fecal Shedding of Salmonella in 91 US Dairy Herds in 1996. Prev. Vet. Med. 2000, 43, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USDA. Beef 2017: Beef Cow-Calf Management Practices in the United States. 2017. Available online: https://www.aphis.usda.gov/sites/default/files/beef2017_dr_parti.pdf (accessed on 11 August 2024).
- Gutema, F.D.; Agga, G.E.; Abdi, R.D.; De Zutter, L.; Duchateau, L.; Gabriël, S. Prevalence and Serotype Diversity of Salmonella in Apparently Healthy Cattle: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Published Studies, 2000–2017. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.R.; Dohoo, I. Time-to-Event Analysis of Predictors for Recovery from Salmonella Dublin Infection in Danish Dairy Herds between 2002 and 2012. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 110, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelzer, K.; Switt, A.I.M.; Wiedmann, M. Animal Contact as a Source of Human Non-Typhoidal Salmonellosis. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuirk, S.M.; Peek, S. Salmonellosis in Cattle: A Review. In Proceedings of the American Association of Bovine Practitioners 36th Annual Conference, Columbus, OH, USA, 18–20 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Vanselow, B.A.; Hum, S.; Hornitzky, M.A.; Eamens, G.J.; Quinn, K. Salmonella Typhimurium Persistence in a Hunter Valley Dairy Herd. Aust. Vet. J. 2007, 85, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.R.; Dohoo, I. Culling Decisions of Dairy Farmers during a 3-Year Salmonella Control Study. Prev. Vet. Med. 2011, 100, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, L.R.; van den Borne, B.; van Schaik, G. Salmonella Dublin Infection in Young Dairy Calves: Transmission Parameters Estimated from Field Data and an SIR-Model. Prev. Vet. Med. 2007, 79, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wray, C.; Todd, N.; Mclaren, I.; Beedell, Y.; Rowe, B. The Epidemiology of Salmonella Infection of Calves: The Role of Dealers. Epidemiol. Infect. 1990, 105, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassaye, D.; Kassa, T.; Sebhat, B. Isolation of Nontyphoidal Salmonella in Cattle, Sheep and Goats among Three Different Agro-Ecologies of Eastern Hararghe, Ethiopia. Int. J. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 8, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Koeppel, L.; Siems, T.; Fischer, M.; Lentz, H.H.K. Automatic Classification of Farms and Traders in the Pig Production Chain. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 150, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langvad, B.; Skov, M.N.; Rattenborg, E.; Olsen, J.E.; Baggesen, D.L. Transmission Routes of Salmonella Typhimurium DT 104 between 14 Cattle and Pig Herds in Denmark Demonstrated by Molecular Fingerprinting. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, M.L.; Kemp, R.; Christley, R.M. Direct and Indirect Contacts between Cattle Farms in North-West England. Prev. Vet. Med. 2008, 84, 242–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mweu, E.; English, M. Typhoid Fever in Children in Africa. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2008, 13, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellman, S.; Beck-Johnson, L.M.; Hallman, C.; Miller, R.S.; Bonner, K.A.O.; Portacci, K.; Webb, C.T.; Lindström, T. Modeling U.S. Cattle Movements until the Cows Come Home: Who Ships to Whom and How Many? Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 203, 107483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messenger, A.M.; Barnes, A.N.; Gray, G.C. Reverse Zoonotic Disease Transmission (Zooanthroponosis): A Systematic Review of Seldom-Documented Human Biological Threats to Animals. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, J.H.; Price, J.T. The Significant but Understudied Impact of Pathogen Transmission from Humans to Animals. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 2009, 76, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, T.D.; Nielsen, L.R.; Toft, N. Bayesian Estimation of True Between-Herd and within-Herd Prevalence of Salmonella in Danish Veal Calves. Prev. Vet. Med. 2011, 100, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karodia, A.B.; Shaik, T.; Qekwana, D.N. Occurrence of Salmonella Spp. in Animal Patients and the Hospital Environment at a Veterinary Academic Hospital in South Africa. Vet. World 2024, 17, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzitey, F.; Bukari, R.; Ayamdoh, Y.I. Surveillance of Bacterial Contamination of Fomites in Tamale Veterinary Clinic with Special Focus on Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Ghana. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 10, 132–140. [Google Scholar]
- Nyokabi, N.S.; Wood, J.L.N.; Gemechu, G.; Berg, S.; Mihret, A.; Lindahl, J.F.; Moore, H.L. The Role of Syndromic Knowledge in Ethiopian Veterinarians’ Treatment of Cattle. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1364963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyokabi, N.S.; Phelan, L.; Lindahl, J.F.; Berg, S.; Muunda, E.; Mihret, A.; Wood, J.L.N.; Moore, H.L. Exploring Veterinary Students’ Awareness and Perception of Zoonoses Risks, Infection Control Practices, and Biosecurity Measures in Ethiopia. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1385849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, S.R.; Pempek, J.A.; Meyer, R.; Portillo-Gonzalez, R.; Sockett, D.; Aulik, N.; Habing, G. Prevalence and Sources of Salmonella Lymph Node Infection in Special-Fed Veal Calves. J. Food Prot. 2022, 85, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedish Veterinary Agency. Salmonella in Feed. Available online: https://www.sva.se/en/what-we-do/feed-safety/Salmonella-in-feed/ (accessed on 11 August 2024).
- Davis, M.A.; Hancock, D.D.; Rice, D.H.; Call, D.R.; DiGiacomo, R.; Samadpour, M.; Besser, T.E. Feedstuffs as a Vehicle of Cattle Exposure to Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hald, T.; Wingstrand, A.; Pires, S.M.; Vieira, A.; Domingues, A.R.; Lundsby, K.; Andersen, V.D. Assessment of the Human-Health Impact of Salmonella in Animal Feed. Available online: https://backend.orbit.dtu.dk/ws/portalfiles/portal/51295782/Assessment_of_the_human_health_impact.pdf (accessed on 11 August 2024).
- Parker, E.M.; Parker, A.J.; Short, G.; O’Connor, A.M.; Wittum, T.E. Salmonella Detection in Commercially Prepared Livestock Feed and the Raw Ingredients and Equipment Used to Manufacture the Feed: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 198, 105546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.H.; Wray, C. Distribution of Salmonella Contamination in Ten Animal Feedmills. Vet. Microbiol. 1997, 57, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.C.; Poole, T.L.; Runyon, M.; Hume, M.; Herrman, T.J. Prevalence of Nontyphoidal Salmonella and Salmonella Strains with Conjugative Antimicrobial-Resistant Serovars Contaminating Animal Feed in Texas. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.J.; Walker, R.L.; Hird, D.W.; Blanchard, P.C. Case-Control Study of an Outbreak of Clinical Disease Attributable to Salmonella Menhaden Infection in Eight Dairy Herds. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1997, 210, 528–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindqvist, N.; Heinikainen, S.; Toivonen, A.M.; Pelkonen, S. Discrimination between Endemic and Feedborne Salmonella Infantis Infection in Cattle by Molecular Typing. Epidemiol. Infect. 1999, 122, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangloli, P.; Dje, Y.; Ahmed, O.; Doane, C.A.; Oliver, S.P.; Draughon, F.A. Seasonal Incidence and Molecular Characterization of Salmonella from Dairy Cows, Calves, and Farm Environment. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2008, 5, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.W.; Collins, P.; Brown, G.T.H.; Aitken, M. Transmission of Salmonella mbandaka to Cattle from Contaminated Feed. J. Hyg. 1982, 88, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkuijl, C.; Strambo, C.; Hocquet, R.; Butterfield, R.; Achakulwisut, P.; Boyland, M.; Araújo, J.A.V.; Bakhtaoui, I.; Smit, J.; Lima, M.B.; et al. A Just Transition in Animal Agriculture Is Necessary for More Effective and Equitable One Health Outcomes. CABI One Health 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windsor, P.A. Progress With Livestock Welfare in Extensive Production Systems: Lessons from Australia. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 674482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidu, L.; Enea, D.N. Extensive Farming Systems. In Animal Husbandry–Beliefs, Facts and Reality [Working Title]; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, D.; Manteca, X. Animal Welfare in Extensive Production Systems Is Still an Area of Concern. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 545902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, S.; Syed, Z.; Abubabakar, M. Global Perspectives of Intensive Animal Farming and Its Applications. In Intensive Animal Farming–A Cost-Effective Tactic; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023; ISBN 978-1-80356-102-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-González, P.; Bueso-Rodenas, J. Extensive vs. Intensive Farming|YaleGlobal. Available online: https://archive-yaleglobal.yale.edu/content/extensive-vs-intensive-farming (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Meng, X.J.; Lindsay, D.S. Wild Boars as Sources for Infectious Diseases in Livestock and Humans. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2697–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacheck, S.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; König, M.; Stolle, A.; Stephan, R. Wild Boars as an Important Reservoir for Foodborne Pathogens. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boqvist, S.; Vågsholm, I. Risk Factors for Hazard of Release from Salmonella-Control Restriction on Swedish Cattle Farms from 1993 to 2002. Prev. Vet. Med. 2005, 71, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossler, C.P.; Wells, S.J.; Kaneene, J.B.; Ruegg, P.L.; Warnick, L.D.; Bender, J.B.; Eberly, L.E.; Godden, S.M.; Halbert, L.W. Herd-Level Factors Associated with Isolation of Salmonella in a Multi-State Study of Conventional and Organic Dairy Farms: I. Salmonella Shedding in Cows. Prev. Vet. Med. 2005, 70, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koohmaraie, M.; Scanga, J.A.; De La Zerda, M.J.; Koohmaraie, B.; Tapay, L.; Beskhlebnaya, V.; Mai, T.; Greeson, K.; Samadpour, M. Tracking the Sources of Salmonella in Ground Beef Produced from Nonfed Cattle. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 1464–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggita, M.; Herawati, O.; Artanto, S. Molecular Screening of Salmonella sp. from Fecal Sample of Sparrows (Passer domesticus) in Yogyakarta, Indonesia. BIO Web Conf. 2021, 33, 07003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira-Pinto, M.; Morais, L.; Caleja, C.; Themudo, P.; Torres, C.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P.; Martins, C. Salmonella Sp. in Game (Sus scrofa and Oryctolagus cuniculus). Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 739–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnick, L.D.; Crofton, L.M.; Pelzer, K.D.; Hawkins, M.J. Risk Factors for Clinical Salmonellosis in Virginia, USA Cattle Herds. Prev. Vet. Med. 2001, 49, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USDA-Food and Drug Administration. Get the Facts about Salmonella|FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/animal-veterinary/animal-health-literacy/get-facts-about-salmonella (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Brown, T.R.; Edrington, T.S.; Loneragan, G.H.; Hanson, D.L.; Malin, K.; Ison, J.J.; Nisbet, D.J. Investigation into Possible Differences in Salmonella Prevalence in the Peripheral Lymph Nodes of Cattle Derived from Distinct Production Systems and of Different Breed Types. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 2081–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viegas, F.M.; Ramos, C.P.; Xavier, R.G.C.; Lopes, E.O.; Junior, C.A.O.; Bagno, R.M.; Diniz, A.N.; Lobato, F.C.F.; Silva, R.O.S. Fecal Shedding of Salmonella Spp., Clostridium Perfringens, and Clostridioides Difficile in Dogs Fed Raw Meat-Based Diets in Brazil and Their Owners’ Motivation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmael, B.; Abraha, B.; Alemu, S.; Mummed, B.; Hiko, A.; Abdurehman, A. Isolation, Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns, and Risk Factors Assessment of Non-Typhoidal Salmonella from Apparently Healthy and Diarrheic Dogs. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacometti, F.; Magarotto, J.; Serraino, A.; Piva, S. Highly Suspected Cases of Salmonellosis in Two Cats Fed with a Commercial Raw Meat-Based Diet: Health Risks to Animals and Zoonotic Implications. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimschuessel, R.; Grabenstein, M.; Guag, J.; Nemser, S.M.; Song, K.; Qiu, J.; Clothier, K.A.; Byrne, B.A.; Marks, S.L.; Cadmus, K.; et al. Multilaboratory Survey to Evaluate Salmonella Prevalence in Diarrheic and Nondiarrheic Dogs and Cats in the United States between 2012 and 2014. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1350–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, M.N.; Madsen, J.J.; Rahbek, C.; Lodal, J.; Jespersen, J.B.; Jørgensen, J.C.; Dietz, H.H.; Chriél, M.; Baggesen, D.L. Transmission of Salmonella between Wildlife and Meat-Production Animals in Denmark. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herding. Available online: https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/herding/ (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Canine Co-Workers: Herding Dogs from around the World. Available online: https://www.lamlac.co.uk/latest/view,canine-coworkers-herding-dogs-from-around-the-world_120.htm (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Klose, C.; Scuda, N.; Ziegler, T.; Eisenberger, D.; Hanczaruk, M.; Riehm, J.M. Whole-Genome Investigation of Salmonella Dublin Considering Mountain Pastures as Reservoirs in Southern Bavaria, Germany. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Sharma, R.; Aulakh, R.S.; Singh, B.B. Prevalence of Brucella Species in Stray Cattle, Dogs and Cats: A Systematic Review. Prev. Vet. Med. 2023, 219, 106017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawwas, H.A.E.H.; Aboueisha, A.K.M.; Fadel, H.M.; El-Mahallawy, H.S. Salmonella Serovars in Sheep and Goats and Their Probable Zoonotic Potential to Humans in Suez Canal Area, Egypt. Acta Vet. Scand. 2022, 64, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkarim, A.; Khan, M.A.K.B.G.; Aklilu, E. Stray Animal Population Control: Methods, Public Health Concern, Ethics, and Animal Welfare Issues. World’s Vet. J. 2021, 11, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanz, L.; Hintze, S.; Hübner, S.; Barth, K.; Winckler, C. Single- and Multi-Species Groups: A Descriptive Study of Cattle and Broiler Behaviour on Pasture. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2022, 257, 105779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, E.; Fujii, K.; Kayano, M.; Sakurai, Y.; Nakatani, A.; Sasaki, M.; Hertl, J.A.; Grohn, Y.T. Is Salmonella enterica Shared between Wildlife and Cattle in Cattle Farming Areas? An 11-Year Retrospective Study in Tokachi District, Hokkaido, Japan. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagambèga, A.; Lienemann, T.; Aulu, L.; Traoré, A.S.; Barro, N.; Siitonen, A.; Haukka, K. Prevalence and Characterization of Salmonella enterica from the Feces of Cattle, Poultry, Swine and Hedgehogs in Burkina Faso and Their Comparison to Human Salmonella Isolates. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentaberre, G.; Porrero, M.C.; Navarro-Gonzalez, N.; Serrano, E.; Domínguez, L.; Lavín, S. Cattle Drive Salmonella Infection in the Wildlife-Livestock Interface. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, R.G.; Gawish, M.F.; Abotaleb, M.M.; Nada, H.S.; Morsy, K.; Abumandour, M.M.A.; Torky, H. Genetic Relationship between Salmonella Isolates Recovered from Calves and Broilers Chickens in Kafr El-Sheikh City Using ERIC PCR. Animals 2022, 12, 3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palhares, J.C.P.; Kich, J.D.; Bessa, M.C.; Biesus, L.L.; Berno, L.G.; Triques, N.J. Salmonella and Antimicrobial Resistance in an Animal-Based Agriculture River System. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, K.J.; Warnick, L.D.; Alexander, K.A.; Cripps, C.J.; Gröhn, Y.T.; McDonough, P.L.; Nydam, D.V.; Reed, K.E. The Incidence of Salmonellosis among Dairy Herds in the Northeastern United States. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 3766–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, L.R.; Warnick, L.D.; Greiner, M. Risk Factors for Changing Test Classification in the Danish Surveillance Program for Salmonella in Dairy Herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 2815–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohler, V.L.; Izzo, M.M.; House, J.K. Salmonella in Calves. Vet. Clin. N. Am.-Food Anim. Pract. 2009, 25, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huston, C.L.; Wittum, T.E.; Love, B.C.; Keen, J.E. Prevalence of Fecal Shedding of Salmonella spp. in Dairy Herds. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2002, 220, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mweu, M.M.; Fournié, G.; Halasa, T.; Toft, N.; Nielsen, S.S. Temporal Characterisation of the Network of Danish Cattle Movements and Its Implication for Disease Control: 2000–2009. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 110, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofer, K.; Trockenbacher, B.; Sodoma, E.; Khol, J.L.; Dünser, M.; Wittek, T. Establishing a Surveillance Programme for Salmonella Dublin in Austrian Dairy Herds by Comparing Herd-Level vs. Individual Animal Detection Methods. Prev. Vet. Med. 2024, 230, 106277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinton, L.W.; Braithwaite, R.R.; Hall, C.H.; Mackenzie, M.L. Survival of Indicator and Pathogenic Bacteria in Bovine Feces on Pasture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7917–7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheamfour, C.L.; Parveen, S.; Gutierrez, A.; Handy, E.T.; Behal, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.; East, C.; Xiong, R.; Haymaker, J.R.; et al. Detection of Salmonella Enterica and Listeria Monocytogenes in Alternative Irrigation Water by Culture and QPCR-Based Methods in the Mid-Atlantic U.S. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e03536-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, T.; Hoelzle, K.; Philipp, W.; Hoelzle, L.E. Survival of Salmonella typhimurium, Listeria monocytogenes, and ESBL Carrying Escherichia coli in Stored Anaerobic Biogas Digestates in Relation to Different Biogas Input Materials and Storage Temperatures. Agriculture 2022, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boes, J.; Alban, L.; Bagger, J.; Møgelmose, V.; Baggesen, D.L.; Olsen, J.E. Survival of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium in Slurry Applied to Clay Soil on a Danish Swine Farm. Prev. Vet. Med. 2005, 69, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habing, G.G.; Lombard, J.E.; Kopral, C.A.; Dargatz, D.A.; Kaneene, J.B. Farm-Level Associations with the Shedding of Salmonella and Antimicrobial-Resistant Salmonella in U.S. Dairy Cattle. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, J.D.; Aceto, H.W.; Rankin, S.C.; Dou, Z. Short Communication: Survey of Animal-Borne Pathogens in the Farm Environment of 13 Dairy Operations. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 5756–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraitareanu, S.; Vidu, L. Dairy Farms Biosecurity to Protect against Infectious Diseases and Antibiotics Overuse. In Antimicrobial Resistance—A One Health Perspective; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; ISBN 978-1-83962-433-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.J.B.; Carvalho, L.F.O.S.; Garcia, T.B. Experimental Airborne Transmission of Salmonella agona and Salmonella typhimurium in Weaned Pigs. Epidemiol. Infect. 2005, 134, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Riggs, M.R.; Urrutia, A.; Osborne, R.C.; Jackson, A.P.; Bailey, M.A.; Macklin, K.S.; Price, S.B.; Buhr, R.J.; Bourassa, D.V. Investigation of the Potential of Aerosolized Salmonella Enteritidis on Colonization and Persistence in Broilers from Day 3 to 21. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathes, C.M.; Zaidan, W.A.; Pearson, G.R.; Hinton, M.; Todd, N. Aerosol Infection of Calves and Mice with Salmonella typhimurium. Vet. Rec. 1988, 123, 590–594. [Google Scholar]
- Siepker, C.L.; Schwartz, K.J.; Feldhacker, T.J.; Magstadt, D.R.; Sahin, O.; Almeida, M.; Li, G.; Hayman, K.P.; Gorden, P.J. Salmonella Enterica Serovar Brandenburg Abortions in Dairy Cattle. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2022, 34, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, L.R.; Houe, H.; Nielsen, S.S. Narrative Review Comparing Principles and Instruments Used in Three Active Surveillance and Control Programmes for Non-EU-Regulated Diseases in the Danish Cattle Population. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 685857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinton, M. Salmonella Dublin Abortion in Cattle: Studies on the Clinical Aspects of the Condition. Br. Vet. J. 1974, 130, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Animal Disease Information Service, Salmonellosis in Cattle. Available online: https://www.nadis.org.uk/disease-a-z/cattle/salmonellosis-in-cattle/ (accessed on 22 January 2025).
- Hanson, D.L.; Loneragan, G.H.; Brown, T.R.; Nisbet, D.J.; Hume, M.E.; Edrington, T.S. Evidence Supporting Vertical Transmission of Salmonella in Dairy Cattle. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres, S.; Moreno, J.; Crespo, B.; Silvan, G.; Illera, J.C. Physiological Stress Responses in Cattle Used in the Spanish Rodeo. Animals 2023, 13, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.R. Review of Pathogenesis and Diagnostic Methods of Immediate Relevance for Epidemiology and Control of Salmonella Dublin in Cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Knegt, L.V.; Kudirkiene, E.; Rattenborg, E.; Sørensen, G.; Denwood, M.J.; Olsen, J.E.; Nielsen, L.R. Combining Salmonella Dublin Genome Information and Contact-Tracing to Substantiate a New Approach for Improved Detection of Infectious Transmission Routes in Cattle Populations. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 181, 104531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuja, B.K.; Manuja, A.; Singh, R.K. Globalization and Livestock Biosecurity. Agric. Res. 2014, 3, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleere, J.; Gill, R.; Dement, A.; Biosecurity for Beef Cattle Operations. Texas A&M Agrilife Ext. Available online: https://extensionpublications.unl.edu/assets/pdf/g1411.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Bovine Alliance on Management and Nutrition. An Introduction to Infectious Disease Control. 2001. Available online: https://www.aphis.usda.gov/sites/default/files/bamn01_introbiosecurity.pdf (accessed on 11 August 2024).
- Renault, V.; Humblet, M.F.; Pham, P.N.; Saegerman, C. Biosecurity at Cattle Farms: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, H.C.; Sayers, A.R.; Smith, R.P.; Pascoe, S.J.S.; Davies, R.H.; Weaver, J.P.; Evans, S.J. Risk Factors Associated with the Salmonella Status of Dairy Farms in England and Wales. Vet. Rec. 2006, 159, 871. [Google Scholar]
- Blau, D.M.; McCluskey, B.J.; Ladely, S.R.; Dargatz, D.A.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Ferris, K.E.; Headrick, M.L. Salmonella in Dairy Operations in the United States: Prevalence and Antimicrobial Drug Susceptibility. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wells, S.J.; Dee, S.; Godden, S. Biosecurity for Gastrointestinal Diseases of Adult Dairy Cattle. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2002, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Ge, H.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Z.; Geng, S.; Jiao, X.; Chen, X. Safety of the Salmonella Enterica Serotype Dublin Strain Sdu189-Derived Live Attenuated Vaccine—A Pilot Study. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 986332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edrington, T.S.; Arthur, T.M.; Loneragan, G.H.; Genovese, K.J.; Hanson, D.L.; Anderson, R.C.; Nisbet, D.J. Evaluation of Two Commercially-Available Salmonella Vaccines on Salmonella in the Peripheral Lymph Nodes of Experimentally-Infected Cattle. Ther. Adv. Vaccines Immunother. 2020, 8, 2515135520957760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methner, U. Vaccination of Poultry against Salmonella: What Is the Ideal Vaccine (Strain)? 2007. Available online: https://www.cabi.org/Uploads/animal-science/worlds-poultry-science-association/WPSA-czech-republic-2007/8_Methner%20Ulrich.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- Peeters, L.; Dewulf, J.; Boyen, F.; Brossé, C.; Vandersmissen, T.; Rasschaert, G.; Heyndrickx, M.; Cargnel, M.; Mattheus, W.; Pasmans, F.; et al. Evaluation of Group Vaccination of Sows and Gilts against Salmonella Typhimurium with an Attenuated Vaccine in Subclinically Infected Pig Herds. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 182, 104884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holschbach, C.L.; Breuer, R.M.; Pohly, A.E.; Crawford, C.; Aulik, N.A. Multi-Drug Resistant Salmonella Ser. Dublin Cultured from Cryopreserved Holstein Semen. Vet. Rec. Case Rep. 2024, 12, e791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibier, M.; Guerin, B. Hygienic Aspects of Storage and Use of Semen for Artificial Insemination. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2000, 62, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wray, C.; McLaren, I.M.; Beedell, Y.E.; Todd, N. The Epidemiology of Salmonella in Calves: The Role of Markets and Vehicles. Epidemiol. Infect. 1991, 107, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, J.B.; Sreevatsan, S.; Robinson, R.A.; Otterby, D. Animal By-Products Contaminated with Salmonella in the Diets of Lactating Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 3064–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, V.K.; Baek, K.H.; Kang, S.C. Control of Salmonella in Foods by Using Essential Oils: A Review. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.B.; Isaacson, R.E. Salmonella in Swine: Microbiota Interactions. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2017, 5, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobrega, D.B.; French, J.E.; Kelton, D.F. A Scoping Review of the Testing of Bulk Milk to Detect Infectious Diseases of Dairy Cattle: Diseases Caused by Bacteria. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 1986–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melmer, D.J.; O’Sullivan, T.L.; Poljak, Z. A Descriptive Analysis of Swine Movements in Ontario (Canada) as a Contributor to Disease Spread. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 159, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santman-Berends, I.M.G.A.; Mars, M.H.; Weber, M.F.; van Duijn, L.; Waldeck, H.W.F.; Biesheuvel, M.M.; van den Brink, K.M.J.A.; Dijkstra, T.; Hodnik, J.J.; Strain, S.A.J.; et al. Control and Eradication Programs for Non-EU Regulated Cattle Diseases in the Netherlands. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 670419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canada, P.H.A. of Canadian Integrated Program for Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance (CIPARS). 2024. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/surveillance/canadian-integrated-program-antimicrobial-resistance-surveillance-cipars/about-cipars.html (accessed on 22 January 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).