Holistic Approaches to Zoonoses: Integrating Public Health, Policy, and One Health in a Dynamic Global Context
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Addressing Challenges in a Dynamic Global Context
3. Public Health Approaches to Zoonotic Diseases
3.1. Surveillance and Monitoring Systems
3.2. Infection and Disease Prevention
3.3. Community Education
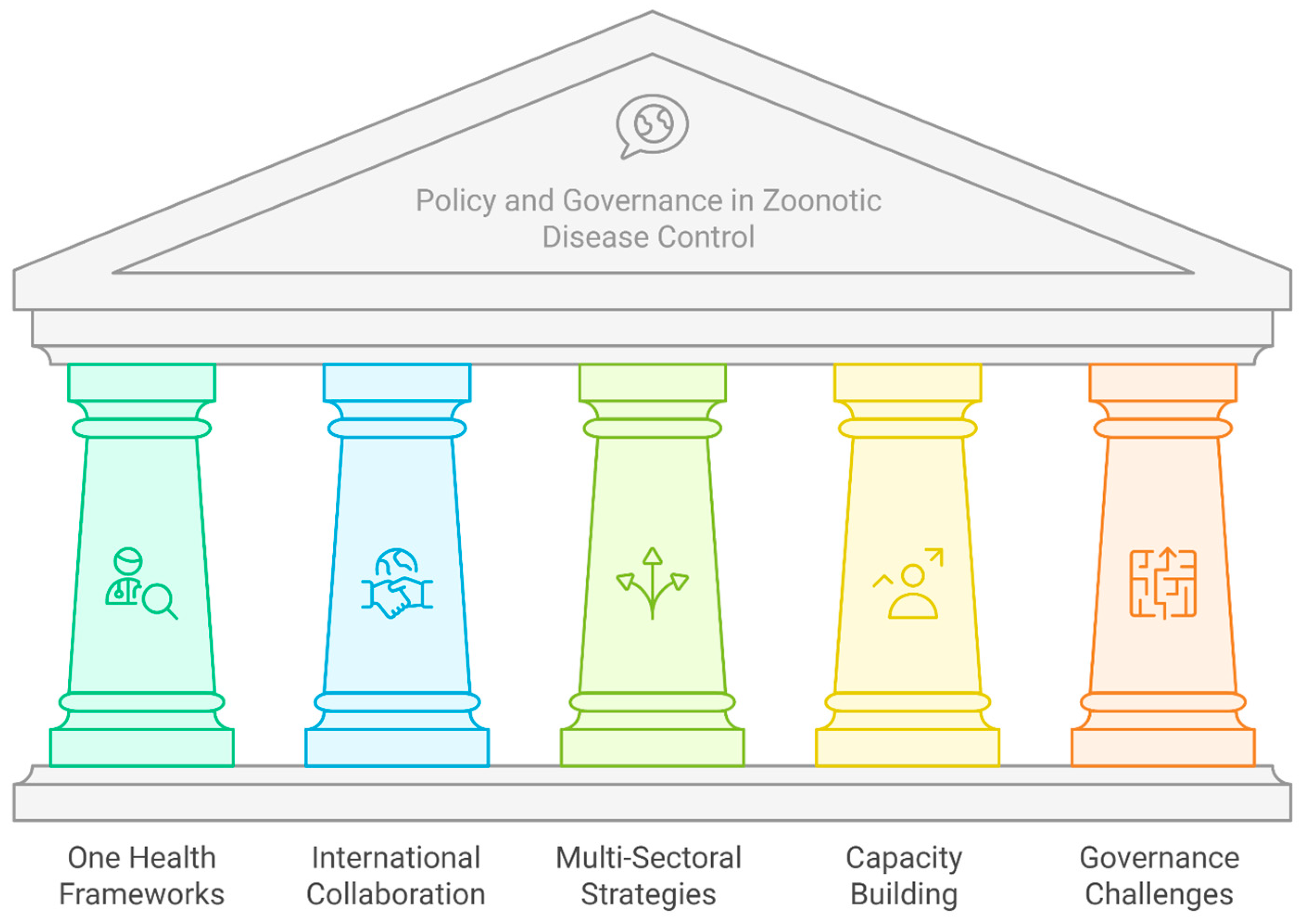
4. Policy and Governance in Zoonotic Disease Control
5. Integrating Public Health, Policy, and One Health
5.1. The PREDICT Project
5.2. Rwanda’s National One Health Program
5.3. The EcoHealth Alliance
5.4. Rabies Elimination Program in the Philippines
6. Future Directions and Recommendations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elsohaby, I.; Villa, L. Zoonotic diseases: Understanding the risks and mitigating the threats. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behravesh, C.B. One Health: People, Animals, and the Environment. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 766–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.R.; Karesh, W.B.; Johnson, C.K.; Gilardi, K.V.K.; Anthony, S.J.; Goldstein, T.; Olson, S.H.; Machalaba, C.; PREDICT Consortium; Mazet, J.A.K. One Health proof of concept: Bringing a transdisciplinary approach to surveillance for zoonotic viruses at the human-wild animal interface. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 137, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messenger, A.M.; Barnes, A.N.; Gray, G.C. Reverse Zoonotic Disease Transmission (Zooanthroponosis): A Systematic Review of Seldom-Documented Human Biological Threats to Animals. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.; Abdelwhab, E.M.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Pleschka, S. Zoonotic Potential of Influenza A Viruses: A Comprehensive Overview. Viruses 2018, 10, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, A.F.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Penadés, J.R. Staphylococcus aureus in Animals. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Zoonotic Disease: Emerging Public Health Threats in the Region. 2014. Available online: https://www.emro.who.int/about-who/rc61/zoonotic-diseases.html (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Bardhan, M.; Ray, I.; Roy, S.M.; Bhatt, P.M.; Patel, S.M.; Asri, S.M.; Shariff, S.; Shree, A.M.; Mitra, S.; Roy, P.; et al. Emerging zoonotic diseases and COVID-19 pandemic: Global Perspective and Indian Scenario. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 3997–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.; Sobur, A.; Islam, S.; Ievy, S.; Hossain, J.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Rahman, A.T.; Ashour, H.M. Zoonotic Diseases: Etiology, Impact, and Control. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigott, D.M.; Millear, A.I.; Earl, L.; Morozoff, C.; Han, B.A.; Shearer, F.M.; Weiss, D.J.; Brady, O.J.; Kraemer, M.U.; Moyes, C.L.; et al. Updates to the zoonotic niche map of Ebola virus disease in Africa. eLife 2016, 5, e16412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.S. The Resurgent Threat of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza HPAI A (H5N1) Virus: A Zoonotic Infectious Disease and Public Health Concern. J. Virol. Res. Rep. 2024, 2024, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.; AlShurman, B.A.; Sehar, H.; Butt, Z.A. Monkeypox: A Mini-Review on the Globally Emerging Orthopoxvirus. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomel, B.B.; Boulouis, H.-J.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Birtles, R.J.; Koehler, J.E.; Dehio, C. Ecological fitness and strategies of adaptation of Bartonella species to their hosts and vectors. Vet. Res. 2009, 40, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danasekaran, R. One Health: A Holistic Approach to Tackling Global Health Issues. Indian. J. Community Med. 2024, 49, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Jeggo, M.; Daszak, P.; Richt, J.A. (Eds.) One Health: The Human-Animal-Environment Interfaces in Emerging Infectious Diseases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, A.; Mukhtar, R.; Ahmed, H.; Ali, M. Emergencies of zoonotic diseases, drivers, and the role of artificial intelligence in tracking the epidemic and pandemics. Decod. Infect. Transm. 2024, 2, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Perrings, C.; Kinzig, A.; Collins, J.P.; Minteer, B.A.; Daszak, P. Economic growth, urbanization, globalization, and the risks of emerging infectious diseases in China: A review. Ambio 2017, 46, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassell, J.M.; Begon, M.; Ward, M.J.; Fèvre, E.M. Urbanization and Disease Emergence: Dynamics at the Wildlife–Livestock–Human Interface. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2017, 32, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Lyon, C.J.; Ying, B.; Hu, T. Climate change, its impact on emerging infectious diseases and new technologies to combat the challenge. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2356143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, H.; Holmes, M.A.; Petrovan, S.O.; Williams, D.R.; Wood, J.L.N.; Balmford, A. Understanding the relative risks of zoonosis emergence under contrasting approaches to meeting livestock product demand. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2022, 9, 211573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaru, I.D.; Walther, B.; Schaumburg, F. Zoonotic sources and the spread of antimicrobial resistance from the perspective of low and middle-income countries. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2023, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, R.; Hedrich, N.; Walker, A.; Dinkita, H.M.; Tschopp, R.; Abongomera, C.; Paris, D.H. Status of zoonotic disease research in refugees, asylum seekers and internally displaced people, globally: A scoping review of forty clinically important zoonotic pathogens. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; He, J.; Liang, Z.; Huang, S.; Wen, F. Birds as reservoirs: Unraveling the global spread of Gamma- and Deltacoronaviruses. MBio 2024, 15, e0232424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, S.; Pascoe, B.; Méric, G.; Mageiros, L.; Yahara, K.; Hitchings, M.D.; Friedmann, Y.; Wilkinson, T.S.; Gormley, F.J.; Mack, D.; et al. Recombination-Mediated Host Adaptation by Avian Staphylococcus aureus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The European Union. Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2020/2021. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e07867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO (World Health Organization). WHO Publishes the WHO Medically Important Antimicrobials List for Human Medicine. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/08-02-2024-who-medically-important-antimicrobial-list-2024 (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- Baudoin, F.; Hogeveen, H.; Wauters, E. Reducing Antimicrobial Use and Dependence in Livestock Production Systems: A Social and Economic Sciences Perspective on an Interdisciplinary Approach. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 584593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Vargas, R.E.; Herrera-Sánchez, M.P.; Rodríguez-Hernández, R.; Rondón-Barragán, I.S. Antibiotic resistance in Salmonella spp. isolated from poultry: A global overview. Vet. World 2020, 13, 2070–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Beyi, A.F.; Yin, Y. Zoonotic and antibiotic-resistant Campylobacter: A view through the One Health lens. One Health Adv. 2023, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mremi, I.R.; Rumisha, S.F.; Sindato, C.; Kimera, S.I.; Mboera, L.E.G. Comparative assessment of the human and animal health surveillance systems in Tanzania: Opportunities for an integrated one health surveillance platform. Glob. Public Health 2023, 18, 2110921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, H.; Agarwalla, R. Public health interventions in the control of emerging diseases. Int. J. Community Med. Public Health 2023, 10, 3398–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe Corrales, N. The significance of education in the preparedness for zoonotic diseases. In Epidemic Preparedness and Control; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharan, M.; Vijay, D.; Yadav, J.P.; Bedi, J.S.; Dhaka, P. Surveillance and response strategies for zoonotic diseases: A comprehensive review. Sci. One Health 2023, 2, 100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheer, A.; Jentner, W.; Kuhn, K.; Wimberly, M.; Vogel, J.; Ebert, D. A comprehensive approach to integrated one health surveillance and response. Open Access Gov. 2024, 43, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glidden, C.K.; Nova, N.; Kain, M.P.; Lagerstrom, K.M.; Skinner, E.B.; Mandle, L.; Sokolow, S.H.; Plowright, R.K.; Dirzo, R.; De Leo, G.A.; et al. Human-mediated impacts on biodiversity and the consequences for zoonotic disease spillover. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, R1342–R1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmeller, D.S.; Courchamp, F.; Killeen, G. Biodiversity loss, emerging pathogens and human health risks. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 3095–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Altermatt, F.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X. Destabilizing Effects of Environmental Stressors on Aquatic Communities and Interaction Networks across a Major River Basin. Env. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 7828–7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajbhandari, R.M.; Napit, R.; Manandhar, P.; Raut, R.; Gurung, A.; Poudel, A.; Shrestha, N.; Sadaula, A.; Karmacharya, D.; Gortázar, C.; et al. Phylogenomic analysis supports Mycobacterium tuberculosis transmission between humans and elephants. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1133823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oude Munnink, B.B.; Sikkema, R.S.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.F.; Molenaar, R.J.; Munger, E.; Molenkamp, R.; van der Spek, A.; Tolsma, P.; Rietveld, A.; Brouwer, M.; et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 on mink farms between humans and mink and back to humans. Science 2021, 371, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulit-Penaloza, J.A.; Jones, J.; Sun, X.; Jang, Y.; Thor, S.; Belser, J.A.; Zanders, N.; Creager, H.M.; Ridenour, C.; Wang, L.; et al. Antigenically Diverse Swine Origin H1N1 Variant Influenza Viruses Exhibit Differential Ferret Pathogenesis and Transmission Phenotypes. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlow, A.W.; Manore, C.; Xu, C.; Kaufeld, K.A.; Del Valle, S.; Ziemann, A.; Fairchild, G.; Fair, J.M. Forecasting Zoonotic Infectious Disease Response to Climate Change: Mosquito Vectors and a Changing Environment. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeyinka, O.T.; Omaghomi, T.T. Wildlife as sentinels for emerging zoonotic diseases: A review of surveillance systems in the USA. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2024, 21, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumford, E.L.; Martinez, D.J.; Tyance-Hassell, K.; Cook, A.; Hansen, G.R.; Labonté, R.; Mazet, J.A.K.; Mumford, E.C.; Rizzo, D.M.; Togami, E.; et al. Evolution and expansion of the One Health approach to promote sustainable and resilient health and well-being: A call to action. Front. Public Health 2023, 10, 1056459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, P.; Mariner, J.; Kock, R. Rinderpest: The veterinary perspective on eradication. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilla, F.; Velleman, Y.; Harrison, W.; Nevel, M. Animal influence on water, sanitation and hygiene measures for zoonosis control at the household level: A systematic literature review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butala, C.; Fyfe, J.; Welburn, S.C. The Contribution of Community Health Education to Sustainable Control of the Neglected Zoonotic Diseases. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 729973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, T.R.; Bunn, D.A.; Joshi, N.P.; Grooms, D.; Devkota, D.; Devkota, N.R.; Paudel, L.N.; Roug, A.; Wolking, D.J.; Mazet, J.A.K. Awareness and Practices Relating to Zoonotic Diseases Among Smallholder Farmers in Nepal. Ecohealth 2018, 15, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Tripartite Zoonoses Guide: Operational Tools and Approaches for Zoonotic Diseases. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/initiatives/tripartite-zoonosis-guide (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- WHO (World Health Organization). FAO, OIE, and WHO Launch a Guide for Countries on Taking a One Health Approach to Addressing Zoonotic Diseases. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/11-03-2019-fao-oie-and-who-launch-a-guide-for-countries-on-taking-a-one-health-approach-to-addressing-zoonotic-diseases (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). Taking a Multisectoral One Health Approach: A Tripartite Guide to Addressing Zoonotic Diseases in Countries. 2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/sustainable-development-goals-helpdesk/champion/article-detail/multisectoral-coordination-mechanisms-operational-tool.-an-operational-tool-of-the-tripartite-zoonoses-guide/en (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- WOAH. One Health. World Organization for Animal Health n.d. Available online: https://www.woah.org/en/what-we-do/global-initiatives/one-health/#ui-id-1 (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Ghai, R.R.; Wallace, R.M.; Kile, J.C.; Shoemaker, T.R.; Vieira, A.R.; Negron, M.E.; Shadomy, S.V.; Sinclair, J.R.; Goryoka, G.W.; Salyer, S.J.; et al. A generalizable one health framework for the control of zoonotic diseases. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Food Safety and Zoonotic Diseases. World Health Organization n.d. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/one-health#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). One Health and Related Policy and Technical Guidance. 2022. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/5dec68ca-db4e-4fac-9585-36409e61c115/content (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- CFR (Council on Foreign Relations). The Global Governance of Emerging Zoonotic Diseases: Challenges and Proposed Reforms. 2022. Available online: https://cdn.cfr.org/sites/default/files/report_pdf/The%20Global%20Governance%20of%20Emerging%20Zoonotic%20Diseases%20-%20Challenges%20and%20Proposed%20Reforms_0.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Hynninen, Y.; Vilkkumaa, E.; Salo, A. Operationalization of Utilitarian and Egalitarian Objectives for Optimal Allocation of Health Care Resources. Decis. Sci. 2021, 52, 1169–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehmann, M.R.; Zink, E.K.; Levin, A.B.; Suarez, J.I.; Belcher, H.M.; Biddison, E.L.D.; Doberman, D.J.; D’souza, K.; Fine, D.M.; Garibaldi, B.T.; et al. Operational Recommendations for Scarce Resource Allocation in a Public Health Crisis. Chest 2021, 159, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belay, E.D.; Kile, J.C.; Hall, A.J.; Barton-Behravesh, C.; Parsons, M.B.; Salyer, S.; Walke, H. Zoonotic Disease Programs for Enhancing Global Health Security. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, S65–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keusch, G.T.; Pappaioanou, M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Scott, K.A.; Tsai, P.; National Research Council. Committee on Achieving Sustainable Global Capacity for Surveillance and Response to Emerging Diseases of Zoonotic Origin. In Governance Challenges for Zoonotic Disease Surveillance, Reporting, and Response; National Academies Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Asaaga, F.A.; Young, J.C.; Oommen, M.A.; Chandarana, R.; August, J.; Joshi, J.; Chanda, M.M.; Vanak, A.T.; Srinivas, P.N.; Hoti, S.L.; et al. Operationalising the “One Health” approach in India: Facilitators of and barriers to effective cross-sector convergence for zoonoses prevention and control. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnyana, I.M.D.M.; Utomo, B.; Eljatin, D.S.; Sudaryati, N.L.G. One Health approach and zoonotic diseases in Indonesia: Urgency of implementation and challenges. Narra J. 2023, 3, e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, D.; Ramachandran, A. One health approach to address zoonotic diseases. Indian J. Community Med. 2020, 45, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbiati, C.; Milano, A.; Declich, S.; Riccardo, F.; Mancini, L.; Di Domenico, K.; Scavia, G.; Dente, M.G. Building a European One Health workforce for prevention and preparedness to health threats. Eur. J. Public Health 2023, 33, ckad160-213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolicki, S.B.; Nuzzo, J.B.; Blazes, D.L.; Pitts, D.L.; Iskander, J.K.; Tappero, J.W. Public Health Surveillance: At the Core of the Global Health Security Agenda. Health Secur. 2016, 14, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, B. The Global Health Security Agenda and the role of the World Organisation for Animal Health. Rev. Sci. Tech. L’oie 2017, 36, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoonotic Disease—Global Health Security Agenda. Global Health Security Agenda n.d. Available online: https://globalhealthsecurityagenda.org/zoonotic-disease/ (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- WHO (World Health Organization). Strengthening Global Health Security at the Human-Animal Interface. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/activities/strengthening-global-health-security-at-the-human-animal-interface (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- HHS (US Department of Health and Human Services). Global Health Security Agenda. 2024. Available online: https://www.hhs.gov/about/agencies/oga/global-health-security/agenda/index.html (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Peyre, M.; Vourc’h, G.; Lefrançois, T.; Martin-Prevel, Y.; Soussana, J.-F.; Roche, B. PREZODE: Preventing zoonotic disease emergence. Lancet 2021, 397, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, K. PREDICT Receives Extension for COVID-19 Pandemic Emergency Response. UCDAVIS. 2020. Available online: https://www.ucdavis.edu/coronavirus/news/predict-receives-extension-covid-19-pandemic-emergency-response?utm_ (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). One Health Strategic Plan 2021–2026. 2021. Available online: https://faolex.fao.org/docs/pdf/rwa210403.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- A Scientific Powerhouse; EcoHealth Alliance: New York, NY, USA, 2024.
- WOAH. Strategic Plan 2020–2025. Department of Health, Philippines. 2020. Available online: https://rr-asia.woah.org/app/uploads/2020/03/final-mtp-rabies_philippines.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- WHO (World Health Organization). Joint Risk Assessment Operational Tool (JRA OT). 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/health-security-preparedness/human-animal-interface/ewho-jra-veng.pdf?sfvrsn=b6cb5274_4 (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Debnath, N.; Flora, M.S.; Shirin, T.; Kalam, A.; Kabir, J.; Sufian, A.; Alamgir, A.; Islam, R.; Husain, M.; Islam, N.; et al. Toward the Institutionalization of a One Health Agenda: What the World can Learn from Bangladesh. One Health Cases 2024, 2024, ohcs20240018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyatanyi, T.; Wilkes, M.; McDermott, H.; Nzietchueng, S.; Gafarasi, I.; Mudakikwa, A.; Kinani, J.F.; Rukelibuga, J.; Omolo, J.; Mupfasoni, D.; et al. Implementing One Health as an integrated approach to health in Rwanda. BMJ Glob. Health 2017, 2, e000121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, S.J. European perspectives on efforts to reduce antimicrobial usage in food animal production. Ir. Vet. J. 2020, 73, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanon, J.I.R. History of the Use of Antibiotic as Growth Promoters in European Poultry Feeds. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 2466–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begemann, S.; Perkins, E.; Van Hoyweghen, I.; Christley, R.; Watkins, F. How Political Cultures Produce Different Antibiotic Policies in Agriculture: A Historical Comparative Case Study between the United Kingdom and Sweden. SociolRuralis 2018, 58, 765–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koluman, A.; Dikici, A. Antimicrobial resistance of emerging foodborne pathogens: Status quo and global trends. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 39, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes Antunes, A.C.; Jensen, V.F. Close to a Decade of Decrease in Antimicrobial Usage in Danish Pig Production–Evaluating the Effect of the Yellow Card Scheme. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, A.G.; Goldsmith-Pinkham, P.; Jackson, M.O.; Thau, S. Interacting regional policies in containing a disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2021520118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gostin, L.O.; Katz, R. The International Health Regulations: The Governing Framework for Global Health Security. Milbank Q. 2016, 94, 264–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hien, T.T.; Boni, M.F.; Bryant, J.E.; Ngan, T.T.; Wolbers, M.; Nguyen, T.D.; Truong, N.T.; Dung, N.T.; Ha, D.Q.; Hien, V.M.; et al. Early Pandemic Influenza (2009 H1N1) in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam: A Clinical Virological and Epidemiological Analysis. PLoS Med. 2010, 7, e1000277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittikraisak, W.; Khamphaphongphane, B.; Xayadeth, S.; Oulay, V.S.; Khanthamaly, V.; Sengvilaipaseuth, O.; Davis, C.T.; Yang, G.; Zanders, N.; Mott, J.A.; et al. Laboratory evaluation of two point-of-care detection systems for early and accurate detection of influenza viruses in the Lao People’s Democratic Republic. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 104, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuisma, E.; Olson, S.H.; Cameron, K.N.; Reed, P.E.; Karesh, W.B.; Ondzie, A.I.; Akongo, M.-J.; Kaba, S.D.; Fischer, R.J.; Seifert, S.N.; et al. Long-term wildlife mortality surveillance in northern Congo: A model for the detection of Ebola virus disease epizootics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UCDAVIS. PREDICT 2020. Available online: https://ohi.vetmed.ucdavis.edu/programs-projects/predict-project?utm (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Al Awaidy, S.; Al Hashami, H. Zoonotic Diseases in Oman: Successes, Challenges, and Future Directions. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwenzi, W.; Skirmuntt, E.C.; Musvuugwa, T.; Teta, C.; Halabowski, D.; Rzymski, P. Grappling with (re)-emerging infectious zoonoses: Risk assessment, mitigation framework, and future directions. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 82, 103350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J. One Health Ethics and the Ethics of Zoonoses: A Silent Call for Global Action. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwu, C.D.; Patrick, S.M. An insight into the implementation of the global action plan on antimicrobial resistance in the WHO African region: A roadmap for action. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 58, 106411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajulo, S.; Awosile, B. Global antimicrobial resistance and use surveillance system (GLASS 2022): Investigating the relationship between antimicrobial resistance and antimicrobial consumption data across the participating countries. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0297921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velazquez-Meza, M.E.; Galarde-López, M.; Carrillo-Quiróz, B.; Alpuche-Aranda, C.M. Antimicrobial resistance: One Health approach. Vet. World 2022, 15, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Guitian, J.; Webster, J.P.; Musallam, I.; Haider, N.; Drewe, J.A.; Song, J. Global prioritization of endemic zoonotic diseases for conducting surveillance in domestic animals to protect public health. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2023, 378, 20220407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra-Santos, M.A.; Mendoza-Roldan, J.A.; Thompson, R.C.A.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Otranto, D. Illegal Wildlife Trade: A Gateway to Zoonotic Infectious Diseases. Trends Parasitol. 2021, 37, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostach, P.K.; Dülsner, A.; Keil, A.; Nagel-Riedasch, S. Management of zoonoses in research institutions-lessons learned from a Coxiella burnetii outbreak case. Lab. Anim. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, A.P.; Pimm, S.L.; Hannah, L.; Kaufman, L.; Ahumada, J.A.; Ando, A.W.; Bernstein, A.; Busch, J.; Daszak, P.; Engelmann, J.; et al. Ecology and economics for pandemic prevention. Science 2020, 369, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, W.; Lv, C. Modern technologies and solutions to enhance surveillance and response systems for emerging zoonotic diseases. Sci. One Health 2024, 3, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, T.R.; Kurteva, A.; DeLong, R.J.; Hilscher, R.; Korte, K.; Fensel, A. Data Protection by Design Tool for Automated GDPR Compliance Verification Based on Semantically Modeled Informed Consent. Sensors 2022, 22, 2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, P.; Pal, N.; Sarma, D.K.; Tiwari, R.; Kumar, M. Holistic One Health Surveillance Framework: Synergizing Environmental, Animal, and Human Determinants for Enhanced Infectious Disease Management. ACS Infect. Dis. 2024, 10, 808–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Lv, C.; Guo, M.; Zhao, Q.; Yin, X.; Zhang, L. Innovative applications of artificial intelligence in zoonotic disease management. Sci. One Health 2023, 2, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factor | Description | Source(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Globalization | Increased movement of people, goods, and animals across borders facilitates the rapid spread of pathogens. | [17] |
| Urbanization | Encroachment into natural ecosystems increases human exposure to wildlife reservoirs of zoonotic pathogens; lack of infrastructure can create breeding grounds for vectors. | [18] |
| Climate Change | Altered temperatures, precipitation, and extreme weather events impact ecosystems, wildlife migration, and vector distribution, increasing the risk of pathogen spillover. | [19] |
| Agricultural Practices | Intensified livestock farming, deforestation, and unsafe food handling create opportunities for pathogens to jump between species. | [20] |
| Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) | Misuse of antibiotics in human and animal medicine leads to the emergence of resistant pathogens, complicating disease management. | [21] |
| Socioeconomic Inequities | Limited access to healthcare, diagnostic tools, and public health infrastructure in low- and middle-income countries hinders early detection and management. | [22] |
| Approach | Description | Source(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Surveillance Systems | Monitoring and early detection of zoonotic pathogens in animals and humans to inform strategic interventions and mitigate impact of outbreaks. | [30] |
| Infection and Disease Prevention | Preventive methods such as vaccination and sanitation programs (WASH) to prevent disease occurrence. | [31] |
| Community Education | Awareness campaigns and training programs to educate the public about risk factors and prevention methods. | [32] |
| Framework/Initiative | Description | Source(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Tripartite Zoonosis Guide (TZG) | A collaborative framework by WHO, WOAH, and FAO for multi-sectoral approach to zoonotic disease control, providing guidance and tools to improve collaboration. | [48,49] |
| Generalizable One Health Framework (GOHF) | A five-step strategy for implementing One Health concepts at various governance levels, aimed at increasing cross-sector collaboration. | [52] |
| Global Health Security Agenda (GHSA) | Multilateral program for global health security, including ZDAP which emphasizes a One Health approach to connect human, animal, and environmental health sectors. | [68] |
| PREZODE (Preventing Zoonotic Disease Emergence) | An innovative international initiative focused on understanding zoonotic disease emergence, developing methods for prevention, early detection, and resilience to ensure rapid response. | [69] |
| PREDICT Project | A global One Health initiative that strengthened surveillance and lab capabilities by fostering transdisciplinary collaboration. | [70] |
| Rwanda’s National One Health Program | A national-level coordinated system involving Ministries of Health, Agriculture, and Environment that resulted in improvements in surveillance, rapid response, and community education. | [71] |
| EcoHealth Alliance | An organization that uses ecological data to predict and prevent zoonotic disease outbreaks by addressing deforestation, wildlife trade, and human–wildlife interactions. | [72] |
| Rabies Elimination Program in the Philippines | A program that successfully reduced human rabies cases by integrating public health and veterinary efforts through mass dog vaccination campaigns, public awareness initiatives, and improved access to post-exposure prophylaxis. | [73] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, M.M.; Okesanya, O.J.; Othman, Z.K.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Adigun, O.A.; Ukoaka, B.M.; Abdi, M.I.; Lucero-Prisno, D.E., III. Holistic Approaches to Zoonoses: Integrating Public Health, Policy, and One Health in a Dynamic Global Context. Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5010005
Ahmed MM, Okesanya OJ, Othman ZK, Ibrahim AM, Adigun OA, Ukoaka BM, Abdi MI, Lucero-Prisno DE III. Holistic Approaches to Zoonoses: Integrating Public Health, Policy, and One Health in a Dynamic Global Context. Zoonotic Diseases. 2025; 5(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Mohamed Mustaf, Olalekan John Okesanya, Zhinya Kawa Othman, Adamu Muhammad Ibrahim, Olaniyi Abideen Adigun, Bonaventure Michael Ukoaka, Muhiadin Ismail Abdi, and Don Eliseo Lucero-Prisno, III. 2025. "Holistic Approaches to Zoonoses: Integrating Public Health, Policy, and One Health in a Dynamic Global Context" Zoonotic Diseases 5, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5010005
APA StyleAhmed, M. M., Okesanya, O. J., Othman, Z. K., Ibrahim, A. M., Adigun, O. A., Ukoaka, B. M., Abdi, M. I., & Lucero-Prisno, D. E., III. (2025). Holistic Approaches to Zoonoses: Integrating Public Health, Policy, and One Health in a Dynamic Global Context. Zoonotic Diseases, 5(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5010005









