Global Distribution and Molecular Evolution of Bat Coronaviruses
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bat Origin of Human Coronaviruses
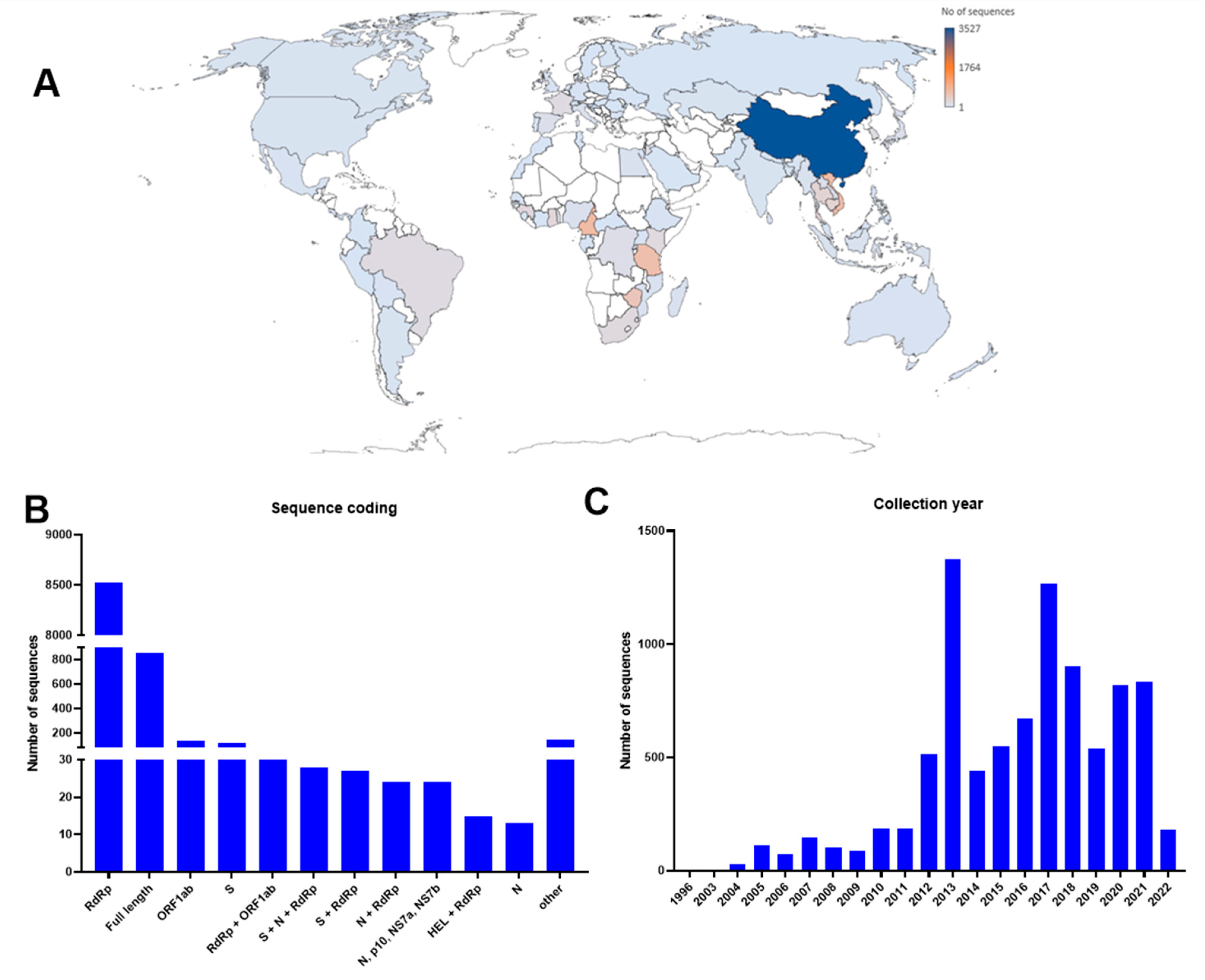
3. Global Distribution of Bat Coronaviruses
3.1. Europe
3.2. North America
3.3. Central and South America
3.4. Africa
3.5. Australia
3.6. Asia
4. Molecular Evolution of Bat Coronaviruses
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kruskop, S.V. Diversity Aspects in Bats: Genetics, Morphology, Community Structure. Diversity 2021, 13, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Ge, X.; Wang, L.F.; Shi, Z. Bat origin of human coronaviruses. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calisher, C.H.; Childs, J.E.; Field, H.E.; Holmes, K.V.; Schountz, T. Bats: Important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clin Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, W.R.; Zheng, Y.; Han, F.; Chen, S.; Ma, S.; Wang, L.F.; Leeansyah, E. Exploring the Role of Innate Lymphocytes in the Immune System of Bats and Virus-Host Interactions. Viruses 2022, 14, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses: ICTV. Available online: https://ictv.global/ (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Coleman, C.M.; Frieman, M.B. Coronaviruses: Important emerging human pathogens. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5209–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Lam, C.S.; Lau, C.C.; Tsang, A.K.; Lau, J.H.; Bai, R.; Teng, J.L.; Tsang, C.C.; Wang, M.; et al. Discovery of seven novel Mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3995–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Wong, G.; Shi, W.; Liu, J.; Lai, A.C.K.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Bi, Y.; Gao, G.F. Epidemiology, Genetic Recombination, and Pathogenesis of Coronaviruses. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.Y.; Lui, P.Y.; Jin, D.Y. A molecular arms race between host innate antiviral response and emerging human coronaviruses. Virol. Sin. 2016, 31, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.F.-W.; To, K.K.-W.; Tse, H.; Jin, D.-Y.; Yuen, K.-Y. Interspecies transmission and emergence of novel viruses: Lessons from bats and birds. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.F.-W.; Kok, K.-H.; Zhu, Z.; Chu, H.; To, K.K.-W.; Yuan, S.; Yuen, K.-Y. Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.-L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucknall, R.A.; King, L.M.; Kapikian, A.Z.; Chanock, R.M. Studies with human coronaviruses II. Some properties of strains 229E and OC43. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1972, 139, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Tsoi, H.-w.; Huang, Y.; Poon, R.W.; Chu, C.-m.; Lee, R.A.; Luk, W.-k.; Wong, G.K.; Wong, B.H. Clinical and molecular epidemiological features of coronavirus HKU1–associated community-acquired pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 1898–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Peiris, J.S.; Zheng, B.; Poon, L.L.; Chan, K.H.; Zeng, F.Y.; Chan, C.W.; Chan, M.N.; Chen, J.D.; Chow, K.Y.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of the novel coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome. Lancet 2004, 363, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Summary of Probable SARS Cases with Onset of Illness from 1 November 2002 to 31 July 2003. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/summary-of-probable-sars-cases-with-onset-of-illness-from-1-november-2002-to-31-july-2003 (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Guan, Y.; Zheng, B.; He, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Cheung, C.; Luo, S.; Li, P.H.; Zhang, L.; Guan, Y. Isolation and characterization of viruses related to the SARS coronavirus from animals in southern China. Science 2003, 302, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan-Yeung, M.; Xu, R.H. SARS: Epidemiology. Respirology 2003, 8, S9–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehr, A.R.; Perlman, S. Coronaviruses: An overview of their replication and pathogenesis. In Coronaviruses: Methods and Protocols; Human Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zaki, A.M.; van Boheemen, S.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV). Available online: http://www.who.int/emergencies/mers-cov/en/ (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Alagaili, A.N.; Briese, T.; Mishra, N.; Kapoor, V.; Sameroff, S.C.; Burbelo, P.D.; de Wit, E.; Munster, V.J.; Hensley, L.E.; Zalmout, I.S.; et al. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection in dromedary camels in Saudi Arabia. mBio 2014, 5, e00884-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, B.; Muller, M.A.; Corman, V.M.; Reusken, C.B.; Ritz, D.; Godeke, G.J.; Lattwein, E.; Kallies, S.; Siemens, A.; van Beek, J.; et al. Antibodies against MERS coronavirus in dromedary camels, United Arab Emirates, 2003 and 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memish, Z.A.; Cotten, M.; Meyer, B.; Watson, S.J.; Alsahafi, A.J.; Al Rabeeah, A.A.; Corman, V.M.; Sieberg, A.; Makhdoom, H.Q.; Assiri, A.; et al. Human infection with MERS coronavirus after exposure to infected camels, Saudi Arabia, 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1012–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Cheon, S.; Min, C.K.; Sohn, K.M.; Kang, Y.J.; Cha, Y.J.; Kang, J.I.; Han, S.K.; Ha, N.Y.; Kim, G.; et al. Spread of Mutant Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus with Reduced Affinity to Human CD26 during the South Korean Outbreak. mBio 2016, 7, e00019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memish, Z.A.; Zumla, A.I.; Al-Hakeem, R.F.; Al-Rabeeah, A.A.; Stephens, G.M. Family cluster of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2487–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drosten, C.; Muth, D.; Corman, V.M.; Hussain, R.; Al Masri, M.; HajOmar, W.; Landt, O.; Assiri, A.; Eckerle, I.; Al Shangiti, A.; et al. An observational, laboratory-based study of outbreaks of middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in Jeddah and Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia, 2014. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2015, 60, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azhar, E.I.; El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Farraj, S.A.; Hassan, A.M.; Al-Saeed, M.S.; Hashem, A.M.; Madani, T.A. Evidence for camel-to-human transmission of MERS coronavirus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2499–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azhar, E.I.; Hashem, A.M.; El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Sohrab, S.S.; Aburizaiza, A.S.; Farraj, S.A.; Hassan, A.M.; Al-Saeed, M.S.; Jamjoom, G.A.; Madani, T.A. Detection of the middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus genome in an air sample originating from a camel barn owned by an infected patient. mBio 2014, 5, e01555-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.A.; Corman, V.M.; Jores, J.; Meyer, B.; Younan, M.; Liljander, A.; Bosch, B.-J.; Lattwein, E.; Hilali, M.; Musa, B.E. MERS coronavirus neutralizing antibodies in camels, Eastern Africa, 1983–1997. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.K.; Li, K.S.; Tsang, A.K.; Lam, C.S.; Ahmed, S.; Chen, H.; Chan, K.-H.; Woo, P.C.; Yuen, K.-Y. Genetic characterization of Betacoronavirus lineage C viruses in bats reveals marked sequence divergence in the spike protein of pipistrellus bat coronavirus HKU5 in Japanese pipistrelle: Implications for the origin of the novel Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 8638–8650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hemida, M.G.; Chu, D.K.; Poon, L.L.; Perera, R.A.; Alhammadi, M.A.; Ng, H.-Y.; Siu, L.Y.; Guan, Y.; Alnaeem, A.; Peiris, M. MERS coronavirus in dromedary camel herd, Saudi Arabia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, R.J.; Baker, S.C.; Baric, R.S.; Brown, C.S.; Drosten, C.; Enjuanes, L.; Fouchier, R.A.; Galiano, M.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Memish, Z.A. Commentary: Middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus (mers-cov): Announcement of the coronavirus study group. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7790–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Ithete, N.L.; Richards, L.R.; Schoeman, M.C.; Preiser, W.; Drosten, C.; Drexler, J.F. Rooting the phylogenetic tree of middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus by characterization of a conspecific virus from an African bat. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11297–11303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Du, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, C.; Tang, J.; Baric, R.S.; Jiang, S.; Li, F. Receptor usage and cell entry of bat coronavirus HKU4 provide insight into bat-to-human transmission of MERS coronavirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12516–12521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.M. Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Eden, J.S.; Holmes, E.C.; Wang, L.F. Adaptive evolution of bat dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (dpp4): Implications for the origin and emergence of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salata, C.; Calistri, A.; Parolin, C.; Palù, G. Coronaviruses: A paradigm of new emerging zoonotic diseases. Pathog. Dis. 2019, 77, ftaa006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellam, P.; Barclay, W. The dynamics of humoral immune responses following SARS-CoV-2 infection and the potential for reinfection. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Baker, S.C.; Baric, R.S.; de Groot, R.J.; Drosten, C.; Gulyaeva, A.A.; Haagmans, B.L.; Lauber, C.; Leontovich, A.M.; Neuman, B.W.; et al. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, S.E. The behaviour of recent isolates of human respiratory coronavirus in vitro and in volunteers: Evidence of heterogeneity among 229E-related strains. J. Med. Virol. 1984, 13, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferle, S.; Oppong, S.; Drexler, J.F.; Gloza-Rausch, F.; Ipsen, A.; Seebens, A.; Müller, M.A.; Annan, A.; Vallo, P.; Adu-Sarkodie, Y.; et al. Distant relatives of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and close relatives of human coronavirus 229E in bats, Ghana. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouchier, R.A.; Hartwig, N.G.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Niemeyer, B.; de Jong, J.C.; Simon, J.H.; Osterhaus, A.D. A previously undescribed coronavirus associated with respiratory disease in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6212–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, B.C. Human coronavirus NL63: A clinically important virus? Future Microbiol. 2011, 6, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, E.F.; Haskew, A.N.; Gates, J.E.; Huynh, J.; Moore, C.J.; Frieman, M.B. Metagenomic analysis of the viromes of three North American bat species: Viral diversity among different bat species that share a common habitat. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 13004–13018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, J.; Li, S.; Yount, B.; Smith, A.; Sturges, L.; Olsen, J.C.; Nagel, J.; Johnson, J.B.; Agnihothram, S.; Gates, J.E.; et al. Evidence supporting a zoonotic origin of human coronavirus strain NL63. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12816–12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Shi, M.; Chommanard, C.; Queen, K.; Zhang, J.; Markotter, W.; Kuzmin, I.V.; Holmes, E.C.; Tong, S. Surveillance of bat coronaviruses in Kenya identifies relatives of human coronaviruses NL63 and 229E and their recombination history. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01953-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Chu, C.M.; Chan, K.H.; Tsoi, H.W.; Huang, Y.; Wong, B.H.; Poon, R.W.; Cai, J.J.; Luk, W.K.; et al. Characterization and complete genome sequence of a novel coronavirus, coronavirus HKU1, from patients with pneumonia. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloots, T.P.; McErlean, P.; Speicher, D.J.; Arden, K.E.; Nissen, M.D.; Mackay, I.M. Evidence of human coronavirus HKU1 and human bocavirus in Australian children. J. Clin. Virol. Off. Publ. Pan Am. Soc. Clin. Virol. 2006, 35, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, H.E.; Reed, S.E.; Tyrrell, D.A. Isolation of rhinoviruses and coronaviruses from 38 colds in adults. J. Med. Virol. 1980, 5, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.K.; Li, K.S.; Huang, Y.; Shek, C.-T.; Tse, H.; Wang, M.; Choi, G.K.; Xu, H.; Lam, C.S.; Guo, R. Ecoepidemiology and complete genome comparison of different strains of severe acute respiratory syndrome-related Rhinolophus bat coronavirus in China reveal bats as a reservoir for acute, self-limiting infection that allows recombination events. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2808–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.K.; Woo, P.C.; Li, K.S.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Lam, C.S.; Xu, H.; Guo, R.; Chan, K.-H.; Zheng, B.-J. Complete genome sequence of bat coronavirus HKU2 from Chinese horseshoe bats revealed a much smaller spike gene with a different evolutionary lineage from the rest of the genome. Virology 2007, 367, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Du, L.; Jiang, S.; Shi, Z.; Baric, R.S.; Li, F. Two mutations were critical for bat-to-human transmission of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9119–9123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, S.; Watanabe, S.; Masangkay, J.S.; Mizutani, T.; Alviola, P.; Ueda, N.; Iha, K.; Taniguchi, S.; Fujii, H.; Kato, K. Genomic and serological detection of bat coronavirus from bats in the Philippines. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 2349–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subudhi, S.; Rapin, N.; Bollinger, T.K.; Hill, J.E.; Donaldson, M.E.; Davy, C.M.; Warnecke, L.; Turner, J.M.; Kyle, C.J.; Willis, C.K.R.; et al. A persistently infecting coronavirus in hibernating Myotis lucifugus, the North American little brown bat. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2297–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.; Smith, C.S.; Peel, A.J.; Plowright, R.K.; Kerlin, D.H.; McBroom, J.; McCallum, H. Persistent infections support maintenance of a coronavirus in a population of Australian bats (Myotis macropus). Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, R.J.; Wang, J.; Peacey, M.; Moore, N.E.; McInnes, K.; Tompkins, D.M. New alphacoronavirus in Mystacina tuberculata bats, New Zealand. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, S.J.; Ojeda-Flores, R.; Rico-Chávez, O.; Navarrete-Macias, I.; Zambrana-Torrelio, C.M.; Rostal, M.K.; Epstein, J.H.; Tipps, T.; Liang, E.; Sanchez-Leon, M.; et al. Coronaviruses in bats from Mexico. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Zeus, V.; Kwasnitschka, L.; Kerth, G.; Haase, M.; Groschup, M.H.; Balkema-Buschmann, A. Insectivorous bats carry host specific astroviruses and coronaviruses across different regions in Germany. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2016, 37, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monchatre-Leroy, E.; Boué, F.; Boucher, J.M.; Renault, C.; Moutou, F.; Ar Gouilh, M. Identification of Alpha and Beta Coronavirus in Wildlife Species in France: Bats, Rodents, Rabbits, and Hedgehogs. Viruses 2017, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wacharapluesadee, S.; Duengkae, P.; Rodpan, A.; Kaewpom, T.; Maneeorn, P.; Kanchanasaka, B.; Yingsakmongkon, S.; Sittidetboripat, N.; Chareesaen, C.; Khlangsap, N.; et al. Diversity of coronavirus in bats from Eastern Thailand. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wacharapluesadee, S.; Sintunawa, C.; Kaewpom, T.; Khongnomnan, K.; Olival, K.J.; Epstein, J.H.; Rodpan, A.; Sangsri, P.; Intarut, N.; Chindamporn, A.; et al. Group C betacoronavirus in bat guano fertilizer, Thailand. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1349–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, V.; Dumonceaux, T.; Dubois, J.; Willis, C.; Nadin-Davis, S.; Severini, A.; Wandeler, A.; Lindsay, R.; Artsob, H. Detection of polyoma and corona viruses in bats of Canada. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2015–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.P. SARS molecular epidemiology: A Chinese fairy tale of controlling an emerging zoonotic disease in the genomics era. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 1063–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Tian, X.; Qin, P.; Wang, B.; Zhao, P.; Yang, Y.L.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Discovery of a novel swine enteric alphacoronavirus (SeACoV) in southern China. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 211, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Fan, H.; Lan, T.; Yang, X.L.; Shi, W.F.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.W.; Xie, Q.M.; Mani, S.; et al. Fatal swine acute diarrhoea syndrome caused by an HKU2-related coronavirus of bat origin. Nature 2018, 556, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, C.; Wen, Z.; Cao, Y. A New Bat-HKU2-like Coronavirus in Swine, China, 2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1607–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ksiazek, T.G.; Erdman, D.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Zaki, S.R.; Peret, T.; Emery, S.; Tong, S.; Urbani, C.; Comer, J.A.; Lim, W.; et al. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1953–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.K.; Woo, P.C.; Li, K.S.; Huang, Y.; Tsoi, H.W.; Wong, B.H.; Wong, S.S.; Leung, S.Y.; Chan, K.H.; Yuen, K.Y. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in Chinese horseshoe bats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14040–14045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Wong, A.C.P.; Lau, T.C.K.; Woo, P.C.Y. Molecular Evolution of MERS Coronavirus: Dromedaries as a Recent Intermediate Host or Long-Time Animal Reservoir? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Zhang, L.; Luk, H.K.H.; Xiong, L.; Peng, X.; Li, K.S.M.; He, X.; Zhao, P.S.; Fan, R.Y.Y.; Wong, A.C.P.; et al. Receptor Usage of a Novel Bat Lineage C Betacoronavirus Reveals Evolution of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus Spike Proteins for Human Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Binding. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Liu, W.J.; Xu, W.; Jin, T.; Zhao, Y.; Song, J.; Shi, Y.; Ji, W.; Jia, H.; Zhou, Y.; et al. A Bat-Derived Putative Cross-Family Recombinant Coronavirus with a Reovirus Gene. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, S.J.; Gilardi, K.; Menachery, V.D.; Goldstein, T.; Ssebide, B.; Mbabazi, R.; Navarrete-Macias, I.; Liang, E.; Wells, H.; Hicks, A.; et al. Further Evidence for Bats as the Evolutionary Source of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. mBio 2017, 8, e00373-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, L.; Ren, X.; He, G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Qian, Z.; Dong, J.; Sun, L.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Deciphering the bat virome catalog to better understand the ecological diversity of bat viruses and the bat origin of emerging infectious diseases. ISME J. 2016, 10, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihtaric, D.; Hostnik, P.; Steyer, A.; Grom, J.; Toplak, I. Identification of SARS-like coronaviruses in horseshoe bats (Rhinolophus hipposideros) in Slovenia. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fu, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Yang, W.; Nie, K.; Ma, X.; Liang, G. Discovery and genetic analysis of novel coronaviruses in least horseshoe bats in southwestern China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ar Gouilh, M.; Puechmaille, S.J.; Diancourt, L.; Vandenbogaert, M.; Serra-Cobo, J.; Lopez Roïg, M.; Brown, P.; Moutou, F.; Caro, V.; Vabret, A.; et al. SARS-CoV related Betacoronavirus and diverse Alphacoronavirus members found in western old-world. Virology 2018, 517, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauly, M.; Pir, J.B.; Loesch, C.; Sausy, A.; Snoeck, C.J.; Hübschen, J.M.; Muller, C.P. Novel Alphacoronaviruses and Paramyxoviruses Cocirculate with Type 1 and Severe Acute Respiratory System (SARS)-Related Betacoronaviruses in Synanthropic Bats of Luxembourg. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01326-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.C.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhang, S.Y.; Wang, P.; Fan, X.H.; Li, L.F.; Li, G.; Dong, B.Q.; Liu, W.; Cheung, C.L.; et al. Prevalence and genetic diversity of coronaviruses in bats from China. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7481–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, J.F.; Gloza-Rausch, F.; Glende, J.; Corman, V.M.; Muth, D.; Goettsche, M.; Seebens, A.; Niedrig, M.; Pfefferle, S.; Yordanov, S.; et al. Genomic characterization of severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus in European bats and classification of coronaviruses based on partial RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene sequences. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11336–11349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, P.L.; Firth, C.; Street, C.; Henriquez, J.A.; Petrosov, A.; Tashmukhamedova, A.; Hutchison, S.K.; Egholm, M.; Osinubi, M.O.; Niezgoda, M.; et al. Identification of a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in a leaf-nosed bat in Nigeria. mBio 2010, 1, e00208-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Jo, S.D.; Son, K.; An, I.; Jeong, J.; Wang, S.J.; Kim, Y.; Jheong, W.; Oem, J.K. Genetic Characteristics of Coronaviruses from Korean Bats in 2016. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 75, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C.; Wang, M.; Lau, S.K.; Xu, H.; Poon, R.W.; Guo, R.; Wong, B.H.; Gao, K.; Tsoi, H.W.; Huang, Y.; et al. Comparative analysis of twelve genomes of three novel group 2c and group 2d coronaviruses reveals unique group and subgroup features. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1574–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, B.; Jiang, R.-D.; Hu, B.-J.; Luo, D.-S.; Zhu, G.-J.; Hu, B.; Liu, H.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Yang, X.-L. Longitudinal surveillance of betacoronaviruses in fruit bats in Yunnan Province, China during 2009–2016. Virol. Sin. 2018, 33, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, A.; Lelli, D.; de Sabato, L.; Zaccaria, G.; Boni, A.; Sozzi, E.; Prosperi, A.; Lavazza, A.; Cella, E.; Castrucci, M.R.; et al. Detection and full genome characterization of two beta CoV viruses related to Middle East respiratory syndrome from bats in Italy. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.K.W.; Poon, L.L.M.; Chan, K.H.; Chen, H.; Guan, Y.; Yuen, K.Y.; Peiris, J.S.M. Coronaviruses in bent-winged bats (Miniopterus spp.). J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 2461–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, J.F.; Corman, V.M.; Drosten, C. Ecology, evolution and classification of bat coronaviruses in the aftermath of SARS. Antivir. Res. 2014, 101, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloza-Rausch, F.; Ipsen, A.; Seebens, A.; Göttsche, M.; Panning, M.; Drexler, J.F.; Petersen, N.; Annan, A.; Grywna, K.; Müller, M. Detection and prevalence patterns of group I coronaviruses in bats, northern Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, L.L.; Chu, D.K.; Chan, K.H.; Wong, O.K.; Ellis, T.M.; Leung, Y.H.; Lau, S.K.; Woo, P.C.; Suen, K.Y.; Yuen, K.Y.; et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in bats. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2001–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Li, K.S.; Poon, R.W.; Wong, B.H.; Tsoi, H.W.; Yip, B.C.; Huang, Y.; Chan, K.H.; Yuen, K.Y. Molecular diversity of coronaviruses in bats. Virology 2006, 351, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, S.J.; Johnson, C.K.; Greig, D.J.; Kramer, S.; Che, X.; Wells, H.; Hicks, A.L.; Joly, D.O.; Wolfe, N.D.; Daszak, P.; et al. Global patterns in coronavirus diversity. Virus Evol. 2017, 3, vex012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reusken, C.B.; Lina, P.H.; Pielaat, A.; de Vries, A.; Dam-Deisz, C.; Adema, J.; Drexler, J.F.; Drosten, C.; Kooi, E.A. Circulation of group 2 coronaviruses in a bat species common to urban areas in Western Europe. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sabato, L.; Lelli, D.; Faccin, F.; Canziani, S.; Di Bartolo, I.; Vaccari, G.; Moreno, A. Full genome characterization of two novel Alpha-coronavirus species from Italian bats. Virus Res. 2019, 260, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelli, D.; Papetti, A.; Sabelli, C.; Rosti, E.; Moreno, A.; Boniotti, M.B. Detection of coronaviruses in bats of various species in Italy. Viruses 2013, 5, 2679–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Benedictis, P.; Marciano, S.; Scaravelli, D.; Priori, P.; Zecchin, B.; Capua, I.; Monne, I.; Cattoli, G. Alpha and lineage C betaCoV infections in Italian bats. Virus Genes 2014, 48, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcón, A.; Vázquez-Morón, S.; Casas, I.; Aznar, C.; Ruiz, G.; Pozo, F.; Perez-Brena, P.; Juste, J.; Ibánez, C.; Garin, I. Detection of alpha and betacoronaviruses in multiple Iberian bat species. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- August, T.A.; Mathews, F.; Nunn, M.A. Alphacoronavirus detected in bats in the United Kingdom. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazov, C.M.; Chriél, M.; Baagøe, H.J.; Fjederholt, E.; Deng, Y.; Kooi, E.A.; Belsham, G.J.; Bøtner, A.; Rasmussen, T.B. Detection and Characterization of Distinct Alphacoronaviruses in Five Different Bat Species in Denmark. Viruses 2018, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemenesi, G.; Dallos, B.; Görföl, T.; Boldogh, S.; Estók, P.; Kurucz, K.; Kutas, A.; Földes, F.; Oldal, M.; Németh, V.; et al. Molecular survey of RNA viruses in Hungarian bats: Discovering novel astroviruses, coronaviruses, and caliciviruses. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balboni, A.; Gallina, L.; Palladini, A.; Prosperi, S.; Battilani, M. A real-time PCR assay for bat SARS-like coronavirus detection and its application to Italian greater horseshoe bat faecal sample surveys. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 989514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balboni, A.; Palladini, A.; Bogliani, G.; Battilani, M. Detection of a virus related to betacoronaviruses in Italian greater horseshoe bats. Epidemiol. Infect. 2011, 139, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecis, R.; Mucedda, M.; Pidinchedda, E.; Pittau, M.; Alberti, A. Molecular identification of Betacoronavirus in bats from Sardinia (Italy): First detection and phylogeny. Virus Genes 2019, 55, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annan, A.; Baldwin, H.J.; Corman, V.M.; Klose, S.M.; Owusu, M.; Nkrumah, E.E.; Badu, E.K.; Anti, P.; Agbenyega, O.; Meyer, B.; et al. Human betacoronavirus 2c EMC/2012-related viruses in bats, Ghana and Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brnić, D.; Lojkić, I.; Krešić, N.; Zrnčić, V.; Ružanović, L.; Mikuletič, T.; Bosilj, M.; Steyer, A.; Keros, T.; Habrun, B.; et al. Circulation of SARS-CoV-Related Coronaviruses and Alphacoronaviruses in Bats from Croatia. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemnani, M.; da Silva, P.G.; Thompson, G.; Poeta, P.; Rebelo, H.; Mesquita, J.R. Presence of Alphacoronavirus in Tree- and Crevice-Dwelling Bats from Portugal. Viruses 2024, 16, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, I.V.; Ohlopkova, O.V.; Donnik, I.M.; Zolotukhin, P.V.; Umanets, A.; Golovin, S.N.; Malinovkin, A.V.; Belanova, A.A.; Lipilkin, P.V.; Lipilkina, T.A.; et al. Detection of coronaviruses in insectivorous bats of Fore-Caucasus, 2021. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, S.R.; O’Shea, T.J.; Oko, L.M.; Holmes, K.V. Detection of group 1 coronaviruses in bats in North America. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, C.; Cryan, P.M.; O’Shea, T.J.; Oko, L.M.; Ndaluka, C.; Calisher, C.H.; Berglund, A.D.; Klavetter, M.L.; Bowen, R.A.; Holmes, K.V. Alphacoronaviruses in New World bats: Prevalence, persistence, phylogeny, and potential for interaction with humans. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, F.E.; Campos, F.S.; Kunert Filho, H.C.; Batista, H.B.; Carnielli, P., Jr.; Cibulski, S.P.; Spilki, F.R.; Roehe, P.M.; Franco, A.C. Detection of Alphacoronavirus in velvety free-tailed bats (Molossus molossus) and Brazilian free-tailed bats (Tadarida brasiliensis) from urban area of Southern Brazil. Virus Genes 2013, 47, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Rasche, A.; Diallo, T.D.; Cottontail, V.M.; Stöcker, A.; Souza, B.F.d.C.D.; Correˆa, J.I.; Carneiro, A.J.B.; Franke, C.R.; Nagy, M. Highly diversified coronaviruses in neotropical bats. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1984–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero Arteaga, F.; Miragaya, M.; Molina, N.; Mondino, M.; Bracamonte, C.; Capitelli, G.; Mundo, S.; Torres, C.; Bratanich, A. Identification of coronaviruses in bats and rodents in northern and central Argentina. Arch Virol 2023, 168, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geldenhuys, M.; Mortlock, M.; Epstein, J.H.; Pawęska, J.T.; Weyer, J.; Markotter, W. Overview of Bat and Wildlife Coronavirus Surveillance in Africa: A Framework for Global Investigations. Viruses 2021, 13, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffrin, L.; Goodman, S.M.; Wilkinson, D.A.; Ramasindrazana, B.; Lagadec, E.; Gomard, Y.; Le Minter, G.; Dos Santos, A.; Corrie Schoeman, M.; Sookhareea, R. Bat coronavirus phylogeography in the Western Indian Ocean. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambe, L.A.M.; Mathobo, P.; Munzhedzi, M.; Bessong, P.O.; Mavhandu-Ramarumo, L.G. Prevalence and Molecular Epidemiology of Human Coronaviruses in Africa Prior to the SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak: A Systematic Review. Viruses 2023, 15, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehata, M.M.; Chu, D.K.; Gomaa, M.R.; AbiSaid, M.; El Shesheny, R.; Kandeil, A.; Bagato, O.; Chan, S.M.; Barbour, E.K.; Shaib, H.S.; et al. Surveillance for Coronaviruses in Bats, Lebanon and Egypt, 2013-2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchinski, K.S.; Loos, K.D.; Suchan, D.M.; Russell, J.N.; Sies, A.N.; Kumakamba, C.; Muyembe, F.; Mbala Kingebeni, P.; Ngay Lukusa, I.; N’Kawa, F.; et al. Targeted genomic sequencing with probe capture for discovery and surveillance of coronaviruses in bats. Elife 2022, 11, e79777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, J.T.; Mollerup, S.; Jensen, R.H.; Olofsson, J.K.; Nguyen, N.D.; Hansen, T.A.; Vinner, L.; Monadjem, A.; McCleery, R.A.; Hansen, A.J. Metagenomic Analysis Reveals Previously Undescribed Bat Coronavirus Strains in Eswatini. Ecohealth 2021, 18, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, J.K.; Negash, Y.; Randhawa, N.; Kebede, N.; Wells, H.; Ayalew, G.; Anthony, S.J.; Smith, B.; Goldstein, T.; Kassa, T.; et al. Coronavirus and Paramyxovirus Shedding by Bats in a Cave and Buildings in Ethiopia. Ecohealth 2022, 19, 216–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoarau, A.O.G.; Goodman, S.M.; Al Halabi, D.; Ramasindrazana, B.; Lagadec, E.; Le Minter, G.; Köster, M.; Dos Santos, A.; Schoeman, M.C.; Gudo, E.S.; et al. Investigation of astrovirus, coronavirus and paramyxovirus co-infections in bats in the western Indian Ocean. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Tang, K.; Shi, M.; Conrardy, C.; Li, K.S.; Lau, S.K.; Anderson, L.J.; Tong, S. Genomic characterization of seven distinct bat coronaviruses in Kenya. Virus Res. 2012, 167, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, A.; Vidal, N.; Keita, A.K.; Thaurignac, G.; Esteban, A.; De Nys, H. Wide Diversity of Coronaviruses in Frugivorous and Insectivorous Bat Species: A Pilot Study in Guinea, West Africa. Viruses 2020, 12, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razanajatovo, N.H.; Nomenjanahary, L.A.; Wilkinson, D.A.; Razafimanahaka, J.H.; Goodman, S.M.; Jenkins, R.K.; Jones, J.P.; Heraud, J.M. Detection of new genetic variants of Betacoronaviruses in Endemic Frugivorous Bats of Madagascar. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markotter, W.; Geldenhuys, M.; Jansen van Vuren, P.; Kemp, A.; Mortlock, M.; Mudakikwa, A.; Nel, L.; Nziza, J.; Paweska, J.; Weyer, J. Paramyxo- and Coronaviruses in Rwandan Bats. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nziza, J.; Goldstein, T.; Cranfield, M.; Webala, P.; Nsengimana, O.; Nyatanyi, T.; Mudakikwa, A.; Tremeau-Bravard, A.; Byarugaba, D.; Tumushime, J.C. Coronaviruses detected in bats in close contact with humans in Rwanda. Ecohealth 2020, 17, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgarel, M.; Pfukenyi, D.M.; Boué, V.; Talignani, L.; Chiweshe, N.; Diop, F.; Caron, A.; Matope, G.; Missé, D.; Liégeois, F. Circulation of Alphacoronavirus, Betacoronavirus and Paramyxovirus in Hipposideros bat species in Zimbabwe. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2018, 58, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corman, V.M.; Baldwin, H.J.; Tateno, A.F.; Zerbinati, R.M.; Annan, A.; Owusu, M.; Nkrumah, E.E.; Maganga, G.D.; Oppong, S.; Adu-Sarkodie, Y. Evidence for an ancestral association of human coronavirus 229E with bats. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11858–11870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maganga, G.D.; Pinto, A.; Mombo, I.M.; Madjitobaye, M.; Mbeang Beyeme, A.M.; Boundenga, L.; Ar Gouilh, M.; N’Dilimabaka, N.; Drexler, J.F.; Drosten, C. Genetic diversity and ecology of coronaviruses hosted by cave-dwelling bats in Gabon. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.; Conrardy, C.; Ruone, S.; Kuzmin, I.V.; Guo, X.; Tao, Y.; Niezgoda, M.; Haynes, L.; Agwanda, B.; Breiman, R.F. Detection of novel SARS-like and other coronaviruses in bats from Kenya. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meta Djomsi, D.; Lacroix, A.; Soumah, A.K.; Kinganda Lusamaki, E.; Mesdour, A.; Raulino, R.; Esteban, A.; Ndong Bass, I.; Mba Djonzo, F.A.; Goumou, S.; et al. Coronaviruses Are Abundant and Genetically Diverse in West and Central African Bats, including Viruses Closely Related to Human Coronaviruses. Viruses 2023, 15, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, U.; George, O.; Oguzie, J.; Osasona, O.; Motayo, B.; Kamani, J.; Eromon, P.; Folarin, O.; Happi, A.; Komolafe, I.; et al. Genomic characterization of Alphacoronavirus from Mops condylurus bats in Nigeria. Virus Res. 2023, 334, 199174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ithete, N.L.; Stoffberg, S.; Corman, V.M.; Cottontail, V.M.; Richards, L.R.; Schoeman, M.C.; Drosten, C.; Drexler, J.F.; Preiser, W. Close relative of human Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in bat, South Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokelmann, M.; Balkema-Buschmann, A. Coronaviruses in Bats. Berl. Und Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2021, 134, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.; De Jong, C.; Meers, J.; Henning, J.; Wang, L.-F.; Field, H. Coronavirus infection and diversity in bats in the Australasian region. Ecohealth 2016, 13, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boardman, W.S.J.; Baker, M.L.; Boyd, V.; Crameri, G.; Peck, G.R.; Reardon, T.; Smith, I.G.; Caraguel, C.G.B.; Prowse, T.A.A. Serological evidence of exposure to a coronavirus antigenically related to severe acute respiratory syndrome virus (SARS-CoV-1) in the Grey-headed flying fox (Pteropus poliocephalus). Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 2628–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortosa, P.; McInnes, K.; O’Donnell, C.F.; Pryde, M.; Gomard, Y.; Lebarbenchon, C.; Poulin, R. Coronavirus shedding in New Zealand bats: Insights and future perspectives. N. Z. J. Ecol. 2023, 47, 3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.-M.; Wang, N.; Yang, X.-L.; Liu, H.-Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Hu, B.; Peng, C.; Geng, Q.-B.; Zhu, G.-J. Discovery of novel bat coronaviruses in South China that use the same receptor as Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00116-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendenhall, I.H.; Borthwick, S.; Neves, E.S.; Low, D.; Linster, M.; Liang, B.; Skiles, M.; Jayakumar, J.; Han, H.; Gunalan, V.; et al. Identification of a Lineage D Betacoronavirus in Cave Nectar Bats (Eonycteris spelaea) in Singapore and an Overview of Lineage D Reservoir Ecology in SE Asian Bats. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1790–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, F.; Yang, W.; Jiang, T.; Lu, G.; He, B.; Li, X.; Hu, T.; Chen, G.; Feng, Y.; et al. Detection and characterization of diverse alpha- and betacoronaviruses from bats in China. Virol. Sin. 2016, 31, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandeil, A.; Abi-Said, M.; Badra, R.; El-Shesheny, R.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A.; Alnajjar, R.; Khalid, Z.; Kamel, M.N.; Abi Habib, W.; Abdallah, J.; et al. Detection of Coronaviruses in Bats in Lebanon during 2020. Pathogens 2023, 12, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, S.; Kitamura, T.; Matsugo, H.; Kamiki, H.; Oyabu, K.; Sekine, W.; Takenaka-Uema, A.; Sakai-Tagawa, Y.; Kawaoka, Y.; Horimoto, T. Isolation of Bat Sarbecoviruses, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 2500–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharmayanti, N.; Nurjanah, D.; Nuradji, H.; Maryanto, I.; Exploitasia, I.; Indriani, R. Molecular detection of bat coronaviruses in three bat species in Indonesia. J. Vet. Sci. 2021, 22, e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Ullah, S.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Ali, M. Bats-associated beta-coronavirus detection and characterization: First report from Pakistan. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2023, 108, 105399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhao, K.; Peng, X.; He, X.; Deng, J.; Wang, B.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L. Pangolin HKU4-related coronaviruses found in greater bamboo bats from southern China. Virol Sin. 2023, 38, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Database of Bat-Associated Viruses. Available online: http://www.mgc.Ac.cn/DBatVir/ (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- de Groot, R.; Baric, R.; Enjuanes, L.; Gorbalenya, A.; Holmes, K.; Perlman, S. Family Coronaviridae Virus Taxonomy. Classification and Nomenclature of Viruses: Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.Y.; Li, J.L.; Yang, X.L.; Chmura, A.A.; Zhu, G.; Epstein, J.H.; Mazet, J.K.; Hu, B.; Zhang, W.; Peng, C.; et al. Isolation and characterization of a bat SARS-like coronavirus that uses the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2013, 503, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zeng, L.P.; Yang, X.L.; Ge, X.Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Xie, J.Z.; Shen, X.R.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Wang, N.; et al. Discovery of a rich gene pool of bat SARS-related coronaviruses provides new insights into the origin of SARS coronavirus. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Hu, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, M.N.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wu, L.J.; Ge, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Daszak, P.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Bat Coronavirus Closely Related to the Direct Progenitor of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 3253–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldenhuys, M.; Mortlock, M.; Weyer, J.; Bezuidt, O.; Seamark, E.C.J.; Kearney, T.; Gleasner, C.; Erkkila, T.H.; Cui, H.; Markotter, W. A metagenomic viral discovery approach identifies potential zoonotic and novel mammalian viruses in Neoromicia bats within South Africa. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, S.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Tsai, C.Y.; Kao, C.L.; Yang, J.Y.; Liu, H.W.; Su, I.J.; Tsai, S.F.; Chen, D.S.; Chen, P.J. Characterization of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus genomes in Taiwan: Molecular epidemiology and genome evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2542–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plante, J.A.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Xia, H.; Johnson, B.A.; Lokugamage, K.G.; Zhang, X.; Muruato, A.E.; Zou, J.; Fontes-Garfias, C.R.; et al. Spike mutation D614G alters SARS-CoV-2 fitness. Nature 2021, 592, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korber, B.; Fischer, W.M.; Gnanakaran, S.; Yoon, H.; Theiler, J.; Abfalterer, W.; Hengartner, N.; Giorgi, E.E.; Bhattacharya, T.; Foley, B.; et al. Tracking Changes in SARS-CoV-2 Spike: Evidence that D614G Increases Infectivity of the COVID-19 Virus. Cell 2020, 182, 812–827.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, H.K.H.; Li, X.; Fung, J.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y. Molecular epidemiology, evolution and phylogeny of SARS coronavirus. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2019, 71, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menachery, V.D.; Yount, B.L., Jr.; Sims, A.C.; Debbink, K.; Agnihothram, S.S.; Gralinski, L.E.; Graham, R.L.; Scobey, T.; Plante, J.A.; Royal, S.R.; et al. SARS-like WIV1-CoV poised for human emergence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3048–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Moore, M.J.; Vasilieva, N.; Sui, J.; Wong, S.K.; Berne, M.A.; Somasundaran, M.; Sullivan, J.L.; Luzuriaga, K.; Greenough, T.C.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature 2003, 426, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeager, C.L.; Ashmun, R.A.; Williams, R.K.; Cardellichio, C.B.; Shapiro, L.H.; Look, A.T.; Holmes, K.V. Human aminopeptidase N is a receptor for human coronavirus 229E. Nature 1992, 357, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, V.S.; Mou, H.; Smits, S.L.; Dekkers, D.H.; Müller, M.A.; Dijkman, R.; Muth, D.; Demmers, J.A.; Zaki, A.; Fouchier, R.A.; et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC. Nature 2013, 495, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, N.; Fernandez, I.; Planchais, C.; Michel, V.; Rajah, M.M.; Baquero Salazar, E.; Postal, J.; Porrot, F.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Blanc, C.; et al. TMPRSS2 is a functional receptor for human coronavirus HKU1. Nature 2023, 624, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Sayes, M.; Badra, R.; Ali, M.A.; El-Shesheny, R.; Kayali, G. Global Distribution and Molecular Evolution of Bat Coronaviruses. Zoonotic Dis. 2024, 4, 146-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4020014
El Sayes M, Badra R, Ali MA, El-Shesheny R, Kayali G. Global Distribution and Molecular Evolution of Bat Coronaviruses. Zoonotic Diseases. 2024; 4(2):146-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Sayes, Mohamed, Rebecca Badra, Mohamed A. Ali, Rabeh El-Shesheny, and Ghazi Kayali. 2024. "Global Distribution and Molecular Evolution of Bat Coronaviruses" Zoonotic Diseases 4, no. 2: 146-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4020014
APA StyleEl Sayes, M., Badra, R., Ali, M. A., El-Shesheny, R., & Kayali, G. (2024). Global Distribution and Molecular Evolution of Bat Coronaviruses. Zoonotic Diseases, 4(2), 146-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4020014








