Simple Summary
Toxoplasma gondii is considered one of the most successful parasites in the world, potentially infecting any vertebrates, including humans. Its complex life cycle encompasses many transmission pathways, which remain enigmatic in northern ecosystems. The aim of our study was to assess Canada lynx as potential reservoir of and sentinel for T. gondii by (1) using serological and molecular assays to detect T. gondii, (2) determining if lynx are definitive hosts for the parasite, and (3) identifying potential risk factors that may contribute to lynx exposure. For the first time, T. gondii DNA was found in tissue and feces of Canada lynx, indicating that they can be both intermediate and definitive hosts in northern regions. Our findings would help identify high-risk regions for infections in northern Canada, with lynx serving as indicator for potential human exposure of T. gondii.
Abstract
Toxoplasma gondii is a zoonotic parasite globally infecting a wide range of species, including humans. Felids are the only known hosts that can excrete environmentally resistant oocysts into ecosystems. In boreal regions, Canada lynx (Lynx canadensis) are sought by hunters primarily for their fur, and they are occasionally eaten. We examined carcasses salvaged from trappers from boreal regions of eastern (n = 97) and western (n = 357) Canada. We detected T. gondii antibodies in fluid from thawed heart tissue using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, DNA in brain and heart via magnetic capture and real-time PCR assay, and presence of DNA in feces using a real-time PCR with melt curve analysis. We detected antibodies against T. gondii and DNA in tissues in 24% and 19% of lynx, respectively. One lynx was positive for DNA of T. gondii in feces, which could indicate intestinal infection and potential for shedding oocysts. Our results indicate that lynx may be a useful sentinel species for monitoring environmental circulation of T. gondii in northern boreal regions and may pose a risk for transmission to other wildlife and to people handling or consuming lynx.
Keywords:
Canada lynx; ELISA; MC-qPCR; melt-curve analysis; sentinel species; Toxoplasma gondii; zoonosis 1. Introduction
Toxoplasma gondii is a global, zoonotic protozoan parasite that is capable of infecting and adversely impacting a wide range of vertebrates, especially if the immune system is compromised or if a mammal becomes infected while pregnant [1]. Three infective stages characterized T. gondii: sporulated oocysts, bradyzoites, and tachyzoites. The life cycle of this parasite is complex; felids are the only natural definitive hosts excreting environmentally resistant oocysts in their feces, and virtually all warm-blooded animals may act as intermediate hosts, following consumption of sporulated oocysts (from contaminated water/soil) or tissue cysts containing bradyzoites in other infected hosts [2]. Therefore, once introduced into a food web, T. gondii can be maintained through trophic interactions (such as predation) and vertical transmission (tachyzoites from mother to foetus).
In addition to the domestic cats as definitive hosts, wild Felidae have the potential to shed millions of oocysts into the environment [3]. For instance, following a waterborne outbreak of toxoplasmosis in humans [4], T. gondii was isolated from feces of two naturally infected cougars (Puma concolor) from British Columbia, Canada [5]. Ingestion of infected tissues is likely the most efficient means of transmission of T. gondii among felids [6,7]. Canada lynx (Lynx canadensis) likely acquire infection from consuming infected prey, which themselves may become infected by consumption of oocysts in the environment or possibly by vertical transmission. Lynx primarily prey on snowshoe hares (Lepus americanus) and red squirrel (Tamiasciurus hudsonicus). Although infrequent, lynx can also demonstrate cannibalism or scavenging behavior, especially in years of food shortage [8,9,10]. Lynx are hunted primarily for their fur, but are also occasionally consumed by local people [11]. Thus, infected lynx could represent a risk of transmission of T. gondii to people that consume their meat (containing tissue cysts) if not thoroughly frozen or cooked.
In the Nearctic boreal region, Canada lynx are often the only wild felid present. To date, efforts to detect oocysts in feces of Canada lynx have not been successful [12], possibly due to the short period of time that oocysts are shed, and the difficulty in detecting the small oocysts on routine fecal examination. Previous studies have reported Canada lynx seropositive for T. gondii, indicating exposure to the parasite [12,13,14], but active tissue infection based on detection of DNA in tissues has not been demonstrated. Therefore, this study was conducted with the primary objective to understand whether lynx could act as a definitive and intermediate host for, as well as sentinels of, T. gondii in northern Canada. We performed an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) on fluid from thawed heart; magnetic capture and a real-time (MC-PCR) technique on tissues; a real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) assay with fluorescent melting curve analysis (MCA) on fecal samples that can detect, differentiate, and identify DNA from multiple coccidian species, including T. gondii [15]; and fecal flotation on suspicious samples. Association between T. gondii exposure and potential risk factors was also assessed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Locations and Lynx Sampling
During the fur trapping seasons of 2015–2020, we collected carcasses of skinned lynx or gastrointestinal tracts (GIT) from licensed fur trappers in boreal regions of eastern (Labrador and Québec, n = 97) and western (Yukon, n = 357) Canada (Figure 1). Carcasses and GIT were kept frozen at −20 °C until shipped to the Department of Environment in Whitehorse, Yukon; the Western College of Veterinary Medicine in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan; the Faculté de Médecine Vétérinaire in Saint-Hyacinthe, Québec; the Nunavik Research Centre in Kuujjuaq, Québec; or the wildlife division office at the Department of Fisheries, Forestry and Agriculture in Goose Bay, Newfoundland and Labrador. We collected whole hearts, brains, and feces, and recorded sex, age, body condition, and harvest location when possible. We determined sex during necropsy by inspecting internal reproductive organs [16]. We counted cementum annuli (Matson’s laboratory, Manhattan, Montana, USA) to determine age, or used the total body length when not possible. We classified lynx as juveniles (≤1 year old) and adults (≥2 years old) [17]. A body condition index (BCI) was obtained by visually estimating the relative amount of fat deposits, using a scale of 1–3 as follows: 1, no to very little visceral fat deposits in abdominal and peritoneal cavity; 2, moderate visceral fat deposits; 3, abundant visceral fat deposits, as described in Bouchard et al. (2022) [18].
Figure 1.
Regions where lynx (Lynx canadensis) were collected during 2015–2020 by trappers from eastern and western Canada.
2.2. Serological Analysis
Since commercially available serological assays are not validated in lynx, we evaluated (using a subset of samples) heart fluid dilutions for two different techniques, ELISA and the indirect fluorescent antibody test (IFAT), using magnetic capture (MC)-qPCR as the gold standard. As validated in Sharma et al. (2019) [19] and described by Bouchard et al. (2022), we detected antibodies to T. gondii in fluid from thawed hearts (diluted 1:2) using the commercially available ID Screen® Toxoplasmosis Indirect Multi-Species enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (IDvet, Grabels, France). Heart fluid was collected from the heart of individual lynx and processed as per the work of Bouchard et al. (2022) before being transferred to a labeled 1.5 mL Eppendorf tube. Heart fluids were stored at 4 °C for use within the next 3 days or at −20 °C until used for testing.
2.3. Molecular Analysis
2.3.1. Detection of DNA of T. gondii in Tissue Samples
As validated by Opsteegh et al. (2010) [20] and described by Bouchard et al. (2022), we extracted sequence-specific DNA of T. gondii from whole heart and brain combined (or heart only if brain was not available) for each lynx using the MC-qPCR technique to determine infection status using the Tox 9F (5′-aggagagata tcaggactgtag-3′) and Tox 11R (5′-gcgtcgtctc gtctagatcg-3′) primers, for the detection of the 188 bp T. gondii sequence within the 529 repeat-element. We quantified parasites using the following formula (1):
log10 (tachyzoites) = (43.3 − Cq)/3.07)
We expressed this value as the number of tachyzoite-equivalents (TE) and calculated the intensity of infection by dividing TE by the weight of the tissue processed, expressed as tachyzoite equivalents per gram (TEG) [21].
As described in the work of Bouchard et al. (2022), we sent frozen aliquots of template DNA (50 µL) to a specialized laboratory (Department of Microbiology, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA) for further genetic characterization, using a multiplex multilocus nested PCR-RFLP with ten genetic markers (SAG1, SAG2, SAG3, BTUB, GRA6, c22-8, c29-2, L358, PK1, and Apico) [22].
2.3.2. Detection of DNA of T. gondii in Fecal Samples
Genomic DNA from 300 mg of fecal sample was extracted using the Fast-DNA kit for feces (MP Biomedicals, Solon, OH, USA), followed by a PCR Purification kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) to remove any additional inhibitors. We detected coccidian species in each fecal sample using a universal coccidia primer cocktail designed to amplify a ≈315 bp region of 18S rDNA in a real-time quantitative PCR assay [15]. Genetically distinct coccidian species can be differentiated by the melt curve shape and the PCR product melting temperature (on the basis of the nucleotide sequence, length, and G-C content) and identified by comparison to in-run controls and/or sequencing [15]. We performed all PCR analyses as described previously [15], except for a few changes. For positive controls, we included wells containing DNA from T. gondii (genomic, American Type Culture Collection (ATCC), Manassas, VA, USA), Cryptosporidium parvum (genomic, ATCC, and Cystoisospora (genomic, ATCC). We also included a negative control, two no-template controls, and a standard curve consisting of DNA from Hammondia (105 to 101 oocysts) provided by the Centre for Food-Borne and Animal Parasitology (CFAP). All samples were run in duplicate. Melt curves from positive samples were visually compared to the controls for preliminary identification, and amplified DNA from positive reactions were sequenced (Macrogen, Seoul, South Korea) for confirmation using original primers. Forward and reverse sequences were assembled with PreGap4 and Gap4 (Staden Package) and consensus sequences were compared with reference sequences in GenBankTM using the nucleotide Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLASTN, https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 31 March 2021).
2.4. Fecal Flotation
To detect oocysts of T. gondii in feces, fecal flotation was performed. We thawed, weighed, and mixed 4 g of feces thoroughly in a paper cup with 40 mL of Sheather’s sucrose solution to create a homogenized mixture. After sieving the fluid through a cheesecloth into a second cup, we poured a 10 mL aliquot (≈25%, representing 1 g of feces) into a test tube then topped it up with ≈5 mL of Sheather’s sucrose solution to form a slight convex meniscus. We placed a coverslip on top and centrifuged the tube at 491 rcf for 10 min, after which we lifted the coverslip and placed it on a glass slide. We viewed slides under the microscope at 10–40X magnification and identified coccidian oocysts on the basis of size and morphology [23].
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The agreement between serological and molecular tests, the association between quantitative MC-qPCR and ELISA results, and the calculation for prevalences [24] were performed as per the work of Bouchard et al. (2022). We used the term “prevalence” to indicate proportion of positive results (positive on at least one test). We built binary logistic regression models to test for (1) the presence of antibodies to T. gondii (sero-positive or sero-negative), (2) the presence of T. gondii DNA (tissue-positive or tissue-negative), and (3) the presence of antibodies to and/DNA of T. gondii (at least positive on one test or negative on both tests). We evaluated age-class (juvenile and adult), sex (female and male), body condition score (low, medium, and high), and location (eastern or western Canada) for inclusion in our final multivariable model. Stepwise forward multivariable regression analysis was performed to include risk factors and confounders in the final model. Variables associated at a significance level of p < 0.05 were retained in the final model. Goodness-of-fit of the final model was evaluated by the Hosmer Lemeshow test. Finally, we used a generalized linear model to evaluate the effects of predictors on the infection intensity. We performed all statistical analysis using IBM SPSS (ver. 24; Armonk, New York, NY, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
In total, 409 whole lynx carcasses and 45 GIT (28 from southern QC, 17 from Yukon) were collected from the years 2015 to 2021. Male to female ratio was 3:2 (238 of 397 (60%) vs. 159 of 397 (40%); information on sex was not available for 57 lynx). BCI score was determined for 303 lynx; the highest proportion (61%, 186 of 303) of lynx had a medium BCI score, followed by low (30%, 92 of 303) and high (8%, 25 of 303). More juveniles than adults were collected (64% vs. 36%; age was determined only for 100 lynx). Most lynx (79%: 357 of 454) were from western Canada. Moreover, the number of lynx varied annually (range = 28–137), with no carcass submitted during the winters of 2015–2016 and 2020–2021 from eastern Canada.
3.2. Cut-off Values and Best-Performing Serological Assay
We determined dilution cut-off values and best-performing serological test as per the work of Bouchard et al. (2022) (Supplementary Tables S1 and S2).
3.3. Association between serological and molecular tests
We found that 308 lynx (75%) were negative on both serology and PCR, 75 (18%) were positive on both, 22 (5%) were seropositive and tissue negative, and four (1%) were seronegative but tissue positive. Using the McNemar chi-squared test (Χ21 = 11.1, p < 0.001, n = 409), we found a significant difference between serological and molecular results; a Kappa test was thus not performed [25]. No correlation (Spearman’s correlation coefficient = −0.064, p = 0.522) was found between antibody concentration (S/P%) and quantification cycle (Cq) values on MC-qPCR.
3.4. Prevalence and Potential Risk Factors Associated with T. gondii
Overall, seroprevalence (exposure to T. gondii indicated by presence of antibodies) was 24% (95% CI = 20–28), and tissue prevalence (infection of T. gondii indicated by presence of DNA) was 19% (95% CI = 16–23) (Table 1). Prevalence of T. gondii (on the basis of positivity on at least one test) was 25% (95% CI = 21–29). Results of univariate logistic regressions (for the three models) are given in Table 1. Because a significant difference was observed between the results of ELISA and MC-qPCR, and due to higher sensitivity when using both tests together, multivariate analysis was performed only for the third model (positive on ELISA and/or MC-qPCR).

Table 1.
Univariate analysis on variables associated with Toxoplasma gondii sero-positivity, tissue positivity, and overall positivity among Canada lynx (Lynx canadensis).
In general, prevalence was higher in lynx in eastern (41%, 95% CI = 30–52) as opposed to western (22%, 95% CI = 17–26) Canada. Prevalence was higher in adult (59%, 95% CI = 42–74) as opposed to juvenile (8%, 95% CI = 4–18) lynx. Due to a large number of missing values for age (354 of 454) and BCI (151 of 454), only sex and location were included in the multivariable analysis, which included 360 complete observations. The odds of being positive to T. gondii were two times (OR = 1.83, 95% CI = 1.10–3.06, p = 0.021) higher in male than female lynx, and two and half times higher in lynx from eastern (OR = 2.49, 95% CI = 1.41–4.40, p = 0.002) than those from western Canada (Table 2).

Table 2.
Multivariable analysis on variables associated with Toxoplasma gondii positivity among Canada lynx (Lynx canadensis).
3.5. Quantification of Infection Intensity and Risk Factors
A total of 72 observations with complete data were included in our generalized linear model, with a mean infection intensity of 4361 TEG (95% CI: 2193–6584). Since more than 10% missing values were observed for age and BCI, only sex and region were included. The mean infection intensity for the western (n = 51) and eastern (n = 21) regions were 5479.14 (2233.25–8725.03) and 1645.05 (173.10–3117.00), respectively. The mean infection intensity for males (n = 49) and females (n = 23) were 4389.69 (1274.28–7505.11) and 4299.43 (800.48–7798.39), respectively. Our generalized linear model revealed a significant association between region and TEG (Table 3).

Table 3.
Potential risk factors for infection intensity (tachyzoites equivalent per gram; log transformed) of Toxoplasma gondii in Canada lynx (Lynx canadensis).
3.6. CoproPCR and DNA Sequencing
Of 345 fecal samples tested, only one lynx from eastern Canada tested positive for T. gondii on real-time PCR with melt-curve analysis following sequencing. The sequence was trimmed to ensure that any low-quality portions were not included, and the BLAST result gave 98.8% similarity with T. gondii. The PCR product melting temperature was similar to the in-run controls of T. gondii genomic DNA (83 °C). Of 17 lynx tissue samples (Cq value < 30), none amplified following sequencing.
3.7. Fecal Flotation
We tested 62 samples following suspicious results on melting-curve analysis. In the one positive sample following sequencing, we observed a dozen oocyst-like structures resembling T. gondii (Figure 2) with similar shape and size (spherical, 10–12 um).
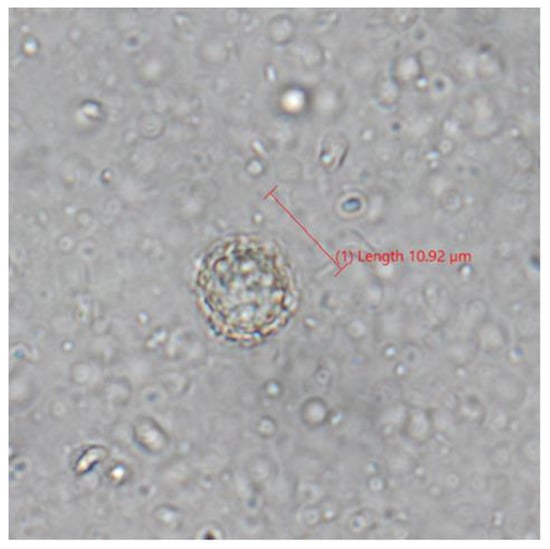
Figure 2.
Photograph of oocyst-like structure in lynx (Lynx canadensis) feces following fecal flotation visualized on compound microscopy.
4. Discussion
Our study supports the fact that Canadian lynx are both intermediate and definitive hosts for T. gondii; they may thus play an important role in contaminating the freshwater environments and infecting wildlife [26,27] in boreal regions. They may also pose a risk for transmission to people consuming lynx. These findings provide critical data in understanding better the epidemiology of T. gondii in northern ecosystems and highlight the impact lynx may have, which was previously unknown, on contaminating the environment with oocysts in northern regions and maintaining transmission by infecting their prey.
We detected DNA of T. gondii in lynx tissues for the first time, which indicates that lynx are suitable intermediate hosts for T. gondii. Lynx are occasionally consumed by hunters and trappers which, in addition to skinning the animal for fur, may result in the pathway for transmission to humans [11,28]. Most reports of T. gondii in wild felids are from serosurveys [7], which give little information on tissue infection. Detection of T. gondii DNA in tissues is thus of greater significance from a food safety perspective. As we only tested brain and heart, future research should target consumed tissue (i.e., skeletal muscle) and consumption trends in order to provide more insight on the food safety risks in this species. Canada lynx can also be preyed on by coyote (Canis latrans), wolverine (Gulo gulo), wolf (Canis lupus), cougar, and fisher (Pekania pennanti) [29], thus representing a risk of transmission to other carnivore species and maintaining T. gondii in wildlife populations regardless of shedding. However, further studies are needed to determine the degree of infectivity of the parasite in tissue cysts from these lynx populations.
Our finding of DNA of T. gondii in one sample of feces emphasizes lynx as a potential source of oocyst contamination in freshwater and snowmelt run-off in boreal regions of Canada, as well as transporting oocysts north through marine currents [30]. Multiple oocyst-like structures of around 10–12 um fit the description of T. gondii but lacked definition. However, we should be cautious when interpreting these results, and the negative results on fecal flotation on 61 other individuals since oocysts are likely shed only on first exposure and for only a few weeks in the lifetime of the animal. Moreover, the intestines and feces underwent ≥1 freeze–thaw cycles that could have affected the structural integrity of the oocysts. Of note, the fragment of the sequence analyzed was non-discriminatory for T. gondii and Neospora caninum, meaning that DNA material of N. caninum could have been found in feces following ingestion of N. caninum oocysts through canid prey or feces. Nevertheless, T. gondii DNA would be more likely, and we are confident in our finding since the melting temperature was a match to the control, our sequences were of high quality, and the BLAST match was above 98%. Lynx may therefore be a significant reservoir and useful sentinel species for environmental circulation in boreal regions.
We found some disagreement following serological and molecular testing. As is often the case, seroprevalence tends to be higher than tissue prevalence [18,31,32]. Adult lynx had higher seroprevalence and tissue prevalence compared to juveniles. This likely reflects an increase in exposure with age due to the persistence of both tissue cysts and antibodies, often described in other wildlife studies [18,33,34]. Low exposure in juveniles suggests that vertical transmission (mother to fetus) might not represent an important route of transmission in lynx [6]. Moreover, male lynx were found to be at higher risk of being positive to T. gondii compared to females. This may be due to males requiring greater food intake, thus increasing the chance of ingesting contaminated prey, or differences in diet between the sexes.
Higher seroprevalence and tissue prevalence were observed in eastern compared to western Canada. Seroprevalence of 41% in eastern regions was quite similar to 36% reported in a previous study on T. gondii in lynx from the boreal region of Québec, eastern Canada [14]. However, Simon et al. (2013) found a seroprevalence of 14% in the same region, which suggests spatio-temporal dynamics that may be a result of variation in prey–predator cycles [12]. Methodological differences between studies (modified agglutination tests vs. ELISA) could also explain these divergent results, although they both proved to be good serological techniques to detect T. gondii antibodies [21,35]. Our finding of 20% seroprevalence in lynx from the Yukon is comparable to 15% in previous work from Alaska [11]. These results are also similar to the low seroprevalence (3%) found in people in Alaska [36] and in recent Inuit health surveys (≈8% in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region) [37], supporting genuinely lower levels of circulation of T. gondii in northwestern North America.
It is unlikely that the difference in prevalence between eastern and western regions are caused by variations in diet since lynx consume mostly snowshoe hare throughout their range; however, the proportion of hare in the diet may vary annually with their abundance, which cycles on a 9–11-year basis [38,39]. During period of increasing density of lynx and hares, we would thus expect higher transmission of T. gondii in both species [12]. Due to the non-uniform distribution of samples in different years from both regions in the present study, we were not able to explore this further. Abiotic factors such as a colder and drier climate could also explain a lower prevalence in western northern boreal regions, thus affecting the survival or the infectivity of T. gondii. Sporulated oocysts can remain infectious for at least 18 months in moist conditions [40]. A higher prevalence in the eastern lynx population, especially in Kuujjuaq (86%), could be due to them being adjacent to large watershed that are potentially disseminating infectious sporulated oocysts coming from temperate regions into northern coastal environment and surrounding wildlife. Snowshoe hares could thus be more exposed from contaminated herbage (from snowmelt and water run-off for example), and potentially through meat. Hares have been seen scavenging a variety of different species that could act as intermediate hosts for T. gondii, including lynx [41]. Future studies investigating prevalence in snowshoe hare from different regions are required to understand better T. gondii transmission pathways in northern boreal regions. Contrary to prevalence, the infection intensity in lynx from the Yukon was significantly higher than from eastern Canada. The parasite stage when infected, strain virulence, and age could play a role in intensity of infection [18,42,43]. Younger individuals with lower immunity could have been trapped in the Yukon, as observed for wolverine (Gulo gulo), a species similarly trapped in the Yukon [44]. Alternatively, a more transmissible genotype could be present in the western boreal forest.
Knowledge of genotypes and strains circulating in a particular geographical region is thus important to better understand the epidemiology of T. gondii. We were not successful in genotyping even our strongly positive samples from tissues, which is not uncommon when working with previously frozen tissue samples from naturally exposed wildlife (in which amplification in vivo or in vitro is not possible). Unrecognized genetic diversity has been increasingly reported in North American wildlife, but findings still remain scarce [45,46]. Some strains may have more localized circulation in wild felids and their prey species, which would allow us to better understand the molecular epidemiology and biological significance of genetic diversity of this parasite in boreal regions and connected ecosystems. However, recovering sufficient DNA in naturally infected wildlife to determine which genotypes/strains are present remains a challenge [18,21]. To maximize chances of recovering sufficient target DNA, future studies should seek fresh tissues from which the parasite can be cultured and amplified to recover sufficient DNA to determine genotypes of T. gondii circulating in lynx and other wildlife species in northern regions.
Annual temperature and precipitation are projected to increase throughout northern Canada [47]; a changing climate will likely accelerate the development of T. gondii in endemic areas. As a consequence of temperature and precipitation change, the distributional range of lynx and their primary prey, the snowshoe hare, will likely move northward, thus facilitating oocyst transmission in more northern ecosystems. Moreover, lynx can serve as a source of infection for humans consuming its meat or handling carcasses. Wearing gloves during the skinning process, disinfecting tools, and thoroughly freezing and cooking meat before consumption is recommended. Further studies aiming at detecting viable T. gondii tissue cysts are needed to truly assess food safety risks to trappers and consumers of lynx. Moreover, further investigation into the genetics of T. gondii is required to better understand the ecological drivers for its introduction, persistence, and emergence in northern latitudes, especially the western North American where prevalence in wildlife and people is currently relatively low.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/zoonoticdis3010002/s1, Table S1: Comparison of Toxoplasma gondii results for heart fluid samples using serological methods (ELISA and IFAT) relative to magnetic capture real-time PCR to determine the best dilution for cut-off values. Table S2: Comparison of optimized serological methods (ELISA and IFAT) relative to magnetic capture qPCR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, É.B., P.L., E.J.J.; methodology, É.B., R.S.; software, É.B., R.S.; formal analysis, É.B., R.S.; investigation, É.B., R.S., A.H.-O., T.S.J., C.N.W., R.B., Y.N.M., M.J.L.P., G.-G.G., B.A.-A., A.S.; resources, T.S.J., N.J.H., R.B., G.-G.G., B.A.-A., P.L., E.J.J.; writing—original draft preparation, É.B.; writing—review and editing, all authors; supervision, P.L., E.J.J.; project administration, P.L., E.J.J.; funding acquisition, P.L., T.S.J., E.J.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (RGPIN-2012-386666, RGPNS-2012-424278, RGPIN-2018-04900, NRS-2018-517969), ArcticNet Networks of Centres of Excellence (P63), Polar Knowledge (NST-1718-0012), Government of Yukon, and Weston Family Foundation.
Institutional Review Board Statement
In accordance with the Canadian Council on Animal Care guidelines, this research was exempt from Animal Research Ethic Board review in Canada because all samples were collected from animals previously harvested for non-research purposes.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data relating to this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all fur trappers and coordinators that contributed to this study by submitting samples, without whom this project could not have taken place. In particular, we thank William Harrower, Pierre Canac-Marquis, Pierre-Yves Collin, Yves Jetée, Claude Grenier, Frank Phillips, Ford Taylor, and Luke Parsons. We also thank Maud Henaff, Justine Benjamin, Kaz Kuba, Ariane Massé, Ellen Avard, Richard Neville, Bruce Rodrigues, and Hugh Whitney for valuable help in sample logistics. We are thankful to Brent Wagner, Champika Fernando, Michelle Sniatynski, Pratap Kafle, and Laura Lalonde for help in laboratory analyses, and to Vladislav Lobanov as an internal reviewer for the Canadian Food Inspection Agency. We are grateful to the personnel of the Faculté de Médecine Vétérinaire and the Centre québécois sur la santé des animaux sauvages (CQSAS); the Nunavik Research Centre (Makivik Corporation); regional and local Nunavimmi Umajulivijiit Katujaqatigininga (LNUK and RNUK); and the wildlife division office at the Department of Fisheries, Forestry and Agriculture in Goose Bay for storage of carcasses, logistic help, and transport.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tenter, A.M.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma gondii: From animals to humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1217–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; p. 313. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, N.L.; Frenkel, J.K.; Dubey, J.P. Oral infections with Toxoplasma cysts and oocysts in felines, other mammals, and in birds. J. Parasitol. 1972, 58, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowie, W.R.; King, A.S.; Werker, D.H.; Isaac-Renton, J.L.; Bell, A.; Eng, S.B.; Marion, S.A. Outbreak of toxoplasmosis associated with municipal drinking water. The BC Toxoplasma Investigation Team. Lancet 1997, 350, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramini, J.J.; Stephen, C.; Dubey, J.P.; Engelstoft, C.; Schwantje, H.; Ribble, C.S. Potential contamination of drinking water with Toxoplasma gondii oocysts. Epidemiol. Infect. 1999, 122, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Bocanegra, I.; Dubey, J.P.; Martínez, F.; Vargas, A.; Cabezón, O.; Zorrilla, I.; Arenas, A.; Almería, S. Factors affecting seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in the endangered Iberian lynx (Lynx pardinus). Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 167, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatam-Nahavandi, K.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Rahimi, M.T.; Pagheh, A.S.; Zarean, M.; Dezhkam, A.; Ahmadpour, E. Toxoplasma gondii infection in domestic and wild felids as public health concerns: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowat, G.; Poole, K.G.; O’Donoghue, M. Ecology of lynx in northern Canada and Alaska. In Ecology and Conservation of Lynx in the United States; Ruggerio, L.F., Aubry, K.B., Buskirk, S.W., Koehler, G.M., Krebs, C.J., McKelvey, K.S., Squires, J.R., Eds.; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2000; pp. 265–306. [Google Scholar]
- Peers, M.J.L.; Konkolics, S.M.; Lamb, C.T.; Majchrzak, Y.N.; Menzies, A.K.; Studd, E.K.; Boonstra, R.; Kenney, A.J.; Krebs, C.J.; Martinig, A.R.; et al. Prey availability and ambient temperature influence carrion persistence in the boreal forest. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 2156–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T. Raven (Corvus corax) as a novel food item for lynx (Lynx canadensis). Can. Field Nat. 2021, 136, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnke, R.L.; Dubey, J.P.; Ver Hoef, J.M.; McNay, M.E.; Kwok, O.C. Serologic survey for Toxoplasma gondii in lynx from interior Alaska. J. Wildl. Dis. 2001, 37, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Bigras Poulin, M.; Rousseau, A.N.; Dubey, J.P.; Ogden, N.H. Spatiotemporal dynamics of Toxoplasma gondii infection in Canadian lynx (Lynx canadensis) in western Quebec, Canada. J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Adhami, B.H.; Simard, M.; Hernández-Ortiz, A.; Boireau, C.; Gajadhar, A.A. Development and evaluation of a modified agglutination test for diagnosis of Toxoplasma infection using tachyzoites cultivated in cell culture. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2016, 2, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labelle, P.; Dubey, J.P.; Mikaelian, I.; Blanchette, N.; Lafond, R.; St-Onge, S.; Martineau, D. Seroprevalence of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in lynx (Lynx canadensis) and bobcats (Lynx rufus) from Quebec, Canada. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 1194–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalonde, L.F.; Gajadhar, A.A. Detection and differentiation of coccidian oocysts by real-time PCR and melting curve analysis. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, T.S.; Kukka, P.M.; Peers, M.J.L.; Schmiegelow, F.K.A.; Boonstra, R.; Boutin, S.; Majchrzak, Y.N. Error in trapper-reported sex of lynx (Lynx canadensis) and wolverine (Gulo gulo): Implications for analyses of harvest records. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2020, 66, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slough, B.G. Estimating lynx population age ratio with pelt data. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 1996, 24, 495–499. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchard, É.; Sharma, R.; Hernández-Ortiz, A.; Buhler, K.; Al-Adhami, B.; Su, C.; Fenton, H.; Gouin, G.G.; Roth, J.D.; Rodrigues, C.W.; et al. Are foxes (Vulpes spp.) good sentinel species for Toxoplasma gondii in northern Canada? Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Parker, S.; Al-Adhami, B.; Bachand, N.; Jenkins, E. Comparison of tissues (heart vs. brain) and serological tests (MAT, ELISA and IFAT) for detection of Toxoplasma gondii in naturally infected wolverines (Gulo gulo) from the Yukon, Canada. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opsteegh, M.; Langelaar, M.; Sprong, H.; den Hartog, L.; De Craeye, S.; Bokken, G.; Ajzenberg, D.; Kijlstra, A.; van der Giessen, J. Direct detection and genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii in meat samples using magnetic capture and PCR. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachand, N.; Ravel, A.; Leighton, P.; Stephen, C.; Ndao, M.; Avard, E.; Jenkins, E. Serological and molecular detection of Toxoplasma gondii in terrestrial and marine wildlife harvested for food in Nunavik, Canada. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Shwab, E.K.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, X.Q.; Dubey, J.P. Moving towards an integrated approach to molecular detection and identification of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitology 2010, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryden, M.W.; Payne, P.A.; Ridley, R.; Smith, V. Comparison of common fecal flotation techniques for the recovery of parasite eggs and oocysts. Vet. Ther. 2005, 6, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sergeant, E.S.G. Epitools Epidemiological Calculators. Ausvet. 2018. Available online: http://epitools.ausvet.com.au (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Dohoo, I.R.; Martin, W.; Stryhn, H. Veterinary Epidemiologic Research, 2nd ed.; Atlantic Veterinary College Inc., University of Prince Edward Island: Charlottetown, PE, Canada, 2010; p. 865. [Google Scholar]
- Chester, S. The Arctic Guide: Wildlife of the Far North; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 71–72. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, A.; Poulin, M.B.; Rousseau, A.N.; Ogden, N.H. Fate and transport of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts in seasonally snow covered watersheds: A conceptual framework from a melting snowpack to the Canadian arctic coasts. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.C.; Gyorkos, T.W.; Alberton, B.; MacLean, J.D.; Richer, G.; Juranek, D. An outbreak of toxoplasmosis in pregnant women in northern Quebec. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 161, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoie, M.; Renard, A.; Larivière, S. Lynx canadensis (Carnivora: Felidae). Mamm. Species 2019, 51, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Rousseau, A.N.; Savary, S.; Bigras-Poulin, M.; Ogden, N.H. Hydrological modelling of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts transport to investigate contaminated snowmelt runoff as a potential source of infection for marine mammals in the Canadian Arctic. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 127, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Murata, F.H.A.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.H. Recent epidemiologic and clinical Toxoplasma gondii infections in wild canids and other carnivores: 2009–2020. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 290, 109337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, A.T.; Fooks, A.R.; Hayman, D.T.; Horton, D.L.; Muller, T.; Plowright, R.; Peel, A.J.; Bowen, R.; Wood, J.L.; Mills, J.; et al. Deciphering serology to understand the ecology of infectious diseases in wildlife. EcoHealth 2013, 10, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Parker, S.; Elkin, B.; Mulders, R.; Branigan, M.; Pongracz, J.; Godson, D.L.; Larter, N.C.; Jenkins, E. Risk factors and prevalence of antibodies for Toxoplasma gondii in diaphragmatic fluid in wolverines (Gulo gulo) from the Northwest Territories, Canada. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.C.M.; Torelli, F.; Klein, S.; Fyumagwa, R.; Karesh, W.B.; Hofer, H.; Seeber, F.; East, M.L. Evidence of high exposure to Toxoplasma gondii in free-ranging and captive African carnivores. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 8, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, É.; Elmore, S.A.; Alisauskas, R.T.; Samelius, G.; Gajadhar, A.A.; Schmidt, K.; Ross, S.; Jenkins, E.J. Transmission dynamics of Toxoplasma gondii in Arctic foxes (Vulpes lagopus): A long-term mark-recapture serologic study at Karrak Lake, Nunavut, Canada. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miernyk, K.M.; Bruden, D.; Parkinson, A.J.; Hurlburt, D.; Klejka, J.; Berner, J.; Stoddard, R.A.; Handali, S.; Wilkins, P.P.; Kersh, G.J.; et al. Human seroprevalence to 11 zoonotic pathogens in the U. S. Arctic, Alaska. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyette, S.; Cao, Z.R.; Libman, M.; Ndao, M.; Ward, B.J. Seroprevalence of parasitic zoonoses and their relationship with social factors among the Canadian Inuit in Arctic regions. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 78, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elton, C.; Nicholson, M. The ten-year cycle in numbers of the lynx in Canada. J. Anim. Ecol. 1942, 11, 215–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, C.J.; Boonstra, R.; Boutin, S.; Sinclair, A.R.E. What drives the 10-year cycle of snowshoe hares?: The ten-year cycle of snowshoe hares—One of the most striking features of the boreal forest—Is a product of the interaction between predation and food supplies, as large-scale experiments in the yukon have demonstrated. Bioscience 2001, 51, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, J.K.; Ruiz, A.; Chinchilla, M. Soil survival of toxoplasma oocysts in Kansas and Costa Rica. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1975, 24, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peers, M.J.L.; Majchrzak, Y.N.; Konkolics, S.M.; Boonstra, R.; Boutin, S. Scavenging by snowshoe hares (Lepus americanus) in Yukon, Canada. Northwest Nat. 2018, 99, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koethe, M.; Straubinger, R.K.; Pott, S.; Bangoura, B.; Geuthner, A.C.; Daugschies, A.; Ludewig, M. Quantitative detection of Toxoplasma gondii in tissues of experimentally infected turkeys and in retail turkey products by magnetic-capture PCR. Food Microbiol. 2015, 52, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert Algaba, I.; Verhaegen, B.; Jennes, M.; Rahman, M.; Coucke, W.; Cox, E.; Dorny, P.; Dierick, K.; De Craeye, S. Pork as a source of transmission of Toxoplasma gondii to humans: A parasite burden study in pig tissues after infection with different strains of Toxoplasma gondii as a function of time and different parasite stages. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukka, P.M.; Jung, T.S.; Robitaille, J.-F.; Schmiegelow, F.K.A. Temporal variation in the population characteristics of harvested wolverine (Gulo gulo) in northwestern Canada. Wildl. Res. 2017, 44, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Velmurugan, G.V.; Rajendran, C.; Yabsley, M.J.; Thomas, N.J.; Beckmen, K.B.; Sinnett, D.; Ruid, D.; Hart, J.; Fair, P.A.; et al. Genetic characterisation of Toxoplasma gondii in wildlife from North America revealed widespread and high prevalence of the fourth clonal type. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, É.; Jokelainen, P.; Sharma, R.; Fenton, H.; Jenkins, E.J. Toxoplasmosis in northern regions. In Arctic One Health: Challenges for Northern Animals and People; Tryland, M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 297–314. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, E.; Lemmen, D.S. Canada’s Changing Climate Report; Government of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2019; p. 444.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).