Fibrinolytic Enzyme from Green Microalgae: A New Potential Drug for Thrombolytic Therapy?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture Media and Growth Conditions
2.2. Kinetic Parameters
2.3. Fibrinolytic Enzyme Extraction
2.4. Precipitation Methods
2.5. Protein Purification
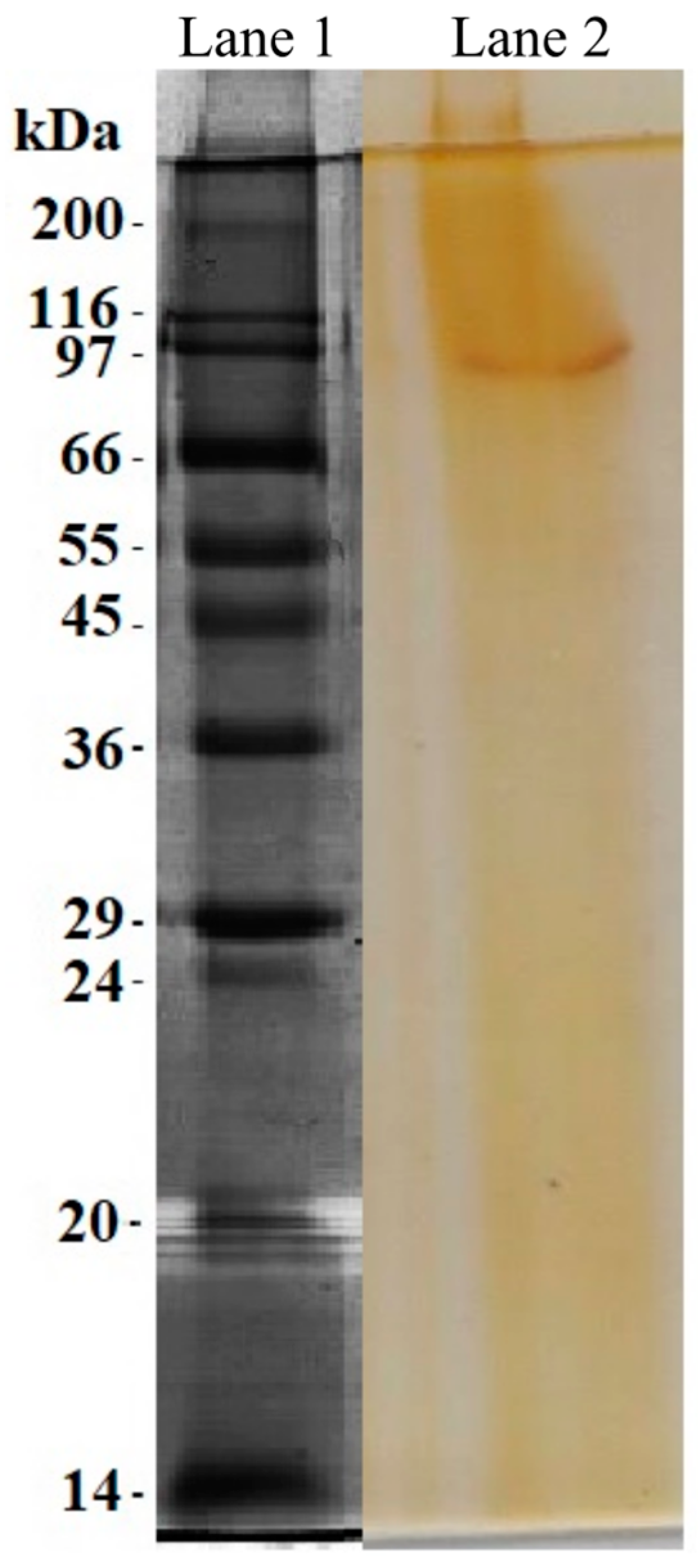
2.6. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
2.7. Protein Concentration Analysis
2.8. Protease Activity Assay
2.9. Determination of Fibrinolytic Enzyme
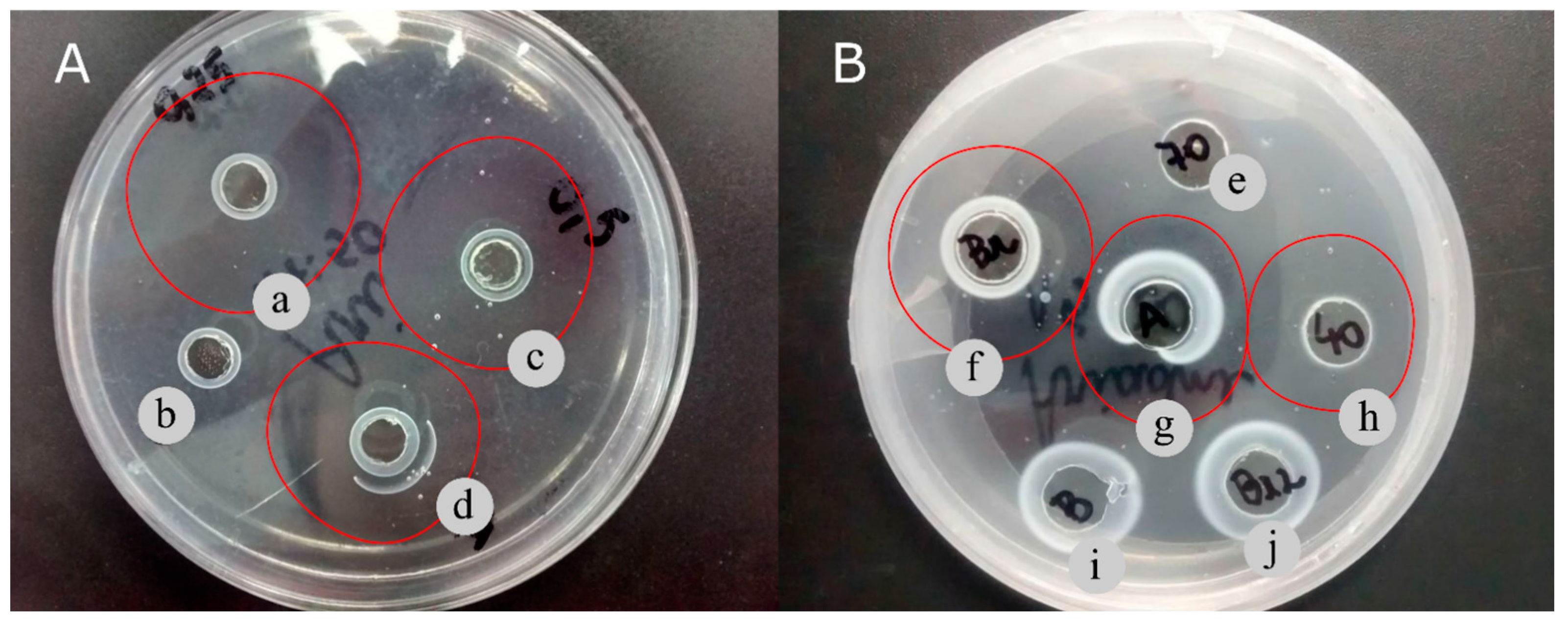
2.9.1. Fibrinolytic Plate Assay
2.9.2. Fibrinolytic Assay Using Spectrophotometry
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cell Growth Profile and Kinetic Parameters of T. obliquus Cultivation under Different Growth Conditions
3.2. Protease and Fibrinolytic Productions
3.3. Effect of Extraction Methods on the Enzymatic Activities
3.4. Effect of Precipitation Methods on the Enzymatic Activities
3.5. Fibrinolytic Activity in Fibrin Plate
3.6. Enzyme Purification
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization, Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs). 2021. Available online: Https://Www.Who.Int/News-Room/Fact-Sheets/Detail/Cardiovascular-Diseases-(Cvds) (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Zhao, L.; Lin, X.; Fu, J.; Zhang, J.; Tang, W.; He, Z. A Novel Bi-Functional Fibrinolytic Enzyme with Anticoagulant and Thrombolytic Activities from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus versicolor ZLH-1. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendelboe, A.M.; Raskob, G.E. Global Burden of Thrombosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metharom, P.; Berndt, M.C.; Baker, R.I.; Andrews, R.K. Current State and Novel Approaches of Antiplatelet Therapy. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, Q.; Singh, P.; Abid, M.; Jairajpuri, M.A. Limitations of conventional anticoagulant therapy and the promises of non-heparin based conformational activators of antithrombin. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2012, 34, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Yu, B.; Chen, G.; Liang, Z. Purification and Characterization of a Fibrinolytic Enzyme from Marine Bacillus velezensis Z01 and Assessment of Its Therapeutic Efficacy In Vivo. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa e Silva, P.E.; de Barros, R.C.; Albuquerque, W.W.C.; Brandão, R.M.P.; Bezerra, R.P.; Porto, A.L.F. In vitro thrombolytic activity of a purified fibrinolytic enzyme from Chlorella vulgaris. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1092, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Barros, P.D.S.; da Costa e Silva, P.E.; Nascimento, T.P.; Costa, R.M.P.B.; Bezerra, R.P.; Porto, A.L.F. Fibrinolytic enzyme from Arthrospira platensis cultivated in medium culture supplemented with corn steep liquor. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3446–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DA Silva, T.A.; Silva, P.E.D.C.E.; Nascimento, T.P.; Costa, R.M.; Converti, A.; Porto, A.L.F.; Bezerra, R.P. Cost-effective fibrinolytic enzyme production by microalga Dunaliella tertiolecta using medium supplemented with corn steep liquor. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências 2023, 95, e20220552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Júnior, J.N.; De Aguiar, E.M.; Mota, R.A.; Bezerra, R.P.; Porto, A.L.F.; Herculano, P.N.; Marques, D.A.V. Antimicrobial Activity of Photosynthetic Microorganisms Biomass Extract against Bacterial Isolates Causing Mastitis. J. Dairy Vet. Sci. 2019, 10, 555788. [Google Scholar]
- Marrez, D.A.; Naguib, M.M.; Sultan, Y.Y.; Higazy, A.M. Antimicrobial and anticancer activities of Scenedesmus obliquus metabolites. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, A.P.; Habibi, K.; Bijarpas, Z.K.; Tolami, H.F.; Alkinani, T.A.; Jameh, M.; Dehkaei, A.A.; Monhaser, S.K.; Daemi, H.B.; Mahmoudi, A.; et al. Cytotoxic Effect of a Novel GaFe2O4@Ag Nanocomposite Synthesized by Scenedesmus obliquus on Gastric Cancer Cell Line and Evaluation of BAX, Bcl-2 and CASP8 Genes Expression. J. Clust. Sci. 2023, 34, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.J.; Janssen, M.; Südfeld, C.; D’adamo, S.; Wijffels, R.H. Hypes, hopes, and the way forward for microalgal biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 452–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morillas-España, A.; Villaró, S.; Ciardi, M.; Acién, G.; Lafarga, T. Production of Scenedesmus almeriensis Using Pilot-Scale Raceway Reactors Located inside a Greenhouse. Phycology 2022, 2, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.; Cerqueira, K.; Rodrigues, J.; Silva, K.; Coelho, D.; Souza, R. Cultivation of Microalgae Chlorella vulgaris in Open Reactor for Bioethanol Production. Phycology 2023, 3, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentahar, J.; Doyen, A.; Beaulieu, L.; Deschênes, J.-S. Investigation of β-galactosidase production by microalga Tetradesmus obliquus in determined growth conditions. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecka, A.; Nawrocka, A.; Wiącek, D.; Krzemińska, I. Agro-industrial by-product in photoheterotrophic and mixotrophic culture of Tetradesmus obliquus: Production of ω3 and ω6 essential fatty acids with biotechnological importance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lim, D.; Lee, D.; Yu, J.; Lee, T. Valorization of corn steep liquor for efficient paramylon production using Euglena gracilis: The impact of precultivation and light-dark cycle. Algal Res. 2022, 61, 102587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiani, M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Farhangi, A.; Mehrabi, M.R. Production of Desferrioxamine B (Desferal) using Corn Steep Liquor in Streptomyces pilosus. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2010, 13, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.M.; Stanier, R.Y. Growth and division of some unicellular blue-greenalgae. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1968, 51, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.J.; Cavalcanti, V.L.R.; Porto, A.L.F.; Gama, W.A.; Brandão-Costa, R.M.P.; Bezerra, R.P. The green microalgae Tetradesmus obliquus (Scenedesmus acutus) as lectin source in the recognition of ABO blood type: Purification and characterization. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liggett, R.W.; Koffler, H. Corn steep liquor in microbiology. Bacteriol. Rev. 1948, 12, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, K.; Hori, K.; Matsuura, Y.; Miyazawa, K. Purification and characterization of a fibrinolytic enzyme and identification of fibrinogen clotting enzyme in a marine green alga, Codium divaricatum. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 125, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Alencar, R.B.; Biondi, M.M.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Vieira, V.L.A.; Carvalho, L.B.; Bezerra, R.S. Alkaline proteases from digestive tract of four tropical fishes. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2003, 6, 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Astrup, T.; Müllertz, S. The fibrin plate method for estimating fibrinolytic activity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1952, 40, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-L.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Liang, T.-W. Purification and biochemical characterization of a nattokinase by conversion of shrimp shell with Bacillus subtilis TKU007. New Biotechnol. 2011, 28, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Mirzaie, M.A.; Kalbasi, M.; Mousavi, S.M.; Ghobadian, B. Statistical evaluation and modeling of cheap substrate-based cultivation medium of Chlorella vulgaris to enhance microalgae lipid as new potential feedstock for biolubricant. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 46, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbib, Z.; Ruiz, J.; Álvarez-Díaz, P.; Garrido-Pérez, C.; Barragan, J.; Perales, J.A. Photobiotreatment: Influence of nitrogen and phosphorus ratio in wastewater on growth kinetics of Scenedesmus obliquus. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2013, 15, 774–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, A.; Hauer, S.; Kroll, P.; Fricke, J.; Herwig, C. In-depth characterization of the raw material corn steep liquor and its bioavailability in bioprocesses of Penicillium chrysogenum. Process. Biochem. 2018, 70, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi-Shotorkhoft, A.; Sharifi, A.; Mirmohammadi, D.; Baluch-Gharaei, H.; Rezaei, J. Effects of feeding different levels of corn steep liquor on the performance of fattening lambs. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 100, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.-H.; Ko, D.-J.; Heo, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-J.; Kim, Y.-M.; Lee, B.-S.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, C.-H.; Seo, J.-W.; Oh, B.-R. Regulation of lipid accumulation using nitrogen for microalgae lipid production in Schizochytrium sp. ABC101. Renew. Energy 2020, 153, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, D.; Lim, D.; Lim, S.; Park, S.; Kang, C.; Yu, J.; Lee, T. Paramylon production from heterotrophic cultivation of Euglena gracilis in two different industrial byproducts: Corn steep liquor and brewer’s spent grain. Algal Res. 2020, 47, 101826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.S.; Rebecca, L.J. Isolation and Characterization of Protease from Marine Algae. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2014, 27, 188–190. [Google Scholar]
- Niccolai, A.; Chini Zittelli, G.; Rodolfi, L.; Biondi, N.; Tredici, M.R. Microalgae of interest as food source: Biochemical composition and digestibility. Algal Res. 2019, 42, 101617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaakob, M.A.; Mohamed, R.M.S.R.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Aswathnarayana Gokare, R.; Ambati, R.R. Influence of Nitrogen and Phosphorus on Microalgal Growth, Biomass, Lipid, and Fatty Acid Production: An Overview. Cells 2021, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukor, N.F.; Jusoh, R.; Kamarudin, N.S.; Abdul Halim, N.A.; Sulaiman, A.Z.; Abdullah, S.B. Synergistic effect of probe sonication and ionic liquid for extraction of phenolic acids from oak galls. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 62, 104876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjha, M.M.A.N.; Irfan, S.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Shafique, B.; Kanwal, R.; Pateiro, M.; Arshad, R.N.; Wang, L.; Nayik, G.A.; Roobab, U.; et al. Sonication, a Potential Technique for Extraction of Phytoconstituents: A Systematic Review. Processes 2021, 9, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, A.; Rimauro, J.; Casella, P.; Cerbone, A.; Larocca, V.; Chianese, S.; Karatza, D.; Mehariya, S.; Ferraro, A.; Hristoforou, E.; et al. Extraction of astaxanthin from microalga Haematococcus pluvialis in red phase by using generally recognized as safe solvents and accelerated extraction. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 283, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickerson, J.L.; Doucette, A.A. Rapid and Quantitative Protein Precipitation for Proteome Analysis by Mass Spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 2035–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongpia, A.; Mahatheeranont, S.; Lomthaisong, K.; Niamsup, H. Evaluation of Sample Preparation Methods from Rice Seeds and Seedlings Suitable for Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 1035–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa e Silva, P.E.; Bezerra, R.P.; Porto, A.L.F. An overview about fibrinolytic enzymes from microorganisms and algae: Production and characterization. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-W.; Sapkota, K.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-J. Direct acting anti-thrombotic serine protease from brown seaweed Costaria costata. Process. Biochem. 2013, 48, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Sapkota, K.; Park, S.-E.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-J. Thrombolytic, anticoagulant and antiplatelet activities of codiase, a bi-functional fibrinolytic enzyme from Codium fragile. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-R.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, D.-W.; Park, S.-E.; Sapkota, K.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-J. A bifunctional protease from green alga Ulva pertusa with anticoagulant properties: Partial purification and characterization. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzkar, N.; Jahromi, S.T.; Vianello, F. Marine Microbial Fibrinolytic Enzymes: An Overview of Source, Production, Biochemical Properties and Thrombolytic Activity. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heide, H.; Kalisz, H.M.; Follmann, H. The oxygen evolving enhancer protein 1 (OEE) of photosystem II in green algae exhibits thioredoxin activity. J. Plant Physiol. 2004, 161, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Growth Conditions | Xm (mg·L−1) | Px (mg∙L−1∙day−1) | µmax (day−1) | Methods | Total Protein (mg∙mL−1) | Protease Activity (U∙mg−1) | Fibrinolytic Activity (U∙mg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autotrophic | 1970 ± 231 a | 112 ± 13.5 a | 0.19 ± 0.03 a | Homogenization | 0.93 ± 0.00 a | 12.5 ± 1.35 a | 430 ± 40.2 a |
| Sonication | 2.99 ± 0.50 b | 4.50 ± 0.40 a | 149 ± 3.8 b | ||||
| Mixotrophic (CSL 0.25%) | 1625 ± 207 a | 130 ± 12.8 a | 0.17 ± 0.00 a | Homogenization | 0.86 ± 0.00 a | 12.5 ± 2.94 a | 391 ± 40.0 a |
| Sonication | 3.32 ± 0.22 b | 84.7 ± 3.51 b | 243 ± 11.5 c | ||||
| Mixotrophic (CSL 0.50%) | 936 ± 82.8 b | 93.4 ± 10.9 a | 0.12 ± 0.00 a | Homogenization | 2.90 ± 0.09 b | 4.64 ± 3.06 a | 130 ± 1.0 b |
| Sonication | 2.76 ± 0.14 b | 5.85 ± 3.68 a | 135 ± 7.0 b |
| Precipitating Agents | Volume (mL) | Total Protein (mg) | Total Protease Activity (U) | Specific Protease Activity (U∙mg−1) | P.F | Yield (%) | Total Fibrinolytic Activity (U) | Specific Fibrinolytic Activity (U∙mg−1) | P.F | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell extract | 50 | 23.3 ± 1.2 a | 4740 ± 1039 a | 203 ± 56.3 a | 100 | 11,520 ± 1420 a | 494 ± 86.1 a | 100 | ||
| Ammonium sulfate (0–40%) | 40 | 4.80 ± 0.00 b | 3144 ± 332 b | 655 ± 69.3 b | 3.22 | 66.3 | 3000 ± 97 b | 625 ± 20.2 a,b | 1.26 | 26.0 |
| Ammonium sulfate (40–70%) | 40 | 5.20 ± 1.38 b | 3240 ± 72 b | 623 ± 192 b | 3.06 | 68.3 | 2448 ± 0 b | 470 ± 157 b | 0.95 | 21.7 |
| Acetone | 40 | 16.4 ± 0.9 c | 3384 ± 125 c | 206 ± 17.5 a | 1.01 | 71.3 | 9312 ± 396 c | 567 ± 49.3 a,b | 1.14 | 80.3 |
| Purification Step | Volume (mL) | Total Protein (mg) | Total Protease Activity (U) | Specific Protease Activity (U∙mg−1) | P.F | Yield (%) | Total Fibrinolytic Activity (U) | Specific Fibrinolytic Activity (U∙mg−1) | P.F | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell extract | 50 | 23.3 ± 1.2 a | 4740 ± 1039 a | 203 ± 56.3 a | 100 | 11,520 ± 1420 a | 494 ± 86.1 a | 100 | ||
| Acetone precipitation | 40 | 16.4 ± 0.9 b | 3384 ± 125 a | 206 ± 17.5 a | 1.01 | 71.3 | 9312 ± 396 b | 567 ± 49.3 b | 1.14 | 80.8 |
| DEAE-Sephadex | 4.5 | 0.84 ± 0.02 c | 297 ± 4.2 b | 353 ± 12.4 b | 1.73 | 6.26 | 1026 ± 0 c | 1221 ± 31 c | 2.47 | 8.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moura, Y.A.S.; De Souza, A.T.V.; Da Costa e Silva, P.E.; Da Silva, M.M.; Porto, A.L.F.; Bezerra, R.P. Fibrinolytic Enzyme from Green Microalgae: A New Potential Drug for Thrombolytic Therapy? Phycology 2023, 3, 436-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040029
Moura YAS, De Souza ATV, Da Costa e Silva PE, Da Silva MM, Porto ALF, Bezerra RP. Fibrinolytic Enzyme from Green Microalgae: A New Potential Drug for Thrombolytic Therapy? Phycology. 2023; 3(4):436-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040029
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoura, Yanara Alessandra Santana, Ariadne Tennyle Vieira De Souza, Páblo Eugênio Da Costa e Silva, Marllyn Marques Da Silva, Ana Lúcia Figueiredo Porto, and Raquel Pedrosa Bezerra. 2023. "Fibrinolytic Enzyme from Green Microalgae: A New Potential Drug for Thrombolytic Therapy?" Phycology 3, no. 4: 436-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040029
APA StyleMoura, Y. A. S., De Souza, A. T. V., Da Costa e Silva, P. E., Da Silva, M. M., Porto, A. L. F., & Bezerra, R. P. (2023). Fibrinolytic Enzyme from Green Microalgae: A New Potential Drug for Thrombolytic Therapy? Phycology, 3(4), 436-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040029






