A Model-Based Method Applying Sliding Mode Methodology for SynRM Sensorless Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
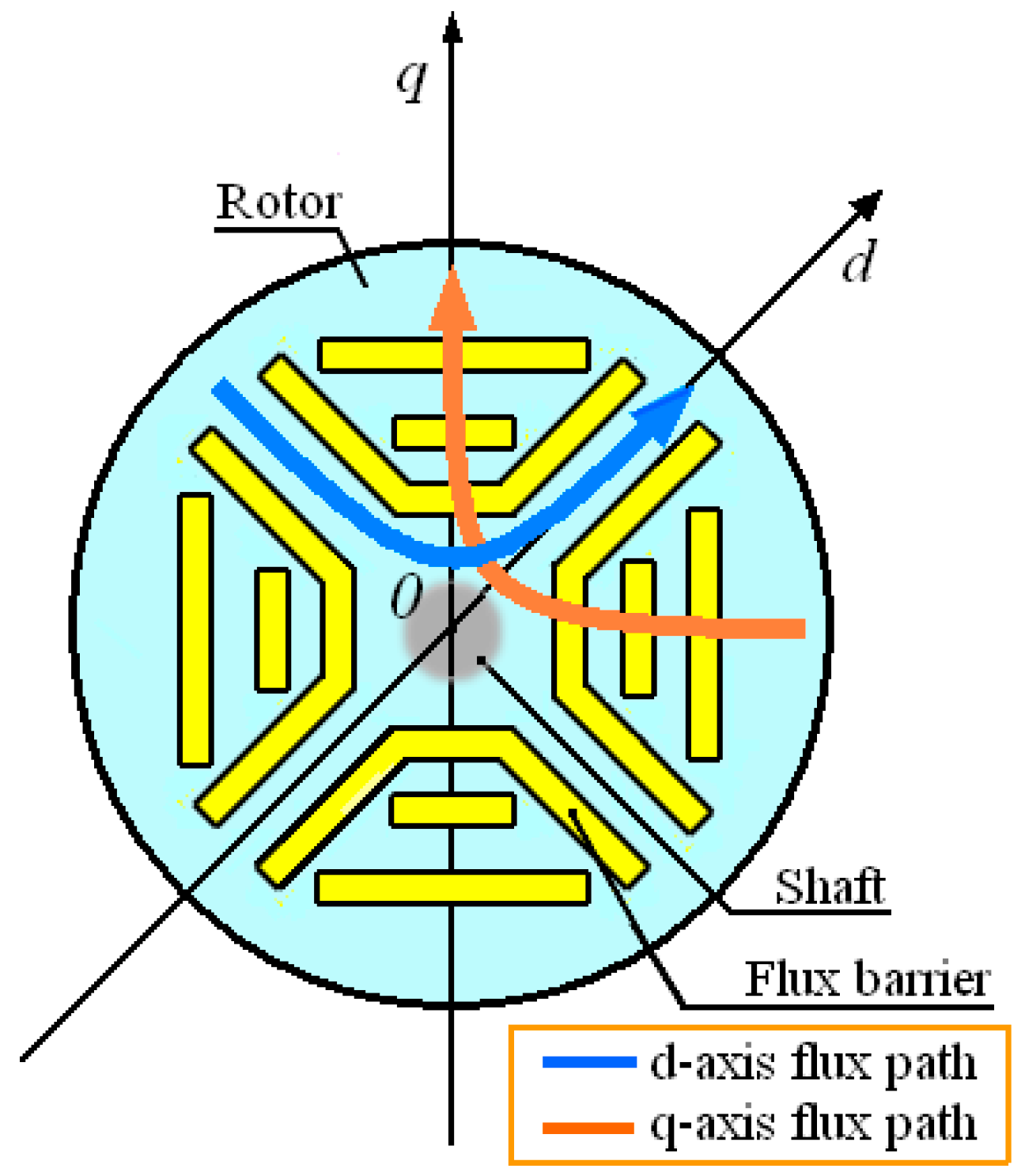
2. Analysis of the Modified SynRM Model in the γδ-Estimated Rotating Frame
2.1. Voltage and Flux/Current Model of SynRM, and Modified Rotor Flux in the dq Synchronous Rotating Frame
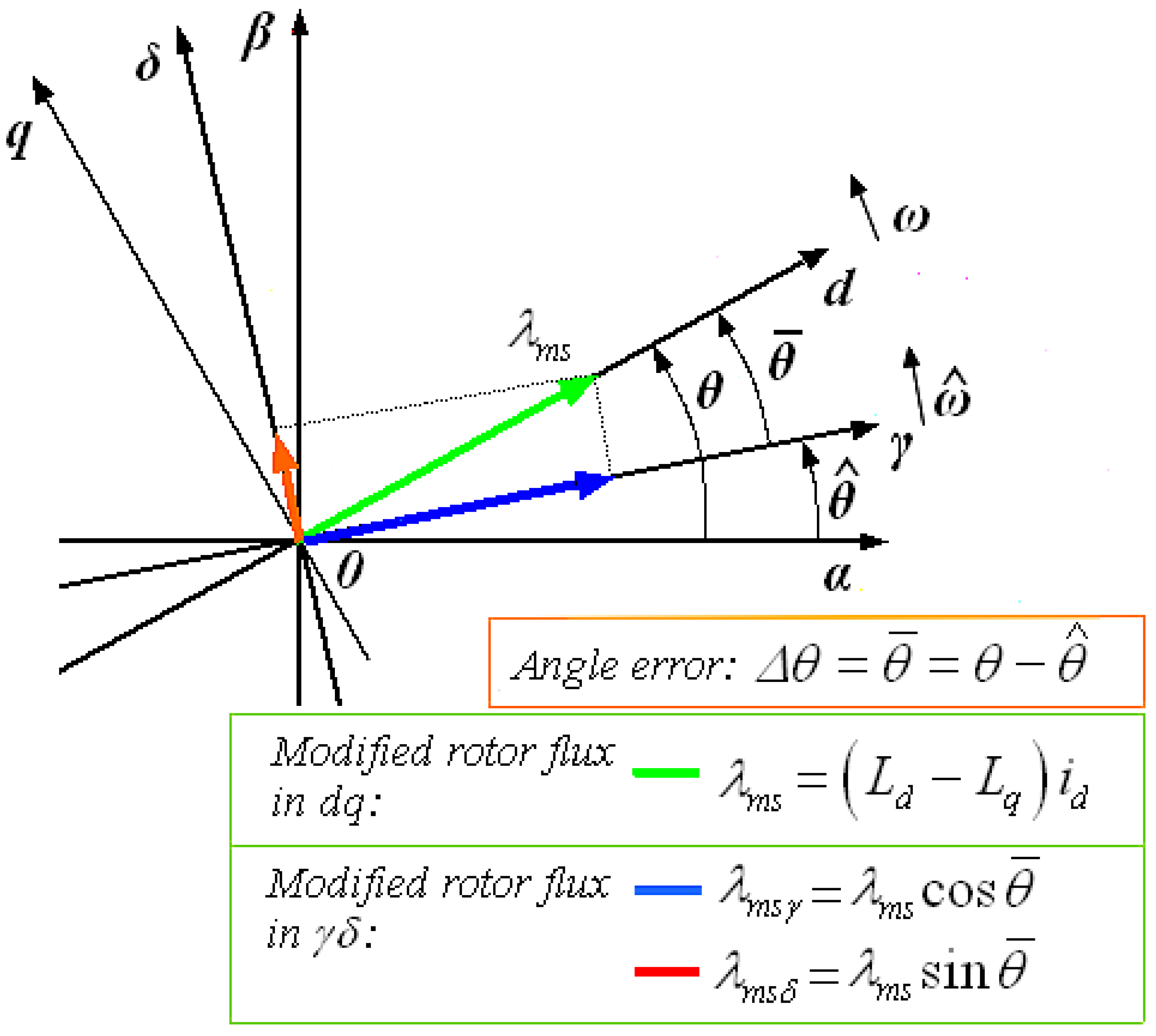
2.2. Modified SynRM Voltage and the Flux/Current Model in the Estimated Reference Frame γδ
2.3. Analysis of Modified Rotor Flux in γδ Reference Frame
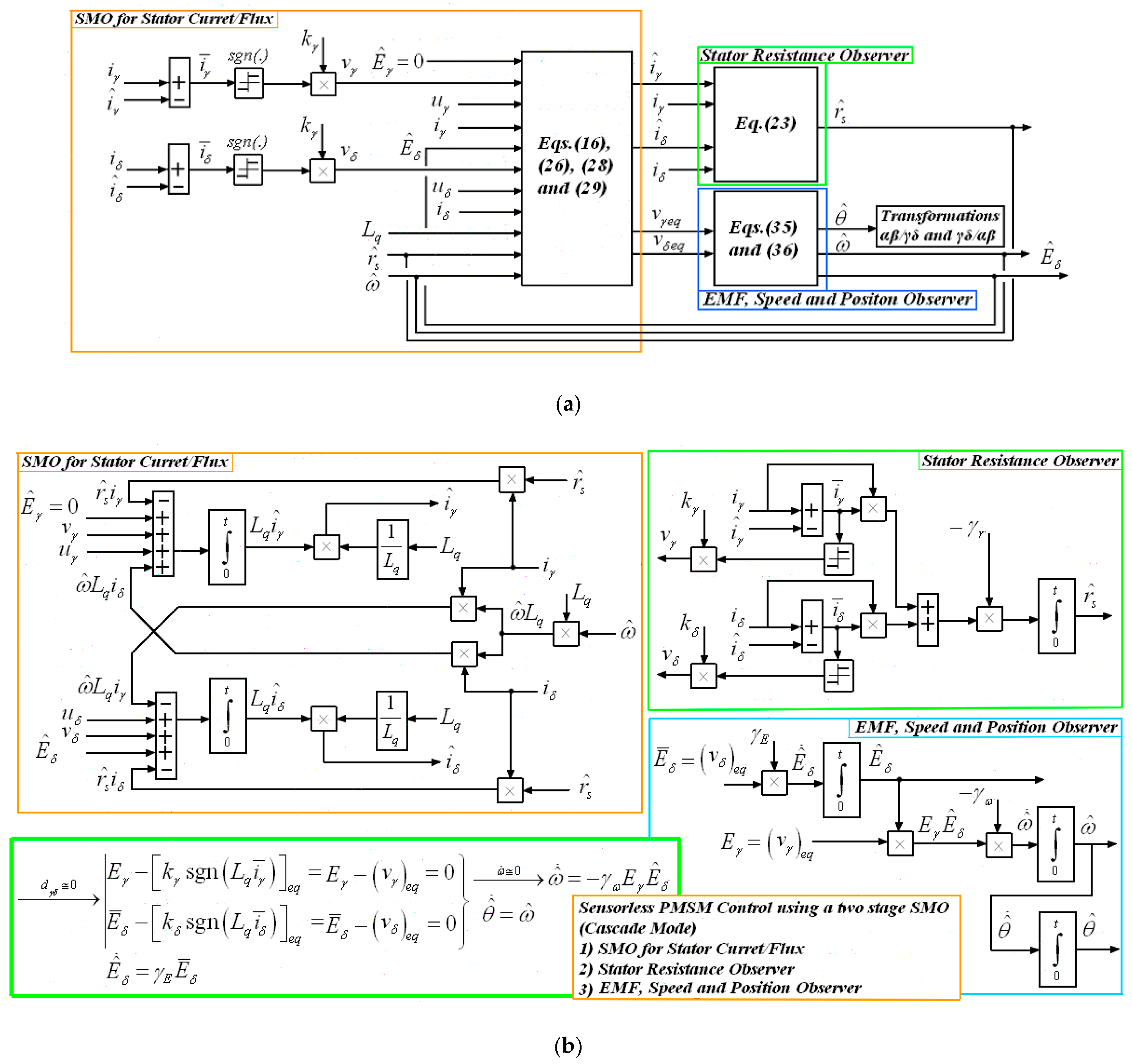
3. Flux/Current Observer Based on Sliding Mode and Equivalent Control Methodologies
3.1. Design of Flux/Current Observer
3.2. Observer Dynamics and Stability in the Sense of Lyapunov
3.3. Sliding Mode Observer and Equivalent Control Inputs
4. Modified EMF Observer for Estimating the Speed and Position of SynRM
4.1. Design of Modified EMF Observer for Speed and Position
4.2. Stability of the Modified EMF Observer
4.3. Speed and Position Estimation
5. Simulation Results
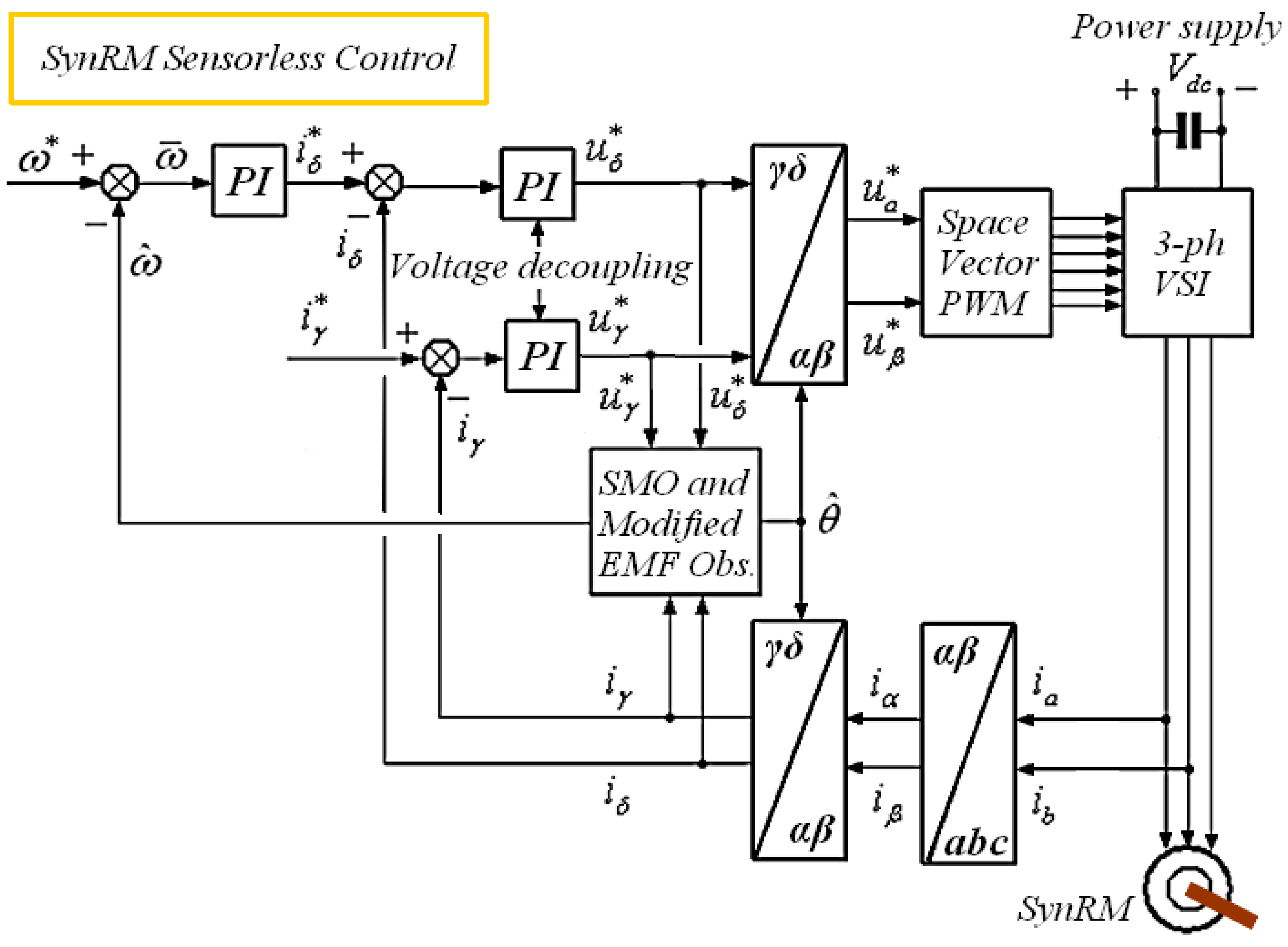
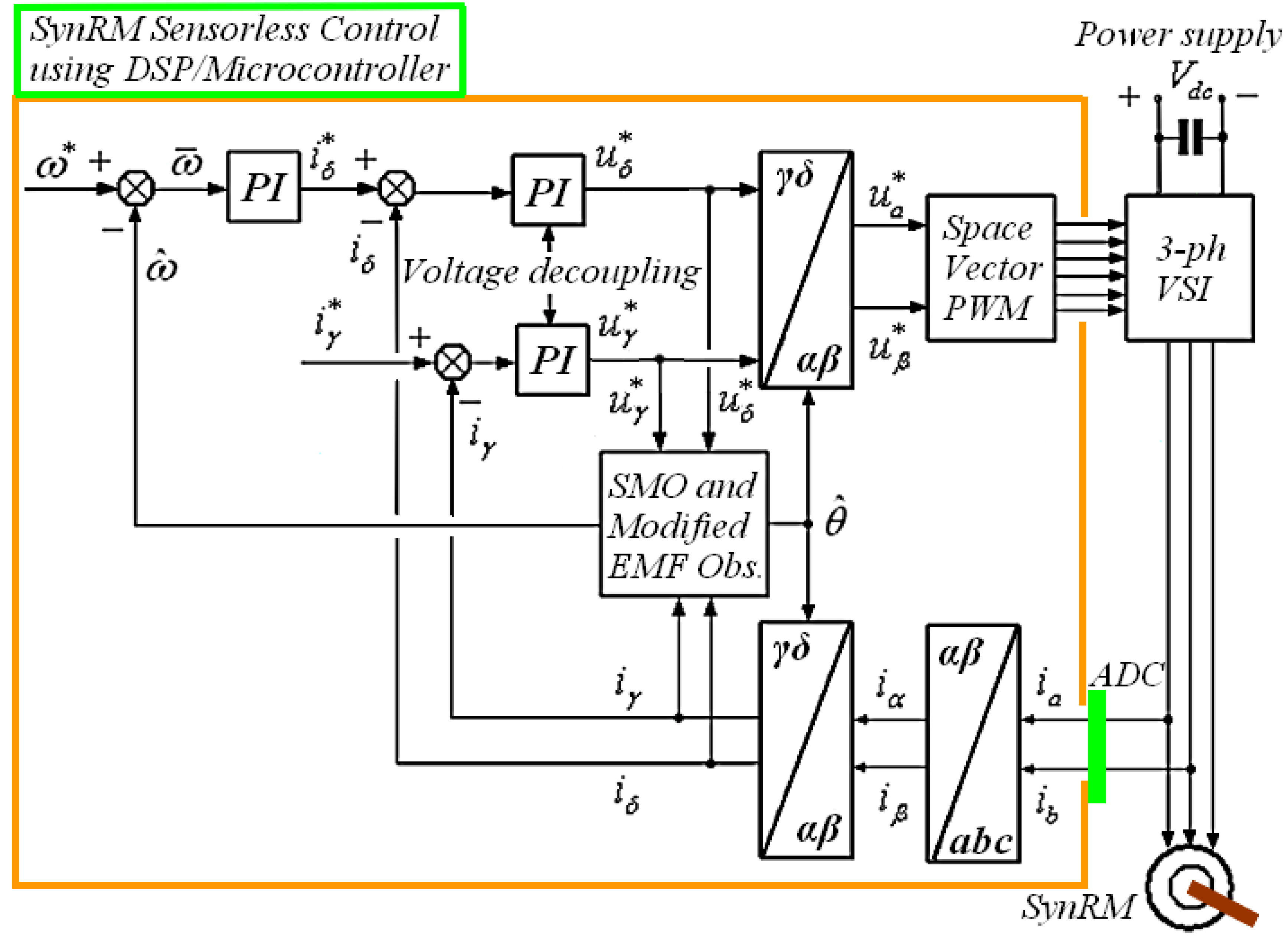
5.1. Description of the Controller–Observer System, Simulated SynRM Model, and Voltage Source Inverter (VSI)
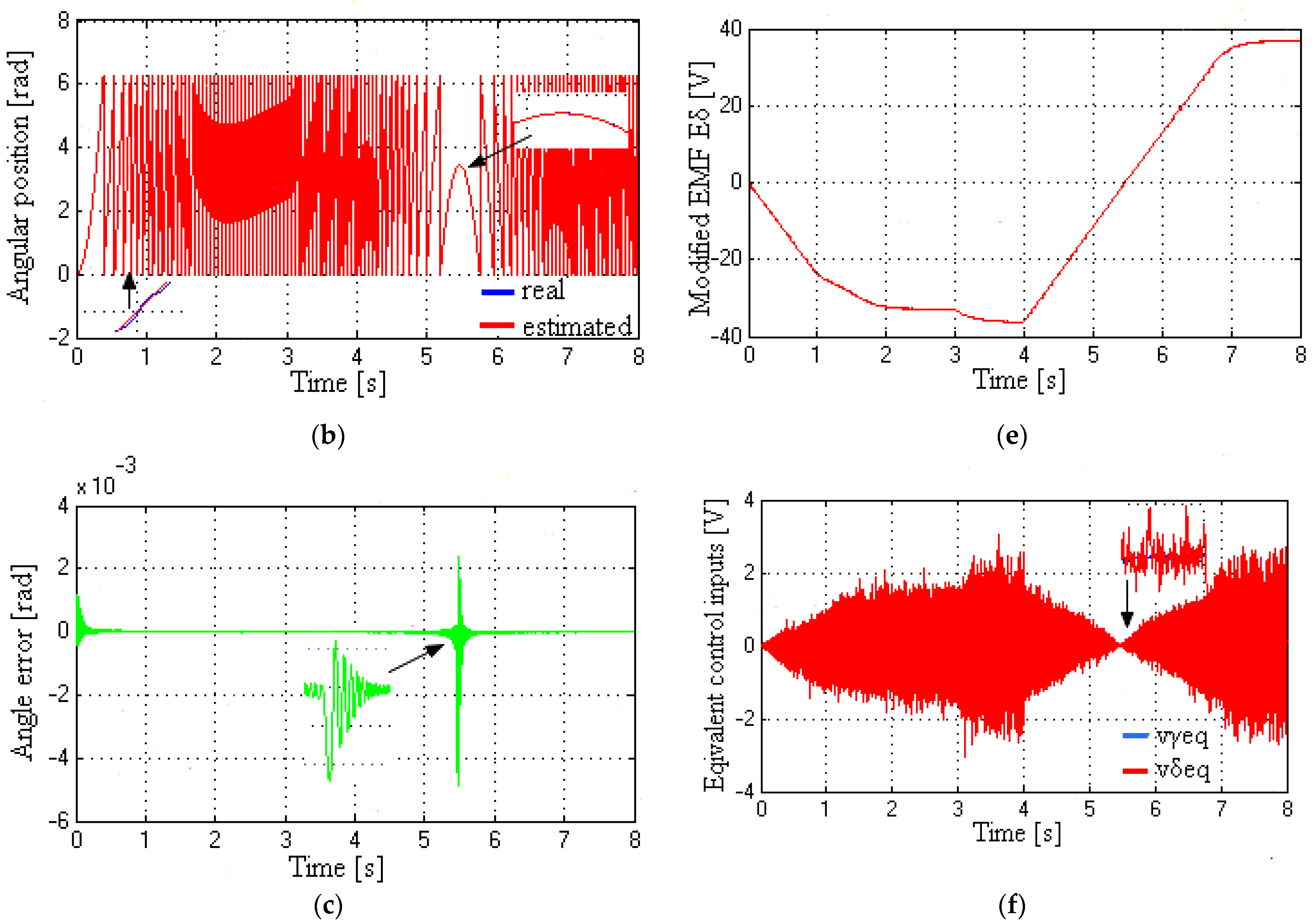
5.2. SMO and EMF Observer Response at Low Speed and Standstill
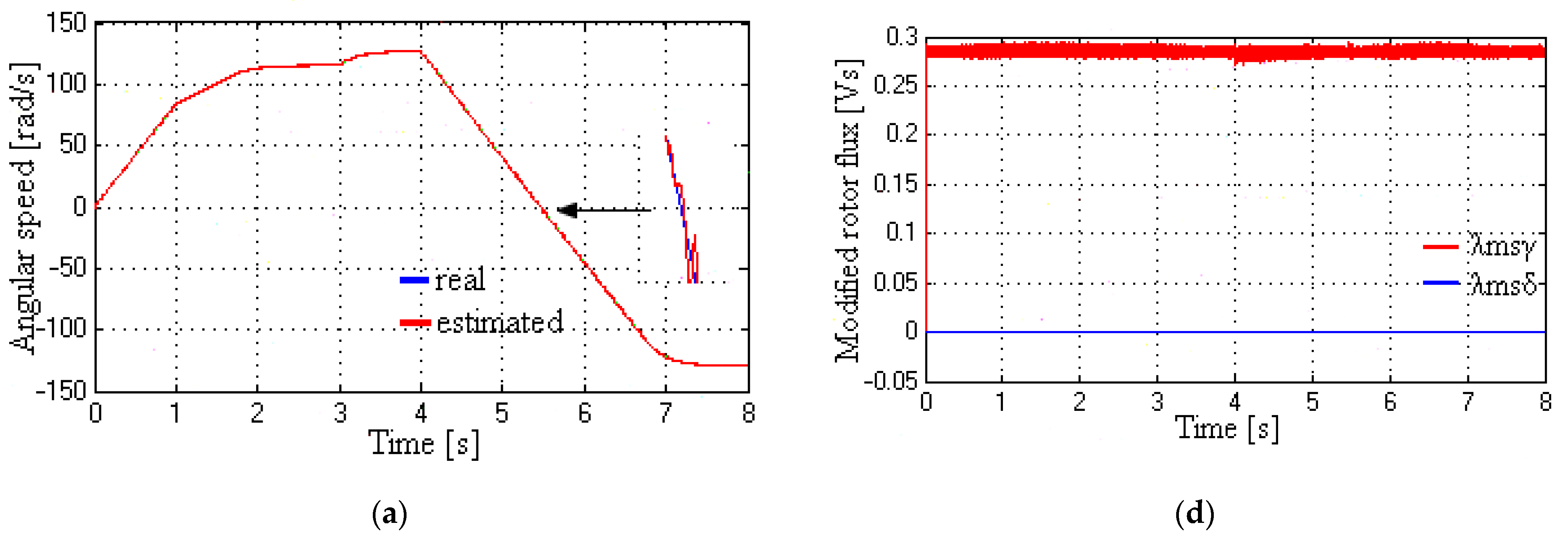
5.3. Modified Rotor Flux and EMF Observer Response at Medium Speed
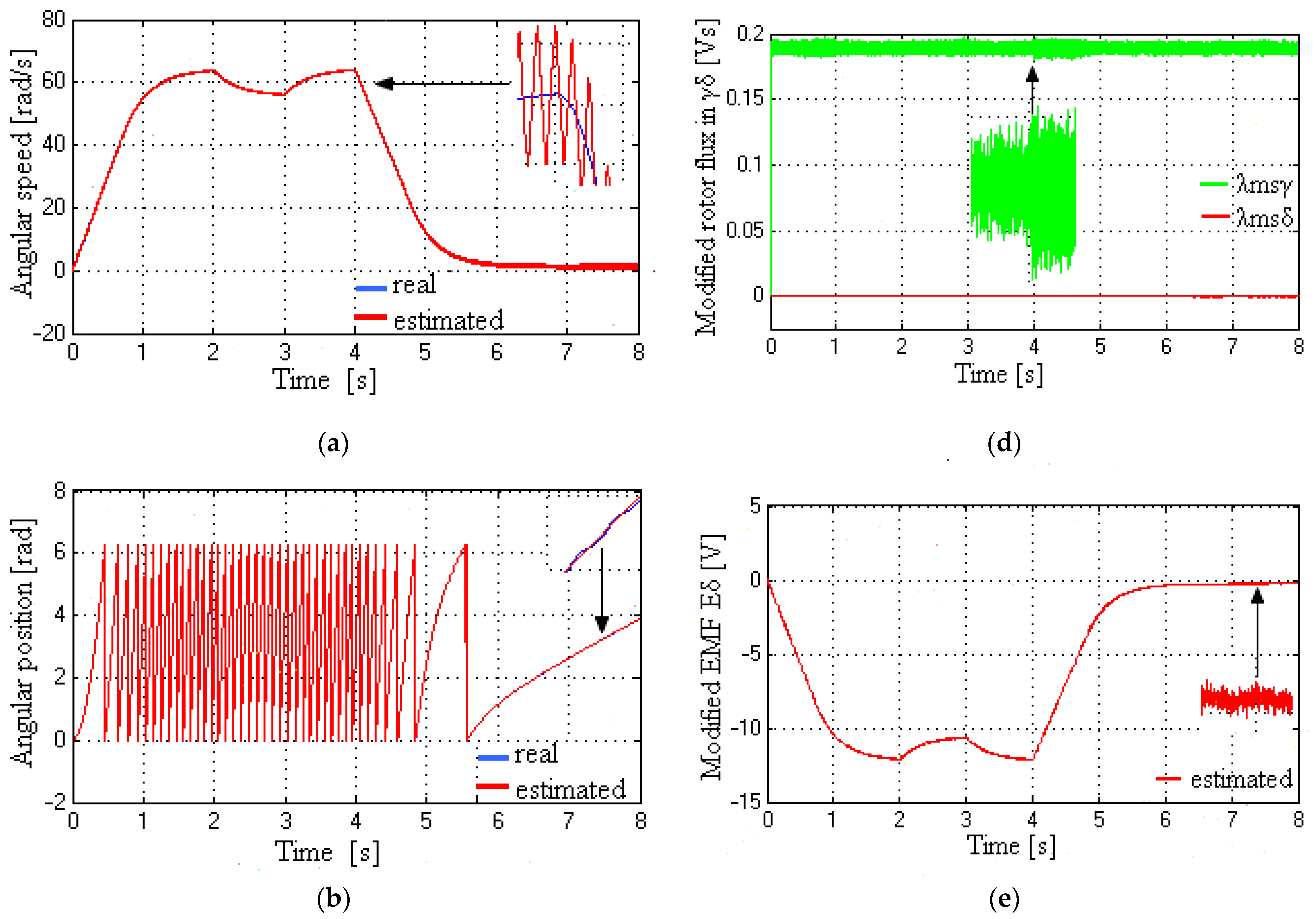
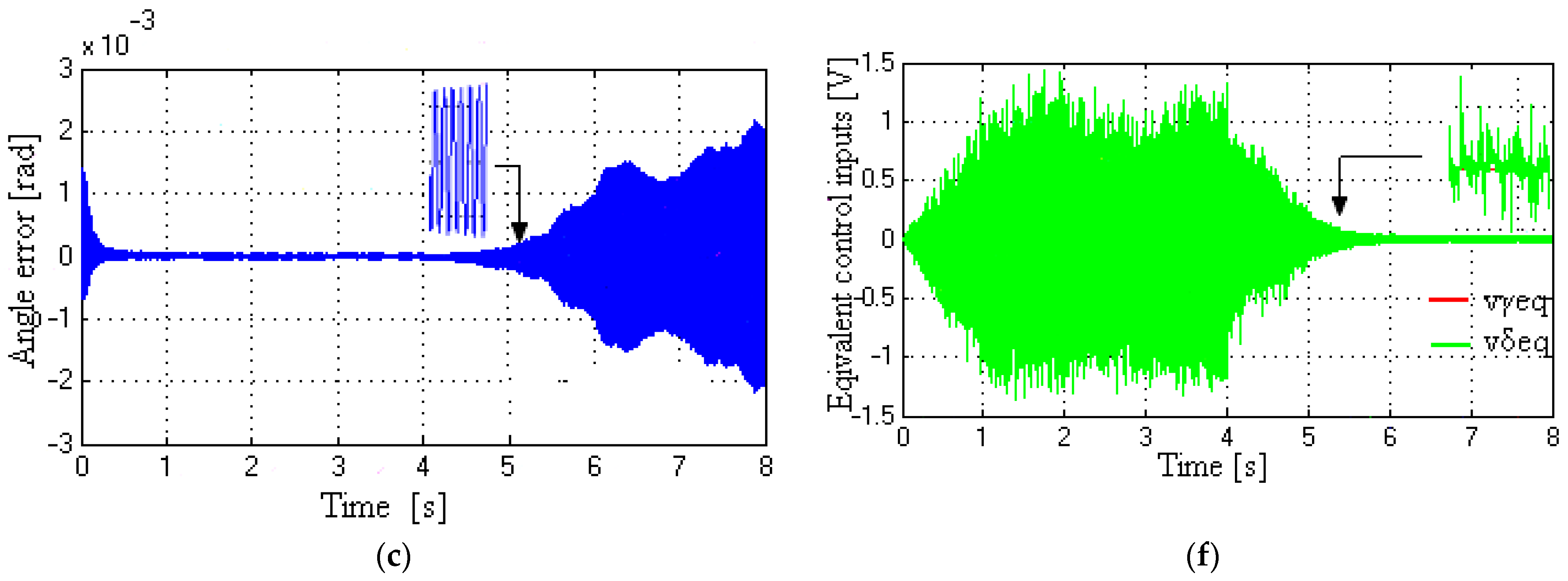
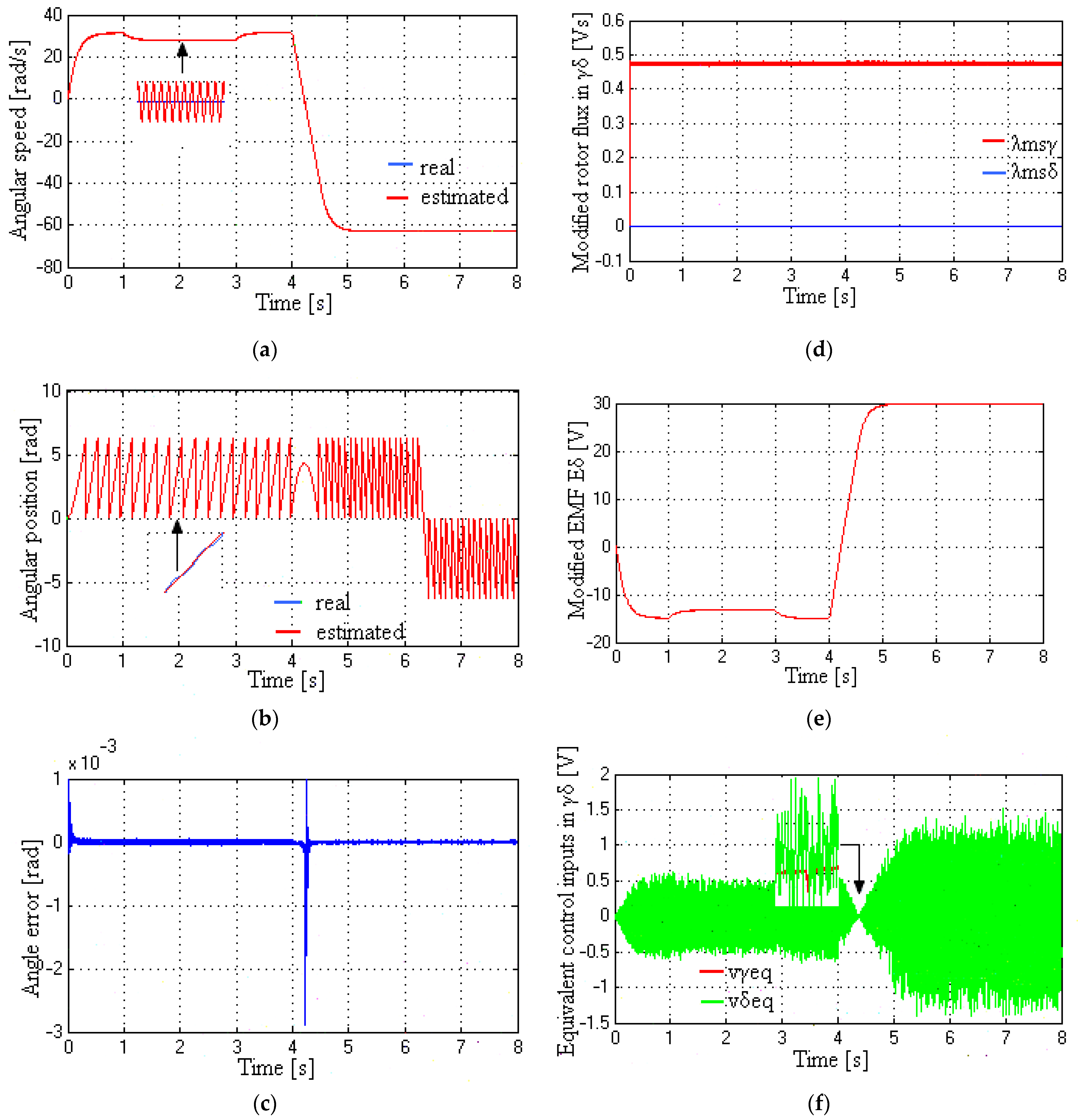
5.4. Speed, Angle, Modified Rotor Flux, Modified EMF, and Control Inputs at Very Low to Medium Speeds
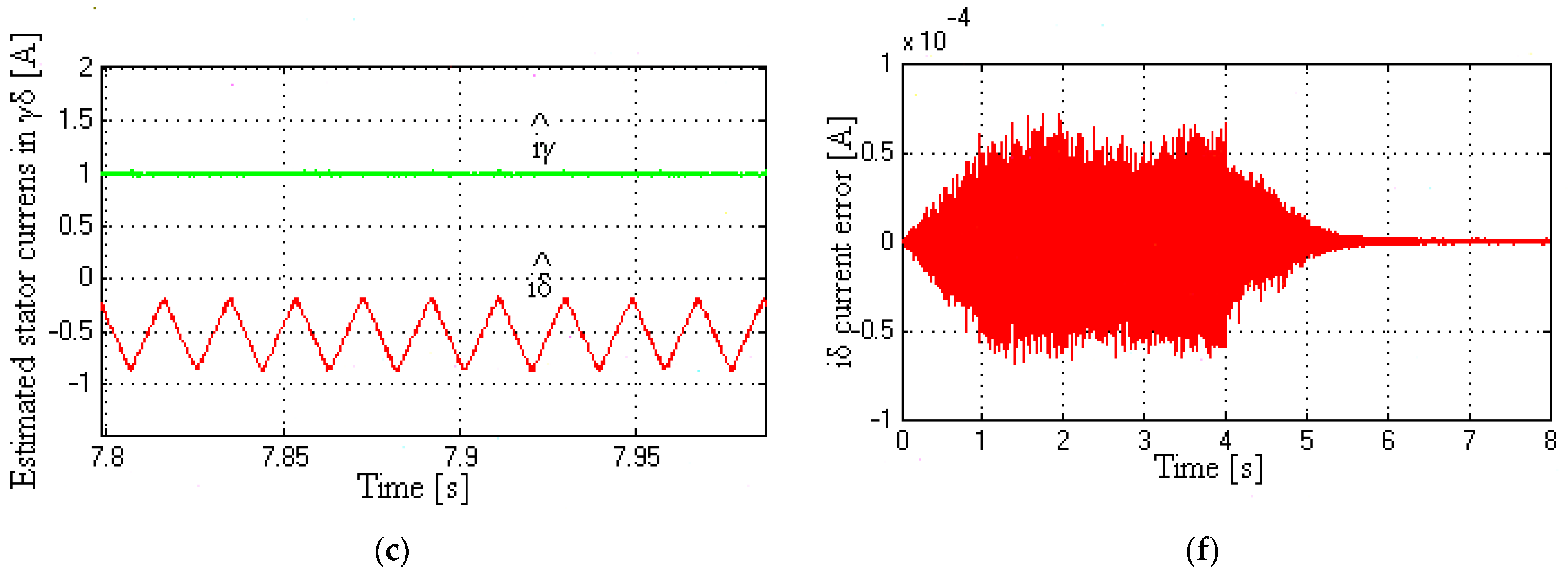
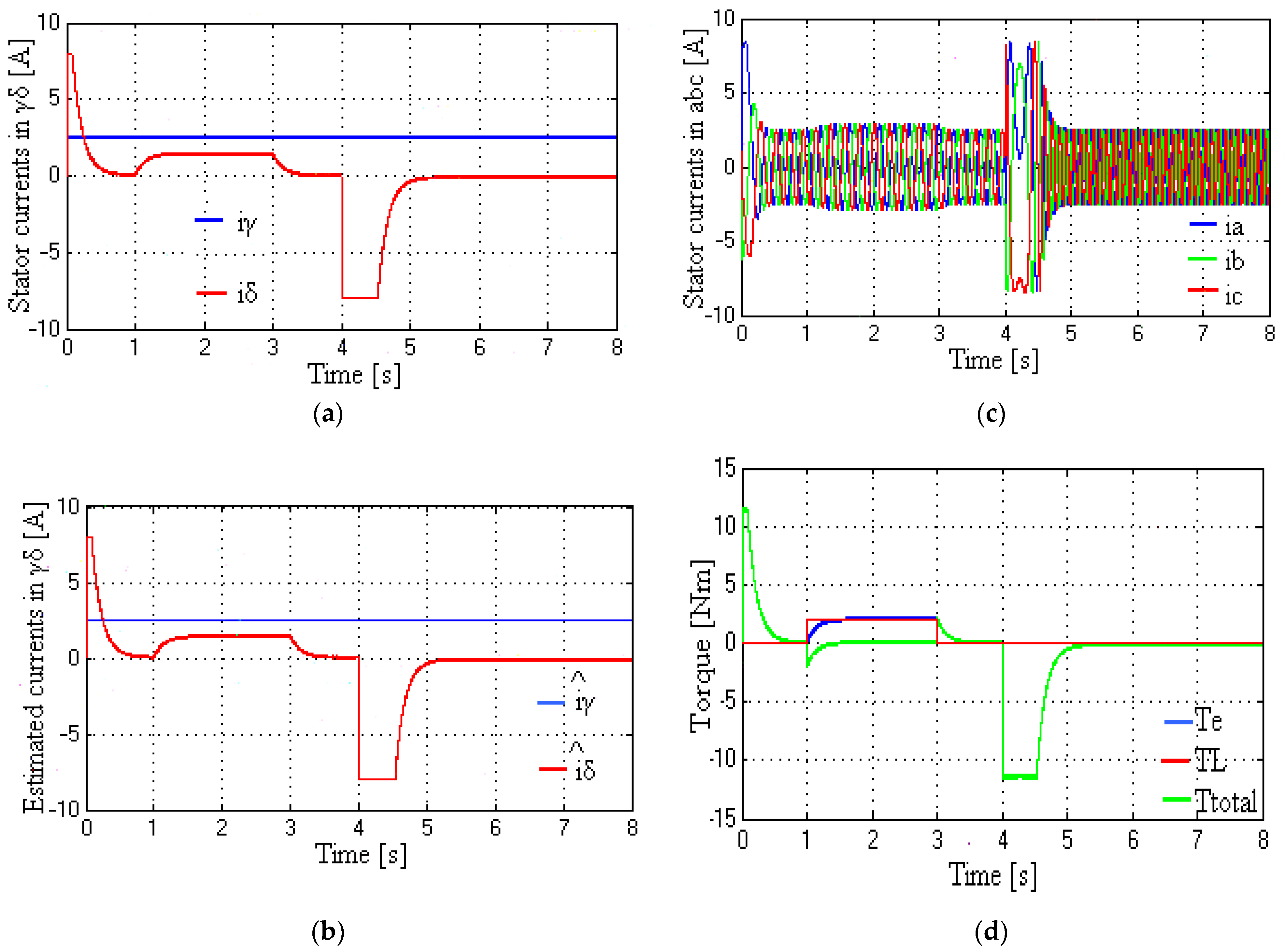
5.5. Responses of Stator Currents (Real and Estimated) and Torque Response at Very Low to Medium Speeds
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Notation
| ud, uq | dq axis stator voltages |
| id, iq | dq axis stator currents |
| λd, λq | dq axis stator magnetic fluxes |
| Ld, Lq | dq axis inductances |
| λms = (Ld − Lq)id | modified rotor magnetic flux due to the saliency and id current |
| rs | stator resistance |
| uγ, uδ | γδ axis stator voltages |
| iγ, iδ | γδ axis stator currents |
| λγ, λδ | γδ axis stator magnetic fluxes |
| λmsγδ | γδ axis of modified rotor magnetic flux |
| p | number of pole pairs |
| θ = θe | electrical angular position |
| ω = ωe | electrical angular speed |
References
- Lipo, T.A.; Miller, T.J.; Vagati, A.; Boldea, I.; Malesani, L.; Fukao, T. Synchronous Reluctance Drives. In Proceedings of the IEEE IAS Annual Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 2–6 October 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kamper, M.J.; Volschenk, A.F. Effect of rotor dimensions and cross magnetization on Ld and Lq inductances of reluctance synchronous machine with cage less flux barrier rotor. IEE Proc. Electric Power Appl. 1994, 141, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, N.; Bolognani, S.; Bon, D.; Dai Pré, M. Rotor Flux-Barrier Design for Torque Ripple Reduction in Synchronous Reluctance and PM-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradkar, M.; Boecker, J. Design of a High Performance Ferrite Magnet-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motor for an Electric Vehicle. In Proceedings of the IECON 2012-38th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Montreal, QC, Canada, 25–28 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sanada, M.; Morimoto, S.; Tokuda, T. Influence of rotor structure on performance of permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS 2009), Tokyo, Japan, 15–18 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, N. Synchronous Reluctance and Interior Permanent Magnet Motors. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Workshop on Electrical Machines Design Control and Diagnosis (WEMDCD), Paris, France, 11–12 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.-R.; Yang, S.-C.; Hsu, Y.-L.; Li, K. Position and Speed Estimation of Permanent Magnet Machine Sensorless Drive at High Speed Using an Improved Phase-Locked Loop. Energies 2017, 10, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Huang, S.; Huang, K.; Wang, L. Sensorless Speed Control with Initial Rotor Position Estimation for Surface Mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drive in Electric Vehicles. Energies 2015, 8, 11030–11046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lorenz, R. Surface permanent-magnet machine self-Sensing at zero and low speeds using improved observer for position, velocity, and disturbance torque estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacas, M. Sensorless drives in industrial applications. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2011, 5, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staines, C.S.; Caruana, C.; Raute, R. A review of saliency-based sensorless control methods for alternating current machines. IEEJ-J. Ind. Appl. 2014, 3, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y. Improved Sensorless Control of Interior Permanent Magnet Sensorless Motors Using an Active Damping Control Strategy. Energies 2016, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piippo, A.; Salomäki, J.; Luomi, J. Signal injection in sensorless PMSM drives equipped with inverter output filter. In Proceedings of the Fourth Power Conversion Conference (PCC 2007), Nagoya, Japan, 2–5 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bolognani, S.; Calligaro, S.; Petrella, R. Design issues and estimation errors analysis of back-EMF-Based position and speed observer for SPM synchronous motors. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2014, 2, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kennel, R.M. Analysis of permanent-Magnet machine for sensorless control based on high-frequency signal injection. In Proceedings of the IEEE 7th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC 2012), Harbin, China, 2–5 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, O.C.; Kennel, R. Encoderless Control of Industrial Servo Drives. In Proceedings of the 12th International EPE-PEMC. Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, Portoroz, Slovenia, 30 August–1 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Tomita, M.; Ichikawa, S.; Doki, S.; Okuma, S. Sensorless control of interior permanent magnet synchronous motor by estimation of an extended electromotive force. In Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE Industry Applications Conference, Thirty-Fifth IAS Annual Meeting and World Conference on Industrial Applications of Electrical Energy (Cat. No.00CH37129), Rome, Italy, 8–12 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, S.; Kawamoto, K.; Sanada, M.; Takeda, Y. Sensorless control strategy for salient-Pole PMSM based on extended EMF in rotating reference frame. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2002, 38, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betin, F.; Capolino, G.A.; Casadei, D.; Kawkabani, B.; Bojoi, R.I.; Harnefors, L.; Levi, E.; Parsa, L.; Fahimi, B. Trends in electrical machines control samples for classical, sensorless, and fault-Tolerant techniques. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2014, 8, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidat, F.; Lecointe, J.P.; Morganti, F.; Brudny, J.F.; Jacq, T.; Streiff, F. Non Invasive Sensors for Monitoring the Efficiency of AC Electrical Rotating Machines. Sensors 2010, 10, 7874–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.C.; Tomita, M.; Doki, S.; Okuma, S. An extended electromotive force model for sensorless control of interior permanent-Magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2003, 50, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhan, H.; Zhang, G.; Gui, X.; Xu, D. Adaptive compensation method of position estimation harmonic error for EMF-based observer in sensorless IPMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 3055–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejny, R.W.; Lorenz, R.D. Evaluating the practical low-Speed limits for back-EMF tracking-Based sensorless speed control using drive stiffness as a key metric. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognani, S.; Tubiana, L.; Zigliotto, M. Extended Kalman filter tuning in sensorless PMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preindl, M.; Schaltz, E. Sensorless Model Predictive Direct Current Control Using Novel Second-Order PLL Observer for PMSM Drive Systems. Ind. Electron. IEEE Trans. 2011, 58, 4087–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trancho, E.; Ibarra, E.; Arias, A.; Salazar, C.; Lopez, I.; de Guereñu, A.D.; Peña, A. A novel PMSM hybrid sensorless control strategy for EV applications based on PLL and HFI. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2016), Florence, Italy, 23–26 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hammel, W.; Kennel, R.M. Position sensorless control of PMSM by synchronous injection and demodulation of alternating carrier voltage. In Proceedings of the 2010 First Symposium on Sensorless Control for Electrical Drives (SLED 2010), Padova, Italy, 9–10 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.Y.; Yang, S.H.; Tu, K.H. Comparative Evaluation of a Permanent Magnet Machine Saliency-Based Drive with Sine-Wave and Square-Wave Voltage Injection. Energies 2018, 11, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonhoven, G.; Uddin, M.N. Harmonic Injection-Based adaptive control of IPMSM motor drive for reduced motor current THD. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao, H.; Capolino, G.A.; Razik, H. Analytical Approach of the Stator Current Frequency Harmonics Computation for Detection of Induction Machine Rotor Faults. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Diagnostic for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (SDEMPED 2003), Atlanta, GA, USA, 24–26 August 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Harke, M.C.; Lorenz, R.D. Sensorless control of interior permanent-magnet machine drives with zero-Phase lag position estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1726–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Ilioudis, V.C. Sensorless Control Applying Signal Injection Methodology on Modified Model of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine. In Proceedings of the Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT 2019), Paris, France, 23–26 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Piippo, A.; Luomi, J. Inductance harmonics in permanent magnet synchronous motors and reduction of their effects in sensorless control. In Proceedings of the XVII International Conference on Electric Machines (ICEM 2006), Chania, Crete Island, Greece, 2–5 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ilioudis, V.C. Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine with Magnetic Saliency Tracking Based on Voltage Signal Injection. Machines 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Gong, L.M. Investigation of effectiveness of sensorless operation in carrier signal injection based sensorless control Methods. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 8, 3431–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Verma, V.; Khan, Y.A.; Shiva, B.S. Q-MRAS Based Speed Sensorless Vector Controlled Synchronous Reluctance Motor Drive. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Power Electronics Applications and Technology in Present Energy Scenario (PETPES), Mangalore, India, 29–31 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tuovinen, T.; Hinkkanen, M. Signal-injection-assisted full-order observer with parameter adaptation for synchronous reluctance motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3392–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, S.; Sato, Y.; Goto, T.; Tomita, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Doki, S.; Kato, S. Position and velocity sensorless control for synchronous reluctance motor at low speeds and under loaded conditions using high-frequency extended EMF observer and heterodyne detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Electrical Machines 2014 (ICEM 2014), Berlin, Germany, 2–5 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa, S.; Tomita, M.; Doki, S.; Okuma, S. Initial position estimation and low speed sensorless control of synchronous motors in consideration of magnetic saturation based on system identification theory. In Proceedings of the IEEE Industry Applications Conference, 39th IAS Annual Meeting, Seattle, WA, USA, 3–7 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kuehl, S.; Landsmann, P.; Kennel, R.M. Compensating angle estimation errors caused by magnetic saturation in anisotropy-based sensorless control schemes. In Proceedings of the 3rd Symposium on Sensorless Control Electrical Drives 2012 (SLED 2012), Milwaukee, WI, USA, 21–22 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, P.C.; Wasynczuk, O.; Sudhoff, S.D.; Pekarek, S. Analysis of Electric Machinery and Drive Systems, 3rd ed.; Wiley-IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 142–210. [Google Scholar]
- Ilioudis, V.C.; Margaris, N.I. Speed and position estimation technique for PMSM based on modified machine model. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Optimization of Electrical and Electronic Equipment (OPTIM 2010), Brasov, Romania, 20–22 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Boldea, I.; Paicu, M.C.; Andreescu, G.-D. Active flux concept for motion-sensorless unified AC drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 2612–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lamb, J. Active Q Flux Concept for Sensorless Control of Synchronous Reluctance Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 4526–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fop, G.; Rahman, M.F. Sensorless sliding mode MTPA control of an IPM synchronous motor drive using a sliding-mode observer and HF signal injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Shtessel, Y.B. Sliding Mode Control with Applications: Tutorial. In Proceedings of the ICEECSAS-2008, UNAM, Mexico City, Mexico, 12 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Utkin, V.I. Sliding Mode Control Design Principles and Applications to Electric Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 40, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.; Spurgeon, S.K. Sliding Mode Control: Theory and Applications, 1st ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 1998; pp. 1–237. [Google Scholar]
- Spurgeon, S.K. Sliding Mode Observers: A Survey. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2008, 39, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtessel, Y.; Edwards, C.; Fridman, L.; Levant, A. Sliding Mode Control and Observation (Control Engineering), 1st ed.; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Levant, A. Chattering Analysis. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2010, 55, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Utkin, V.I. Chattering suppression methods in sliding mode control systems. J. Annu. Rev. Control. 2007, 31, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, V.I.; Lee, H. Chattering Analysis. In Proceedings of the Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (EPE-PEMC 2006), Portoroz, Slovenia, 30 August–1 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shtessel, Y.B.; Shkolnikov, I.A.; Brown, M. An Asymptotic Second-Order Smooth Sliding Mode Control. Asian J. Control. 2003, 5, 498–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Utkin, V. Chattering analysis, in Advances in Variable Structure and Sliding Mode Control. In Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences, 1st ed.; Edwards, C., Fossas, C., Fridman, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; Volume 334, pp. 107–123. [Google Scholar]
- Utkin, V.; Poznyak, A.; Orlov, Y.V.; Polyakov, A. High-Order Sliding Mode Control. In Road Map for Sliding Mode Control Design; SpringerBriefs in Mathematics; Springer Nature: London, UK, 2020; pp. 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Defoort, M.; Floquet, T.; Kokosy, A.; Perruquetti, W. A novel higher order sliding mode control scheme. J. Syst. Control. Lett. 2009, 58, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plestan, F.; Shtessel, Y.; Brégeault, V.; Poznyak, A. Sliding mode control with gain adaptation-Application to an electropneumatic actuator. J. Control. Eng. Pract. 2013, 21, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reigosa, D.D.; Briz, F.; Degner, M.W.; García, P.; Guerrero, J.M. Temperature issues in saliency-tracking-based sensorless methods for PM synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawazish, A.S.M.; Hossain, M.J.; Wang, D.; Lu, K. Robust Sensorless Control Against Thermally Degraded Speed Performance in an IM Drive Based Electric Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 896–907. [Google Scholar]
- dSPACE GmbH. DS1104 R&D Controller Board. Available online: https://www.dspace.com/en/pub/home/products/hw/singbord/ds1104.cfm (accessed on 2 October 2024).
- Pate, M.; Texas Instruments Incorporated. Application Note: The Essential Guide for Developing with C2000 Real-Time Microcontrollers (Rev. F). SPRACN0F, Oct. 2021 (Revised Mar. 2023). Available online: https://www.ti.com/lit/an/spracn0f/spracn0f.pdf?ts=1735390108649 (accessed on 3 October 2024).


| Symbol | Quantity | Expressed in SI |
|---|---|---|
| P | Power | 4.4 kW |
| Vl-l | Line to line voltage | 380 V |
| rs | Stator resistance | 2.5 Ω |
| Ld | d-axis inductance | 0.400 H |
| Lq | q-axis inductance | 0.210 H |
| J | Moment of inertia | 0.089 kgm2 |
| p | Magnetic pole pairs | 1 |
| ωm | Mechanical angular speed | 3000 rpm |
| Symbol | Quantity | Value |
|---|---|---|
| kγ | γ-axis gain of SMO | 20,000 |
| kδ | δ-axis gain of SMO | 20,000 |
| γr | gain of stator resistance estimator | 75 |
| Symbol | Quantity | Value |
|---|---|---|
| γE | gain of modified EMF observer | 80 |
| γω | gain of angular speed observer | 400 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilioudis, V.C. A Model-Based Method Applying Sliding Mode Methodology for SynRM Sensorless Control. Magnetism 2025, 5, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5010004
Ilioudis VC. A Model-Based Method Applying Sliding Mode Methodology for SynRM Sensorless Control. Magnetism. 2025; 5(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlioudis, Vasilios C. 2025. "A Model-Based Method Applying Sliding Mode Methodology for SynRM Sensorless Control" Magnetism 5, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5010004
APA StyleIlioudis, V. C. (2025). A Model-Based Method Applying Sliding Mode Methodology for SynRM Sensorless Control. Magnetism, 5(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5010004






