Challenges in Sewer System Maintenance
Definition
1. Introduction
2. History of Sewer Systems
3. Sewer System Types
- Continuous collection of wastewater in a defined system area;
- Safe transport of wastewater to wastewater treatment plants;
- Necessary treatment of the processing to a required level prior to its release into the recipient [39].
- Collection of all wastewater;
- Treatment of all wastewater;
- Wastewater treatment to the level prescribed by law;
- Sustainable solutions according to the lifespan of the building;
- An acceptable level of protection for people and their property;
- An acceptable level of environmental protection and water resources [40].
- The simplest solution;
- The smallest construction costs;
- The minimum costs of use and maintenance [40].
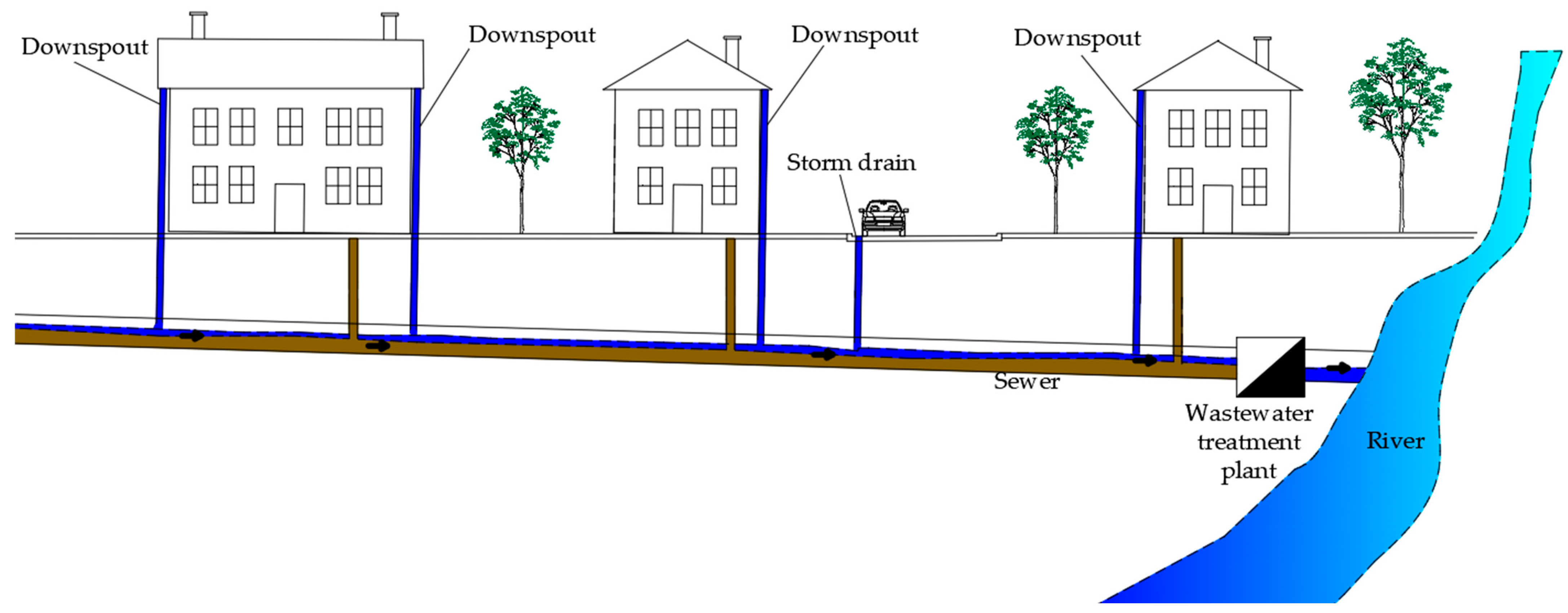
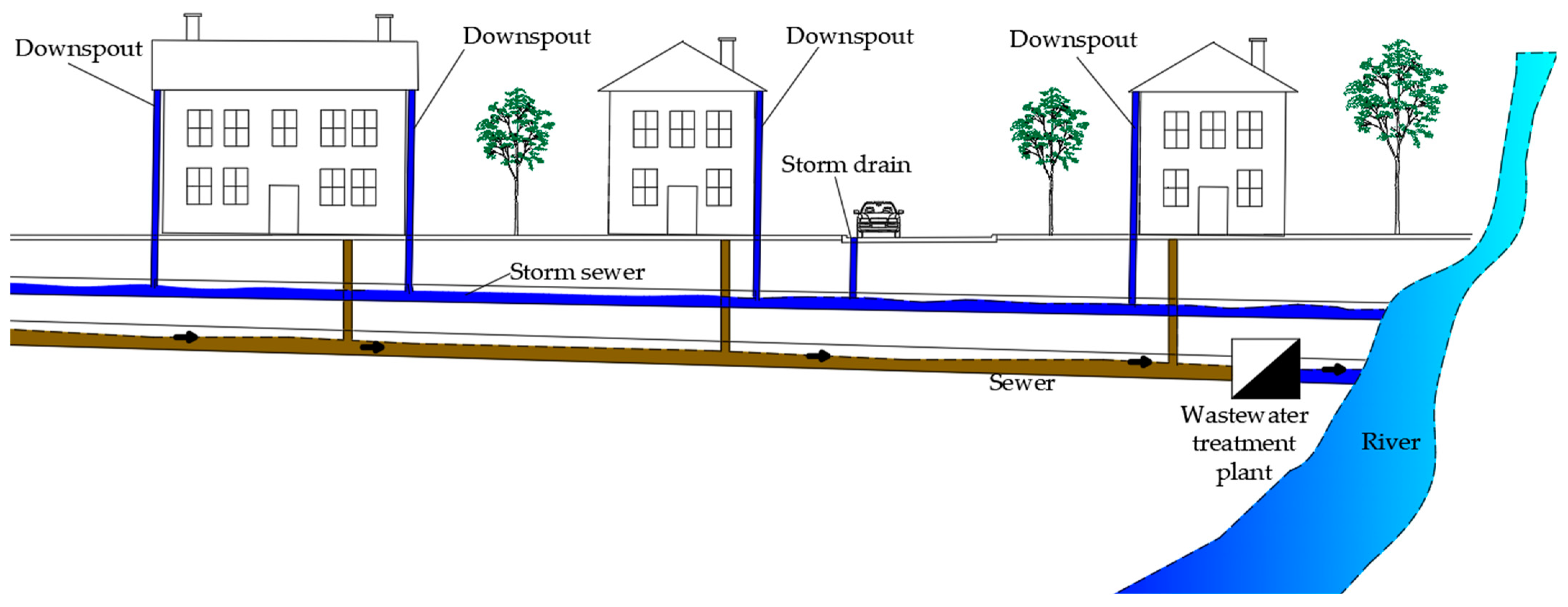
- Combined sewer system;
- Separated sewer system;
- Partially separated sewer system.
- Gravity;
- Pressure;
- Vacuum [38].
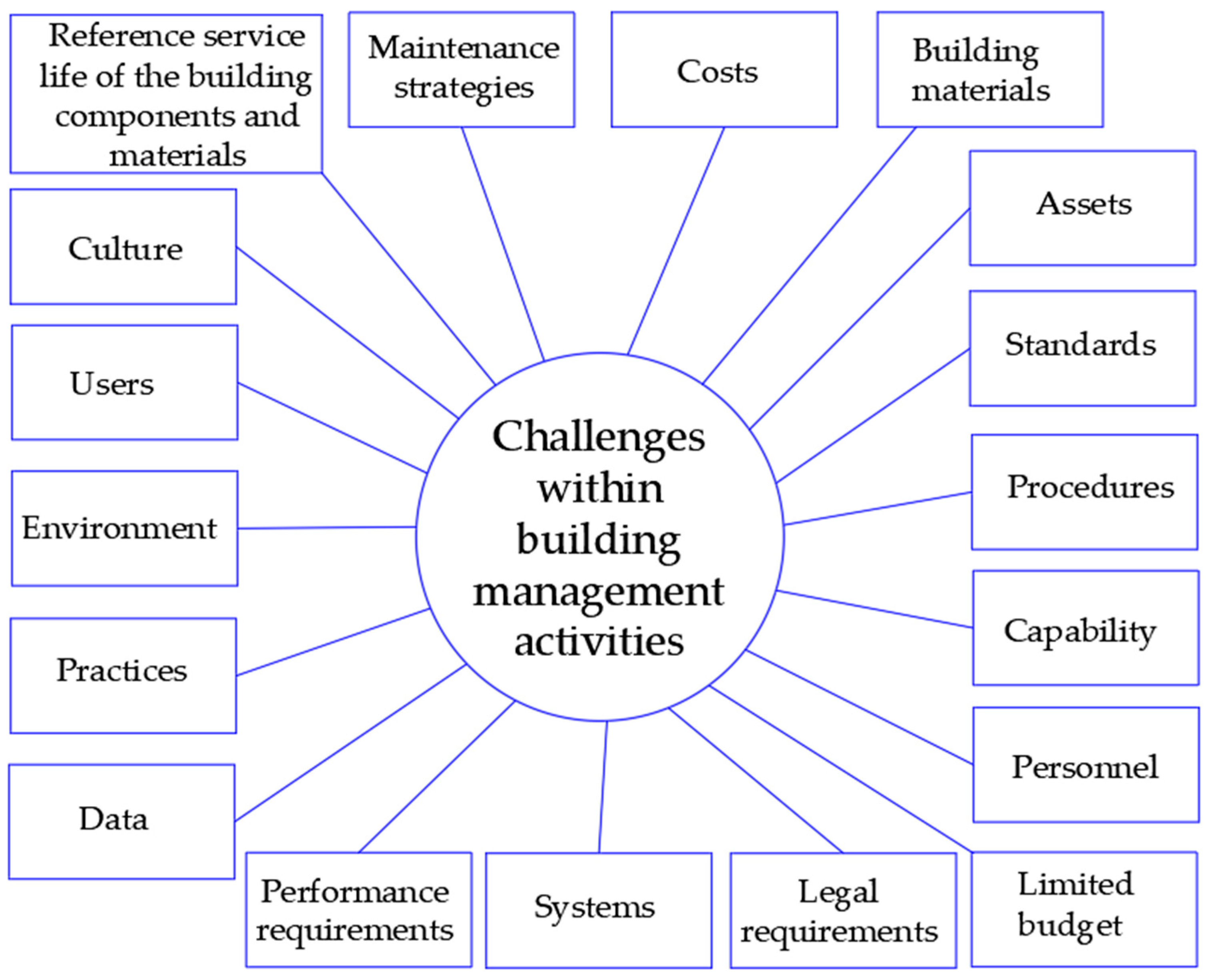
4. Challenges of the Maintenance of Sewer Systems
4.1. Types of Sewer Maintenance
- Longitudinal slopes less than the minimum allowed;
- Small minimum pipe profiles;
- Poorly performed joints, longitudinal slopes and shafts;
- A large number of cracks, deformations and fractures due to poor installation;
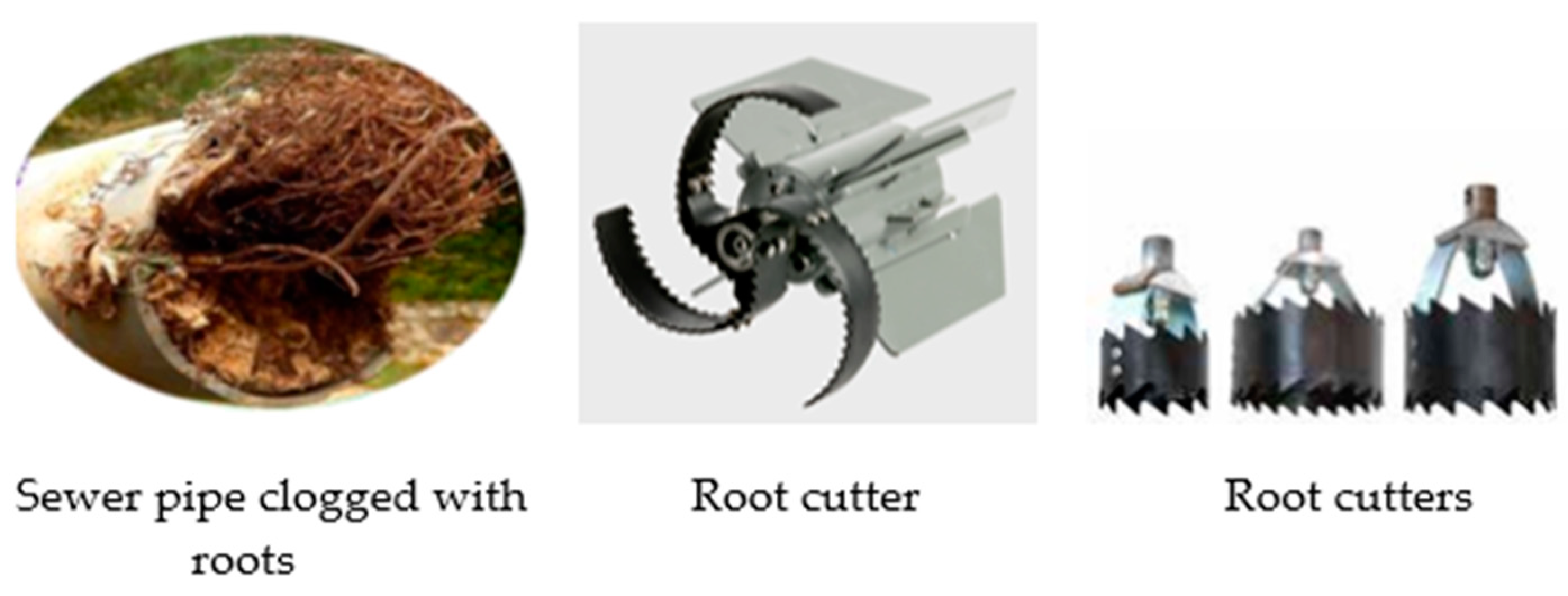
- Undisciplined users who omit substances and things that they should not omit into the sewer [74].
- Knowledge of the work to be done;
- Importance of the work done;
- The designation of persons responsible;
- Specification of measurable standards;
- All of these require good education and supervision training [76].
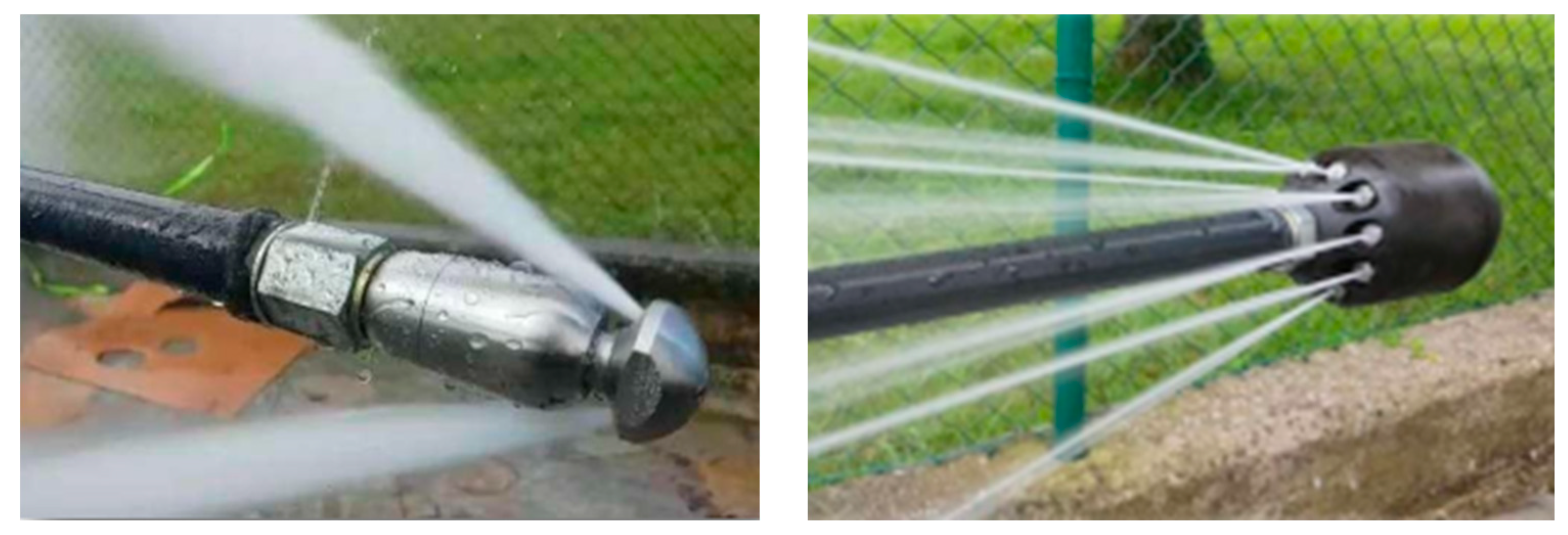
4.2. Sewer System Cleaning
4.3. Damages and Repairs of Sewer Pipes
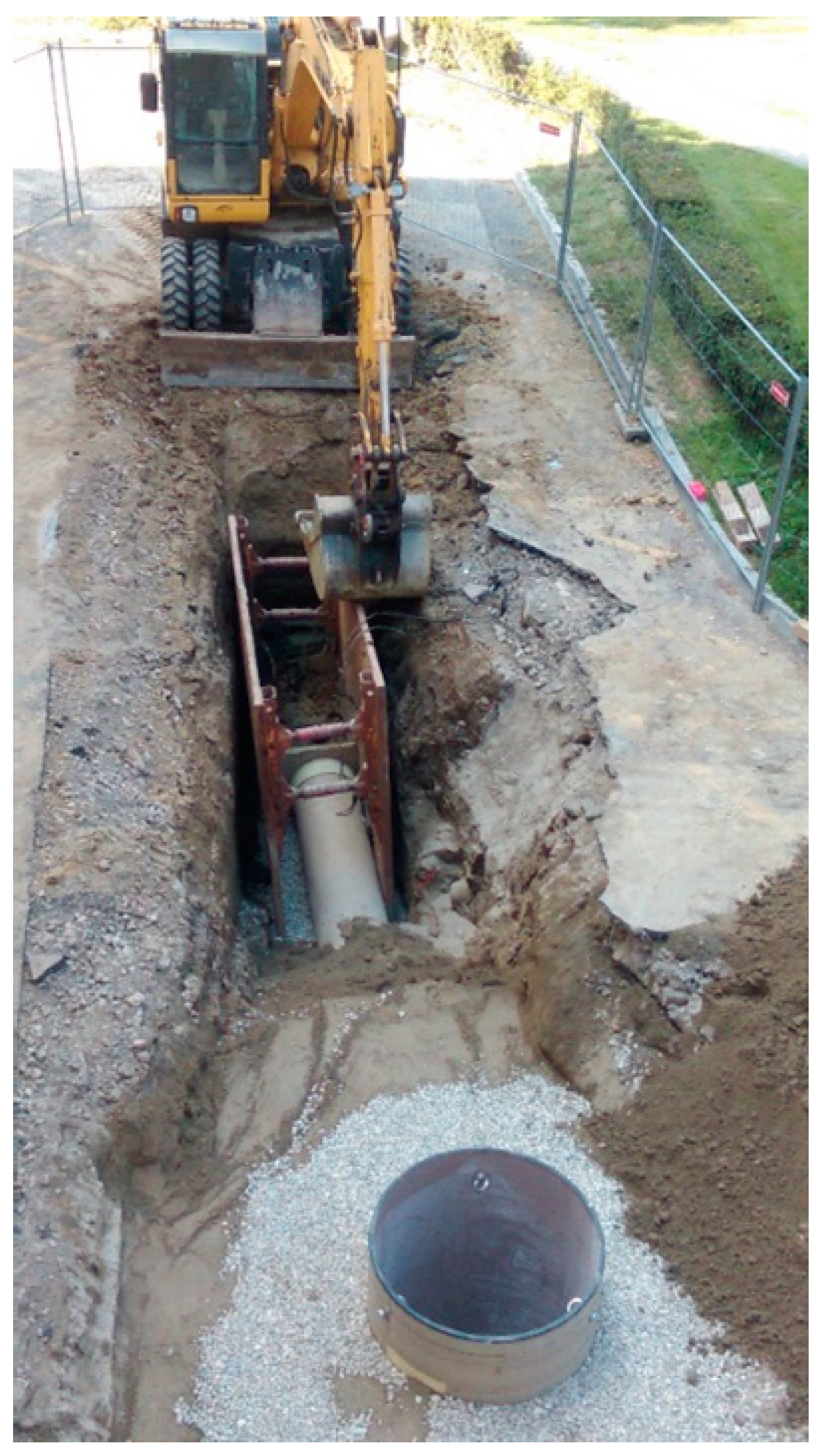
- Removal of asphalt layer and disposal of materials;
- Trench excavation;
- Removal of the old pipe;
- Installation of new pipes;
- Backfilling the trench;
- Relaying the asphalt layer [100].
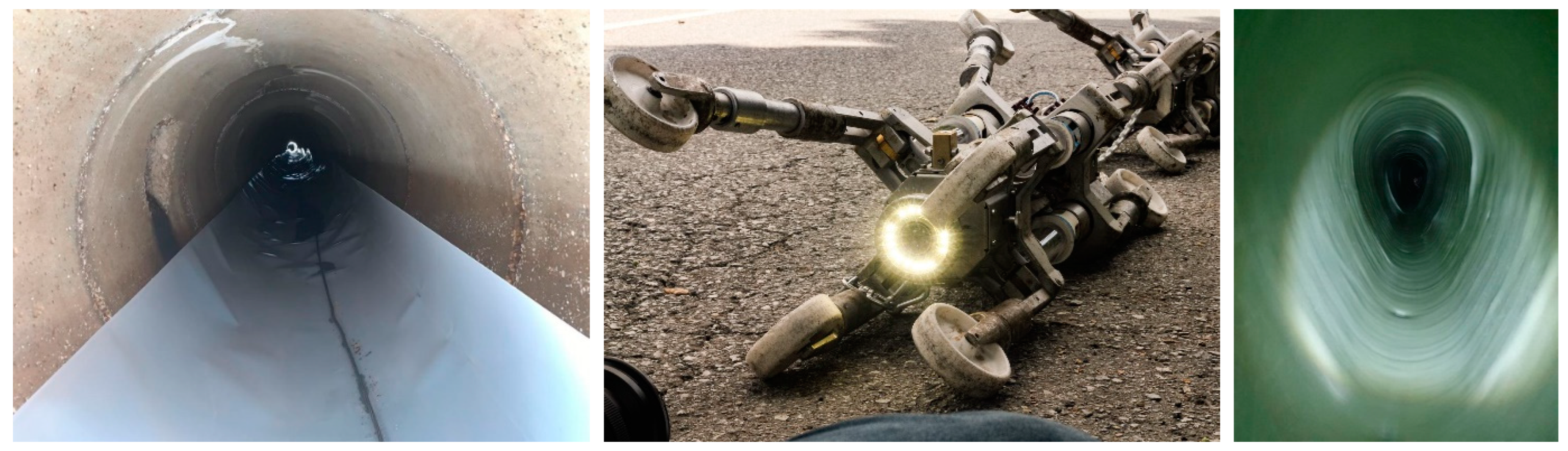
4.4. Trencheless Sewer Rehabilitation
- Punching or line expansion method (In-Line extension; Pipe Bursting);
- Inserting a new pipe into an existing, slip lining method (Sliplining);
- The Cured-in-Place Pipe method (CIPP);
- The Modified Cross Section Liner method [101].

- No excavations are needed between the access points (often existing manholes) that are mainly set at a considerable distance.
- It is necessary to have a certain, smaller number of construction machinery, and activities are concentrated only in the places where it works, i.e., access points where new pipes are usually introduced.
- A continuous operating environment of 24 h is possible, with minimal interference in the work of the surrounding buildings or obstruction of the neighbourhood where it works.
- The visibility of construction activities is significantly reduced, which can lead to a smaller number of insurance claims and complaints from citizens.
- The result of the completed and restored sewer system (pipe) is in some cases better and stronger than the original.
- The final restored sewer system can have better flow characteristics than the original sewer system before rehabilitation [104].
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Obradović, D. The impact of tree root systems on wastewater pipes. In Proceedings of the Zajednički Temelji 2017—Peti skup mladih istraživača iz područja građevinarstva i srodnih tehničkih znanosti—Zbornik Radova, Zagreb, Croatia, 18–19 September 2017; University of Zagreb Faculty of Civil Engineering: Zagreb, Croatia, 2017; pp. 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Angel, S.; Parent, J.; Civico, D.L.; Blei, M.A. Atlas of Urban Expansion; Lincoln Institute of Lang Policy: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fontecha, J.E.; Guaje, O.O.; Duque, D.; Akhavan-Tabatabaei, R.; Rodríguez, J.P.; Medaglia, A.L. Combined maintenance and routing optimization for large-scale sewage cleaning. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 286, 441–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Počuča, N. Ekohidrologija, Zagađenje i Zaštita Voda; Građevinska knjiga: Beograd, Serbia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gudelj, I. Jedno od ključnih načela EE politike u području upravljanja vodom je pristup koji uključuje širu suradnju. Hrvat. Vode 2021, 29, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- Karleuša, R. Problemi i promašaji u odvodnji. In Proceedings of the Odvodnja otpadnih i oborinskih Voda—Uvjet održivog razvoja, Zagreb, Croatia, 15–17 March 2004; Tušar, B., Ed.; Društvo Građevinskih Inženjera Zagreb: Zagreb, Croatia, 2004; pp. 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Trbojević, V. Zaštita Potrošača Korisnika Vodne Usluge Opskrbe Vodom; Republika Hrvatska, Ministarstvo zaštite okoliša i energetike: Zagreb, Croatia, 2018. Available online: https://www.szp.hr/UserDocsImages//dokumenti/Objave/Voda.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- United Nations. The Human Right to Water and Sanitation: Resolution; General Assembly Resolution Adopted by the General Assembly on 28 July 2010; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Available online: https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/687002 (accessed on 21 September 2022).
- Oreščanin, V.; Kollar, R.; Crnojević, H.; Nađ, K.; Halkijević, I.; Kuspilić, M. Pročišćavanje podzemnih voda s područja Vukovarsko-srijemske županije kombinacijom elektrokemijskih metoda i naprednih oksidacijskih procesa. Hrvat. Vode 2020, 28, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Frangopol, D.M.; Saydam, D.; Kim, S. Maintenance, management, life-cycle design and performance of structures and infrastructures: A brief review. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2012, 8, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yi, S.; Lee, W. Life Cycle Assessment of Sewer System: Comparison of Pipe Materials. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research (ACEM’ 12), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 26–29 August 2012; pp. 2963–2975. [Google Scholar]
- Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Nielsen, H.P.; Lopez-Vazquez, M.C.; Brdjanovic, D. Eksperimentalne Metode u Obradi Otpadnih Voda; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kučić Grgić, D.; Bera, L.; Miloloža, M.; Cvetnić, M.; Ignjatić Zokić, T.; Miletić, B.; Leko, T.; Ocelić Bulatović, V. Obrada aktivnog mulja s uređaja za pročušćavanje komunalnih otpadnih voda procesom kompostiranja. Hrvat. Vode 2020, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kujundžić, B. Kanalizacija Beograda 1905–1975.; Dragoslav, K., Ed.; NIP “Export-Press”: Beograd, Serbia, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Tait, S.J.; Ashley, R.M.; Cashman, A.; Blanksby, J.; Saul, A.J. Sewer system operation into the 21st century, study of selected responses from a UK perspective. Urban Water J. 2008, 5, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidi, E.; Jin, E.; Das, M.; Singh, M.; Zhao, F. Environmental life cycle analysis of pipe materials for sewer systems. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 27, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujundžić, B. Kanalizacioni sistem—definicija, karakteristike, delovi i zadaci. In Savremena Eksploatacija i Održavanje Objekata i Opreme Vodovoda i Kanalizacije; Kujundžić, B., Ed.; Udruženje za Tehnologiju Vode i Sanitarno Inženjerstvo: Beograd, Serbia, 2010; pp. 345–354. ISBN 978-86-82931-33-1. [Google Scholar]
- Obradović, D. Prevencija kvarova sprječavanjem rasta i uklanjanjem korijenja drveća u kanalizacijskim cijevima. Vodoprivreda 2018, 50, 165–173. [Google Scholar]
- Wijnia, Y.C.; Herder, P.M. The state of Asset Management in the Netherlands. In Engineering Asset Lifecycle Management; Springer London: London, UK, 2010; pp. 164–172. [Google Scholar]
- Lofrano, G.; Brown, J. Wastewater management through the ages: A history of mankind. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5254–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuorinen, H.S.; Juuti, P.S.; Katko, T.S. History of water and health from ancient civilizations to modern times. Water Supply 2007, 7, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanalizacija 1892–1992; Kosić, K., Ed.; Javno Poduzeće “Kanalizacija” Zagreb: Zagreb, Croatia, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, B.; Helgertz, J. Urban sanitation and the decline of mortality. Hist. Fam. 2019, 24, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinde, A.; Harris, B. Mortality decline by cause in urban and rural England and Wales, 1851–1910. Hist. Fam. 2019, 24, 377–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillingham, R.; Guerrant, R.L. Childhood stunting: Measuring and stemming the staggering costs of inadequate water and sanitation. Lancet 2004, 363, 94–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, L.; Rotella, E. Death and spending: Urban mortality and municipal expenditure on sanitation. Ann. Demogr. Hist. (Paris) 2001, 1, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, Z. Vodoprivreda Gornjeg Jadrana: Povijest Vodnoga Graditeljstva na Vodnom Području Primorsko-Istarskih Slivova, II. Kanalizacijski Sustavi, Knjiga 1. Istarska Županija; Butorac, F., Ed.; Adamić: Rijeka, Croatia, 2006; ISBN 953-219-263-8. [Google Scholar]
- Alić, M. Otpadne vode kroz povijest. Hrvat. Vodoprivr. 2017, XXV, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Kružić, S. Evakuacija, Kondicioniranje i Dispozicija Otpadnih Voda; Sveučilište u Rijeci, Fakultet graditeljskih znanosti: Rijeka, Croatia, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Zrnić, J.; Zrnić, P. Tehničar 5 Građevinski priručnik; Lazin, D., Ed.; Građevinska Knjiga: Beograd, Serbia, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Kavoulaki, E.; Dialynas, E.G. Sanitation and wastewater technologies in Minoan Era. In Evolution of Sanitation and Wastewater Technologies through the Centuries; Rose, J.B., Angelakis, A.N., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- De Feo, G.; Antoniou, G.; Fardin, H.; El-Gohary, F.; Zheng, X.; Reklaityte, I.; Butler, D.; Yannopoulos, S.; Angelakis, A. The Historical Development of Sewers Worldwide. Sustainability 2014, 6, 3936–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grozdanović, S. Hidrotehnička infrastruktura Starorimskog Viminacijuma. Vodoprivreda 2015, 47, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Rubeša, J. Kanalizacija Grada Pariza. Hrvat. Vode 2018, 26, 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Projektiranje Sustava Odvodnje (Kanalizacijskih Sustava) 2018. Available online: http://www.grad.hr/nastava/hidrotehnika/gf/odvodnja/vjezbe/Projektiranjesustavaodvodnje-zaweb.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Radonić, M. Vodovod i Kanalizacija u Zgradama; Lazin, D., Ed.; Građevinska knjiga: Beograd, Serbia, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Balacco, G.; Iacobellis, V.; Portincasa, F.; Ragno, E.; Totaro, V.; Piccinni, A.F. Analysis of a Large Maintenance Journal of the Sewer Networks of Three Apulian Provinces in Southern Italy. Water 2020, 12, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margeta, J. Kanalizacija Naselja; Građevinski fakultet Sveučilišta u Splitu, Građevinski fakultet Sveučilišta J. J. Strossmayera u Osijeku; Institut Građevinarstva Hrvatske: Zagreb, Croatia, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Uskoković, P. Osnovne karakteristike sistema za snabdevanje vodom i odvođenje otpadnih voda bitnih za razmatranje njihovog održavanja. In Savremena Eksploatacija i Održavanje Objekata i Opreme Vodovoda i Kanalizacije; Kujundžić, B., Ed.; Udruženje za tehnologiju vode i sanitarno inženjerstvo: Beograd, Serbia, 2010; pp. 79–101. [Google Scholar]
- Margeta, J. Oborinske i Otpadne vode: Teret onečišćenja, mjere zaštite; Sveučilište u Splitu, Građevinsko-arhitektonski fakultet: Split, Croatia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Botturi, A.; Ozbayram, E.G.; Tondera, K.; Gilbert, N.I.; Rouault, P.; Caradot, N.; Gutierrez, O.; Daneshgar, S.; Frison, N.; Akyol, Ç.; et al. Combined sewer overflows: A critical review on best practice and innovative solutions to mitigate impacts on environment and human health. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 1585–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margeta, J. Kontrola negativnih utjecaja preljevnih voda kanalizacije. Građevinar 2011, 63, 651–660. [Google Scholar]
- Tarr, J.A. The Separate vs. Combined Sewer Problem. J. Urban Hist. 1979, 5, 308–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blagojević, B. Vodovod i Kanalizacija sa Propisima i Standardima; 3. dopunjeno izdanje; Tehnička knjiga: Beograd, Serbia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Simović, V. (Ed.) Leksikon Građevinarstva; Masmedia: Zagreb, Croatia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hrskanović, I. Održavanje sustava odvodnje naselja. Master’s Thesis, Sveučilište J. J. Strossmayera u Osijeku, Građevinski fakultet Osijek, Osijek, Croatia, 2016. Available online: https://urn.nsk.hr/urn:nbn:hr:133:839845 (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Ljubisavljević, D.; Obrenović, M. Nestandardni kanalizacioni sistemi: Vakumska kanalizacija i kanalizacija pod pritiskom. Vodoprivreda 2010, 42, 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, A. The Liernur system at Amsterdam. J. Soc. Arts 1876, 24, 671. [Google Scholar]
- Obradović, D.; Šperac, M.; Marenjak, S. Maintenance issues of the vacuum sewer system. Environ. Eng. 2019, 6, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, M.; Sleigh, A.; Tayler, K. PC-Based Simplified Sewer Design; School of Civil Engineering, University of Leeds: Leeds, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Runko Luttenberger, L. Prilog uspostavi decentraliziranih sustva otpadnih voda. Pomor. Zb. 2002, 40, 553–560. [Google Scholar]
- Šperac, M.; Obradović, D. Odvodnja otpadnih voda alternativnim kondominijalnim kanalizacijskim sustavom. In Proceedings of the 9th international natural gas, heat and water conference—PLIN 2018, Osijek, Croatia, 26–28 September 2018; Raos, P., Ed.; Strojarski fakultet u Slavonskom Brodu: Osijek, Croatia, 2018; pp. 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, S.P.; Matos, J.S. Small diameter gravity sewers: Self-cleansing conditions and aspects of wastewater quality. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Decentralized Systems Technology Fact Sheet Small Diameter Gravity Sewers; US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Nawrot, T.; Matz, R.; Błażejewski, R.; Spychała, M. A Case Study of a Small Diameter Gravity Sewerage System in Zolkiewka Commune, Poland. Water 2018, 10, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek Mohammadi, M.; Najafi, M.; Kermanshachi, S.; Kaushal, V.; Serajiantehrani, R. Factors Influencing the Condition of Sewer Pipes: State-of-the-Art Review. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2020, 11, 03120002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawari, A.; Alkadour, F.; Elmasry, M.; Zayed, T. A state of the art review on condition assessment models developed for sewer pipelines. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 93, 103721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Chen, Y.; Bouferguene, A.; Al-Hussein, M. Data-driven bi-level sewer pipe deterioration model: Design and analysis. Autom. Constr. 2020, 116, 103181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, T.; Kokkonen, T.; Mellin, I.; Vahala, R. Sewer Life Span Prediction: Comparison of Methods and Assessment of the Sample Impact on the Results. Water 2019, 11, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, D.M. Life Cycle Cost Integration for the Rehabilitation of Wastewater Infrastructure. In Proceedings of the Construction Research Congress, Honolulu, HI, USA, 19–21 March 2003; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2003; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Plihal, H.; Kretschmer, F.; Schwarz, D.; Ertl, T. Innovative sewer inspection as a basis for an optimised condition-based maintenance strategy. Water Pract. Technol. 2014, 9, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blažević, D. Predviđanje Održavanja Tehničkog Sustava Procjenom Stanja. Ph.D. Thesis, Sveučilište Josipa Jurja Strossmayera u Osijeku, Elektrotehnički fakultet Osijek, Osijek, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, L.J. Predictive Engineering for Aging Infrastructure. In Proceedings of the SPIE Conference on Nondestructive Evaluation of Utilities and Pipelines, Newport Beach, CA, USA, 4 March 1999; Reuter, W.G., Ed.; Society of Photo Optical: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1999; pp. 2–13. [Google Scholar]
- Aihua, L. A method for condition evaluation based on DSmT. In Proceedings of the 2010 2nd IEEE International Conference on Information Management and Engineering, Chengdu, China, 16–18 April 2010; pp. 263–266. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, L.; Saxena, A.; Knapp, G.M. Statistical-based or condition-based preventive maintenance? J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 1995, 1, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujjan, G.M.; Ali Taur, M.; Lashari, B.K. Operation and Maintenance Cost of Drainage System: The Case Study of Bareji Distributary, Mirpurkhas, Sindh, Pakistan. In Proceedings of the National seminar on: Drainage in Pakistan, Muet, Jamshoro, 16–18 August 2000; International Water Management Institute: Jamshoro, Pakistan, 2000; pp. 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Šperac, M.; Moser, V.; Stvorić, T. Održavanje kanalizacijskog sustava uz primjenu GIS-A. Elektron. Časopis Građevinskog Fak. Osijek e-GFOS 2012, 3, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradović, D. A short review: Techniques for trenchless sewer rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the Young Scientist 2018, Tatranská Lomnica, Slovakia, 26–27 April 2018; Kvočák, V., Ed.; Technical University of Košice, Faculty of Civil Engineering: Tatranská Lomnica, Slovakia, 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Obradović, D.; Šperac, M.; Marenjak, S. Possibilities of using expert methods for sewer system maintenance optimisation. J. Croat. Assoc. Civ. Eng. 2019, 71, 769–779. [Google Scholar]
- Anbari, M.J.; Tabesh, M.; Roozbahani, A. Risk assessment model to prioritize sewer pipes inspection in wastewater collection networks. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 190, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Velasco, A.; Cortés, P.; Muñuzuri, J.; Onieva, L. Estimation of a logistic regression model by a genetic algorithm to predict pipe failures in sewer networks. OR Spectr. 2021, 43, 759–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilber, M. Eksploatacija i održavanje kanalizacione mreže. In Savremena Eksploatacija i Održavanje Objekata i Opreme Vodovoda i Kanalizacije; Kujundžić, B., Ed.; Udruženje za Tehnologiju Vode i Sanitarno Inženjerstvo: Beograd, Serbia, 2010; pp. 373–398. [Google Scholar]
- Zaman, H.; Bouferguene, A.; Al-Hussein, M.; Lorentz, C. Improving the productivity of drainage operations activities through schedule optimisation. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malus, D.; Kovačević, D.; Vouk, D. Razmak okana na kanalizacijskoj mreži. Građevinar 2008, 60, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Šperac, M.; Hrskanović, I.; Šreng, Ž. Održavanje gravitacijskih kanalizacijskih sustava. In Proceedings of the 26. Međunarodni Znanstveno-Stručni Skup „Organizacija i Tehnologija Održavanja“—OTO 2017, Osijek, Croatia, 26 May 2017; Zbornik, R., Glavaš, H., Barić, T., Nyarko, K.E., Barukčić, M., Keser, T., Karakašić, M., Eds.; Fakultet Elektrotehnike, Računarstva i Informacijskih Tehnologija Osijek (FERIT): Osijek, Croatia, 2017; pp. 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, A.R. Sustainable Sewerage: Guidelines for Community Schemes; Intermediate Technology Publications & Water, Engineering and Development Centre: London, UK, 1995; ISBN 1853393053. [Google Scholar]
- Marsalek, J.; Schillling, W. Operation of sewer systems. In Proceedings of the Hydroinformatics Tools for Planning, Design, Operation and Rehabilitation of Sewer Systems, Harrachov, Czech Republic, 16–19 June 1996; Marsalek, J., Maksimovic, C., Zeman, E., Price, K.R., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 393–414. [Google Scholar]
- Milojković, I.; Despotović, J.; Karanović, I. Model for maintenance of sewerage system based on inspection. In Proceedings of the IWA 7 th Eastern European Young Water Professionals Conference, Belgrade, Serbia, 17–19 September 2015; pp. 538–543. [Google Scholar]
- Milojković, I.; Despotović, J.; Popović, M. Sewer System Inspection and Maintenance Model for Groundwater Protection. Water Res. Manag. 2016, 6, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wirahadikusumah, R.; Abraham, D.; Iseley, T. Challenging Issues in Modeling Deterioration of Combined Sewers. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2001, 7, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazraeializadeh, S.; Gay, L.F.; Bayat, A. Comparative analysis of sewer physical condition grading protocols for the City of Edmonton. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2014, 41, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek Mohammadi, M.; Najafi, M.; Salehabadi, N.; Serajiantehrani, R.; Kaushal, V. Predicting Condition of Sanitary Sewer Pipes with Gradient Boosting Tree. In Proceedings of the Pipelines 2020, San Antonio, TX, USA, 9–12 August 2020; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; pp. 80–89. [Google Scholar]
- American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE). 2021 Infrastructure Report Card; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, D.E. 15 Year Old Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Sewer Pipe; A Durability and Performance Review. In Buried Plastic Pipe Technology; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1990; pp. 393–399. [Google Scholar]
- Meerman, H. Lifetime Expectancy of PVC-U pipelines for sewer systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference Plastics Pipes XIV, Budapest, Hungary, 22–24 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Institute for Environmental Research & Environment Life Cycle Assessment of PVC Water and Sewer Pipe and Comparative Sustainability Analyis of Pipe Materials. 2017. Available online: https://www.uni-bell.org/files/Reports/Life_Cycle_Assessment_of_PVC_Water_and_Sewer_Pipe_and_Comparative_Sustainability_Analysis_of_Pipe_Materials.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2022).
- Omana, C.; Thorson, R. Future Wastewater Infrastructure Needs and Capital Costs; Minesota Pollution Control Agency: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Prevention and Control of Sewer System Overflows, 3rd ed.; Water Environment Federation (WEF): Alexandria, VA, USA, 2011.
- Le Gat, Y. Modelling the deterioration process of drainage pipelines. Urban Water J. 2008, 5, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Collection Systems O&M Fact Sheet: Sewer Cleaning and Inspection; US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- Hoffman, D.E.; Buchberger, S.G.; Flanders, M.U. Preventing Sewer Blowouts during High-Velocity Jet Cleaning Operations. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2010, 16, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradović, D. Doprinos Povećanju Učinkovitosti Održavanja Kanalizacijskih Sustava Primjenom Modela Procjene Troškova Održavanja. Ph.D. Thesis, Josip Juraj Strossmayer University of Osijek, Faculty of Civil Engineering and Architecture Osijek, Osijek, Croatia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hennlich d.o.o. Oprema za Čišćenje Odvodnih Cijevi i Kanalizacije. Available online: https://www.hennlich.hr/proizvodi/oprema-za-ciscenje-odvodnih-cijevi-i-kanalizacije-oprema-za-visokotlacne-strojeve-za-ciscenje-odvodnih-cijevi-i-kanalizacije-12745.html (accessed on 27 December 2022).
- Svihra, P. Ranking of trees according to damage of sewage pipes. Ornam. Northwest Arch. 1987, 11, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Randrup, T.B.; McPherson, E.G.; Costello, L.R. Tree Root Intrusion in Sewer Systems: Review of Extent and Costs. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2001, 7, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukić, I.; Veledar, H. Deratizacija kanalizacijske mreže. In Proceedings of the Odvodnja Otpadnih i Oborinskih Voda—Uvjet Održivog Razvoja, Zagreb, Croatia, 15–17 March 2004; Tušar, B., Ed.; Društvo Građevinskih Inženjera Zagreb: Zagreb, Croatia, 2004; pp. 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Feeney, S.C.; Thayer, S.; Bonomo, M.; Martel, K. White Paper on Conditon Assesment of Wastewater Collection Systems; US Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2009.
- Thomson, C.J.; Hayward, P.; Hazelden, G.; Morisson, R.S.; Sangster, T.; Williams, D.S.; Kopchynkski, R.K. An Examination of Innovative Methods Used in the Inspection of Wastewater Collection Systems; WERF: Alexandria, VA, USA; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lampola, T.; Kuikka, S. Condition Assessment and Sewer Inspection (CASI) Methods—Guide Book; Finnish Water Utilities Association: Helsinki, Finska, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Morera, S.; Remy, C.; Comas, J.; Corominas, L. Life cycle assessment of construction and renovation of sewer systems using a detailed inventory tool. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Collection Systems O&M Fact Sheet: Trenchless Sewer Rehabilitation; US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- Solmex d.o.o Bezrovovska Sanacija Odvodnje UV-CIPP Metodom. Available online: https://solmex.hr/odrzavanje-i-sanacija/bezrovovska-sanacija-odvodnje-uv-cipp-metodom/ (accessed on 27 December 2022).
- North Coast Resource Partnership; GHD Inc. Trenchless Sewer Rehabilitation; GHD Inc.: Melbourne, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Koerner, G.R.; Koerner, R.M. Geosynthetic use in trenchless pipe remediation and rehabilitation. Geotext. Geomembr. 1996, 14, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Maintenance Activity | Average (% of System/Year) |
|---|---|
| Cleaning | 29.9 |
| Root removal | 2.9 |
| Manhole inspection | 19.8 |
| CCTV inspection | 6.8 |
| Smoke testing | 7.8 |
| Defect | Types of Sewer Pipes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | AC | PCCP | CI | S | CL | Br | PVC | HDPE | |
| Roots | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Fat, Oil and Grease | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Cracks | • | • | • | ||||||
| Inner corrosion | • | • | • | • | • | ||||
| Outer corrosion | • | • | • | ||||||
| Infiltration/inflow (I/I) | • | • | • | • | • | ||||
| I/I of joints | • | • | • | ||||||
| I/I of house connections | • | • | |||||||
| Wrong procedure | • | • | • | ||||||
| Wrong connection procedure | • | • | • | ||||||
| Deformation | • | • | • | ||||||
| Other | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||||
| Method | Pipe Diameter [cm] | Installation Lengths [m] | Liner Material | Cost Range [$/m] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pipe bursting | 10–60 | 230 | PE, PP, PVC, GRP | 130–260 |
| Sliplining | 10–400 | 300 | PE, PP, PVC, GRP | 260–550 |
| Cured in Place Pipe | 10–275 | 150–900 | Thermoset Resin/Fabric Composite | 80–215 |
| Modified Cross Section Liner | 10–40 | 760 | HDPE | 58–162 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obradović, D.; Šperac, M.; Marenjak, S. Challenges in Sewer System Maintenance. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 122-142. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3010010
Obradović D, Šperac M, Marenjak S. Challenges in Sewer System Maintenance. Encyclopedia. 2023; 3(1):122-142. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleObradović, Dino, Marija Šperac, and Saša Marenjak. 2023. "Challenges in Sewer System Maintenance" Encyclopedia 3, no. 1: 122-142. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3010010
APA StyleObradović, D., Šperac, M., & Marenjak, S. (2023). Challenges in Sewer System Maintenance. Encyclopedia, 3(1), 122-142. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3010010









