Modeling the Mutual Enhancement of Regional Economy and Personal Quality of Life (QOL): A Case Study on the Mumbai–Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail Corridor in India
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology and Data
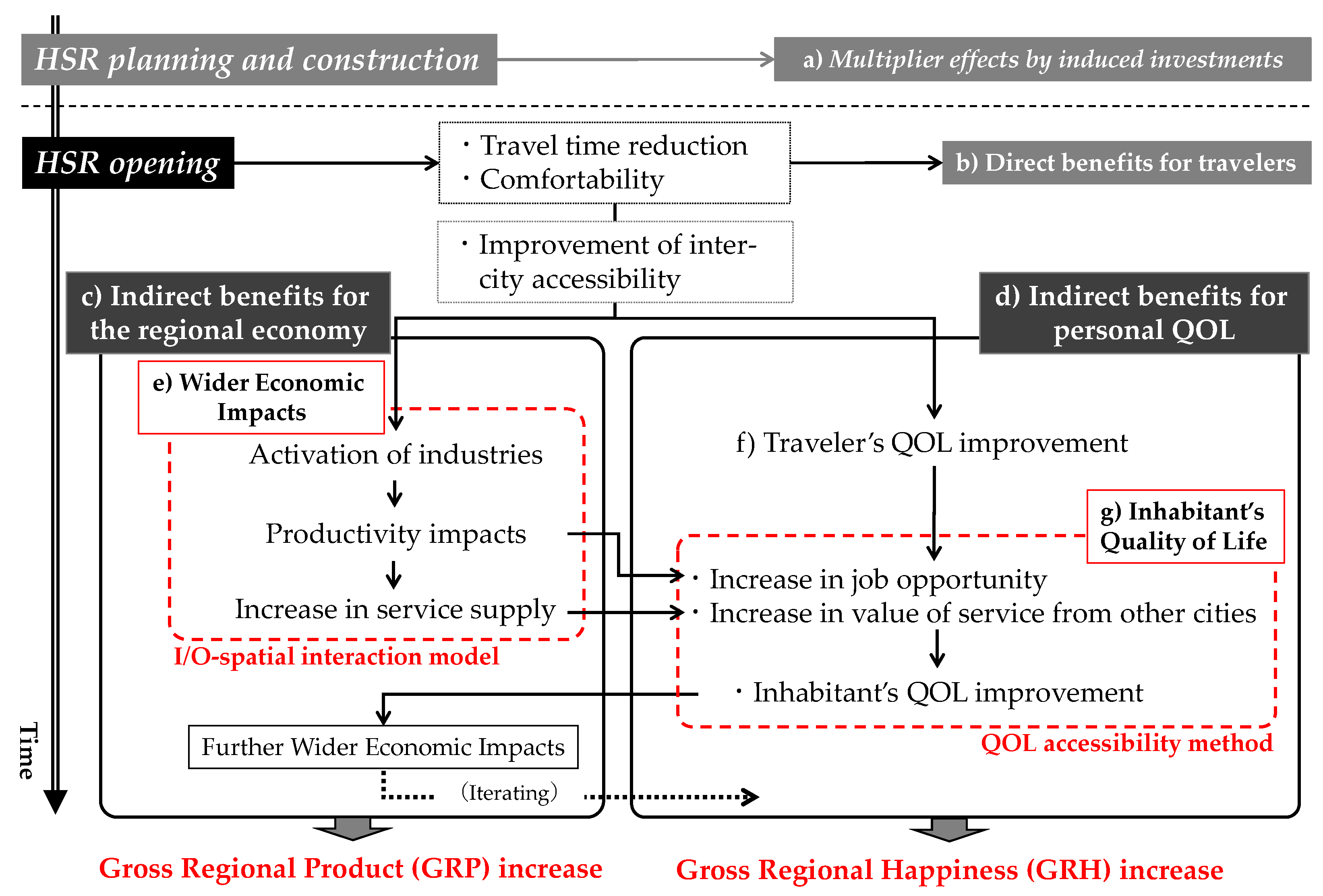
3.1. I/O–Spatial Interaction Model
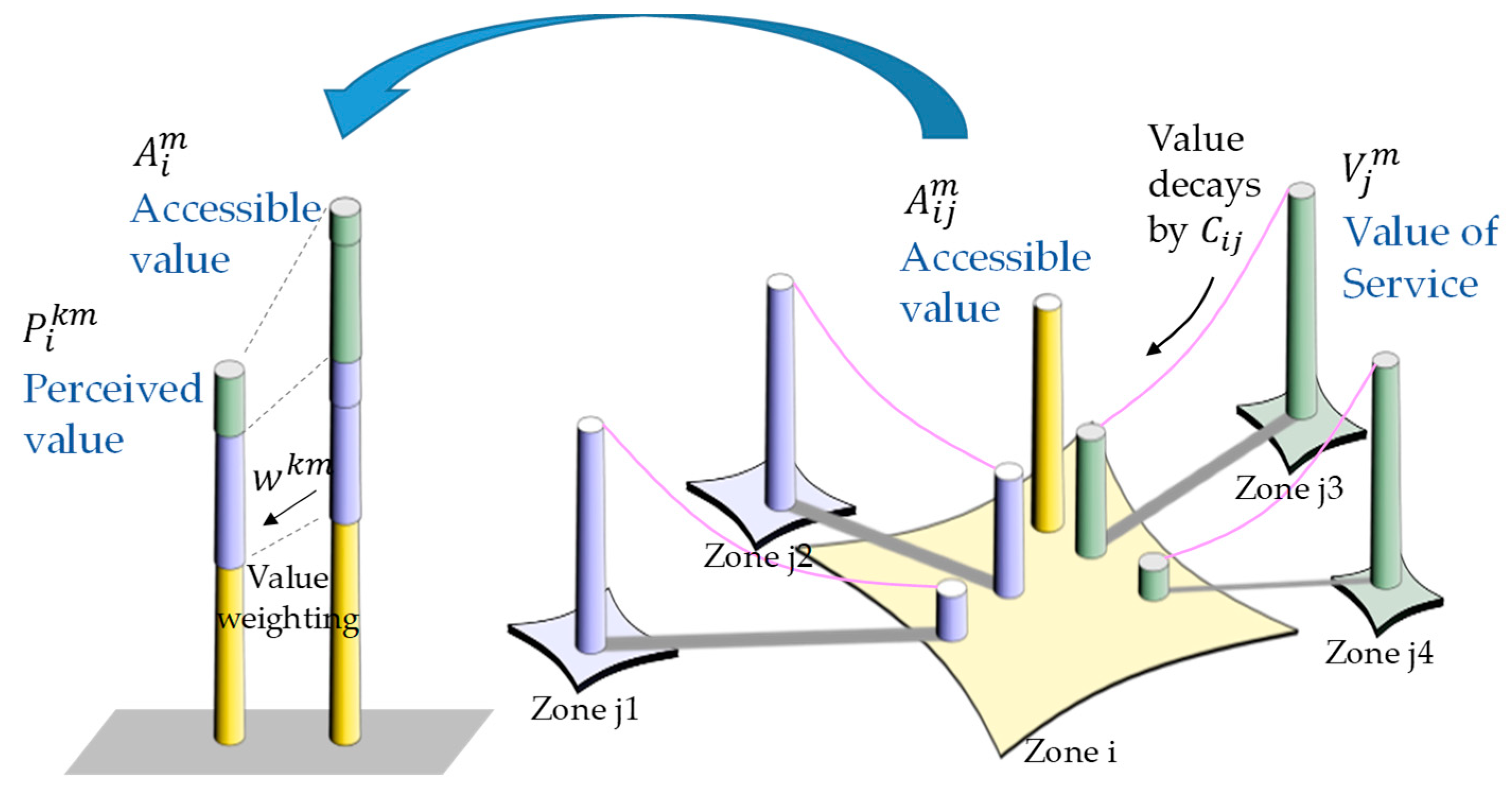
3.2. QOL Accessibility Method
3.2.1. Model Setting
3.2.2. Data Used
3.2.3. Parameter Estimation
3.2.4. Questionnaire Survey
4. Results of Analysis and Interpretations
4.1. Results of I/O–Spatial Interaction Model
4.1.1. Estimated Parameter
4.1.2. Estimated Productivity Impacts
4.2. Mutual Enhancement of Regional Economy and Personal QOL
4.2.1. Estimated Parameter of QOL and QOT by QOL Accessibility Method
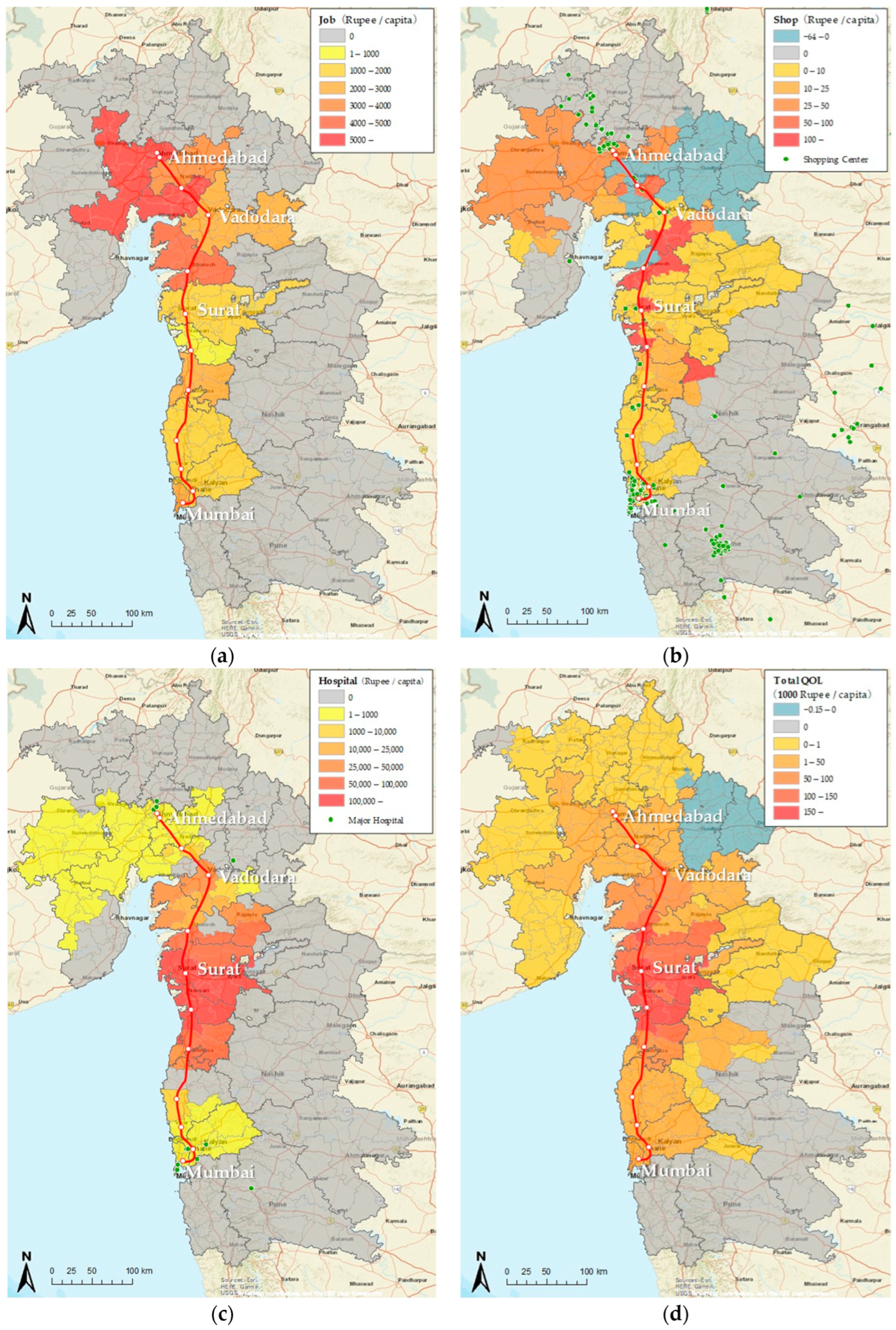
4.2.2. Mapping with Personal QOL Impacts
4.2.3. QOL Impacts by Personal Attributes
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rothengatter, W.; Hayashi, Y.; Fujisaki, K.; Kato, H.; Okuda, T.; Shibahara, N. Climate change impacts of intercity transport in the context of external costs and their internalisation. In Intercity Transport and Climate Change: Strategies for Reducing the Carbon Footprint, 2015th ed.; Hayashi, Y., Morichi, S., Oum, T.H., Rothengatter, W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 89–175. [Google Scholar]
- Indian Railways, Indian Railways Enquiry. Available online: http://www.indianrail.gov.in/enquiry/StaticPages/StaticEnquiry.jsp?StaticPage=index.html&locale=en (accessed on 31 July 2022).
- MAHSR Operational Plan. Available online: https://www.nhsrcl.in/en/project/mahsr-project-operational-planss (accessed on 31 July 2022).
- Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India, Census Tables, D-01. Available online: https://censusindia.gov.in/census.website/data/census-tables (accessed on 31 July 2022).
- Statistics Bureau of Japan, 1960 Population Census, Population, Area and Population Density for Shi, Ku, Machi and Mura: 1960. Available online: https://www.e-stat.go.jp/en/stat-search/files?page=1&layout=datalist&toukei=00200521&tstat=000001036867&cycle=0&tclass1=000001037497&tclass2val=0 (accessed on 31 July 2022).
- Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), Ministry of Railways, Republic of India (MOR), Joint Feasibility Study for Mumbai-Ahmedabad High Speed Railway Corridor, Final Report. July 2015. Available online: https://www.nhsrcl.in/en/project/feasibility-study-report (accessed on 31 July 2022).
- Source: OpenStreetMap. Available online: https://www.openstreetmap.org (accessed on 31 July 2022).
- Hayashi, Y.; Sugiyama, I. Dual strategies for the environmental and financial goals of sustainable cities: De-suburbanization and social capitalization. Built Environ. 2003, 29, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department for Transport, Transport Analysis Guidance (TAG) Unit A2-1 Wider Economic Impacts Appraisal. May 2019. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/guidance/transport-analysis-guidance-tag#overview (accessed on 31 July 2022).
- Chen, G.; Silva, J.A. Estimating the provincial economic impacts of high-speed rail in Spain: An application of structural equation modelling. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 111, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, B.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y. Exploring the impact of high speed railways on the spatial redistribution of economic activities-Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration as a case study. J. Transp. Geogr. 2016, 57, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickerman, R. High-speed rail and regional development: The case of intermediate stations. J. Transp. Geogr. 2015, 42, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Loo, B.P.Y.; Vickerman, R. High-speed rail networks, economic integration and regional specialisation in China and Europe. Travel Behav. Soc. 2015, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Kim, E. Spatial economic impact of road and railroad accessibility on manufacturing output: Inter-modal relationship between road and railroad. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 66, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hall, P. The wider spatial-economic impacts of high-speed trains: A comparative case study of Manchester and Lille sub-regions. J. Transp. Geogr. 2012, 24, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komikado, H.; Morikawa, S.; Bhatt, A.; Kato, H. High-speed rail, inter-regional accessibility, and regional innovation: Evidence from Japan. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 167, 120697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Miyamoto, K. A land use-transport model for metropolitan areas. Pap. Reg. Sci. Assoc. 1983, 51, 43–63. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Hayashi, Y.; Jia, P.; Yuan, Q. Economic Effect of High-Speed Rail: Empirical Analysis of Shinkansen’s Impact on Industrial Location. J. Transp. Eng. 2012, 138, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.J.; Gibbons, S. Quantifying wider economic impacts of agglomeration for transport appraisal: Existing evidence and future directions. Econ. Transp. 2019, 19, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chèze, C.; Nègre, R. Wider economic impacts of high-speed rail: Example of agglomeration benefits assessment on Bretagne Pays de Loire high speed rail project. Transport. Res. Procedia 2017, 25, 5307–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, B.; Rinaldi, A.; Roccotelli, M.; Fanti, M.P. Innovative Baseline Estimation Methodology for Key Performance Indicators in the Electro-Mobility Sector. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT), Paris, France, 23–26 April 2019; pp. 1367–1372. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, Y.; Morita, H.; Takeshita, H.; Kachi, N.; Kato, H. (Eds.) Mainstreaming Quality of Life in Evaluation of Transport and Spatial Planning, 1st ed.; Akashi Shoten: Tokyo, Japan, 2021; 380p. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Sugimori, S.; Hayashi, Y.; Takeshita, H. Empirical analysis on industrial sectors for quality of life improvement along high-speed rail corridors. In Frontiers in High-Speed Rail Development, 1st ed.; Hayashi, Y., Rothengatter, W., Seetha Ram, K.E., Eds.; Asian Development Bank Institute: Tokyo, Japan, 2021; pp. 218–228. [Google Scholar]
- Sugimori, S.; Hayashi, Y.; Takeshita, H.; Isobe, T. Evaluating the Regional Economic Impacts of High-Speed Rail and Interregional Disparity: A Combined Model of I/O and Spatial Interaction. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y. QOL Accessibility Method for Project Evaluation. Expressway Automob. 2020, 63, 6–10. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Kachi, N.; Kato, H.; Hayashi, Y. A computable model for optimizing residential relocation based on quality of life and social cost in built-up areas. J. East. Asia Soc. Transport. Stud. 2007, 7, 1460–1474. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, K.; Kii, M.; Nakanishi, H. An integrated evaluation method of accessibility, quality of life, and social interaction. Environ. Plan. B 2008, 35, 1098–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Hayashi, Y.; Shi, F.; Zhang, H.; Kato, H. Measuring and mapping the spatial distribution of the quality of life in a city: A case study in Nanjing. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2016, 20, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Doi, K.; Sugiyama, I. Evaluating infrastructure projects by means of measures of the quality of life. Proc. JSCE 2004, 751, 55–70. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MPI Results for Districts in India. Available online: https://ophi.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/Table-5a-India-District-MPI-2018-1.xlsx (accessed on 31 July 2022).
- India Style. Available online: https://warp.da.ndl.go.jp/info:ndljp/pid/11066444/www.jetro.go.jp/ext_images/_Reports/02/2018/fe2e7bc10241316e/7_all.pdf (accessed on 31 July 2022).
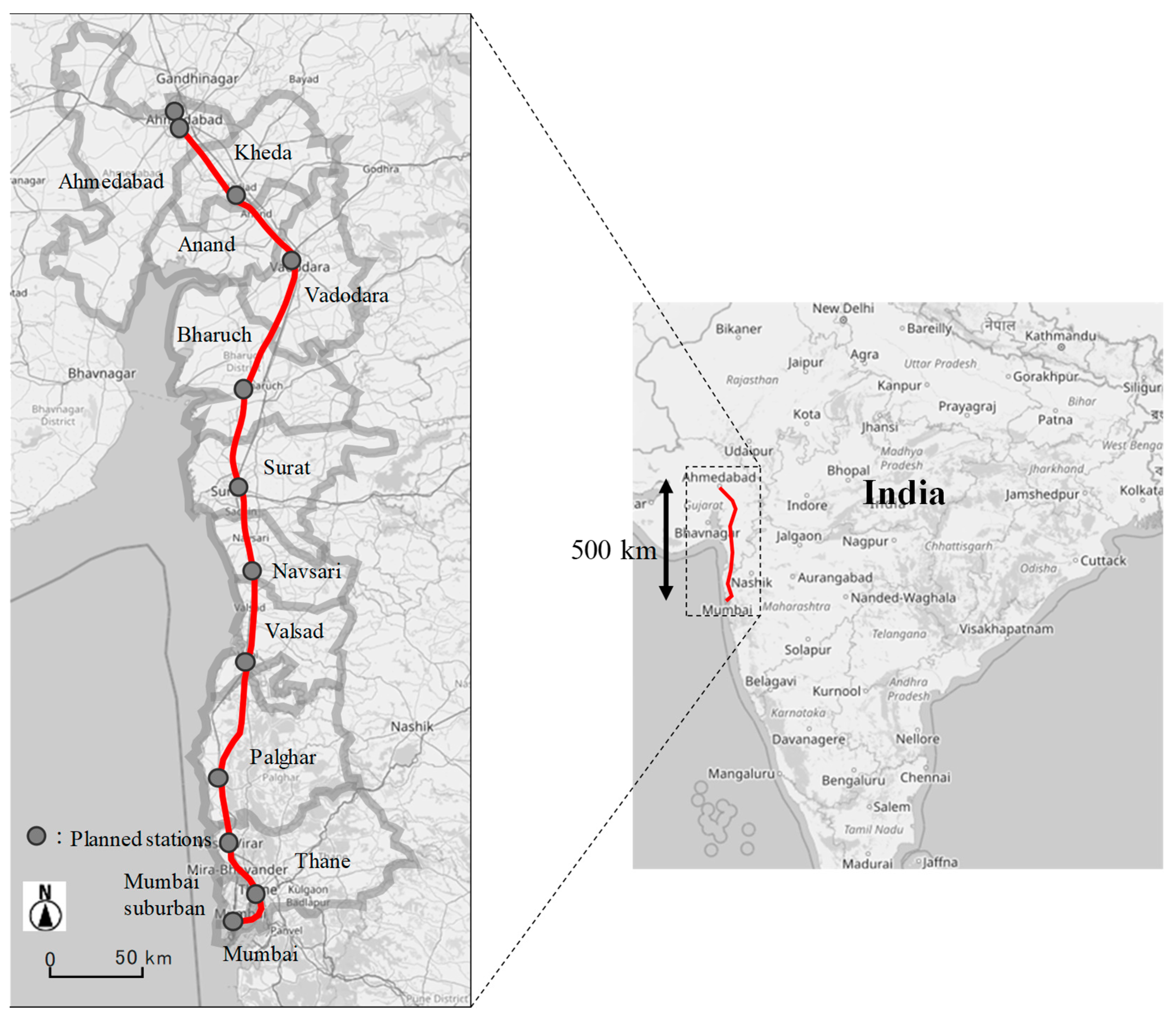


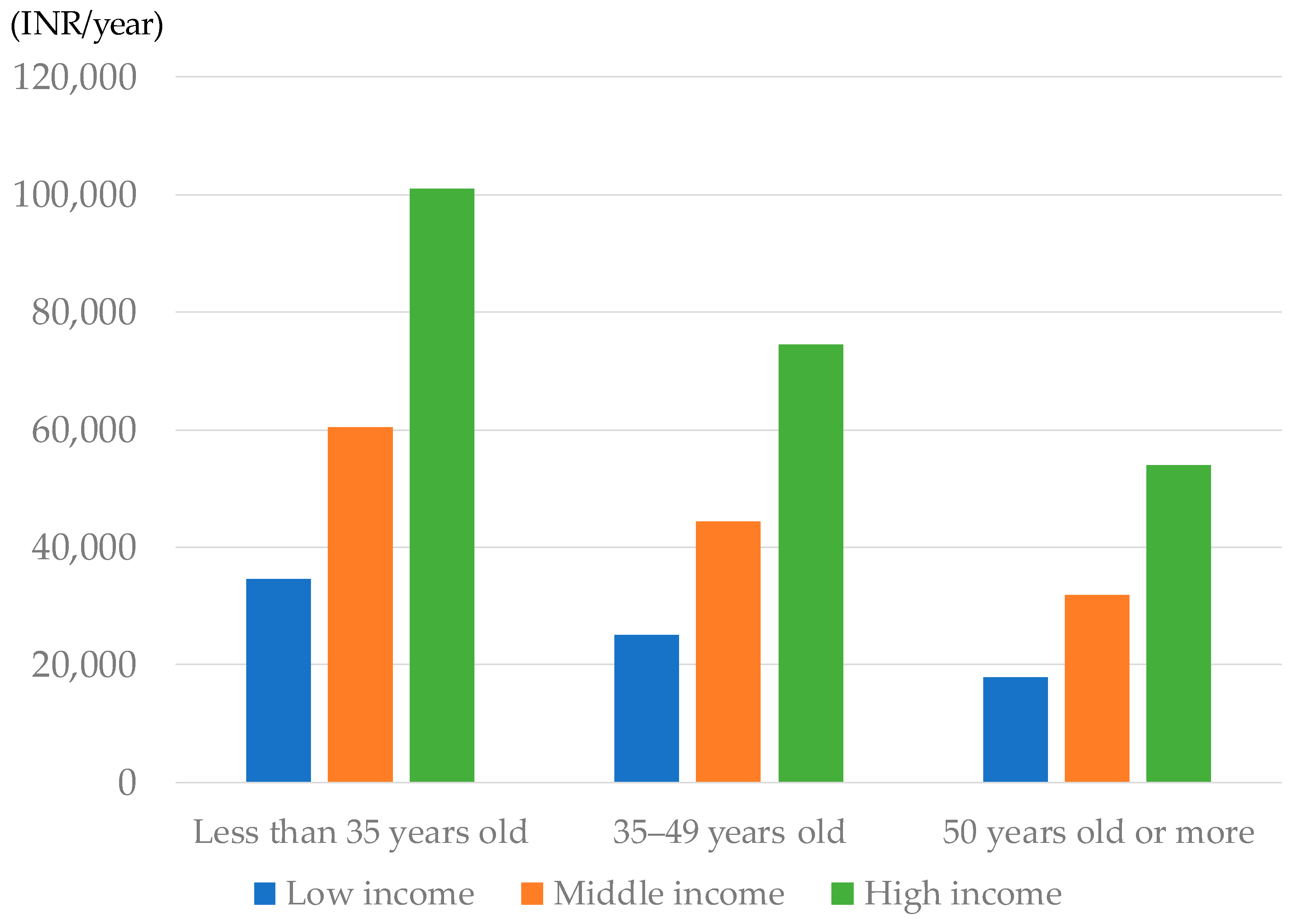
| State | District | Population | Area (km2) | Population Density (per km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gujarat | Ahmedabad | 7,214,225 | 8107 | 890 |
| Kheda | 2,299,885 | 3953 | 582 | |
| Anand | 2,092,745 | 3204 | 653 | |
| Vadodara | 4,165,626 | 7546 | 552 | |
| Bharuch | 1,551,019 | 6509 | 238 | |
| Surat | 6,081,322 | 4549 | 1337 | |
| Navsari | 1,329,672 | 2246 | 592 | |
| Valsad | 1,705,678 | 3008 | 567 | |
| Maharashtra | Thane (including Palghar) | 11,060,148 | 9558 | 1157 |
| Mumbai (including suburban) | 12,442,373 | 603 | 20,634 | |
| Total | 49,942,693 | 49,283 | 1013 (average) | |
| Category | Factors | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Economic opportunity | Access to office | Commuting time (min) |
| Job opportunity | Job opportunities (%) | |
| Residence | Housing cost (INR) | |
| Living and cultural opportunity | Medical care | Travel time to major hospitals (min) |
| Educational opportunity | Travel time to college/university (min) | |
| Tourism | Travel time to tourist locations (min) | |
| Shopping opportunity | Travel time to shopping centers (min) | |
| Recreational opportunity | Travel time to entertainment facilities (min) | |
| Travel time to cultural places (min) | ||
| Travel time to sporting facilities (min) | ||
| Amenity | Comfort of living | Floor space (sq. ft.) |
| Cleanliness | Cleanliness (level) | |
| Greenness | Greenery (%) | |
| Safety and security | Safe neighborhood | Crime rate (dummy) |
| Road safety | Traffic accidents (dummy) | |
| Disaster risk | Flood risk (dummy) | |
| Environmental burden | Air pollution | Air quality (AQI) |
| Noise pollution | Noise level (dB) | |
| Water quality | Drinking water quality (level) |
| Indicators | Detail |
|---|---|
| Total travel cost (INR) | The cost to travel from the origin to the destination |
| Total travel time (min) | The time need to travel from the origin to the destination |
| Delays in scheduled time (min) | How many minutes for which the journey is delayed |
| Prior booking time for seat reservation (days) | How many days before the journey should tickets be booked |
| Air conditioning (A/C) (dummy) | Whether air conditioning is available |
| Freedom while traveling (dummy) | Ability to work, read books, eat, etc., during the journey |
| Number of transfers | The number of transfers required from the origin to the destination |
| Wi-Fi (dummy) | Whether Wi-Fi is available |
| Link Type | Speed (km/h) | Fare (INR/km) |
|---|---|---|
| MAHSR | (Derived from Table 5) | 5 |
| Rail (Intercity) | 50 | 3.5 |
| Rail (Express) | 50 | 2 |
| Rail (Local) | 25 | 0.25 |
| Metro | 35 | 2 |
| Expressway | 50 | 2 |
| Road | 25 | 0.8 |
| Station | Distance from the Origin (km) | Travel Time (min) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fastest | Local | ||
| Mumbai | 0.0 | 0:00 | 0:00 |
| Thane | 28.0 | - | 0:10 |
| Virar | 65.2 | - | 0:24 |
| Boisar | 104.2 | - | 0:39 |
| Vapi | 167.9 | - | 0:59 |
| Bilimora | 216.6 | - | 1:15 |
| Surat | 264.6 | 0:58 | 1:32 |
| Bharuch | 323.1 | - | 1:52 |
| Vadodara | 397.1 | 1:32 | 2:14 |
| Anand/Nadiad | 447.4 | - | 2:32 |
| Ahmedabad | 500.2 | 1:59 | 2:50 |
| Sabarmati | 505.8 | 2:07 | 2:58 |
| Item | Category | Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 70% |
| Female | 30% | |
| Age | Young (Less than 35 years old) | 63% |
| Middle (35–49 years old) | 21% | |
| Old (50 years old or more) | 16% | |
| Income | Low (Less than INR 25,000/month) | 36% |
| Middle (INR 25,000–100,000/month) | 47% | |
| High (INR 100,000/month or more) | 17% |
| R2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture, forestry, and fishery | 0.988 | 0.144 | 0.53 |
| (3.34) | (0.04) | ||
| Manufacturing (including mining) | 0.959 | 0.634 | 0.99 |
| (35.01) | (1.63) | ||
| Construction | 0.976 | 0.290 | 0.97 |
| (16.71) | (0.39) | ||
| Infrastructure services | 1.031 | −0.536 | 0.94 |
| (11.42) | (-0.46) | ||
| Commerce | 0.957 | 0.548 | 0.97 |
| (15.69) | (0.71) | ||
| Hotels and restaurants | 1.077 | −1.191 | 0.92 |
| (10.48) | (−1.04) | ||
| Other services | 0.971 | 0.349 | 0.95 |
| (12.85) | (0.35) | ||
| Public services | 1.186 | −2.611 | 0.91 |
| (9.29) | (−1.90) |
| Indicators | Const. | Female | Young (Less Than 35 Years Old) | Old (50 Years Old or More) | Low Income (Less Than INR 25,000/Month) | High Income (INR 100,000/Month or More) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commuting time | 1.00 *** | – | – | – | −0.31 ** | – |
| Job opportunities | 1.11 *** | 0.33 ** | – | −0.63 *** | – | – |
| Housing cost | 0.84 *** | – | – | – | – | – |
| Travel time to major hospitals | 1.74 *** | – | 0.34 * | – | −0.40 ** | 0.30 |
| Travel time to college/university | 0.73 *** | 0.21 | – | – | – | – |
| Travel time to tourist locations | 0.14 | – | 0.27 * | – | – | – |
| Travel time to shopping centers | 0.34 *** | – | – | – | – | – |
| Travel time to entertainment facilities | 0.54 *** | – | 0.25 * | – | −0.22 * | – |
| Travel time to cultural places | 0.75 *** | – | – | – | – | – |
| Travel time to sporting facilities | 0.67 *** | −0.23 * | – | – | – | – |
| Floor space | 0.60 *** | – | – | −0.47 ** | – | – |
| Cleanliness | 0.81 *** | – | – | – | -0.17 | – |
| Greenery | 0.43 ** | – | 0.29 * | 0.33 | −0.31 ** | – |
| Crime rate | 2.60 *** | – | – | −0.39 * | −0.47 ** | – |
| Traffic accidents | 0.70 *** | – | – | – | – | 0.49 * |
| Flood risk | 0.56 *** | – | – | – | – | −0.55 * |
| Air quality | 1.26 *** | −0.31 * | – | −0.23 | −0.18 | – |
| Noise level | 0.84 *** | – | – | −0.36 * | – | – |
| Drinking water quality | 0.51 *** | – | 0.22 | – | – | – |
| Indicators | Const. | Female | Young (Less Than 35 Years Old) | Old (50 Years Old or More) | Low Income (Less Than INR 25,000/Month) | High Income (INR 100,000/Month or More) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total travel cost (INR) | 0.0014 *** | −0.0003 *** | −0.0002 ** | – | 0.0005 *** | −0.0005 *** |
| Total travel time (min) | 0.0050 *** | −0.0007 ** | – | −0.0008 ** | – | – |
| Delay in scheduled time (min) | 0.0153 *** | −0.0046 * | – | −0.0030 | – | – |
| Prior booking time for the seat reservation (days) | 0.0954 *** | – | – | – | – | – |
| Air conditioning (A/C) (dummy) | 0.6628 *** | – | – | −0.2472 * | −0.3509 *** | 0.4259 *** |
| Freedom while traveling (dummy) | 0.7357 *** | – | -0.1369 | −0.2702 * | – | – |
| Number of transfers (dummy) | 0.4408 *** | – | −0.1665 *** | 0.1359 * | – | – |
| Wi-Fi (dummy) | 0.5232 *** | – | −0.2596 ** | −0.2290 | – | – |
| Age | Income Class | QOL Increase (INR Million/Year) | Population | Averaged Personal QOL Increase (INR/Year) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Young (less than 35) | Low | 77,361 | 2,186,543 | 35,380 |
| Middle | 169,885 | 2,733,180 | 62,157 | ||
| High | 56,954 | 546,638 | 104,190 | ||
| Middle (35–49) | Low | 38,726 | 1,522,511 | 25,436 | |
| Middle | 86,585 | 1,903,128 | 45,496 | ||
| High | 29,313 | 380,623 | 77,012 | ||
| Old (50 or more) | Low | 19,798 | 1,126,476 | 17,575 | |
| Middle | 44,527 | 1,408,101 | 31,622 | ||
| High | 15,092 | 281,619 | 53,590 | ||
| Female | Young (less than 35) | Low | 63,133 | 1,875,982 | 33,653 |
| Middle | 137,260 | 2,344,982 | 58,534 | ||
| High | 45,698 | 468,996 | 97,438 | ||
| Middle (35–49) | Low | 33,331 | 1,360,352 | 24,502 | |
| Middle | 73,377 | 1,700,437 | 43,152 | ||
| High | 24,318 | 340,084 | 71,506 | ||
| Old (50 or more) | Low | 19,982 | 1,100,226 | 18,162 | |
| Middle | 44,408 | 1,375,286 | 32,290 | ||
| High | 14,968 | 275,058 | 54,419 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sugimori, S.; Hayashi, Y.; Takano, T.; Morita, H.; Takeshita, H.; Rao, K.V.K.; Isobe, T. Modeling the Mutual Enhancement of Regional Economy and Personal Quality of Life (QOL): A Case Study on the Mumbai–Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail Corridor in India. Future Transp. 2022, 2, 828-845. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp2040046
Sugimori S, Hayashi Y, Takano T, Morita H, Takeshita H, Rao KVK, Isobe T. Modeling the Mutual Enhancement of Regional Economy and Personal Quality of Life (QOL): A Case Study on the Mumbai–Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail Corridor in India. Future Transportation. 2022; 2(4):828-845. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp2040046
Chicago/Turabian StyleSugimori, Shuji, Yoshitsugu Hayashi, Tsuyoshi Takano, Hiroyoshi Morita, Hiroyuki Takeshita, K. V. Krishna Rao, and Tomohiko Isobe. 2022. "Modeling the Mutual Enhancement of Regional Economy and Personal Quality of Life (QOL): A Case Study on the Mumbai–Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail Corridor in India" Future Transportation 2, no. 4: 828-845. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp2040046
APA StyleSugimori, S., Hayashi, Y., Takano, T., Morita, H., Takeshita, H., Rao, K. V. K., & Isobe, T. (2022). Modeling the Mutual Enhancement of Regional Economy and Personal Quality of Life (QOL): A Case Study on the Mumbai–Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail Corridor in India. Future Transportation, 2(4), 828-845. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp2040046






