Quantified Explainability: Convolutional Neural Network Focus Assessment in Arrhythmia Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Electrocardiography Classification
2.2. Explainability in Electrocardiography Classification
3. Materials and Methods
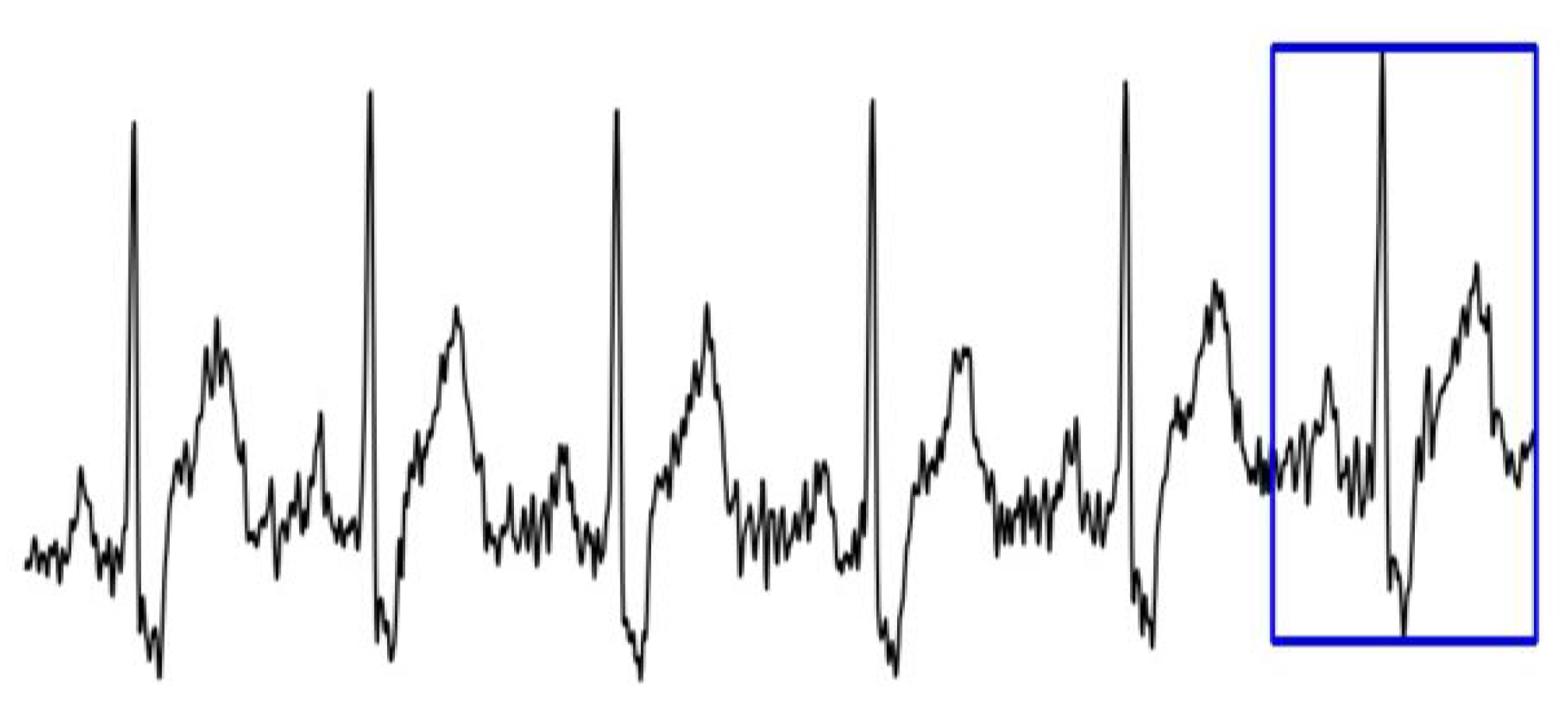
3.1. Dataset Description
- 1.
- Dataset 1—the binary label of each image corresponds to the label of the last heartbeat;
- 2.
- Dataset 2—the binary label of each image corresponds to the label of the first heartbeat.
3.2. Model Description
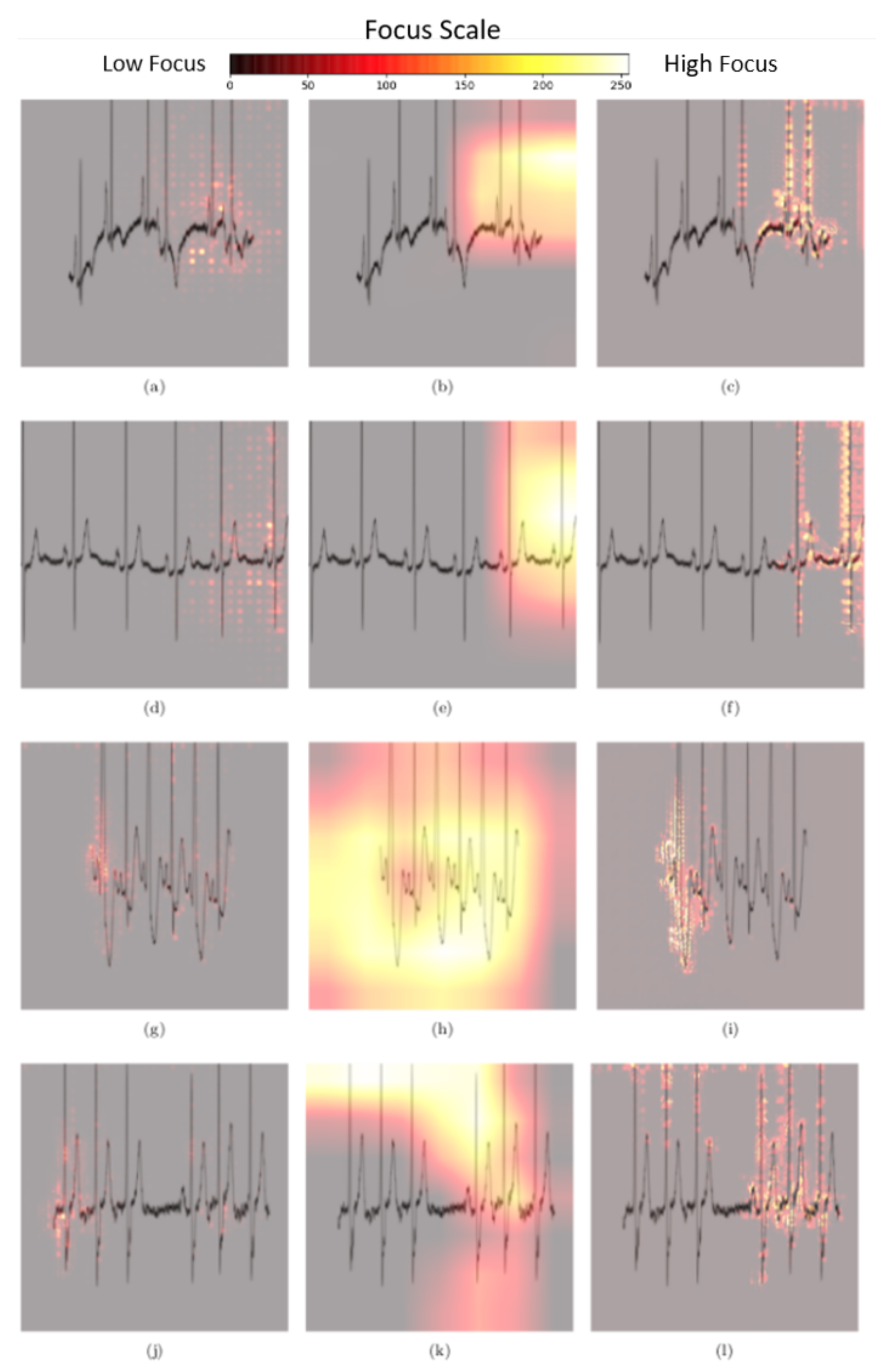
3.3. Explainability Methods
3.3.1. Gradients Method
3.3.2. Gradient-Weighted Class Activation Mapping
3.3.3. Guided Backpropagation Gradient-Weighted Class Activation Mapping
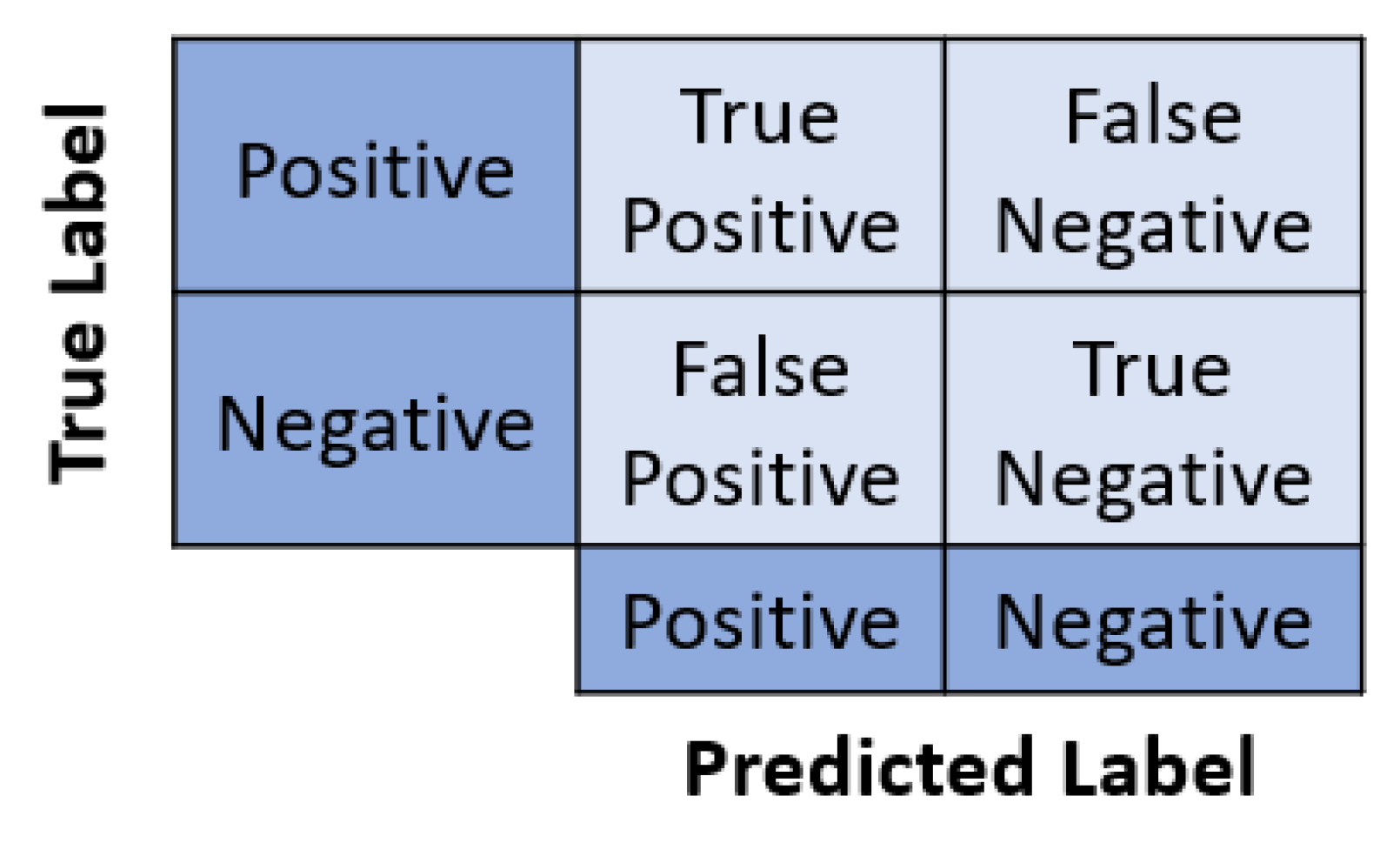
3.4. Quantitative Analysis of Pixel Attribution Maps
4. Results
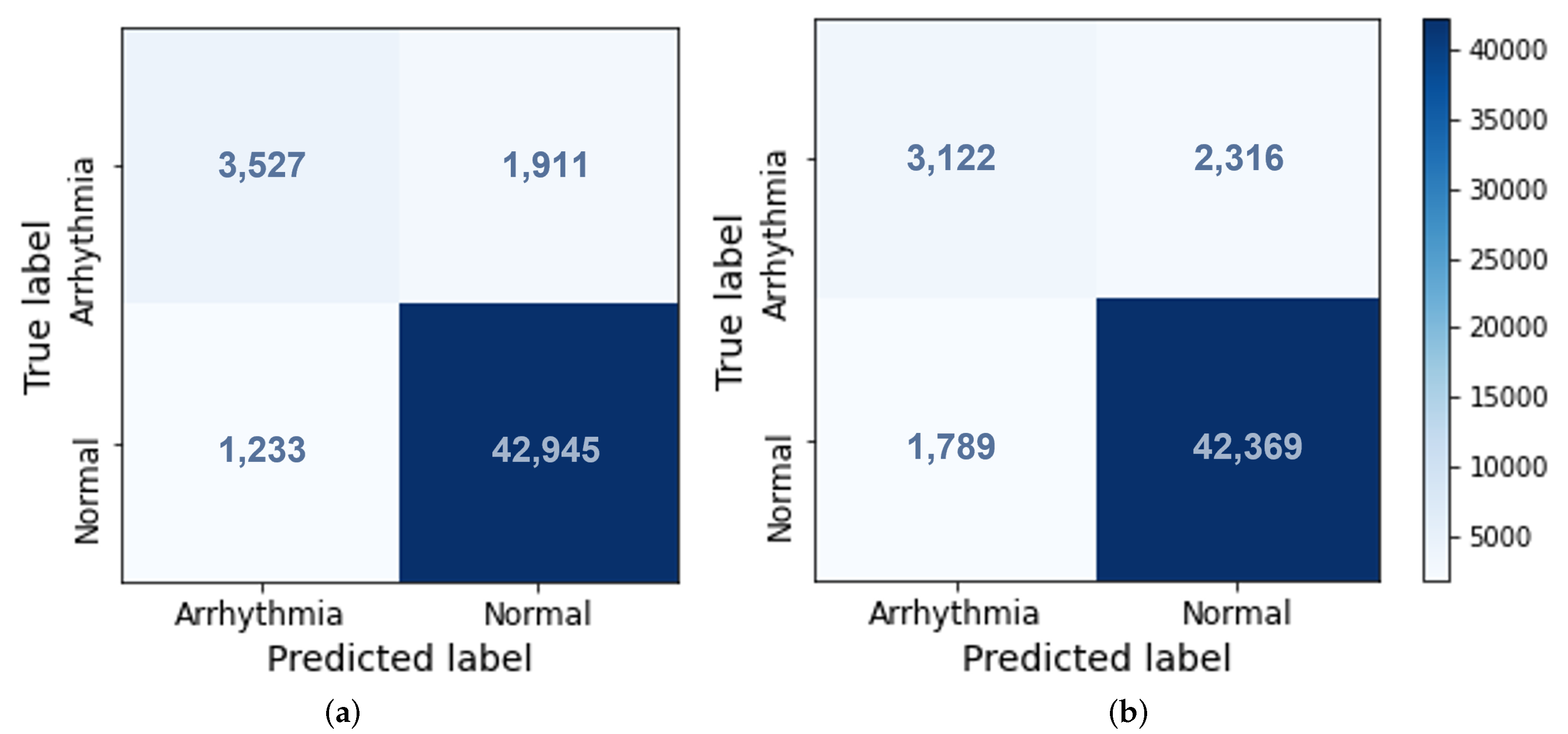
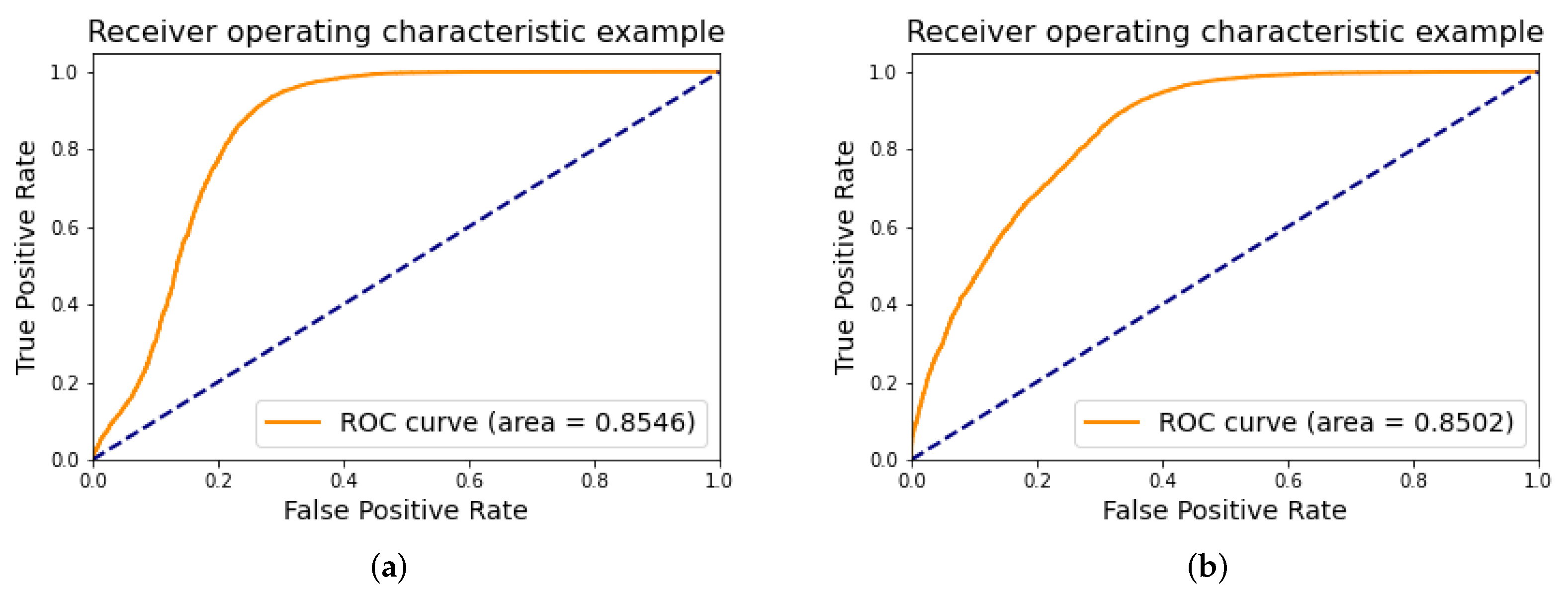
4.1. Classification
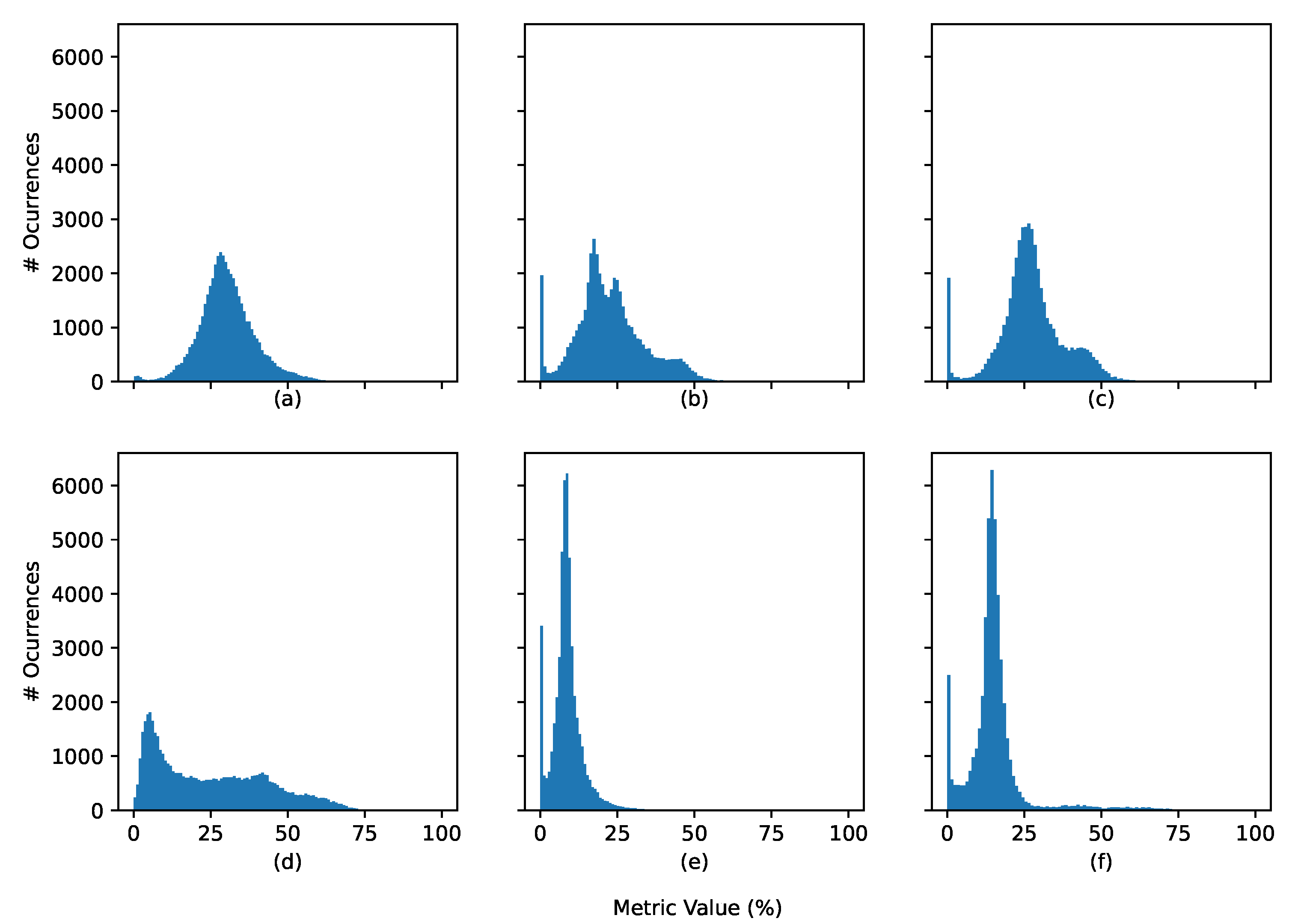
4.2. Explainability Metric
4.2.1. Generic Scenario
4.2.2. Correct vs. Incorrect Classification
4.2.3. Normal vs. Arrhythmia
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vellido, A. Societal Issues Concerning the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. Kidney Dis. 2019, 5, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Li, S.; Yan, C.; Li, M.; Jiang, C. Explaining the black-box model: A survey of local interpretation methods for deep neural networks. Neurocomputing 2021, 419, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamon, R.; Junklewitz, H.; Sanchez, I. Robustness and Explainability of Artificial Intelligence; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020; p. 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C. Stop explaining black box machine learning models for high stakes decisions and use interpretable models instead. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019, 1, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molnar, C. Interpretable Machine Learning. 2019. Available online: https://christophm.github.io/interpretable-ml-book/ (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Linardatos, P.; Papastefanopoulos, V.; Kotsiantis, S. Explainable ai: A review of machine learning interpretability methods. Entropy 2021, 23, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploug, T.; Holm, S. The four dimensions of contestable AI diagnostics—A patient-centric approach to explainable AI. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 107, 101901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapter 3—Rights of the Data Subject|General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). 2018. Available online: https://gdpr-info.eu/chapter-3/ (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Clarke, N.; Vale, G.; Reeves, E.P.; Kirwan, M.; Smith, D.; Farrell, M.; Hurl, G.; McElvaney, N.G. GDPR: An impediment to research? Ir. J. Med Sci. 2019, 188, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luz, E.J.d.S.; Schwartz, W.R.; Cámara-Chávez, G.; Menotti, D. ECG-based heartbeat classification for arrhythmia detection: A survey. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 127, 144–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, E.J.D.S.; Nunes, T.M.; De Albuquerque, V.H.C.; Papa, J.P.; Menotti, D. ECG arrhythmia classification based on optimum-path forest. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 3561–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, X.; Wang, C.; Si, W. ECG beat classification via deterministic learning. Neurocomputing 2017, 240, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyakillya, B.; Kazachenko, N.; Mikhailovsky, N. Deep Learning for ECG Classification. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 913, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, B.; Sung, N.J.; Min, S.; Hong, M. Deep learning in physiological signal data: A survey. Sensors 2020, 20, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Somani, S.; Russak, A.J.; Richter, F.; Zhao, S.; Vaid, A.; Chaudhry, F.; Freitas, J.K.D.; Naik, N.; Miotto, R.; Nadkarni, G.N.; et al. Deep learning and the electrocardiogram: Review of the current state-of-the-art. Europace 2021, 23, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, Z.; Loni, M.; Daneshtalab, M.; Gharehbaghi, A. A review on deep learning methods for ECG arrhythmia classification. Expert Syst. Appl. X 2020, 7, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahhal, M.M.; Bazi, Y.; Alhichri, H.; Alajlan, N.; Melgani, F.; Yager, R.R. Deep learning approach for active classification of electrocardiogram signals. Inf. Sci. 2016, 345, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degirmenci, M.; Ozdemir, M.A.; Izci, E.; Akan, A. Arrhythmic Heartbeat Classification Using 2D Convolutional Neural Networks. IRBM 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, M.; Shah, J.H.; Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Raza, M.; Damaševičius, R. From ECG signals to images: A transformation based approach for deep learning. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.G.; Muthukumar, B. Arrhythmia and Disease Classification Based on Deep Learning Techniques. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2021, 31, 835–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Afghah, F.; Acharya, U.R. HAN-ECG: An interpretable atrial fibrillation detection model using hierarchical attention networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 127, 104057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maweu, B.M.; Dakshit, S.; Shamsuddin, R.; Prabhakaran, B. CEFEs: A CNN Explainable Framework for ECG Signals. Artif. Intell. Med. 2021, 115, 102059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.Y.; Kwon, J.M.; Jeon, K.H.; Cho, Y.H.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Jung, M.S.; Ban, J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Detection and classification of arrhythmia using an explainable deep learning model. J. Electrocardiol. 2021, 67, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.; Jun, T.J.; Kim, Y.H. xECGNet: Fine-tuning attention map within convolutional neural network to improve detection and explainability of concurrent cardiac arrhythmias. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 208, 106281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moody, G.B.; Mark, R.G. The impact of the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2001, 20, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Li, F. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Sengupta, S.; Lakshminarayanan, V. Explainable deep learning models in medical image analysis. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Deep Inside Convolutional Networks: Visualising Image Classification Models and Saliency Maps. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1312.6034. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Springenberg, J.T.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Brox, T.; Riedmiller, M. Striving for simplicity: The all convolutional net. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015—Workshop Track Proceedings, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and Understanding Convolutional Networks. In Analytical Chemistry Research; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 12, pp. 818–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Why did you say that? visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. Rev. Hosp. Clin. 2016, 17, 331–336. [Google Scholar]
- Varandas, R.; Gonçalves, B. Quantified Explainability: Convolutional Neural Network Focus Assessment in Arrhythmia Detection. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Models | Train | Validation | Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Epochs | Accuracy | F-Score | Accuracy | F-Score | Precision | |
| Model 1 | 42 min | 7 | 94.06 | 96.82 | 93.66 | 96.47 | 74.10 |
| Model 2 | 33 min | 5 | 96.23 | 98.00 | 91.72 | 95.38 | 63.57 |
| Set | Gradients | Grad-CAM | GB Grad-CAM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | |||
| 2 |
| Set | Gradients | Grad-CAM | GB Grad-CAM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correct | Incorrect | Correct | Incorrect | Correct | Incorrect | |
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | ||||||
| Set | Gradients | Grad-CAM | GB Grad-CAM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abnormal | Normal | Abnormal | Normal | Abnormal | Normal | |
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varandas, R.; Gonçalves, B.; Gamboa, H.; Vieira, P. Quantified Explainability: Convolutional Neural Network Focus Assessment in Arrhythmia Detection. BioMedInformatics 2022, 2, 124-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2010008
Varandas R, Gonçalves B, Gamboa H, Vieira P. Quantified Explainability: Convolutional Neural Network Focus Assessment in Arrhythmia Detection. BioMedInformatics. 2022; 2(1):124-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarandas, Rui, Bernardo Gonçalves, Hugo Gamboa, and Pedro Vieira. 2022. "Quantified Explainability: Convolutional Neural Network Focus Assessment in Arrhythmia Detection" BioMedInformatics 2, no. 1: 124-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2010008
APA StyleVarandas, R., Gonçalves, B., Gamboa, H., & Vieira, P. (2022). Quantified Explainability: Convolutional Neural Network Focus Assessment in Arrhythmia Detection. BioMedInformatics, 2(1), 124-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2010008







