Mycophenolate Mofetil in the Management of Oral Mucocutaneous Diseases: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. History
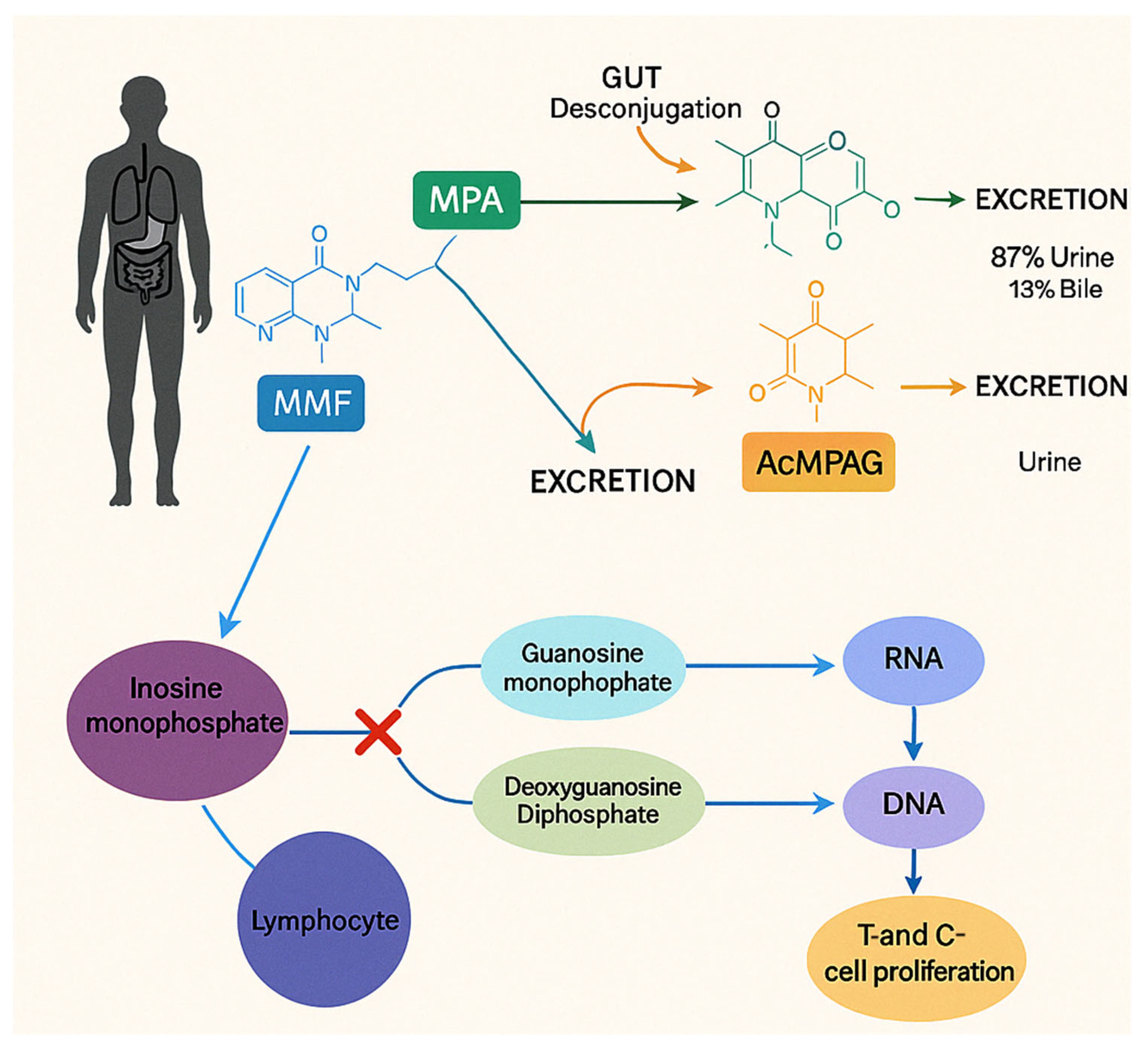
4. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
5. Adverse Effects
6. MMF’s Role in Oral Mucocutaneus and Inflammatory Disease
6.1. Oral Lichen Planus
6.2. Pemphigus Vulgaris
6.3. Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
6.4. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
6.5. Erythema Multiforme
6.6. Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis
7. Mechanism of Action
8. Limitations
9. Recommendations and Emerging Strategies
10. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Alhindi, N.A.; Sindi, A.M.; Binmadi, N.O.; Elias, W.Y. A retrospective study of oral and maxillofacial pathology lesions diagnosed at the Faculty of Dentistry, King Abdulaziz University. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2019, 11, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaty, C.S.; Short, A.G.; Mewar, P. Oral Mucosal Lesions, Immunologic Diseases. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, S.; Gs, V.; Sarode, G.S.; Sarode, S.C.; Khurayzi, T.A.; Mohamed Beshir, S.E.; Gadbail, A.R.; Gondivkar, S. Exploring the role of immunotherapeutic drugs in autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac Res. 2021, 11, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccucci, M.; Di Carlo, G.; Bossù, M.; Giovarruscio, F.; Salucci, A.; Polimeni, A. Autoimmune diseases and their manifestations on oral cavity: Diagnosis and clinical management. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 6836728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Casado, C.; Sanchez-Solares, J.; Izquierdo, E.; Díaz-Perales, A.; Barber, D.; Escribese, M.M. Oral Mucosa as a Potential Site for Diagnosis and Treatment of Allergic and Autoimmune Diseases. Foods 2021, 10, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mays, J.W.; Sarmadi, M.; Moutsopoulos, N.M. Oral manifestations of systemic autoimmune and inflammatory diseases: Diagnosis and clinical management. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2012, 12, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ship, J.A.; Chavez, E.M.; Doerr, P.A.; Henson, B.S.; Sarmadi, M. Recurrent Aphthous stomatitis. Quintessence Int. 2000, 31, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S. Oral manifestations of dermatologic disease: A focus on lichenoid lesions. Head Neck Pathol. 2011, 5, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, S.V.; de Carvalho, F.R.; Boggio, P.; Sotto, M.N.; Vilela, M.A.; Rivitti, E.A.; Nico, M.M. Lupus erythematosus: Clinical and histopathological study of oral manifestations and immunohistochemical profile of the inflammatory infiltrate. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2007, 34, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kridin, K. Subepidermal autoimmune bullous diseases: Overview, epidemiology, and associations. Immunol. Res. 2018, 66, 6–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn-Ristic, K.; Rzany, B.; Amagai, M.; Brocker, E.B.; Zillikens, D. Increased incidence of Pemphigus vulgaris in southern Europeans living in Germany compared with native Germans. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2002, 16, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.S.; Ahmed, A.R.; Anhalt, G.J.; Bernauer, W.; Cooper, K.D.; Elder, M.J.; Fine, J.D.; Foster, C.S.; Ghohestani, R.; Hashimoto, T.; et al. The first international consensus on mucous membrane pemphigoid: Definition, diagnostic criteria, pathogenic factors, medical treatment and prognostic indicators. Arch. Dermatol. 2002, 138, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayangco, L.; Rogers, R.S., 3rd. Oral manifestations of erythema multiforme. Dermatol. Clin. 2003, 21, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.B.; Porter, S.R.; Smoller, B.R.; Sitaru, C. Oral mucosal manifestations of autoimmune skin diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 930–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossù, M.; Montuori, M.; Casani, D.; Di Giorgio, G.; Pacifici, A.; Ladniak, B.; Polimeni, A. Altered transcription of inflammation-related genes in dental pulp of coeliac children. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2016, 26, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossù, M.; Bartoli, A.; Orsini, G.; Luppino, E.; Polimeni, A. Enamel hypoplasia in coeliac children: A potential clinical marker of early diagnosis. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2007, 8, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leuci, S.; Ruoppo, E.; Adamo, D.; Calabria, E.; Mignogna, M.D. Oral autoimmune vesicobullous diseases: Classification, clinical presentations, molecular mechanisms, diagnostic algorithms, and management. Periodontology 2000 2019, 80, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Goyal, A.; Sonthalia, S. Corticosteroid Adverse Effects. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hengge, U.R.; Ruzicka, T.; Schwartz, R.A.; Cork, M.J. Adverse effects of topical glucocorticosteroids. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 54, 1–15, quiz 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, G.; Al-Mashat, H.; Desta, T.; Graves, D.T. Diabetes prolongs the inflammatory response to a bacterial stimulus through cytokine dysregulation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruh, J.; Foster, C.S. Corticosteroid-sparing agents: Conventional systemic immunosuppressants. Dev. Ophthalmol. 2012, 51, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivhare, P.; Shankarnarayan, L.; Singh, A.; Patil, S.T.; Yadav, M. Role of immunomodulators in oral diseases. Int. J. Oral Health Med. Res. 2015, 2, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Staatz, C.E.; Tett, S.E. Pharmacology and toxicology of mycophenolate in organ transplant recipients: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1351–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, F.F.; Xie, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Ai, J.; Nie, S.; Liang, M.; Wang, G.; Jia, N.; et al. Effectiveness of mycophenolate mofetil among patients with progressive IgA nephropathy: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw. Open. 2023, 6, e2254054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Mycophenolate Mofetil. Available online: https://bnf.nice.org.uk/drugs/mycophenolate-mofetil/ (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Orvis, A.K.; Wesson, S.K.; Breza, T.S., Jr.; Church, A.A.; Mitchell, C.L.; Watkins, S.W. Mycophenolate mofetil in dermatology. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 60, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, J.S.; Shirlaw, P.J.; Challacombe, S.J.; Fetterfield, J.F. Efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil in severe mucocutaneous lichen planus: A retrospective review of 10 patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 167, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, K.K.; Hrin, M.L.; Jorizzo, J.L.; Strowd, L.C. Mycophenolate mofetil as a steroid-sparing agent in oral mucous membrane pemphigoid: A retrospective review. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2025, 39, e404–e406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, R.; Taylor, J.; Shephard, M.; Ahmed, R.; Carrozzo, M.; Setterfield, J.; Grando, S.; Mignogna, M.; Kuten-Shorrer, M.; Musbah, T.; et al. World Workshop on Oral Medicine VI: A systematic review of the treatment of mucocutaneous Pemphigus vulgaris. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2015, 120, 132–142.e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, G.B.; Contreras, G.; Dooley, M.A.; Ginzler, E.M.; Isenberg, D.; Jayne, D.; Li, L.S.; Mysler, E.; Sa, J.; Solomons, N.; et al. Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide for induction treatment of Lupus nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.M.; Tse, K.C.; Tang, C.S.; Mok, M.Y.; Li, F.K.; Hong Kong Nephrology Study Group. Long-term study of mycophenolate mofetil as continuous induction and maintenance treatment for diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, G.; Pardo, V.; Leclercq, B.; Lenz, O.; Tozman, E.; O’Nan, P.; Roth, D. Sequential therapies for proliferative lupus nephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, M.A.; Jayne, D.; Ginzler, E.M.; Isenberg, D.; Olsen, N.J.; Wofsy, D.; Eitner, F.; Appel, G.B.; Contreras, G.; Lisk, L.; et al. Mycophenolate versus azathioprine as maintenance therapy for Lupus nephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1886–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafey, E.M.; Abdou, S.H.; Shareef, M.M. Is mycophenolate mofetil superior to pulse intravenous cyclophosphamide for induction therapy of proliferative Lupus nephritis in Egyptian patients? Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2010, 14, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginzler, E.M.; Dooley, M.A.; Aranow, C.; Kim, M.Y.; Buyon, J.; Merrill, J.T.; Petri, M.; Gilkeson, G.S.; Wallace, D.J.; Weisman, M.H.; et al. Mycophenolate mofetil or intravenous cyclophosphamide for Lupus nephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2219–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginzler, E.M.; Wofsy, D.; Isenberg, D.; Gordon, C.; Lisk, L.; Dooley, M.A.; ALMS Group. Nonrenal disease activity following mycophenolate mofetil or intravenous cyclophosphamide as induction treatment for lupus nephritis: Findings in a multicenter, prospective, randomized, open-label, parallel-group clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houssiau, F.A.; D’Cruz, D.; Sangle, S.; Remy, P.; Vasconcelos, C.; Petrovic, R.; Fiehn, C.; de Ramon Garrido, E.; Gilboe, I.M.; Tektonidou, M.; et al. Azathioprine versus mycophenolate mofetil for long-term immunosuppression in Lupus nephritis: Results from the MAINTAIN Nephritis Trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 2083–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wu, X.; Xu, Y.; Shen, P.; Chen, N. Mycophenolate mofetil or tacrolimus compared with intravenous cyclophosphamide in the induction treatment for active lupus nephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, L.M.; Hooi, L.S.; Lim, T.O.; Goh, B.L.; Ahmad, G.; Ghazalli, R.; Teo, S.M.; Wong, H.S.; Tan, S.Y.; Shaariah, W.A.N.; et al. Randomized controlled trial of pulse intravenous cyclophosphamide versus mycophenolate mofetil in the induction therapy of proliferative Lupus nephritis. Nephrology 2005, 10, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.W.; Li, D.M.; Xu, G.S.; Sun, S.R. Comparison of the therapeutic effects of leflunomide and mycophenolate mofetil in the treatment of immunoglobulin A nephropathy manifesting with nephrotic syndrome. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 48, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.C.; Tang, A.W.; Wong, S.S.; Leung, J.C.; Ho, Y.W.; Lai, K.N. Long-term study of mycophenolate mofetil treatment in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Liu, C.; Xie, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, L. Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide for inducing remission of ANCA vasculitis with moderate renal involvement. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiemstra, T.F.; Walsh, M.; Mahr, A.; Savage, C.O.; De Groot, K.; Harper, L.; Hauser, T.; Neumann, I.; Tesar, V.; Wissing, K.M.; et al. Mycophenolate mofetil vs azathioprine for remission maintenance in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2010, 304, 2381–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chams-Davatchi, C.; Esmaili, N.; Daneshpazhooh, M.; Valikhani, M.; Balighi, K.; Hallaji, Z.; Barzegari, M.; Akhyani, M.; Ghodsi, S.Z.; Seirafi, H.; et al. Randomized controlled open-label trial of four treatment regimens for Pemphigus vulgaris. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 57, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beissert, S.; Werfel, T.; Frieling, U.; Böhm, M.; Sticherling, M.; Stadler, R.; Zillikens, D.; Rzany, B.; Hunzelmann, N.; Meurer, M.; et al. A comparison of oral methylprednisolone plus azathioprine or mycophenolate mofetil for the treatment of pemphigus. Arch. Dermatol. 2006, 142, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannides, D.; Apalla, Z.; Lazaridou, E.; Rigopoulos, D. Evaluation of mycophenolate mofetil as a steroid-sparing agent in pemphigus: A randomized, prospective study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhyani, M.; Chams-Davatchi, C.; Hemami, M.R.; Fateh, S. Efficacy and safety of mycophenolate mofetil vs. methotrexate for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 24, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Muscle Study Group. A trial of mycophenolate mofetil with prednisone as initial immunotherapy in Myasthenia gravis. Neurology 2008, 71, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meriggioli, M.N.; Rowin, J.; Richman, J.G.; Leurgans, S. Mycophenolate mofetil for myasthenia gravis: A double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 998, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemadifar, M.; Kazemi, M.; Chitsaz, A.; Hekmatnia, A.; Tayari, N.; Ghazavi, A.; Maghzi, A.H. Mycophenolate mofetil in combination with interferon beta-1a in the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: A preliminary study. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2011, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Frohman, E.M.; Cutter, G.; Remington, G.; Gao, H.; Rossman, H.; Weinstock-Guttman, B.; Durfee, J.E.; Conger, A.; Carl, E.; Treadaway, K.; et al. A randomized, blinded, parallel-group, pilot trial of mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept) compared with interferon beta-1a (Avonex) in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2010, 3, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remington, G.M.; Treadaway, K.; Frohman, T.; Salter, A.; Stüve, O.; Racke, M.K.; Hawker, K.; Agosta, F.; Sormani, M.P.; Filippi, M.; et al. A one-year prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, quadruple-blinded, phase II safety pilot trial of combination therapy with interferon beta-1a and mycophenolate mofetil in early relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (TIME MS). Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2010, 3, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, G.H.; Hassan, A.H.; Al-Hazmi, F.; Kurakula, M.; Al-Dharrabh, A.; Alkhalidi, H.M.; Al-Ahdal, A.M.; Hamed, M.T.; Pashley, D.H. Zein based magnesium oxide nanowires: Effect of anionic charge on size, release and stability. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2017, 12, 741–749. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhalidi, H.M.; Naguib, G.H.; Kurakula, M.; Hamed, M.T.; Attar, M.H.; Almatrook, Z.H.; Aldryhim, A.Y.; Bahmdan, R.H.; Khallaf, R.A.; El Sisi, A.M.; et al. In vitro and preclinical assessment of factorial design based nanoethosomal transdermal film formulation of mefenamic acid. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, G.H.; Abd El-Aziz, G.S.; Kayal, R.A.; Mira, A.I.; Hajjaj, M.S.; Mously, H.A.; Hamed, M.T. Cytotoxic effects of dose dependent inorganic magnesium oxide nanoparticles on the reproductive organs of rats. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2258917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, G.H.; Abd El-Aziz, G.S.; Almehmadi, A.; Bayoumi, A.; Mira, A.I.; Hassan, A.H.; Hamed, M.T. Evaluation of the time-dependent osteogenic activity of glycerol incorporated magnesium oxide nanoparticles in induced calvarial defects. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, G.H.; Abd El-Aziz, G.S.; Mously, H.A.; Alhazmi, W.A.; Alnowaiser, A.M.; Hassan, A.H.; Hamed, M.T. In vitro Investigation of the Antimicrobial Activity of Mouth Washes Incorporating Zein-Coated Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2021, 13, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, G.H.; Hosny, K.M.; Hassan, A.H.; Al Hazmi, F.; Al Dharrab, A.; Alkhalidi, H.M.; Hamed, M.T.; Alnowaiser, A.M.; Pashley, D.H. Zein based magnesium oxide nanoparticles: Assessment of antimicrobial activity for dental implications. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 31 (Suppl. 1), 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifian, S.; Loghmani, A.; Nayyerain, S.; Javanbakht Samani, S.; Daneii, P. Application of magnesium oxide nanoparticles in dentistry: A literature review. Eur. J. Gen. Dent. 2023, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueira, T.B.; Kildegaard, K.R.; Hansen, B.G.; Mortensen, U.H.; Hertweck, C.; Nielsen, J. Molecular basis for mycophenolic acid biosynthesis in Penicillium brevicompactum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3035–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchin, J.E.; Pomeranz, M.K.; Pak, G.; Washenik, K.; Shupack, J.L. Rediscovering mycophenolic acid: A review of its mechanism, side effects, and potential uses. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1997, 37 Pt 1, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, G. Anthony Clifford Allison. Lancet 2014, 383, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, A.C.; Kowalski, W.J.; Muller, C.D.; Eugui, E.M. Mechanisms of action of mycophenolic acid. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 696, 63–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.H.; Eugui, E.; Wang, C.C.; Allison, A.C. Synthesis and immunosuppressive activity of some side-chain variants of mycophenolic acid. J. Med. Chem. 1990, 33, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eugui, E.M.; Allison, A.C. Immunosuppressive activity of mycophenolate mofetil. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 685, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, A.C.; Eugui, E.M. Purine metabolism and immunosuppressive effects of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF). Clin. Transplant. 1996, 10, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, A.C.; Eugui, E.M. The design and development of an immunosuppressive drug, mycophenolate mofetil. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 1993, 14, 353–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, A.C.; Eugui, E.M. Immunosuppressive and other effects of mycophenolic acid and an ester prodrug, mycophenolate mofetil. Immunol. Rev. 1993, 136, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechstein, W.O.; Suzuki, Y.; Kawamura, T.; Jaffee, B.; Allison, A.; Hullett, D.A.; Sollinger, H.W. Low-dose combination therapy of DUP-785 and RS-61443 prolongs cardiac allograft survival in rats. Transpl. Int. 1992, 5 (Suppl. 1), S482–S483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, T.; Hullett, D.A.; Suzuki, Y.; Bechstein, W.O.; Allison, A.M.; Sollinger, H.W. Enhancement of allograft survival by combination RS-61443 and DUP-785 therapy. Transplantation 1993, 55, 691–694; discussion 694–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.O.; Ensley, R.D.; Olsen, S.L.; Dunn, D.; Renlund, D.G. Mycophenolate mofetil (RS-61443): Preclinical, clinical, and three-year experience in heart transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 1994, 13, 571–582. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. “CellCept (Mycophenolate Mofetil) Capsules and Oral Suspension Approval History.” FDA Drugs@FDA Database. 30 August 1995. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=overview.process&ApplNo=050722 (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. “Assessment report: Mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept).” EMA/CHMP/150558/1996. July 1996. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/cellcept (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Rochecom. Cellcept Registry Data Demonstrated Superior Long-Term Organ Transplant Outcomes; F. Hoffmann—La Roche Ltd.: Basel, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. Myfortic [Package Insert]; Novartis: East Hanover, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Budde, K.; Dürr, M.; Liefeldt, L.; Neumayer, H.H.; Glander, P. Enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2010, 9, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, K.; Bauer, S.; Hambach, P.; Hahn, U.; Röblitz, H.; Mai, I.; Diekmann, F.; Neumayer, H.H.; Glander, P. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic comparison of enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium and mycophenolate mofetil in maintenance renal transplant patients. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Rahman, A.N.; Tett, S.E.; Staatz, C.E. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of mycophenolate in patients with autoimmune disease. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 52, 303–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shipkova, M.; Armstrong, V.W.; Oellerich, M.; Wieland, E. Mycophenolate mofetil in organ transplantation: Focus on metabolism, safety and tolerability. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2005, 1, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tett, S.E.; Saint-Marcoux, F.; Staatz, C.E.; Brunet, M.; Vinks, A.A.; Miura, M.; Marquet, P.; Kuypers, D.R.; van Gelder, T.; Cattaneo, D. Mycophenolate, clinical pharmacokinetics, formulations, and methods for assessing drug exposure. Transplant. Rev. 2011, 25, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiyama, N.; Miura, M.; Kato, S.; Sone, T.; Isobe, M.; Satoh, S. Involvement of carboxylesterase 1 and 2 in the hydrolysis of mycophenolate mofetil. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 2210–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullingham, R.E.S.; Nicholls, A.J.; Kanmm, B.R. Clinical pharmacokinetics of mycophenolate mofetil. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1998, 34, 429–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, G.; Bullingham, R.; Kamm, B.; Hale, M. Pharmacokinetics of oral mycophenolate mofetil in volunteer subjects with varying degrees of hepatic oxidative impairment. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1996, 36, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.M.; Korecka, M.; Venkataramanan, R.; Goldberg, L.; Bloom, R.; Brayman, K.L. Mycophenolic acid pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics provide a basis for rational monitoring strategies. Am. J. Transplant. 2003, 3, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staatz, C.E.; Tett, S.E. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of mycophenolate in solid organ transplant recipients. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2007, 46, 13–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, V.; Sangkuhl, K.; Sanghavi, K.; Thorn, C.F.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Hebert, J.M.; Altman, R.B. PharmGKB summary: Mycophenolic acid pathway. Pharmacogenet Genom. 2014, 24, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.M.; Figurski, M.; Milone, M.C.; Leichtman, A.B.; Sollinger, H.W. Therapeutic drug monitoring of mycophenolic acid. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, P.I. Identification of uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferases involved in the metabolism and clearance of mycophenolic acid. Ther. Drug Monit. 2000, 22, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, N.; Ratanasavanh, D.; Premaud, A.; Berdeaux, A.; Jeanneau, C.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Dreyer, C. Identification of the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase isoforms involved in mycophenolic acid phase II metabolism. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005, 33, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shipkova, M.; Wieland, E.; Schutz, E.; Armstrong, V.W.; Oellerich, M. The acyl glucuronide metabolite of mycophenolic acid inhibits the proliferation of human mononuclear leukocytes. Transplant. Proc. 2001, 33, 1080–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uwai, Y.; Motohashi, H.; Tsuji, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Tanigawara, Y. Interaction and transport characteristics of mycophenolic acid and its glucuronide via human organic anion transporters hOAT1 and hOAT3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, N.A.; Burckhardt, B.C.; Burckhardt, G.; Koeppel, C.; Arndt, M. Mycophenolic acid and its glucuronide metabolites interact with transport systems in the basolateral membrane of the human kidney. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22, 2497–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, M.; Satoh, S.; Inoue, K.; Kagaya, H.; Ogawa, K.; Nakanishi, T. Influence of SLCO1B1, 1B3, 2B1 and ABCC2 genetic polymorphisms on mycophenolic acid pharmacokinetics in Japanese renal transplant recipients. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 63, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, M.; Kagaya, H.; Satoh, S.; Inoue, K.; Nakanishi, T.; Ogawa, K. Influence of drug transporters and UGT polymorphisms on pharmacokinetics of phenolic glucuronide metabolite of mycophenolic acid in Japanese renal transplant recipients. Ther. Drug Monit. 2008, 30, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, N.; Yee, S.W.; Woillard, J.B.; Hulot, J.S.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Dreyer, C.; Ratanasavanh, D. Role of organic anion transporting polypeptides and their genetic variants in mycophenolic acid pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 87, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, F.; Jiao, Z.; Dao, Y.J.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Zhou, J. Association of UGT1A8, SLCO1B3 and ABCC2/ABCG2 polymorphisms with pharmacokinetics of mycophenolic acid in Chinese individuals. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 683–690. [Google Scholar]
- Naesens, M.; Kuypers, D.R.; Verbeke, K.; Vanrenterghem, Y.; Lerut, E.; Evenepoel, P. MDR protein 2 polymorphisms influence mycophenolic acid exposure in renal allograft recipients. Transplantation 2006, 82, 1074–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloberas, N.; Torras, J.; Cruzado, J.M.; Rivera, F.; Vidal, C.; Grinyo, J.M. Influence of MRP2 on MPA pharmacokinetics: Results of the Symphony Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3784–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Meur, Y.; Borrows, R.; Pescovitz, M.D.; Rostaing, L.; Kahan, B.D.; Shaw, L.M. Therapeutic drug monitoring of mycophenolates in kidney transplantation: Report of The Transplantation Society consensus meeting. Transplant. Rev. 2011, 25, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gelder, T.; Le Meur, Y.; Shaw, L.M.; de Fijter, J.W.; Haufroid, V.; Budde, K. Therapeutic drug monitoring of mycophenolate mofetil in transplantation. Ther. Drug Monit. 2006, 28, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woillard, J.-B.; Saint-Marcoux, F.; Monchaud, C.; Youdarène, R.; Pouche, L.; Marquet, P. Mycophenolic mofetil optimized pharmacokinetic modelling, and exposure-effect associations in adult heart transplant recipients. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedstrom, L. IMP Dehydrogenase: Structure, mechanism, and inhibition. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2903–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glander, P.; Hambach, P.; Liefeldt, L.; Budde, K. Inosine 5′-monophosphate dehydrogenase activity as a biomarker in the field of transplantation. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, A.; Glander, P.; Vitt, E.; Budde, K.; Zidek, W.; Djuric, Z.; Schneeberger, H. Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase activity in paediatrics: Age-related regulation and response to mycophenolic acid. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 68, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, V.; Pandit, R.A.; Ambapurkar, S.; Sengar, M.; Kulkarni, A.P. Drug interactions between antimicrobial and immunosuppressive agents in solid organ transplant recipients. Indian. J. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 25, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Benjanuwattra, J.; Pruksakorn, D.; Koonrungsesomboon, N. Mycophenolic acid and its pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions in humans: Review of the evidence and clinical implications. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 60, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naesens, M.; Kuypers, D.R.; Streit, F.; Armstrong, V.W.; Oellerich, M.; Verbeke, K.; Vanrenterghem, Y. Rifampin induces alterations in mycophenolic acid glucuronidation and elimination: Implications for drug exposure in renal allograft recipients. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 80, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderer, O.J.; Dupuis, R.E.; Heinzen, E.L.; Remmel, R.P.; Sellers, E.M. The influence of norfloxacin and metronidazole on the disposition of mycophenolate mofetil. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 45, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, L.E.; Rasmussen, A.; Norrelykke, M.R.; Krag, A.; Møller, S. The effect of selective bowel decontamination on the pharmacokinetics of mycophenolate mofetil in liver transplant recipients. Liver Transpl. 2001, 7, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrows, R.; Chusney, G.; Loucaidou, M.; Briggs, J.D.; Moran, S.M. The magnitude and time course of changes in mycophenolic acid 12-hour predose levels during antibiotic therapy in mycophenolate mofetil-based renal transplantation. Ther. Drug Monit. 2007, 29, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratna, P.; Mathew, B.S.; Annapandian, V.M.; Pillai, H.; Simon, S. Pharmacokinetic drug interaction of mycophenolate with co-amoxiclav in renal transplant patients. Transplantation 2011, 91, e36–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullingham, R.E.; Shah, J.; Goldblum, R.; Kamm, B.R. Effects of food and antacid on the pharmacokinetics of single doses of mycophenolate mofetil in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1996, 41, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaier, M.; Scholl, C.; Scharpf, D.; Budde, K.; Zidek, W.; Reuter, S. Proton pump inhibitors interfere with the immunosuppressive potency of mycophenolate mofetil. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 2061–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fukuda, T.; Brunner, H.I.; Sagcal-Gironella, A.C.P.; Vinks, A.A. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may reduce enterohepatic recirculation of mycophenolic acid in patients with childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Ther Drug Monit. 2011, 33, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasić, A.; Catić-Đorđević, A.; Veličković-Radovanović, R.; Stefanović, N.; Džodić, P.; Cvetković, T. Adverse effects of mycophenolic acid in renal transplant recipients: Gender differences. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2019, 41, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharfan-Dabaja, M.; Mhaskar, R.; Reljic, T.; Pidala, J.; Perkins, J.B.; Djulbegovic, B.; Kumar, A. Mycophenolate mofetil versus methotrexate for prevention of graft-versus-host disease in people receiving allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD010280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Earley, A.K.; Webster, A.C.; Schmid, C.H.; Balk, E.M.; Uhlig, K. Mycophenolic acid versus azathioprine as primary immunosuppression for kidney transplant recipients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD007746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.C. Mycophenolate mofetil for Lupus nephritis: An update. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 11, 1353–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H. The emergence of mycophenolate mofetil in dermatology: From its roots in the world of organ transplantation to its versatile role in the dermatology treatment room. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2011, 4, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moder, K.G. Mycophenolate mofetil: New applications for this immunosuppressant. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2003, 90, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvadori, M.; Holzer, H.; De Mattos, A.; Sollinger, H.; Arns, W.; Oppenheimer, F.; Maca, J.; Hall, M. Enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium is therapeutically equivalent to mycophenolate mofetil in de novo renal transplant patients. Am J Transplant. 2004, 4, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geevasinga, N.; Wallman, L.; Katelaris, C.H. Mycophenolate mofetil; a review of indications and use in a large tertiary hospital. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005, 4, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnason, I. Enteric coating of mycophenolate sodium: A rational approach to limit topical gastrointestinal lesions and extend the therapeutic index of mycophenolate. Transplant. Proc. 2001, 33, 3238–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arns, W.; Breuer, S.; Choudhury, S.; Taccard, G.; Lee, J.; Binder, V.; Roettele, J.; Schmouder, R. Enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium delivers bioequivalent MPA exposure compared with mycophenolate mofetil. Clin Transplant. 2005, 19, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrend, M. Adverse gastrointestinal effects of mycophenolate mofetil. Drug Saf. 2001, 24, 645–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, V.; Mackool, B.T. Mycophenolate in dermatology. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2003, 14, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arns, W. Noninfectious gastrointestinal (GI) complications of mycophenolic acid therapy: A consequence of local GI toxicity? Transplant. Proc. 2007, 39, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipkova, M.; Armstrong, V.W.; Oellerich, M.; Wieland, E. Acyl glucuronide drug metabolites: Toxicological and analytical implications. Ther. Drug Monit. 2003, 25, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieland, E.; Shipkova, M.; Schellhaas, U.; Schütz, E.; Niedmann, P.D.; Armstrong, V.W.; Oellerich, M. Induction of cytokine release by the acyl glucuronide of mycophenolic acid: A link to side effects? Clin. Biochem. 2000, 33, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calmet, F.H.; Yarur, A.J.; Pukazhendhi, G.; Ahmad, J.; Bhamidimarri, K.R. Endoscopic and histological features of mycophenolate mofetil colitis in patients after solid organ transplantation. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 366–373. [Google Scholar]
- Roche. CellCept Capsule Data Sheet. Roche. 2012. Available online: http://www.medsafe.govt.nz/profs/Datasheet/c/CellCeptcapsuspinf.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Novartis. Myfortic (Mycophenolic Acid) Delayed-Release Tablets. U.S. Prescribing Information. Silver Spring, MD: U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2012. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/050791s007lbl.pdf (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- Yun, J.S.W.; Yap, T.; Martyres, R.; Kern, J.S.; Varigos, G.; Scardamaglia, L. The association of mycophenolate mofetil and human herpesvirus infection. J. Dermatolog Treat. 2020, 31, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Service. Shared care guideline: Mycophenolate mofetil. British Association of Dermatologists. 2013. Available online: https://www.skinhealthinfo.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/Mycophenolate-Mofetil-Update-September-2017-Lay-review-August-20173.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2024).
- George, L.; Hamann, I.; Chen, K.; Choi, J.; Fernandez-Peñas, P. An analysis of the dermatological uses of mycophenolate mofetil in a tertiary hospital. J. Dermatolog Treat. 2015, 26, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoopler, E.T.; Sollecito, T.P. Oral mucosal diseases: Evaluation and management. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 98, 1323–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, A.; Woo, S.-B. Adverse drug events in the oral cavity. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2015, 119, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, T.G.; Duvic, M.; Van Voorhees, A.S.; VanBeek, M.J.; Frieden, I.J. American Academy of Dermatology Association Task Force. The use of topical calcineurin inhibitors in dermatology: Safety concerns. Report of the American Academy of Dermatology Association Task Force. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 54, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennis, P.; Gelfand, J.M.; Rothman, K.J. Evaluation of cancer risk related to atopic dermatitis and use of topical calcineurin inhibitors. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltenborn, A.; Schrem, H. Mycophenolate mofetil in liver transplantation: A review. Ann. Transplant. 2013, 18, 685–696. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, R.V.; Clark, L.N.; Lebwohl, M.; Weinberg, J.M. Treatments for psoriasis and the risk of malignancy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 60, 1001–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Electronic Medicines Compendium. Cellcept 500mg Film-Coated Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/1103/ (accessed on 2 November 2024).
- Nazemi, T.M.; Esmaeli, N.; Sedaghat, Y.; Mostafa, S. Efficacy of oral metronidazole in patients with generalized cutaneous lichen planus. Iran. J. Dermatol. 2006, 9, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Glick, M. Chapter 5: Red and white lesions of the oral mucosa. In Burket’s Oral Medicine, 12th ed.; PMPH-USA Ltd.: Shelton, CT, USA, 2015; pp. 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Beigom Taheri, J.; Anbari, F.; Maleki, Z.; Boostani, S.; Zarghi, A.; Pouralibaba, F. Efficacy of Elaeagnus angustifolia topical gel in the treatment of symptomatic oral lichen planus. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospects 2010, 4, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Frieling, U.; Bonsmann, G.; Schwarz, T.; Luger, T.A.; Beissert, S. Treatment of severe lichen planus with mycophenolate mofetil. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2003, 49, 1063–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, S.; Rogers, H.; Cowie, R.; Staines, K.; Hollén, L.; Shanahan, D. Mycophenolate mofetil-based treatment for oral mucosal disease in a UK oral medicine department. Fac. Dent. J. 2023, 14, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setterfield, J.F.; Neill, S.; Shirlaw, P.J.; Challacombe, S.J.; Orchard, G.E.; Porter, S.R. The vulvovaginal gingival syndrome: A severe subgroup of lichen planus with characteristic clinical features and a novel association with the class II HLA-DQB1*0201 allele. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 55, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizpour, A.; Hatami, P.; Lajevardi, V.; Mohammadi, M.; Aryanian, Z.; Mohandesi, N.A. Clinical efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil in treating lichen planopilaris. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiee, N.; Taghavi Zenuz, A.; Mehdipour, M.; Shokri, J. Treatment of oral lichen planus with mucoadhesive mycophenolate mofetil patch: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2020, 6, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, P.; Litrowski, N. Pemphigus group (vulgaris, vegetans, foliaceus, herpetiformis, brasiliensis). Clin. Dermatol. 2011, 29, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, M.S.; Glick, M.; Ship, J.A. Burket’s Oral Medicine; Decker Inc.: Ontario, BC, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chams-Davatchi, C.; Valikhani, M.; Daneshpazhooh, M.; Esmaili, N.; Balighi, K.; Hallaji, Z.; Barzegari, M.; Akhiani, M.; Ghodsi, Z.; Mortazavi, H.; et al. Pemphigus: Analysis of 1209 cases. Int. J. Dermatol. 2005, 44, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.; Kasperkiewicz, M.; Joly, P. Pemphigus. Lancet 2019, 394, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joly, P.; Maho-Vaillant, M.; Prost-Squarcioni, C.; Hebert, V.; Houivet, E.; Calbo, S.; Caillot, F.; Golinski, M.L.; Labeille, B.; Picard-Dahan, C.; et al. First-line rituximab combined with short-term prednisone versus prednisone alone for the treatment of pemphigus (Ritux 3): A prospective, multicentre, parallel-group, open-label randomised trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2031–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bystryn, J.C.; Steinman, N.M. The adjuvant therapy of pemphigus. An update. Arch. Dermatol. 1996, 132, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, P.J.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, A.R. Influence of treatment on the clinical course of Pemphigus vulgaris. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1996, 34, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, F.R.; Sanders, S.; Nelson, C.T. Pemphigus: A 20-year review of 107 patients treated with corticosteroids. Arch. Dermatol. 1976, 112, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kridin, K. Emerging treatment options for the management of Pemphigus vulgaris. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 757–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzmony, L.; Hodak, E.; Leshem, Y.A.; Rosenbaum, O.; Gdalevich, M.; Anhalt, G.J.; Mimouni, D. The role of adjuvant therapy in pemphigus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, K.E.; Brown, D.; Exton, L.S.; Groves, R.W.; Hampton, P.J.; Mohd Mustapa, M.F.; Setterfield, J.F.; Yesudian, P.D.; McHenry, P.M.; Gibbon, K.; et al. British Association of Dermatologists’ guidelines for the management of Pemphigus vulgaris 2017. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 1170–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, R.; Locci, C.; Biondi, G.; Manconi, A.; Mannazzu, R.; Abis, L.; Sucato, F.; Satta, R.; Lissia, A.; Montesu, M.A. Mycophenolate mofetil in the treatment of childhood Pemphigus vulgaris. Pediatr. Int. 2020, 62, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, E.; Gebauer, K.; Mclean-Tooke, A. Treatment of pemphigus in Australia: Aligning current practises with global recommendations. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2022, 63, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porro, A.M.; Hans Filho, G.; Santi, C.G. Consensus on the treatment of autoimmune bullous dermatoses: Pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus—Brazilian Society of Dermatology. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2019, 94 (Suppl. S1), S20–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cholera, M.; Chainani-Wu, N. Management of Pemphigus vulgaris. Adv. Ther. 2016, 33, 910–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, N.; Patel, N.S.; Cohen, G.F. Mycophenolate mofetil as a first-line steroid sparing agent in the treatment of Pemphigus vulgaris. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2013, 12, 210–216. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, L.K.; Werth, V.P.; Villaneuva, E.V.; Murrell, D.F. A systematic review of randomized controlled trials for Pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 64, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beissert, S.; Mimouni, D.; Kanwar, A.J.; Solomons, N.; Kalia, V.; Anhalt, G.J. Treating pemphigus vulgaris with prednisone and mycophenolate mofetil: A multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukanjanapong, S.; Thongtan, D.; Kanokrungsee, S.; Wiwanitkit, V.; Rojanawatsirivej, C. A comparison of azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil as adjuvant drugs in patients with pemphigus: A retrospective cohort study. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 10, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werth, V.P.; Joly, P.; Mimouni, D.; Maverakis, E.; Caux, F.; Lehane, P.; Gearhart, L.; Kapre, A.; Pordeli, P.; Chen, D.M. Rituximab versus mycophenolate mofetil in patients with pemphigus vulgaris. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2295–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, C.S. Cicatricial pemphigoid. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 1986, 84, 527–663. [Google Scholar]
- Cizenski, J.D.; Michel, P.E.; Watson, I.T.; Foster, C.S.; Laibson, P.R. Spectrum of orocutaneous disease associations: Immune-mediated conditions. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohki, M.; Kikuchi, S. Nasal, oral, and pharyngolaryngeal manifestations of Pemphigus vulgaris: Endoscopic ororhinolaryngologic examination. Ear Nose Throat J. 2017, 96, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staines, K.; Hampton, P.J. Treatment of mucous membrane pemphigoid with the combination of mycophenolate mofetil, dapsone, and prednisolone: A case series. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2012, 114, e49–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, D.J.; Graham, C.; Holt, D.J.; Rogers, R.S., 3rd; Challacombe, S.J. Management of mucous membrane pemphigoid in a joint oral medicine–dermatology clinic. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 45, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrin, M.L.; Jorizzo, J.L.; Feldman, S.R.; Shah, R.E.; Huang, W.W. Dermatologic management of ocular mucous membrane pemphigoid with mycophenolate mofetil in 38 patients. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 87, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fremont, F.; Pelissier-Suarez, C.; Fournié, P.; Porterie, M.; Thevenin, A.; Astudillo, L.; Paricaud, K.; Gualino, V.; Soler, V.; Pugnet, G. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of ocular cicatricial pemphigoid: A cohort study and literature review. Cornea 2019, 38, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, E.; Thorne, J.E.; Newcomb, C.W.; Pujari, S.S.; Kaçmaz, R.O.; Levy-Clarke, G.A.; Nussenblatt, R.B.; Rosenbaum, J.T.; Suhler, E.B.; Foster, C.S.; et al. Mycophenolate mofetil for ocular inflammation. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 149, 423–432.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doycheva, D.; Deuter, C.; Blumenstock, G.; Foster, C.S.; Koenig, S. Long-term results of therapy with mycophenolate mofetil in ocular mucous membrane pemphigoid. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2011, 19, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, V.P.J.; Dart, J.K.G.; Rauz, S.; Shah, P.; Hillenkamp, J.; Foster, C.S. Immunosuppressive therapy for ocular mucous membrane pemphigoid. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 253–261.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woillard, J.B.; Assikar, S.; Monchaud, C.; Youdarène, R.; Marquet, P.; Saint-Marcoux, F. Towards therapeutic drug monitoring of mycophenolic acid in mucous membrane pemphigoid: A retrospective single-centre study. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 35, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, F.; Doherty, M.; Grainge, M.J.; Lanyon, P.; Zhang, W. The worldwide incidence and prevalence of systemic Lupus erythematosus: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1945–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Tziolos, N.; Bertsias, G.; Boumpas, D.T. Update in the diagnosis and management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsokos, G.C. Systemic Lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2110–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, C.; Putterman, C. Genetics and pathogenesis of systemic Lupus erythematosus and Lupus nephritis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Takagi, J.; Miyamae, T.; Funauchi, M.; Ishikawa, O. Milk fat globule EGF factor 8 in the serum of human patients of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perl, A. Activation of mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin) in rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsokos, G.C.; Lo, M.S.; Costa Reis, P.; Sullivan, K.E. New insights into the immunopathogenesis of systemic Lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 716–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benli, M.; Batool, F.; Stutz, C.; Hiss, J.; Mahr, A. Orofacial manifestations and dental management of systemic lupus erythematosus: A review. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordi-Ros, J.; Sáez-Comet, L.; Pérez-Conesa, M.; Vidal, X.; Mitjavila, F.; Salomó, A.C.; Pedragosa, J.C.; Ortiz-Santamaria, V.; Plana, M.M.; Cortés-Hernández, J. Enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium versus azathioprine in patients with active systemic Lupus erythematosus: A randomised clinical trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyes, E.; Jobanputra, A.; Feng, R.; Ahmad, A.; Werth, V.P. Comparative responsiveness of cutaneous lupus erythematosus patients to methotrexate and mycophenolate mofetil: A cohort study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 87, 447–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayano, M.; Kimoto, Y.; Mitoma, H.; Ishizu, T.; Fujii, T.; Kawaguchi, Y. Comparative efficacy and safety of mizoribine and mycophenolate mofetil for treating systemic lupus erythematosus: A retrospective cohort study. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2022, 14, 1759720X221096367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Kostopoulou, M.; Alunno, A.; Aringer, M.; Bajema, I.; Boletis, J.N.; Cervera, R.; Doria, A.; Gordon, C.; Govoni, M.; et al. 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic Lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, G.; Ceccarelli, F.; Natalucci, F.; Pirone, C.; Orefice, V.; Pacucci, V.A.; Garufi, C.; Truglia, S.; Spinelli, F.R.; Alessandri, C.; et al. Five-years drug survival of mycophenolate mofetil therapy in patients with systemic Lupus erythematosus: Comparison between renal and non-renal involvement. Jt. Bone Spine 2021, 88, 105246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevisonno, M.; Hall, A.; Rosengarten, S.; Ginzler, E.M. Mycophenolate mofetil for systemic Lupus erythematosus: Our 20-year experience. Cureus 2023, 15, e34413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celentano, A.; Tovaru, S.; Yap, T.; Farah, C.S.; Porter, S.; Savage, N.W. Oral erythema multiforme: Trends and clinical findings of a large retrospective European case series. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2015, 120, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinze, A.; Tollefson, M.; Holland, K.E.; Chiu, Y.E. Characteristics of pediatric recurrent erythema multiforme. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2018, 35, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokumbi, O.; Wetter, D.A. Clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of erythema multiforme: A review for the practicing dermatologist. Int. J. Dermatol. 2012, 51, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trayes, K.P.; Love, G.; Studdiford, J.S. Erythema multiforme: Recognition and management. Am. Fam. Physician 2019, 100, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wetter, D.A.; Davis, M.D.P. Recurrent erythema multiforme: Clinical characteristics, etiologic associations, and treatment in a series of 48 patients at Mayo Clinic, 2000 to 2007. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 62, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, J.C.; Weston, W.L.; Tonnesen, M.G. Erythema multiforme: A critical review of characteristics, diagnostic criteria, and causes. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1983, 8, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Risi-Pugliese, T.; Sbidian, E.; Ingen-Housz-Oro, S.; Le Cleach, L. Interventions for erythema multiforme: A systematic review. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.; Sokumbi, O. Recent updates in the treatment of erythema multiforme. Medicina 2021, 57, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, T.; Jin, X.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Q.; Zeng, X. Recurrent oral erythema multiforme: A case series report and review of the literature. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2020, 129, e224–e229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, G.; Ingen-Housz-Oro, S.; Fite, C.; Fett, N.; Aractingi, S. Rituximab, a new treatment for difficult-to-treat chronic erythema multiforme major? Five cases. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 1140–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Shetty, K.V. Recurrent Aphthous stomatitis. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 44, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilodeau, E.A.; Lalla, R.V. Recurrent oral ulceration: Etiology, classification, management, and diagnostic algorithm. Periodontology 2000 2019, 80, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maweri, S.A.; Halboub, E.; Al-Sufyani, G.; Almasri, M.; Alhajj, M. Is vitamin D deficiency a risk factor for recurrent aphthous stomatitis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2019, 26, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim Dos Santos, J.; Costa Normando, A.G.; de Toledo, I.P.; de Souza, L.B.; Guerra, E.N.; Canto, G.L. Laser therapy for recurrent aphthous stomatitis: An overview. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, A.; Diamond, B. Autoimmune diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, A.C.; Eugui, E.M. Mechanisms of action of mycophenolate mofetil in preventing acute and chronic allograft rejection. Transplantation 2005, 80, S181–S190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, A.C. Mechanisms of action of mycophenolate mofetil. Lupus 2005, 14, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, K.; Panavelil, T.A. Pharmacology; North American Edition; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; p. 625. ISBN 9781451191776. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, A.C.; Eugui, E.M. Mycophenolate mofetil and its mechanisms of action. Immunopharmacology 2000, 47, 85–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnham, F.P.; Nijkamp, M.J. (Eds.) Principles of Immunopharmacology, 2nd ed.; Birkhäuser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland, 2005; p. 453. ISBN 9783764358044. [Google Scholar]
- Graff, J.; Scheuermann, E.H.; Brandhorst, G.; Oellerich, M.; Gossmann, J. Pharmacokinetic analysis of mycophenolate mofetil and enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium in calcineurin inhibitor–free renal transplant recipients. Ther. Drug Monit. 2016, 38, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, S.L.; Chan, L.Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhu, W.; Chan, T.M.; Fung, P.C.; Lai, K.N. Effect of mycophenolate mofetil on nitric oxide production and inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression during renal ischaemia–reperfusion injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2001, 16, 1577–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljkovic, D.J.; Cvetkovic, I.; Stosic-Grujicic, S.; Trajkovic, V. Mycophenolic acid inhibits activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase in rodent fibroblasts. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 132, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljkovic, D.J.; Markovic, M.; Trajkovic, V. Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibition by mycophenolic acid. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniassi, T.; Júnior, F.N.F.; Spessoto, L.C.F.; Guerra, L.H.; Campos, S.S.; Taboga, S. Anti-fibrotic effect of mycophenolate mofetil on Peyronie’s disease experimentally induced with TGF-β. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2020, 32, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chau, M.K.; Chan, T.M. Distinct effects of mycophenolate mofetil and cyclophosphamide on renal fibrosis in NZBWF1/J mice. Autoimmunity. 2015, 48, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihovilović, K.; Maksimović, B.; Kocman, B.; Guštin, D.; Vidas, Ž.; Bulimbašić, S.; Ljubanović, D.G.; Matovinović, M.S.; Knotek, M. Effect of mycophenolate mofetil on progression of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy after kidney transplantation: A retrospective study. BMJ Open. 2014, 4, e005005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klangjorhor, J.; Chaiyawat, P.; Teeyakasem, P.; Sirikaew, N.; Phanphaisarn, A.; Settakorn, J.; Lirdprapamongkol, K.; Yama, S.; Svasti, J.; Pruksakorn, D. Mycophenolic acid is a drug with the potential to be repurposed for suppressing tumor growth and metastasis in osteosarcoma treatment. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 3397–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, B.; Xu, H.; Sharma, A.; Liu, H.; Yu, H.; Yi, B.; Liu, X.; He, M.; Zeng, L.; She, J.X. Delineation of biological and molecular mechanisms underlying the diverse anticancer activities of mycophenolic acid. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 2880–2886. [Google Scholar]
- Benjanuwattra, J.; Chaiyawat, P.; Pruksakorn, D.; Koonrungsesomboon, N. Therapeutic potential and molecular mechanisms of mycophenolic acid as an anticancer agent. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 887, 173580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majd, N.; Sumita, K.; Yoshino, H.; Chen, D.; Terakawa, J.; Daikoku, T.; Kofuji, S.; Curry, R.; Wise-Draper, T.M.; Warnick, R.E.; et al. A review of the potential utility of mycophenolate mofetil as a cancer therapeutic. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Condition | MMF Dosage | Efficacy | Adverse Effects | Study Design Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pemphigus Vulgaris (PV) | 2–3 g/day | Complete remission in most cases; steroid-sparing effects reported | GI issues common; manageable with dose adjustments | Randomized controlled trials support efficacy; study designs vary |
| Oral Lichen Planus (OLP) | 500 mg–2 g/day | Clinical improvement in 80% of cases, especially severe/refractory forms | GI upset at higher doses; generally well tolerated | Studies with variable dosing; often retrospective or observational |
| Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid (MMP) | 500 mg–2 g/day | 89% response rate; steroid-sparing effects; recommended for mild to moderate cases | GI upset, fatigue and urinary difficulties reported; discontinuation in some cases | Variable study designs; mostly observational or case series |
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) | 1440 mg/day (EC-MPS) or variable for non-renal manifestations | High remission rates, especially in renal involvement (up to 71% in EC-MPS) | GI intolerance and hematological issues at high doses; infection risk noted | Supported by randomized trials in renal SLE; limited for non-renal |
| Erythema Multiforme (EM) | Not specified | Limited efficacy; response observed in a minority of cases | Minor adverse effects in limited cases | Case series and expert opinions; lack of randomized trials |
| Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) | 2 g/day (reported partial improvement) | Partial improvement in severe cases; insufficient evidence for broad efficacy | Limited data on adverse effects | Anecdotal evidence; no controlled trials available |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aljohani, K.; Naguib, G.H.; Mira, A.I.; Alnowaiser, A.; Hamed, M.T.; Abougazia, A.O.; Alzarani, G.A.; Noorsaeed, R.M.; Kayal, R.A. Mycophenolate Mofetil in the Management of Oral Mucocutaneous Diseases: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Oral 2025, 5, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5020035
Aljohani K, Naguib GH, Mira AI, Alnowaiser A, Hamed MT, Abougazia AO, Alzarani GA, Noorsaeed RM, Kayal RA. Mycophenolate Mofetil in the Management of Oral Mucocutaneous Diseases: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Oral. 2025; 5(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5020035
Chicago/Turabian StyleAljohani, Khalid, Ghada H. Naguib, Abdulghani I. Mira, Abeer Alnowaiser, Mohamed T. Hamed, Ahmed O. Abougazia, Ghaida A. Alzarani, Raghad M. Noorsaeed, and Rayyan A. Kayal. 2025. "Mycophenolate Mofetil in the Management of Oral Mucocutaneous Diseases: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives" Oral 5, no. 2: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5020035
APA StyleAljohani, K., Naguib, G. H., Mira, A. I., Alnowaiser, A., Hamed, M. T., Abougazia, A. O., Alzarani, G. A., Noorsaeed, R. M., & Kayal, R. A. (2025). Mycophenolate Mofetil in the Management of Oral Mucocutaneous Diseases: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Oral, 5(2), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5020035








