The Impact of Psychological and Risk Factors on Tourists’ Loyalty Toward Nature-Based Destinations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Theoretical Framework
2.2. Loyalty in the Context of Tourism
2.2.1. Satisfaction
2.2.2. Perceived Value
2.2.3. Attachment
2.2.4. Familiarity
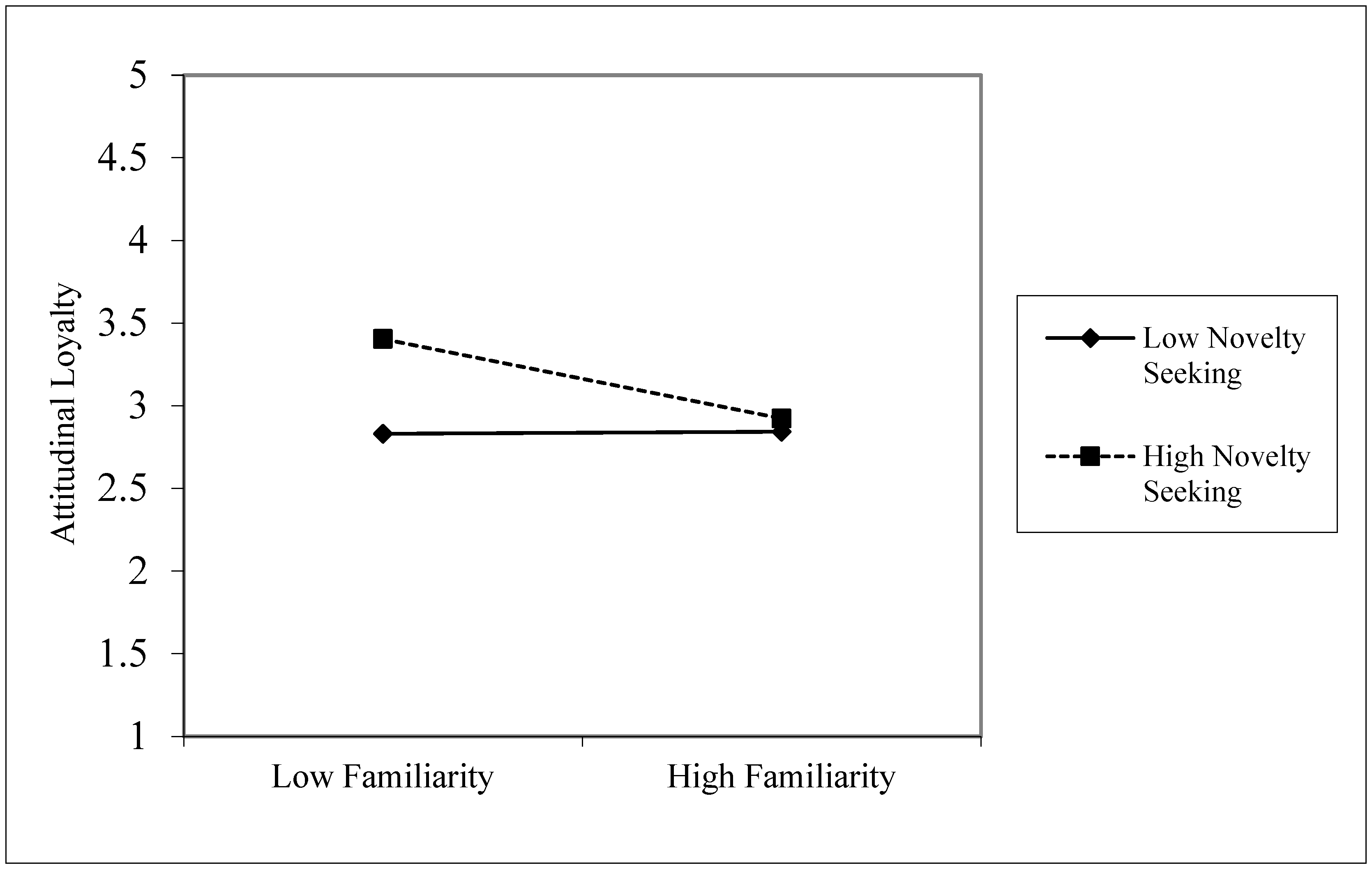
2.2.5. Novelty Seeking as Moderator
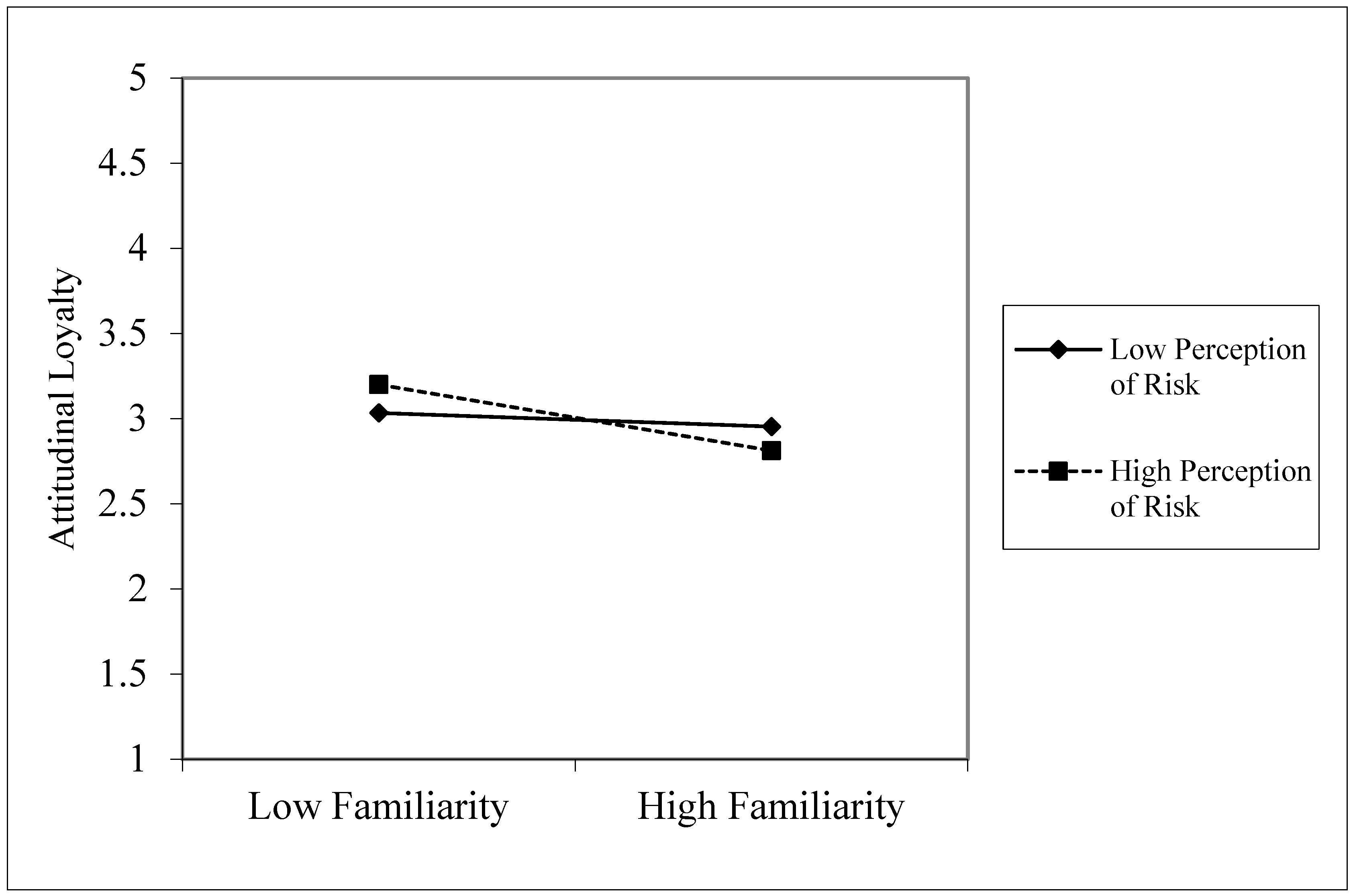
2.2.6. Perceived Risk as Moderator
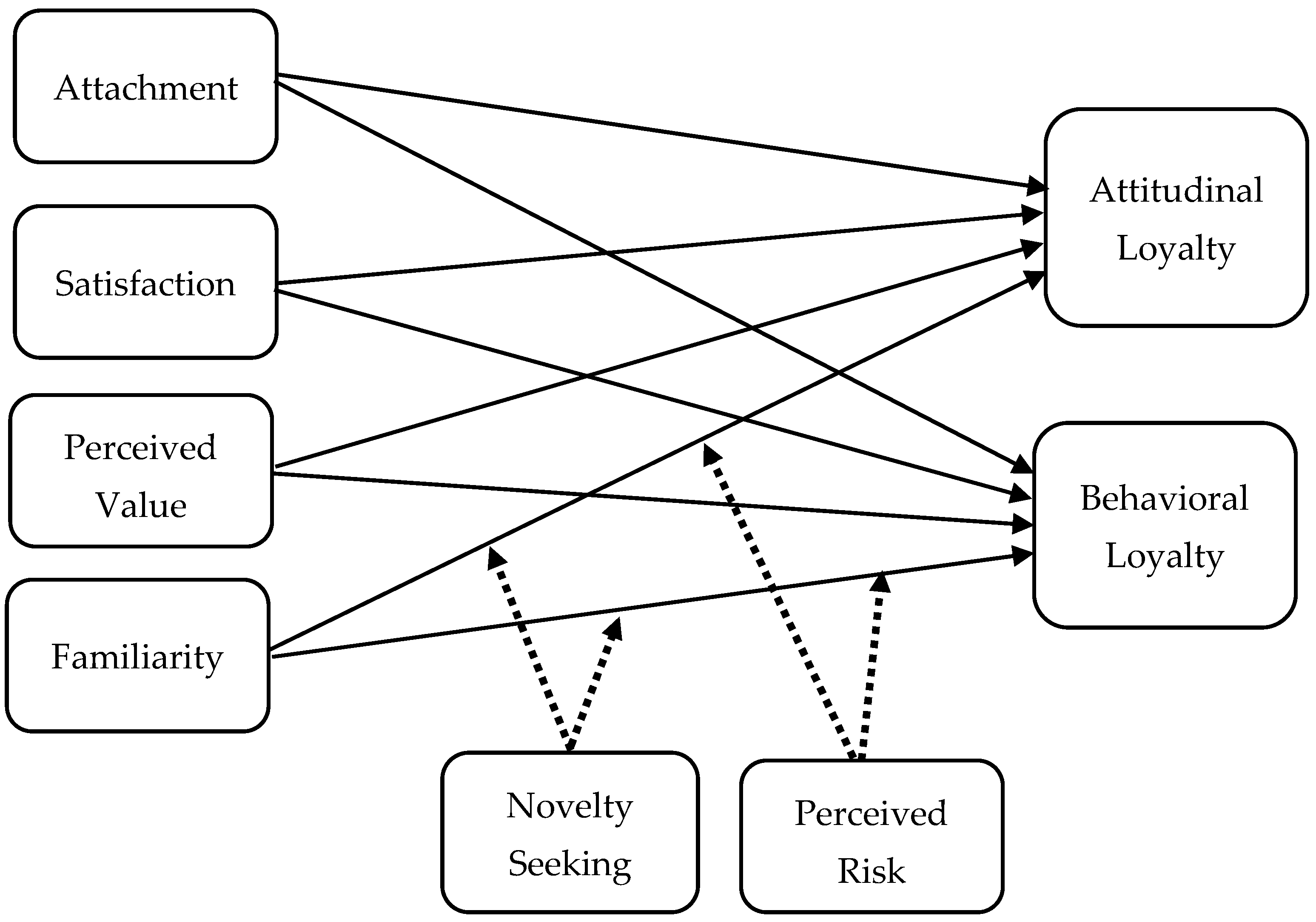
3. Research Model and Hypotheses
4. Materials and Methods
5. Data Analysis and Results
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aarabe, M., Ben Khizzou, N., Alla, L., & Benjelloun, A. (2025). Customer experience management in the tourism sector: Insights from a bibliometric and thematic analysis. Tourism and Hospitality, 6(2), 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50(2), 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Abri, I., Al Hinai, O., Al Raisi, S., Al Harrasi, A., Al Jabri, Z., & Al Maskari, M. (2023a). Economic growth and the demand for foreign labor in the oil-exporting and labor-importing states of the Arab Gulf: Case of Oman. Cogent Business & Management, 10(3), 2256083. [Google Scholar]
- Al Abri, I., Alkazemi, M., Abdeljalil, W., Al Harthi, H., & Al Maqbali, F. (2023b). Attitudinal and behavioral loyalty: Do psychological and political factors matter in tourism development? Sustainability, 15(6), 5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Abri, I., Gulseven, O., & Yousuf, J. B. (2023c). Estimating the recreational value of a rural mountain area in the presence of heterogeneous agricultural density on Al-Jabal Al-Akhdar Oman. Journal of Outdoor Recreation and Tourism, 42, 100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abri, I., Önel, G., & Grogan, K. A. (2019). Oil revenue shocks and the growth of the non-oil sector in an oil-dependent economy: The case of Oman. Theoretical Economics Letters, 9(4), 785–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazaizeh, M. M., Jamaliah, M. M., Alzghoul, Y. A., & Mgonja, J. T. (2024). Tour guide and tourist loyalty toward cultural heritage sites: A signaling theory perspective. Tourism Planning & Development, 21(3), 255–275. [Google Scholar]
- Alegre, J., & Juaneda, C. (2006). Destination loyalty: Consumers’ economic behavior. Annals of Tourism Research, 33(3), 684–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ismaili, S., Al Abri, I., Gulseven, O., Al-Masroori, H., & Dutta, S. (2024). Recreational value of different coral reefs richness levels in Oman. Journal of Outdoor Recreation and Tourism, 46, 100775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mahruqi, A. M. A. (2023). Investigating psychological and risk factors influencing tourists’ loyalty in Oman as a nature-based tourism destination. Sultan Qaboos University (Oman). Available online: https://www.proquest.com/docview/3195709426 (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Altınay, L., & Kozak, M. (2021). Revisiting destination competitiveness through chaos theory: The butterfly competitiveness model. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 49, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardani, W., Rahyuda, K., Giantari, I. G. A. K., & Sukaatmadja, I. P. G. (2019). Customer satisfaction and behavioral intentions in tourism: A literature review. Journal of Applied Business and Management (IJABIM), 4(3), 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arina, K. K., Lemy, D. M., Bernarto, I., Antonio, F., & Fatmawati, I. (2025). How beautiful memories stay and encourage intention to recommend the destination: The moderating role of coastal destination competitiveness. Tourism and Hospitality, 6(3), 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. (1991). Social cognitive theory of self-regulation. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50(2), 248–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J. M., Cheah, J. H., Gholamzade, R., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2023). PLS-SEM’s most wanted guidance. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 35(1), 321–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomstervik, I. H., Prebensen, N. K., Campos, A. C., & Pinto, P. (2021). Novelty in tourism experiences: The influence of physical staging and human interaction on behavioural intentions. Current Issues in Tourism, 24(20), 2921–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojanic, D. C. (1996). Consumer perceptions of price, value and satisfaction in the hotel industry. Journal of Hospitality & Leisure Marketing, 4(1), 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, M. K., Zhang, Z., & Yuan, K. H. (2017). Univariate and multivariate skewness and kurtosis for measuring nonnormality: Prevalence, influence and estimation. Behavior Research Methods, 49, 1716–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambra-Fierro, J., Blasco, M. F., Huerta-Álvarez, R., & Olavarría-Jaraba, A. (2021). Destination recovery during COVID-19 in an emerging economy: Insights from Perú. European Research on Management and Business Economics, 28(3), 100188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, G., & Figini, P. (2012). The economics of tourism destinations. Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvache-Franco, M., Alvarez-Risco, A., Carvache-Franco, W., Carvache-Franco, O., Del-Aguila-Arcentales, S., & Estrada-Merino, A. (2022). Push and pull motivations as predictors of satisfaction and loyalty in coastal cities: A study in Lima, Peru. Journal of Policy Research in Tourism, Leisure and Events, 16(4), 692–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvache-Franco, M., Carvache-Franco, W., Hernández-Lara, A. B., & Carvache-Franco, O. (2023). Effects of motivations in marine protected areas: The case of Galápagos Islands. PLoS ONE, 18(11), e0293480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casali, G. L., Liu, Y., Presenza, A., & Moyle, C. L. (2021). How does familiarity shape destination image and loyalty for visitors and residents? Journal of Vacation Marketing, 27(2), 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. F., & Tsai, M. H. (2008). Perceived value, satisfaction, and loyalty of TV travel product shopping: Involvement as a moderator. Tourism Management, 29(6), 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S. Y., Teh, J. L. C., Ong, H. Y., & Wong, W. W. (2018). Factors influencing tourists’ loyalty towards food tourism in Malaysia (Final Year Project). UTAR. Available online: http://eprints.utar.edu.my/3079/1/fyp_BA_2018_CSY.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Chin, W. W., Marcolin, B. L., & Newsted, P. R. (2003). A partial least squares latent variable modeling approach for measuring interaction effects: Results from a Monte Carlo simulation study and an electronic-mail emotion/adoption study. Information Systems Research, 14(2), 189–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossío-Silva, F. J., Revilla-Camacho, M. Á., & Vega-Vázquez, M. (2019). The tourist loyalty index: A new indicator for measuring tourist destination loyalty? Journal of Innovation & Knowledge, 4(2), 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, J. J., Brady, M. K., & Hult, G. T. M. (2000). Assessing the effects of quality, value, and customer satisfaction on consumer behavioral intentions in service environments. Journal of Retailing, 76(2), 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, G. I. (1992). Effect of income and price on international tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 19(4), 643–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dann, G. M. S. (1977). Anomie, ego-enhancement and tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 4(4), 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakos, K., & Kutan, A. M. (2003). Regional effects of terrorism on tourism in three Mediterranean countries. Journal of Conflict Resolution, 47(5), 621–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, R., El-Kassrawy, Y. A., & Agag, G. (2019). Integrating destination attributes, political (In)stability, destination image, tourist satisfaction, and intention to recommend: A study of UAE. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, 43(6), 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Adly, M. I. (2019). Modelling the relationship between hotel perceived value, customer satisfaction, and customer loyalty. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 50, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, I. A., Azazz, A. M., Fayyad, S., Aljoghaiman, A., Fathy, E. A., & Fouad, A. M. (2025). From asymmetry to satisfaction: The dynamic role of perceived value and trust to boost customer satisfaction in the tourism industry. Tourism and Hospitality, 6(2), 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajriyati, I., Afiff, A. Z., Gayatri, G., & Hati, S. R. H. (2022). Attributes influencing overall tourist satisfaction and its consequences for Muslim-majority destination. SAGE Open, 12(1), 21582440211068462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J., & Morakabati, Y. (2008). Tourism activity, terrorism and political instability within the Commonwealth: The cases of Fiji and Kenya. Journal of Tourism Research, 10(6), 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, V., Selvaag, S. K., Junker-Köhler, B., & Zouhar, Y. (2024). Visitors’ relations to recreational facilities and attractions in a large vulnerable mountain region in Norway: Unpacking the roles of tourists and locals. Journal of Outdoor Recreation and Tourism, 47, 100807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, E. D., & Ang, S. H. (2017). From the editors: New directions in the reporting of statistical results in the Journal of World Business. Journal of World Business, 52(2), 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2017). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Sage Publications Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., Sarstedt, M., Danks, N. P., & Ray, S. (2021). Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) using R: A workbook. Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J. F., Thomas, G., Hult, M., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2022). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (3rd ed.). Sage. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J., Paddison, B., & Crawforth, D. (2025). Slowing-down tourism in heritage cities: The role of independent businesses in achieving just and regenerative futures. Tourism Planning & Development, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J. C. (2015). The development of tourist destinations in the Gulf: Oman and Qatar compared. Tourism Planning & Development, 12(3), 350–361. [Google Scholar]
- Henseler, J. (2017). Partial least squares path modeling. In M. Sarstedt, J. F. Hair, & C. Nitzl (Eds.), Advanced methods for modeling markets (pp. 361–381). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C. C., & Lin, W. R. (2023). How does tourist learning affect destination attachment in nature-based tourism: Multiple mediations comparison and distal mediation analysis. Journal of Outdoor Recreation and Tourism, 43, 100665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, S., Kusairi, S., & Ismail, F. (2021). The impact of educational tourism on economic growth: A panel data analysis. International Journal of Business and Globalisation, 28, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jöreskog, K. G. (1971). Simultaneous factor analysis in several populations. Psychometrika, 36(4), 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoi, B. H., An, P. T. H., & Van Tuan, N. (2022). Applying the PLS-SEM model for the loyalty of domestic travelers. In Prediction and causality in econometrics and related topics (pp. 392–400). Springer International Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K. H., & Park, D. B. (2017). Relationships among perceived value, satisfaction, and loyalty: Community-based ecotourism in Korea. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 34(2), 171–191. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, N. (2015). Common method bias in PLS-SEM: A full collinearity assessment approach. International Journal of e-Collaboration (IJEC), 11(4), 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, N. (2017). Which is the best way to measure job performance: Self-perceptions or official supervisor evaluations? International Journal of e-Collaboration (IJEC), 13(2), 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, N., & Lynn, G. (2012). Lateral collinearity and misleading results in variance-based SEM: An illustration and recommendations. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 13(7), 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G., & Tussyadiah, I. P. (2012). Exploring familiarity and destination choice in tourism. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 17(2), 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T. H., & Crompton, J. (1992). Measuring novelty seeking in tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 19(4), 732–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T. H., & Hsu, F. Y. (2013). Examining how attending motivation and satisfaction affects the loyalty for attendees at aboriginal festivals. Journal of Tourism Research, 15(1), 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepp, A., & Gibson, H. (2008). Sensation seeking and tourism: Tourist role, perception of risk and destination choice. Tourism Management, 29(4), 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T., Liao, C., Law, R., & Zhang, M. (2023). An integrated model of destination attractiveness and tourists’ environmentally responsible behavior: The mediating effect of place attachment. Behavioral Sciences, 13(3), 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X., Li, C., & McCabe, S. (2020). Expanding theory of tourists’ destination loyalty: The role of sensory impressions. Tourism Management, 77, 104026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhas, P. S., Sharma, P., & Quintela, J. A. (2025). Wellness tourism in the Himalayas: A structural analysis of motivation, experience, and satisfaction in spa resorts. Tourism and Hospitality, 6(2), 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKercher, B., Denizci-Guillet, B., & Ng, E. (2012). Rethinking loyalty. Annals of Tourism Research, 39(2), 708–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechinda, P., Serirat, S., & Gulid, N. (2009). An examination of tourists’ attitudinal and behavioral loyalty: Comparison between domestic and international tourists. Journal of Vacation Marketing, 15(2), 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, O. M., María, A. L., Jessenia, M. M., & Tannia, A. S. (2025). Sociodemographic determinants of consumer experience and loyalty in a food hall. Tourism and Hospitality, 6(3), 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitas, O., & Bastiaansen, M. (2018). Novelty: A mechanism of tourists’ enjoyment. Annals of Tourism Research, 72, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlozi, S., & Pesämaa, O. (2013). Adventure tourist destination choice in Tanzania. Current Issues in Tourism, 16(1), 63–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A. R. J., Mohd Zahari, M. S., Hanafiah, M. H., & Rahman, A. R. A. (2022). Foreign tourist satisfaction, commitment and revisit intention: Exploring the effect of environmental turbulence in the Arab region. Journal of Islamic Marketing, 13(11), 2480–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, D. B., & Lin, C. H. (2010). Why do first-time and repeat visitors patronize a destination? Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 27(2), 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusair, K., Okumus, F., Karatepe, O. M., Alfarhan, U. F., & de Larrea, G. L. (2023). From tourist motivations to buying decisions: A multilevel engagement perspective. Tourism Management Perspectives, 48, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppermann, M. (1999). Predicting destination choice—A discussion of destination loyalty. Journal of Vacation Marketing, 5(1), 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, A. B., Bilgihan, A., Nusair, K., & Okumus, F. (2016). What keeps the mobile hotel booking users loyal? Investigating the roles of self-efficacy, compatibility, perceived ease of use, and perceived convenience. International Journal of Information Management, 36(6), 1350–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestana, M. H., Parreira, A., & Moutinho, L. (2020). Motivations, emotions and satisfaction: The keys to a tourism destination choice. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, 16, 100332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, K. A. (2011). Framing Islam: An analysis of US media coverage of terrorism since 9/11. Communication Studies, 62(1), 90–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proshansky, H. M. (1978). The city and self-identity. Environment and Behavior, 10(2), 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, S., Arora, R., Nunkoo, R., Goolaup, S., & Das, M. (2023). Airbnb experiences: Travelers’ purchase behavior and word-of-mouth. Journal of Travel Research, 62(7), 1569–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. K. (2014). Motivating factors of Islamic tourist’s destination loyalty: An empirical investigation in Malaysia. Journal of Tourism and Hospitality Management, 2(1), 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ramayah, T., Cheah, J., Chuah, F., Ting, H., & Memon, M. A. (2018). Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) using SmartPLS 3.0: An updated guide and practical guide to statistical analysis. Pearson Education. [Google Scholar]
- Rejan, K., & Ahn, Y. J. (2024). Challenges, experiences, and coping behaviors among SMEs in the adventure tourism industry after the COVID-19 pandemic: A case from Pokhara, Nepal. Journal of Outdoor Recreation and Tourism, 47, 100797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, L. K., & Waugh, W. L. (1986). Terrorism and tourism as logical companions. Tourism Management, 7(4), 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringle, C. M., Wende, S., & Becker, J.-M. (2024). SmartPLS 4. SmartPLS. Available online: https://www.smartpls.com (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Saha, S., & Yap, G. (2014). The moderation effects of political instability and terrorism on tourism development: A cross-country panel analysis. Journal of Travel Research, 53(4), 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem Khalifa, A. (2004). Customer value: A review of recent literature and an integrative configuration. Management Decision, 42(5), 645–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E., Oliveira, M. F., & Tavares, F. O. (2024). How COVID-19 affected Portuguese travel intentions—A PLS-SEM model. Tourism and Hospitality, 5(3), 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sánchez, M. D., de Pablos-Heredero, C., & Montes-Botella, J. L. (2025). Contributions of sustainable tourist behavior in food events to the cultural identity of destinations. Tourism and Hospitality, 6(2), 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmueli, G., Sarstedt, M., Hair, J. F., Cheah, J. H., Ting, H., Vaithilingam, S., & Ringle, C. M. (2019). Predictive model assessment in PLS-SEM: Guidelines for using PLSpredict. European Journal of Marketing, 53(11), 2322–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, N., Singh, G., & Sharma, S. (2020). Impact of perceived value on the satisfaction of supermarket customers: Developing country perspective. Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 48(11), 1235–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Stokols, D., & Shumaker, S. A. (1981). People in place: A transactional view of settings. In J. Harvey (Ed.), Cognition, social behavior and the environment (pp. 441–488). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. [Google Scholar]
- Tomić, S., Leković, K., & Tadić, J. (2019). Consumer behaviour: The influence of age and family structure on the choice of activities in a tourist destination. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja, 32(1), 755–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S. (2012). Place attachment and tourism marketing: Investigating tourists in Singapore. Journal of Tourism Research, 14(2), 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, V. W. S., & Ritchie, J. B. (2011). Exploring the essence of memorable tourism experiences. Annals of Tourism Research, 38(4), 1367–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, P. E. L., Cornejo, J. M., Morales, M. V. S., & Esparza-Huamanchumo, R. M. (2025). Motivation, satisfaction, place attachment, and return intention to natural destinations: A structural analysis of Ayabaca moorlands, Peru. Tourism and Hospitality, 6(4), 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., Zhang, Q., & Wong, P. P. W. (2022). Impact of familiarity and green image on satisfaction and loyalty among young green hotels’ guests—A developing country’s perspective. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 899118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, J. C., & Wicker, P. (2025). The effect of event quality on participants’ intention to revisit a sport event: Monetary valuation and mitigation of hypothetical bias. Journal of Outdoor Recreation and Tourism, 50, 100862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D. R., & Vaske, J. J. (2003). The measurement of place attachment: Validity and generalizability of a psychometric approach. Forest Science, 49(6), 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, S. F., & Witt, C. A. (1995). Forecasting tourism demand: A review of empirical research. Journal of Forecasting, 11(3), 447–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M. J., Zhao, K., & Fils-Aime, F. (2022). Response rates of online surveys in published research: A meta-analysis. Computers in Human Behavior Reports, 7, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y., & Wong, K. K. (2012). A spatial econometric approach to model spillover effects in tourism flows. Journal of Travel Research, 51(6), 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z., & Peterson, R. T. (2004). Customer perceived value, satisfaction, and loyalty: The role of switching costs. Psychology & Marketing, 21(10), 799–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeithaml, V. A. (2000). Service quality, profitability, and the economic worth of customers: What we know and what we need to learn. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 28, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Descriptions | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Less than 30 | 5 (4%) |
| 30–49 | 65 (54%) | |
| 50 and higher | 51 (42%) | |
| Gender | Female | 68 (56%) |
| Male | 53 (43%) | |
| Income | Less than $50,000 | 81 (66%) |
| $50,000 and more | 40 (33%) | |
| Not specified | 0 (0%) | |
| Marital status | Married | 101 (83%) |
| Single | 15 (12%) | |
| Divorced | 2 (2%) | |
| Separated | 2 (2%) | |
| Widowed | 1 (1%) | |
| Children | Yes | 74 (61%) |
| No | 47 (39%) | |
| Education | Less than a bachelor’s degree | 5 (4%) |
| Bachelor’s degree or higher | 116 (96%) | |
| Occupation | Professional | 103 (85%) |
| Administrative/Managerial/Entrepreneur | 5 (4%) | |
| Production/Agriculture worker | 0 (0%) | |
| Govt. officer state enterprise | 7 (6%) | |
| Housewife/Student/Retired/Unemployed/Other | 6 (5%) | |
| Residence | GCC countries | 25 (21%) |
| Other Arab countries | 15 (12%) | |
| Asia | 54 (45%) | |
| Europe | 12 (10%) | |
| The Americas | 2 (2%) | |
| Oceania | 0 (0%) | |
| Africa | 3 (2%) | |
| Others | 10 (8%) |
| Variable | A | AL | F | PV | RPME | S | NS | BL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIF | 1.12 | 3.567 | 2.125 | 2.158 | 1.056 | 3.51 | 2.978 | 2.785 |
| Variables | Items | Loadings | CR | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attitudinal Loyalty | AL1 | 0.963 | 0.961 | 0.924 |
| AL2 | 0.960 | |||
| Attachment | A1 | 0.871 | 0.922 | 0.798 |
| A2 | 0.882 | |||
| A3 | 0.925 | |||
| Familiarity | F1 | 0.950 | 0.948 | 0.900 |
| F2 | 0.948 | |||
| Novelty Seeking | NS1 | 0.780 | 0.912 | 0.722 |
| NS2 | 0.897 | |||
| NS3 | 0.848 | |||
| NS4 | 0.865 | |||
| Perceived Value | PV2 | 0.953 | 0.954 | 0.912 |
| PV3 | 0.957 | |||
| Behavioral Loyalty | BL1 | 0.923 | 0.922 | 0.855 |
| BL2 | 0.908 | |||
| Satisfaction | S1 | 0.904 | 0.937 | 0.831 |
| S2 | 0.909 | |||
| S3 | 0.899 |
| Variables | A | AL | BL | F | NS | PV | RP | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | ||||||||
| AL | 0.771 | |||||||
| BL | 0.869 | 0.774 | ||||||
| F | 0.872 | 0.652 | 0.834 | |||||
| NS | 0.826 | 0.822 | 0.690 | 0.774 | ||||
| PV | 0.814 | 0.601 | 0.865 | 0.743 | 0.716 | |||
| RP | 0.111 | 0.050 | 0.031 | 0.055 | 0.041 | 0.109 | ||
| S | 0.832 | 0.886 | 0.827 | 0.826 | 0.883 | 0.821 | 0.065 |
| Hypothesis | Relationships | Std. Beta | Std. Errors | t-Value | p-Value | PCI LL | PCI UL | f2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | A → AL | 0.274 | 0.106 | 2.584 | 0.005 *** | 0.110 | 0.460 | 0.08 |
| H2 | A → BL | 0.293 | 0.117 | 2.503 | 0.006 *** | 0.118 | 0.504 | 0.08 |
| H3 | F → AL | −0.117 | 0.097 | 1.211 | 0.113 | −0.283 | 0.032 | 0.02 |
| H4 | F → BL | 0.211 | 0.118 | 1.797 | 0.036 ** | 0.001 | 0.389 | 0.05 |
| H5 | S → AL | 0.547 | 0.076 | 2.159 | 0.015 ** | 0.046 | 0.293 | 0.03 |
| H6 | S → BL | 0.190 | 0.113 | 1.673 | 0.047 ** | 0.001 | 0.373 | 0.03 |
| H7 | PV → AL | −0.155 | 0.081 | 1.920 | 0.027 ** | −0.301 | −0.033 | 0.04 |
| H8 | PV → BL | 0.345 | 0.127 | 2.731 | 0.003 *** | 0.141 | 0.554 | 0.14 |
| H9 | RP × F → AL | 0.077 | 0.052 | 1.486 | 0.069 * | 0.000 | 0.169 | 0.02 |
| H10 | RP × F → BL | −0.057 | 0.060 | 0.944 | 0.173 | −0.153 | 0.044 | 0.01 |
| H11 | NS × F → AL | −0.123 | 0.039 | 3.174 | 0.001 *** | −0.183 | −0.063 | 0.11 |
| H12 | NS × F → BL | −0.029 | 0.038 | 0.766 | 0.222 | −0.087 | 0.034 | 0.01 |
| MV | PLS-SEM_RMSE | LM_RMSE | PLS-LM | Q2 Predict |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AL1 | 0.582 | 0.611 | −0.029 | 0.649 |
| AL2 | 0.557 | 0.624 | −0.067 | 0.641 |
| BL1 | 0.802 | 0.842 | −0.040 | 0.538 |
| BL2 | 0.777 | 0.772 | 0.005 | 0.522 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Mahruqi, A.; Al Abri, I.; Ramayah, T.; Zaibet, L. The Impact of Psychological and Risk Factors on Tourists’ Loyalty Toward Nature-Based Destinations. Tour. Hosp. 2025, 6, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/tourhosp6040197
Al Mahruqi A, Al Abri I, Ramayah T, Zaibet L. The Impact of Psychological and Risk Factors on Tourists’ Loyalty Toward Nature-Based Destinations. Tourism and Hospitality. 2025; 6(4):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/tourhosp6040197
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Mahruqi, Abdullah, Ibtisam Al Abri, T. Ramayah, and Lokman Zaibet. 2025. "The Impact of Psychological and Risk Factors on Tourists’ Loyalty Toward Nature-Based Destinations" Tourism and Hospitality 6, no. 4: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/tourhosp6040197
APA StyleAl Mahruqi, A., Al Abri, I., Ramayah, T., & Zaibet, L. (2025). The Impact of Psychological and Risk Factors on Tourists’ Loyalty Toward Nature-Based Destinations. Tourism and Hospitality, 6(4), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/tourhosp6040197









