Coprological Survey of Helminths in Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) in 50 Selected Zoos and Menageries in Russia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Fecal Analysis
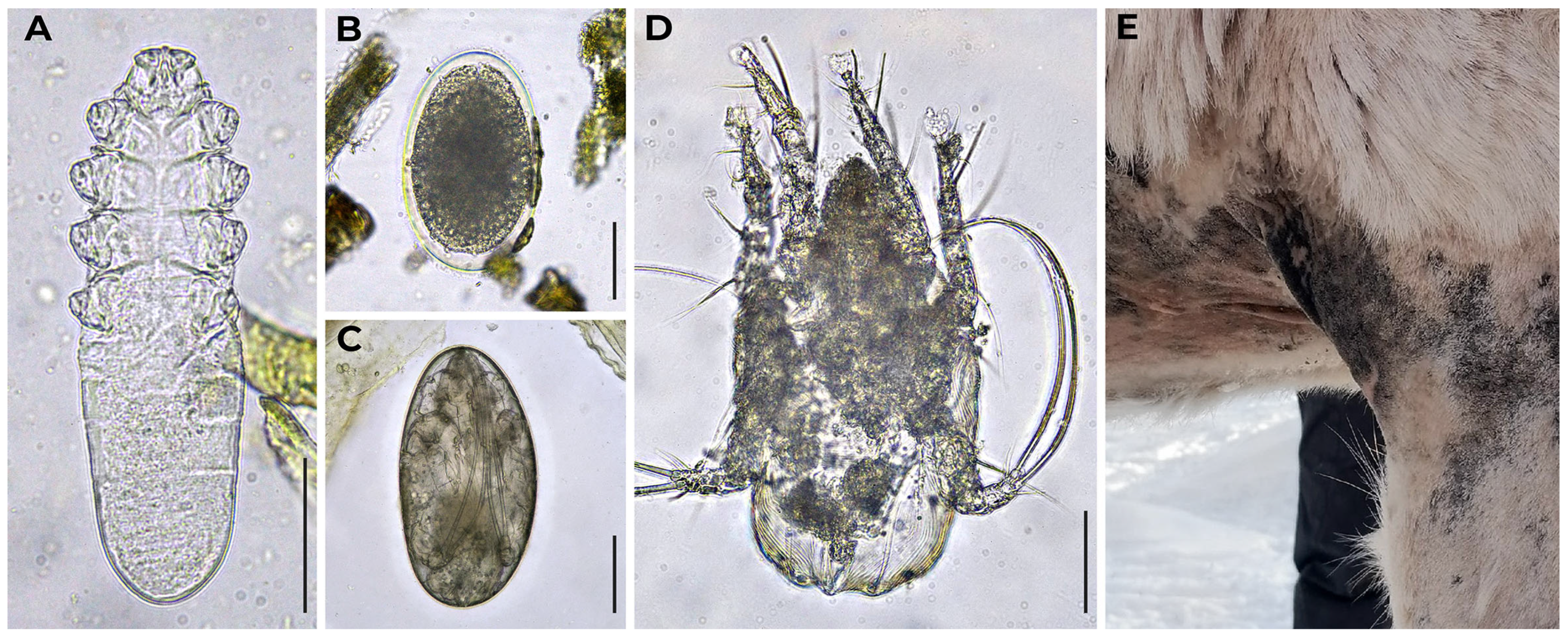
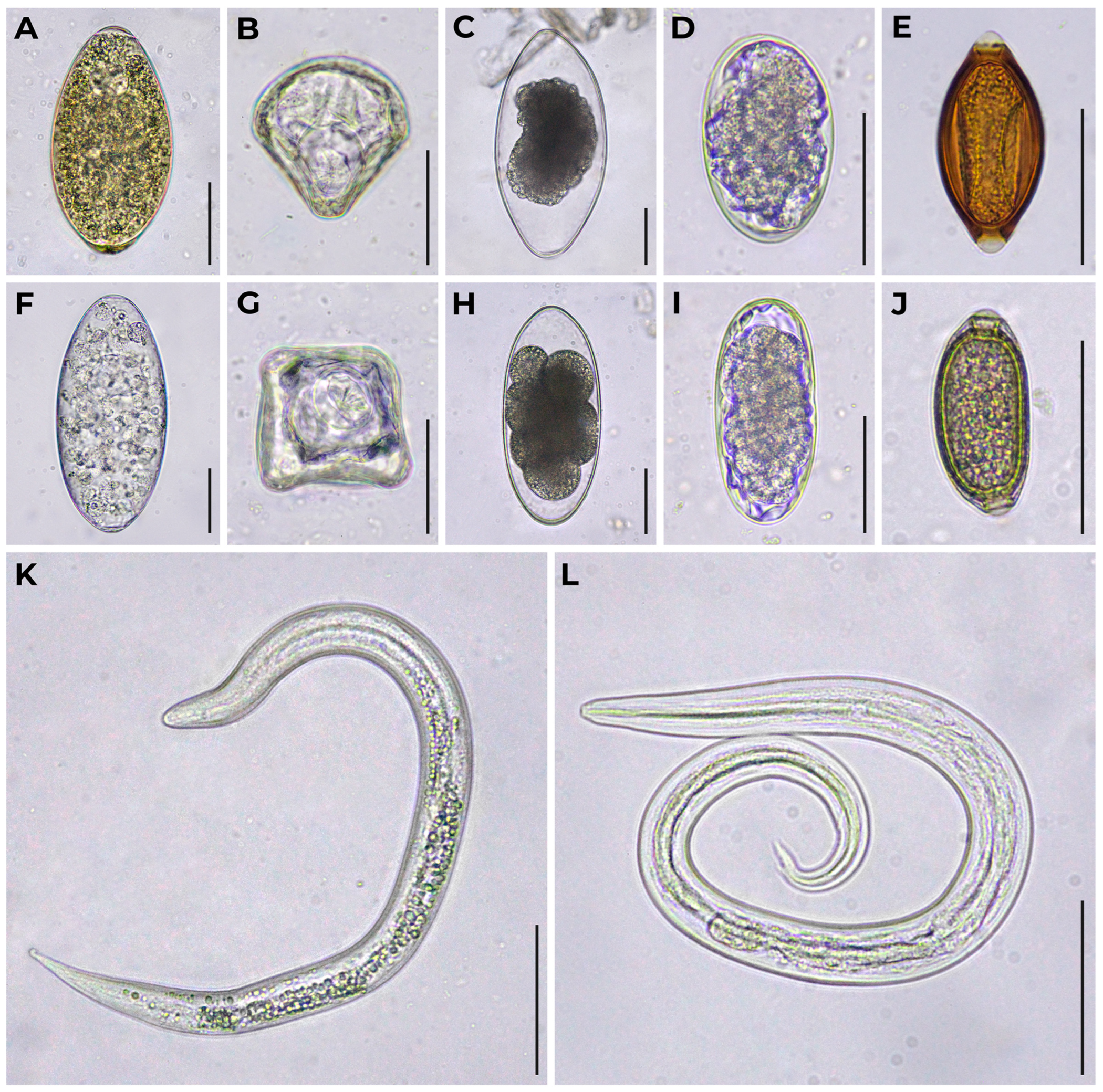
2.3. Helminths Identification
2.4. DNA Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
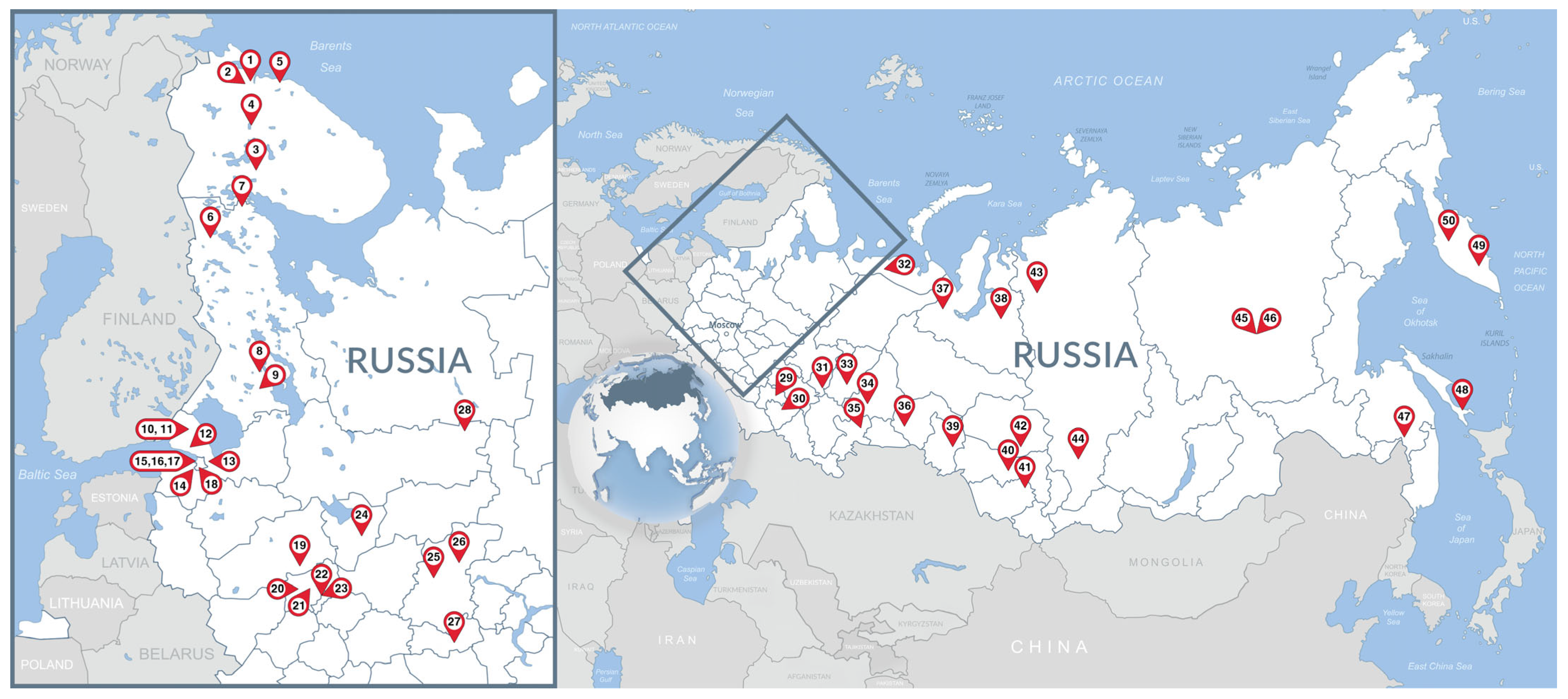
| Zoo ID | Ownership Type (S/P) 1 | Location (Federal Subject of Russia) | Coordinates (Decimal Degrees) | Number of Fecal Samples 3 | Date Collected |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P | Murmansk Oblast | 68.98716 33.07261 | 2 | November 2023 |
| 2 | P | Murmansk Oblast | 68.85722 33.19556 | 12 | November 2023 |
| 3 | P | Murmansk Oblast | 67.56317 33.36571 | 2 | November 2023 |
| 4 | P | Murmansk Oblast | 67.65276 33.66051 | 11 | November 2023 |
| 5 | P | Murmansk Oblast | 69.16835 35.13280 | 3 | November 2023 |
| 6 | P | Republic of Karelia | 65.76340 31.07419 | 1 | March 2024 |
| 7 | P | Republic of Karelia | 66.43669 32.85459 | 7 | June 2022 |
| 8 | P | Republic of Karelia | 62.33297 34.00604 | 3 | March 2024 |
| 9 | P | Republic of Karelia | 61.87838 34.07819 | 9 | March 2024 |
| 10 | P | Leningrad Oblast | 60.59067 30.00422 | 1 | July 2020 |
| 11 | P 2 | Leningrad Oblast | 60.59161 30.11204 | 8 | May 2019 |
| 12 | P | Leningrad Oblast | 60.14195 30.32823 | 11 | August 2018 |
| 13 | P | Leningrad Oblast | 59.94762 30.68122 | 3 | May 2023 |
| 14 | P | Saint Petersburg | 59.84108 30.06470 | 2 | June 2019 |
| 15 | P | Saint Petersburg | 59.98017 30.24438 | 3 | March 2024 |
| 16 | P | Saint Petersburg | 59.97054 30.25672 | 4 | January 2020 |
| 17 | S 2 | Saint Petersburg | 59.95210 30.30891 | 9 | March 2024 |
| 18 | P | Saint Petersburg | 59.67605 30.42401 | 2 | February 2018 |
| 19 | P | Tver Oblast | 56.75051 36.36719 | 1 | June 2020 |
| 20 | S 2 | Moscow Oblast | 55.94012 36.21055 | 7 | January 2024 |
| 21 | P | Moscow Oblast | 56.13343 36.50051 | 2 | March 2024 |
| 22 | S 2 | Moscow | 55.76347 37.57537 | 3 | December 2023 |
| 23 | P 2 | Moscow | 55.83306 37.62197 | 1 | October 2023 |
| 24 | S 2 | Yaroslavl Oblast | 57.67709 39.90005 | 6 | November 2023 |
| 25 | P 2 | Nizhny Novgorod Oblast | 56.33468 43.85420 | 6 | November 2023 |
| 26 | P | Nizhny Novgorod Oblast | 56.92384 45.40185 | 4 | August 2022 |
| 27 | S 2 | Republic of Mordovia | 54.17500 45.18599 | 3 | November 2023 |
| 28 | S 2 | Vologda Oblast | 60.74784 46.17739 | 5 | November 2023 |
| 29 | P 2 | Ulyanovsk Oblast | 54.35485 48.52409 | 3 | February 2024 |
| 30 | P | Samara Oblast | 53.34493 50.22240 | 21 | August 2021 |
| 31 | S 2 | Udmurt Republic | 56.86555 53.17413 | 2 | November 2023 |
| 32 | S | Nenets Autonomous Okrug | 67.63436 53.24135 | 1 | February 2024 |
| 33 | S 2 | Perm Krai | 58.01672 56.23728 | 4 | November 2023 |
| 34 | P | Sverdlovsk Oblast | 57.17585 60.65764 | 11 | February 2024 |
| 35 | S 2 | Chelyabinsk Oblast | 55.16894 61.36764 | 5 | November 2023 |
| 36 | P | Tyumen Oblast | 56.99540 65.73485 | 7 | February 2024 |
| 37 | S | Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug | 66.59257 66.85846 | 3 | January 2024 |
| 38 | S 2 | Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug | 66.07485 76.65427 | 2 | November 2023 |
| 39 | S 2 | Omsk Oblast | 56.08978 74.64219 | 5 | November 2023 |
| 40 | S 2 | Novosibirsk Oblast | 55.05612 82.88010 | 7 | December 2023 |
| 41 | P 2 | Altai Krai | 53.35593 83.68230 | 2 | November 2023 |
| 42 | S 2 | Tomsk Oblast | 56.60427 84.86807 | 1 | March 2024 |
| 43 | P | Krasnoyarsk Krai | 69.42091 88.26126 | 1 | February 2024 |
| 44 | S 2 | Krasnoyarsk Krai | 55.96669 92.73100 | 5 | November 2023 |
| 45 | S 2 | Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) | 61.67818 129.35184 | 5 | April 2024 |
| 46 | P | Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) | 62.03243 129.72416 | 5 | August 2020 |
| 47 | S 2 | Khabarovsk Krai | 48.62218 135.06819 | 6 | December 2019 |
| 48 | S 2 | Sakhalin Oblast | 46.96788 142.75403 | 2 | December 2019 |
| 49 | S 2 | Kamchatka Krai | 53.18850 158.38604 | 1 | April 2019 |
| 50 | P | Kamchatka Krai | 55.92095 158.69500 | 3 | March 2024 |
Appendix B
References
- Skrjabin, K.I. Glistnye Invazii Severnogo Olenya (Helminth Diseases of Reindeer); Selkhozgiz: Moscow, Russia, 1931; 88p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Polyanskaya, M.V. Gel’mintosy Severnykh Oleney (Helminthiases of Reindeer); Knizhnoe Izdatelstvo: Murmansk, Russia, 1963; 47p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mizkewitsch, V.Y. Gel’minty Severnogo Olenya i Vyzyvayemyye imi Zabolevaniya (Reindeer Helminths and the Diseases They Cause); Kolos: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 1967; 308p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Golosov, I.M.; Mizkewitsch, V.Y. Helminthiases. In Parazitarnye Bolezni Severnykh Oleney (Parasitic Diseases of Reindeer); Lyzhin, K., Ed.; Krasnoyarskoe Knizhnoe Izdatelstvo: Krasnoyarsk, Russia, 1964; pp. 57–141. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Laaksonen, S. Trematoda. Cestoda. Nematoda. In TUNNE PORO. Poron Sairaudet ja Terveydenhoito (FEEL THE REINDEER. Reindeer Diseases and Health Care); Livonia Print: Riga, Latvia, 2016; pp. 220–251. (In Finnish) [Google Scholar]
- Belova, L.M.; Loginova, O.A. Helminthiases. In Bolezni Severnykh Oleney (Diseases of Reindeer); Zabrodin, V.A., Laishev, K.A., Eds.; Knizhnoe Izdatelstvo: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 2019; pp. 94–113. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kutz, S.J.; Ducrocq, J.; Verocai, G.G.; Hoar, B.M.; Colwell, D.D.; Beckmen, K.B.; Polley, L.; Elkin, B.T.; Hoberg, E.P. Parasites in ungulates of Arctic North America and Greenland: A view of contemporary diversity, ecology, and impact in a world under change. Adv. Parasitol. 2012, 79, 99–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutz, S.J.; Laaksonen, S.; Asbakk, K.; Nilssen, A.C. Helminths. In Reindeer and Caribou. Health and Disease; Tryland, M., Kutz, S.J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 180–205. [Google Scholar]
- Hrabok, J.T.; Oksanen, A.; Nieminen, M.; Waller, P.J. Population dynamics of nematode parasites of reindeer in the sub-arctic. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 142, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokelainen, P.; Moroni, B.; Hoberg, E.; Oksanen, A.; Laaksonen, S. Gastrointestinal parasites in reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus): A review focusing on Fennoscandia. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2019, 17, 100317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emelyanova, A.; Savolainen, A.; Oksanen, A.; Nieminen, P.; Loginova, O.; Abass, K.; Rautio, A. Research on Selected Wildlife Infections in the Circumpolar Arctic—A Bibliometric Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, E.R.; Orsel, K.; Cuyler, C.; Kutz, S.J. Life history matters: Differential effects of abomasal parasites on caribou fitness. Int. J. Parasitol. 2023, 53, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, C.L.; Wagner, B.; Harms, N.J.; Jenkins, E.J.; Jung, T.S. Comparative Prevalence and Intensity of Endoparasites in a Dynamic Boreal Ungulate Community. Diversity 2024, 16, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verocai, G.G.; Kutz, S.J.; Simard, M.; Hoberg, E.P. Varestrongylus eleguneniensis sp. n. (Nematoda: Protostrongylidae): A widespread, multi-host lungworm of wild North American ungulates, with an emended diagnosis for the genus and explorations of biogeography. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loginova, O.A.; Kolpashchikov, L.A.; Spiridonov, S.E. First report of Orthostrongylus sp. (Nematoda: Protostrongylidae) in wild reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) from the Taimyr, Russia: Nearctic parasites in a Palearctic host. Parasitol. Res. 2023, 122, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoberg, E.P.; Kocan, A.A.; Rickard, L.G. Gastrointestinal strongyles in wild ruminants. In Parasitic Diseases of Wild Mammals; Samuel, W.M., Pybus, M.J., Kocan, A.A., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 193–227. [Google Scholar]
- Tryland, M.; Kutz, S.J. Reindeer and Caribou. Health and Disease; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2019; p. 3. ISBN 978-1-4822-5068-8. [Google Scholar]
- Species 360. Data Science for Zoos and Aquariums. Available online: https://species360.org/products-services/zoo-aquarium-animal-management-software-2/ (accessed on 31 May 2024).
- Haigh, J.C.; Mackintosh, C.; Griffin, F. Viral, parasitic and prion diseases of farmed deer and bison. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2002, 21, 219–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flach, E. Cervidae and Tragulidae. In Zoo and Wild Animal Medicine, 5th ed.; Fowler, M.E., Miller, E.R., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 634–649. [Google Scholar]
- Goossens, E.; Vercruysse, J.; Boomker, J.; Vercammen, F.; Dorny, P. A 12-month survey of gastrointestinal helminth infections of cervids kept in two zoos in Belgium. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2005, 36, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manninen, S.M.; Thamsborg, S.M.; Laaksonen, S.; Oksanen, A. The reindeer abomasal nematode (Ostertagia gruehneri) is naturally transmitted to sheep when sharing pastures. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 4033–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utaaker, K.S.; Ytrehus, B.; Davey, M.L.; Fossøy, F.; Davidson, R.K.; Miller, A.L.; Robertsen, P.-A.; Strand, O.; Rauset, G.R. Parasite spillover from domestic sheep to wild reindeer—The role of salt licks. Pathogens 2023, 12, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latypov, D.G.; Timerbayeva, R.R.; Kirillov, E.G. Parazitologiya i Invazionnyye Bolezni Zhvachnykh Zhivotnykh (Parasitology and Invasive Diseases of Ruminants); Lan: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 2019; pp. 59–67. ISBN 978-5-8114-3561-6. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Verocai, G.G.; Chaudhry, U.N.; Lejeune, M. Diagnostic Methods for Detecting Internal Parasites of Livestock. Vet. Clin. Food. Anim. 2020, 36, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loginova, O.; Efeykin, B.; Krutikova, A.; Mizin, I.; Spiridonov, S. Fasciola hepatica: Updates on egg morphology, host range, and distribution. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2024, 36, e00237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holterman, M.; van der Wurff, A.; van den Elsen, S.; van Megen, H.; Bongers, T.; Holovachov, O.; Bakker, J.; Helder, J. Phylum-Wide Analysis of SSU rDNA Reveals Deep Phylogenetic Relationships among Nematodes and Accelerated Evolution toward Crown Clades. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loginova, O.A.; Belova, L.M.; Spiridonov, S.E. The First Report on Elaphostrongylus rangiferi (Reindeer Invasive Parasite) in Leningrad Oblast. Russ. J. Biol. Invasions 2022, 13, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luton, K.; Walker, D.; Blair, D. Comparisons of ribosomal internal transcribed spacers from two congeneric species of flukes (Platyhelminthes: Trematoda: Digenea). Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1992, 56, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahami-Oskouei, M.; Dalimi, A.; Forouzandeh-Moghadam, M.; Rokni, M.B. Molecular identification and differentiation of Fasciola isolates using PCR-RFLP method based on internal transcribed spacer (ITS1, 5.8 S rDNA, ITS2). Iranian J. Parasitol. 2011, 6, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gasser, R.B.; Chilton, N.B.; Hoste, H.; Beveridge, I. Rapid sequencing of rDNA from single worms and eggs of parasitic helminths. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 2525–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrain, T.C.; Wakarchuk, D.A.; Levesque, A.C.; Hamilton, R.I. Intraspecific rDNA restriction fragment length polymorphism in the Xiphinema americanum group. Fundam. Appl. Nematol. 1992, 15, 563–573. [Google Scholar]
- Loginova, O.A.; Rozenfeld, S.B.; Sipko, T.P.; Mizin, I.A.; Panchenko, D.V.; Laishev, K.A.; Bondar, M.G.; Kolpashchikov, L.A.; Gruzdev, A.R.; Kulemeev, P.S.; et al. Diversity and Distribution of Helminths in Wild Ruminants of the Russian Arctic: Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus), Muskoxen (Ovibos moschatus), and Snow Sheep (Ovis nivicola). Diversity 2023, 15, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handeland, K.; Slettbakk, T. Outbreaks of Clinical Cerebrospinal Elaphostrongylosis in Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) in Finnmark, Norway, and their Relation to Climatic Conditions. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 1994, 41, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, L.M. Odomashnivaniye Severnogo Olenya. Ot Okhotnika do Pastukha i Ranchevoda (Reindeer Domestication. From Hunter to Herdsman and Rancher); Tovarishchestvo Nauchnykh Izdaniy KMK: Moscow, Russia, 2021; p. 280. ISBN 978-5-907372-89-4. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Holand, Ø.; Mizin, I.; Weladji, R.B. Reindeer Rangifer tarandus (Linnaeus, 1758). In Handbook of the Mammals of Europe; Hackländer, K., Zachos, F.E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 247–277. ISBN 978-3-030-24474-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T. Velvet Antlers, Velvet Nose. The Story of a Reindeer Family; Coronet Books, Hodder and Stoughton: London, UK, 1995; p. 90. ISBN 0-340-66003-1. [Google Scholar]
- Wella, Y. Azbuka Olenevoda (Reindeer Herder’s ABC); Studiya O.K.: Surgut, Russia, 2011; 43p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mosgovoy, A.A. Sparrows as agent distributing helminthic infections among domestic animals. In Papers on Helminthology; Schultz, R.-E.S., Gnedina, M.P., Eds.; All-Union Lenin Academy of Agricultural Sciences: Moscow, Russia, 1937; pp. 398–402. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Izdebska, J.N.; Fryderyk, S. Demodex acutipes Bukva et Preisler, 1988 (Acari, Demodecidae)—A rare parasite of red deer (Cervus elaphus L.). Ann. Parasitol. 2012, 58, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vasilevich, F.I.; Belova, L.M.; Burmistrova, M.I. Parazitarnye Zoonozy (Parasitic Zoonoses); ZooVetKniga: Moscow, Russia, 2020; pp. 21–28. ISBN 978-5-6045650-5-6. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Bargues, M.D.; Valero, M.A. Human fascioliasis infection sources, their diversity, incidence factors, analytical methods and prevention measures. Parasitology 2018, 145, 1665–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattes, S.; Ferte, H.; Delaunay, P.; Depaquit, J.; Vassallo, M.; Vittier, M.; Kokcha, S.; Coulibaly, E.; Marty, P. Trichostrongylus colubriformis Nematode Infections in Humans, France. Emerg. Inf. Dis. 2011, 17, 1301–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, B.B.S.; Juyal, P.D. Textbook of Parasitic Zoonoses; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 46–110. ISBN 978-81-322-1550-9. [Google Scholar]
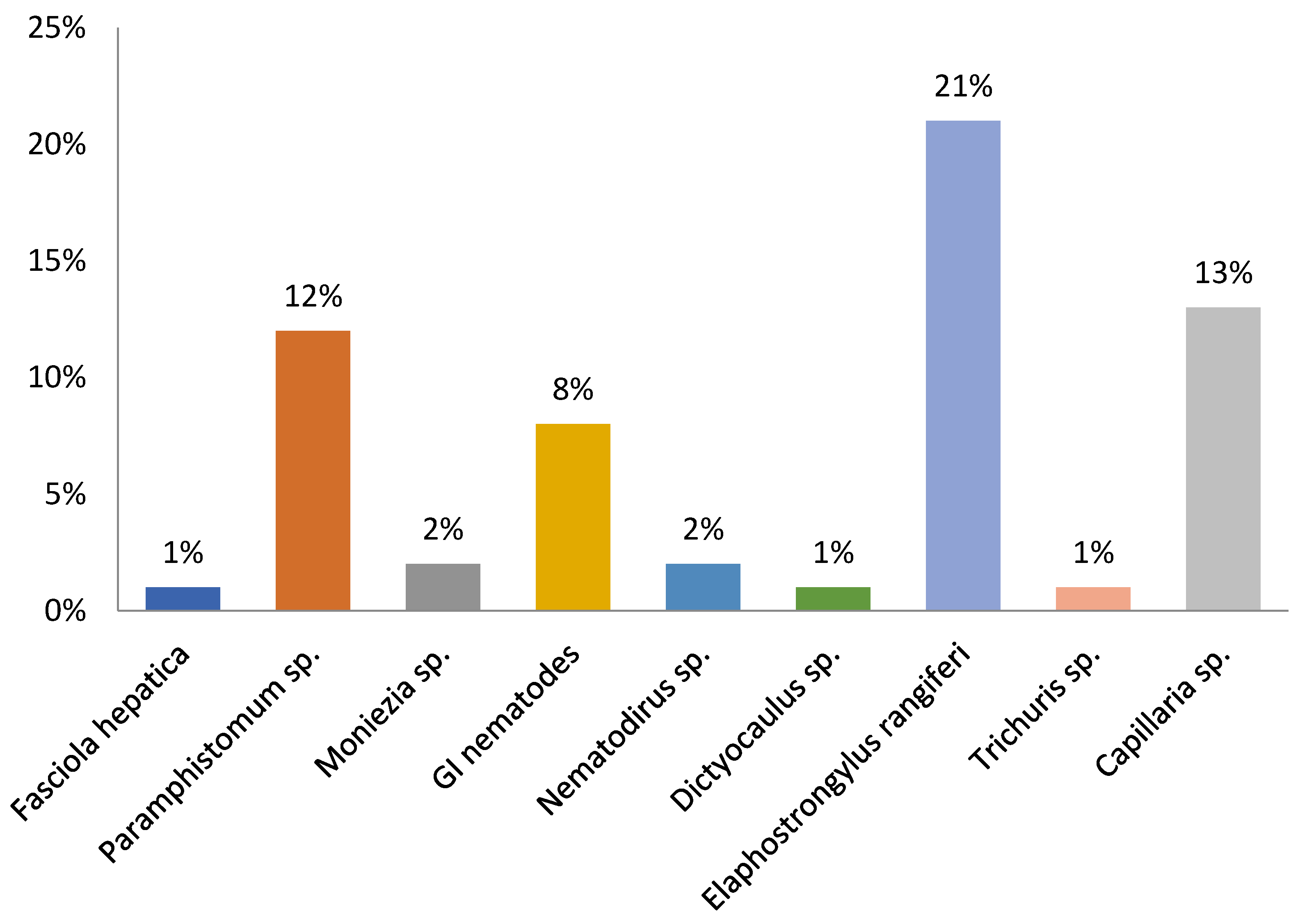
| Zoo ID | Species | GenBank 1 | Vouchers 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | Fasciola hepatica 3 | PP328913 | IPEE_Parasites 14320 |
| 4 | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi 4 | PP843608 | IPEE_Parasites 14319 |
| 5 | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi 4 | PP843600 | IPEE_Parasites 14339 |
| 6 | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi 4 | PP843598 | IPEE_Parasites 14343 |
| 7 | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi 4 | PP843592 | IPEE_Parasites 14344 |
| 8 | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi 4 | PP845195 | IPEE_Parasites 14345 |
| 9 | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi 4 | PP845196 | IPEE_Parasites 14346 |
| 12 | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi 5 | MW848820 | IPEE_Parasites 14282 |
| 13 | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi 4 | PP843584 | IPEE_Parasites 14347 |
| 25 | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi 4 | PP845193 | IPEE_Parasites 14348 |
| 29 | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi 4 | PP845194 | IPEE_Parasites 14349 |
| 30 | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi 4 | PP845192 | IPEE_Parasites 14350 |
| Zoo ID | Trematodes | Cestodes | Nematodes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasciola hepatica | Paramphistomum sp. | Moniezia spp. | Strongyle-Type | Nematodirus spp. | Dictyocaulus sp. | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi | Trichuris sp. | Capillaria sp. | |
| 2 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 4 (33%) |
| 4 | – | 2 (18%) | – | – | – | – | 4 (36%) | – | 2 (18%) |
| 5 | – | 2 (67%) | – | – | – | – | 3 (100%) | – | – |
| 6 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (100%) | – | – |
| 7 | – | – | – | 3 (43%) | – | – | 4 (57%) | – | 1 (14%) |
| 8 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (33%) | – | 1 (33%) |
| 9 | – | 3 (33%) | 1 (11%) | – | – | – | 6 (67%) | – | 1 (11%) |
| 10 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (100%) |
| 11 | – | 4 (50%) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 12 | – | – | – | 4 (37%) | 2 (18%) | – | 7 (63%) | – | 5 (45%) |
| 13 | 1 (33%) | 2 (67%) | – | – | – | – | 1 (33%) | – | – |
| 14 | – | – | 1 (50%) | 2 (100%) | – | – | – | 1 (50%) | – |
| 16 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 2 (50%) |
| 18 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (50%) |
| 21 | 2 (100%) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 22 | – | – | – | 3 (100%) | – | – | – | 1 (33%) | – |
| 24 | – | – | 1 (17%) | 1 (17%) | – | – | – | – | – |
| 25 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (17%) | – | 1 (17%) |
| 26 | – | – | 1 (25%) | – | – | – | – | – | 2 (50%) |
| 28 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (20%) |
| 29 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 2 (67%) | – | – |
| 30 | – | 8 (38%) | – | 1 (5%) | – | 1 (5%) | 6 (29%) | – | 3 (14%) |
| 34 | – | – | 1 (9%) | 2 (18%) | – | – | – | – | 2 (18%) |
| 36 | – | – | – | – | 2 (29%) | – | 4 (57%) | – | – |
| 37 | – | 1 (33%) | – | – | – | – | 3 (100%) | – | – |
| 38 | – | 2 (100%) | – | 2 (100%) | – | – | – | – | – |
| 39 | – | 4 (80%) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 44 | – | – | – | – | 1 (20%) | – | – | – | – |
| 46 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 5 (100%) | – | – |
| 47 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (17%) |
| 48 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 2 (100%) |
| Helminths | Intensity of Infestation Depending on the Number of Detected Helminth Eggs and Larvae, Specimens per 1 g of Feces | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Medium | High | Very High | |
| Nematodes, Cestodes | 1–100 | 101–500 1 | 501–1000 | >1000 |
| GINs (eggs) | 1–56 (zoos #7, 12, 14, 22, 24, 30, 34, 39) | – | – | – |
| Nematodirus spp. (eggs) | 1–4 (zoos #12, 36, 44) | – | – | – |
| Dictyocaulus sp. (L1) | 1 (zoo #30) | – | – | – |
| E. rangiferi (L1) | 1–98 (zoos #4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 12, 13, 25, 29, 30, 36, 37, 46) | 15–537 (zoo #9) | – | – |
| Trichuris sp. (eggs) | 1 (zoos #14, 22) | – | – | – |
| Capillaria sp. (eggs) | 1–8 (zoos #2, 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 16, 18, 25, 26, 28, 30, 34, 47, 48) | – | – | – |
| Moniezia spp. (eggs) 2 | 1–17 (zoos # 9,14, 24, 26, 34) | – | – | – |
| Trematodes | 1–10 | 11–100 | >100 | – |
| F. hepatica (eggs) | 1–3 (zoos #13, 21) | – | – | |
| Paramphistomum sp. (eggs) | 1–8 (zoos #4, 5, 9, 11, 13, 37, 38, 38) | 9–56 (zoo #30) | – | – |
| Helminth 1 | Helminth 2 | Helminth 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Fasciola hepatica | Paramphistomum sp. | – |
| Paramphistomum sp. | Small strongylids | – |
| Paramphistomum sp. | Dictyocaulus sp. | – |
| Paramphistomum sp. | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi | – |
| Paramphistomum sp. | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi | Capillaria sp. |
| Moniezia expansa | Moniezia sp. | – |
| Moniezia sp. | Small strongylids | – |
| Moniezia sp. | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi | – |
| Moniezia sp. | Trichuris sp. | – |
| Moniezia sp. | Capillaria sp. | – |
| Small strongylids | Elaphostrongylus rangiferi | – |
| Small strongylids | Trichuris sp. | – |
| Small strongylids | Capillaria sp. | – |
| Nematodirus sp. type 1 | Nematodirus sp. type 2 | – |
| Elaphostrongylus rangiferi | Nematodirus sp. | – |
| Elaphostrongylus rangiferi | Capillaria sp. | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loginova, O.A.; Akulova, S.V.; Egorov, D.N.; Egorova, N.S.; Spiridonov, S.E.; Plotnikova, I.K.; Belova, L.M.; Kuznetsov, Y.E.; Chuprak, D.I.; Krutikova, A.A.; et al. Coprological Survey of Helminths in Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) in 50 Selected Zoos and Menageries in Russia. J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2024, 5, 492-506. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg5030033
Loginova OA, Akulova SV, Egorov DN, Egorova NS, Spiridonov SE, Plotnikova IK, Belova LM, Kuznetsov YE, Chuprak DI, Krutikova AA, et al. Coprological Survey of Helminths in Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) in 50 Selected Zoos and Menageries in Russia. Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens. 2024; 5(3):492-506. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg5030033
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoginova, Olga A., Svetlana V. Akulova, Dmitry N. Egorov, Natalia S. Egorova, Sergei E. Spiridonov, Iuliia K. Plotnikova, Larisa M. Belova, Yuriy E. Kuznetsov, Daria I. Chuprak, Anna A. Krutikova, and et al. 2024. "Coprological Survey of Helminths in Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) in 50 Selected Zoos and Menageries in Russia" Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens 5, no. 3: 492-506. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg5030033
APA StyleLoginova, O. A., Akulova, S. V., Egorov, D. N., Egorova, N. S., Spiridonov, S. E., Plotnikova, I. K., Belova, L. M., Kuznetsov, Y. E., Chuprak, D. I., Krutikova, A. A., Vasilkova, I. V., Gelashvili, D. A., Shchepanovsky, Y. A., Mizin, I. A., Panchenko, D. V., Bondar, M. G., & Sipko, T. P. (2024). Coprological Survey of Helminths in Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) in 50 Selected Zoos and Menageries in Russia. Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens, 5(3), 492-506. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg5030033









