Immunology and Biologics in the Treatment of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis in Cystic Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diagnosis
3. Management
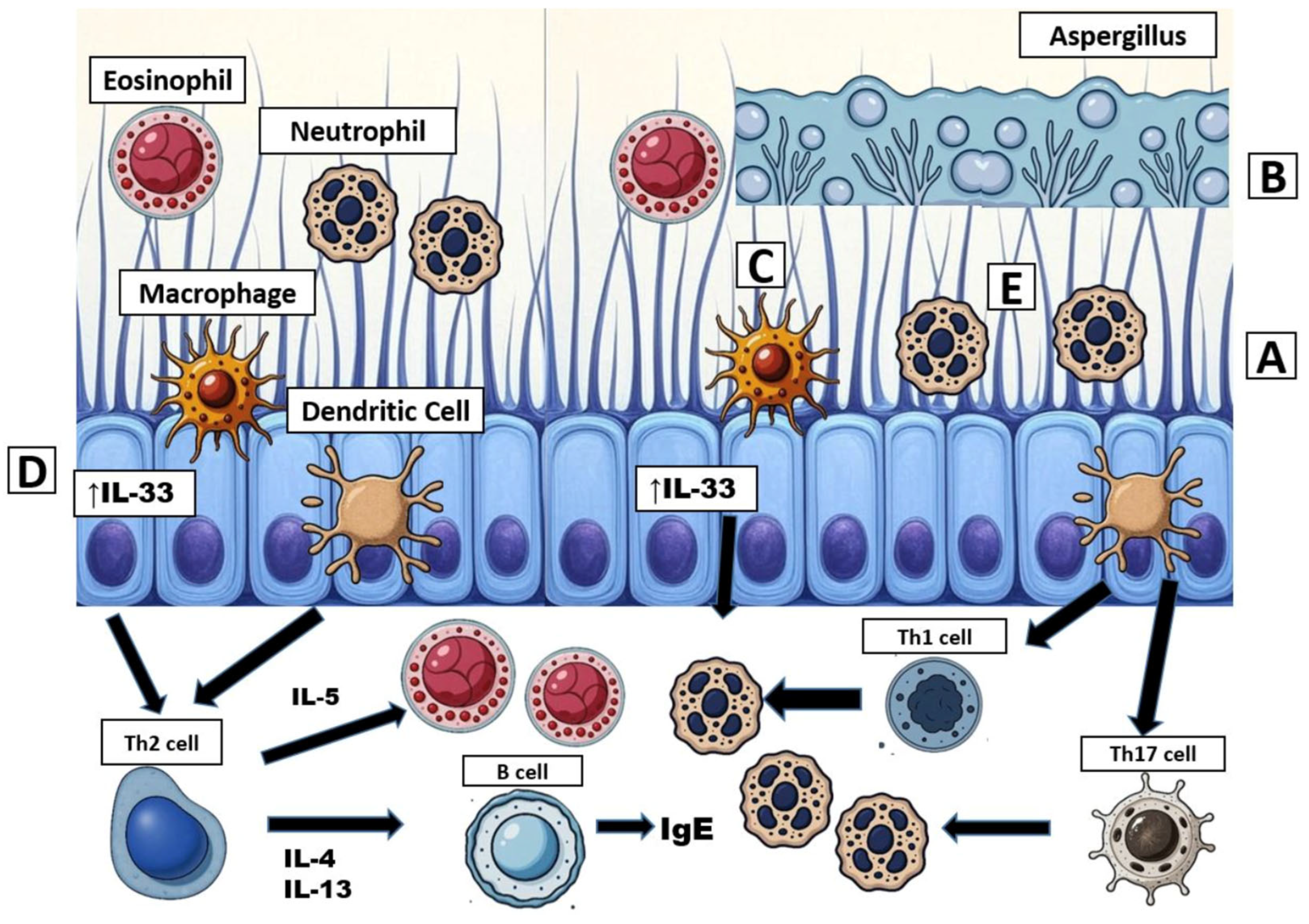
4. Immunology in Cystic Fibrosis
4.1. Omalizumab
4.2. Dupilumab
4.3. Mepolizumab
4.4. Benralizumab
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABPA | Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis |
| CF | Cystic Fibrosis |
| CFF | Cystic Fibrosis Foundation |
| CFTR | Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| CYP3A4 | Cytochrome P450 3A4 |
| EGPA | Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis |
| FDA | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| FEV1 | Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 s |
| HEMT | Highly Effective Modulator Therapy |
| HSV | Herpes Simplex Virus |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin |
| IL | Interleukin |
| PwCF | People with Cystic Fibrosis |
| Th2 | T-helper cell type 2 |
References
- Grasemann, H.; Ratjen, F. Cystic Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1693–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, B.P.; Freedman, S.D. Cystic fibrosis. The Lancet 2009, 373, 1891–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, P.G.; Mall, M.A.; Dřevínek, P.; Lands, L.C.; McKone, E.F.; Polineni, D.; Ramsey, B.W.; Taylor-Cousar, J.L.; Tullis, E.; Vermeulen, F.; et al. Elexacaftor–Tezacaftor–Ivacaftor for Cystic Fibrosis with a Single Phe508del Allele. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. 2024 Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Patient Registry Highlights; Cystic Fibrosis Foundation: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard, A.C.; Waters, V.J. Opportunistic Pathogens in Cystic Fibrosis: Epidemiology and Pathogenesis of Lung Infection. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2022, 11, S3–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgel, P.-R.; Paugam, A.; Hubert, D.; Martin, C. Aspergillus fumigatus in the cystic fibrosis lung: Pros and cons of azole therapy. Infect. Drug Resist. 2016, 9, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yu, W. Interaction between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Aspergillus fumigatus in cystic fibrosis. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Psoter, K.J.; Jennings, M.T.; Merlo, C.A.; Boyle, M.P.; Hadjiliadis, D.; Kawut, S.M.; Lechtzin, N. Risk factors for persistent Aspergillus respiratory isolation in cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2018, 17, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.R.; Patel, A.R.; Singh, S.; Singh, S.; Khawaja, I. Treating Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis: A Review. Cureus 2019, 11, e4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Panjabi, C. Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis: A Perplexing Clinical Entity. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2016, 8, 282–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, C.; Braag, S.A.; Keeler, A.; Hodges, C.; Drumm, M.; Flotte, T.R. Lack of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in CD3+ lymphocytes leads to aberrant cytokine secretion and hyperinflammatory adaptive immune responses. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 44, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.A.; Moss, R.B.; Kurup, V.P.; Knutsen, A.P.; Greenberger, P.; Judson, M.A.; Denning, D.W.; Crameri, R.; Brody, A.S.; Light, M.; et al. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis--state of the art: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Consensus Conference. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2003, 37 (Suppl. 3), S225–S264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tompkins, M.G.; Pettit, R. Beyond the Guidelines: Treatment of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis in Cystic Fibrosis. Ann. Pharmacother. 2022, 56, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maturu, V.N.; Agarwal, R. Prevalence of Aspergillus sensitization and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 45, 1765–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janahi, I.A.; Rehman, A.; Al-Naimi, A.R. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with cystic fibrosis. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2017, 12, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiff, D.B.; Wells, A.U.; Carr, D.H.; Cole, P.J.; Hansell, D.M. CT findings in bronchiectasis: Limited value in distinguishing between idiopathic and specific types. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1995, 165, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.; White, C.S.; Templeton, P.A.; Britt, E.J.; Rubin, L.J. High attenuation mucous plugs in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: CT appearance. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1992, 16, 649–650. [Google Scholar]
- Phuyal, S.; Garg, M.K.; Agarwal, R.; Gupta, P.; Chakrabarti, A.; Sandhu, M.S.; Khandelwal, N. High-Attenuation Mucus Impaction in Patients With Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis: Objective Criteria on High-Resolution Computed Tomography and Correlation With Serologic Parameters. Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 2016, 45, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufer, P.; Fink, J.N.; Bruns, W.T.; Unger, G.F.; Kalbfleisch, J.H.; Greenberger, P.A.; Patterson, R. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1984, 73, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutcheson, P.S.; Knutsen, A.P.; Rejent, A.J.; Slavin, R.G. A 12-year longitudinal study of Aspergillus sensitivity in patients with cystic fibrosis. Chest 1996, 110, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Panjabi, C. Allergic aspergillosis of the respiratory tract. Eur. Respir. Rev. Off. J. Eur. Respir. Soc. 2014, 23, 8–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el-Dahr, J.M.; Fink, R.; Selden, R.; Arruda, L.K.; Platts-Mills, T.A.; Heymann, P.W. Development of immune responses to Aspergillus at an early age in children with cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 150, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vrankrijker, A.M.M.; van der Ent, C.K.; van Berkhout, F.T.; Stellato, R.K.; Willems, R.J.L.; Bonten, M.J.M.; Wolfs, T.F.W. Aspergillus fumigatus colonization in cystic fibrosis: Implications for lung function? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.; Patterson, R.; Mintzer, R.; Cooper, B.J.; Roberts, M.; Harris, K.E. Clinical and immunologic criteria for the diagnosis of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1977, 86, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Chakrabarti, A.; Shah, A.; Gupta, D.; Meis, J.F.; Guleria, R.; Moss, R.; Denning, D.W.; ABPA Complicating Asthma ISHAM Working Group. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: Review of literature and proposal of new diagnostic and classification criteria. Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 43, 850–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gothe, F.; Schmautz, A.; Häusler, K.; Tran, N.-B.; Kappler, M.; Griese, M. Treating Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis with Short-Term Prednisone and Itraconazole in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 2608–2614.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Dhooria, S.; Singh Sehgal, I.; Garg, M.; Saikia, B.; Behera, D.; Chakrabarti, A. A randomised trial of glucocorticoids in acute-stage allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis complicating asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.A.; Schwartz, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Moskovitz, B.L.; Jerome, D.C.; Catanzaro, A.; Bamberger, D.M.; Weinmann, A.J.; Tuazon, C.U.; Judson, M.A.; et al. A randomized trial of itraconazole in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glackin, L.; Leen, G.; Elnazir, B.; Greally, P. Voriconazole in the treatment of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis. Ir. Med. J. 2009, 102, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Cymberknoh, M.; Blau, H.; Shoseyov, D.; Mei-Zahav, M.; Efrati, O.; Armoni, S.; Kerem, E. Intravenous monthly pulse methylprednisolone treatment for ABPA in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2009, 8, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, K.; Tomomatsu, K.; Okada, N.; Tanaka, J.; Oguma, T. Treatment of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis with biologics. Chin. Med. J. Pulm. Crit. Care Med. 2025, 3, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wark, P.A.B.; Hensley, M.J.; Saltos, N.; Boyle, M.J.; Toneguzzi, R.C.; Epid, G.D.C.; Simpson, J.L.; McElduff, P.; Gibson, P.G. Anti-inflammatory effect of itraconazole in stable allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, J.; Oguma, T.; Ishiguro, T.; Taniguchi, H.; Nishiuma, T.; Tateno, H.; Matsumoto, H.; Koshimizu, N.; Ito, Y.; Matsunaga, K.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Difficult-To-Treat Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis and Its Prediction Score. Allergy 2025, 80, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.; Shi, A.; Beringer, P. Drug-drug interactions involving CFTR modulators: A review of the evidence and clinical implications. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2023, 19, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, A.M.E.; Eggermont, M.N.; Wilms, E.B.; Aziz, S.; Reijers, M.; Roukema, J.; Warris, A.; Brüggemann, R.J.M.; van der Meer, R. Evaluation of the drug-drug interaction between triazole antifungals and cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator modulators in a real-life cohort. Med. Mycol. 2024, 62, myae020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purkayastha, D.; Agtarap, K.; Wong, K.; Pereira, O.; Co, J.; Pakhale, S.; Kanji, S. Drug-drug interactions with CFTR modulator therapy in cystic fibrosis: Focus on Trikafta®/Kaftrio®. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2023, 22, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeets, T.J.L.; van der Sijs, H.; Janssens, H.M.; Ruijgrok, E.J.; de Winter, B.C.M. Subtherapeutic triazole concentrations as result of a drug-drug interaction with lumacaftor/ivacaftor. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2024, 23, 563–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun-Vignes, B.; Archer, V.C.; Diquet, B.; Levron, J.C.; Chosidow, O.; Puech, A.J.; Warot, D. Effect of itraconazole on the pharmacokinetics of prednisolone and methylprednisolone and cortisol secretion in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2001, 51, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillan, J.L.; Davidson, D.J.; Gray, R.D. Targeting cystic fibrosis inflammation in the age of CFTR modulators: Focus on macrophages. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2003502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruscia, E.M.; Bonfield, T.L. Cystic Fibrosis Lung Immunity: The Role of the Macrophage. J. Innate Immun. 2016, 8, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Riehle, A.; Ma, J.; Kamler, M.; Gulbins, E.; Grassmé, H. Staphylococcus aureus Survives in Cystic Fibrosis Macrophages, Forming a Reservoir for Chronic Pneumonia. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00883-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxerbaum, B.; Kagumba, A.; Matthews, L.W. Selective inhibition of phagocytic activity of rabbit alveolar macrophages by cystic fibrosis serum. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1973, 108, 777–783. [Google Scholar]
- Zaman, M.M.; Gelrud, A.; Junaidi, O.; Regan, M.M.; Warny, M.; Shea, J.C.; Kelly, C.; O’Sullivan, B.P.; Freedman, S.D. Interleukin 8 secretion from monocytes of subjects heterozygous for the deltaF508 cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene mutation is altered. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2004, 11, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellems, D.; Hu, Y.; Jennings, S.; Wang, G. Loss of CFTR function in macrophages alters the cell transcriptional program and delays lung resolution of inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1242381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taggart, C.; Coakley, R.J.; Greally, P.; Canny, G.; O’Neill, S.J.; McElvaney, N.G. Increased elastase release by CF neutrophils is mediated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-8. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2000, 278, L33–L41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacalone, V.D.; Dobosh, B.S.; Gaggar, A.; Tirouvanziam, R.; Margaroli, C. Immunomodulation in Cystic Fibrosis: Why and How? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, M.A.; Hartl, D. CFTR: Cystic fibrosis and beyond. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruscia, E.M.; Bonfield, T.L. Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Cystic Fibrosis. Clin. Chest Med. 2016, 37, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, D.; Gaggar, A.; Bruscia, E.; Hector, A.; Marcos, V.; Jung, A.; Greene, C.; McElvaney, G.; Mall, M.; Döring, G. Innate immunity in cystic fibrosis lung disease. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2012, 11, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusselle, G.G.; Koppelman, G.H. Biologic Therapies for Severe Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.P.; Thomas, C.M.; Wu, A.Y.; Rusznak, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, W.; Cephus, J.-Y.; Gibson-Corley, K.N.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Norlander, A.E.; et al. Cystic Fibrosis Reprograms Airway Epithelial IL-33 Release and Licenses IL-33-Dependent Inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 1486–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonker, L.M.; Marand, A.; Muldur, S.; Hopke, A.; Leung, H.M.; De La Flor, D.; Park, G.; Pinsky, H.; Guthrie, L.B.; Tearney, G.J.; et al. Neutrophil dysfunction in cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2021, 20, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, D.Y.; Urbanek, R.; Götz, M. Increased degranulation of eosinophil and neutrophil granulocytes in cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.L.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Smeekens, S.P.; Jacobs, C.W.; Magis-Escurra, C.; Jaeger, M.; Wang, X.; Lubbers, R.; Oosting, M.; Joosten, L.A.B.; et al. Pattern recognition pathways leading to a Th2 cytokine bias in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis patients. Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 45, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochner, B.S. Systemic activation of basophils and eosinophils: Markers and consequences. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, S292–S302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsen, A.P.; Chauhan, B.; Slavin, R.G. Cell-mediated immunity in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Immunol. Allergy Clin. 1998, 18, 575–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendra, D.; Blixt, J.; Hanania, N.A. Immunological biomarkers in severe asthma. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 46, 101332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacharier, L.B.; Geha, R.S. Molecular mechanisms of IgE regulation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, S547–S558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; McClellan, J.S.; Knutsen, A.P. Increased sensitivity to IL-4 in patients with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2000, 123, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, L.F.; Tarchevskaya, S.; Brigger, D.; Sathiyamoorthy, K.; Graham, M.T.; Nadeau, K.C.; Eggel, A.; Jardetzky, T.S. Structural basis of omalizumab therapy and omalizumab-mediated IgE exchange. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Douglass, J.A.; Elborn, J.S.; Agarwal, R.; Calhoun, W.J.; Lazarewicz, S.; Jaumont, X.; Yan, M. Omalizumab in Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2023, 11, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals. An Exploratory, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Study to Assess the Efficacy of Multiple Doses of Omalizumab in Cystic Fibrosis Complicated by Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA). clinicaltrials.gov; 2011. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00787917 (accessed on 29 July 2025).
- Emiralioglu, N.; Dogru, D.; Tugcu, G.D.; Yalcin, E.; Kiper, N.; Ozcelik, U. Omalizumab Treatment for Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis in Cystic Fibrosis. Ann. Pharmacother. 2016, 50, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nové-Josserand, R.; Grard, S.; Auzou, L.; Reix, P.; Murris-Espin, M.; Brémont, F.; Mammar, B.; Mely, L.; Hubert, D.; Durieu, I.; et al. Case series of omalizumab for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis patients. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2017, 52, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, G.F.; Portale, A.; Papale, M.; Tardino, L.; Rotolo, N.; Licari, A.; Leonardi, S. Successful treatment with omalizumab of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with cystic fibrosis: Case reports and literature review. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 1636–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, S.; Pfannenstiel, C.; Friedrichs, F.; Kröger, K.; Wagner, N.; Tenbrock, K. Omalizumab: A new treatment option for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with cystic fibrosis. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2014, 8, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazi, M.; Sity, S.; Sarouk, I.; Bar Aluma, B.E.; Dagan, A.; Bezalel, Y.; Bentur, L.; De Boeck, K.; Efrati, O. Omalizumab in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Asthma Allergy 2018, 11, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsokera, A.; Corriveau, S.; Sykes, J.; Coriati, A.; Cortes, D.; Vadas, P.; Chaparro, C.; McIntyre, K.; Tullis, E.; Stephenson, A.L. Omalizumab for asthma and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in adults with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2020, 19, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Bellido, F.J.; Moreno, E.; Dávila, I. Dupilumab: A Review of Present Indications and Off-Label Uses. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 32, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mümmler, C.; Kemmerich, B.; Behr, J.; Kneidinger, N.; Milger, K. Differential response to biologics in a patient with severe asthma and ABPA: A role for dupilumab? Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. Off. J. Can. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Veer, T.; Dallinga, M.A.; van der Valk, J.P.M.; Kappen, J.H.; In ’t Veen, J.C.C.M.; van der Eerden, M.M.; Braunstahl, G.-J. Reduced exacerbation frequency and prednisone dose in patients with ABPA and asthma treated with dupilumab. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2021, 11, e12081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Green, O. Dupilumab: A new contestant to corticosteroid in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Oxf. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 2021, omaa029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramonell, R.P.; Lee, F.E.-H.; Swenson, C.; Kuruvilla, M. Dupilumab treatment for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: A case series. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 742–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikura, S.; Saraya, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Oda, M.; Ishida, M.; Honda, K.; Nakamoto, K.; Tamura, M.; Takata, S.; Shimoyamada, H.; et al. Successful Treatment of Mepolizumab- and Prednisolone-resistant Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis with Dupilumab. Intern. Med. Tokyo Jpn. 2021, 60, 2839–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamothe, P.A.; Pruett, C.L.H.; Smirnova, N.; Shepherd, A.; Runnstrom, M.C.; Park, J.; Zhang, R.H.; Zhao, L.; Swenson, C.; Lee, F.E.-H. Anti-IL-4Ra therapy is superior to other biologic classes in treating allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Glob. 2025, 4, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaliere, C.; Frati, F.; Ridolo, E.; Greco, A.; de Vincentiis, M.; Masieri, S.; Makri, E.; Incorvaia, C. The spectrum of therapeutic activity of mepolizumab. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abonia, J.P.; Putnam, P.E. Mepolizumab in eosinophilic disorders. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 7, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Borish, L.; Smith, A.; Somerville, L.; Albon, D. Use of mepolizumab in adult patients with cystic fibrosis and an eosinophilic phenotype: Case series. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. Off. J. Can. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, M.; Mulrennan, S.; Morey, S.; Vekaria, S.; Popowicz, N.; Tai, A. Mepolizumab use in cystic fibrosis-associated allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Respirol. Case Rep. 2021, 9, e00696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolebeyan, A.; Mohammadi, O.; Vaezi, Z.; Amini, A. Mepolizumab as Possible Treatment for Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis: A Review of Eight Cases. Cureus 2020, 12, e9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moni, S.S.; Al Basheer, A. Molecular targets for cystic fibrosis and therapeutic potential of monoclonal antibodies. Saudi Pharm. J. SPJ 2022, 30, 1736–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubouchi, K.; Arimura-Omori, M.; Inoue, S.; Okamatsu, Y.; Inoue, K.; Harada, T. A case of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis with marked peripheral blood eosinophilia successfully treated with benralizumab. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 32, 101339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaga, A.; Ashraff, K.; Din Khan, N.H. Rapid onset of effect of benralizumab in a severe eosinophilic and allergic asthma patient with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Respirol. Case Rep. 2023, 11, e01167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomomatsu, K.; Yasuba, H.; Ishiguro, T.; Imokawa, S.; Hara, J.; Soeda, S.; Harada, N.; Tsurikisawa, N.; Oda, N.; Katoh, S.; et al. Real-world efficacy of anti-IL-5 treatment in patients with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canon, N.; Modena, B. M202 Benralizumab for management of ABPA in a CF patient. Ann. Allergy. Asthma. Immunol. 2020, 125, S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ABPA Diagnostic Criteria Proposed by the CFF | |
|---|---|
| Clinical | Acute or subacute clinical respiratory deterioration not attributable to another etiology |
| Serologic | Total serum IgE concentration > 1000 IU/mL (or >500 IU/mL for minimal diagnostic criteria) off any systemic corticosteroids Precipitating antibodies to A. fumigatus or serum IgG antibody to A. fumigatus Immediate cutaneous reactivity to Aspergillus (prick skin test wheal > 3 mm in diameter with surrounding erythema) or IgE antibody to A. fumigatus |
| Radiographic | New or recent abnormalities on chest radiograph or CT that do not clear with antibiotics or chest physiotherapy |
| Agent | Mechanism of Action | Indications | Dose/Route of Administration | Adverse Effects | Clinical Benefits in PwCF with ABPA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omalizumab | Humanized antibody that binds free IgE at the Cε3 domain of heavy chain | Allergic asthma, chronic urticaria, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, Ig-E mediated food allergy | Subcutaneous injection every 2 to 4 weeks | Arthralgia, pain, fatigue, dizziness, dermatitis, injection site reaction | Possible corticosteroid sparing effect and reduced pulmonary exacerbations related to ABPA |
| Dupilumab | IL-4 receptor alpha antagonist, inhibits downstream effectors IL-4 and IL-13 | Atopic dermatitis, asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis, eosinophilic esophagitis, prurigo nodularis, eosinophilic phenotype COPD, chronic spontaneous urticaria, bullous pemphigoid | Subcutaneous injection every 2 to 4 weeks | Injection site reaction, conjunctivitis, eosinophilia, upper respiratory tract infections, HSV infection, arthralgia, dizziness, headache | Limited data on PwCF, possible corticosteroid sparing effect, reduced pulmonary exacerbations and function in asthmatic patients |
| Mepolizumab | Monoclonal antibody that binds IL-5 receptor α | Add on therapy for severe eosinophilic asthma or chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis, eosinophilic phenotype COPD, EGPA, hypereosinophilic syndrome | Subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks | Headache, injection site reaction, back pain, fatigue, diarrhea, cough, oropharyngeal pain | Possible corticosteroid sparing effect, reduced Ig-E level, and improved eosinophilia |
| Benralizumab | IL-5 receptor alpha directed cytolytic monoclonal antibody | Add on therapy for severe eosinophilic asthma, EGPA | Subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks for first 3 doses followed by once every 8 weeks | Headache, pharyngitis | Limited data on PwCF, possible corticosteroid sparing effect and clinical improvement in asthmatic patients |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, E.S.; Wang, J. Immunology and Biologics in the Treatment of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Respir. 2025, 5, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor5040019
Kim ES, Wang J. Immunology and Biologics in the Treatment of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis in Cystic Fibrosis. Journal of Respiration. 2025; 5(4):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor5040019
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Esther S., and Janice Wang. 2025. "Immunology and Biologics in the Treatment of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis in Cystic Fibrosis" Journal of Respiration 5, no. 4: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor5040019
APA StyleKim, E. S., & Wang, J. (2025). Immunology and Biologics in the Treatment of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis in Cystic Fibrosis. Journal of Respiration, 5(4), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor5040019






