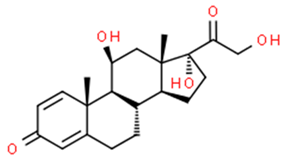
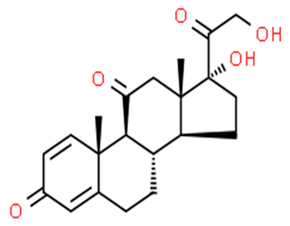
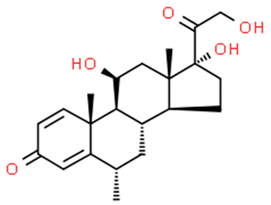
Abstract
Numerous micropollutants, especially endocrine-disrupting compounds (EDCs), can pollute natural aquatic environments causing great concern for human and ecosystem health. While most of the conversation revolves around estrogen and androgen, glucocorticoids (GCs) are also prevalent in natural waters. Despite the fact that GCs play a crucial role in both inflammatory and immunologic development activities, they are also detected in natural waters and considered as one of the EDCs. Although many researchers have mentioned the adverse effect of GCs on aquatic organisms, a complete management technology to remove these pollutants from surface and coastal waters is yet to be established. In the current study, six glucocorticoids (prednisone, prednisolone, cortisone, cortisol, dexamethasone, and 6R-methylprednisolone) have been selected according to their higher detection frequency in environmental waters. The concentration of selected GCs ranged from 0.05 ng/L to 433 ng/L and their removal efficiency ranged from 10% to 99% depending on the water source and associated removal technologies. Although advanced technologies are available for achieving successful removal of GCs, associated operational and economic considerations make implementation of these processes unsustainable. Further studies are necessary to resolve the entry routes of GCs compounds into the surface water or drinking water permanently as well as employ sustainable detection and removal technologies.
1. Introduction
In the past few decades, thousands of endocrine-disrupting compounds (EDCs) entered into the water cycle through different ways [1,2,3,4]. According to EPA, endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), which can be both natural and synthetic substances in our environment, are typically pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) and foods that interfere with hormone biosynthesis and metabolism resulting in a deviation from normal homeostatic control or reproduction [5]. Humans and animals are exposed primarily through ingestion of contaminated foods (e.g., fish, meat, and dairy products) [6]. Incidentally, steroid and hormone mimics have also been addressed among chemicals (natural or synthetic) used for preparing and preserving foods [7,8]. Processed and packaged foods (Finnish foods mostly meat and fish, tinned food, infant formula etc.) can accumulate the traces of EDCs that leaching out of materials used in assembling, processing, transporting, and storage [9,10,11].
Discharge of hospital waste, household sewage, agricultural and industrial waste, husbandry waste, and usually inadequate removal in many wastewaters treatment plants (WWTPs) are the most common sources for EDC’s hazardous presence in the environment [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. It is worthwhile to note that primary and secondary treatments target organic matter, carbon, nutrients removal which are generally 106 times higher in concentration in a typical wastewater compared to GCs. Therefore, GCs would be outcompeted by carbon or nutrients in primary and secondary treatments and employment of tertiary treatment for removal of GCs would be more effective. Several studies have reported and mentioned that chronic exposure to these chemicals or compounds can cause exotic and unanticipated side effects [4,12,13,14,15]. Despite being warned of in the past few years, EDCs still were not considered as a priority pollutant that would require mandatory removal from wastewater. Currently adopted treatment processes in WWTPs unfortunately are generally not successful in eliminating EDCs completely [2,3]. Moreover, identification of these compounds is challenging in a conventional WWTP as they are present at a very low concentration, typically at the range of ng/L [16]. Researchers have introduced new analytical techniques for EDCs detection. As a result, recently published works focused on detection of EDCs in natural waters, and a lot of evidence and examples suggest that the impact of EDCs on aquatic wildlife and human is very concerning [12,16,17,18]. There has been a shift towards more awareness regarding the presence of EDCs in the environmental waters and their associated impacts [19]. Moreover, steroid hormones have also attracted increased concerns, such as EDCs [14,16]. Although estrogen and androgen have occupied most of the debate, glucocorticoid (GCs) have become a major concern due to their detection in the environment [1,21,22]. It is reported that the amount of excretion masses of natural and synthetic GCs is quite a bit higher than estrogen and androgen [23,24]. Considering the usage of GCs to be of both synthetic and natural sources, the existence and fate of these compounds in the environment requires greater consideration.
Natural GCs, such as cortisol, cortisone and other metabolites are linked with the control of energy supply, suppress the responses to inflammation and infection in vertebrates [25]. On the other hand, synthetic GCs (prednisone, prednisolone, dexamethasone, and 6R-methylprednisolone) have been used greatly in human and muscle size in animals [26]. GCs can be classified into five groups on the basis of their structure: hydrocortisone, acetonide, betamethasone, halogenated and prodrug esters [27,28,29]. Therefore, a large volume of GCs (both natural and synthetic) may be released into surface water through the effluent of sewage treatment plants (STPs) or runoff and become a major potential warning for the aquatic environments [30].
Livestock manure carries several organic contaminants; mostly steroids such as GCs, and their fates in the course of composting are still undetermined. For an example, the amount of synthetic glucocorticoid prednisolone detected in feces ranged from (3.0 to 32.0 ng/g), in flush water (88.6 to 1390 ng/L), and suspended particles (8.0 to 42.6 ng/g) respectively [31,32]. On the other hand, detection amount of dexamethasone in the flush water and suspended particles was about 260 ± 27.9 ng/L and 35.0 ± 5.1 ng/g, respectively [33].
The principal use of GCs is for inflammation treatment of asthma, skin issue and joint pain problems [24,34,35,36]. GCs are also being used in significant amounts in many personal care products, like creams and lotions for face and body skin related issues [37,38,39,40,41,42]. Hence, a significant amount of natural and synthetic GCs may be drained into nearby surface water and finally infiltrate into ground water [30]. As a result of inadequate removal from WWTPs, GC activity has been demonstrated in 27% of surface water samples (n = 115) collected in more than 14 states in the US, more than 10 countries in Europe, and many riverine areas of China, Japan, Australia, etc. [40,43,44,45].
GC compounds can severely damage the reproduction of both domestic and wild animals, leading to sexual abnormalities, intersex development, reduced sperm counts, decreased fertility rate, and hormone-dependent cancer in humans [20,22,24,34,40]. There is a growing concern that aquatic organisms are in great danger due to the abundance of GCs in the environment. In this study, we have investigated the pathways for GCs’ introduction into environmental waters and consequences of along with the removal of GCs in conventional wastewater treatment processes. This review included literature published from different scientific databases and publishers including Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, Elsevier, Springer, Scopus, NCBI, and NIH. The search item included: glucocorticoids (GCs), hormone (GCs) removal, micro pollutant removal, removal of GCs from wastewater, steroidal hormones, and removal efficiency of GCs as the search keywords.
2. Properties of Frequently Found Glucocorticoids in Water
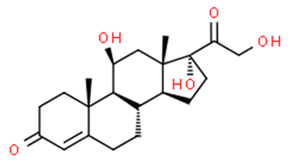
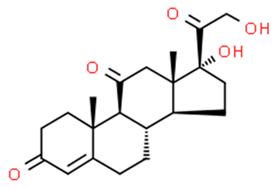
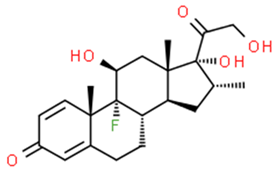
Some natural and synthetic GCs from different sources of waste disrupt the normal activities of the endocrine glands [25,45,46,47,48,49]. Some of these GCs adversely affect the growth and production of fish and plants [4,22,45,49]. GCs are categorized into five structural groups: acetonide, hydrocortisone, betamethasone, halogenated and labile prodrug esters [28,29,30,50]. Natural and synthetic glucocorticoids hormones: betamethasone, betamethasone D5, budesonide, clobetasol, clobetasol propionate, clobetasol propionate, corticosterone, cortisone, cyproterone acetate, desonide, dexamethasone, dexamethasone-21-acetate, DMS, flumetasone, fluorometholone, fluticasone propionate, halometasone, hydrocortisone (cortisol), hydroxycortisol, medroxyprogesterone, megestrol, megestrol acetate, methylprednisolone, 6α- mifepristone, prednisolone, prednisone, prednisone, triamcinolone acetonide, triamcinolone acetonide and many more [51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65]. Among them, six of the most frequently found GCs in water—cortisol, cortisone, dexamethasone, prednisolone, prednisone, and 6α-methylprednisolone—were considered in this review [36].
The human body employs natural GCs as a vital part of the feedback mechanism to reduce inflammation [66,67]. Synthetic glucocorticoids, sometime known as exogenous GCs are used to treat different diseases caused by an overactive immune system [66,67,68,69,70,71]. Common diseases like asthma, allergies, both human and animal autoimmune diseases as well as sepsis are some of the examples of conditions caused by an overactive immune system [21,72,73,74,75,76,77]. In typical wastewater, these compounds are present at a lower concertation (ng/L) which is generally 106 times lower than carbon or nutrients content of wastewater. The degradation of micropollutant can be classified into four categories, e.g., easily degradable, moderately degradable, poorly and very poorly degradable. Removal of these GCs compounds in wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) has been extensively studied and the scientists has considered biological treatment technology as critical to micropollutant removal [78]. Biological wastewater treatments have to consider some factors regarding micropollutant removal, such as solid retention time (SRT) [79,80] pH, hydraulic retention time (HRT) [81], nitrification [82,83] redox conditions [84,85], suspended/attached growth [86], and heterotrophic activity [87]. Although the main driving factor for the permanently biological micropollutant removal at WWTPs is still unknown [88]. The reason behind this issue can be some critical parameters being unknown or the degradation of different micropollutants having different structures in mixed micropollutant groups. Hence, due to competition between the targeted compounds, a conventional WWTP generally cannot remove micropollutants effectively which eventually poses a threat to aquatic beings once they are released into the receiving waterbodies with the treated wastewater effluent [89,90,91].
GCs have a tetra cyclic structure: three cyclohexane rings as well as cyclopentane rings [92,93]. Although natural and synthetic GCS have different cyclic networks, they have some common ring networks all around their physical properties (Table 1) [94]. To predict their occurrence and fate into the natural and engineered scientific environment, physical and chemical characteristics of GCs compounds need to be considered. GCs do not dissolve well in water [89]. Octanol–water partition coefficient (Kow) is a partition coefficient defined as a ratio of dissolving a chemical compound in octanol phase and concentration in water of aqueous phase at a specific temperature mostly under the equilibrium conditions [95,96,97,98,99]. Kow value represents the absorption and dissolution of any compounds [76,77,100]. Although dispersion of GCs between aqueous solution and natural surroundings is always relative in nature, octanol-water partition coefficient is a good choice for solubility characterization [95,96]. From Table 1, the log of Kow for frequently found GCs compounds is in the range of 1.4–3.5 [89,91,94,101]. Although comparing with some of the estrogens (e.g., 17 α-ethinylestradiol (3.67–4.15) [102,103], 17 β-estradiol (3,94–4.01) [102,103], estrone (2.45–3.43) [102,103], estriol (2.55–2.81) [102,103], the Kow values of GCs are moderately low. This range means that, GCs compounds hydrophilicity is moderate, and they tend to be predominantly distributed which means they tend to adsorb onto solid surface in the solid waste environments [95,98]. A considerable number of total GCs released by humans and animals are in the form of conjugated metabolites in their urine [98]. Although the polar conjugates are inactive biologically, their solubility is higher compared to those not conjugated [101].

Table 1.
Properties of six frequently found glucocorticoids (GCs) in water.
3. Glucocorticoids’ Sources and Pathways in Environment
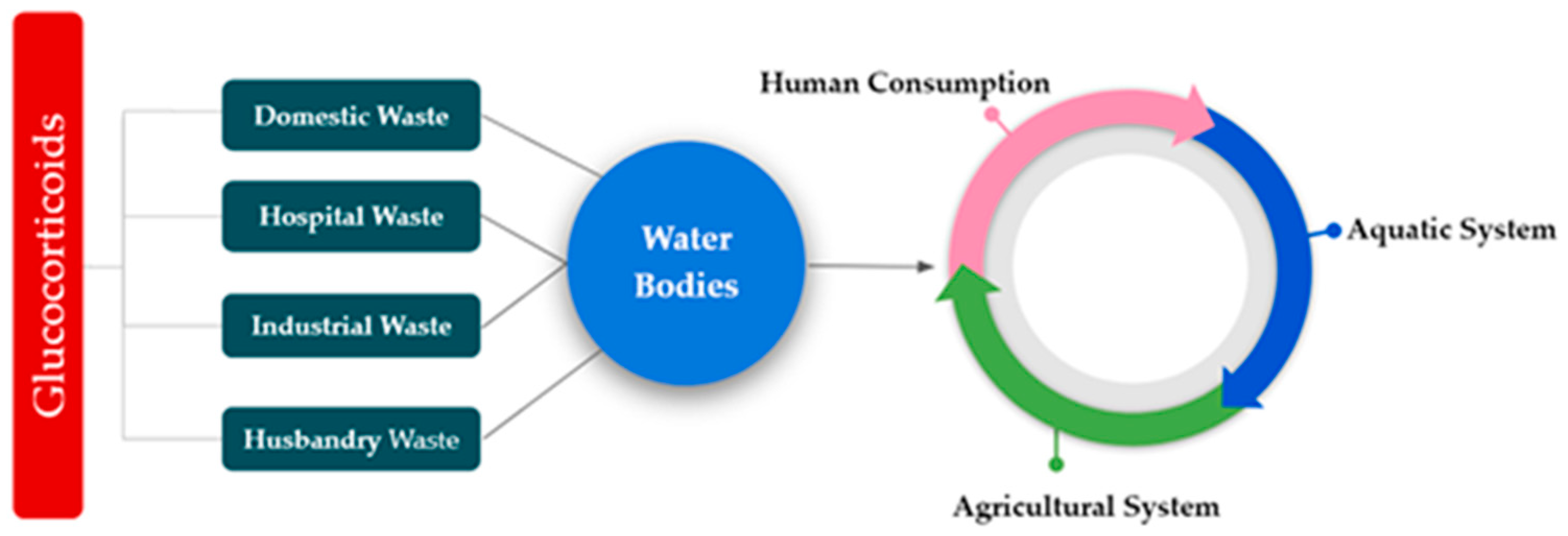
There are two major ways for GCs to get into the environment. It can enter natural environment firstly, through point sources (for an example, WWTPs) and secondly, nonpoint sources (such as agricultural runoff) [104,105,106,107]. Glucocorticoids are generally used in veterinary medicine to recover or reconstruct muscle strength as well as muscle growth and development in animals [95]. As a result, a huge portion of glucocorticoids, excreted mainly by mammals’ urine, is considered to be discharged into the aquatic environment. These compounds are released into the environment through STPs effluent, seasonal wet runoff, and thus contribute as potential pollutants in the environment [96]. A mixture of GCs has been detected in drinking water which were then tracked back to the source river water used as the influent for the drinking water treatment process [106]. Presence of GCs was detected in both the influent and effluent (ending in the water supply systems and tap water) of the drinking water processes in those cases [107]. Table 2 shows all the targeted GCs found in wastewater in different countries which eventually end up in natural waterbodies due to lack of effective treatment of GCs in wastewater. As stated above, not only human, but also animal, wastes are the primary sources of GCs in aquatic environments. Both treated solid and liquid wastes are recognized as potential pathways for these compounds to make their way into the environment [108,109,110,111,112]. Figure 1 shows the contamination of the different parts of the environment due to the GCs.

Table 2.
Environmental and health impact of glucocorticoids.
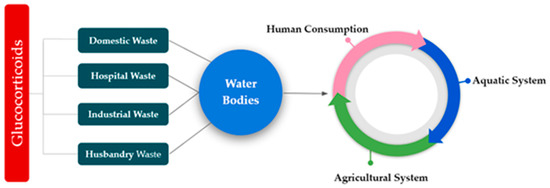
Figure 1.
Fate of glucocorticoids (GCs) in different sectors of the environment.
4. Adverse Effects of Glucocorticoids’ in Natural Environment
The adverse effects GCs’ due to the discharge of effluents from WWTPs to the aquatic environments are affected by several factors including effluent volume, the concentration of the targeted compounds in wastewater, the water flow rate of the receiving river, meteorological or climate conditions, and probably some other factors that affect dissipation through dilution and/or degradation. Table 2 summarizes all the findings collected from the respective articles. Some of the studies reported detection of GCs in environmental samples and showed adverse effects on fishes even at a lower concentration (in the range of ng/L) [116,118,119,120,126].
Exposure to cortisol (concentration range of 100–145 ng/L) and clobetasol propionate (concentration range of 60–91 ng/L) could damage the immune system of zebrafish severely [119,120]. Increased heart rate, contractions of muscle degradation, acceleration of hatching, and changes in generic expressions are some of the major incidents reported due to cortisol and clobetasol propionate exposure [116]. As genes encode proteins, so do proteins control cell function [127]. In consequence, the thousands of genes asserted in a singular cell determine the exact activity or capability of that cell [128]. A glucocorticoid receptor works as a hormone-dependent major component that controls the expression of glucocorticoid-responsive genes [129,130,131]. Prednisolone exposure up to 100 ng/L concentration can lead to shifts in the morphology, swimming nature and physiology of zebrafish [126]. Dexamethasone exposure might negatively affect the reproductivity, muscle growth and cause deviation in mRNA expression of amphibians and fish [118,121,126].
A recently published study showed that the individual exposure of zebrafish to cortisone at a concentration of 0.7–1 µg/L, 6α-methylprednisolone at a concentration of 0.5–1 µg/L and clobetasol propionate at about 60–91 ng/L resulted in transcriptional and physiological effects [132]. All the six GCs showed adverse effects including increased heart rate and, in some extent, fold changes in the transcripts of genes. Prednisolone metabolite was reported to show some activities of mineralocorticoid and influences sedative, anticonvulsant and anxiolytic effects in fishes [133,134]. Rainbow darter (Etheostoma caeruleum) was also reported to be impacted by GCs near in Grand River Canada [132]. Presence of GCs in the water changed the diversity as well as the structure of the gut content microbiome of the rainbow fish [132,135].
On the other hand, halogen atoms (Cl, F) presence in some GCs can make their activity very strong in contrast to their natural counterparts and make them more recalcitrant in WWTPs and other water treatment plants [136,137,138,139,140]. Some studies mentioned low sperm count in men, sexual health deterioration, and breast cancer in women due to the exposure to GCs [36,141,142,143,144]. Additionally, some natural and synthetic GCs that were not emphasized in this study could also affect aquatic environments negatively [144]. Fundamental understanding of environmental and health impacts of GCs on humans and animals are challenging as the process involves long-term studies investigating side effects long-term after the exposure, and variable age and time of exposure. [113,145,146].
5. Glucocorticoids Compounds Removal Methods Efficiency
Despite the fact that the existing wastewater treatment plants are designed for the removal of nutrients, partial removal of GCs has been detected in different cases [124]. Nonetheless, large differences in the efficiency of GC removal have been varied. The removal efficiency varies between 10 to 98% in different countries based on location and concentrations [147]. Different removing technologies accentuate on the relevance of geographical location parameters [148]. For the last two decades, advancement in technical analysis has empowered scientists to rethink about the occurrence and fate of natural and synthetic GCs in wastewater treatment plants even in ng/L level [108,147]. Removal efficiency of treatment plants regarding the six major GCs are listed in Table 3. The conventional treatment plants have three major facilities, namely as preliminary, primary, and secondary. Tertiary treatment is needed while discharging the effluent to the ground water or surface waters. Possible removal methods of GCs from treatment units include volatilization, photocatalysis, biological degradation, nanotechnology, chlorination, adsorption, Fe (VI) treatment as a tertiary treatment technology [117,149,150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157]. Table 3 shows the effect of each reported method in various studies.

Table 3.
Engineering processes and their efficiency for Glucocorticoid’s removal.
6. Conclusions
Water quality issues have garnered a significant attention worldwide. Over the years, the challenge is to conserve aquatic ecosystems, to secure quality of aquatic lives and to minimize negative impacts on human health. Conventional WWTPs generally cannot remove GCs effectively, affecting the receiving environment and human health negatively eventually. Therefore, potentially unsafe GCs may enter the surface waters and sometime in ground water. As a result, a majority number of GCs compounds remain a problem within the existing legal norms. Among all the treatment processes, absorption with activated carbon, other absorbents or nanoparticles, oxidation methods relative to other technologies show greater efficiency in GCs removal. Although filtration alone cannot effectively remove GCs, combination of filtration with other technologies can remove GCs efficiently [151,152,153,154]. Across many countries, wastewater effluent is considered as one of the major sources of GCs in aquatic environments. However, surface runoff, as well as livestock sewage, are also significant sources of these compounds. Removal technologies and their efficiency varies according to the wastewater composition and treatment infrastructures. This leads to differences in degree of accuracy in implementation of removal technologies for GCs removal. Consequently, there is an inconsistency in inspecting GC’s fate and occurrences in different types and stages of wastewater treatment processes, especially quantification of very low concentrations of GCs in stabilized sludge. There are some operational factors such as temperature, pH, solubility, and many other engineering parameters that are still not analyzed well for GCs characterization and removal purposes. Based on the investigations of the secondary data in this study, it can be concluded that more scientific case-study-based research should be conducted to determine GCs compounds fate and transport in water resources, their selection and detection techniques, along with the best management practices and the most economically feasible removal technologies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.S.Y. and M.T.A.; methodology, M.M.S.Y.; software, M.M.S.Y. and M.T.A.; validation, M.M.S.Y.; S.P.M. and M.T.A.; formal analysis, M.M.S.Y. and M.T.A.; investigation, M.M.S.Y. and M.T.A.; resources, M.M.S.Y.; S.P.M.; Z.M.; I.J. and M.T.A.; data curation, M.M.S.Y. and M.T.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.S.Y.; S.P.M.; Z.M.; I.J. and M.T.A.; writing—review and editing, M.M.S.Y.; S.P.M.; Z.M.; I.J. and M.T.A.; visualization, M.M.S.Y.; S.P.M.; Z.M.; I.J. and M.T.A.; supervision, M.M.; project administration, M.M.S.Y.; M.T.A.; funding acquisition, M.M.S.Y.; S.P.M.; Z.M.; I.J. and M.T.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sossalla, N.A.; Nivala, J.; Escher, B.I.; Reemtsma, T.; Schlichting, R.; van Afferden, M.; Müller, R.A. Resilience of Micropollutant and Biological Effect Removal in an Aerated Horizontal Flow Treatment Wetland. Water 2020, 12, 3050. [Google Scholar]
- Aborkhees, G.; Raina-Fulton, R.; Thirunavokkarasu, O. Determination of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Water and Wastewater Samples by Liquid Chromatography-Negative Ion Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2020, 25, 3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Shen, X.; Zhang, A.; Yan, S.; Li, X.; Miruka, A.C.; Wu, S.; Guo, Y.; Ognier, S. Degradation of glucocorticoids in aqueous solution by dielectric barrier discharge: Kinetics, mechanisms, and degradation pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.M.; Wahba, M.; Yu, L.; Achari, G.; Habibi, H.R. Health Impact Assessment of Sulfolane on Embryonic Development of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxics 2019, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA, U. Endocrine Disruptor Screening Program Weight-of-Evidence: Evaluating Results of EDSP Tier 1 Screening to Identify the Need for Tier 2 Testing; Office of Chemical Safety and Pollution Prevention: Washington, WA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, A.-M.; Skakkebaek, N.E. Exposure to exogenous estrogens in food: Possible impact on human development and health. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 140, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotan, M.; Frizzell, C.; Robinson, V.; Elliott, C.T.; Connolly, L. Endocrine disruptor activity in bottled mineral and flavoured water. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotons, J.A.; Olea-Serrano, M.F.; Villalobos, M.; Pedraza, V.; Olea, N. Xenoestrogens Released from Lacquer Coatings in Food Cans. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 608–612. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, J.S. Environmental anti-androgens and male reproductive health: Focus on phthalates and testicular dysgenesis syndrome. Reproduction 2004, 127, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguignon, J.-P.; Parent, A.-S. Early homeostatic disturbances of human growth and maturation by endocrine disrupters. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2010, 22, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zama, A.M.; Uzumcu, M. Epigenetic effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on female reproduction: An ovarian perspective. Front. Neuroendocr. 2010, 31, 420–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hryniewicka, M.; Starczewska, B.; Gołębiewska, A. Determination of Budesonide and Sulfasalazine in Water and Wastewater Samples Using DLLME-SFO-HPLC-UV Method. Water 2019, 11, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allijn, I.E.; Oldenkamp, R.; Storm, G.; Ragas, A.M.J.; Schiffelers, R.M. Environmental impact of switching from the synthetic glucocorticoid prednisolone to the natural alkaloid berberine. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, A.K.; Halden, R.U. Effective Strategies for Monitoring and Regulating Chemical Mixtures and Contaminants Sharing Pathways of Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 10549–10557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paragliola, R.M.; Papi, G.; Pontecorvi, A.; Corsello, S.M. Treatment with Synthetic Glucocorticoids and the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, A.; Nebot, C.; Vázquez, B.I.; Coronel-Olivares, C.; Abuín, C.M.F.; Cepeda, A. Monitoring the Presence of 13 Active Compounds in Surface Water Collected from Rural Areas in Northwestern Spain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 5251–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdan, M.M.S.; Ahad, T.; Jahan, I.; Mazumder, M. Review on the Evaluation of the Impacts of Wastewater Disposal in Hydraulic Fracturing Industry in the United States. Technologies 2020, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdan, M.M.S.; Rahaman, A.Z.; Noor, F.; Duti, B.M. Establishment of Co-Relation between Remote Sensing Based Trmm Data and Ground Based Precipitation Data in North-East Region of Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD-2014), KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh, 17–19 April 2014; pp. 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte, S.; Habauzit, D.; Charlier, T.D.; Pakdel, F. Emerging Estrogenic Pollutants in the Aquatic Environment and Breast Cancer. Genes 2017, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasona, N.A.; AlRashidi, A.A.; Aldugieman, T.Z.; Alshdokhi, A.M.; Ahmed, M.Q. Vitis vinifera Extract Ameliorate Hepatic and Renal Dysfunction Induced by Dexamethasone in Albino Rats. Toxics 2017, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øverli, Ø.; Kotziana, S.; Winberg, S. Effects of Cortisol on Aggression and Locomotor Activity in Rainbow Trout. Horm. Behav. 2002, 42, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.J.; Hällman, H.; Förlin, L. More Male Fish Embryos near a Pulp Mill. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2000, 19, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Ying, G.-G.; Zhao, J.-L.; Zhou, L.-J.; Yang, B.; Chen, Z.-F.; Lai, H.-J. Occurrence and fate of androgens, estrogens, glucocorticoids and progestagens in two different types of municipal wastewater treatment plants. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runnalls, T.J.; Margiotta-Casaluci, L.; Kugathas, S.; Sumpter, J.P. Pharmaceuticals in the Aquatic Environment: Steroids and Anti-Steroids as High Priorities for Research. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2010, 16, 1318–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, A.E.; Chapman, K.E. The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 335, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huetos, O.; Ramos, M.; De Pozuelo, M.M.; Reuvers, T.B.A.; Andrés, M.S. Determination of dexamethasone in feed by TLC and HPLC. Analyst 1999, 124, 1583–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morren, M.A.; Dooms-Goossens, A. Contact allergy to corticosteroids. Diagnosis and management. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 1996, 14, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.E.; Steele, T. Corticosteroid classes: A quick reference guide including patch test substances and cross-reactivity. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 54, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.J.; Canto, G. Hypersensitivity reactions to corticosteroids. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 10, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Zhou, G.-J.; Liu, S.-S.; Yue, W.-Z.; Yu, S.; Sun, K.-F.; Cheng, H.; Ying, G.-G.; Xu, X.-R. Occurrence, source analysis and risk assessment of androgens, glucocorticoids and progestagens in the Hailing Bay region, South China Sea. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 536, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, S.; Dahan, O.; Elhanany, S.; Cohen, K.; Pankratov, I.; Gross, A.; Ronen, Z.; Baram, S.; Shore, L.S. Transport of Testosterone and Estrogen from Dairy-Farm Waste Lagoons to Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5521–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarth, J.; Akre, C. Presence and Metabolism of Endogenous Steroid Hormones in Meat-producing Animals; Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC): London, UK, 2009; pp. 48–96. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Ying, G.-G.; Zhou, L.-J.; Zhang, R.-Q.; Chen, Z.-F.; Lai, H.-J. Steroids in a typical swine farm and their release into the environment. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3754–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziej, E.; Gray, J.L.; Sedlak, D.L. Quantification of Steroid Hormones with Pheromonal Properties in Municipal Wastewater Effluent. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 2622–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, E.F.; Kolok, A.S.; Binzcik, G.A.; Gates, J.L.; Horton, M.K.; Lambright, C.S.; Gray, L.E., Jr.; Soto, A.M.; Guillette, L.J., Jr. Endocrine-Disrupting Effects of Cattle Feedlot Effluent on an Aquatic Sentinel Species, the Fathead Minnow. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 353–358. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.; Hu, J.; Shao, B. Occurrence of Natural and Synthetic Glucocorticoids in Sewage Treatment Plants and Receiving River Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3462–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piram, A.; Salvador, A.; Gauvrit, J.-Y.; Lantéri, P.; Faure, R. Development and optimisation of a single extraction procedure for the LC/MS/MS analysis of two pharmaceutical classes residues in sewage treatment plant. Talanta 2008, 74, 1463–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Wan, Y.; Hu, J. Determination and Source Apportionment of Five Classes of Steroid Hormones in Urban Rivers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7691–7698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wu, S.; Chang, H.; Hu, J. Behaviors of Glucocorticoids, Androgens and Progestogens in a Municipal Sewage Treatment Plant: Comparison to Estrogens. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2725–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammann, A.A.; Macikova, P.; Groh, K.J.; Schirmer, K.; Suter, M.J. LC-MS/MS Determination of Potential Endocrine Disruptors of Cortico Signalling in Rivers and Wastewaters. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7653–7665. [Google Scholar]
- Isobe, T.; Sato, K.; Joon-Woo, K.; Tanabe, S.; Suzuki, G.; Nakayama, K. Determination of natural and synthetic glucocorticoids in effluent of sewage treatment plants using ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14127–14135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weizel, A.; Schluesener, M.P.; Dierkes, G.; Ternes, T.A. Occurrence of Glucocorticoids, Mineralocorticoids, and Progestogens in Various Treated Wastewater, Rivers, and Streams. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5296–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavreva, D.A.; George, A.; Klausmeyer, P.; Varticovski, L.; Sack, D.A.; Voss, T.C.; Schiltz, R.L.; Blazer, V.S.; Iwanowicz, L.R.; Hager, G.L. Prevalent Glucocorticoid and Androgen Activity in US Water Sources. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tölgyesi, Á.; Verebey, Z.; Sharma, V.; Kovacsics, L.; Fekete, J. Simultaneous determination of corticosteroids, androgens, and progesterone in river water by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macikova, P.; Groh, K.; Ammann, A.A.; Schirmer, K.; Suter, M.J.-F. Endocrine Disrupting Compounds Affecting Corticosteroid Signaling Pathways in Czech and Swiss Waters: Potential Impact on Fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12902–12911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Rieder, M.J.; Tucker, M.J. Mechanisms of Glucocorticoid-Mediated Anti-Inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Action. Paed Perinat. Drug Ther. 2004, 6, 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, R.; Leigh, R.; Giembycz, M.A. Pharmacological strategies for improving the efficacy and therapeutic ratio of glucocorticoids in inflammatory lung diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 125, 286–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxtall, J.D.; Van Hal, P.T.W.; Choudhury, Q.; Gilroy, D.W.; Flower, R.J. Different glucocorticoids vary in their genomic and non-genomic mechanism of action in A549 cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoak, K.A.; Cidlowski, J.A. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid receptor signaling during inflammation. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2004, 125, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coopman, S.; Degreef, H.; Dooms-Goossens, A. Identification of cross-reaction patterns in allergic contact dermatitis from topical corticosteroids. Br. J. Dermatol. 1989, 121, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galon, J.; Franchimont, D.; Hiroi, N.; Frey, G.; Boettner, A.; Ehrhart-Bornstein, M.; O’Shea, J.J.; Chrousos, G.P.; Bornstein, S.R. Gene profiling reveals unknown enhancing and suppressive actions of glucocorticoids on immune cells. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.L.; Auchus, R.J. The Molecular Biology, Biochemistry, and Physiology of Human Steroidogenesis and Its Disorders. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 81–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaber, G.; Jondal, M.; Okret, S. Extra-adrenal glucocorticoid synthesis: Immune regulation and aspects on local organ homeostasis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 380, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornstein, S.; Ziegler, C.; Krug, A.; Kanczkowski, W.; Rettori, V.; McCann, S.; Wirth, M.; Zacharowski, K. The Role of Toll-like Receptors in the Immune-Adrenal Crosstalk. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1088, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, S.; Benedict, C.; Heutling, D.; Westermann, J.; Born, J.; Lange, T. Cortisol and epinephrine control opposing circadian rhythms in T cell subsets. Blood 2009, 113, 5134–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemberton, P.A.; Stein, P.E.; Pepys, M.B.; Potter, J.M.; Carrell, R.W. Hormone binding globulins undergo serpin conformational change in inflammation. Nat. Cell Biol. 1988, 336, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, M.J.; De Boer, J.; Heidorn, S.; Hubank, M.; Kioussis, D.; Williams, O.; Brady, H.J.M. Tnfaip8 is an essential gene for the regulation of glucocorticoid-mediated apoptosis of thymocytes. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 17, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, G. History of Cortisone and Related Compounds. In eLS; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Thompson, E.B. Gene regulation by the glucocorticoid receptor: Structure:function relationship. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 94, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, R.H.; Cidlowski, J. Cellular Processing of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene and Protein: New Mechanisms for Generating Tissue-specific Actions of Glucocorticoids. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 3177–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevyver, S.; Dejager, L.; Libert, C. On the Trail of the Glucocorticoid Receptor: Into the Nucleus and Back. Traffic 2011, 13, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisi, B.F.; Xu, W.X.; Otwinowski, Z.; Freedman, L.P.; Yamamoto, K.R.; Sigler, P.B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nat. Cell Biol. 1991, 352, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratman, D.; Berghe, W.V.; Dejager, L.; Libert, C.; Tavernier, J.; Beck, I.; De Bosscher, K. How glucocorticoid receptors modulate the activity of other transcription factors: A scope beyond tethering. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 380, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddie, S.; John, S.; Sabo, P.J.; Thurman, R.E.; Johnson, T.A.; Schiltz, R.L.; Miranda, T.B.; Sung, M.-H.; Trump, S.; Lightman, S.; et al. Transcription Factor AP1 Potentiates Chromatin Accessibility and Glucocorticoid Receptor Binding. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuckermann, J.P.; Reichardt, H.M.; Arribas, R.; Richter, K.H.; Schütz, G.; Angel, P. The DNA Binding-Independent Function of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Mediates Repression of Ap-1–Dependent Genes in Skin. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 147, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfroid, A.; Van der Horst, A.; Vethaak, A.; Schäfer, A.; Rijs, G.; Wegener, J.; Cofino, W. Analysis and occurrence of estrogenic hormones and their glucuronides in surface water and waste water in The Netherlands. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 225, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpin, D.W.; Furlong, E.; Meyer, M.T.; Thurman, E.M.; Zaugg, S.D.; Barber, L.B.; Buxton, H.T. Pharmaceuticals, Hormones, and Other Organic Wastewater Contaminants in U.S. Streams, 1999−2000: A National Reconnaissance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, G.-G.; Kookana, R.; Ru, Y.-J. Occurrence and fate of hormone steroids in the environment. Environ. Int. 2002, 28, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.V.; Hurst, M.R.; Matthiessen, P.; McHugh, M.; Smith, A.; Waldock, M.J. An Assessment of in Vitro Androgenic Activity and the Identification of Environmental Androgens in United Kingdom Estuaries. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2002, 21, 1456–1461. [Google Scholar]
- Peck, M.; Gibson, R.W.; Kortenkamp, A.; Hill, E.M. Sediments Are Major Sinks of Steroidal Estrogens in Two United Kingdom Rivers. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xiao, B.; Huang, W.; Peng, P. Sorption of Steroid Estrogens to Soils and Sediments. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labadie, P.; Budzinski, H. Determination of Steroidal Hormone Profiles along the Jalle d’Eysines River (near Bordeaux, France). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5113–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S.; Sapolsky, R.M. Stress and cognitive function. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1995, 5, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holsboer, F.; Barden, N. Antidepressants and Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenocortical Regulation. Endocr. Rev. 1996, 17, 187–205. [Google Scholar]
- Halpenny, C.M.; Kocan, R.M.; Winton, J.R.; Perry, J.A.; Hershberger, P.K. Elevated Temperature Exacerbates Ichthyophonus Infections in Buffalo Sculpin. Fish Health Newsl. 2002, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour, K.M.; Dibattista, J.D.; Thomas, J.B. Physiological Causes and Consequences of Social Status in Salmonid Fish. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2005, 45, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frerichs, V.A.; Tornatore, K.M. Determination of the glucocorticoids prednisone, prednisolone, dexamethasone, and cortisol in human serum using liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 802, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorita, S.; Mårtensson, L.; Mathiasson, L. Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals in a municipal sewage treatment system in the south of Sweden. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2760–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, B.; McAdam, E.; Lester, J.N.; Cartmell, E. Assessing potential modifications to the activated sludge process to improve simultaneous removal of a diverse range of micropollutants. Water Res. 2014, 62, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeng, S.K.; Choi, B.G.; Lee, K.T.; Song, K.G. Influences of solid retention time, nitrification and microbial activity on the attenuation of pharmaceuticals and estrogens in membrane bioreactors. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3151–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulde, R.; Helbling, D.E.; Scheidegger, A.; Fenner, K. PH-Dependent Biotransformation of Ionizable Organic Micropollutants in Activated Sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13760–13768. [Google Scholar]
- Sathyamoorthy, S.; Chandran, K.; Ramsburg, A. Biodegradation and Cometabolic Modeling of Selected Beta Blockers during Ammonia Oxidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12835–12843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbling, D.E.; Johnson, D.R.; Honti, M.; Fenner, K. Micropollutant Biotransformation Kinetics Associate with WWTP Process Parameters and Microbial Community Characteristics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10579–10588. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.; Wu, C.; Xiao, K.; Huang, X.; Zhou, H.; Tsuno, H.; Tanaka, H. Elimination and fate of selected micro-organic pollutants in a full-scale anaerobic/anoxic/aerobic process combined with membrane bioreactor for municipal wastewater reclamation. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5999–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, S.; Lema, J.M.; Omil, F. Removal of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) under nitrifying and denitrifying conditions. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3214–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupanc, M.; Kosjek, T.; Petkovšek, M.; Dular, M.; Kompare, B.; Širok, B.; Blažeka, Ž.; Heath, E. Removal of pharmaceuticals from wastewater by biological processes, hydrodynamic cavitation and UV treatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewsky, M.; Gallé, T.; Zwank, L.; Fischer, K. Influence of microbial activity on polar xenobiotic degradation in activated sludge systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Falås, P.; Wick, A.; Castronovo, S.; Habermacher, J.; Ternes, T.A.; Joss, A. Tracing the limits of organic micropollutant removal in biological wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2016, 95, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, L.K.; Gray, S.; Oberdörster, E. Vitellogenin induction in painted turtle, Chrysemys picta, as a biomarker of exposure to environmental levels of estradiol. Aquat. Toxicol. 2001, 55, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrási, N.; Molnár, B.; Dobos, B.; Vasanits-Zsigrai, A.; Záray, G.; Molnár-Perl, I. Determination of steroids in the dissolved and in the suspended phases of wastewater and Danube River samples by gas chromatography, tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2013, 115, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufartová, J.; Mahugo-Santana, C.; Sosa-Ferrera, Z.; Santana-Rodríguez, J.J.; Nováková, L.; Solich, P. Determination of steroid hormones in biological and environmental samples using green microextraction techniques: An overview. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 704, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, S.; Arias, J.; Rombaldi, C.; Mello, L.; Cerqueira, M.B.R.; Martins, A.; Primel, E. Occurrence of Pesticides and PPCPs in Surface and Drinking Water in Southern Brazil: Data on 4-Year Monitoring. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2018, 30, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, W.T.; de Farias, M.B.; Spaolonzi, M.P.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Endocrine-disrupting compounds: Occurrence, detection methods, effects and promising treatment pathways—A critical review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassotis, C.; Vandenberg, L.N.; Demeneix, B.A.; Porta, M.; Slama, R.; Trasande, L. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Economic, regulatory, and policy implications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ru, J.; Qu, J.; Dai, R.; Wang, Z.; Hu, C. Removal of persistent organic pollutants from micro-polluted drinking water by triolein embedded absorbent. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2995–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Lepp, T.L.; Stevens, R. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in biosolids/sewage sludge: The interface between analytical chemistry and regulation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 387, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Lin, Y. Solvent Effects on the Silylation-Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometric Determination of Natural and Synthetic Estrogenic Steroid Hormones, Comment on Formation of Chlorinated Estrones via Hypochlorous Disinfection of Wastewater Effluent Containing Estrone by Hideyuki Nakamura, Ryoko Kuruto-Niwa, Mitsuo Uchida and Yoshiyasu Terao [Chemosphere 66 (2007) 1441–1448]. Chemosphere 2007, 7, 1175–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Carballa, M.; Omil, F.; Lema, J. Comparison of predicted and measured concentrations of selected pharmaceuticals, fragrances and hormones in Spanish sewage. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballa, M.; Omil, F.; Lema, J.M.; Llompart, M.; García-Jares, C.; Rodríguez, I.; Gomez, M.; Ternes, T. Behavior of Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics and Hormones in a Sewage Treatment Plant. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2918–2926. [Google Scholar]
- Nagarnaik, P.; Mills, M.; Boulanger, B. Concentrations and mass loadings of hormones, alkylphenols, and alkylphenol ethoxylates in healthcare facility wastewaters. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Navas, C.; Björklund, E.; Halling-Sørensen, B.; Hansen, M. Biogas final digestive byproduct applied to croplands as fertilizer contains high levels of steroid hormones. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 180, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayles, G.; Marsh, T. Biological Fate of Estrogenic Compounds Associated with Sewage Treatment: A Review. In Proceedings of the Effective Risk Management of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals Workshop, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 18–19 September 2001; pp. 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, K.M.; Johnson, K.L.; Scrimshaw, M.D.; Lester, J.N. Binding of Waterborne Steroid Estrogens to Solid Phases in River and Estuarine Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3890–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, J.N.; Edge, D.R. Sewage and sewage sludge treatment. Pollution 2007, 113–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrup, M.; Jensen, R.L.; Schäfer, A.I.; Khan, S. Fate Modeling-an Important Tool for Water Recycling. In Recent Advances in Water Recycling Technologies; Schäfer, A.I., Sherman, P., Waite, T.D., Eds.; Libraries Australia: Brisbane, Australia, 2001; pp. 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Senn, D.; Moran, R.E.; Shine, J.P. Prioritizing environmental risk of prescription pharmaceuticals. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.-Q.; Zhou, Z.; Sharma, V.K. Occurrence, Transportation, Monitoring and Treatment of Emerging Micro-Pollutants in Waste Water—A Review from Global Views. Microchem. J. 2013, 110, 292–300. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratola, N.; Cincinelli, A.; Alves, A.; Katsoyiannis, A. Occurrence of organic microcontaminants in the wastewater treatment process. A mini review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 239–240, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnaga, G. Integrated assessment of pollution in the Baltic Sea. Ekologija 2013, 58, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Tiritan, M.E.; De Voogt, P. Priority Substances and Emerging Organic Pollutants in Portuguese Aquatic Environment: A Review. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 238, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, J.M.; Evans, N.; Cardon, M.C.; Rosenblum, L.; Iwanowicz, L.R.; Hartig, P.C.; Schenck, K.M.; Bradley, P.M.; Wilson, V.S. Occurrence and In Vitro Bioactivity of Estrogen, Androgen, and Glucocorticoid Compounds in a Nationwide Screen of United States Stream Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4781–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ascenzo, G.; Di Corcia, A.; Gentili, A.; Mancini, R.; Mastropasqua, R.; Nazzari, M.; Samperi, R. Fate of natural estrogen conjugates in municipal sewage transport and treatment facilities. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 302, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, P.L.; Nebot, C.; Sloman, K.A. Physiological and Behavioral Effects of Exposure to Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Prednisolone During Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryogenesis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5294–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grdulska, A.; Kowalik, R. Pharmaceuticals in Water and Wastewater-Overview (Farmaceutyki w Wodach i Ściekach). Struct. Environ. 2020, 12, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Lalone, C.A.; Villeneuve, D.L.; Olmstead, A.W.; Medlock, E.K.; Kahl, M.D.; Jensen, K.M.; Durhan, E.J.; Makynen, E.A.; Blanksma, C.A.; Cavallin, J.E.; et al. Effects of a glucocorticoid receptor agonist, dexamethasone, on fathead minnow reproduction, growth, and development. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, B.; Nikolaus, A.; Hedman, C.; Klaper, R.; Grundl, T. Evaluating the degradation, sorption, and negative mass balances of pharmaceuticals and personal care products during wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willi, R.A.; Salgueiro-González, N.; Carcaiso, G.; Fent, K. Glucocorticoid mixtures of fluticasone propionate, triamcinolone acetonide and clobetasol propionate induce additive effects in zebrafish embryos. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 374, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokate, T.G.; Svensson, B.E.; Rogawski, M.A. Anticonvulsant activity of neurosteroids: Correlation with gamma-aminobutyric acid-evoked chloride current potentiation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994, 270, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, D.S.; Rogawski, M.A. Stress-Induced Deoxycorticosterone-Derived Neurosteroids Modulate GABAA Receptor Function and Seizure Susceptibility. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 3795–3805. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, D.S. Pharmacology of Endogenous Neuroactive Steroids. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 2004, 15, 197–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambirajah, A.A.; Koide, E.M.; Imbery, J.J.; Helbing, C.C. Contaminant and Environmental Influences on Thyroid Hormone Action in Amphibian Metamorphosis. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 276. [Google Scholar]
- Guedes-Alonso, R.; Montesdeoca-Esponda, S.; Herrera-Melián, J.A.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, R.; Ojeda-González, Z.; Landívar-Andrade, V.; Sosa-Ferrera, Z.; Santana-Rodríguez, J.J. Pharmaceutical and personal care product residues in a macrophyte pond-constructed wetland treating wastewater from a university campus: Presence, removal and ecological risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, N.; Jonker, W.; Ten Broek, R.; de Boer, J.; Somsen, G.; Kool, J.; Hamers, T.; Houtman, C.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Identification of Mutagenic and Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Surface Water and Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents Using High-Resolution Effect-Directed Analysis. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115204. [Google Scholar]
- Willi, R.A.; Faltermann, S.; Hettich, T.; Fent, K. Active Glucocorticoids Have a Range of Important Adverse Developmental and Physiological Effects on Developing Zebrafish Embryos. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margiotta-Casaluci, L.; Owen, S.F.; Huerta, B.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Kugathas, S.; Barceló, D.; Rand-Weaver, M.; Sumpter, J.P. Internal Exposure Dynamics Drive the Adverse Outcome Pathways of Synthetic Glucocorticoids in Fish. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wiley, J.W.; Higgins, G.; Athey, B.D. Stress and glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional programming in time and space: Implications for the brain-gut axis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, M.Y.; Choi, C.S.; Sohn, Y.W.; Park, B.R.; Choi, M.-G.; Nah, Y.-H.; Choi, S.C. The effect of chronic variable stress on bowel habit and adrenal function in rats. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, K.; Shih, W.; Videlock, E.J.; Presson, A.P.; Naliboff, B.D.; Mayer, E.A.; Chang, L. Association Between Early Adverse Life Events and Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 385–390.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larauche, M.; Mulak, A.; Taché, Y. Stress and visceral pain: From animal models to clinical therapies. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 233, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larauche, M.; Mulak, A.; Taché, Y. Stress-Related Alterations of Visceral Sensation: Animal Models for Irritable Bowel Syndrome Study. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 17, 213–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restivo, V.; Kidd, K.A.; Surette, M.G.; Servos, M.R.; Wilson, J.Y. Rainbow darter (Etheostoma caeruleum) from a river impacted by municipal wastewater effluents have altered gut content microbiomes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umland, S.P.; Schleimer, R.P.; Johnston, S. Review of the Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Action of Glucocorticoids for Use in Asthma. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 15, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, A.; Kitaichi, Y.; Uchikura, K. Degradation of Corticosteroids during Activated Sludge Processing. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 62, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, A.; Wu, S.; Daniels, K.; Snyder, S.A. Balancing the Budget: Accounting for Glucocorticoid Bioactivity and Fate during Water Treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2870–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-J.; Kim, J.D.; Lee, W.-Y.; Chung, B.C.; Choi, M.H. Quantitative metabolic profiling of 21 endogenous corticosteroids in urine by liquid chromatography–triple quadrupole-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 632, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leet, J.K.; Sassman, S.; Amberg, J.J.; Olmstead, A.W.; Lee, L.S.; Ankley, G.T.; Sepúlveda, M.S. Environmental hormones and their impacts on sex differentiation in fathead minnows. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 158, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, M.S.; Dubé, M.G.; Schryer, R. Investigating the link between pulp mill effluent and endocrine disruption: Attempts to explain the presence of intersex fish in the Wabigoon River, Ontario, Canada. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 952–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, N.R. Clover phytoestrogens in sheep in Western Australia. Pure Appl. Chem. 1998, 70, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Panter, G.; Thompson, R.; Sumpter, J. Adverse reproductive effects in male fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas) exposed to environmentally relevant concentrations of the natural oestrogens, oestradiol and oestrone. Aquat. Toxicol. 1998, 42, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alda, M.J.L.; Cruz, S.D.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Liquid chromatography–(tandem) mass spectrometry of selected emerging pollutants (steroid sex hormones, drugs and alkylphenolic surfactants) in the aquatic environment. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1000, 503–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemical Pollution: Why the EPA Should Regulate These Chemicals under the Clean Water Act. Sustain. Dev. L. Pol’y 2009, 10, 19. [Google Scholar]
- López-Fernández, R.; Martínez, L.; Villaverde, S. Membrane bioreactor for the treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater containing corticosteroids. Desalination 2012, 300, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Meng, S.; Dong, Y.; Hu, J.; Gao, W. Capturing hormones and bisphenol A from water via sustained hydrogen bond driven sorption in polyamide microfiltration membranes. Water Res. 2013, 47, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnarowicz, P.; Yang, W.; Zhou, H.; Parker, W.J.; Helbing, C.C. Changes in hormone and stress-inducing activities of municipal wastewater in a conventional activated sludge wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2014, 66, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baronti, C.; Curini, R.; D’Ascenzo, G.; Di Corcia, A.; Gentili, A.; Samperi, R. Monitoring Natural and Synthetic Estrogens at Activated Sludge Sewage Treatment Plants and in a Receiving River Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 5059–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, A.; Ballesteros, E. Combined microwave-assisted extraction and continuous solid-phase extraction prior to gas chromatography–mass spectrometry determination of pharmaceuticals, personal care products and hormones in soils, sediments and sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 419, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaneian, M.T.; Peirovi, R.; Ebrahimi, A.A. A Review on the Importance of Hormones Monitoring and Their Removal in Conventional Wastewater Treatment Systems. J. Environ. Health Sustain. Dev. 2017, 2, 310–318. [Google Scholar]
- Nuzzo, J.B. The Biological Threat to U.S. Water Supplies: Toward a National Water Security Policy. Biosecur. Bioterror. Biodef. Strat. Pr. Sci. 2006, 4, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völker, J.; Stapf, M.; Miehe, U.; Wagner, M. Systematic Review of Toxicity Removal by Advanced Wastewater Treatment Technologies via Ozonation and Activated Carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7215–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Ying, G.-G.; Zhao, J.-L.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L.-J.; Chen, F. Removal of selected endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) during ferrate(VI) treatment of secondary wastewater effluents. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2194–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendergast, M.T.M.; Nygaard, J.M.; Ghosh, A.K.; Hoek, E.M. Using nanocomposite materials technology to understand and control reverse osmosis membrane compaction. Desalination 2010, 261, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnik, B.S.; Davies, S.H.; Baumann, M.J.; Masten, S.J. Fabrication of Catalytic Membranes for the Treatment of Drinking Water Using Combined Ozonation and Ultrafiltration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7656–7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Vandecasteele, C. Removal of Pollutants from Surface Water and Groundwater by Nanofiltration: Overview of Possible Applications in the Drinking Water Industry. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 122, 435–445. [Google Scholar]
- Humplik, T.; Lee, J.; O’Hern, S.C.; Fellman, B.A.; Baig, M.A.; Hassan, S.F.; Atieh, M.; Rahman, F.; Laoui, T.; Karnik, R.; et al. Nanostructured materials for water desalination. Nanotechnol. 2011, 22, 292001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Economic and Health Effects of Increasing Coverage of Low Cost Household Drinking-Water Supply and Sanitation Interventions to Countries off-Track to Meet MDG Target 10: Background Document to the “Human Development Report 2006"; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- WHO/UNICEF. Progress on Sanitation and Drinking Water: 2015 Update and MDG Assessment; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Jiang, W.; Chen, L.; Xu, P.; Wang, H. Treatment of Produced Water with Photocatalysis: Recent Advances, Affecting Factors and Future Research Prospects. Catalysts 2020, 10, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretali, L.; Albini, A.; Cantalupi, A.; Maraschi, F.; Nicolis, S.; Sturini, M. TiO2-Photocatalyzed Water Depollution, a Strong, yet Selective Depollution Method: New Evidence from the Solar Light Induced Degradation of Glucocorticoids in Freshwaters. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, A.M.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Sanromán, M.A.; Pazos, M. Optimization of photo-Fenton process for the treatment of prednisolone. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 27768–27782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauson, D.; Pilnik-Sudareva, J.; Pronina, N.; Budarnaja, O.; Krichevskaya, M.; Käkinen, A.; Juganson, K.; Preis, S. Aqueous photocatalytic oxidation of prednisolone. Open Chem. 2013, 11, 1620–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romao, J.; Hamdy, M.S.; Mul, G.; Baltrusaitis, J. Photocatalytic decomposition of cortisone acetate in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 282, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Li, X.; Sun, W.; Ren, D.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Pan, X. Occurrence, Removal, and Fate of Progestogens, Androgens, Estrogens, and Phenols in Six Sewage Treatment Plants around Dianchi Lake in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 12898–12908. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.; Waite, T.D.; Ong, P.E.A.; Schäfer, A.I.; Fane, A.G. Assessment of Trace Estrogenic Contaminants Removal by Coagulant Addition, Powdered Activated Carbon Adsorption and Powdered Activated Carbon/Microfiltration Processes. J. Environ. Eng. 2004, 130, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Das, S.; Ray, N.M.; Wan, J.; Khan, A.; Chakraborty, T.; Ray, M.B. Micropollutants in Wastewater: Fate and Removal Processes. Phys. Chem. Wastewater Treat. Resour. Recovery 2017, 3, 75–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).